Localization and Single Molecule Dynamics of Bacillus subtilis Penicillin-Binding Proteins Depend on Substrate Availability and Are Affected by Stress Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Preparation
2.2. Cell Cultivation
2.3. Sample Preparation for Fluorescence Microscopy
2.4. Single Molecule Tracking Microscopy and Data Processing
2.5. Western Blot
3. Results
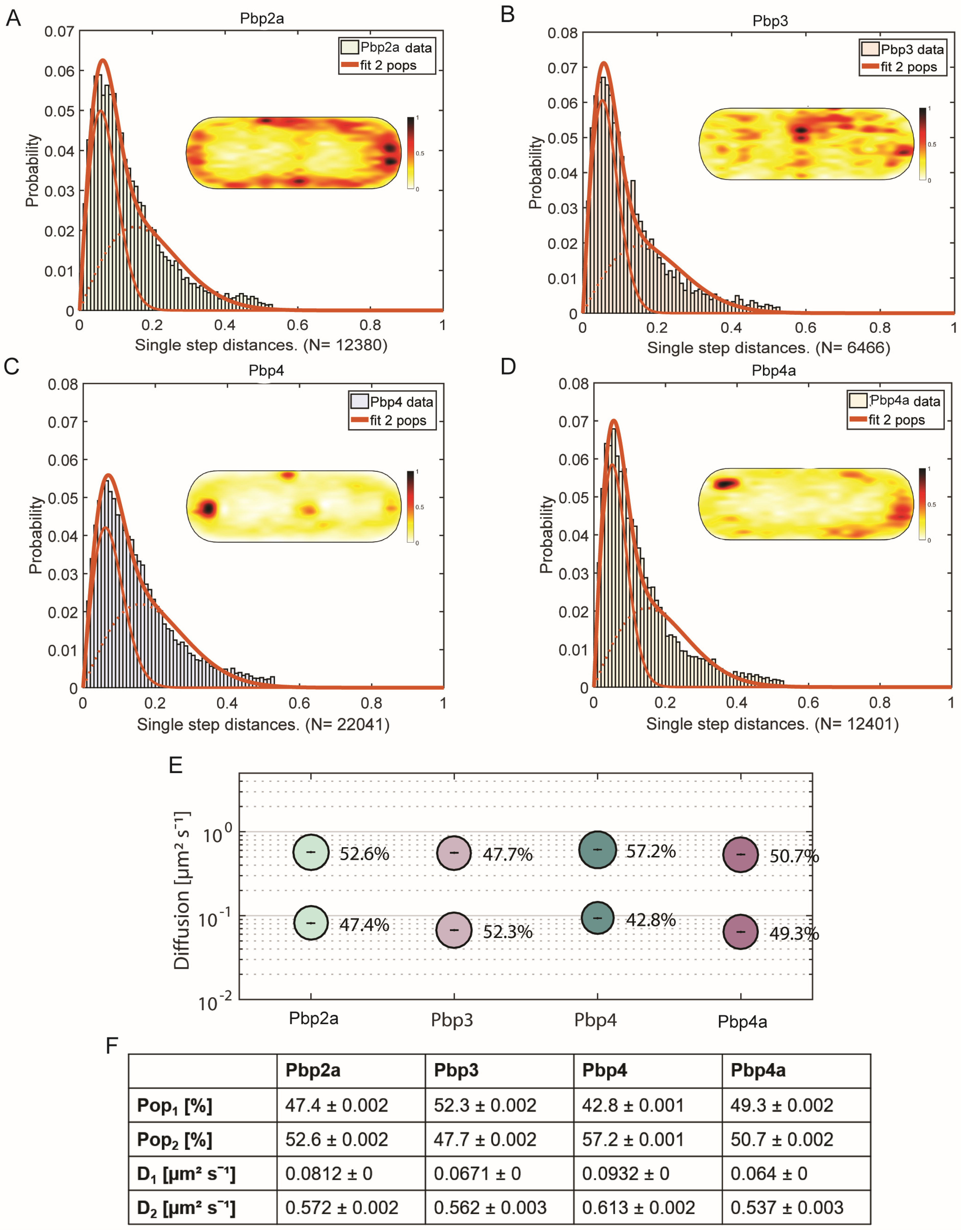
3.1. SMT-Based Determination of the Spatial Pattern of the PBPs
3.2. PBPs Move as Two Populations with Distinct Mobilities
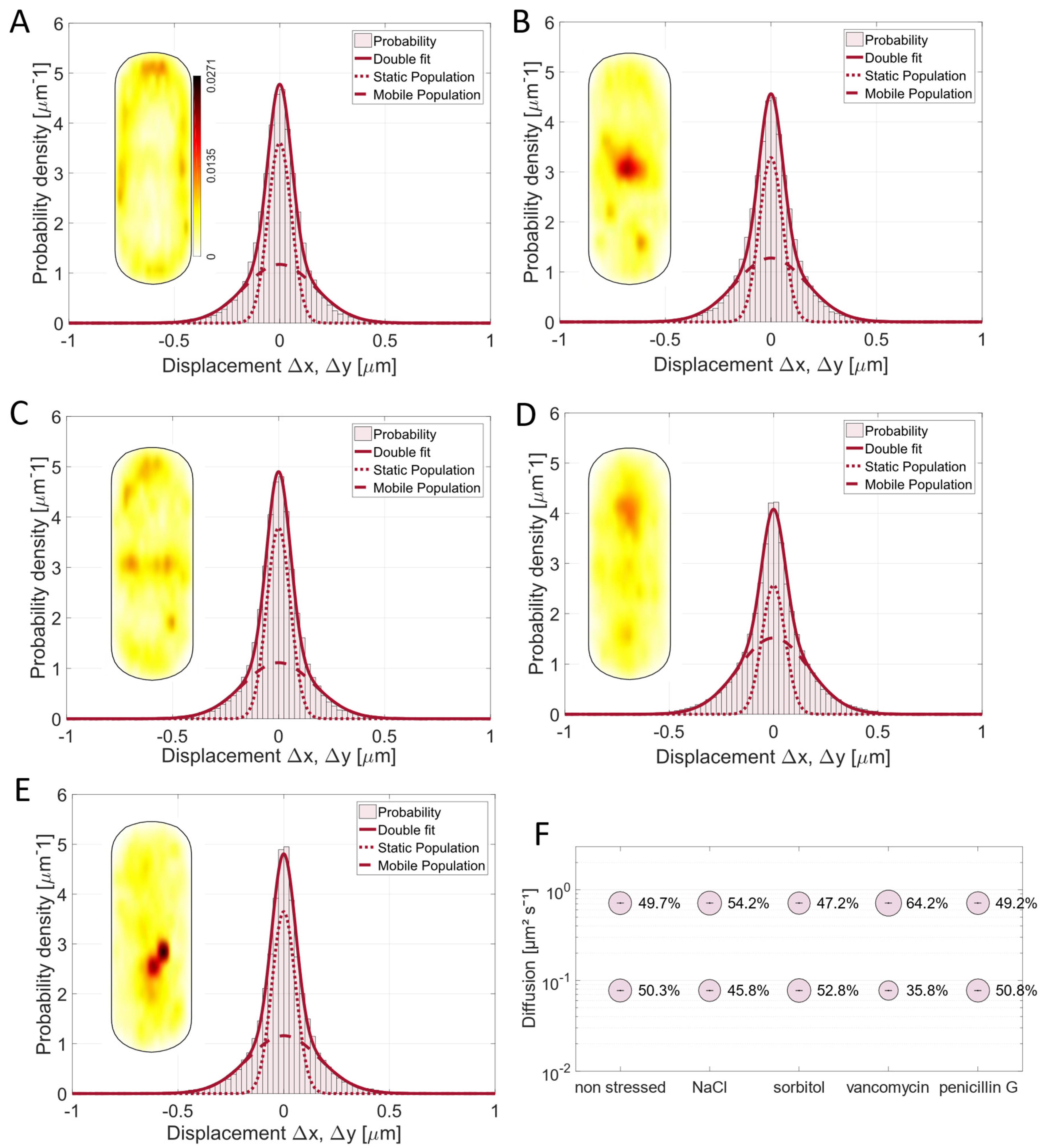
3.3. The Mobility of the PGEM (Peptidoglycan Elongation Machinery) Transpeptidase Pbp2a Is Influenced by Ionic Stress and the Antibiotic Vancomycin
3.4. Pbp3 Mobility Changes Markedly Under Osmotic Stress and Antibiotic Treatment
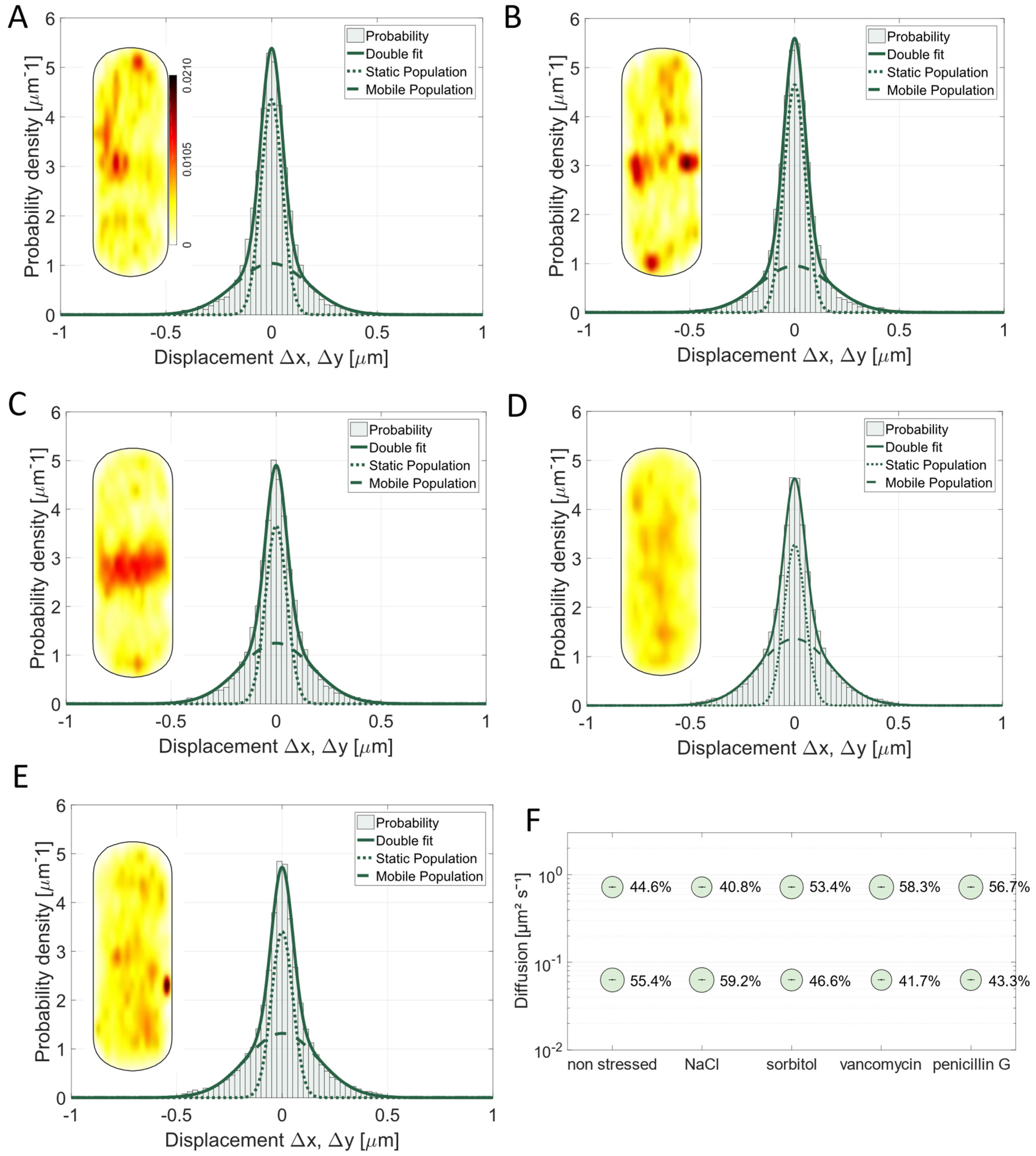
3.5. Osmotic Stress Leads to an Altered Localization of Pbp4 but Not Substrate Availability Based on Vancomycin Treatment
3.6. Pbp4a Motion Is Mainly Affected by Vancomycin and Undergoes Relocalization Under Stress Conditions
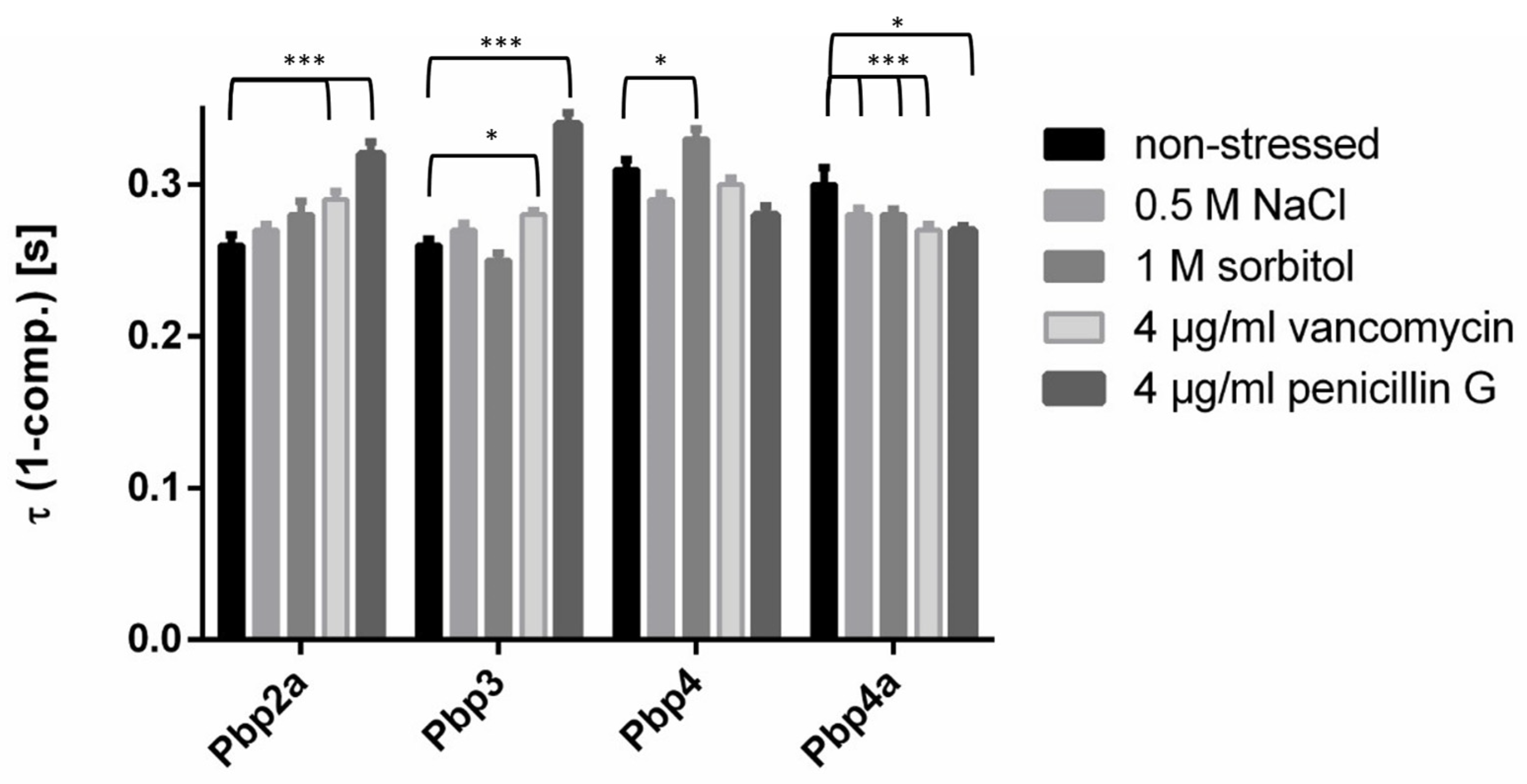
3.7. PBPs Have Different Average Residence Times
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egan, A.J.F.; Cleverley, R.M.; Peters, K.; Lewis, R.J.; Vollmer, W. Regulation of bacterial cell wall growth. FEBS J. 2016, 284, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Typas, A.; Banzhaf, M.; Gross, C.A.; Vollmer, W. From the regulation of peptidoglycan synthesis to bacterial growth and morphology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 10, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, W.; Seligman, S.J. Architecture of peptidoglycan: More data and more models. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höltje, J.V. Growth of the stress-bearing and shape-maintaining murein sacculus of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 1998, 62, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, D.J.; Jones, L.J.; Errington, J. Several distinct localization patterns for penicillin-binding proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 749–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvage, E.; Kerff, F.; Terrak, M.; Ayala, J.A.; Charlier, P. The penicillin-binding proteins: Structure and role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duez, C.; Vanhove, M.; Gallet, X.; Bouillenne, F.; Docquier, J.; Brans, A.; Frere, J. Purification and characterization of PBP4a, a new low-molecular-weight penicillin-binding protein from Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvage, E.; Duez, C.; Herman, R.; Kerff, F.; Petrella, S.; Anderson, J.W.; Adediran, S.A.; Pratt, R.F.; Frere, J.M.; Charlier, P. Crystal structure of the Bacillus subtilis penicillin-binding protein 4a, and its complex with a peptidoglycan mimetic peptide. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 371, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vigouroux, A.; Cordier, B.; Aristov, A.; Alvarez, L.; Ozbaykal, G.; Chaze, T.; Oldewurtel, E.R.; Matondo, M.; Cava, F.; Bikard, D.; et al. Class-A penicillin binding proteins do not contribute to cell shape but repair cell-wall defects. Elife 2020, 9, e51998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lages, M.C.; Beilharz, K.; Morales Angeles, D.; Veening, J.W.; Scheffers, D.J. The localization of key Bacillus subtilis penicillin binding proteins during cell growth is determined by substrate availability. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 3272–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersch, S.; Mehl, J.; Stuckenschneider, L.; Mayer, B.; Roth, J.; Rohrbach, A.; Graumann, P.L. Super-Resolution Microscopy and Single-Molecule Tracking Reveal Distinct Adaptive Dynamics of MreB and of Cell Wall-Synthesis Enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, Y.; Daniel, R.A.; Errington, J. Regulation of cell wall morphogenesis in Bacillus subtilis by recruitment of PBP1 to the MreB helix. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 71, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dion, M.F.; Kapoor, M.; Sun, Y.; Wilson, S.; Ryan, J.; Vigouroux, A.; van Teeffelen, S.; Oldenbourg, R.; Garner, E.C. Bacillus subtilis cell diameter is determined by the opposing actions of two distinct cell wall synthetic systems. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Escobar, J.; Chastanet, A.; Crevenna, A.H.; Fromion, V.; Wedlich-Soldner, R.; Carballido-Lopez, R. Processive Movement of MreB-Associated Cell Wall Biosynthetic Complexes in Bacteria. Science 2011, 333, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, E.C.; Bernard, R.; Wang, W.; Zhuang, X.; Rudner, D.Z.; Mitchison, T. Coupled, Circumferential Motions of the Cell Wall Synthesis Machinery and MreB Filaments in B. subtilis. Science 2011, 333, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Teeffelen, S.; Wang, S.; Furchtgott, L.; Huang, K.C.; Wingreen, N.S.; Shaevitz, J.W.; Gitai, Z. The bacterial actin MreB rotates, and rotation depends on cell-wall assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15822–15827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbaykal, G.; Wollrab, E.; Simon, F.; Vigouroux, A.; Cordier, B.; Aristov, A.; Chaze, T.; Matondo, M.; van Teeffelen, S. The transpeptidase PBP2 governs initial localization and activity of the major cell-wall synthesis machinery in E. coli. Elife 2020, 9, e50629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshausen, P.V.; Defeu Soufo, H.J.; Wicker, K.; Heintzmann, R.; Graumann, P.L.; Rohrbach, A. Superresolution imaging of dynamic MreB filaments in B. subtilis—A multiple-motor-driven transport? Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemiss, S.; Blandenet, M.; Roberts, D.M.; McMahon, A.; Grimshaw, J.; Edwards, J.M.; Sun, Z.; Whitley, K.D.; Blu, T.; Strahl, H.; et al. Molecular motor tug-of-war regulates elongasome cell wall synthesis dynamics in Bacillus subtilis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotto, N.; Agudo-Canalejo, J.; Colin, R.; Golestanian, R.; Malengo, G.; Sourjik, V. Dependence of diffusion in Escherichia coli cytoplasm on protein size, environmental conditions, and cell growth. Elife 2022, 11, e82654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defeu Soufo, H.J.; Graumann, P.L. Dynamic movement of actin-like proteins within bacterial cells. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaacks, K.J.; Healy, J.; Losick, R.; Grossman, A.D. Identification and characterization of genes controlled by the sporulation-regulatory gene spo0H in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 4121–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Hoffmann, T.; Smits, S.H.; Bremer, E. Dimethylglycine provides salt and temperature stress protection to Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2773–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.; Wensing, A.; Brosius, M.; Steil, L.; Volker, U.; Bremer, E. Osmotic control of opuA expression in Bacillus subtilis and its modulation in response to intracellular glycine betaine and proline pools. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Wang, T.; Ye, R.; Helmann, J.D. Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall biosynthesis induce expression of the Bacillus subtilisσW and σM regulons. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 45, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanski, M.A.; Dwyer, D.J.; Collins, J.J. How antibiotics kill bacteria: From targets to networks. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomino, M.M.; Sanchez-Rivas, C.; Ruzal, S.M. High salt stress in Bacillus subtilis: Involvement of PBP4* as a peptidoglycan hydrolase. Res. Microbiol. 2009, 160, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibany, S.; Kleine Borgmann, L.A.K.; Rosch, T.C.; Knust, T.; Ulbrich, M.H.; Graumann, P.L. Single molecule tracking reveals that the bacterial SMC complex moves slowly relative to the diffusion of the chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 7805–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paintdakhi, A.; Parry, B.; Campos, M.; Irnov, I.; Elf, J.; Surovtsev, I.; Jacobs-Wagner, C. Oufti: An integrated software package for high-accuracy, high-throughput quantitative microscopy analysis. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaqaman, K.; Loerke, D.; Mettlen, M.; Kuwata, H.; Grinstein, S.; Schmid, S.L.; Danuser, G. Robust single-particle tracking in live-cell time-lapse sequences. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosch, T.C.; Oviedo-Bocanegra, L.M.; Fritz, G.; Graumann, P.L. SMTracker: A tool for quantitative analysis, exploration and visualization of single-molecule tracking data reveals highly dynamic binding of B. subtilis global repressor AbrB throughout the genome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, A.J.F.; Errington, J.; Vollmer, W. Regulation of peptidoglycan synthesis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.L.; Kearns, D.B.; Carlson, E.E. Penicillin-binding protein redundancy in Bacillus subtilis enables growth during alkaline shock. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e0054823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeles, D.M.; Scheffers, D.J. The Cell Wall of Bacillus subtilis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 41, 539–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, T.; Popham, D.L.; Setlow, P. Identification and characterization of pbpC, the gene encoding Bacillus subtilis penicillin-binding protein 3. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 6001–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Havasy, T.; McPherson, D.C.; Popham, D.L. Rod shape determination by the Bacillus subtilis class B penicillin-binding proteins encoded by pbpA and pbpH. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 4717–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, D.C.; Popham, D.L. Peptidoglycan synthesis in the absence of class A penicillin-binding proteins in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popham, D.L.; Setlow, P. Phenotypes of Bacillus subtilis mutants lacking multiple class A high-molecular-weight penicillin-binding proteins. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Meng, K.; Shi, H.; Huang, K.C. Single-molecule imaging reveals modulation of cell wall synthesis dynamics in live bacterial cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Tropini, C.; Hsin, J.; Desmarais, S.M.; Ursell, T.S.; Gong, E.; Gitai, Z.; Monds, R.D.; Huang, K.C. A dynamically assembled cell wall synthesis machinery buffers cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4554–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Wivagg, C.N.; Kapoor, M.; Barry, Z.; Rohs, P.D.A.; Suh, H.; Marto, J.A.; Garner, E.C.; Bernhardt, T.G. Bacterial cell wall biogenesis is mediated by SEDS and PBP polymerase families functioning semi-autonomously. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgenstein, R.M.; Bratton, B.P.; Nguyen, J.P.; Ouzounov, N.; Shaevitz, J.W.; Gitai, Z. RodZ links MreB to cell wall synthesis to mediate MreB rotation and robust morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12510–12515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, D.R.; Graumann, P.L. Visualization, Quantification, and Statistical Evaluation of Dynamics for DNA-Binding Proteins in Bacteria by Single-Molecule Tracking. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2819, 189–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo-Bocanegra, L.M.; Hinrichs, R.; Rotter, D.A.O.; Dersch, S.; Graumann, P.L. Single molecule/particle tracking analysis program SMTracker 2.0 reveals different dynamics of proteins within the RNA degradosome complex in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassine, J.; Xu, M.; Sidiq, K.R.; Emmins, R.; Errington, J.; Daniel, R.A. Functional redundancy of division specific penicillin-binding proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 106, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucena, D.; Mauri, M.; Schmidt, F.; Eckhardt, B.; Graumann, P.L. Microdomain formation is a general property of bacterial membrane proteins and induces heterogeneity of diffusion patterns. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Mommer, M.S.; Sourjik, V. Mobility of cytoplasmic, membrane, and DNA-binding proteins in Escherichia Coli. Biophys. J. 2010, 98, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, B.; Schaab, C.; Albrecht, S.; Borgmann, M.; Brunner, N.A.; Freiberg, C.; Ziegelbauer, K.; Rock, C.O.; Ivanov, I.; Loferer, H. Prediction of mechanisms of action of antibacterial compounds by gene expression profiling. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, L.I.; Luo, Y.; Hachmann, A.B.; Mascher, T.; Helmann, J.D. The Bacillus subtilis GntR family repressor YtrA responds to cell wall antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5793–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, B.G. Distinct penicillin binding proteins involved in the division, elongation, and shape of Escherichia coli K12. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 2999–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Bogaart, G.; Hermans, N.; Krasnikov, V.; Poolman, B. Protein mobility and diffusive barriers in Escherichia coli: Consequences of osmotic stress. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 858–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csonka, L.N. Physiological and Genetic Responses of Bacteria to Osmotic Stress. Microbiol. Rev. 1989, 53, 121–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, R.A.; Errington, J. Control of cell morphogenesis in bacteria: Two distinct ways to make a rod-shaped cell. Cell 2003, 113, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.M.; Bramkamp, M. Cell wall synthesizing complexes in Mycobacteriales. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2024, 79, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, E.S.; Kado, T.; Garcia-Heredia, A.; Gupta, K.R.; Meniche, X.; Morita, Y.S.; Sassetti, C.M.; Rego, E.H.; Siegrist, M.S. Cell Wall Damage Reveals Spatial Flexibility in Peptidoglycan Synthesis and a Nonredundant Role for RodA in Mycobacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e0054021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Kannan, S.; Rao, V.A.; Biboy, J.; Vollmer, D.; Erickson, S.W.; Lewis, R.J.; Young, K.D.; Vollmer, W. The Redundancy of Peptidoglycan Carboxypeptidases Ensures Robust Cell Shape Maintenance in Escherichia coli. mBio 2016, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Localization | Salt | Sorbitol | Vancomycin | Penicillin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | |||||
| Pbp4 | polar | - | peripheral | dispersed | dispersed |
| 40% static | - * | more static * | - | more static | |
| Pbp3 | peripheral | more septal | more septal | dispersed | dispersed |
| 55% static | more static | more diffusive | more diffusive | more diffusive | |
| Class B | |||||
| Pbp2a | peripheral | more septal | more septal | delocalized | delocalized |
| 50% static | - | - | more diffusive | - | |
| Class C | |||||
| Pbp4a | polar | - | septal | dispersed | dispersed |
| 65% static | - | - | more diffusive | more diffusive |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stuckenschneider, L.; Graumann, P.L. Localization and Single Molecule Dynamics of Bacillus subtilis Penicillin-Binding Proteins Depend on Substrate Availability and Are Affected by Stress Conditions. Cells 2025, 14, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060429
Stuckenschneider L, Graumann PL. Localization and Single Molecule Dynamics of Bacillus subtilis Penicillin-Binding Proteins Depend on Substrate Availability and Are Affected by Stress Conditions. Cells. 2025; 14(6):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060429
Chicago/Turabian StyleStuckenschneider, Lisa, and Peter L. Graumann. 2025. "Localization and Single Molecule Dynamics of Bacillus subtilis Penicillin-Binding Proteins Depend on Substrate Availability and Are Affected by Stress Conditions" Cells 14, no. 6: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060429
APA StyleStuckenschneider, L., & Graumann, P. L. (2025). Localization and Single Molecule Dynamics of Bacillus subtilis Penicillin-Binding Proteins Depend on Substrate Availability and Are Affected by Stress Conditions. Cells, 14(6), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060429




