Epigallocatechin Gallate Promotes Cuproptosis via the MTF1/ATP7B Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture Studies
2.3. Cell Death Assays
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.5. Crystal Violet Staining
2.6. Western Blotting Analysis
2.7. Immunofluorescence (IF)
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis of the Cellular ROS
2.9. Determination of Copper Content in Cells
2.10. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.11. Detection of Intracellular GSH
2.12. Cu-ATPase Activity Measurement
2.13. Mice Xenograft Model
2.14. Statistics and Reproducibility
3. Results
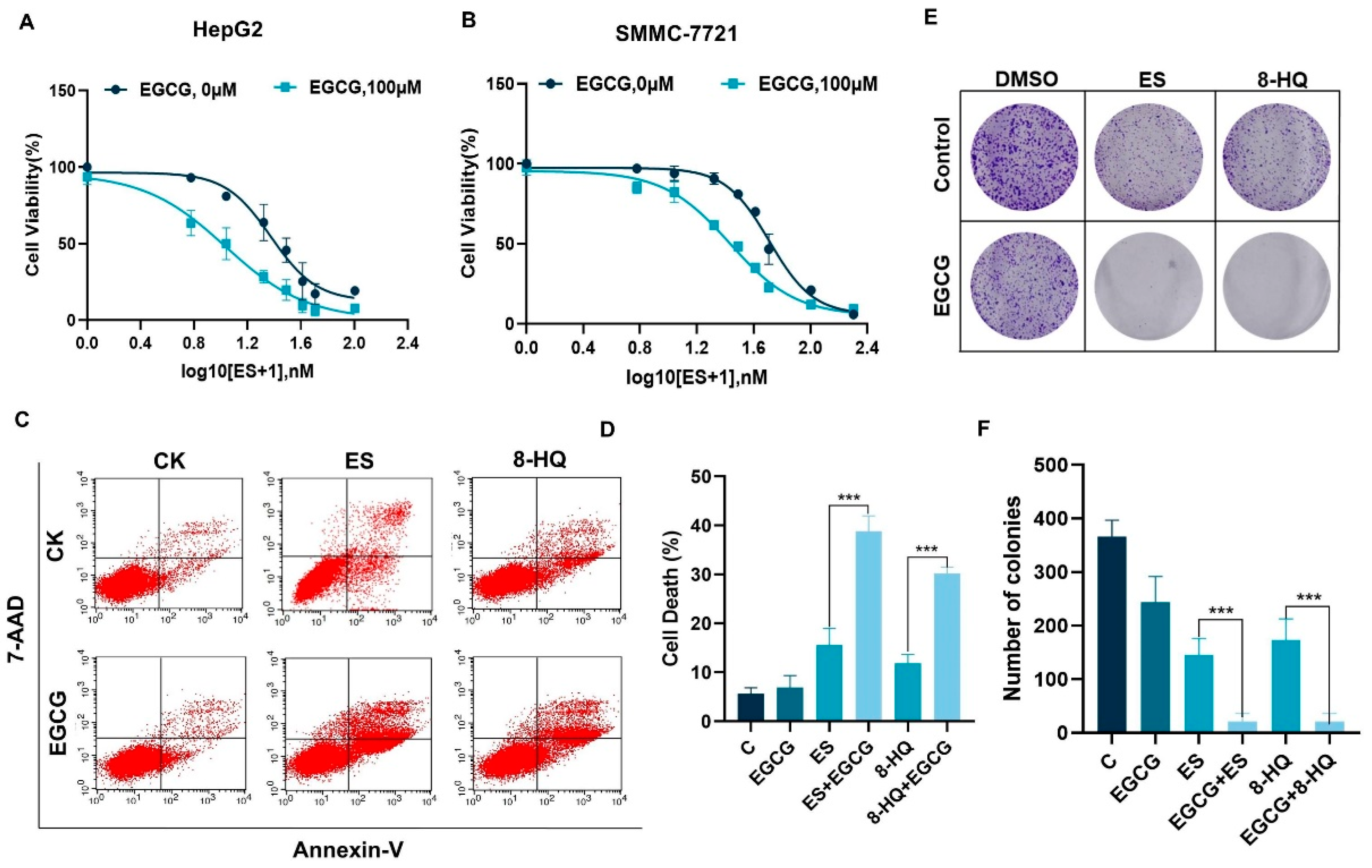
3.1. EGCG and Copper Ionophore Combinational Treatment Promotes Cell Death
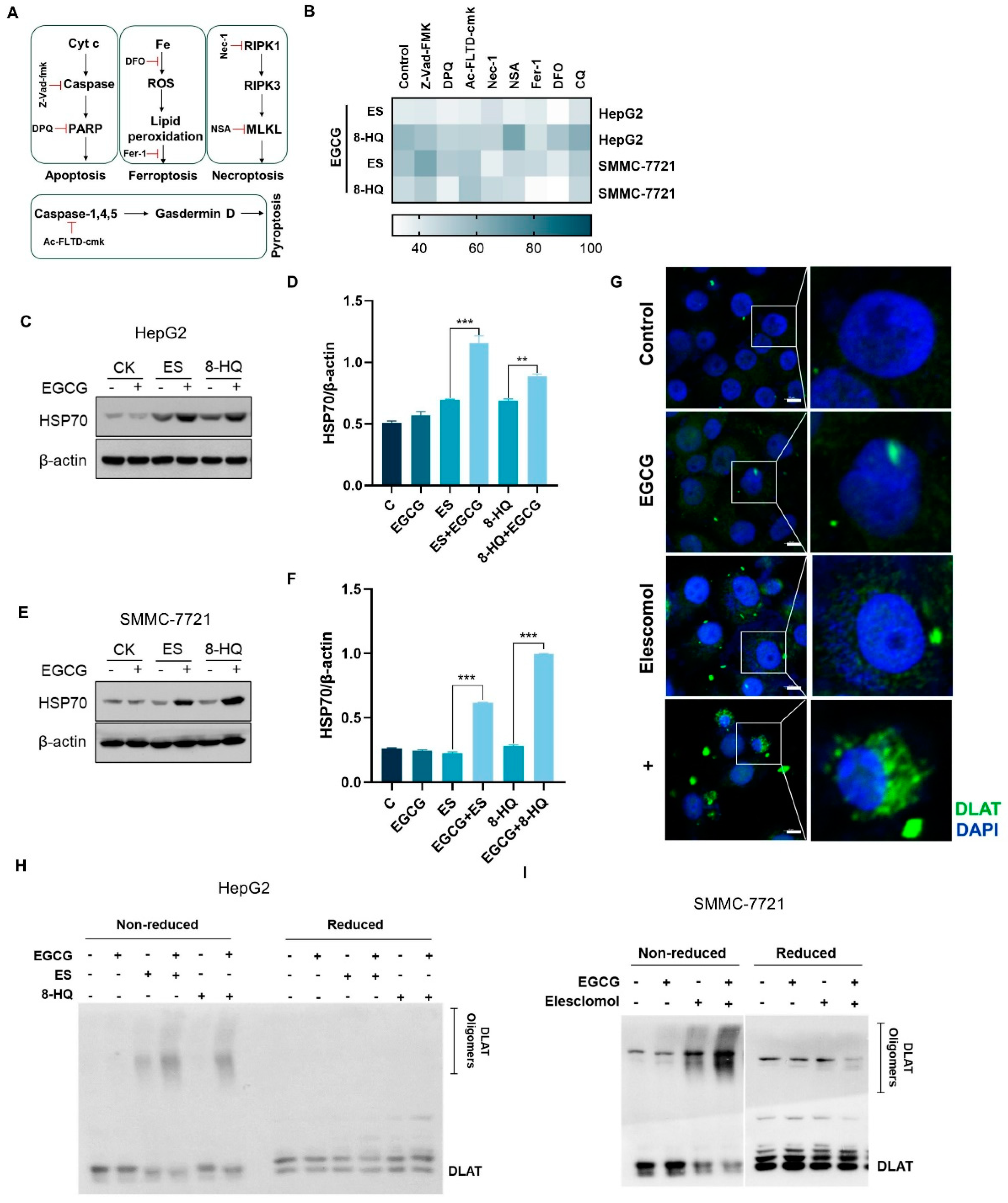
3.2. EGCG and Copper Ionophore Combinational Treatment Induces Cuproptosis
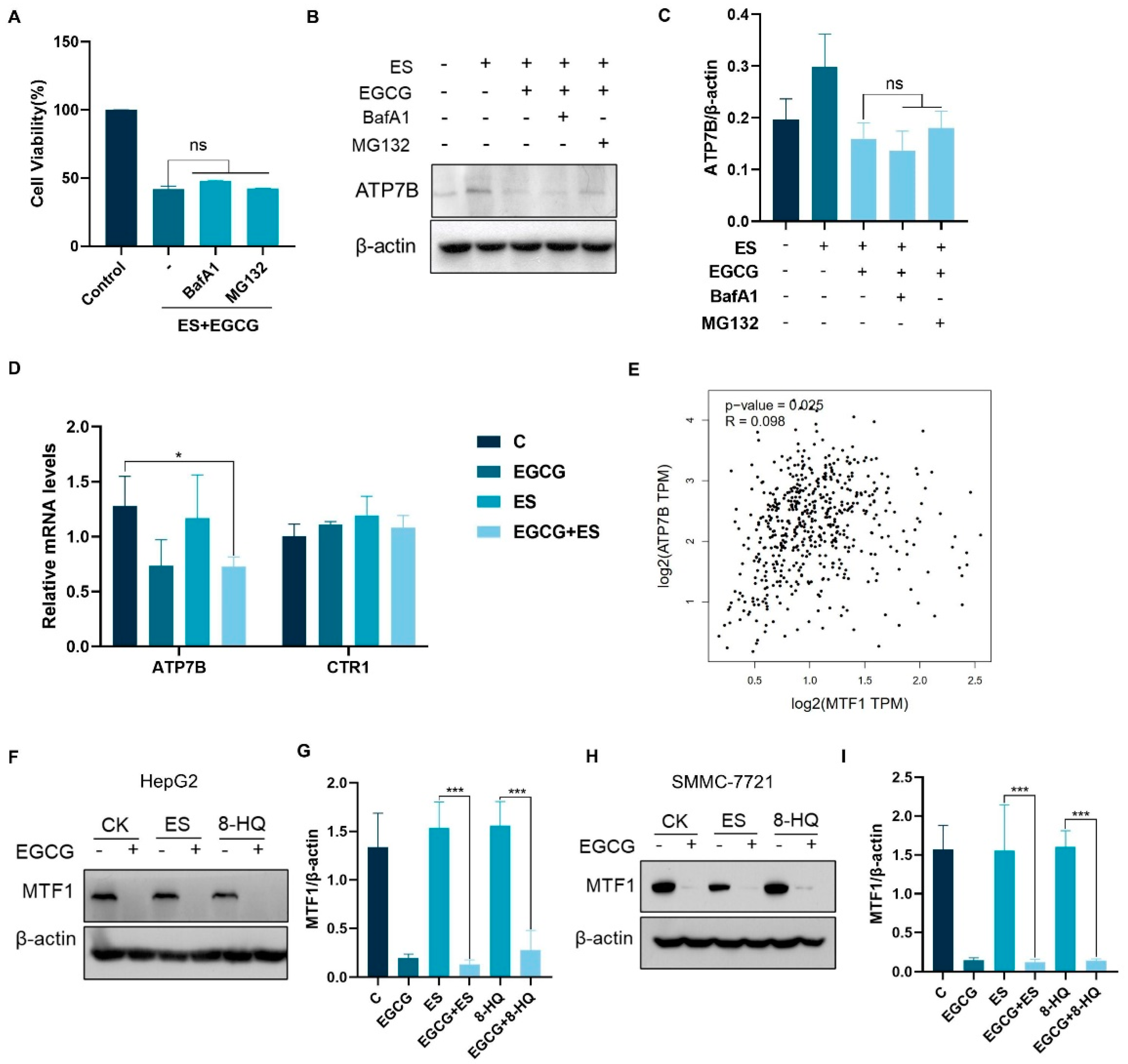
3.3. EGCG Increases Intracellular Copper Accumulation by Down-Regulating ATP7B Expression
3.4. EGCG Regulates ATP7B Transcription by Inhibiting MTF1 Expression
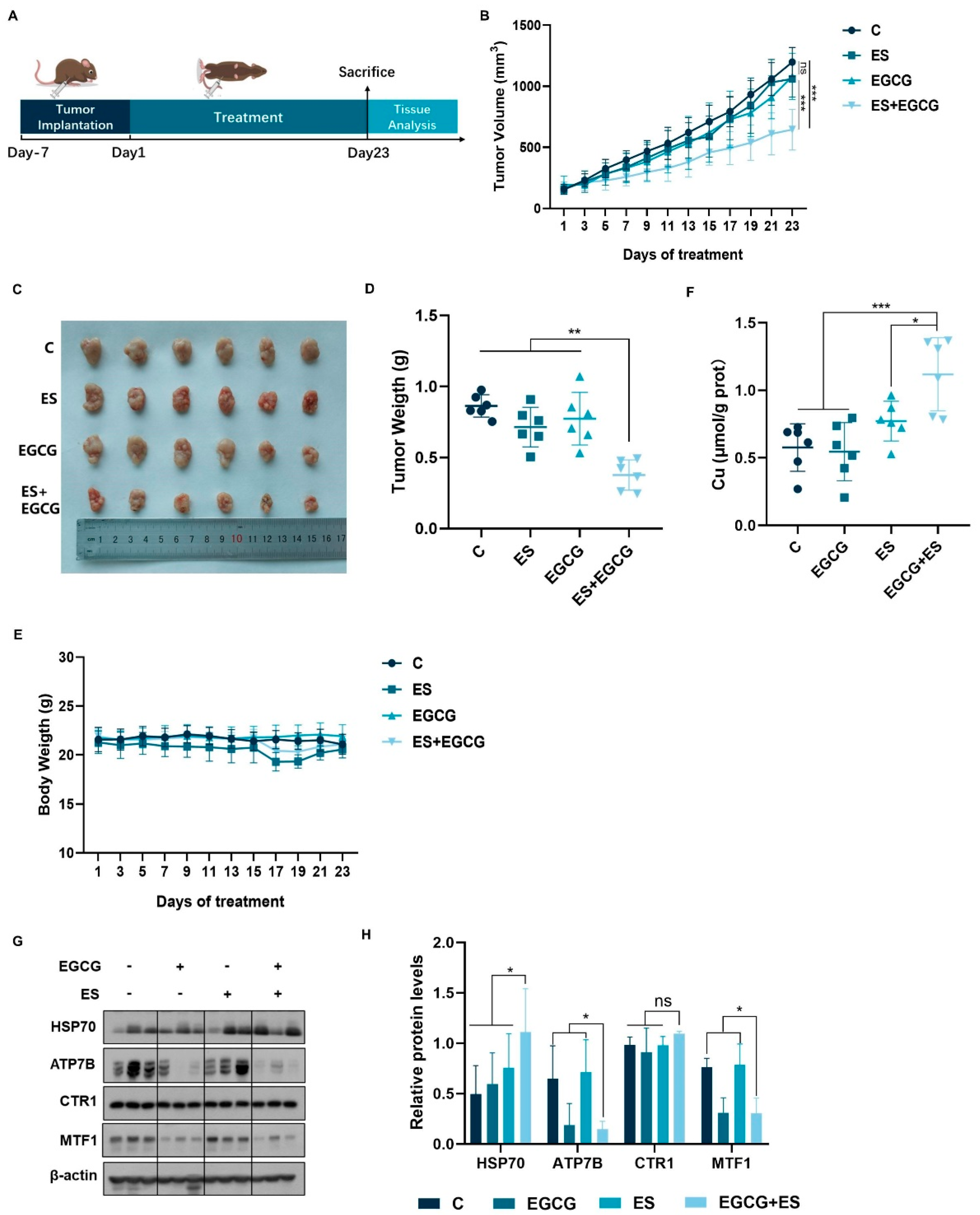
3.5. Combination of EGCG and ES Exhibits Enhanced Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Effects In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 7-AAD | 7-Aminoactinomycin D |
| CAT | Catalase |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| DLAT | Dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase |
| Fe-S cluster | Iron–sulfur cluster |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin gallate |
| MTF1 | Metal regulatory transcription factor |
| ATP7B | Copper-transporting P-type ATPase |
| ES | Elesclomol |
| 8-HQ | 8-Hydroxyquinoline |
| DSF | Disulfiram |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| DCF | 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| TTM | Tetrathiomolybdate |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| BSO | Buthionine sulfoximine |
| HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| CTR1 | Copper transporter 1 |
| TGN | Trans-Golgi network |
| CQ | Chloroquine |
| BafA1 | Bafilomycin A1 |
| FINs | Class I ferroptosis inducers |
| MBDs | Metal binding domains |
| MREs | Metal response elements |
| CS1 | Coppersensor 1 |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas Program |
| LIHC | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase-1 |
| ICP-MS | Inductively coupled plasma mass |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023, 42, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergholz, J.S.; Wang, Q.; Kabraji, S.; Zhao, J.J. Integrating Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy in Cancer Treatment: Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5557–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, E.J.; Bush, A.I.; Casini, A.; Cobine, P.A.; Cross, J.R.; DeNicola, G.M.; Dou, Q.P.; Franz, K.J.; Gohil, V.M.; Gupta, S.; et al. Connecting copper and cancer: From transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2022, 22, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, P.; Coy, S.; Petrova, B.; Dreishpoon, M.; Verma, A.; Abdusamad, M.; Rossen, J.; Joesch-Cohen, L.; Humeidi, R.; Spangler, R.D.; et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 2022, 375, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacko, S.M.; Thambi, P.T.; Kuttan, R.; Nishigaki, I. Beneficial effects of green tea: A literature review. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braicu, C.; Irimie, A.I.; Zanoaga, O.; Gherman, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Campian, R.S.; Pileczki, V. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis and autophagy in oral cancer SSC-4 cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Ye, H.-L.; Zhang, G.; Yao, W.-M.; Chen, X.-Z.; Zhang, F.-C.; Liang, G. Autophagy inhibition contributes to the synergistic interaction between EGCG and doxorubicin to kill the hepatoma Hep3B cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, P.; Yang, C.S.; Wang, X.; Feng, Q. EGCG Enhances Cisplatin Sensitivity by Regulating Expression of the Copper and Cisplatin Influx Transporter CTR1 in Ovary Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125402. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Han, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lv, X.; Gao, M. S100A4/NF-κB axis mediates the anticancer effect of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. iScience 2024, 27, 108885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.N.; Yin, J.J.; Shen, S.R. Growth inhibition of prostate cancer cells by epigallocatechin gallate in the presence of Cu2+. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, M.; Rizvi, A.; Naseem, I.; Hadi, S.M.; Ahmad, A. Targeting increased copper levels in diethylnitrosamine induced hepatocellular carcinoma cells in rats by epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8861–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Fleishman, J.S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Cuproptosis: A novel therapeutic target for overcoming cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2024, 72, 101018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowburn, A.S.; White, J.F.; Deighton, J.; Walmsley, S.R.; Chilvers, E.R. z-VAD-fmk augmentation of TNF alpha-stimulated neutrophil apoptosis is compound specific and does not involve the generation of reactive oxygen species. Blood 2005, 105, 2970–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, R.; Rathkey, J.K.; Pinkard, O.W.; Shi, W.; Chen, Y.; Dubyak, G.R.; Abbott, D.W.; et al. Mechanism of gasdermin D recognition by inflammatory caspases and their inhibition by a gasdermin D-derived peptide inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6792–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Wen, L.; Armstrong, J.A.; Chvanov, M.; Latawiec, D.; Cai, W.; Awais, M.; Mukherjee, R.; Huang, W.; Gough, P.J.; et al. Protective Effects of Necrostatin-1 in Acute Pancreatitis: Partial Involvement of Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase 1. Cells 2021, 10, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, T.; Deng, Z.; Song, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, F.; Li, Q.; Lin, S.; et al. EF24 induces ferroptosis in osteosarcoma cells through HMOX1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Vo, N.H.; Ogawa, L.S.; Chimmanamada, D.; Inoue, T.; Chu, J.; Beaudette-Zlatanova, B.C.; Lu, R.; Blackman, R.K.; Barsoum, J.; et al. The oncology drug elesclomol selectively transports copper to the mitochondria to induce oxidative stress in cancer cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 2142–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pei, R.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, J.; Yu, W.; Qiao, N.; Han, Q.; Li, Y.; Hu, L.; Guo, J.; et al. Copper induces oxidative stress and apoptosis through mitochondria-mediated pathway in chicken hepatocytes. Toxicol. In Vitro 2019, 54, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.M.; Xu, L.; Wang, R.M.; Tao, X.; Zheng, Z.W.; Chang, S.; Ma, D.; Zhao, C.; Dong, Y.; Wu, S.; et al. Structures of the human Wilson disease copper transporter ATP7B. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stalke, A.; Pfister, E.-D.; Baumann, U.; Illig, T.; Reischl, E.; Sandbothe, M.; Vajen, B.; Huge, N.; Schlegelberger, B.; Von Neuhoff, N.; et al. MTF1 binds to metal-responsive element e within the atp7b promoter and is a strong candidate in regulating the ATP7B expression. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2020, 84, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Nakajima, T.; Moriguchi, M.; Jo, M.; Sekoguchi, S.; Ishii, M.; Takashima, H.; Katagishi, T.; Kimura, H.; Minami, M.; et al. A green tea polyphenol, epigalocatechin-3-gallate, induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma, possibly through inhibition of Bcl-2 family proteins. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Tong, Y.; Gowd, V.; Wang, M.; Chen, F.; Cheng, K.W. Oral administration of EGCG solution equivalent to daily achievable dosages of regular tea drinkers effectively suppresses miR483-3p induced metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3381–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Li, W.; Duan, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, R. A new molecular mechanism underlying the EGCG-mediated autophagic modulation of AFP in HepG2 cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Quon, M.J.; Kim, J.A. New insights into the mechanisms of polyphenols beyond antioxidant properties; lessons from the green tea polyphenol, epigallocatechin 3-gallate. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, M.H.; Adhami, V.M.; Lee, J.S.; Mukhtar, H. Constitutive overexpression of Nrf2-dependent heme oxygenase-1 in A549 cells contributes to resistance to apoptosis induced by epigallocatechin 3-gallate. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 33761–33772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Hao, M.; Rayman, M.P.; Zhang, J. Prooxidant activity-based guideline for a beneficial combination of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and chlorogenic acid. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zischka, H.; Einer, C. Mitochondrial copper homeostasis and its derailment in Wilson disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 102, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikova, E.V.; Garbuz, M.M.; Ovchinnikova, A.A.; Kumeiko, V.V. Epidemiology of Wilson’s Disease and Pathogenic Variants of the atp7b Gene Leading to Diversified Protein Disfunctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakanthan, S.; Braiterman, L.T.; Hasan, N.M.; Unger, V.M.; Lutsenko, S. Human copper transporter ATP7B (Wilson disease protein) forms stable dimers in vitro and in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 18760–18774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Nakaoka, H.J.; Hofmann, L.; Zhou, J.J.; Yu, C.; Zeng, L.; Nan, J.; Seo, G.; Vargas, R.E.; Yang, B.; et al. The Hippo pathway kinases LATS1 and LATS2 attenuate cellular responses to heavy metals through phosphorylating MTF1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Huang, M.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, S.; Wan, J.; Ahmadi, A.R.; Sun, Z.; et al. The epigenetic regulator SIRT6 protects the liver from alcohol-induced tissue injury by reducing oxidative stress in mice. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, R.; Commons, E.; Camakaris, J. Expression and localisation of the essential copper transporter DmATP7 in Drosophila neuronal and intestinal tissues. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.I.; Jagadeesh, K.A.; Birgmeier, J.; Wenger, A.M.; Guturu, H.; Schelley, S.; Bernstein, J.A.; Bejerano, G. An MTF1 binding site disrupted by a homozygous variant in the promoter of atp7b likely causes Wilson Disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Cottet, J.; Rodriguez-Otero, M.R.; Wasuwanich, P.; Furst, A.L. Metal-Phenolic Networks as Versatile Coating Materials for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4687–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Hou, L.; Han, K.; Zhao, C.; Hu, H.; Yin, S. Epigallocatechin Gallate Promotes Cuproptosis via the MTF1/ATP7B Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2025, 14, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060391
Fu Y, Hou L, Han K, Zhao C, Hu H, Yin S. Epigallocatechin Gallate Promotes Cuproptosis via the MTF1/ATP7B Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells. 2025; 14(6):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060391
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yuhan, Lirui Hou, Kai Han, Chong Zhao, Hongbo Hu, and Shutao Yin. 2025. "Epigallocatechin Gallate Promotes Cuproptosis via the MTF1/ATP7B Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cells 14, no. 6: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060391
APA StyleFu, Y., Hou, L., Han, K., Zhao, C., Hu, H., & Yin, S. (2025). Epigallocatechin Gallate Promotes Cuproptosis via the MTF1/ATP7B Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells, 14(6), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14060391




