Loss of γ-aminobutyric acid D-Type Motor Neurons in Young Adult Caenorhabditis elegans Following Exposition with Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Particles
2.2. C. elegans Strains
2.3. Particle Exposures in Liquid Media
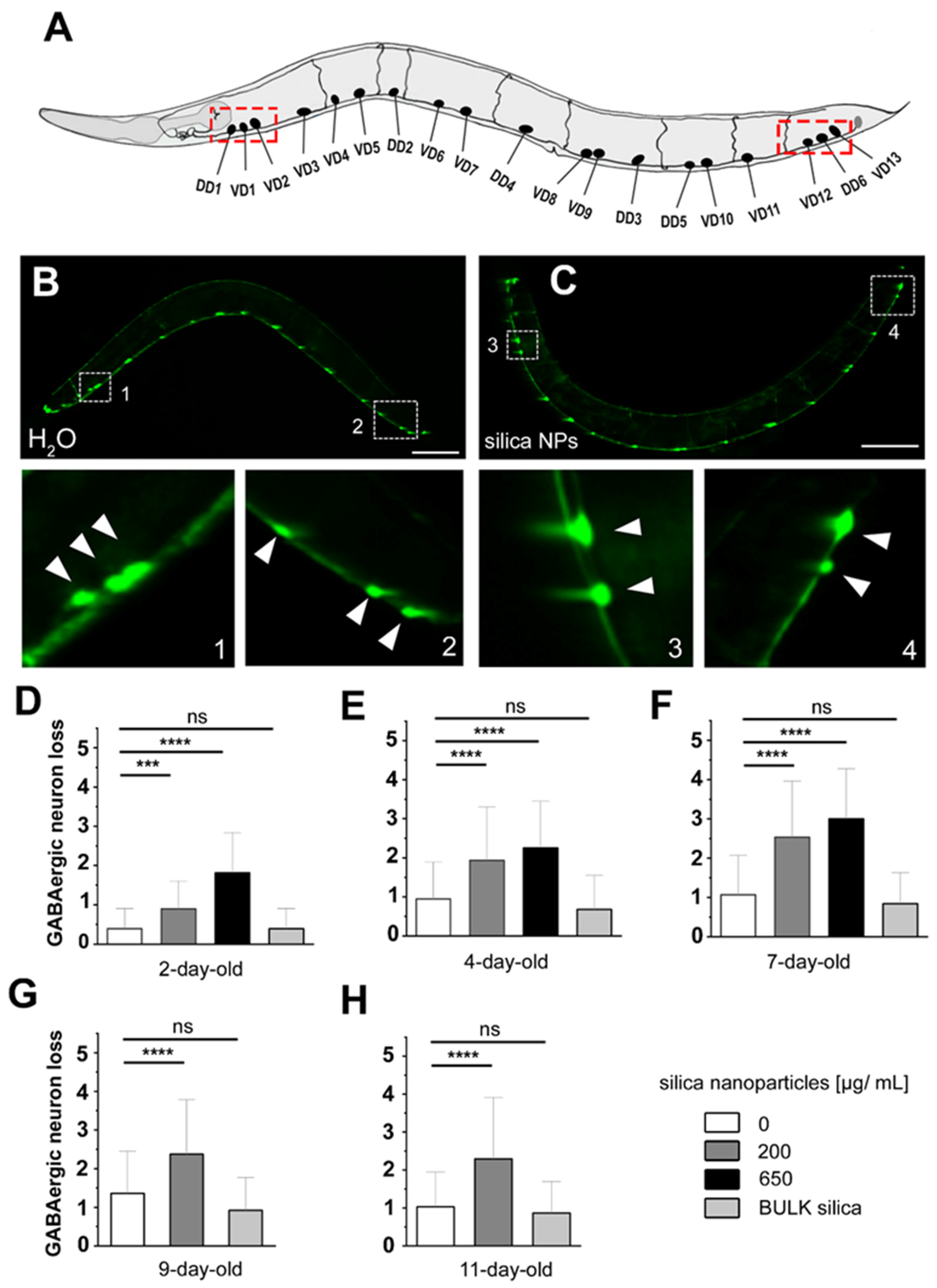
2.4. Microscopy and Quantification of Neurodegeneration
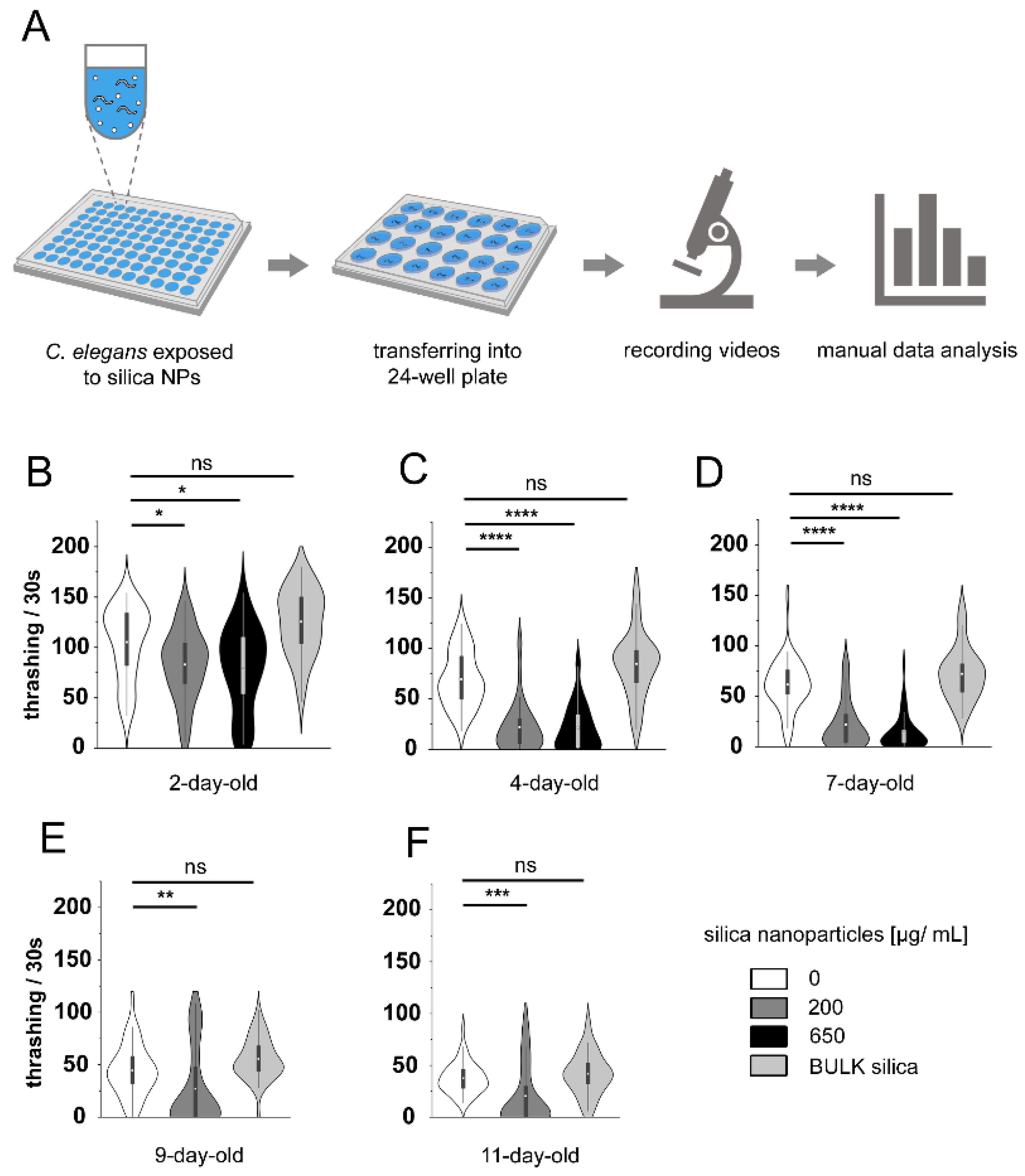
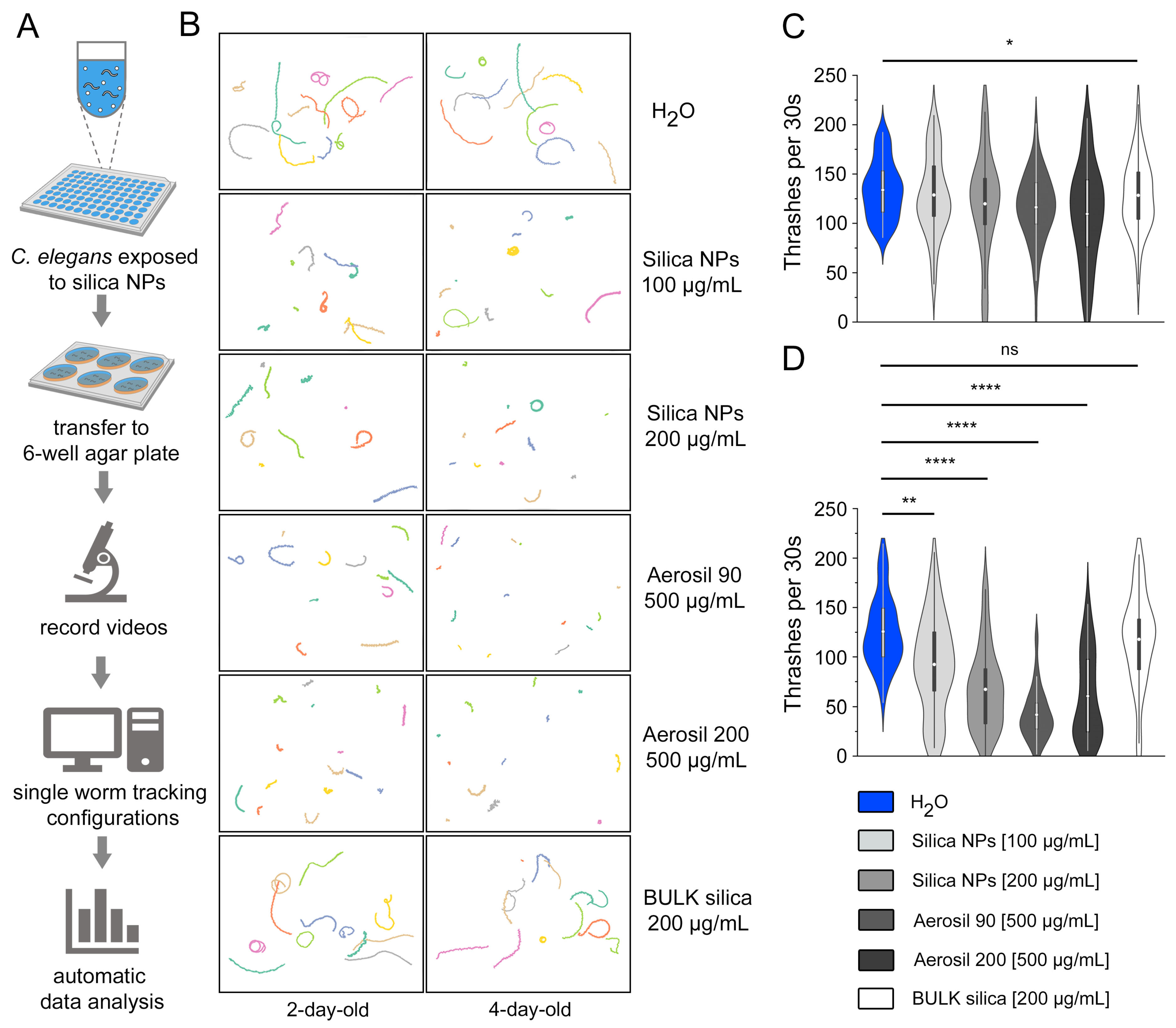
2.5. Behavior Assays
2.6. Sample Preparation for Proteomic Analysis
2.7. Worm Lysis, Protein Determination, and PAA Gel Quality Control
2.8. Protein Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometric Analysis
2.9. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of the C. elegans Proteome
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Silica NPs Induced Loss of GABAergic D-Type Motor Neurons
3.2. Silica NPs Reduce C. elegans Locomotion
3.3. Visualization and Automatic Quantification of Silica NP-Induced Locomotion Deficits
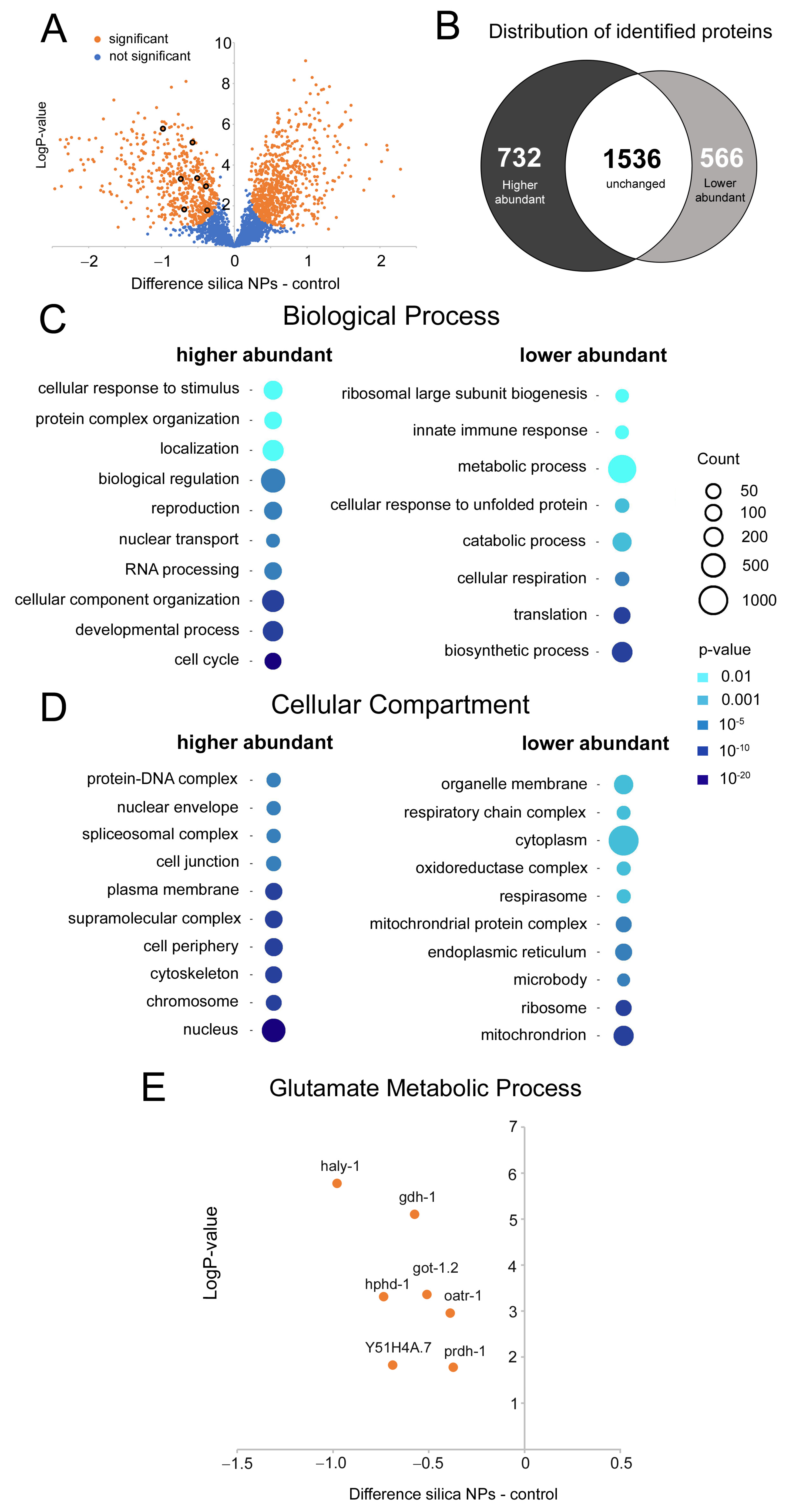
3.4. Silica NPs Target GABA Metabolic Pathways
3.5. Silica NPs Reduce Global Protein Levels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on pollution and health. Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Nowack, B. Dynamic probabilistic material flow analysis of nano-SiO2, nano iron oxides, nano-CeO2, nano-Al2O3, and quantum dots in seven European regions. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivenbark, K.J.; Fawkes, L.S.; Nikkhah, H.; Wang, M.; Sansom, G.T.; Beykal, B.; Wade, T.L.; Phillips, T.D. Using L. minor and C. elegans to assess the ecotoxicity of real-life contaminated soil samples and their remediation by clay- and carbon-based sorbents. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Mikecz, A. Elegant Nematodes Improve Our Understanding of Human Neuronal Diseases, the Role of Pollutants and Strategies of Resilience. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 16755–16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, A.K.; Wightman, B.; Chalfie, M. A Transparent window into biology: A primer on Caenorhabditis elegans. WormBook 2015, 18, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, B.; Aghayeva, U.; Sun, H.; Wang, C.; Glenwinkel, L.; Bayer, E.A.; Hobert, O. An atlas of Caenorhabditis elegans chemoreceptor expression. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2004218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripoll-Sánchez, L.; Watteyne, J.; Sun, H.; Fernandez, R.; Taylor, S.R.; Weinreb, A.; Bentley, B.L.; Hammarlund, M.; Miller, D.M., 3rd; Hobert, O.; et al. The neuropeptidergic connectome of C. elegans. Neuron 2023, 111, 3570–3589.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntire, S.L.; Jorgensen, E.; Kaplan, J.; Horvitz, H.R. The GABAergic nervous system of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1993, 364, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, E.M. GABA. WormBook 2005, 31, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Bellemer, A.; Koelle, M.R. An evolutionarily conserved switch in response to GABA affects development and behavior of the locomotor circuit of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2015, 199, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamber, B.A.; Twyman, R.E.; Jorgensen, E.M. Pharmacological characterization of the homomeric and heteromeric UNC-49 GABA receptors in C. elegans. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 138, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Marín, L.; Sánchez-Borzone, M.; García, D.A. Neuroprotective effects of gabaergic phenols correlated with their pharmacological and antioxidant properties. Life Sci. 2017, 175, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limke, A.; Poschmann, G.; Stühler, K.; Petzsch, P.; Wachtmeister, T.; von Mikecz, A. Silica Nanoparticles Disclose a Detailed Neurodegeneration Profile throughout the Life Span of a Model Organism. J. Xenobiot. 2024, 14, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrascheck, M.; Ye, X.; Buck, L.B. An antidepressant that extends lifespan in adult Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2007, 450, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, M.; Peter, Q.; Seinstra, R.I.; Perni, M.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Nollen, E.A.A. Assessing motor-related phenotypes of Caenorhabditis elegans with the wide field-of-view nematode tracking platform. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 2071–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenig, K.; Grube, L.; Schwarzländer, M.; Köhrer, K.; Stühler, K.; Poschmann, G. The Proteomic Landscape of Cysteine Oxidation That Underpins Retinoic Acid-Induced Neuronal Differentiation. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1923–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Müller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demichev, V.; Messner, C.B.; Vernardis, S.I.; Lilley, K.S.; Ralser, M. DIA-NN: Neural networks and interference correction enable deep proteome coverage in high throughput. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusher, V.G.; Tibshirani, R.; Chu, G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5116–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nass, R.; Hall, D.H.; Miller, D.M., 3rd; Blakely, R.D. Neurotoxin-induced degeneration of dopamine neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 3264–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Hudry, E.; Hashimoto, T.; Uemura, K.; Fan, Z.Y.; Berezovska, O.; Grosskreutz, C.L.; Bacskai, B.J.; Hyman, B.T. Distinct dendritic spine and nuclear phases of calcineurin activation after exposure to amyloid-β revealed by a novel fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 5298–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, A.L.A.; Meelkop, E.; Linton, C.; Giordano-Santini, R.; Sullivan, R.K.; Donato, A.; Nolan, C.; Hall, D.H.; Xue, D.; Neumann, B.; et al. The Apoptotic Engulfment Machinery Regulates Axonal Degeneration in C. elegans Neurons. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Ebert, D.; Muruganujan, A.; Mills, C.; Albou, L.P.; Mushayamaha, T.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 16: A revised family classification, tree-based classification tool, enhancer regions and extensive API. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D394–D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lander, S.S.; Chornyy, S.; Safory, H.; Gross, A.; Wolosker, H.; Gaisler-Salomon, I. Glutamate dehydrogenase deficiency disrupts glutamate homeostasis in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex and impairs recognition memory. Genes Brain Behav. 2020, 19, e12636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Saiz, E.; Gulez, B.; Pereira, L.; Gendrel, M.; Kerk, S.Y.; Vidal, B.; Feng, W.; Wang, C.; Kratsios, P.; Rand, J.B.; et al. Modular Organization of Cis-regulatory Control Information of Neurotransmitter Pathway Genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2020, 215, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loring, H.S.; Czech, V.L.; Icso, J.D.; O’Connor, L.; Parelkar, S.S.; Byrne, A.B.; Thompson, P.R. A phase transition enhances the catalytic activity of SARM1, an NAD(+) glycohydrolase involved in neurodegeneration. Elife 2021, 10, e66694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roza, E.; Vladâcenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechulek, A.; Berwanger, L.C.; von Mikecz, A. Silica nanoparticles disrupt OPT-2/PEP-2-dependent trafficking of nutrient peptides in the intestinal epithelium. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kwong, J.C.; Copes, R.; Tu, K.; Villeneuve, P.J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Hystad, P.; Martin, R.V.; Murray, B.J.; Jessiman, B.; et al. Living near major roads and the incidence of dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis: A population-based cohort study. Lancet 2017, 389, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonet, T.; Maher, B.A. Airborne, Vehicle-Derived Fe-Bearing Nanoparticles in the Urban Environment: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9970–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P. The exposome in the era of One Health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaletta, T.; Hengartner, M.O. Finding function in novel targets: C. elegans as a model organism. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le, D.T.; Pauls, S.; Poschmann, G.; Stühler, K.; von Mikecz, A. Loss of γ-aminobutyric acid D-Type Motor Neurons in Young Adult Caenorhabditis elegans Following Exposition with Silica Nanoparticles. Cells 2025, 14, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030190
Le DT, Pauls S, Poschmann G, Stühler K, von Mikecz A. Loss of γ-aminobutyric acid D-Type Motor Neurons in Young Adult Caenorhabditis elegans Following Exposition with Silica Nanoparticles. Cells. 2025; 14(3):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030190
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe, Dang Tri, Stella Pauls, Gereon Poschmann, Kai Stühler, and Anna von Mikecz. 2025. "Loss of γ-aminobutyric acid D-Type Motor Neurons in Young Adult Caenorhabditis elegans Following Exposition with Silica Nanoparticles" Cells 14, no. 3: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030190
APA StyleLe, D. T., Pauls, S., Poschmann, G., Stühler, K., & von Mikecz, A. (2025). Loss of γ-aminobutyric acid D-Type Motor Neurons in Young Adult Caenorhabditis elegans Following Exposition with Silica Nanoparticles. Cells, 14(3), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030190






