HOTAIR Participation in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Through Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. HOTAIR Knockdown and Overexpression
2.3. Proliferation Assay
2.4. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and qRT-PCR
2.5. RNA Binding Protein Immunoprecipitation (RIP) Assay
2.6. Measurements of Glucose, Lactate, Glutamine/Glutamate, and ATP Levels
2.7. Tissue Expression for In Silico Meta-Analysis
2.8. Visualization of the Protein–Protein Interaction Network
2.9. HIF-1α and HOTAIR Co-Localization Assay
2.10. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
2.11. Database Search
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
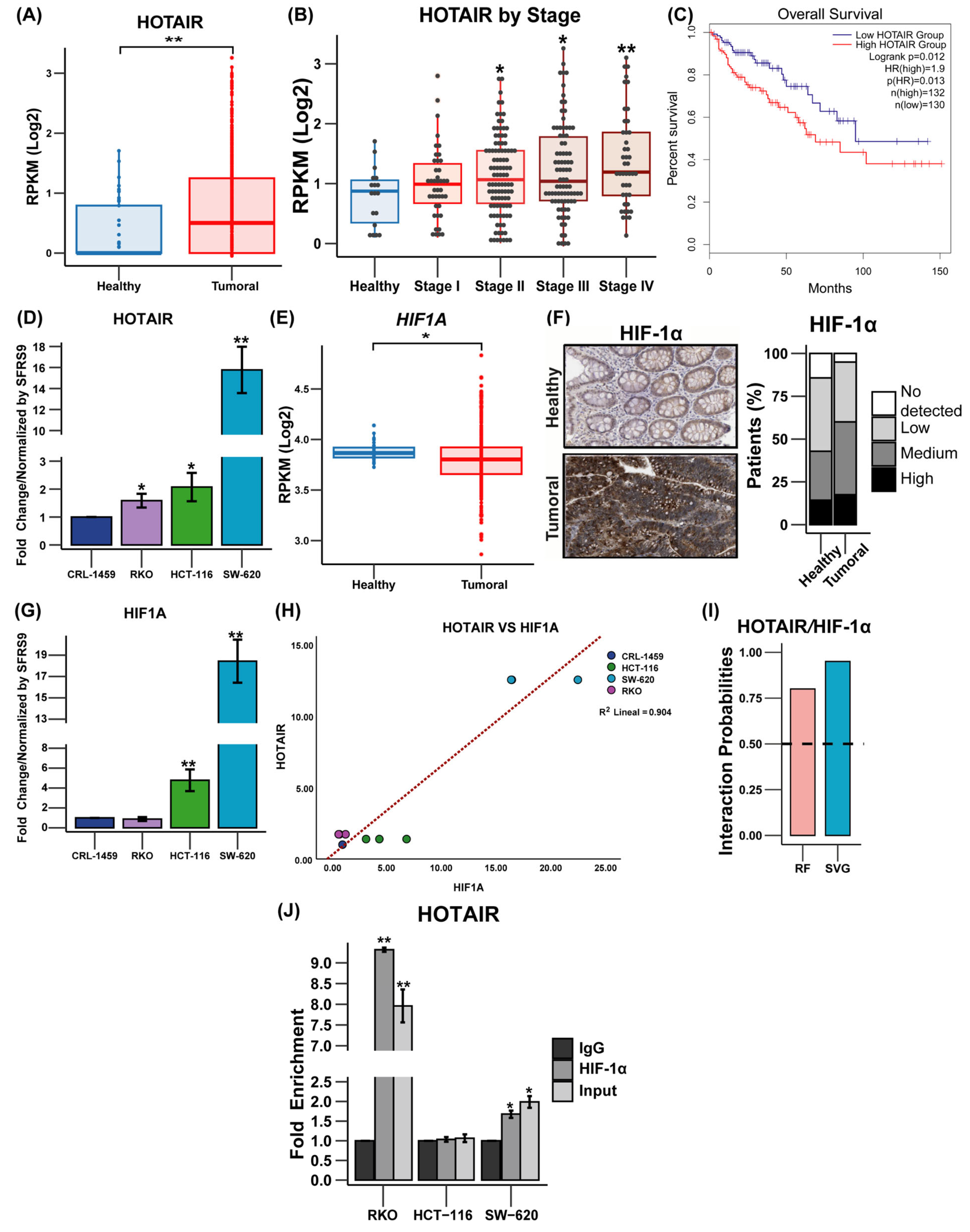
3.1. Evaluation of HOTAIR and HIF-1α Expression in Colorectal Cancer
3.2. Probability of Regulation of Proteins Involved in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis by the HIF1α/HOTAIR Axis
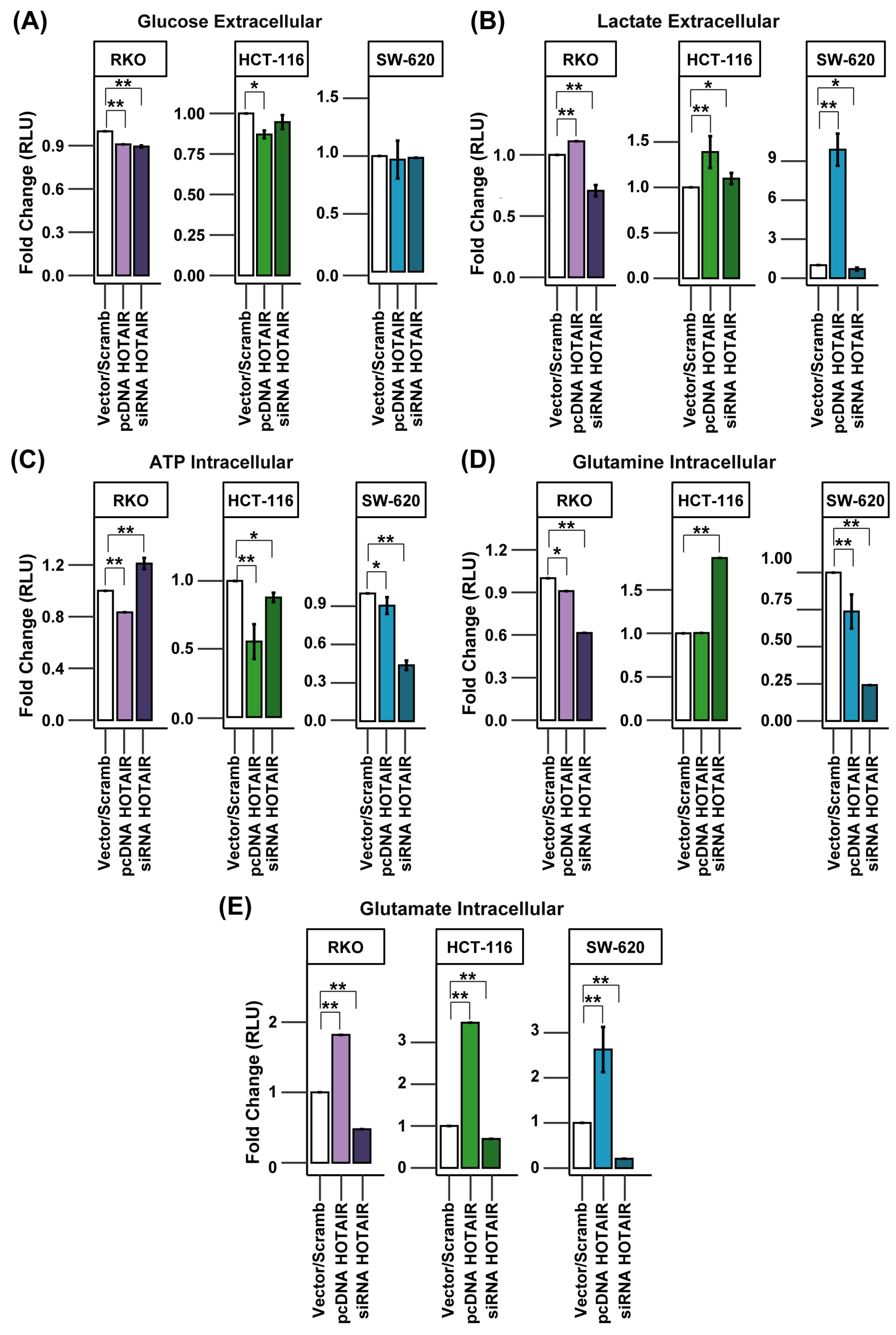
3.3. HOTAIR Promotes Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Enzyme Expression
3.4. HOTAIR Regulates Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer Cells
3.5. The Role of Hif-1α in the Transcriptional Regulation of Metabolic Enzymes Modulated by HOTAIR
3.6. Effect of the Pharmacological Inhibition of HOTAIR on Colorectal Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today (Version 1.1). Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Thanikachalam, K.; Khan, G. Colorectal Cancer and Nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lohlamoh, W.; Soontornworajit, B.; Rotkrua, P. Anti-Proliferative Effect of Doxorubicin-Loaded AS1411 Aptamer on Colorectal Cancer Cell. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 2209–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Chandel, N.S. Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pavlova, N.N.; Zhu, J.; Thompson, C.B. The hallmarks of cancer metabolism: Still emerging. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tan, Y.T.; Lin, J.F.; Li, T.; Li, J.J.; Xu, R.H.; Ju, H.Q. LncRNA-mediated posttranslational modifications and reprogramming of energy metabolism in cancer. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sellitto, A.; Pecoraro, G.; Giurato, G.; Nassa, G.; Rizzo, F.; Saggese, P.; Martinez, C.A.; Scafoglio, C.; Tarallo, R. Regulation of Metabolic Reprogramming by Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, S.; Shen, X. Long noncoding RNAs: Functions and mechanisms in colon cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ortiz-Pedraza, Y.; Muñoz-Bello, J.O.; Olmedo-Nieva, L.; Contreras-Paredes, A.; Martínez-Ramírez, I.; Langley, E.; Lizano, M. Non-Coding RNAs as Key Regulators of Glutaminolysis in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Chu, F.; Zhou, X.; Xie, R.; Wei, Q.; Yang, S.; Li, T.; Liang, S.; Lü, M. Long non-coding RNAs: Key regulators involved in metabolic reprogramming in cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermúdez, M.; Aguilar-Medina, M.; Lizárraga-Verdugo, E.; Avendaño-Félix, M.; Silva-Benítez, E.; López-Camarillo, C.; Ramos-Payán, R. LncRNAs as Regulators of Autophagy and Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xin, X.; Li, Q.; Fang, J.; Zhao, T. LncRNA HOTAIR: A Potential Prognostic Factor and Therapeutic Target in Human Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 679244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, L.; Qian, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X. The HOTAIR lncRNA: A remarkable oncogenic promoter in human cancer metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2015, 1856, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, J.O.; Jun, H.H.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.S.; Ryu, C.S.; Kim, S.; Oh, D.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, N.K. Genetic Variants of HOTAIR Associated With Colorectal Cancer Susceptibility and Mortality. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Price, R.L.; Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. HOTAIR beyond repression: In protein degradation, inflammation, DNA damage response, and cell signaling. DNA Repair 2021, 105, 103141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, X.; Huang, H.; Fu, W.; Liang, J.; Wu, W. The HIF-1α antisense long non-coding RNA drives a positive feedback loop of HIF-1α mediated transactivation and glycolysis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, Z.; Hu, Z.; Sui, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Liang, J.; Lu, T.; Zhan, C.; Lin, Z.; et al. LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 facilitates tumor proliferation and the migration via the HIF-1α/ glycolysis axis in lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 522–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wolf, D.; Muralidharan, A.; Mohan, S. Role of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins in bone metabolism. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia. 2022, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, X.; Geng, H.; Zuo, D.; Zhao, Q. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway-related long non-coding RNAs: Roles and mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.; Li, O.; Zheng, W.; Xiao, W.Z.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Cai, G.Y.; He, J.C.; Chen, X.M. LncRNA HOTAIR regulates HIF-1α/AXL signaling through inhibition of miR-217 in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, S.; Fan, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Zong, Z.; Hua, X.; Su, D.; Sun, H.; Li, H.; et al. Promotion of glycolysis by HOTAIR through GLUT1 upregulation via mTOR signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1902–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Fu, Q.; Jing, C.; Zhang, X.; Qin, T.; Pan, Y. LncRNA HOTAIR knockdown inhibits glycolysis by regulating miR-130a-3p/HIF1A in hepatocellular carcinoma under hypoxia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Vecchia, S.; Sebastián, C. Metabolic pathways regulating colorectal cancer initiation and progression. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 98, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Mou, J.; Shao, B.; Wei, Y.; Liang, H.; Takano, N.; Semenza, G.L.; Xie, G. Glutaminase 1 expression in colorectal cancer cells is induced by hypoxia and required for tumor growth, invasion, and metastatic colonization. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yun, H.J.; Li, M.; Guo, D.; Jeon, S.M.; Park, S.H.; Lim, J.S.; Lee, S.B.; Liu, R.; Du, L.; Kim, S.H.; et al. AMPK-HIF-1α signaling enhances glucose-derived de novo serine biosynthesis to promote glioblastoma growth. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- García-Castillo, V.; López-Urrutia, E.; Villanueva-Sánchez, O.; Ávila-Rodríguez, M.Á.; Zentella-Dehesa, A.; Cortés-González, C.; López-Camarillo, C.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.J.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. Targeting Metabolic Remodeling in Triple Negative Breast Cancer in a Murine Model. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Coronel-Hernández, J.; Salgado-García, R.; Cantú-De León, D.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; Millan-Catalan, O.; Delgado-Waldo, I.; Campos-Parra, A.D.; Rodríguez-Morales, M.; Delgado-Buenrostro, N.L.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. Combination of Metformin, Sodium Oxamate and Doxorubicin Induces Apoptosis and Autophagy in Colorectal Cancer Cells via Downregulation HIF-1α. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 594200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Delgado-Waldo, I.; Contreras-Romero, C.; Salazar-Aguilar, S.; Pessoa, J.; Mitre-Aguilar, I.; García-Castillo, V.; Pérez-Plasencia, C.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.J. A triple-drug combination induces apoptosis in cervical cancer-derived cell lines. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long Noncoding RNA and Cancer: A New Paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3965–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.Q.; Zhu, L.; Bi, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. LncRNAs regulate metabolism in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taniue, K.; Akimitsu, N. The Functions and Unique Features of LncRNAs in Cancer Development and Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tufail, M. HOTAIR in colorectal cancer: Structure, function, and therapeutic potential. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, B.; Ren, X.; Qi, X.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, C.; Jia, L. HOTAIR/miR-326/FUT6 axis facilitates colorectal cancer progression through regulating fucosylation of CD44 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 750–760, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.02.004; Erratum in: Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2019, 1866, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, D. HOTAIR regulates colorectal cancer stem cell properties and promotes tumorigenicity by sponging miR-211-5p and modulating FLT-1. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Long, W.B.; Pu, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; She, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Guo, Q.X. Arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase 1 Regulates Glycolysis in Colorectal Cancer via the PI3K/AKT/HIF1α Pathway. Curr. Med. Sci. 2022, 42, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.C.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Kwon, K.A.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Park, K.J.; Lee, H.S.; Roh, M.S.; et al. Clinicopathological significance of nuclear factor-kappa B, HIF-1 alpha, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage III colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ioannou, M.; Paraskeva, E.; Baxevanidou, K.; Simos, G.; Papamichali, R.; Papacharalambous, C.; Samara, M.; Koukoulis, G. HIF-1α in colorectal carcinoma: Review of the literature. J. Buon. 2015, 20, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuomisto, A.; García-Solano, J.; Sirniö, P.; Väyrynen, J.; Pérez-Guillermo, M.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Conesa-Zamora, P. HIF-1α expression and high microvessel density are characteristic features in serrated colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch. 2016, 469, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, L.; Jiang, C.; Bai, J.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, H. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR, a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activated driver of malignancy, enhances hypoxic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 9179–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujano-Camacho, S.; Cantú-de León, D.; Pérez-Yepez, E.; Contreras-Romero, C.; Coronel-Hernandez, J.; Millan-Catalan, O.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M.; López-Camarillo, C.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, C.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; et al. HOTAIR Promotes the Hyperactivation of PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways via PTEN Hypermethylation in Cervical Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, X.H.; Sun, M.; Nie, F.Q.; Ge, Y.B.; Zhang, E.B.; Yin, D.D.; Kong, R.; Xia, R.; Lu, K.H.; Li, J.H.; et al. Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, K.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Qiu, G.D.; She, Y.Q.; Zheng, J.T.; Chen, C.; Fang, L.; et al. Down-Regulated LncRNA-HOTAIR Suppressed Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration by Mediating p21. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2320–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.K.; Zhang, H.J.; Zou, M.X.; Wang, C.; Yan, Y.G.; Zhan, X.L.; Li, X.L.; Wang, W.J. LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell proliferation via miR-130b/PTEN/AKT axis in IDD. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fu, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X. LncRNA HOTAIR facilitates proliferation and represses apoptosis of retinoblastoma cells through the miR-20b-5p/RRM2/PI3K/AKT axis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2022, 17, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, P.; Tchernyshyov, I.; Chang, T.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Kita, K.; Ochi, T.; Zeller, K.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Mendell, J.T.; et al. c-Myc suppression of miR-23a/b enhances mitochondrial glutaminase expression and glutamine metabolism. Nature 2009, 458, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kwon, D.H.; Cha, H.J.; Lee, H.; Hong, S.H.; Park, C.; Park, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Hwang, H.J.; et al. Protective Effect of Glutathione against Oxidative Stress-induced Cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 Macrophages through Activating the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor-2/Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ghasemi, M.; Turnbull, T.; Sebastian, S.; Kempson, I. The MTT Assay: Utility, Limitations, Pitfalls, and Interpretation in Bulk and Single-Cell Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ma, J.; Fan, Y.; Feng, T.; Chen, F.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Lin, Q.; He, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. HOTAIR regulates HK2 expression by binding endogenous miR-125 and miR-143 in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86410–86422, https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21195; Erratum in: Oncotarget 2018, 9, 23843. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.25377; Erratum in: Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Gao, Y.; Liang, H. HOTAIR/miR-125 axis-mediated Hexokinase 2 expression promotes chemoresistance in human glioblastoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 5707–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xu, X.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Oyang, L.; Lin, J.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications in cancer: From the impacts and mechanisms to the treatment potential. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cluntun, A.A.; Lukey, M.J.; Cerione, R.A.; Locasale, J.W. Glutamine Metabolism in Cancer: Understanding the Heterogeneity. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, J.; Shay, C.; Saba, N.F.; Teng, Y. Cancer metabolism and carcinogenesis. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fichtner, M.; Bozkurt, E.; Salvucci, M.; McCann, C.; McAllister, K.A.; Halang, L.; Düssmann, H.; Kinsella, S.; Crawford, N.; Sessler, T.; et al. Molecular subtype-specific responses of colon cancer cells to the SMAC mimetic Birinapant. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kikuchi, H.; Pino, M.S.; Zeng, M.; Shirasawa, S.; Chung, D.C. Oncogenic KRAS and BRAF differentially regulate hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8499–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mu, H.; Yu, G.; Li, H.; Wang, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, T.; Song, T.; Liu, C. Mild chronic hypoxia-induced HIF-2α interacts with c-MYC through competition with HIF-1α to induce hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 1151–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Fang, R.; Cai, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L. HBXIP and LSD1 Scaffolded by lncRNA Hotair Mediate Transcriptional Activation by c-Myc. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, S.; Zhu, H. The sequence, structure and evolutionary features of HOTAIR in mammals. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- An, X.; Liu, Y. HOTAIR in solid tumors: Emerging mechanisms and clinical strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 154, 113594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, J.; Du, R.; Xing, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhong, G.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Z.; Jin, X.; et al. HuR-mediated nucleocytoplasmic translocation of HOTAIR relieves its inhibition of osteogenic differentiation and promotes bone formation. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmad, F.; Sudesh, R.; Ahmed, A.T.; Haque, S. Roles of HOTAIR Long Non-coding RNA in Gliomas and Other CNS Disorders. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 44, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hugo, F.; Mazurek, S.; Zander, U.; Eigenbrodt, E. In vitro effect of extracellular AMP on MCF-7 breast cancer cells: Inhibition of glycolysis and cell proliferation. J. Cell Physiol. 1992, 153, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Tan, H.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Lu, J.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, M.; et al. ACAT1-Mediated ME2 Acetylation Drives Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer by Linking Glutaminolysis to Lactate Production. Adv. Sci. 2025, e2416467, Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Díez, M.; Alegría-Aravena, N.; López-Montes, M.; Quiroz-Troncoso, J.; González-Martos, R.; Menéndez-Rey, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.L.; Pastor, J.M.; Ramírez-Castillejo, C. Implication of Different Tumor Biomarkers in Drug Resistance and Invasiveness in Primary and Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]





| Name | Sequence Forward | Sequence Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| HOTAIR | GGTAGAAAAAGCAACCACGAAGC | ACATAAACCTCTGTCTGTGAGTGCC |
| HIF1A | GAT AGT GAT ATG GTC AAT GAA TTC | GTC TGC TGG AAT ACT GTA ACT GTG |
| SFRS9 | CCC TGC GTA AAC TGG ATG | ACC GAG ACC GTG AGT AGC C |
| SLC2A1 | TGGCATCAACGCTGTCTTCT | CTAGCGCGATGGTCATGAGT |
| HK2 | TCGCCGGTAGCCTTCTTTGT | AGAGATACTGGTCAACCTTCTGC |
| GPI | CGACTAGTGCACAGGGAGTG | CCATGGCGGGACTCTTGC |
| PFKFB4 | GTCTCCAGCATCCTGCAAGT | TATCGATCTGGCCGTTCCTG |
| ALDOC | ATCGAGCAGTAACCAGTGGG | GCCACAAGAAGGACCTGAAG |
| TPI1 | AGCAGACAAAGGTCATCGCA | CCAGTCACAGAGCCTCCATA |
| GAPDH | TCA AGA AGG TGG TGA AGC AG | AAA GGT GGA GGA GTG GGT GT |
| PKG1 | TGGAGCTCCTGGAAGGTAAAG | GTTCCTGGCACTGCATCTCT |
| PGAM1 | CCGGAATCTGCTAATCCCAGT | ACTCATAGCCAGCATCTCGTAG |
| PKLR | AGCATGTCGATCCAGGAGAAC | CCAGTAGGCAGAGGTGTTCC |
| LDHA | CCGGATCTCATTGCCACGC | CAAGTTCATCTGCCAAGTCCTTCA |
| SLC1A5 | TTT TTC CTG GTC ACC ACG CTG | TCA TAG GTG GTA GAG TAT GAG CGA |
| GLS2 | CAA GCT GGG GAA CAG CCA TA | GCT GAC AAG GCA AAC CTT CG |
| GLUD1 | CCT GCA AGG GAG GTA TCC GT | ATG TCT GGA GCA GGC ACA TC |
| GOT1 | TCG TGC GGA TTA CTT GGT CC | CTC AAC CTG CTT GGG GTT CA |
| SLC2A1-ChiP-1 | GGCTCCACCATTTTGCTAGAGA | CGGACCGTAGCGTTTATAGGA |
| SLC2A1-ChiP-2 | GCAAAAGCAAGGCTTGGCTC | TGGGTGACTTCGGTGCACTA |
| LDHA-ChiP-1 | GCACCTTACTTAGACTCCCAGCG | CGGGAGGGGCCTTAAGTGGA |
| LDHA-ChiP-2 | AGGCTTCACTGTGAGTGGGAGC | GGGAGGTTACTCTCAGGAAGGC |
| SLC1A5-ChiP-1 | GGAACGAACCCCTGTGGTTTAAGG | TGCAGAGCGTTCGGAGACTGGA |
| SLC1A5-ChiP-2 | GGGTTTCACCATGTTGGCCAGG | GCCCTGAGTTTGGTCTTTAGTCG |
| GLUD1-ChiP-1 | GCACATACCTGAGAGCCCCG | AGGACGGACTTCGGGGACAG |
| GLUD1-ChiP-2 | GCTTTCCTGCCCACGTGTCAGC | TGTAGGGCGCTCAGAGGCCGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-García, L.C.; García-Castillo, V.; Pérez-Toledo, E.; Trujano-Camacho, S.; Millán-Catalán, O.; Pérez-Yepez, E.A.; Coronel-Hernández, J.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; Pérez-Plasencia, C. HOTAIR Participation in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Through Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2025, 14, 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050388
Flores-García LC, García-Castillo V, Pérez-Toledo E, Trujano-Camacho S, Millán-Catalán O, Pérez-Yepez EA, Coronel-Hernández J, Rodríguez-Dorantes M, Jacobo-Herrera N, Pérez-Plasencia C. HOTAIR Participation in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Through Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer. Cells. 2025; 14(5):388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050388
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-García, Laura Cecilia, Verónica García-Castillo, Eduardo Pérez-Toledo, Samuel Trujano-Camacho, Oliver Millán-Catalán, Eloy Andrés Pérez-Yepez, Jossimar Coronel-Hernández, Mauricio Rodríguez-Dorantes, Nadia Jacobo-Herrera, and Carlos Pérez-Plasencia. 2025. "HOTAIR Participation in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Through Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer" Cells 14, no. 5: 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050388
APA StyleFlores-García, L. C., García-Castillo, V., Pérez-Toledo, E., Trujano-Camacho, S., Millán-Catalán, O., Pérez-Yepez, E. A., Coronel-Hernández, J., Rodríguez-Dorantes, M., Jacobo-Herrera, N., & Pérez-Plasencia, C. (2025). HOTAIR Participation in Glycolysis and Glutaminolysis Through Lactate and Glutamate Production in Colorectal Cancer. Cells, 14(5), 388. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050388







