Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Paralogs of RPs and Ribosome Heterogeneity
3. Functions of Cytosolic RPs
3.1. Cytosolic RPs in Generative Reproduction and Embryonic Development
3.2. Cytosolic RPs in Responses to Stresses
3.3. Cytosolic RPs in Plant Growth and Development
3.4. Cytosolic RPs in Other Processes
4. Functions of Plastid RPs (PRPs)
4.1. Plastid RPs in Plastid/Chloroplast and Overall Plant Development
4.2. Plastid RPs in Stress Response
4.3. Other Plastid RP-Related Functions
5. Functions of Mitochondrial RPs (mitRPs)
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, A.J.; Heazlewood, J.L.; Ito, J.; Millar, A.H. Analysis of the Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosome proteome provides detailed insights into its components and their post-translational modifications. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.F.; Szick-Miranda, K.; Pan, S.; Bailey-Serres, J. Proteomic characterization of evolutionarily conserved and variable proteins of Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosomes. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devis, D.; Firth, S.M.; Liang, Z.; Byrne, M.E. Dosage sensitivity of RPL9 and concerted evolution of ribosomal protein genes in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihama, M.; Uechi, T.; Asakawa, S.; Kawasaki, K.; Kato, S.; Higa, S.; Maeda, N.; Minoshima, S.; Tanaka, T.; Shimizu, N.; et al. The human ribosomal protein genes: Sequencing and comparative analysis of 73 genes. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Xiong, W.; Chen, X.; Mo, B.; Tang, G. Plant cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins: An update on classification, nomenclature, evolution and resources. Plant J. 2022, 110, 292–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpin, M.R.; Busche, M.; Martinez, R.E.; Harper, L.C.; Reiser, L.; Szakonyi, D.; Merchante, C.; Lan, T.; Xiong, W.; Mo, B.; et al. An updated nomenclature for plant ribosomal protein genes. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bheemireddy, S.; Sandhya, S.; Srinivasan, N. Comparative analysis of structural and dynamical features of ribosome upon association with mRNA reveals potential role of ribosomal proteins. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 654164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, A.; Bussiere, C.; Johnson, A.W. Mutational analysis of the ribosomal protein Rpl10 from yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 32630–32639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, M.; Hedges, J.B.; Chen, A.; Johnson, A.W. Defining the order in which Nmd3p and Rpl10p load onto nascent 60S ribosomal subunits. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 3802–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Ma, L.; Xiang, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Xu, P.; Xion, Y. Sulfate-TOR signaling controls transcriptional reprogramming for shoot apex activation. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunkard, J.O. Exaptive evolution of target of rapamycin signaling in multicellular eukaryotes. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sormani, R.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C.; Daniele-Vedele, F.; Chardon, F. Transcriptional regulation of ribosome components are determined by stress according to cellular compartments in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; McCormack, M.; Li, L.; Hall, Q.; Xiang, C.; Sheen, J. Glucose–TOR signalling reprograms the transcriptome and activates meristems. Nature 2013, 496, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpin, M.R.; Leiboff, S.; Brunkard, J.O. Parallel global profiling of plant TOR dynamics reveals a conserved role for LARP1 in translation. eLife 2020, 9, e58795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, M.; Scarpin, M.R.; Hnasko, R.; Brunkard, J.O. TOR coordinates nucleotide availability with ribosome biogenesis in plants. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1615–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Gayatri, M.B.; Reddy, A.B.M.; Datla, R.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Involvement of target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling in the regulation of crosstalk between ribosomal protein small subunit 6 kinase-1 (RPS6K-1) and ribosomal proteins. Plants 2023, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boix, M.; Garcia-Rodriguez, A.; Castillo, L.; Miró, B.; Hamilton, F.; Tolak, S.; Pérez, A.; Monte-Bello, C.; Caldana, C.; Henriques, R. 40S ribosomal protein S6 kinase integrates daylength perception and growth regulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 3039–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakshi, A.; Moin, M.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Target of rapamycin, a master regulator of multiple signalling pathways and a potential candidate gene for crop improvement. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petibon, C.; Ghulam, M.M.; Catala, M.; Elela, S.A. Regulation of ribosomal protein genes: An ordered anarchy. WIREs RNA 2021, 12, e1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, G.; Van Lijsebettens, M.; Candela, H.; Micol, J.L.; Tsukaya, H. Ribosomes and translation in plant developmental control. Plant Sci. 2012, 191–192, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, M.; Bakshi, A.; Saha, A.; Kumar, M.U.; Reddy, A.R.; Rao, K.V.; Siddiq, E.A.; Kirti, P.B. Activation tagging in indica rice identifies ribosomal proteins as potential targets for manipulation of water-use efficiency and abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 2440–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, Z.; Plourde, M.B.; Germain, H. Differential participation of plant ribosomal proteins from the small ribosomal subunit in protein translation under stress. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.S.; Casati, P.; Spampinato, C.P.; Falcone Ferreyra, M.L. Ribosomal protein RPL10A contributes to early plant development and abscisic acid-dependent responses in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 582353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwasniak-Owczarek, M.; Kazmierczak, U.; Tomal, A.; Mackiewicz, P.; Janska, H. Deficiency of mitoribosomal S10 protein affects translation and splicing in Arabidopsis mitochondria. Nucleic Acid Res. 2019, 47, 11790–11806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horiguchi, G.; Mollá-Morales, A.; Pérez-Pérez, J.M.; Kojima, K.; Robles, P.; Ponce, M.R.; Micol, J.L.; Tsukaya, H. Differential contributions of ribosomal protein genes to Arabidopsis thaliana leaf development. Plant J. 2011, 65, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommer, U.A.; Stahl, J. Ribosomal proteins in eukaryotes. In Encyclopedia of Life Sciences, on-line resource ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, I.; Tadini, L.; Rossi, F.; Masiero, S.; Pribil, M.; Jahns, P.; Kater, M.; Leister, D.; Pesaresi, P. Versatile roles of Arabidopsis plastid ribosomal proteins in plant growth and development. Plant J. 2012, 72, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsögön, A.; Szakonyi, D.; Shi, X.; Byrne, M. Ribosomal protein RPL27a promotes female gametophyte development in a dose dependent manner. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Jiang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Chen, S.; Zhou, H.; Gong, X.; Xu, J.; Teng, S.; Dong, Y. Mutation of the rice ASL2 gene encoding plastid ribosomal protein L21 causes chloroplast developmental defects and seedling death. Plant Biol. 2015, 17, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Shi, F.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, H. Proteomic analysis of a plastid gene encoding RPS4 mutant in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2022, 22, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Yin, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhong, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Chen, Z.; Ye, H.; Fang, Y.; et al. WLP3 encodes the ribosomal protein L18 and regulates chloroplast development in rice. Rice 2023, 16, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.D.; Yang, X.F.; Chen, S.T.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, J.K.; Shen, Q.; Liu, X.L.; Guo, F.Q. Downregulation of chloroplast RPS1 negatively modulates nuclear heat-responsive expression of HsfA2 and its target genes in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, N.; Bock, R. The translational apparatus of plastids and its role in plant development. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lan, P.; Gao, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Schmidt, W. Expression changes of ribosomal proteins in phosphate- and iron-deficient Arabidopsis roots predict stress-specific alterations in ribosome composition. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, M.; Bakshi, A.; Saha, A.; Dutta, M.; Madhav, S.M.; Kirti, P.B. Rice ribosomal protein large subunit genes and their spatio-temporal and stress regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Yuan, C.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Lu, Y.; Guo, X. CKB1 regulates expression of ribosomal protein L10 family gene and play a role in UV-B response. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, M.; Saha, A.; Bakshi, A.; Divya, D.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Study on transcriptional responses and identification of ribosomal protein genes for potential resistance against brown planthopper and gall midge pests in rice. Curr. Genom. 2021, 22, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Lan, T.; Mo, B. Extraribosomal functions of cytosolic ribosomal proteins in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 607157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, P.; Quesada, V. Unveiling the functions of plastid ribosomal proteins in plant development and abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 189, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, P.; Quesada, V. Emerging roles of mitochondrial ribosomal proteins in plant development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, N.; Beckmann, R.; Cate, J.H.D.; Dinman, J.D.; Dragon, F.; Ellis, S.R.; Lafontaine, D.L.J.; Lindahl, L.; Liljas, A.; Lipton, J.M.; et al. A new system for naming ribosomal proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2014, 24, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, A.; Szick-Miranda, K.; Chang, I.F.; Guyot, R.; Blanc, G.; Cooke, R.; Delseny, M.; Bailey-Serres, J. The organization of cytoplasmic ribosomal protein genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 398–415. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, K.; Lim, J.; Dale, J.M.; Chen, H.; Shinn, P.; Palm, C.J.; Southwick, A.M.; Wu, H.C.; Kim, C.; Nguye, M.; et al. Empirical analysis of transcriptional activity in the Arabidopsis genome. Science 2003, 302, 842–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, P.; Reddy, M.K.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Sopory, S.K. Transcriptional downregulation of rice rpL32 gene under abiotic stress is associated with removal of transcription factors within the promoter region. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchante, C.; Stepanova, A.N.; Alonso, J.M. Translation regulation in plants: An interesting past, an exciting present and a promising future. Plant J. 2017, 90, 628–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhang, J.; Lan, T.; Kong, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Mo, B. High resolution RNA-seq profiling of genes encoding ribosomal proteins across different organs and developmental stages in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Direct. 2021, 5, e00320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone Ferreyra, M.L.; Biarc, J.; Burlingame, A.L.; Casati, P. Arabidopsis L10 ribosomal protein in UV-B responses. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone Ferreyra, M.L.; Pezza, A.; Biarc, J.; Burlingame, A.L.; Casati, P. Plant L10 ribosomal proteins have different roles during development and translation under ultraviolet-B stress. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 1878–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone Ferreyra, M.L.; Casadevall, R.; Luciani, M.D.; Pezza, A.; Casati, P. New evidence for differential roles of L10 ribosomal proteins from Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik Ghulam, M.; Catala, M.; Abou Elela, S. Differential expression of duplicated ribosomal protein genes modifies ribosome composition in response to stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 1954–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Cordewener, J.H.G.; de Groot, J.C.M.; Smeekens, S.; America, A.H.P.; Hanson, J. Dynamic protein composition of Arabidopsis thaliana cytosolic ribosomes in response to sucrose feeding as revealed by label free MSE proteomics. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1024–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhardt, R.F.; Bonham-Smith, P.C. Evolutionary divergence of ribosomal protein paralogs in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2008, 3, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komili, S.; Farny, N.G.; Roth, F.P.; Silver, P.A. Functional specificity among ribosomal proteins regulates gene expression. Cell 2007, 131, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotenberg, M.O.; Moritz, M.; Woolford, J.L., Jr. Depletion of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein L16 causes a decrease in 60S ribosomal subunits and formation of half-mer polyribosomes. Genes Dev. 1988, 2, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, V.P.; Edelman, G.M. The ribosome filter redux. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2246–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias-Fields, L.; Adamala, K.P. Engineering ribosomes to alleviate abiotic stress in plants: A perspective. Plants 2022, 11, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuth, N.R.; Barna, M. The discovery of ribosome heterogeneity and its implications for gene regulation and organismal life. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, K.J.; Duncan, O.; Li, L.; Troesch, J.; Millar, A.H. The composition and turnover of the Arabidopsis thaliana 80S cytosolic ribosome. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 3019–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.J. The Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosomal proteome: From form to function. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, M.; Dobrenel, T.; Cordewener, J.; Davanture, M.; Meyer, C.; Smeekens, S.; Bailey-Serres, J.; America, T.; Hanson, J. Proteomic LC–MS analysis of Arabidopsis cytosolic ribosomes: Identification of ribosomal protein paralogs and re-annotation of the ribosomal protein genes. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 436–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomal, A.; Kwasniak-Owczarek, M.; Janska, H. An update on mitochondrial ribosome biology: The plant mitoribosome in the spotlight. Cells 2019, 8, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, F.; Giegé, P. Striking diversity of mitochondria-specific translation processes across eukaryotes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 45, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.; Zhan, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, X. Cytoplasmic ribosomal protein L14B is essential for fertilization in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2020, 292, 110394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, F.; Duan, C.Y.; Liu, H.H.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, S.; Zhanga, Y. Arabidopsis KETCH1 is critical for the nuclear accumulation of ribosomal proteins and gametogenesis. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Chen, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, M.; Peng, X. Ribosomal protein L18aB is required for both male gametophyte function and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Yan, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Mao, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, M.; Peng, X. RPL18aB helps maintain suspensor identity during early embryogenesis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Chung, M.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, C.S. Loss of Ribosomal Protein L24A (RPL24A) suppresses proline accumulation of Arabidopsis thaliana ring zinc finger 1 (atrzf1) mutant in response to osmotic stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 494, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, P.; Walbot, V. Crosslinking of ribosomal proteins to RNA in maize ribosomes by UV-B and its effects on translation. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3319–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, P.; Walbot, V. Gene expression profiling in response to ultraviolet radiation in maize genotypes with varying flavonoid content. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 1739–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Ai, J.; Chang, H.; Xiao, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; He, Z.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, X. CKB1 is involved in abscisic acid and gibberellic acid signaling to regulate stress responses in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.; Das, S.; Moin, M.; Dutta, M.; Bakshi, A.; Madhav, M.S.; Kirti, P.B. Genome-wide identification and comprehensive expression profiling of ribosomal protein small subunit (RPS) genes and their comparative analysis with the large subunit (RPL) genes in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Park, S.W.; Chung, Y.S.; Chung, C.H.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.H. Molecular cloning of low-temperature-inducible ribosomal proteins from soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, S.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Zhu, X.; Zou, B.; Hua, J. HsfA1d promotes hypocotyl elongation under chilling via enhancing expression of ribosomal protein genes in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 646–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wei, Y.; Shi, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Sun, B.; Shi, Y. Cucumber ribosomal protein CsRPS21 interacts with P22 protein of cucurbit chlorotic yellows virus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 654697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Dittman, J.D.; Whitham, S.A. Differential requirement of ribosomal protein S6 by plant RNA viruses with different translation initiation strategies. Virology 2009, 390, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helderman, T.A.; Deurhof, L.; Bertran, A.; Richard, M.M.S.; Kormelink, R.; Prins, M.; Joosten, M.H.A.J.; van den Burg, H.A. Members of the ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6) family act as pro-viral factor for tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus infectivity in Nicotiana benthamiana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamäki, M.-L.; Xi, D.; Sikorskaite-Gudziuniene, S.; Valkonen, J.P.T.; Whitham, S.A. Differential requirement of the ribosomal protein S6 and ribosomal protein S6 kinase for plant-virus accumulation and interaction of S6 kinase with potyviral VPg. MPMI 2017, 30, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Z.; Wei, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of ribosomal protein GhRPS6 and its role in cotton Verticillium Wilt resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Butt, H.I.; Chen, E.; He, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Salicylic acid-related cotton (Gossypium arboreum) ribosomal protein GaRPL18 contributes to resistance to Verticillium dahliae. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, V.S.; Dawane, A.; Lee, S.; Oh, S.; Lee, H.K.; Sun, L.; Senthil-Kumar, M.; Mysore, K.S. Ribosomal protein QM/RPL10 positively regulates defense and protein translation mechanisms during nonhost disease resistance. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 21, 1481–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, Z.; Plourde, M.B.; Nkouankou, C.E.T.; Fourcassié, V.; Bourassa, S.; Droit, A.; Germain, H. Specific alterations in riboproteomes composition of isonicotinic acid treated arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Mol. Biol. 2023, 111, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Li, Y.; Zang, Z.; Li, N.; Ran, R.; Cao, Y.; Li, T.; Zhoub, Q.; Lia, W. Expression of the double-stranded RNA of the soybean pod borer Leguminivora glycinivorella (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) ribosomal protein P0 gene enhances the resistance of transgenic soybean plants. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Meng, F.; Zheng, D.; Feng, N. Transcriptomics and physiology reveal the mechanism of potassium indole-3-butyrate (IBAK) mediating rice resistance to salt stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair, M.; Long, H.; Zafar, S.A.; Patil, S.B.; Chun, Y.; Li, L.; Fang, J.; Zhao, J.; Peng, L.; Yuan, S.; et al. Narrow Leaf21, encoding ribosomal protein RPS3A, controls leaf development in rice. Plant Physiol. 2021, 186, 497–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degenhardt, R.F.; Bonham-Smith, P.C. Arabidopsis ribosomal proteins RPL23aA and RPL23aB are differentially targeted to the nucleolus and are disparately required for normal development. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 128–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beekvelt, C.A.; de Graaff-Vincent, M.; Faber, A.W.; van ’t Riet, J.; Venema, J.; Raue, H.A. All three functional domains of the large ribosomal subunit protein L25 are required for both early and late pre-rRNA processing steps in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirnberg, P.; Liu, J.P.; Ward, S.; Kendall, S.L.; Leyser, O. Mutation of the cytosolic ribosomal protein-encoding RPS10B gene affects shoot meristematic function in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, O.; Kim, S.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, W.Y.; Koh, H.J.; Cheon, C.I. Identification of nucleosome assembly protein 1 (NAP1) as an interacting partner of plant ribosomal protein S6 (RPS6) and a positive regulator of rDNA transcription. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, R.; Hicks, G.R.; Raikhel, N.V. Arabidopsis ribosomal proteins control vacuole trafficking and developmental programs through the regulation of lipid metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E89–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Fourdin, R.; Quadrado, M.; Dargel-Graffin, C.; Tolleter, D.; Macherel, D.; Mireau, H. Rerouting of ribosomal proteins into splicing in plant organelles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29979–29987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, N.; Weingartner, M.; Thiele, W.; Maximova, E.; Schöttler, M.A.; Bock, R. The plastid-specific ribosomal proteins of Arabidopsis thaliana can be divided into non-essential proteins and genuine ribosomal proteins. Plant J. 2012, 69, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyall, S.D.; Brown, M.T.; Johnson, P.J. Ancient invasions: From endosymbionts to organelles. Science 2004, 304, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, U.G.; Zauner, S.; Woehle, C.; Bolte, K.; Hempel, F.; Allen, J.F.; Martin, W.F. Massively convergent evolution for ribosomal protein gene content in plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Subramanian, A.R. The plastid ribosomal proteins: Identification of all the proteins in the 50 S subunit of an organelle ribosome (chloroplast). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28466–28482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Subramanian, A.R. Proteomic identification of all plastid-specific ribosomal proteins in higher plant chloroplast 30S ribosomal subunit. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; von Knoblauch, K.; Subramanian, A.R. The plastid ribosomal proteins: Identification of all the proteins in the 30 S subunit of an organelle ribosome (chloroplast). J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28455–28465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoschke, R.; Bock, R. Chloroplast translation: Structural and functional organization, operational control, and regulation. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 745–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.F. Signaling pathways from the chloroplast to the nucleus. Planta 2005, 222, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nott, A.; Jung, H.S.; Koussevitzky, S.; Chory, J. Plastid-to-nucleus retrograde signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 739–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braeutigam, K.; Dietzel, L.; Pfannschmidt, T. Plastid-nucleus communication: Anterograde and retrograde signalling in the development and function of plastids. In Cell and Molecular Biology of Plastids; Bock, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 19, pp. 409–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotewutmontri, P.; Barkan, A. Dynamics of chloroplast translation during chloroplast differentiation in maize. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.R.; Dooner, H.K. A mutation in the nuclear-encoded plastid ribosomal protein S9 leads to early embryo lethality in maize. Plant J. 2004, 37, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Qui, S.; Peng, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Liao, C.; Tang, X.; Wu, J. The nuclear-encoded plastid ribosomal protein L18s are essential for plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 949897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalski, M.; Ruf, S.; Bock, R. Tobacco plastid ribosomal protein S18 is essential for cell survival. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4537–4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalski, M.; Schöttler, M.A.; Thiele, W.; Schulze, W.X.; Bock, R. Rpl33, a nonessential plastid-encoded ribosomal protein in tobacco, is required under cold stress conditions. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2221–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupouy, G.; McDermott, E.; Cashell, R.; Scian, A.; McHale, M.; Ryder, P.; de Groot, J.; Lucca, N.; Brychkova, G.; McKeown, P.C.; et al. Plastid ribosome protein L5 is essential for post-globular embryo development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Reprod. 2022, 35, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Lee, K.; Gu, L.; Kim, J.I.; Kang, H. Functional characterization of a plastid-specific ribosomal protein PSRP2 in Arabidopsis thaliana under abiotic stress conditions. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.R.; Dönhöfer, A.; Barat, C.; Marquez, V.; Datta, P.P.; Fucini, P.; Wilson, D.N.; Agrawal, R.K. PRPS1 is not a ribosomal protein, bit a ribosome binding factor that is recycled by the ribosome-recycling factor (RRF) and elongation factor G (EF-G). J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4006–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, K.; Chotewutmontri, P.; Belcher, S.; Williams-Carrier, R.; Barkan, A. Functional analysis of PSRP1, the chloroplast homolog of cyanobacterial ribosome hibernation factor. Plants 2020, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuell, A.; Beligni, M.V.; Yamaguchi, K.; Mayfield, S.P. Regulation of chloroplast translation: Interactions of RNA elements, RNA-binding proteins and the plastid ribosome. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2004, 32, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, P.; Zagari, N.; Manavski, N.; Gawroński, P.; Matthes, A.; Scharff, L.B.; Meurer, J.; Leistera, D. CHLOROPLAST RIBOSOME ASSOCIATED supports translation under stress and interacts with the ribosomal 30S subunit. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 1539–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultes, N.P.; Sawers, R.J.H.; Brutanell, T.P.; Krueger, R.W. Maize high chlorophyll fluorescent 60 mutation is caused by an Ac disruption of the gene encoding the chloroplast ribosomal small subunit protein 17. Plant J. 2000, 21, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, S.; Ryu, S.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; An, G.; Park, S.K. Impaired plastid ribosomal protein L3 causes albino seedling lethal phenotype in rice. J. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Zheng, K.L.; Gong, X.D.; Xu, J.L.; Huang, J.R.; Lin, D.Z.; Dong, Y.J. The rice TCD11 encoding plastid ribosomal protein S6 is essential for chloroplast development at low temperature. Plant Sci. 2017, 259, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, H.; Yang, Y.; Fish, T.; Lyi, S.M.; Thannhauser, T.W.; Zhang, L.; Li, L. Plastid ribosomal protein S5 is involved in photosynthesis, plant development, and cold stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2731–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Wu, W.; Huang, W.; Huang, J. Down-regulation of specific plastid ribosomal proteins suppresses thf1 leaf variegation, implying a role of THF1 in plastid gene expression. Photosynth. Res. 2015, 126, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Duan, S.; Wang, H.B.; Jin, H.L. Plastid ribosomal protein LPE2 is involved in photosynthesis and the response to C/N balance of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2020, 62, 1418–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita-Yamamuro, C.; Tsutsui, T.; Tanaka, A.; Yamaguchi, J. Knock-out of the plastid ribosomal protein S21 causes impaired photosynthesis and sugar-response during germination and seedling development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.S.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Yang, Q.Q.; Gu, M.H.; Liu, Q.Q. A residue substitution in the plastid ribosomal protein L12/AL1 produces defective plastid ribosome and causes early seedling lethality in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Teng, S.; Lin, D.; Dong, Y. Disruption of the rice plastid ribosomal protein S20 leads to chloroplast development defects and seedling lethality. G3 2013, 3, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Zhang, C.; Xia, J.; Yun, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, Z. Albino seedling lethality 4; chloroplast 30S ribosomal protein S1 is required for chloroplast ribosome biogenesis and early chloroplast development in rice. Rice 2021, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.Z.; Pan, G.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.P.; Zhao, Z.X.; Fu, T.D.; Zhou, Y.M. The chloroplast ribosomal protein L21 gene is essential for plastid development and embryogenesis in Arabidopsis. Planta 2012, 235, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Xu, T.; Zucchi, P.; Bogorad, L. Subpopulations of chloroplast ribosomes change during photoregulated development of Zea mays leaves: Ribosomal proteins L2, L21, and L29. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 8997–9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagrange, T.; Franzetti, B.; Axelos, M.; Mache, R.; Lerbs-Mache, S. Structure and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the chloroplast ribosomal protein L21: Developmental regulation of a housekeeping gene by alternative promoters. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 2614–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, W.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L. Intracellular signaling from plastid to nucleus. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 559–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadini, L.; Pesaresi, P.; Kleine, T.; Rossi, F.; Guljamow, A.; Sommer, F.; Mühlhaus, T.; Schroda, M.; Masiero, S.; Pribil, M.; et al. GUN1 controls accumulation of the plastid ribosomal protein S1 at the protein level and interacts with proteins involved in plastid protein homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S.N.; Liu, Z.Y.; Fei, D.L.; Feng, H. A missense mutation of plastid RPS4 is associated with chlorophyll deficiency in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris ssp. pekinensis). BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, S.; Ryu, S.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; An, G.; Park, S.K. Mutation of plastid ribosomal protein L13 results in an albino seedling-lethal phenotype in rice. Plant Breed. Biotech. 2019, 7, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wei, X.; Shao, G.; Sheng, Z.; Chen, D.; Liu, C.; Jiao, G.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Hu, P. The rice nuclear gene WLP1 encoding a chloroplast ribosome L13 protein is needed for chloroplast development in rice grown under low temperature conditions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 84, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.J.; Xu, X.J.; Yan, Z.Y.; Tettey, C.K.; Fang, L.; Yang, G.L.; Geng, C.; Tian, Y.P.; Li, X.D. The chloroplast ribosomal protein large subunit 1 interacts with viral polymerase and promotes virus infection. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, F.; Zhang, M.D.; Meeley, R.B.; McCarty, D.R.; Tan, B.C. Emb15 encodes a plastid ribosomal assembly factor essential for embryogenesis in maize. Plant J. 2021, 106, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdseye, D.; de Boer, L.A.; Bai, H.; Zhou, P.; Shen, Z.; Schmelz, E.A.; Springer, N.M.; Briggs, S.P. Plant height heterosis is quantitatively associated with expression levels of plastid ribosomal proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2109332118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englmeier, R.; Pfeffer, S.; Förster, F. Structure of the human mitochondrial ribosome studied in situ by cryoelectron tomography. Structure 2017, 25, 1574–1581e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmond, E.; Brochier-Armanet, C.; Forterre, P.; Gribaldo, S. On the last common ancestor and early evolution of eukaryotes: Reconstructing the history of mitochondrial ribosomes. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltz, F.; Nguyen, T.T.; Arrivé, M.; Bochler, A.; Chicher, J.; Hammann, P.; Kuhn, L.; Quadrado, M.; Mireau, H.; Hashem, Y.; et al. Small is big in Arabidopsis mitochondrial ribosome. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltz, F.; Corre, N.; Hashem, Y.; Giegé, P. Specificities of the plant mitochondrial translation apparatus. Mitochondrion 2020, 53, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greber, B.J.; Ban, N. Structure and function of the mitochondrial ribosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 103–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Brown, A.; Amunts, A.; Ramakrishnan, V. The structure of the yeast mitochondrial ribosome. Science 2017, 355, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertgen, L.; Mühlhaus, T.; Herrmann, J.M. Clingy genes: Why were genes for ribosomal proteins retained in many mitochondrial genomes? Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2020, 1861, 148275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, M.; Day, R.C.; Talbot, M.J.; Ivanova, A.; Ashton, A.R.; Chaudhury, A.M.; Macknight, R.C.; Hrmova, M.; Koltunow, A.M. Developmentally regulated HEART STOPPER, a mitochondrially targeted L18 ribosomal protein gene, is required for cell division, differentiation, and seed development in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5867–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yu, F.; Tian, L.; Huang, X.; Tan, H.; Xie, Z.; Hao, X.; Li, D.; Luan, S.; Chen, L. RPS9M, a mitochondrial ribosomal protein, is essential for central cell maturation and endosperm development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xie, Z.; Yu, F.; Tian, L.; Hao, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Li, D. Mitochondrial ribosomal protein S9M is involved in male gametogenesis and seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol. 2020, 22, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portereiko, M.F.; Sandaklie-Nikolova, L.; Lloyd, A.; Dever, C.A.; Otsuga, D.; Drews, G.N. NUCLEAR FUSION DEFECTIVE1 encodes the Arabidopsis RPL21M protein and is required for karyogamy during female gametophyte development and fertilization. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J.; Peng, X.B.; Li, W.W.; He, R.; Xin, H.P.; Sun, M.X. Mitochondrial GCD1 dysfunction reveals reciprocal cell-to-cell signaling during the maturation of Arabidopsis female gametes. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Lu, L.; Huang, S.; Songa, R. Maize Dek44 encodes mitochondrial ribosomal protein L9 and is required for seed development. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 2106–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majewski, P.; Wołoszyńska, M.; Jańska, M. Developmentally early and late onset of Rps10 silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana: Genetic and environmental regulation. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1163–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwasniak, M.; Majewski, P.; Skibior, R.; Adamowicz, A.; Czarna, M.; Sliwinska, E.; Janska, H. Silencing of the nuclear RPS10 gene encoding mitochondrial ribosomal protein alters translation in Arabidopsis mitochondria. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
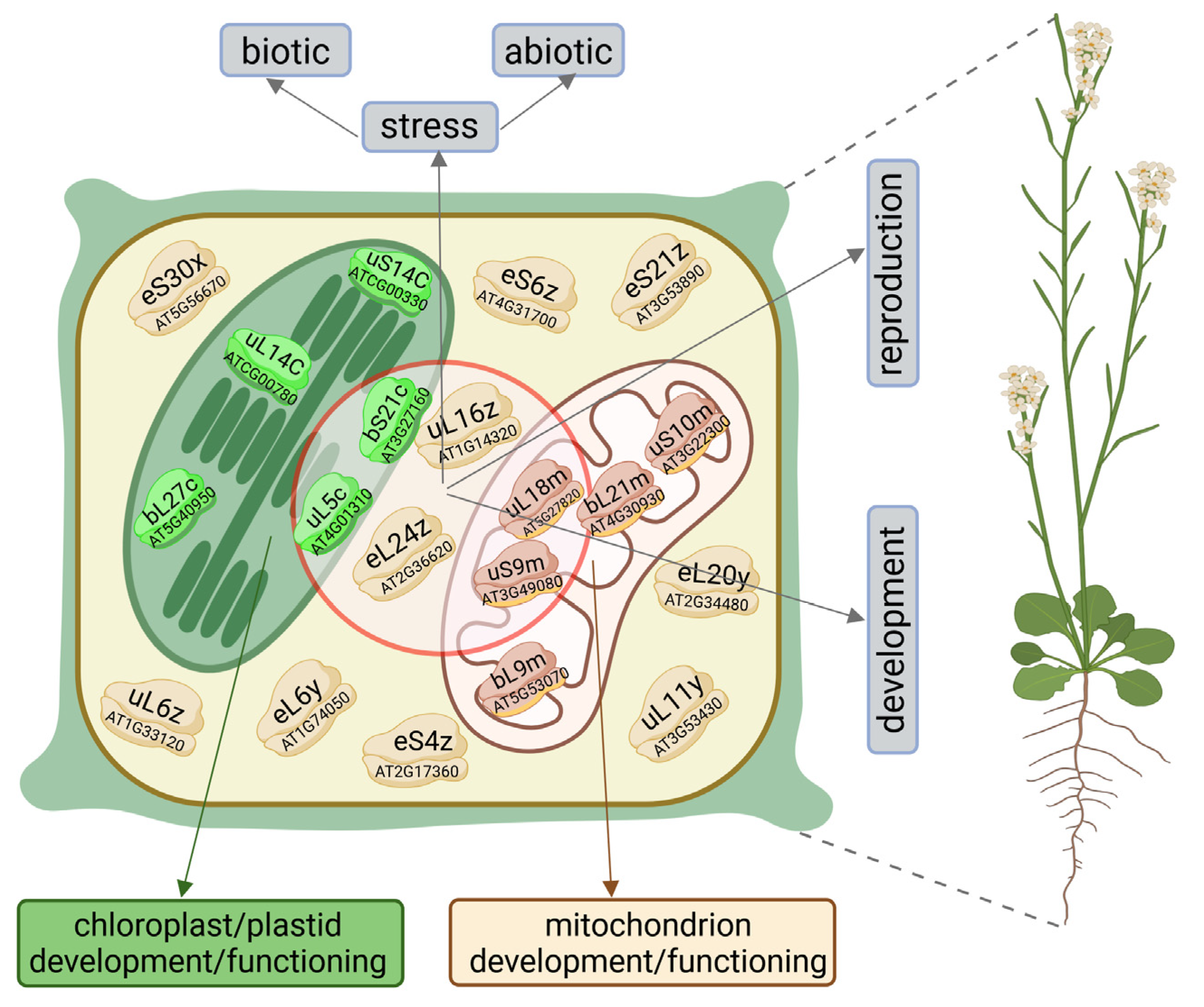
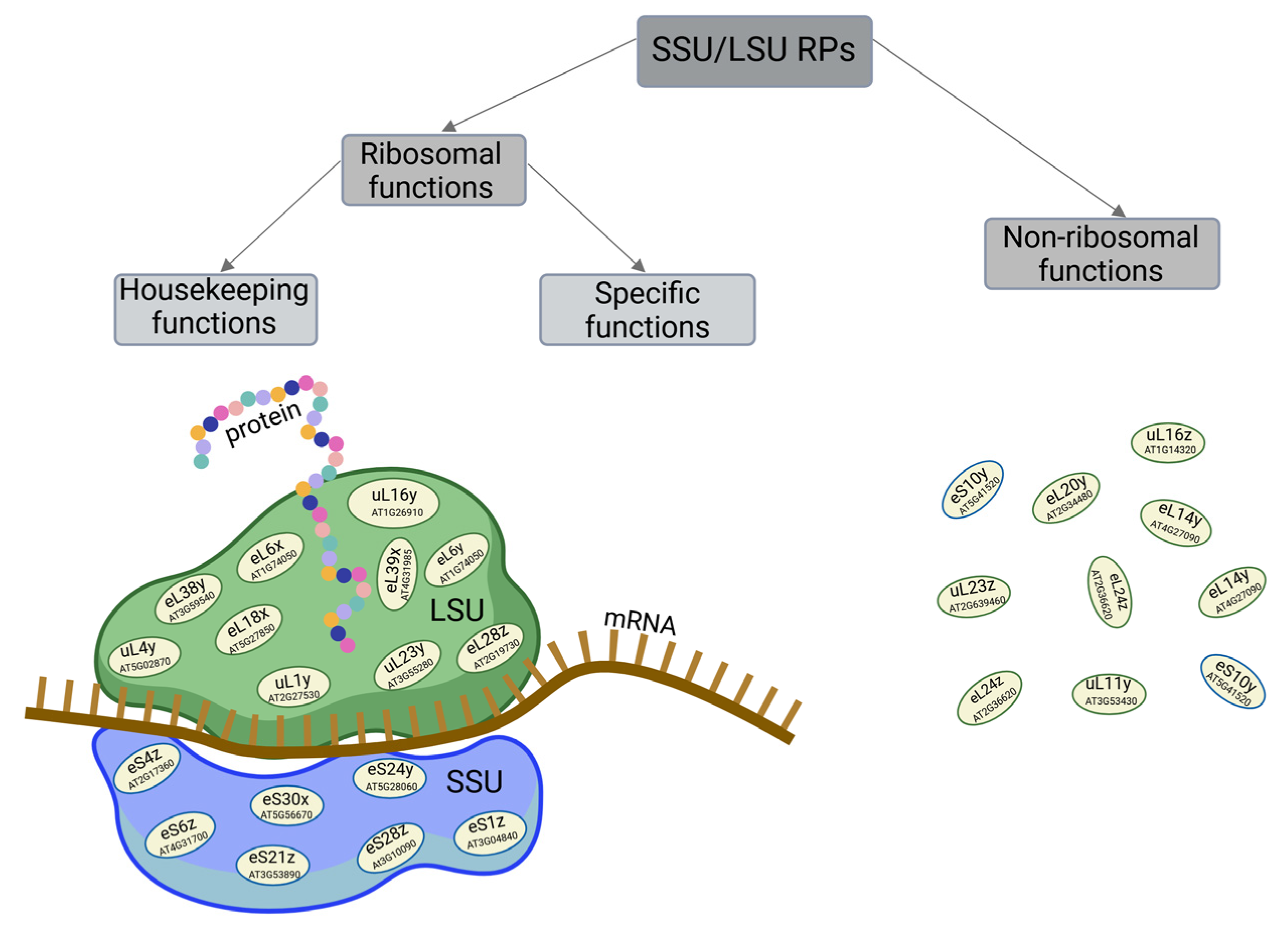
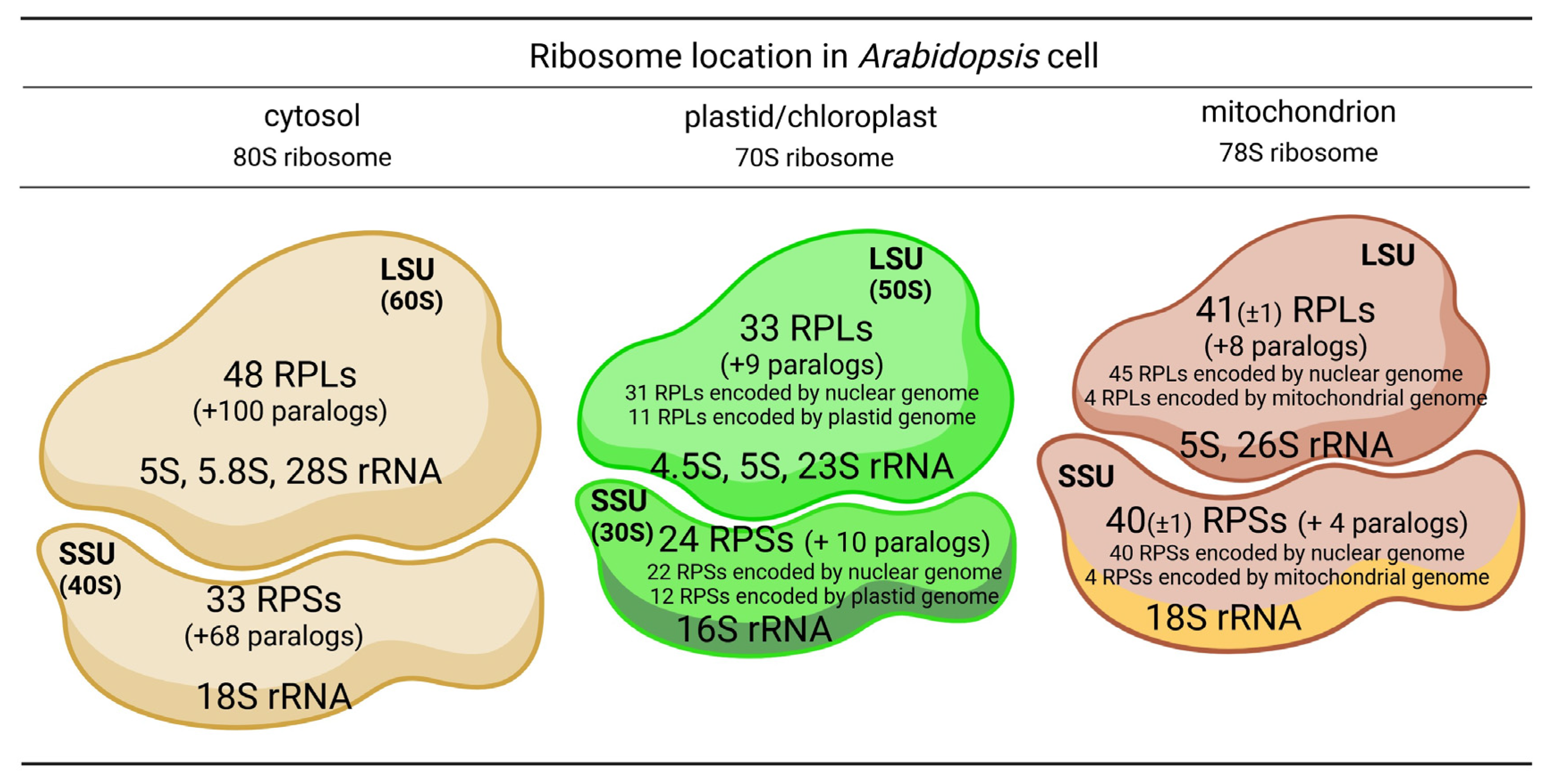
| Cytosolic RP | Species | Function/Process | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Old Name | |||
| uL1y | RPL10aB | A. thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| uL4y | RPL4D | A. thaliana | Leaf development, lipid biosynthesis | [25,89] |
| eL6 | RPL6 | O. sativa | Abiotic stress response (osmotic, drought, salt stress) | [21,35,71] |
| uL6 | RPL9 | A. thaliana | Chilling stress, cold acclimation | [73] |
| uL11y | RPL12B | A. thaliana | Abiotic stress response (Pi deficiency) | [34] |
| eL14y | RPL14B | A. thaliana | Fertilization, embryogenesis, pollen tube development and functionality | [63] |
| eL15 | RPL15 | O. sativa | Biotic stress response (defense against BPH and gall midge) | [37] |
| uL15 | RPL27a | A. thaliana | Male and female gametophyte development, pollen grain, and embryo sac development | [64] |
| uL16 uL16z | RPL10 RPL10A | A. thaliana N. benthamiana A. thaliana | Abiotic stress response (UV-B stress); Biotic stress response (defense against bacterial host and non-host–pathogens); Early stages of plant development | [36,80] [23] |
| eL18x | RPL18C | A. thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| uL18L1/ uL18L8 | A thaliana | Splicing and LSU biogenesis in mitochondria/plastid, overall plant development | [90] | |
| eL20y eL20 | RPL18aB RPL18a | A. thaliana O. sativa | Early embryogenesis, seed development, male gametophyte functioning, suspensor development; Biotic stress response (defense against gall midge) | [65,66] [37] |
| uL22 | RPL22 | O. sativa | Biotic stress response (defense against gall midge) | [37] |
| uL23z uL23z/y | RPL23A RPL23aA/aB | O. sativa A. thaliana | Abiotic stress response (osmotic, drought, salt stress); overall plant development; | [21,35,71] [85,86] |
| eL24z | RPL24A | A. thaliana | Abiotic stress response (osmotic stress) | [67] |
| eL28z | RPL28A | A. thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| uL30y | RPL7B | A. thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| eL32 eL32z | RPL32 RPL32A | O. sativa | Response to various abiotic stresses; cold, salt, drought, sucrose stress | [44] |
| eL36 | RPL36.2 | O. sativa | Biotic stress response (defense against gall midge) | [37] |
| eL37 | RPL37 | G. max | Cold stress response | [72] |
| eL38 eL38y | RPL38 RPL38B | O. sativa A thaliana | Biotic stress response (defense against gall midge); leaf development | [37] [25] |
| eL39x | RPL39C | A thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| eS1z | RPS3A | O. sativa | Leaf development | [84] |
| uS4 | RPS9.2 | O. sativa | Biotic stress response (defense against gall midge) | [37] |
| es6 eS6z | RPS6 RPS6A | G. max N. benthamiana G. hirsutum A. thaliana | Abiotic (cold) cold stress response; Biotic stress response (response to viruses); Positive biotic stress response (defense against V. dahliae); rDNA transcription regulation; Leaf development; | [72] [75,76,77] [78] [88] [25] |
| uS7y/z | RPS5/a | O. sativa | Biotic stress response (insect resistance to BPH and gall midge) | [37] |
| eS10y | RPS10B | A. thaliana | Shoot meristem functioning | [87] |
| us15 | RPS13 | G. max | Cold stress response | [72] |
| eS21 eS21z | RPS21 RPS21B | C. sativus A. thaliana | Positive biotic stress response (defense against CCYV); Leaf development | [74] [25] |
| eS24y | RPS24B | A. thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| eS25 | RPS25a | O. sativa | Biotic stress response (defense against gall midge) | [37] |
| eS28y eS28z | RPS28B RPS28A | A. thaliana | Leaf development | [25] |
| Plastid/Chloroplast RP | Species | Function/Process | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Old Name | |||
| uL1c | RPL1 | A. thaliana N. benthamiana | Early stages of embryo development; Biotic stress response (promotes infection by TVBMV) | [27] [130] |
| uL3c | RPL3 | O. sativa | Chloroplast development and functioning | [129] |
| uL4c | RPL4 | A. thaliana | Early stages of embryo development | [27] |
| uL5c | RPL5 | A. thaliana | Early stages of embryo development | [106] |
| bL12c | RPL12 | O. sativa | Chloroplast development and photosynthesis at early stages of seedling growth | [119] |
| uL13c | RPL13 | O. sativa | Chloroplast development and functioning, particularly under low temperatures | [129] |
| uL18c | RPL18 | A. thaliana, O. sativa | Chloroplast development and functioning, chlorophyll biosynthesis, early embryo/seedling stage development | [31] |
| bL20 | RPL20 | N. tabacum | Photosynthesis, plant development, and survival | [104,105] |
| bL21c | RPL21 | O. sativa | Chloroplast development and photosynthesis at early stages of seedling growth | [29] |
| uL24c | RPL24 | A. thaliana | Photosynthesis | [27] |
| bL27c | RPL27 | A. thaliana | Early stages of embryo development | [27] |
| bL28c | RPL28 | A. thaliana | Later stages of embryo-to-seedling development | [27] |
| bL33C | RPL33 | O. sativa | Abiotic stress response (plant functioning under low temperatures) | [105] |
| bL35 | RPL35 | A. thaliana | Early stages of embryo development | [27] |
| cL37 | PSRP | A. thaliana | Photosynthesis, chloroplast development, plastid rRNA processing, leaf variegation | [91,116] |
| bS1c | RPS1 | A. thaliana O. sativa | Photosynthesis; Abiotic stress response (heat stress); Retrograde signaling | [27] [32] [126] |
| uS2C | RPS2 | N. tabacum | Photosynthesis, plant development, and survival | [104,105] |
| uS4C | RPS4 | N. tabacum C. cabbage | Photosynthesis, plant development and survival; Abiotic stress response (cold stress tolerance) | [104,105] [30] |
| uS5c | RPS5 | A. thaliana | Photosynthesis, overall plant development; Abiotic stress response (cold stress tolerance) | [115] [30] |
| bS6c | RPS6 | O. sativa | Chloroplast development and functioning under low temperatures | [114] |
| uS9c | RPS9 | A. thaliana | Chloroplast development, photosynthesis, plastid rRNA processing, leaf variegation | [116] |
| uS11C | RPS11 | A. thaliana | Plastid rRNA processing | [116] |
| uS17c | RPS17 | A. thaliana Z. mays | Photosynthesis | [27] [112] |
| bS18C | RPS18 | N. tabacum | Photosynthesis, plant development, and survival | [104,105] |
| uS19C | RPS19 | Z. mays | Plastid 16 rRNA maturation | [131] |
| bS20c | RPS20 | A. thaliana O. sativa | Early stages of embryo development; Chloroplast development and photosynthesis at early stages of seedling growth; Retrograde signaling | [27] [120] [126] |
| bS21c | RPS21 | A. thaliana | Photosynthesis, carbon/nitrogen balance regulation, overall plant development; Sensitivity to glucose excess, fertilization | [117] [118] |
| cS22 | PSRP2 | A. thaliana | Negative regulation of seed germination under abiotic stresses (salinity, dehydration, low temperature) | [107] |
| cS23 | PSRP3 | A. thaliana | Photosynthesis | [91] |
| bTHXc | PSRP4 | A. thaliana | Photosynthesis | [91] |
| Mitochondrial RP | Species | Function/Process | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Old Name | |||
| bL9m | RPL9 | Z. mays | Embryo, endosperm, kernel development | [145] |
| uL18m | RPL18 | A. thaliana | Proliferating tissues functioning (embryo and root meristem) | [140] |
| bL20m | RPL20 | A. thaliana | Central cell and endosperm maturation; Embryo, endosperm, seed development | [144] [140] |
| bL21m | RPL21 | A. thaliana | Central cell and endosperm maturation | [143] |
| uS9m | RPS9 | A. thaliana | Reproductive processes (male and female gametogenesis) | [141,142] |
| uS10m | RPS10 | A. thaliana | Plant development during the vegetative phase; Mitochondrial gene expression (transcription, splicing, translation) | [146] [24,147] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stępiński, D. Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games. Cells 2025, 14, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070473
Stępiński D. Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games. Cells. 2025; 14(7):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070473
Chicago/Turabian StyleStępiński, Dariusz. 2025. "Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games" Cells 14, no. 7: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070473
APA StyleStępiński, D. (2025). Decoding Plant Ribosomal Proteins: Multitasking Players in Cellular Games. Cells, 14(7), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14070473





