Humanized FcεRI Expressed on Mouse Eosinophils Mediates IgE-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Preparation of Eosinophils
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Eosinophil Surface hFcεRIα Expression
2.4. In Vivo Migration of hFcεRIα-Bearing Eosinophils
2.5. Texas Red-OVA Internalization by Airway Eosinophils
2.6. Paratracheal Lymph Node Cell Proliferation Assay and Cytokine Release
2.7. FcεRI Cross-Linking and CD40, CD80 and CD86 Expression
3. Results
3.1. Expression of Humanized FcεRI on Mouse Eosinophils
3.2. FcεRI Facilitates Antigen Uptake by Airway Eosinophils in Vivo
3.3. In Vivo Migration of hFcεRI-Bearing Eosinophils
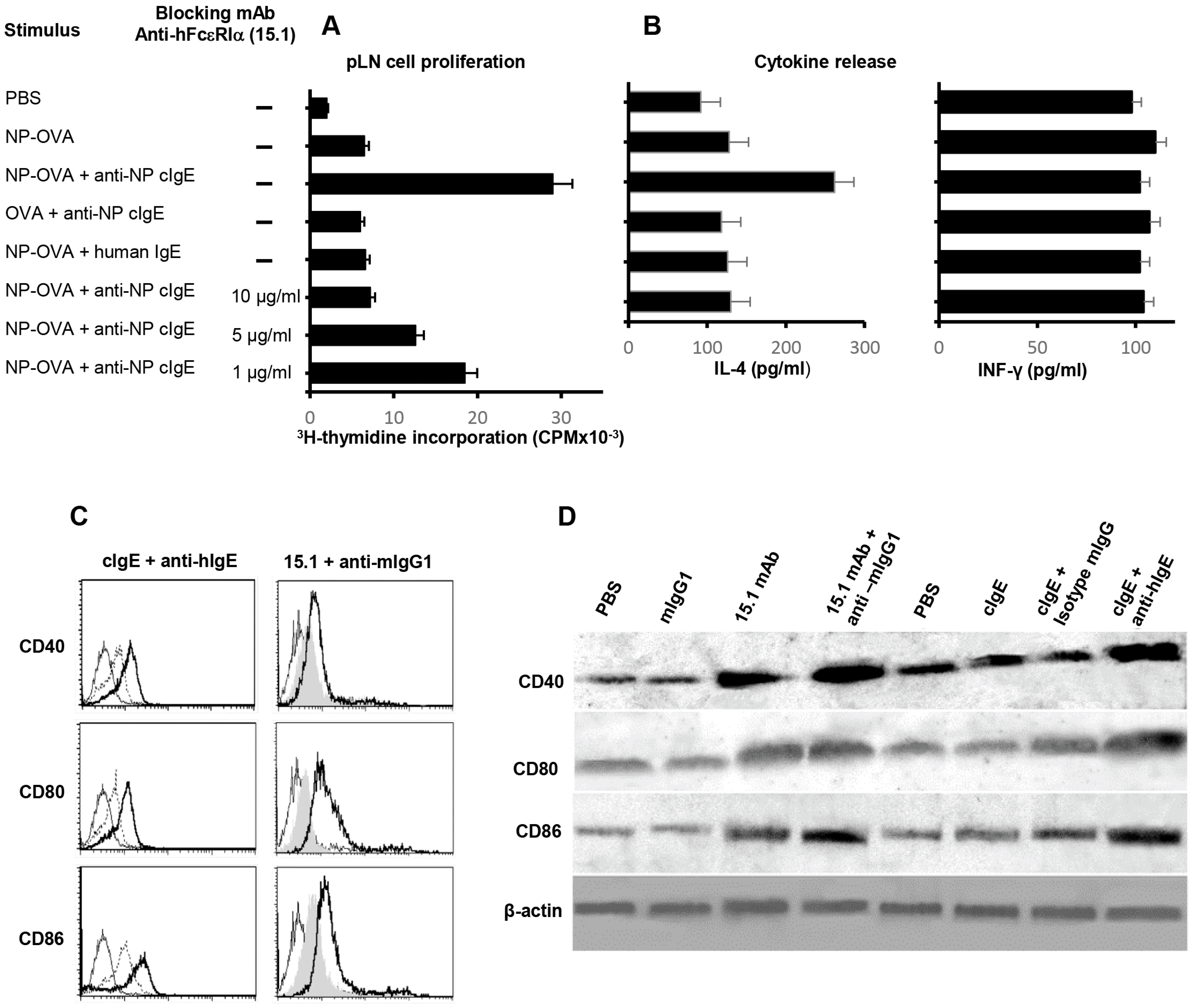
3.4. FcεRI-IgE-Allergen Complexes Facilitate Antigen Presentation In Vivo
3.5. IgE/FcεRI-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation Enhances pLN IL-4 Secretion
3.6. hFcεRI Cross-Linking Increases Eosinophil Expression of Co-Stimulatory Proteins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ab | antibody |
| Ag | antigen |
| APC | antigen-presenting cell |
| BAL | bronchoalveolar lavage |
| cIgE | chimeric human IgE |
| DiIC16(3) | (1,1′-dihexadecyl-3,3,3′,3′-tetramethylindocarbocyanin perchlorate |
| FACS | fluorescent activated cytometer |
| FCS | fetal calf serum |
| hFcεRIα | humanized FcεRI α chain |
| i.t. | intratracheal |
| i.p. | intraperitoneal |
| LN | lymph node |
| mAb | monoclonal antibody |
| NP | 4-Hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl |
| NP-OVA | 4-Hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl acetyl (NP) coupled ovalbumin |
| OVA | ovalbumin |
| pLN | paratracheal lymph nodes |
| PBS | phosphate buffered saline |
| TBS | Tris buffered saline |
| WT | wild type |
References
- McDonnell, J.M.; Dhaliwal, B.; Sutton, B.J.; Gould, H.J. IgE, IgE Receptors and Anti-IgE Biologics: Protein Structures and Mechanisms of Action. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, H.; Kaneko, M.; Bartemes, K.R.; Weiler, D.A.; Schimming, A.W.; Reed, C.E.; Gleich, G.J. Does IgE bind to and activate eosinophils from patients with allergy? J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6901–6911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhiba, K.D.; Kuang, F.L.; Berdnikovs, S.; Kato, A.; Bochner, B.S. Little to no mRNA for the alpha- or beta-chains of FcepsilonRI in human eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, H.; Gleich, G.J. Eosinophils and IgE receptors: A continuing controversy. Blood 1997, 89, 3497–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, N.; Kraft, S.; Bieber, T. Unraveling the mission of FcepsilonRI on antigen-presenting cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaba, H.; Dombrowicz, D.; Woerly, G.; Papin, J.P.; Loiseau, S.; Capron, M. Human eosinophils and human high affinity IgE receptor transgenic mouse eosinophils express low levels of high affinity IgE receptor, but release IL-10 upon receptor activation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinet, J.P. The high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI): From physiology to pathology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999, 17, 931–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowski, T.A.; Jouvin, M.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Kinet, J.P. Minimal requirements for IgE-mediated regulation of surface Fc epsilon RI. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Humbles, A.; Gerard, C.; Jin, Z.; Weller, P.F. Lymph node trafficking and antigen presentation by endobronchial eosinophils. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.B.; Ghiran, I.; Matthaei, K.; Weller, P.F. Airway eosinophils: Allergic inflammation recruited professional antigen-presenting cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7585–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padigel, U.M.; Lee, J.J.; Nolan, T.J.; Schad, G.A.; Abraham, D. Eosinophils can function as antigen presenting cells in primary and secondary immune responses to Strongyloides stercoralis infection in mice. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3232–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, J.R.; Mattes, J.; Dent, L.A.; Foster, P.S. Eosinophils promote allergic disease of the lung by regulating CD4+ Th2 lymphocyte function. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3146–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, R.K.; Vickers, M.A.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M.; Hall, A.M.; Barker, R.N.; Walsh, G.M. Effective antigen presentation to helper T cells by human eosinophils. Immunology 2016, 149, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werfel, T. The role of leukocytes, keratinocytes, and allergen-specific IgE in the development of atopic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1878–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Takenaka, M.; Matsunaga, Y.; Okada, S.; Anan, S.; Yoshida, H.; Ra, C. High affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) expression on eosinophils infiltrating the lesions and mite patch tested sites in atopic dermatitis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1995, 287, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.; Barata, L.T.; Meng, Q.; Grant, J.A.; Barkans, J.; Durham, S.R.; Kay, A.B. High-affinity immunoglobulin E receptor (Fc epsilon RI)-bearing eosinophils, mast cells, macrophages and Langerhans’ cells in allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reactions in atopic subjects. Immunology 1998, 93, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakulasingam, K.; Durham, S.R.; O’Brien, F.; Humbert, M.; Barata, L.T.; Reece, L.; Kay, A.B.; Grant, J.A. Enhanced expression of high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) alpha chain in human allergen-induced rhinitis with co-localization to mast cells, macrophages, eosinophils, and dendritic cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 100, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajakulasingam, K.; Till, S.; Ying, S.; Humbert, M.; Barkans, J.; Sullivan, M.; Meng, Q.; Corrigan, C.J.; Bungre, J.; Grant, J.A.; et al. Increased expression of high affinity IgE (FcepsilonRI) receptor-alpha chain mRNA and protein-bearing eosinophils in human allergen-induced atopic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowicz, D.; Brini, A.T.; Flamand, V.; Hicks, E.; Snouwaert, J.N.; Kinet, J.P.; Koller, B.H. Anaphylaxis mediated through a humanized high affinity IgE receptor. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andres, B.; Rakasz, E.; Hagen, M.; McCormik, M.L.; Mueller, A.L.; Elliot, D.; Metwali, A.; Sandor, M.; Britigan, B.E.; Weinstock, J.V.; et al. Lack of Fc-epsilon receptors on murine eosinophils: Implications for the functional significance of elevated IgE and eosinophils in parasitic infections. Blood 1997, 89, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, S.; Fukuyama, K.; Epstein, W.L. Induction of T-cell independent eosinophilia in mice with polymyxin B and schistosome infection. Lab. Investig. 1980, 43, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Rieger, A.; Kilgus, O.; Ochiai, K.; Maurer, D.; Fodinger, D.; Kinet, J.P.; Stingl, G. Epidermal Langerhans cells from normal human skin bind monomeric IgE via Fc epsilon RI. J. Exp. Med. 1992, 175, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuberger, M.S.; Williams, G.T.; Mitchell, E.B.; Jouhal, S.S.; Flanagan, J.G.; Rabbitts, T.H. A hapten-specific chimaeric IgE antibody with human physiological effector function. Nature 1985, 314, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messingham, K.N.; Holahan, H.M.; Frydman, A.S.; Fullenkamp, C.; Srikantha, R.; Fairley, J.A. Human eosinophils express the high affinity IgE receptor, FcepsilonRI, in bullous pemphigoid. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.G.; Chen, R.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Huang, C.; Oliveria, J.P.; O’Byrne, P.M.; Gauvreau, G.M.; Boulet, L.P.; Lemiere, C.; Martin, J.; et al. Increased numbers of activated group 2 innate lymphoid cells in the airways of patients with severe asthma and persistent airway eosinophilia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 75–86.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraki, M.; Gleich, G.J.; Kita, H. Antigen-specific IgG and IgA, but not IgE, activate the effector functions of eosinophils in the presence of antigen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 154, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminario, M.C.; Saini, S.S.; MacGlashan, D.W., Jr.; Bochner, B.S. Intracellular expression and release of Fc epsilon RI alpha by human eosinophils. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 6893–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihra, B.S.; Kon, O.M.; Grant, J.A.; Kay, A.B. Expression of high-affinity IgE receptors (Fc epsilon RI) on peripheral blood basophils, monocytes, and eosinophils in atopic and nonatopic subjects: Relationship to total serum IgE concentrations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.J.; Ying, S.; Meng, Q.; Sullivan, M.H.; Barkans, J.; Kon, O.M.; Sihra, B.; Larche, M.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Kay, A.B. Blood eosinophils from atopic donors express messenger RNA for the alpha, beta, and gamma subunits of the high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) and intracellular, but not cell surface, alpha subunit protein. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, P.F.; Spencer, L.A. Functions of tissue-resident eosinophils. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, D.; Fiebiger, E.; Reininger, B.; Wolff-Winiski, B.; Jouvin, M.H.; Kilgus, O.; Kinet, J.P.; Stingl, G. Expression of functional high affinity immunoglobulin E receptors (Fc epsilon RI) on monocytes of atopic individuals. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharquie, I.K.; Al-Ghouleh, A.; Fitton, P.; Clark, M.R.; Armour, K.L.; Sewell, H.F.; Shakib, F.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M. An investigation into IgE-facilitated allergen recognition and presentation by human dendritic cells. BMC Immunol. 2013, 14, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehlink, E.; Fiebiger, E. The role of the high-affinity IgE receptor, FcepsilonRI, in eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2009, 29, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuberi, R.I.; Apgar, J.R.; Chen, S.S.; Liu, F.T. Role for IgE in airway secretions: IgE immune complexes are more potent inducers than antigen alone of airway inflammation in a murine model. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2667–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Sun, L.; Ni, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, P.; Cao, J.; Xu, G.; Tao, Y.; Dai, R.; et al. Effective omalizumab treatment influenced eosinophil function in severe allergic asthmatics. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 3115–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Kinet, J.-P.; Weller, P.F. Humanized FcεRI Expressed on Mouse Eosinophils Mediates IgE-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation. Cells 2025, 14, 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040301
Wang H, Kinet J-P, Weller PF. Humanized FcεRI Expressed on Mouse Eosinophils Mediates IgE-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation. Cells. 2025; 14(4):301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040301
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Haibin, Jean-Pierre Kinet, and Peter F. Weller. 2025. "Humanized FcεRI Expressed on Mouse Eosinophils Mediates IgE-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation" Cells 14, no. 4: 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040301
APA StyleWang, H., Kinet, J.-P., & Weller, P. F. (2025). Humanized FcεRI Expressed on Mouse Eosinophils Mediates IgE-Facilitated Eosinophil Antigen Presentation. Cells, 14(4), 301. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040301






