Defining the Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Subcomplexes That Regulate FoxO Transcription Factor Localization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cloning and Cell Culture
2.2. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.3. Chemical Inhibitor Treatments
2.4. Immunoblotting
2.5. Genetic Knockdowns and RT-PCR
2.6. Statistical Analyses and Experimental Replicates
3. Results
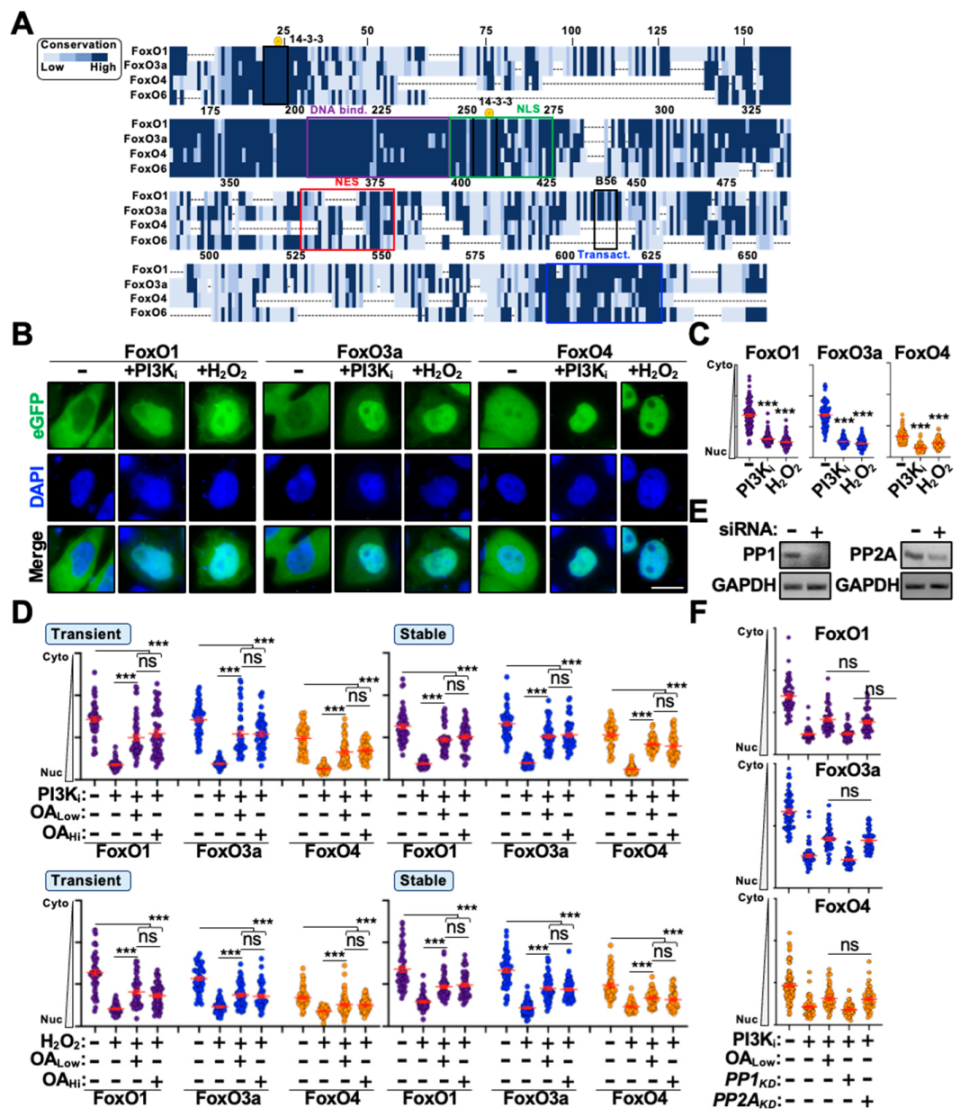
3.1. PP2A Only Partially Regulates FoxO Cytoplasm-to-Nucleus Translocation
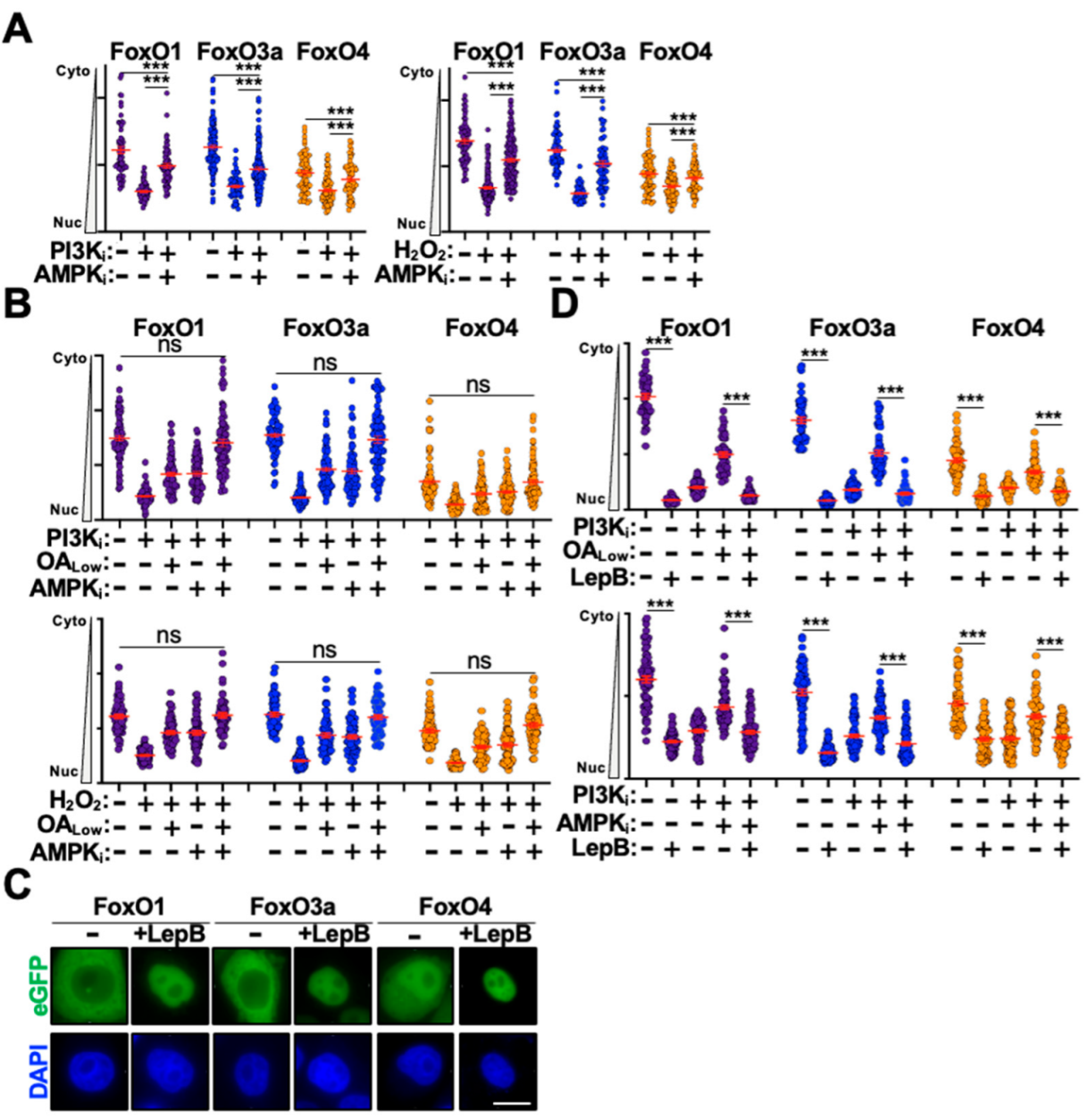
3.2. AMPK and PI3K/AKT Signaling Combine to Regulate FoxO Protein Trafficking
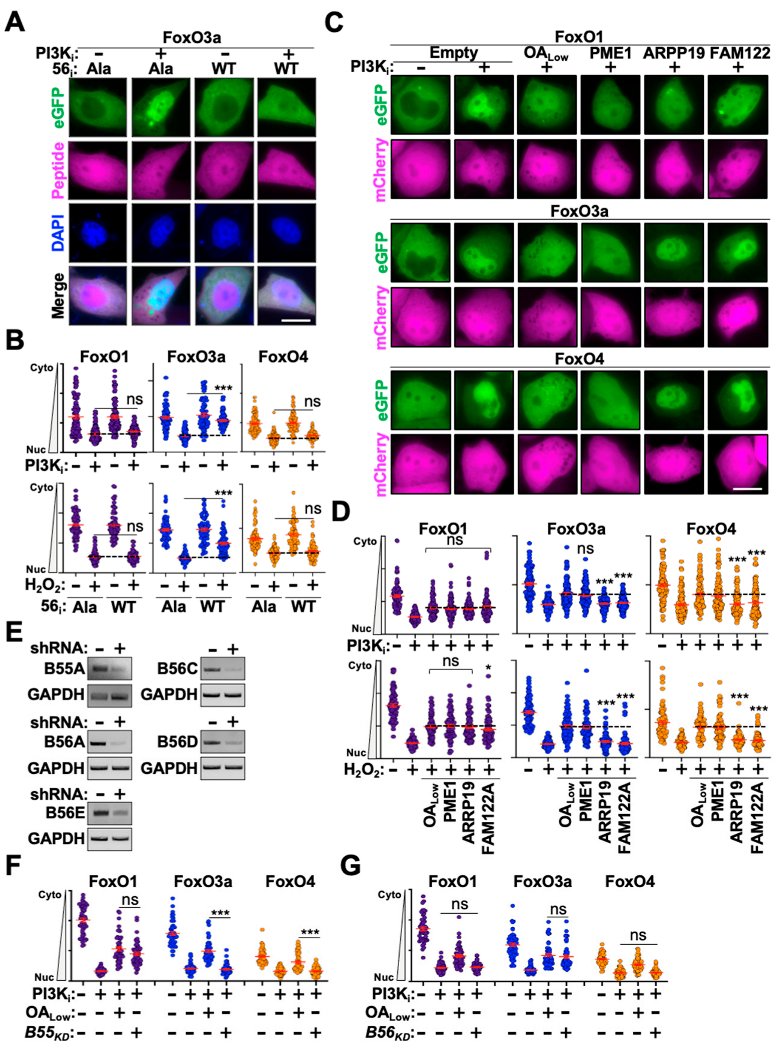
3.3. Defining the PP2A Subcomplexes That Regulate FoxO Nuclear Translocation
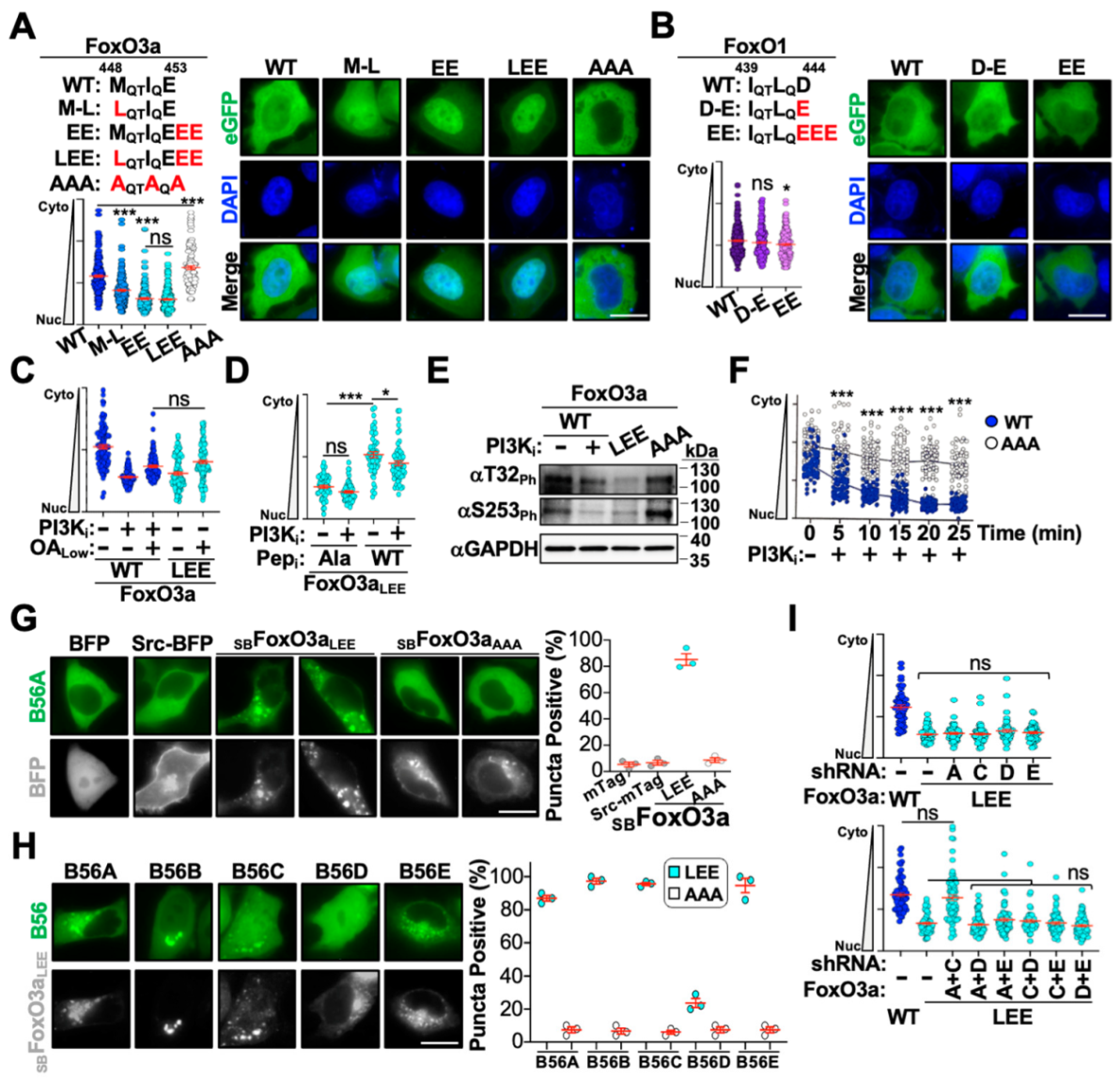
3.4. Altering the FoxO3a B56-Interacting Motif Modulates Nuclear Translocation Kinetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Accili, D.; Arden, K.C. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 2004, 117, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, E.L.; Brunet, A. FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7410–7425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Viars, C.S.; Czekay, S.; Cavenee, W.K.; Arden, K.C. Cloning and characterization of three human forkhead genes that comprise an FKHR-like gene subfamily. Genomics 1998, 47, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Hung, M.C. A new fork for clinical application: Targeting forkhead transcription factors in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Lin, M.; Gu, W.; Su, Z.; Duan, Y.; Song, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, F. The rules and regulatory mechanisms of FOXO3 on inflammation, metabolism, cell death and aging in hosts. Life Sci. 2023, 328, 121877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzivion, G.; Dobson, M.; Ramakrishnan, G. FoxO transcription factors; Regulation by AKT and 14-3-3 proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1938–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J. Mol. Signal 2010, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essers, M.A.; de Vries-Smits, L.M.; Barker, N.; Polderman, P.E.; Burgering, B.M.; Korswagen, H.C. Functional interaction between beta-catenin and FOXO in oxidative stress signaling. Science 2005, 308, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.C.; Bohmann, D.; Jasper, H. JNK extends life span and limits growth by antagonizing cellular and organism-wide responses to insulin signaling. Cell 2005, 121, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calnan, D.R.; Brunet, A. The FoxO code. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2276–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, E.L.; Oskoui, P.R.; Banko, M.R.; Maniar, J.M.; Gygi, M.P.; Gygi, S.P.; Brunet, A. The energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase directly regulates the mammalian FOXO3 transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30107–30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Park, J.; Tran, H.; Hu, L.S.; Hemmings, B.A.; Greenberg, M.E. Protein kinase SGK mediates survival signals by phosphorylating the forkhead transcription factor FKHRL1 (FOXO3a). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 952–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccitto, M.; Kalb, R.G. Regulation of Foxo-dependent transcription by post-translational modifications. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Zong, C.S.; Xia, W.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ding, Q.; Xie, X.; Lang, J.Y.; Lai, C.C.; Chang, C.J.; Huang, W.C.; et al. ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daitoku, H.; Sakamaki, J.; Fukamizu, A. Regulation of FoxO transcription factors by acetylation and protein-protein interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, P.K.; Jiang, H.; Aoki, M. Triple layer control: Phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination of FOXO proteins. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Tindall, D.J. Regulation of FOXO protein stability via ubiquitination and proteasome degradation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 1961–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Horst, A.; de Vries-Smits, A.M.; Brenkman, A.B.; van Triest, M.H.; van den Broek, N.; Colland, F.; Maurice, M.M.; Burgering, B.M. FOXO4 transcriptional activity is regulated by monoubiquitination and USP7/HAUSP. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Oprescu, S.N.; Snyder, M.M.; Kim, A.; Jia, Z.; Yue, F.; Kuang, S. PRMT5 mediates FoxO1 methylation and subcellular localization to regulate lipophagy in myogenic progenitors. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Lavin, V.A.; Moser, L.R.; Cui, Q.; Kanies, C.; Yang, E. PP2A regulates the pro-apoptotic activity of FOXO1. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7411–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ye, M.; Bucur, O.; Zhu, S.; Tanya Santos, M.; Rabinovitz, I.; Wei, W.; Gao, D.; Hahn, W.C.; Khosravi-Far, R. Protein phosphatase 2A reactivates FOXO3a through a dynamic interplay with 14-3-3 and AKT. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, F.M.; van der Heide, L.P.; Wijchers, P.J.; Burbach, J.P.; Hoekman, M.F.; Smidt, M.P. FoxO6, a novel member of the FoxO class of transcription factors with distinct shuttling dynamics. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35959–35967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heide, L.P.; Jacobs, F.M.; Burbach, J.P.; Hoekman, M.F.; Smidt, M.P. FoxO6 transcriptional activity is regulated by Thr26 and Ser184, independent of nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling. Biochem. J. 2005, 391, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowle, H.; Zhao, Z.; Grana, X. PP2A holoenzymes, substrate specificity driving cellular functions and deregulation in cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2019, 144, 55–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamango, D.J.; Johnson, M.C. Characterizing the Murine Leukemia Virus Envelope Glycoprotein Membrane-Spanning Domain for Its Roles in Interface Alignment and Fusogenicity. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 12492–12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamango, D.J.; Ikeda, T.; Moghadasi, S.A.; Wang, J.; McCann, J.L.; Serebrenik, A.A.; Ebrahimi, D.; Jarvis, M.C.; Brown, W.L.; Harris, R.S. HIV-1 Vif Triggers Cell Cycle Arrest by Degrading Cellular PPP2R5 Phospho-regulators. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1057–1065.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamango, D.J.; McCann, J.L.; Demir, O.; Becker, J.T.; Wang, J.; Lingappa, J.R.; Temiz, N.A.; Brown, W.L.; Amaro, R.E.; Harris, R.S. Functional and Structural Insights into a Vif/PPP2R5 Complex Elucidated Using Patient HIV-1 Isolates and Computational Modeling. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00631-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, H.; Zhao, X.; Liang, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Jin, Y.; McNutt, M.A.; Yin, Y. Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Regulates EG5 to Control Mitotic Progression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storz, P. Forkhead homeobox type O transcription factors in the responses to oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, M.K.; Jameson, J.L. Splice variants of the forkhead box protein AFX exhibit dominant negative activity and inhibit AFXalpha-mediated tumor cell apoptosis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunters, A.; Madureira, P.A.; Pomeranz, K.M.; Aubert, M.; Brosens, J.J.; Cook, S.J.; Burgering, B.M.; Coombes, R.C.; Lam, E.W. Paclitaxel-induced nuclear translocation of FOXO3a in breast cancer cells is mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and Akt. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasick, K.A.; Jose, E.; Samayoa, A.M.; Shanks, L.; Pond, K.W.; Thorne, C.A.; Paek, A.L. FOXO nuclear shuttling dynamics are stimulus-dependent and correspond with cell fate. Mol. Biol. Cell 2023, 34, ar21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Holmes, C.F.; Tsukitani, Y. Okadaic acid: A new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1990, 15, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmijewski, J.W.; Banerjee, S.; Bae, H.; Friggeri, A.; Lazarowski, E.R.; Abraham, E. Exposure to hydrogen peroxide induces oxidation and activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33154–33164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Gong, J.; Luo, X.; Zang, M.; Guo, W.; Wen, R.; Luo, Z. AMPK exerts dual regulatory effects on the PI3K pathway. J. Mol. Signal. 2010, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacic, S.; Soltys, C.L.; Barr, A.J.; Shiojima, I.; Walsh, K.; Dyck, J.R. Akt activity negatively regulates phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase in the heart. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39422–39427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn-Windgassen, A.; Nogueira, V.; Chen, C.C.; Skeen, J.E.; Sonenberg, N.; Hay, N. Akt activates the mammalian target of rapamycin by regulating cellular ATP level and AMPK activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32081–32089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, B.K.; Liu, H.-Y.; Francisco, J.; Pandya, D.; Donigan, M.; Gallo-Ebert, C.; Giordano, C.; Bata, A.; Nickels, J.T., Jr. Inhibition of AMP Kinase by the Protein Phosphatase 2A Heterotrimer, PP2APpp2r2d. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10588–10598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Zhang, X.; Xie, D.; Tang, P.; Li, C.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, B.; Xue, C. Targeting PP2A activates AMPK signaling to inhibit colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95810–95823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J.; Ly, R.C.; Niu, N.; Kalari, K.R.; Carlson, E.E.; Wang, L. CDC25B partners with PP2A to induce AMPK activation and tumor suppression in triple negative breast cancer. NAR Cancer 2020, 2, zcaa039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.K.; Webb, A.E. Regulation of FOXO Factors in Mammalian Cells. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2018, 127, 165–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coa, L.L.; Abreu, T.F.; Tashima, A.K.; Green, J.; Pascon, R.C.; Vallim, M.A.; Machado-Jr, J. AKT/protein kinase B associates with beta-actin in the nucleus of melanoma cells. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.Y. Neuroprotection signaling of nuclear akt in neuronal cells. Exp. Neurobiol. 2014, 23, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, A.M.; Tabellini, G.; Bressanin, D.; Ognibene, A.; Goto, K.; Cocco, L.; Evangelisti, C. The emerging multiple roles of nuclear Akt. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 2168–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, N.; Wolff, B.; Sekimoto, T.; Schreiner, E.P.; Yoneda, Y.; Yanagida, M.; Horinouchi, S.; Yoshida, M. Leptomycin B inhibition of signal-mediated nuclear export by direct binding to CRM1. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 242, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J. Protein phosphatase 2A: A highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem. J. 2001, 353, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, E.P.T.; Kruse, T.; Davey, N.E.; López-Méndez, B.; Sigurðsson, J.O.; Montoya, G.; Olsen, J.V.; Nilsson, J. A Conserved Motif Provides Binding Specificity to the PP2A-B56 Phosphatase. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Bajaj, R.; Bollen, M.; Peti, W.; Page, R. Expanding the PP2A Interactome by Defining a B56-Specific SLiM. Structure 2016, 24, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luperchio, A.M.; Jónsson, S.R.; Salamango, D.J. Evolutionary conservation of PP2A antagonism and G2/M cell cycle arrest in Maedi-Visna Virus Vif. Viruses 2022, 14, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruse, T.; Garvanska, D.H.; Varga, J.K.; Garland, W.; McEwan, B.C.; Hein, J.B.; Weisser, M.B.; Benavides-Puy, I.; Chan, C.B.; Sotelo-Parrilla, P.; et al. Substrate recognition principles for the PP2A-B55 protein phosphatase. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadp5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cundell, M.J.; Hutter, L.H.; Nunes Bastos, R.; Poser, E.; Holder, J.; Mohammed, S.; Novak, B.; Barr, F.A. A PP2A-B55 recognition signal controls substrate dephosphorylation kinetics during mitotic exit. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowle, H.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Wasserman, J.S.; Wang, X.; Adeyemi, M.; Feiser, F.; Kurimchak, A.N.; Atar, D.; McEwan, B.C.; et al. PP2A/B55alpha substrate recruitment as defined by the retinoblastoma-related protein p107. eLife 2021, 10, e63181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, T.; Gnosa, S.P.; Nasa, I.; Garvanska, D.H.; Hein, J.B.; Nguyen, H.; Samsoe-Petersen, J.; Lopez-Mendez, B.; Hertz, E.P.T.; Schwarz, J.; et al. Mechanisms of site-specific dephosphorylation and kinase opposition imposed by PP2A regulatory subunits. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, S.; Fisher, L.A.; Wang, W.; Oakley, G.G.; Li, C.; Peng, A. Protein interactomes of protein phosphatase 2A B55 regulatory subunits reveal B55-mediated regulation of replication protein A under replication stress. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, J.C.; Vigneron, S.; Mechali, F.; Robert, P.; Roque, S.; Genoud, C.; Goguet-Rubio, P.; Barthe, P.; Labesse, G.; Cohen-Gonsaud, M.; et al. The study of the determinants controlling Arpp19 phosphatase-inhibitory activity reveals an Arpp19/PP2A-B55 feedback loop. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padi, S.K.R.; Vos, M.R.; Godek, R.J.; Fuller, J.R.; Kruse, T.; Hein, J.B.; Nilsson, J.; Kelker, M.S.; Page, R.; Peti, W. Cryo-EM structures of PP2A:B55-FAM122A and PP2A:B55-ARPP19. Nature 2024, 625, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hached, K.; Goguet, P.; Charrasse, S.; Vigneron, S.; Sacristan, M.P.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. ENSA and ARPP19 differentially control cell cycle progression and development. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aakula, A.; Isomursu, A.; Rupp, C.; Erickson, A.; Gupta, N.; Kauko, O.; Shah, P.; Padzik, A.; Pokharel, Y.R.; Kaur, A.; et al. PP2A methylesterase PME-1 suppresses anoikis and is associated with therapy relapse of PTEN-deficient prostate cancers. Mol. Oncol. 2023, 17, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Stock, J.B.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y. Structural mechanism of demethylation and inactivation of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell 2008, 133, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orea-Soufi, A.; Paik, J.; Braganca, J.; Donlon, T.A.; Willcox, B.J.; Link, W. FOXO transcription factors as therapeutic targets in human diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 43, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiramongkol, Y.; Lam, E.W. FOXO transcription factor family in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 681–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejean, A.S.; Hedrick, S.M.; Kerdiles, Y.M. Highly specialized role of Forkhead box O transcription factors in the immune system. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, I.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Zengin, G.; Negrut, N.; Nistor-Cseppento, D.C.; Pavel, F.M.; Corb Aron, R.A.; Bungau, S. Exploring the Genetic Conception of Obesity via the Dual Role of FoxO. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.G.; Balakrishnan, V.K.; Merrill, R.A.; Parihar, P.S.; Konovolov, K.; Chen, Y.C.; Xu, Z.; Wei, H.; Sundaresan, R.; Cui, Q.; et al. B56delta long-disordered arms form a dynamic PP2A regulation interface coupled with global allostery and Jordan’s syndrome mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2310727120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, V.W.; Hedberg, M.L.; Li, H.; Vangara, B.S.; Pendleton, K.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.; Gilbert, B.R.; et al. Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.W.; Rexer, B.N.; Garrett, J.T.; Arteaga, C.L. Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway: Role in tumor progression and therapeutic implications in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, W.H., 3rd; Meisenhelder, J.; Hunter, T.; Cavenee, W.K.; Arden, K.C. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7421–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Bonni, A.; Zigmond, M.J.; Lin, M.Z.; Juo, P.; Hu, L.S.; Anderson, M.J.; Arden, K.C.; Blenis, J.; Greenberg, M.E. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 1999, 96, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClinch, K.; Avelar, R.A.; Callejas, D.; Izadmehr, S.; Wiredja, D.; Perl, A.; Sangodkar, J.; Kastrinsky, D.B.; Schlatzer, D.; Cooper, M.; et al. Small-Molecule Activators of Protein Phosphatase 2A for the Treatment of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2065–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, D.; Huang, W.; Izadmehr, S.; O’Connor, C.M.; Wiredja, D.D.; Wang, Z.; Zaware, N.; Chen, Y.; Schlatzer, D.M.; Kiselar, J.; et al. Selective PP2A Enhancement through Biased Heterotrimer Stabilization. Cell 2020, 181, 688–701.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenolikar, S. A SMAP in the face for cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2048–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.; Narayan, S.; Sharma, A.K. Altering phosphorylation in cancer through PP2A modifiers. Cancer Cell Int. 2024, 24, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangodkar, J.; Farrington, C.C.; McClinch, K.; Galsky, M.D.; Kastrinsky, D.B.; Narla, G. All roads lead to PP2A: Exploiting the therapeutic potential of this phosphatase. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, L.; Filippone, A.; Casili, G.; Lanza, M.; Bova, V.; Capra, A.P.; Giuffrida, R.; Colarossi, C.; Sciacca, D.; Paterniti, I.; et al. The Pivotal Role of Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) in Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luperchio, A.M.; Salamango, D.J. Defining the Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Subcomplexes That Regulate FoxO Transcription Factor Localization. Cells 2025, 14, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050342
Luperchio AM, Salamango DJ. Defining the Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Subcomplexes That Regulate FoxO Transcription Factor Localization. Cells. 2025; 14(5):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050342
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuperchio, Adeline M., and Daniel J. Salamango. 2025. "Defining the Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Subcomplexes That Regulate FoxO Transcription Factor Localization" Cells 14, no. 5: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050342
APA StyleLuperchio, A. M., & Salamango, D. J. (2025). Defining the Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) Subcomplexes That Regulate FoxO Transcription Factor Localization. Cells, 14(5), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050342





