Nuclear RhoA Activation Regulates Nucleus Size and DNA Content via Nuclear Activation of ROCK and pErk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. DNA Transfection
2.4. Inhibitor Treatment
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Imaging Acquisition
2.7. CellProfiler Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
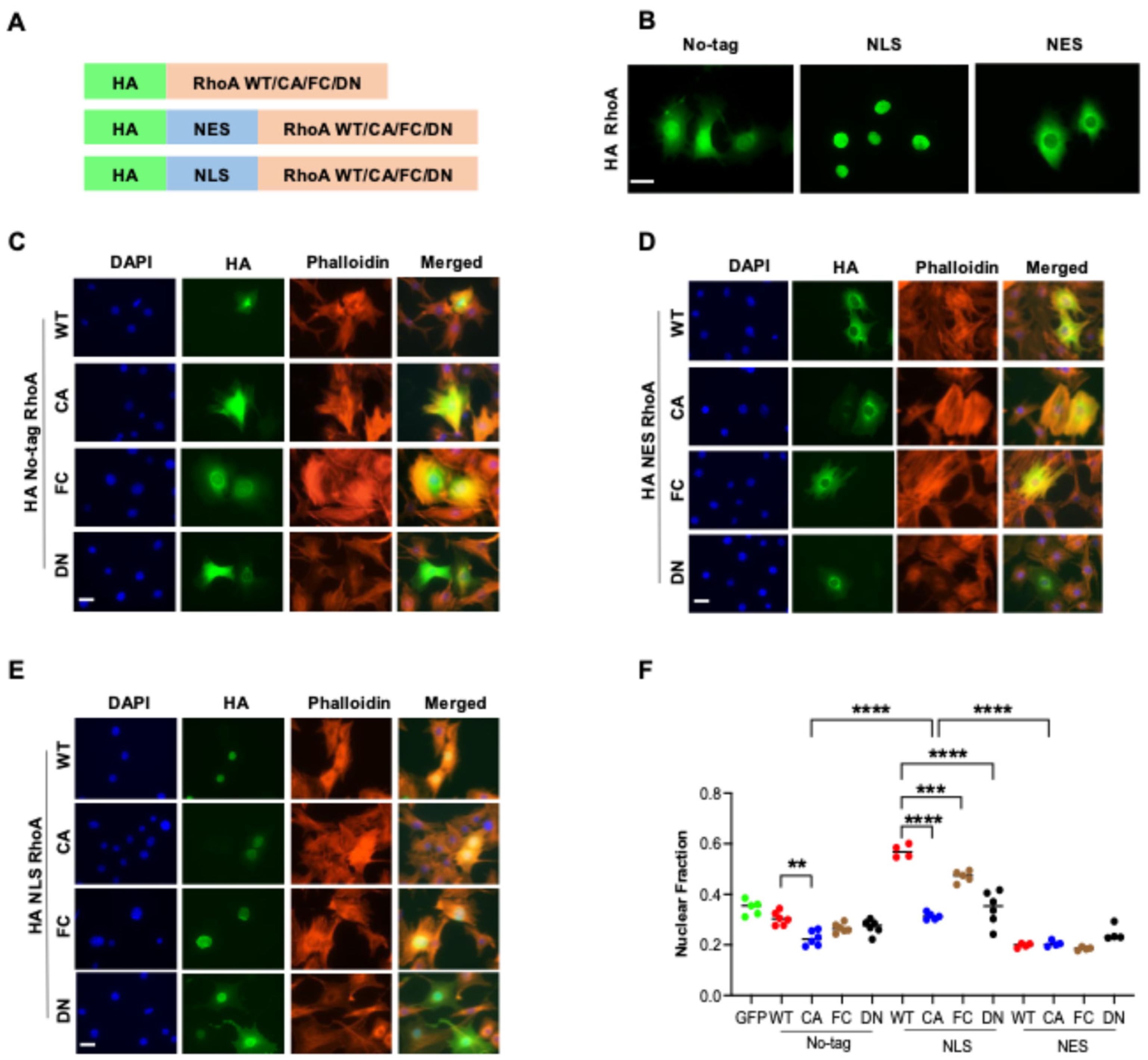
3.1. Establishment of a Platform to Distinguish Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Functions of RhoA
3.2. RhoA Activation Inhibits Nuclear Localization
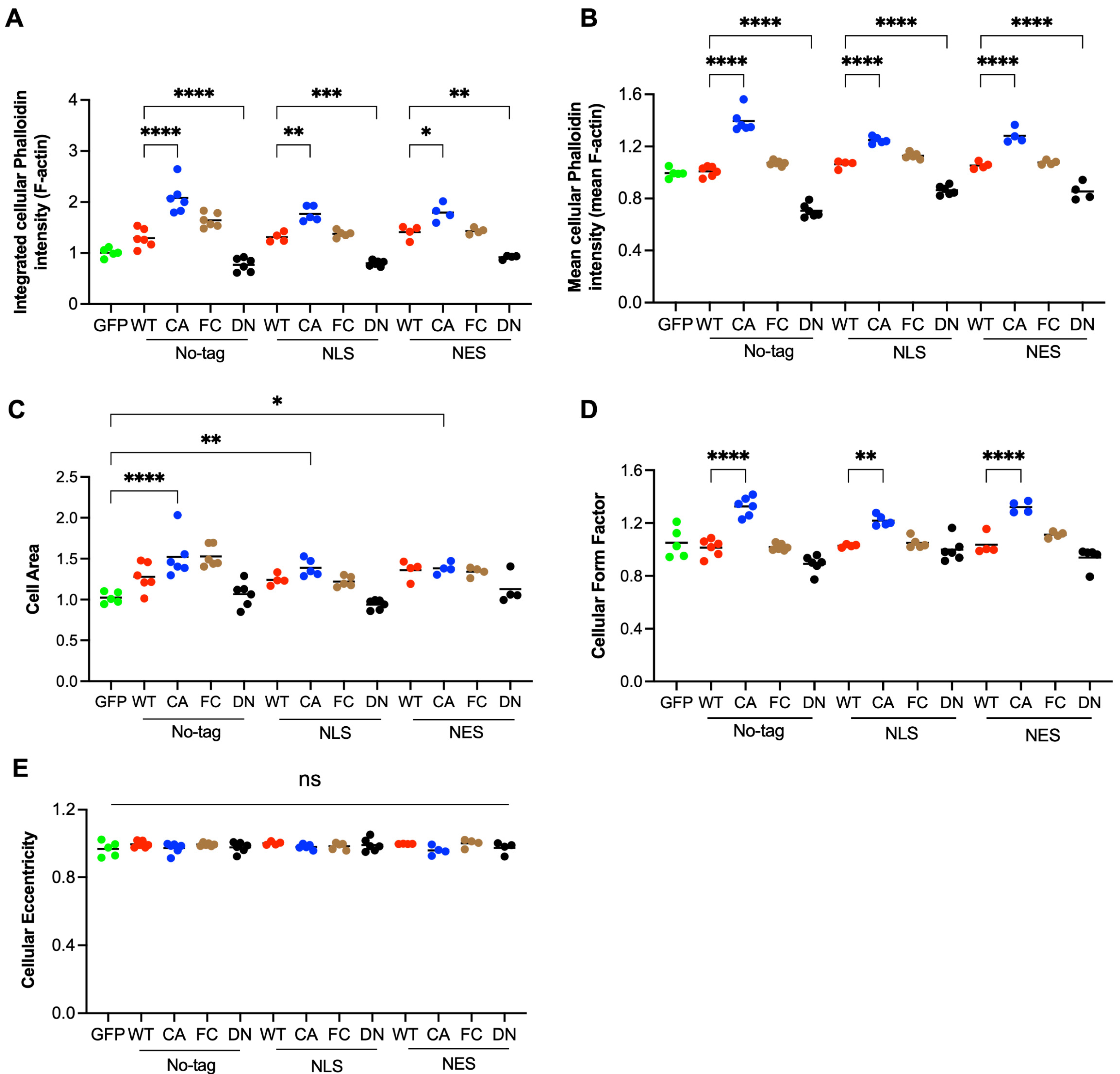
3.3. RhoA Regulates Cell Area and Shape by Total Level and Density of F-Actin
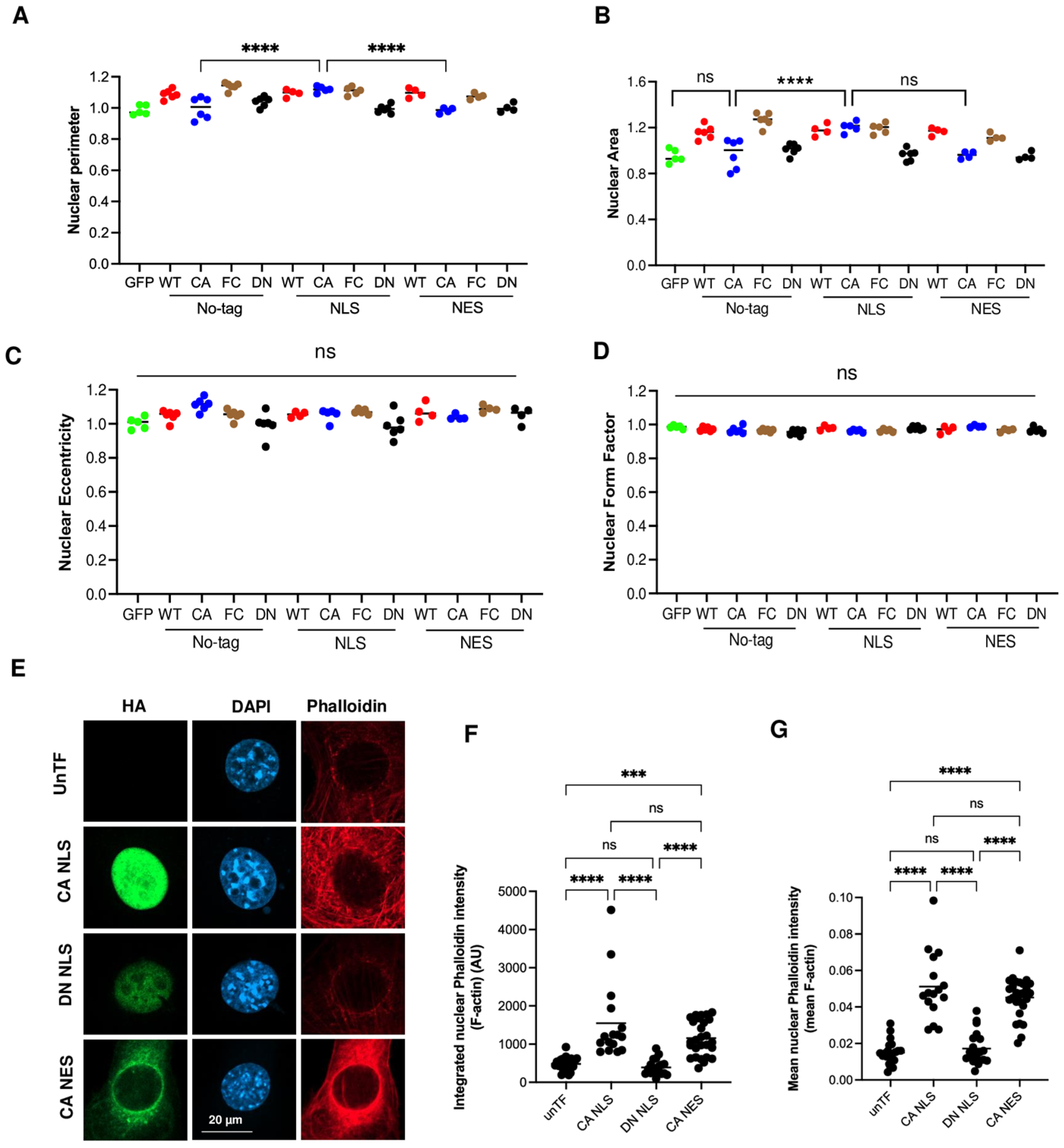
3.4. Activation of RhoA in the Nucleus Is Not Crucial for Nuclear Actin Polymerization
3.5. Nuclear RhoA Activity Regulates DNA Amounts
3.6. Nuclear RhoA Regulates DNA Amounts via ROCK Activation
3.7. No Specific Regulation of DNA Amounts by Nuclear Rac1 and Cdc42
3.8. Nuclear RhoA-ROCK Signaling Regulated DNA Amounts via Nuclear pErk
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heasman, S.J.; Ridley, A.J. Mammalian Rho GTPases: New insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosaddeghzadeh, N.; Ahmadian, M.R. The RHO Family GTPases: Mechanisms of Regulation and Signaling. Cells 2021, 10, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Seze, J.; Gatin, J.; Coppey, M. RhoA regulation in space and time. FEBS Lett. 2023, 597, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulter, E.; Garcia-Mata, R.; Guilluy, C.; Dubash, A.; Rossi, G.; Brennwald, P.J.; Burridge, K. Regulation of Rho GTPase crosstalk, degradation and activity by RhoGDINat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.M.; Rademacher, J.; Bagshaw, R.D.; Wortmann, C.; Barth, C.; van Unen, J.; Alp, K.M.; Giudice, G.; Eccles, R.L.; Heinrich, L.E.; et al. Rocks. Systems analysis of RhoGEF and RhoGAP regulatory proteins reveals spatially organized RAC1 signalling from integrin adhesions. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2020, 22, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.M.; Burridge, K. Mechanotransduction and nuclear function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 40, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, T.; Zhao, Y. Activation Mechanism of RhoA Caused by Constitutively Activating Mutations G14V and Q63L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Cerione, R.A.; Manor, D. Specific contributions of the small GTPases Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 to Dbl transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 23633–23641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, A. Rho GTPases. Integrating integrin signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, F107–F109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensmark, J.H.; Brakebusch, C. Rho GTPases in cancer: Friend or foe? Oncogene 2019, 38, 7447–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreu, I.; Granero-Moya, I.; Garcia-Manyes, S.; Roca-Cusach, P. Understanding the role of mechanics in nucleocytoplasmic transport. APL Bioeng. 2022, 6, 020901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubash, A.D.; Guilluy, C.; Srougi, M.C.; Boulter, E.; Burridge, K.; García-Mata, R. The small GTPase RhoA localizes to the nucleus and is activated by Net1 and DNA damage signals. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e17380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelson, D.; Abidi, W.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Zhou, M.; Ahearn, I.; Pagano, M.; Philips, M.R. Rac1 accumulates in the nucleus during the G2 phase of the cell cycle and promotes cell division. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 181, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.J.; Mitin, N.; Keller, P.J.; Chenette, E.J.; Madigan, J.P.; Currin, R.O.; Cox, A.D.; Wilson, O.; Kirschmeier, P.; Der, C.J. Rho Family GTPase modification and dependence on CAAX motif-signaled posttranslational modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25150–25163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, E.; Despot-Slade, E.; Pichler, M.; Zenobi-Wong, M. RhoA activation and nuclearization marks loss of chondrocyte phenotype in crosstalk with Wnt pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, M. RhoA protein is generally distributed in the nuclei of cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Che, L.; Jia, J.; Chen, M. Nucleolar localization of Small G protein RhoA is associated with active RNA synthesis in human carcinoma HEp-2 cells. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3605–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhowmick, N.A.; Ghiassi, M.; Aakre, M.; Brown, K.; Singh, V.; Moses, H.L. TGF-beta-induced RhoA and p160ROCK activation is involved in the inhibition of Cdc25A with resultant cell-cycle arrest. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15548–15553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nishimura, D.; Wu, R.C.; Amano, M.; Iso, T.; Kedes, L.; Nishida, H.; Kaibuchi, K.; Hamamori, Y. Nuclear Rho kinase, ROCK2, targets p300 acetyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15320–15329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Okawa, K.; Sekimoto, T.; Yoneda, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Ishizaki, T.; Narumiya, S. mDia2 shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm through the importin-alpha/beta- and CRM1-mediated nuclear trans- port mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5753–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarlink, C.; Wang, H.; Grosse, R. Nuclear actin network assembly by formins regulates the SRF coactivator MAL. Science 2013, 340, 864–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhu, R.; Mao, Y. Nuclear Actin Polymerized by mDia2 Confines Centromere Movement during CENP-A Loading. iScience 2018, 9, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisis, N.; Krasinska, L.; Harker, B.; Urbach, S.; Rossignol, M.; Camasses, A.; Dewar, J.; Morin, N.; Fisher, D. Initiation of DNA replication requires actin dynamics and formin activity. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3212–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, J.X.; Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Tsafou, K.; Stolte, C.; O’Donoghue, S.I.; Schneider, R.; Jensen, L.J. Compartments: Unification and visualization of protein subcellular localization evidence. Database 2014, 2014, bau012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulferts, S.; Prajapati, B.; Grosse, R.; Vartiainen, M.K. Emerging Properties and Functions of Actin and Actin Filaments Inside the Nucleus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2021, 13, a040121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.E.; Jones, T.R.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Clarke, C.; Kang, I.H.; Friman, O.; Guertin, D.A.; Chang, J.H.; Lindquist, R.A.; Moffat, J.; et al. CellProfiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuin, C.; Goodman, A.; Chernyshev, V.; Kamentsky, L.; Cimini, B.A.; Karhohs, K.W.; Doan, M.; Ding, L.; Rafelski, S.M.; Thirstrup, D.; et al. CellProfiler 3.0: Next-generation image processing for biology. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2005970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümper, S.; Mardakheh, F.K.; McCarthy, A.; Yeo, M.; Stamp, G.W.; Paul, A.; Worboys, J.; Sadok, A.; Jørgensen, C.; Guichard, S.; et al. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) function is essential for cell cycle progression, senescence and tumorigenesis. elife 2016, 5, e12994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, H.; Gagnon, J.; Therrien, M. ERK signalling: A master regulator of cell behaviour, life and fate. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 607–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, D.R.; Olson, M.F. The Rho GTPase effector ROCK regulates cyclin A, cyclin D1, and p27Kip1 levels by distinct mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 4612–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faried, A.; Faried, L.S.; Kimura, H.; Nakajima, M.; Sohda, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Kato, H.; Usman, N.; Kuwano, H. RhoA and RhoC proteins promote both cell proliferation and cell invasion of human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1455–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, P.; Flors, C.; Olson, M.F. Constitutively active RhoA inhibits proliferation by retarding G(1) to S phase cell cycle progression and impairing cytokinesis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 88, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, G. Overexpression of RhoA promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunier, C.; Prudent, R.; Kapur, R.; Sadoul, K.; Lafanechère, L. LIM kinases: Cofilin and beyond. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 41749–41763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baarlink, C.; Plessner, M.; Sherrard, A.; Morita, K.; Misu, S.; Virant, D.; Kleinschnitz, E.M.; Harniman, R.; Alibhai, D.; Baumeister, S.; et al. A transient pool of nuclear F-actin at mitotic exit controls chromatin organization. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, T.; Li, W.Y.; Hatano, Y.; Takasu, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Ikeda, Z.; Shindo, T.; Plessner, M.; Morita, K.; et al. Zygotic Nuclear F-Actin Safeguards Embryonic Development. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dopie, J.; Skarp, K.P.; Rajakylä, E.K.; Tanhuanpää, K.; Vartiainen, M.K. Active maintenance of nuclear actin by importin 9 supports transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E544–E552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, L.P.; Svensmark, J.; Jiang, X.; Jordan, A.; Brakebusch, C. Nuclear RhoA Activation Regulates Nucleus Size and DNA Content via Nuclear Activation of ROCK and pErk. Cells 2025, 14, 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060404
Nguyen LP, Svensmark J, Jiang X, Jordan A, Brakebusch C. Nuclear RhoA Activation Regulates Nucleus Size and DNA Content via Nuclear Activation of ROCK and pErk. Cells. 2025; 14(6):404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060404
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Lap P., Julius Svensmark, Xin Jiang, Alexander Jordan, and Cord Brakebusch. 2025. "Nuclear RhoA Activation Regulates Nucleus Size and DNA Content via Nuclear Activation of ROCK and pErk" Cells 14, no. 6: 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060404
APA StyleNguyen, L. P., Svensmark, J., Jiang, X., Jordan, A., & Brakebusch, C. (2025). Nuclear RhoA Activation Regulates Nucleus Size and DNA Content via Nuclear Activation of ROCK and pErk. Cells, 14(6), 404. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060404





.png)
