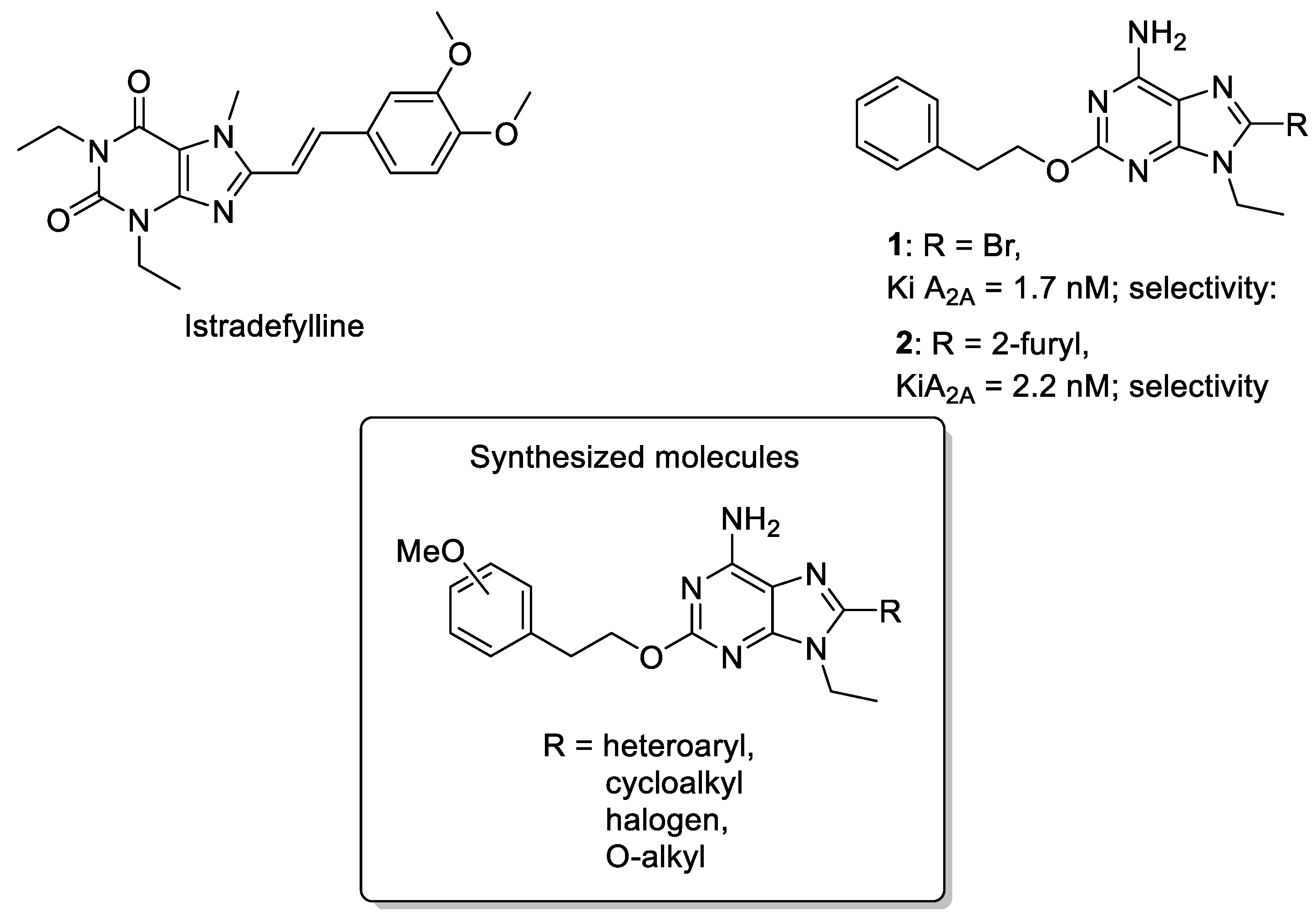
A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists and Their Efficacy in Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemistry
2.1.1. General Methods
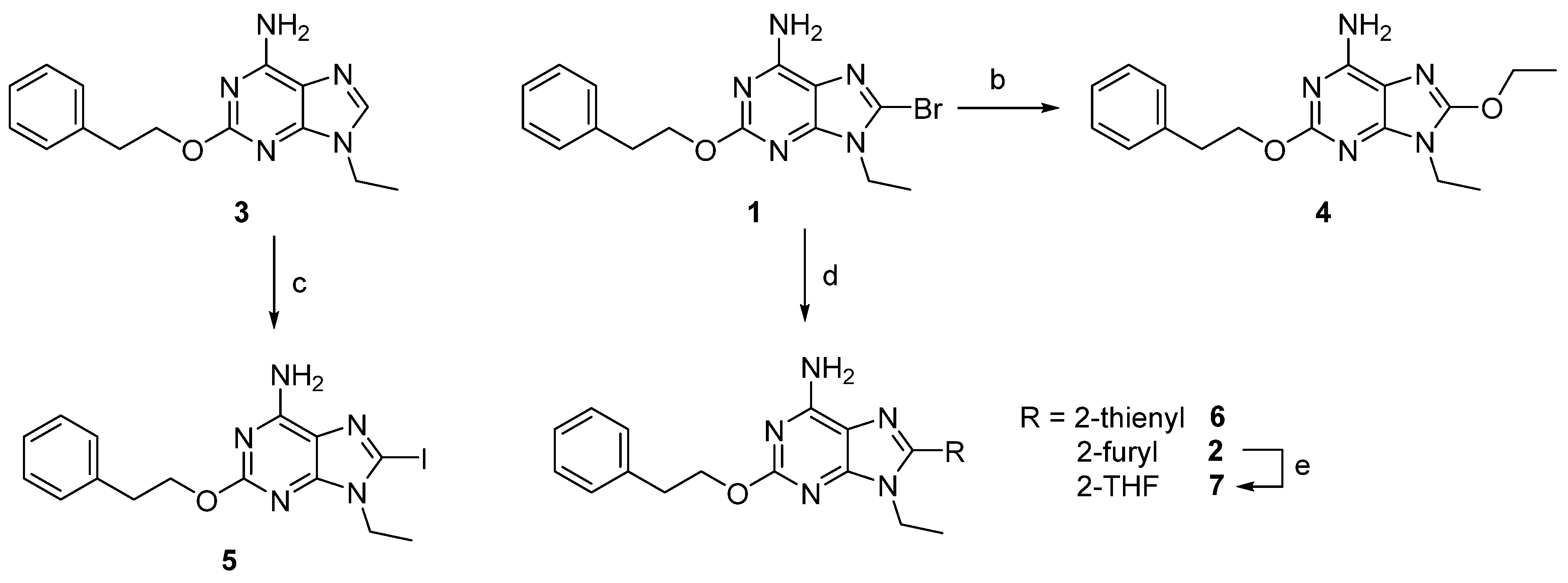
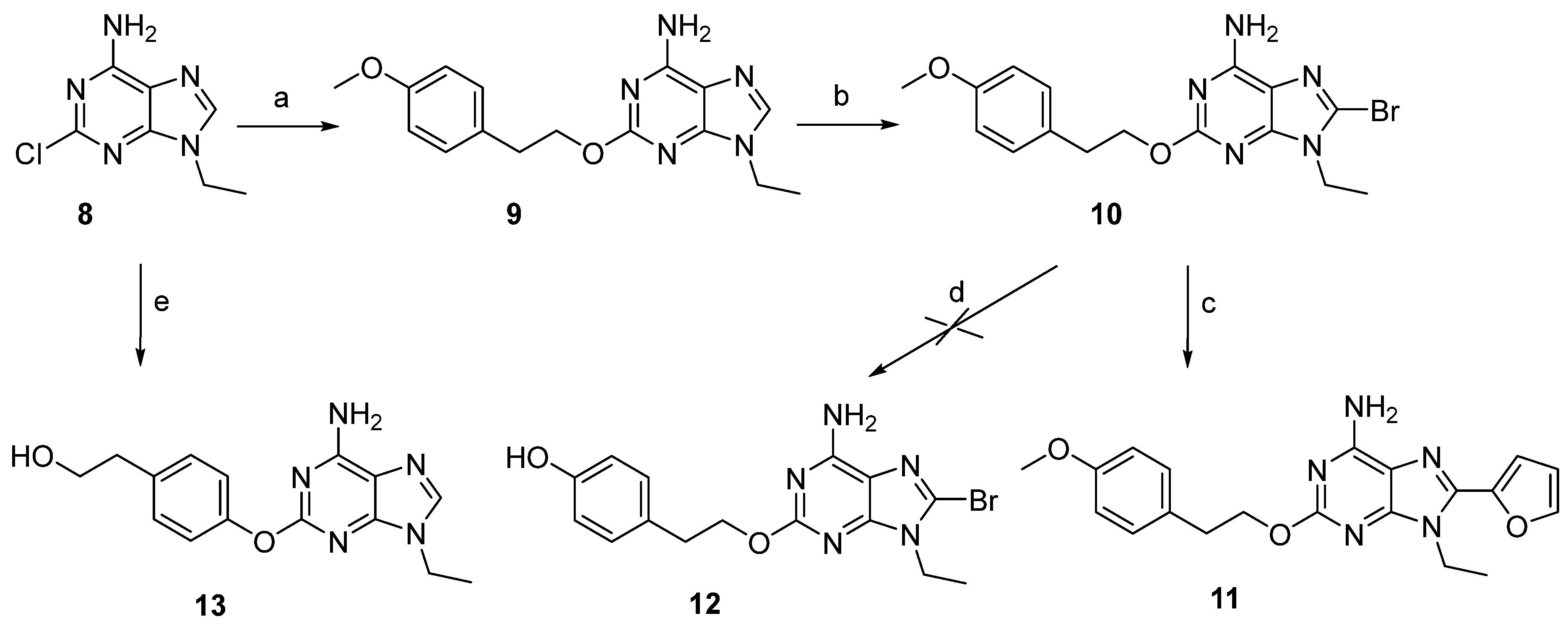
2.1.2. Synthesis of Compounds
2.2. Biological Evaluation In Vitro
2.2.1. Binding Studies and Adenylyl Cyclase Activity at Human ARs
2.2.2. Functional Assays at the A2AAR
2.3. Biological Evaluation In Vivo
2.3.1. Animals
2.3.2. Catalepsy
2.3.3. Tacrine-Induced Tremulous Jaw Movements
2.3.4. 6-OHDA-Lesion
2.3.5. Assessment of Rotational Behavior
2.3.6. Drugs
2.3.7. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Biological Activity In Vitro
3.2.1. Binding Studies
3.2.2. Functional Experiments
3.3. Biological Activities in In Vivo Models of Parkinson’s Disease
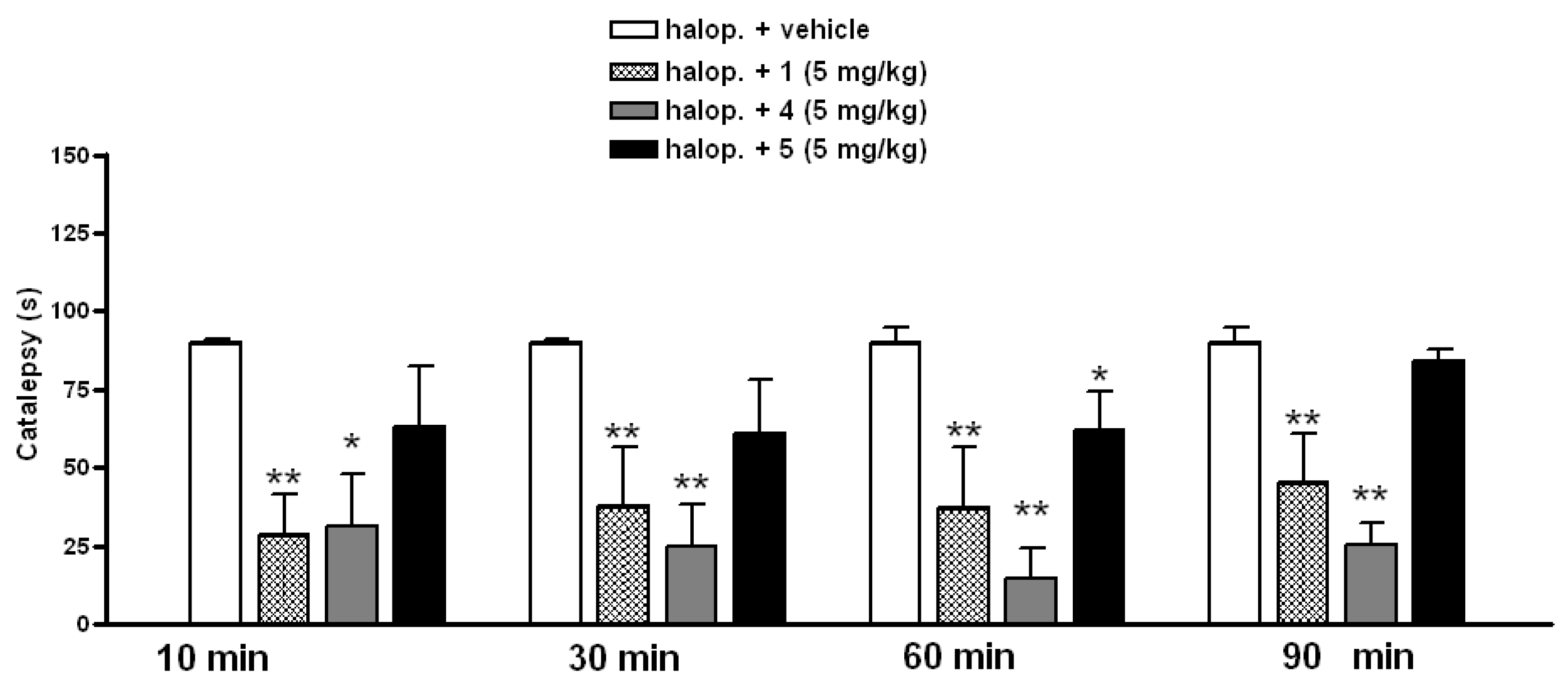
3.3.1. Effect of A2AAR Antagonists on Catalepsy
3.3.2. Potentiation of L-Dopa-Induced Rotational Behavior
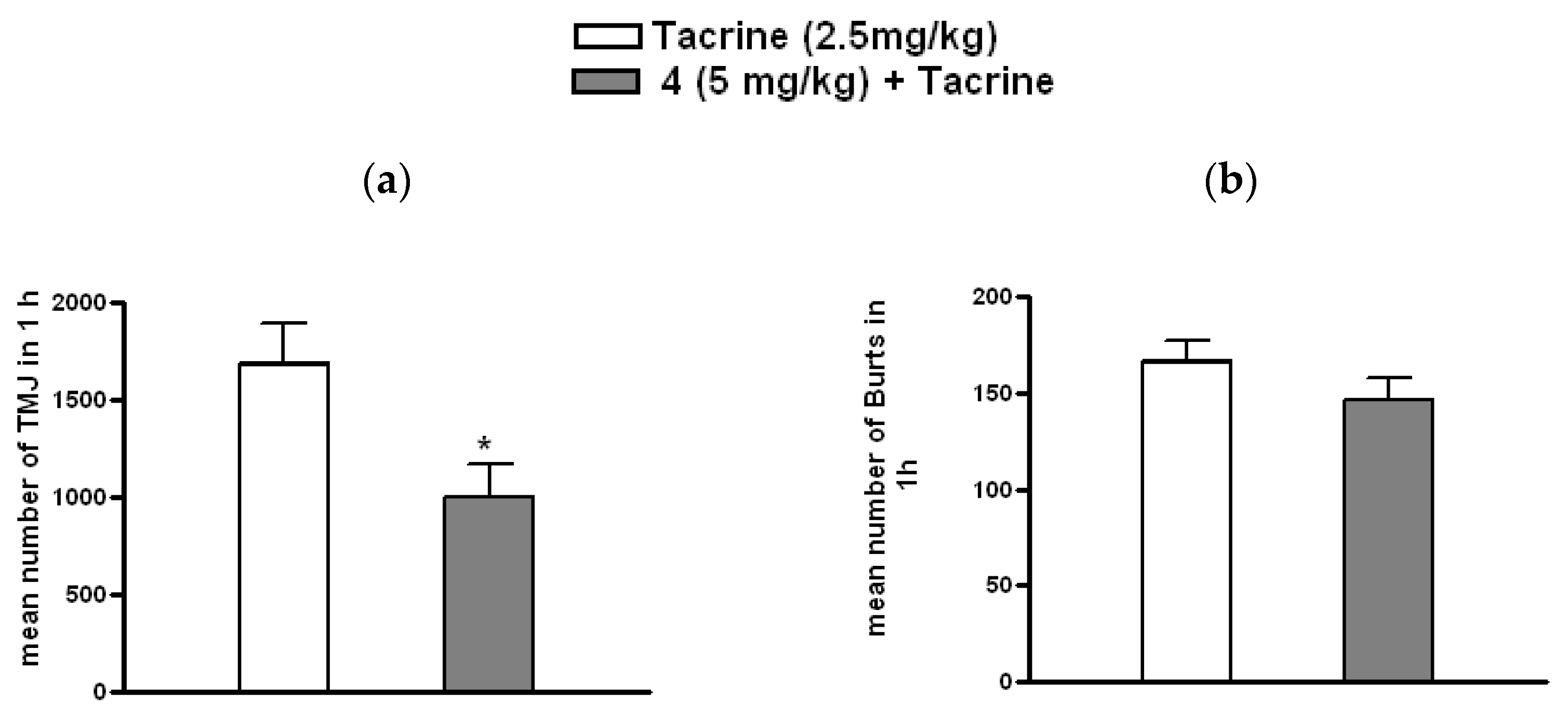
3.3.3. Effect of 4 on Tacrine-Induced Tremulous Jaw Movements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/statistics (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Darweesh, S.; Llibre-Guerra, J.; Marras, C.; San Luciano, M.; Tanner, C. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2024, 403, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.T. Environmental factors in Parkinson’s disease: New insights into the molecular mechanisms. Toxicol. Lett. 2022, 356, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.J.; Pan, J.; Tang, S.H.; Duan, D.P.; Yu, D.F.; Nong, H.Q.; Wang, Z. Global Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Years Lived with Disability of Parkinson’s Disease in 204 Countries/Territories from 1990 to 2019. Front Public Health 2021, 9, 776847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Moreno, T.; García-Morales, V.; Suleiman-Martos, S.; Rivas-Domínguez, A.; Mohamed-Mohamed, H.; Ramos-Rodríguez, J.J.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; González-Acedo, A. Current Treatments and New, Tentative Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, A.; Chen, J.F.; Uchida, S.; Durlach, C.; King, S.M.; Jenner, P. The Pharmacological Potential of Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists for Treating Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Jenner, P. Can adenosine A2A receptor antagonists modify motor behavior and dyskinesia in experimental models of Parkinson’s disease? Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 80 (Suppl. S1), S21–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentero, M.T.; Pinna, A.; Ferre, S.; Lanciego, J.L.; Muller, C.E.; Franco, R. Past, present and future of A(2A) adenosine receptor antagonists in the therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 132, 280–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IJzerman, A.P.; Jacobson, K.A.; Muller, C.E.; Cronstein, B.N.; Cunha, R.A. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CXII: Adenosine Receptors: A Further Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2022, 74, 340–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A. Adenosine Receptors: Structure, Distribution, and Signal Transduction. In The Adenosine Receptors; Borea, P., Varani, K., Gessi, S., Merighi, S., Vincenzi, F., Eds.; Humana Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Gao, Z.G. Adenosine receptors as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2006, 5, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, D.; Lopes, L.V. Adeosine Receptors in Nerodegenerative Diseases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, X. Development of Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: A Recent Update and Challenge. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. Launch of NOURIAST® Tablets 20 mg, in Japan, a Novel Antiparkinsonian Agent. 2013. Available online: https://www.kyowakirin.com/media_center/news_releases/2013/e20130529_01.html (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd. Kyowa Kirin Announces FDA Approval of NOURIANZTM (istradefylline) for Use in Parkinson’s Disease. 2019. Available online: https://www.kyowakirin.com/media_center/news_releases/2019/pdf/e20190828_01.pdf (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- EMA. 2022. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/nouryant (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Spinaci, A.; Buccioni, M.; Chang, C.; Dal Ben, D.; Francucci, B.; Lambertucci, C.; Volpini, R.; Marucci, G. Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists: Chemistry, SARs, and Therapeutic Potential. Top. Med. Chem. 2023, 41, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Pinna, A.; Volpini, R.; Cristalli, G.; Morelli, M. New adenosine A2A receptor antagonists: Actions on Parkinson’s disease models. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 512, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertucci, C.; Vittori, S.; Mishra, R.C.; Dal Ben, D.; Klotz, K.N.; Volpini, R.; Cristalli, G. Synthesis and biological activity of trisubstituted adenines as A2A adenosine receptor antagonists. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2007, 26, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertucci, C.; Spinaci, A.; Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Ngouadjeu Ngnintedem, M.A.; Kachler, S.; Marucci, G.; Klotz, K.N.; Volpini, R. New A2A adenosine receptor antagonists: A structure-based upside-down interaction in the receptor cavity. Bioorg Chem. 2019, 92, 103183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristalli, G. A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists. Patent WO 2003051882 A1, 26 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Cristalli, G. A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists. Patent US_20030149060_A1, 8 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pinna, A.; Tronci, E.; Schintu, N.; Simola, N.; Volpini, R.; Pontis, S.; Cristalli, G.; Morelli, M. A new ethyladenine antagonist of adenosine A(2A) receptors: Behavioral and biochemical characterization as an antiparkinsonian drug. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinna, A.; Morelli, M. A Critical Evaluation of Behavioral Rodent Models of Motor Impairment Used for Screening of Antiparkinsonian Activity: The Case of Adenosine A2A Receptor Antagonists. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 25, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, J.D.; Mayorga, A.J.; Trevitt, J.T.; Cousins, M.S.; Conlan, A.; Nawab, A. Tremulous jaw movements in rats: A model of Parkinsonian tremor. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins-Praino, L.E.; Paul, N.E.; Rychalsky, K.L.; Hinman, J.R.; Chrobak, J.J.; Senatus, P.B.; Salamone, J.D. Pharmacological and physiological characterization of the tremulous jaw movement model of parkinsonian tremor: Potential insights into the pathophysiology of tremor. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwari, K.; Betz, A.; Weber, S.; Felsted, J.; Salamone, J.D. Validation of the tremulous jaw movement model for assessment of the motor effects of typical and atypical antipychotics: Effects of pimozide (Orap) in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Be 2005, 80, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simola, N.; Fenu, S.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Morelli, M. Blockade of adenosine A2A receptors antagonizes parkinsonian tremor in the rat tacrine model by an action on specific striatal regions. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 189, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simola, N.; Fenu, S.; Baraldi, P.G.; Tabrizi, M.A.; Morelli, M. Dopamine and adenosine receptor interaction as basis for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 248, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, K.N.; Hessling, J.; Hegler, J.; Owman, C.; Kull, B.; Fredholm, B.B.; Lohse, M.J. Comparative pharmacology of human adenosine receptor subtypes—Characterization of stably transfected receptors in CHO cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1998, 357, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lean, A.; Hancock, A.A.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol. Pharmacol. 1982, 21, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50% inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Falsini, M.; Ceni, C.; Catarzi, D.; Varano, F.; Dal Ben, D.; Marucci, G.; Buccioni, M.; Marti Navia, A.; Volpini, R.; Colotta, V. New 8-amino-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-3-one derivatives. Evaluation of different moieties on the 6-aryl ring to obtain potent and selective human A2A adenosine receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrino, L.J.; Pellegrino, A.S.; Cushman, A.J. A Stereotaxic Atlas of the Rat Brain; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Ungerstedt, U. Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1971, 367, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinaci, A.; Lambertucci, C.; Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Graiff, C.; Barbalace, M.C.; Hrelia, S.; Angeloni, C.; Tayebati, S.K.; Ubaldi, M.; et al. A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists: Are Triazolotriazine and Purine Scaffolds Interchangeable? Molecules 2022, 27, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccioni, M.; Marucci, G.; Dal Ben, D.; Giacobbe, D.; Lambertucci, C.; Soverchia, L.; Thomas, A.; Volpini, R.; Cristalli, G. Innovative functional cAMP assay for studying G protein-coupled receptors: Application to the pharmacological characterization of GPR17. Purinergic Signal 2011, 7, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, J.D.; Betz, A.J.; Ishiwari, K.; Felsted, J.; Madson, L.; Mirante, B.; Clark, K.; Font, L.; Korbey, S.; Sager, T.N.; et al. Tremorolytic effects of adenosine A2A antagonists: Implications for parkinsonism. Front. Biosci-Landmrk 2008, 13, 3594–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, T.N.; Bibbiani, F.; Bara-Jimenez, W.; Dimitrova, T.; Oh-Lee, J.D. Translating A2A antagonist KW6002 from animal models to parkinsonian patients. Neurology 2003, 61 (Suppl. S6), S107–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.A.; Shulman, L.M.; Trugman, J.M.; Roberts, J.W.; Mori, A.; Ballerini, R.; Sussman, N.M.; Study, I.-U. Study of Istradefylline in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease on Levodopa with Motor Fluctuations. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, J.S.; Weaver, D.R.; Rivkees, S.A.; Peterfreund, R.A.; Pollack, A.E.; Adler, E.M.; Reppert, S.M. Molecular cloning of the rat A2 adenosine receptor: Selective co-expression with D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1992, 14, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenningsson, P.; Le Moine, C.; Fisone, G.; Fredholm, B.B. Distribution, biochemistry and function of striatal adenosine A2A receptors. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 59, 355–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferre’, S.; Fredholm, B.B.; Morelli, M.; Popoli, P.; Fuxe, K. Adenosine-dopamine receptor-receptor interactions as an integrative mechanism in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci. 1997, 20, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; Koga, K.; Kase, H.; Nakamura, J.; Kuwana, Y. Adenosine A2a receptor-mediated modulation of striatal acetylcholine release in vivo. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Shindou, T. Modulation of GABAergic transmission in the striatopallidal system by adenosine A2A receptors: A potential mechanism for the antiparkinsonian effects of A2A antagonists. Neurology 2003, 61 (Suppl. S6), S44–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

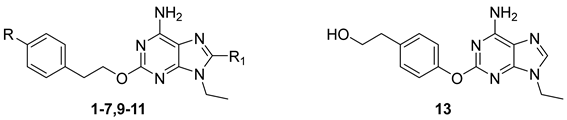
| Cpd. | R | R1 | Ki or IC50 (nM) | Selectivity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 a | A2A b | A2B c | A3 d | A1/A2A | A3/A2A | |||
| 1 [19] | H | Br | 23 (23–24) | 1.7 (1.4–2.2) | 569 (440–734) | 1090 (685–1720) | 14 | 641 |
| 2 [20] | H | 2-Furyl | 5.8 (4.0–8.4) | 2.2 (2.1–2.3) | 521 (467–580) | 16 (11–22) | 2.6 | 7.3 |
| 3 [19] | H | H | 170 (130–230) | 120 (70–220) | 45,800 (29,800–70,500) | 7150 (2950–17,300) | 1.4 | 59 |
| 4 | H | O-CH2CH3 | 86 (70–106) | 3.7 (3.5–3.8) | 6510 (6200–6830) | 359 (290–444) | 23 | 97 |
| 5 | H | I | 25 (21–31) | 1.2 (1.1–1.4) | 719 (464–1120) | 489 (323–741) | 21 | 408 |
| 6 | H | 2-Thiophenyl | 21 (17–25) | 7.7 (7.1–8.2) | 4990 (4060–6140) | 27 (21–36) | 2.7 | 3.5 |
| 7 | H | 2-THF | 509 (426–608) | 81 (49–136) | 38,900 (32,956–44,660) | 1450 (1310–1600) | 6.3 | 18 |
| 9 | OMe | H | 1986 (1470–2680) | 655 (526–816) | 63,700 (40,348–121,220) | 12,300 (11,800–12,800) | 3.0 | 19 |
| 10 | OMe | Br | 197 (152–253) | 28 (21–37) | 9190 (8800–9600) | 4060 (3390–4850) | 7.1 | 146 |
| 11 | OMe | 2-Furyl | 39 (33–47) | 7.1 (5.6–9.0) | >100 µM | 73 (53–100) | 5.5 | 10 |
| 13 | 22,900 (17,300–30,200) | 7080 (5300–9440) | >100 µM | >100 µM | 3.2 | 14 | ||
| Compd. | IC50 [nM] 1 | Ki [nM] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 108 ± 23 | 1.7 |
| 4 | 278 ± 49 | 3.7 |
| 5 | 114 ± 25 | 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spinaci, A.; Buccioni, M.; Dal Ben, D.; Francucci, B.; Klotz, K.-N.; Marucci, G.; Simola, N.; Morelli, M.; Pinna, A.; Volpini, R.; et al. A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists and Their Efficacy in Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050338
Spinaci A, Buccioni M, Dal Ben D, Francucci B, Klotz K-N, Marucci G, Simola N, Morelli M, Pinna A, Volpini R, et al. A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists and Their Efficacy in Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Cells. 2025; 14(5):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050338
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpinaci, Andrea, Michela Buccioni, Diego Dal Ben, Beatrice Francucci, Karl-Norbert Klotz, Gabriella Marucci, Nicola Simola, Micaela Morelli, Annalisa Pinna, Rosaria Volpini, and et al. 2025. "A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists and Their Efficacy in Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease" Cells 14, no. 5: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050338
APA StyleSpinaci, A., Buccioni, M., Dal Ben, D., Francucci, B., Klotz, K.-N., Marucci, G., Simola, N., Morelli, M., Pinna, A., Volpini, R., & Lambertucci, C. (2025). A2A Adenosine Receptor Antagonists and Their Efficacy in Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Cells, 14(5), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14050338











