p27Kip1 and Tumors: Characterization of CDKN1B Variants Identified in MEN4 and Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Antibodies
2.2. Mutagenesis
2.3. Mammalian Cell Culture Growth Conditions and Treatments, Cell Transfection, and Lysis
2.4. Mono- and Bi-Dimensional SDS-PAGE and Immunoblotting
2.5. Cell Count and Flow Cytometry
2.6. Scratch Wound Assay
2.7. Phosphatase Treatment
2.8. Immunoprecipitation and Pull-Down Assay
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
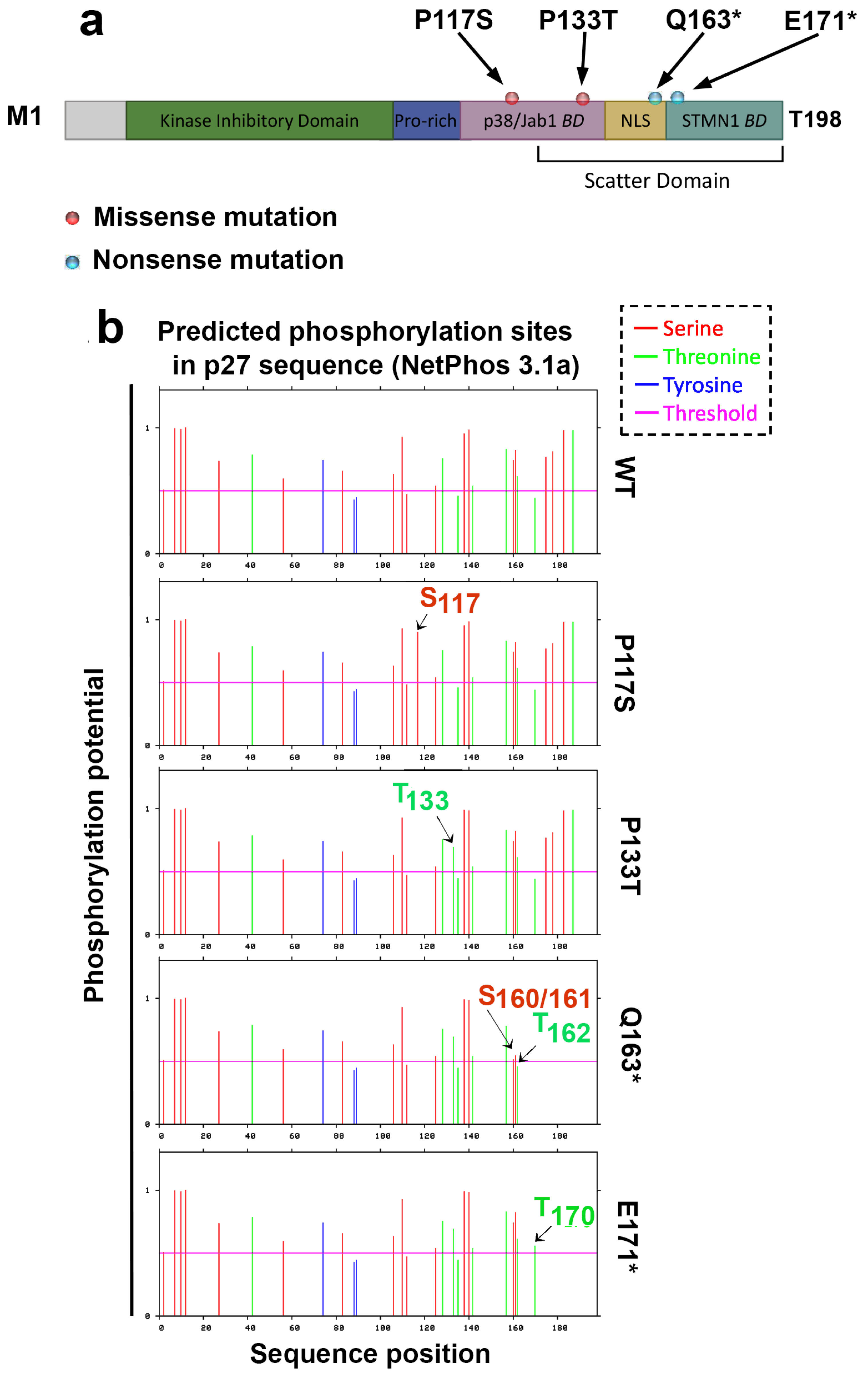
3.1. Selection of CDKN1B Variants and Their In Silico Analysis
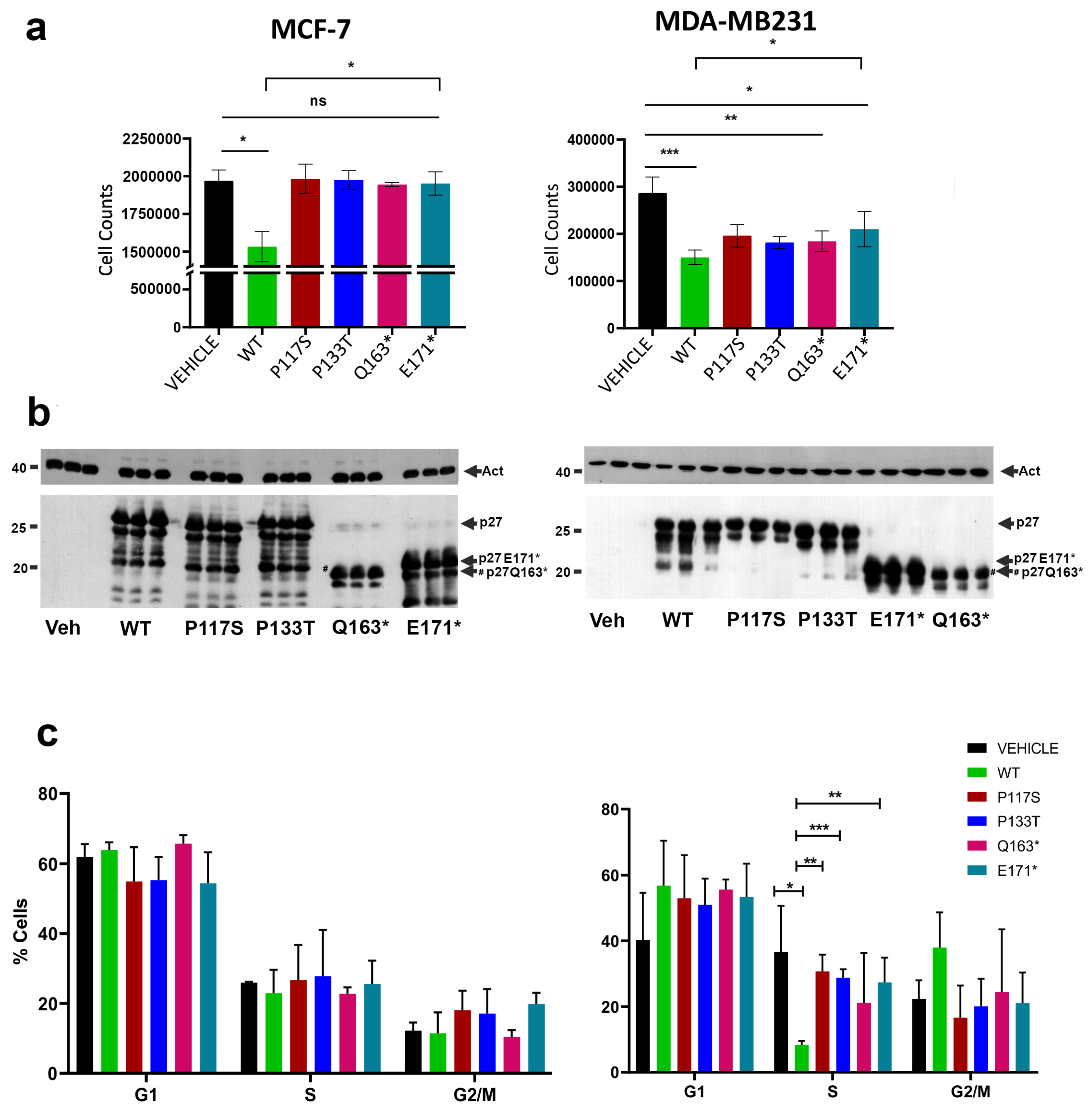
3.2. Phenotypes Correlated to CDKN1B Variants: Studies on Cell Growth and Motility
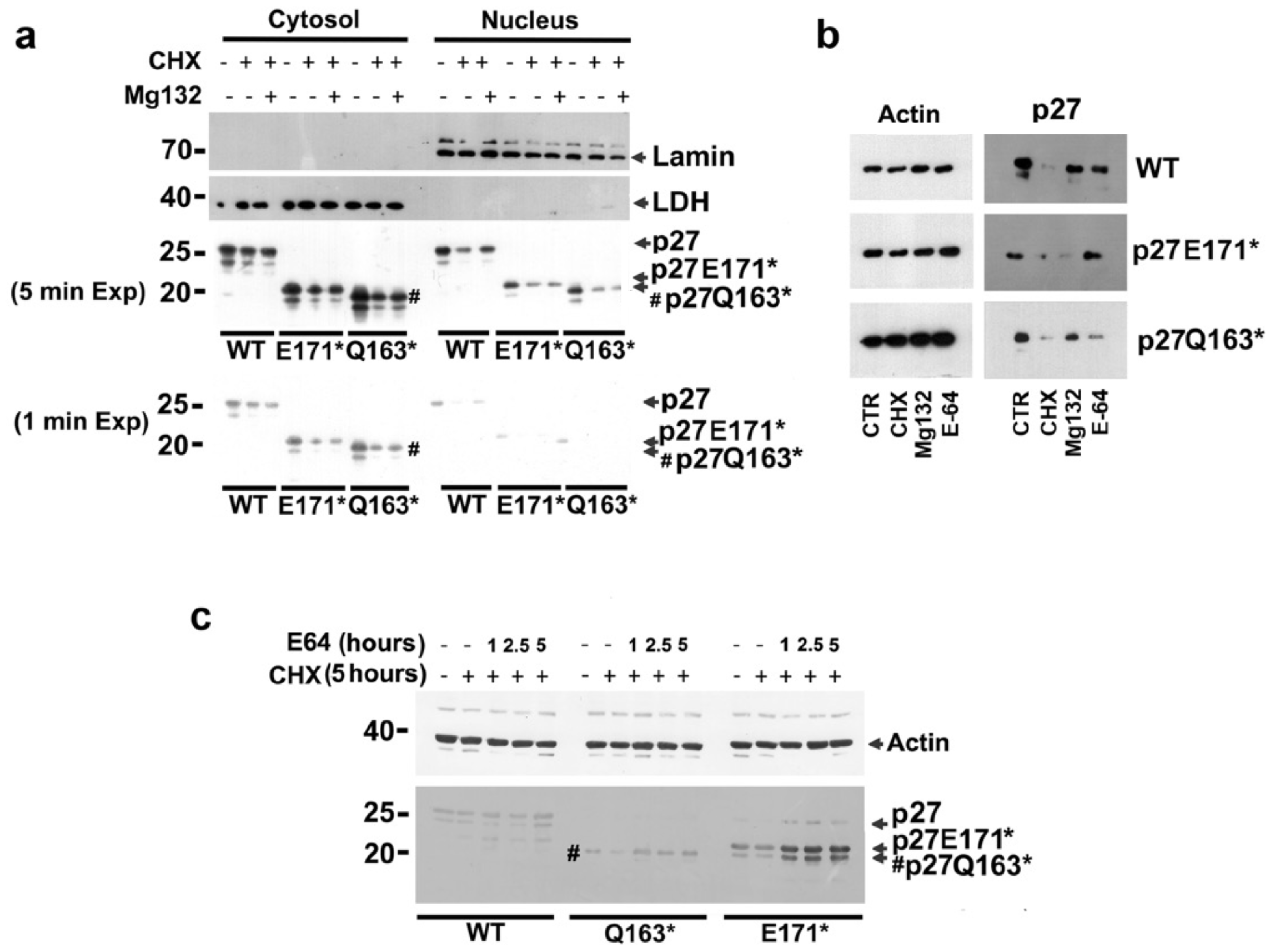
3.3. Subcellular Localization of the p27 Mutants
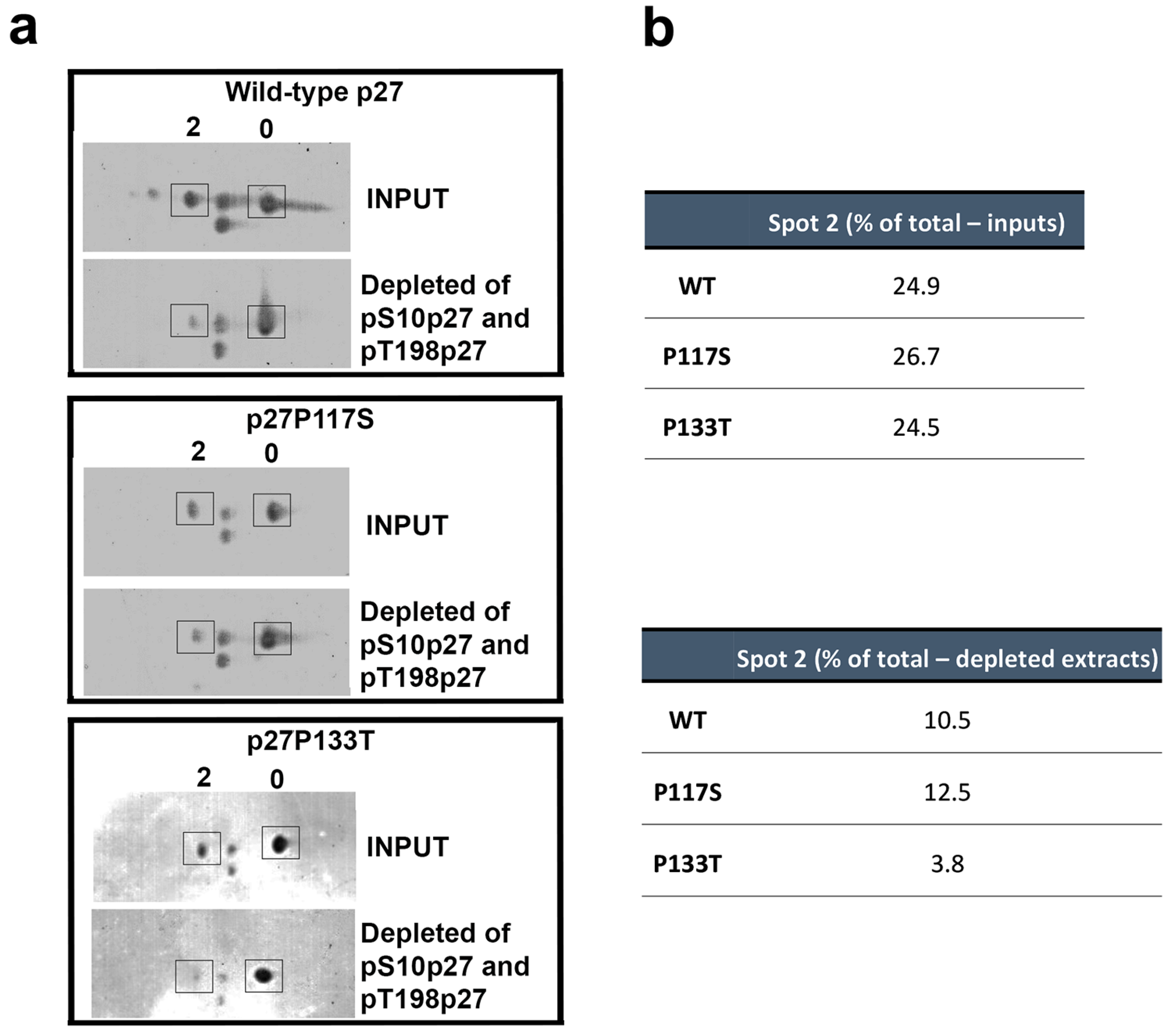
3.4. Analysis of p27 Variants’ Phosphorylation
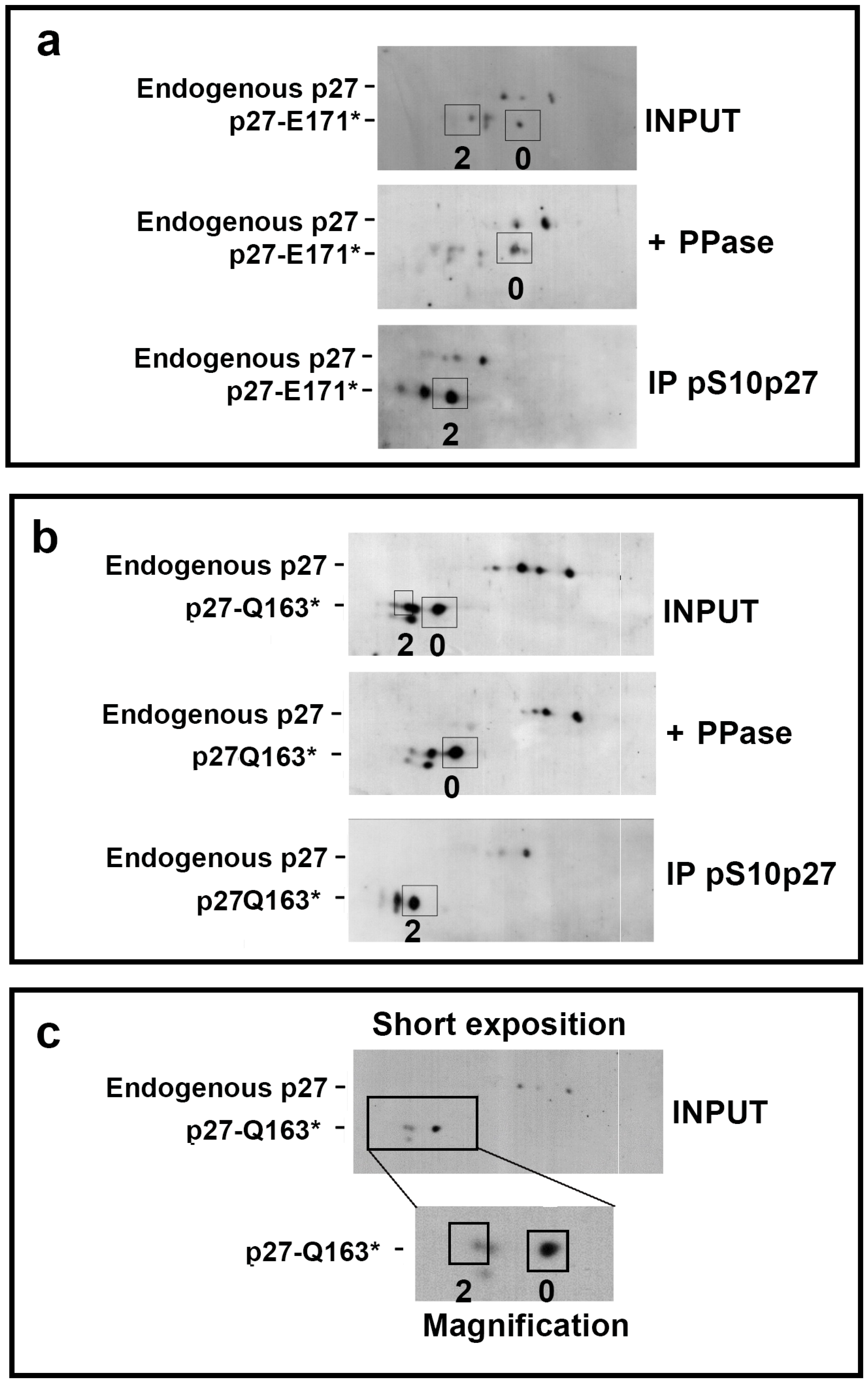
3.5. Analysis of Nonsense p27 HRV Degradation Mechanisms
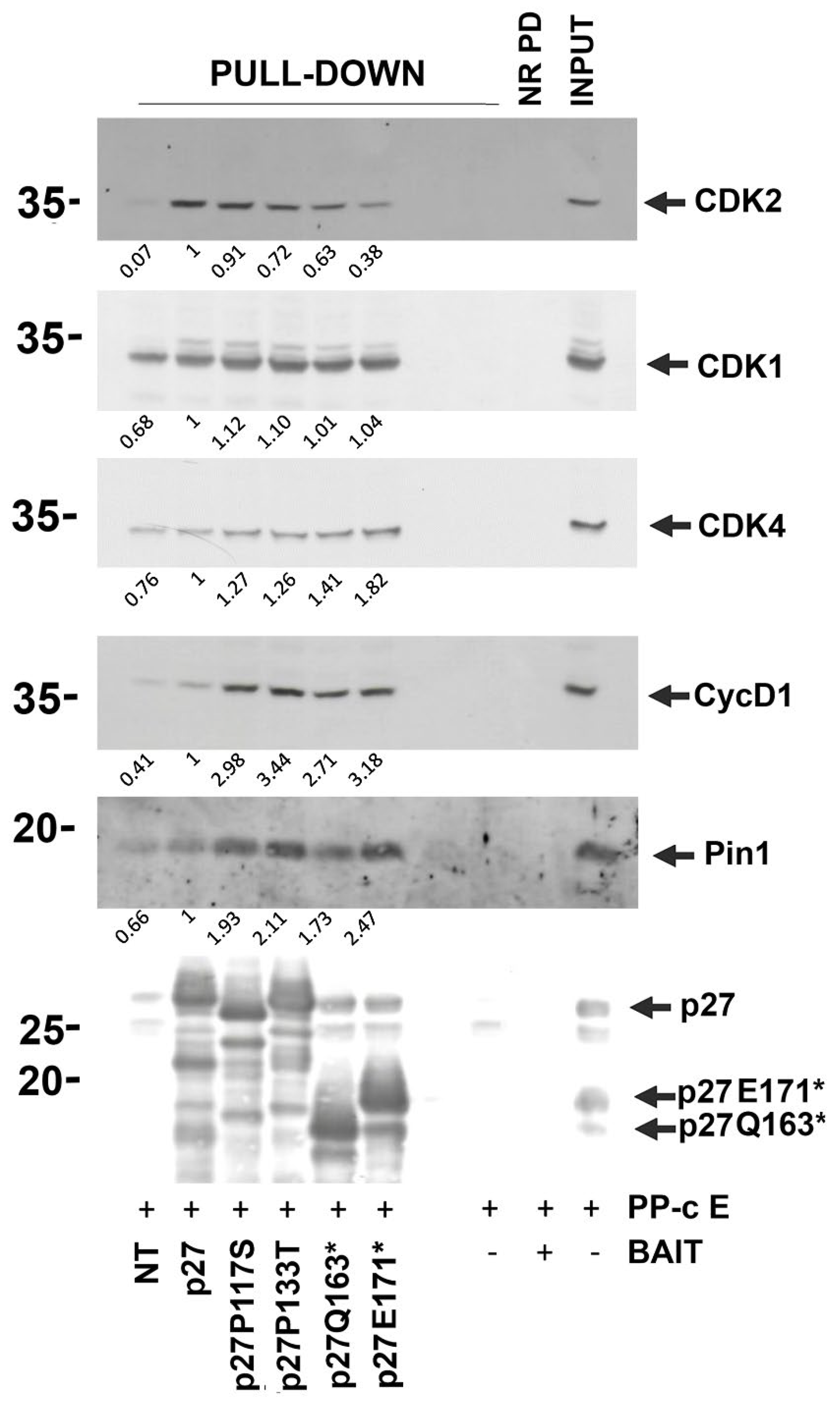
3.6. Effects of Mutations on p27 Interactions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galea, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Sivakolundu, S.G.; Kriwacki, R.W. Regulation of cell division by intrinsically unstructured proteins: Intrinsic flexibility, modularity, and signaling conduits. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7598–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bencivenga, D.; Stampone, E.; Roberti, D.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. p27(Kip1), an Intrinsically Unstructured Protein with Scaffold Properties. Cells 2021, 10, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengst, L.; Reed, S.I. Inhibitors of the Cip/Kip family. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 227, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Stampone, E.; Cervellera, C.; Borriello, A. Regulation of p27(Kip1) and p57(Kip2) Functions by Natural Polyphenols. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, G.; Blasi, C.; La Rocca, S.A.; Pompili, M.; Calconi, A.; Grossi, M. p27Kip1 acts downstream of N-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion to promote myogenesis beyond cell cycle regulation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H.; Su, C.H.; Fang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yeung, S.C.; Lee, M.H. CSN6 deregulation impairs genome integrity in a COP1-dependent pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11779–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, A.E.; Devine, C.; Philpott, A. The cdk inhibitor p27Xic1 is required for differentiation of primary neurones in Xenopus. Development 2003, 130, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Besson, A.; Heng, J.I.; Schuurmans, C.; Teboul, L.; Parras, C.; Philpott, A.; Roberts, J.M.; Guillemot, F. p27kip1 independently promotes neuronal differentiation and migration in the cerebral cortex. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, N.; Miller, J.P.; Gaur, T.; Capellini, T.D.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; de la Hoz, C.; Selleri, L.; Bromage, T.G.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, G.S.; et al. Cooperation between p27 and p107 during endochondral ossification suggests a genetic pathway controlled by p27 and p130. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 5161–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassagh, M.; Philpott, A. Cardiac differentiation in Xenopus requires the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p27Xic1. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, I.; Sun, J.; Arnaout, A.; Kahn, H.; Hanna, W.; Narod, S.; Sun, P.; Tan, C.K.; Hengst, L.; Slingerland, J. p27 phosphorylation by Src regulates inhibition of cyclin E-Cdk2. Cell 2007, 128, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimmler, M.; Wang, Y.; Mund, T.; Cilensek, Z.; Keidel, E.M.; Waddell, M.B.; Jäkel, H.; Kullmann, M.; Kriwacki, R.W.; Hengst, L. Cdk-inhibitory activity and stability of p27Kip1 are directly regulated by oncogenic tyrosine kinases. Cell 2007, 128, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsytlonok, M.; Sanabria, H.; Wang, Y.; Felekyan, S.; Hemmen, K.; Phillips, A.H.; Yun, M.K.; Waddell, M.B.; Park, C.G.; Vaithiyalingam, S.; et al. Dynamic anticipation by Cdk2/Cyclin A-bound p27 mediates signal integration in cell cycle regulation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnoli, A.; Fiore, F.; Eytan, E.; Carrano, A.C.; Draetta, G.F.; Hershko, A.; Pagano, M. Ubiquitination of p27 is regulated by Cdk-dependent phosphorylation and trimeric complex formation. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, A.; Naviglio, S.; Bencivenga, D.; Caldarelli, I.; Tramontano, A.; Speranza, M.C.; Stampone, E.; Sapio, L.; Negri, A.; Oliva, A.; et al. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Increase p27(Kip1) by Affecting Its Ubiquitin-Dependent Degradation through Skp2 Downregulation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2016, 2016, 2481865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Olivier, P.; Diehl, J.A.; Fero, M.; Roussel, M.F.; Roberts, J.M.; Sherr, C.J. The p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) CDK ‘inhibitors’ are essential activators of cyclin D-dependent kinases in murine fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiley, K.Z.; Stevenson, J.W.; Lou, K.; Barkovich, K.J.; Kumarasamy, V.; Wijeratne, T.U.; Bunch, K.L.; Tripathi, S.; Knudsen, E.S.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; et al. p27 allosterically activates cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and antagonizes palbociclib inhibition. Science 2019, 366, eaaw2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, A.; Assoian, R.K.; Roberts, J.M. Regulation of the cytoskeleton: An oncogenic function for CDK inhibitors? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, G.; Belletti, B.; Nicoloso, M.S.; Schiappacassi, M.; Vecchione, A.; Spessotto, P.; Morrione, A.; Canzonieri, V.; Colombatti, A. p27(Kip1)-stathmin interaction influences sarcoma cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowosad, A.; Creff, J.; Jeannot, P.; Culerrier, R.; Codogno, P.; Manenti, S.; Nguyen, L.; Besson, A. p27 controls autophagic vesicle trafficking in glucose-deprived cells via the regulation of ATAT1-mediated microtubule acetylation. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, G.; Even, A.; Gladwyn-Ng, I.; Le Bail, R.; Shilian, M.; Godin, J.D.; Peyre, E.; Hassan, B.A.; Besson, A.; Rigo, J.M.; et al. p27(Kip1) Modulates Axonal Transport by Regulating α-Tubulin Acetyltransferase 1 Stability. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perchey, R.T.; Serres, M.P.; Nowosad, A.; Creff, J.; Callot, C.; Gay, A.; Manenti, S.; Margolis, R.L.; Hatzoglou, A.; Besson, A. p27(Kip1) regulates the microtubule bundling activity of PRC1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiappacassi, M.; Lovisa, S.; Lovat, F.; Fabris, L.; Colombatti, A.; Belletti, B.; Baldassarre, G. Role of T198 modification in the regulation of p27(Kip1) protein stability and function. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sgubin, M.; Pegoraro, S.; Pellarin, I.; Ros, G.; Sgarra, R.; Piazza, S.; Baldassarre, G.; Belletti, B.; Manfioletti, G. HMGA1 positively regulates the microtubule-destabilizing protein stathmin promoting motility in TNBC cells and decreasing tumour sensitivity to paclitaxel. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowosad, A.; Jeannot, P.; Callot, C.; Creff, J.; Perchey, R.T.; Joffre, C.; Codogno, P.; Manenti, S.; Besson, A. p27 controls Ragulator and mTOR activity in amino acid-deprived cells to regulate the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and coordinate cell cycle and cell growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavipour, S.F.; Harikumar, K.B.; Slingerland, J.M. p27 as a Transcriptional Regulator: New Roles in Development and Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3451–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Kim, M.; Jang, K.; Shin, M.; Besser, A.; Xiao, X.; Zhao, D.; Wander, S.A.; Briegel, K.; Morey, L.; et al. p27 transcriptionally coregulates cJun to drive programs of tumor progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7005–7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotake, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Ishida, N.; Nakayama, K.I. Role of serine 10 phosphorylation in p27 stabilization revealed by analysis of p27 knock-in mice harboring a serine 10 mutation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, A.; Cucciolla, V.; Criscuolo, M.; Indaco, S.; Oliva, A.; Giovane, A.; Bencivenga, D.; Iolascon, A.; Zappia, V.; Della Ragione, F. Retinoic acid induces p27Kip1 nuclear accumulation by modulating its phosphorylation. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4240–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossatz, U.; Vervoorts, J.; Nickeleit, I.; Sundberg, H.A.; Arthur, J.S.; Manns, M.P.; Malek, N.P. C-terminal phosphorylation controls the stability and function of p27kip1. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5159–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencivenga, D.; Tramontano, A.; Borgia, A.; Negri, A.; Caldarelli, I.; Oliva, A.; Perrotta, S.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. P27Kip1 serine 10 phosphorylation determines its metabolism and interaction with cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3768–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- De Marco, C.; Rinaldo, N.; De Vita, F.; Forzati, F.; Caira, E.; Iovane, V.; Paciello, O.; Montanaro, D.; D‘Andrea, S.; Baldassarre, G.; et al. The T197A Knock-in Model of Cdkn1b Gene to Study the Effects of p27 Restoration In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishita, D.; Katayama, R.; Sekimizu, K.; Tsuruo, T.; Fujita, N. Pim kinases promote cell cycle progression by phosphorylating and down-regulating p27Kip1 at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5076–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, N.; Hara, T.; Kamura, T.; Yoshida, M.; Nakayama, K.; Nakayama, K.I. Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 on serine 10 is required for its binding to CRM1 and nuclear export. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14355–14358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, M.K.; Kotchetkov, R.; Cariou, S.; Resch, A.; Lupetti, R.; Beniston, R.G.; Melchior, F.; Hengst, L.; Slingerland, J.M. CRM1/Ran-mediated nuclear export of p27(Kip1) involves a nuclear export signal and links p27 export and proteolysis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, N.; Sato, S.; Tsuruo, T. Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 at threonine 198 by p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinases promotes its binding to 14-3-3 and cytoplasmic localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49254–49260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Tsai, L.H. Cyclin-dependent kinases in brain development and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 27, 465–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsihlias, J. p27 (Kip1) in Prostate Cancer, Prognostic Value and Role in Mediating Effect of High-Dose Dihydrotestosterone in LNCaP. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Slingerland, J.; Pagano, M. Regulation of the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 183, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, I.M.; Hengst, L.; Slingerland, J.M. The Cdk inhibitor p27 in human cancer: Prognostic potential and relevance to anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko, D.D. Oncogenic properties and prognostic implications of the ubiquitin ligase Skp2 in cancer. Cancer 2008, 112, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csergeová, L.; Krbušek, D.; Janoštiak, R. CIP/KIP and INK4 families as hostages of oncogenic signaling. Cell Div. 2024, 19, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iolascon, A.; Giordani, L.; Moretti, A.; Basso, G.; Borriello, A.; Della Ragione, F. Analysis of CDKN2A, CDKN2B, CDKN2C, and cyclin Ds gene status in hepatoblastoma. Hepatology 1998, 27, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iolascon, A.; Giordani, L.; Moretti, A.; Tonini, G.P.; Lo Cunsolo, C.; Mastropietro, S.; Borriello, A.; Della Ragione, F. Structural and functional analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor genes (CDKN2A, CDKN2B, and CDKN2C) in neuroblastoma. Pediatr. Res. 1998, 43, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Tarpey, P.S.; Davies, H.; Van Loo, P.; Greenman, C.; Wedge, D.C.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Martin, S.; Varela, I.; Bignell, G.R.; et al. The landscape of cancer genes and mutational processes in breast cancer. Nature 2012, 486, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, C.E.; Baca, S.C.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Blattner, M.; Theurillat, J.P.; White, T.A.; Stojanov, P.; Van Allen, E.; Stransky, N.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, J.M.; Kiezun, A.; Ramos, A.H.; Serra, S.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Qian, Z.R.; Banck, M.S.; Kanwar, R.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Karpathakis, A.; et al. Somatic mutation of CDKN1B in small intestine neuroendocrine tumors. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crona, J.; Gustavsson, T.; Norlén, O.; Edfeldt, K.; Åkerström, T.; Westin, G.; Hellman, P.; Björklund, P.; Stålberg, P. Somatic Mutations and Genetic Heterogeneity at the CDKN1B Locus in Small Intestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22 (Suppl. 3), S1428–S1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viotto, D.; Russo, F.; Anania, I.; Segatto, I.; Rampioni Vinciguerra, G.L.; Dall’Acqua, A.; Bomben, R.; Perin, T.; Cusan, M.; Schiappacassi, M.; et al. CDKN1B mutation and copy number variation are associated with tumor aggressiveness in luminal breast cancer. J. Pathol. 2021, 253, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, S.; Hüllein, J.; Lee, S.C.; Hutter, B.; Gonzalez, D.; Jayne, S.; Dyer, M.J.; Oleś, M.; Else, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Recurrent CDKN1B (p27) mutations in hairy cell leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 1005–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Pellegata, N.S. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 4. Front. Horm. Res. 2013, 41, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molatore, S.; Pellegata, N.S. The MENX syndrome and p27: Relationships with multiple endocrine neoplasia. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 182, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederiksen, A.; Rossing, M.; Hermann, P.; Ejersted, C.; Thakker, R.V.; Frost, M. Clinical Features of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 4: Novel Pathogenic Variant and Review of Published Cases. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 3637–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fero, M.L.; Rivkin, M.; Tasch, M.; Porter, P.; Carow, C.E.; Firpo, E.; Polyak, K.; Tsai, L.H.; Broudy, V.; Perlmutter, R.M.; et al. A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell 1996, 85, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fero, M.L.; Randel, E.; Gurley, K.E.; Roberts, J.M.; Kemp, C.J. The murine gene p27Kip1 is haplo-insufficient for tumour suppression. Nature 1998, 396, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, D.; Circelli, L.; Faggiano, A.; Pancione, M.; Renzullo, A.; Elisei, R.; Romei, C.; Accardo, G.; Coppola, V.R.; De Palma, M.; et al. CDKN1B V109G polymorphism a new prognostic factor in sporadic medullary thyroid carcinoma. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencivenga, D.; Stampone, E.; Aulitto, A.; Tramontano, A.; Barone, C.; Negri, A.; Roberti, D.; Perrotta, S.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. A cancer-associated CDKN1B mutation induces p27 phosphorylation on a novel residue: A new mechanism for tumor suppressor loss-of-function. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 915–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tichomirowa, M.A.; Lee, M.; Barlier, A.; Daly, A.F.; Marinoni, I.; Jaffrain-Rea, M.L.; Naves, L.A.; Rodien, P.; Rohmer, V.; Faucz, F.R.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B) gene variants in AIP mutation-negative familial isolated pituitary adenoma kindreds. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Guda, J.; Marinoni, I.; Molatore, S.; Pellegata, N.S.; Arnold, A. Somatic mutation and germline sequence abnormalities in CDKN1B, encoding p27Kip1, in sporadic parathyroid adenomas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E701–E706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalicchio, M.I.; Improta, G.; Zupa, A.; Cursio, O.E.; Stampone, E.; Possidente, L.; Teresa Gerardi, A.M.; Vita, G.; Martini, M.; Cassano, A.; et al. Pyrosequencing evaluation of low-frequency KRAS mutant alleles for EGF receptor therapy selection in metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucciolla, V.; Borriello, A.; Criscuolo, M.; Sinisi, A.A.; Bencivenga, D.; Tramontano, A.; Scudieri, A.C.; Oliva, A.; Zappia, V.; Della Ragione, F. Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate p57Kip2 level by enhancing its expression through Sp1 transcription factor. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stampone, E.; Bencivenga, D.; Barone, C.; Aulitto, A.; Verace, F.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. High Dosage Lithium Treatment Induces DNA Damage and p57(Kip2) Decrease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampone, E.; Bencivenga, D.; Barone, C.; Di Finizio, M.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. A Beckwith-Wiedemann-Associated CDKN1C Mutation Allows the Identification of a Novel Nuclear Localization Signal in Human p57(Kip2). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borriello, A.; Caldarelli, I.; Speranza, M.C.; Scianguetta, S.; Tramontano, A.; Bencivenga, D.; Stampone, E.; Negri, A.; Nobili, B.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Iron overload enhances human mesenchymal stromal cell growth and hampers matrix calcification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsari, S.; Pardi, E.; Pellegata, N.S.; Lee, M.; Saponaro, F.; Torregrossa, L.; Basolo, F.; Paltrinieri, E.; Zatelli, M.C.; Materazzi, G.; et al. Loss of p27 expression is associated with MEN1 gene mutations in sporadic parathyroid adenomas. Endocrine 2017, 55, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugalho, M.J.; Domingues, R. Uncommon association of cerebral meningioma, parathyroid adenoma and papillary thyroid carcinoma in a patient harbouring a rare germline variant in the CDKN1B gene. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2015213934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, I.; Ibrahimpasic, T.; Boucai, L.; Sinha, R.; Knauf, J.A.; Shah, R.H.; Dogan, S.; Ricarte-Filho, J.C.; Krishnamoorthy, G.P.; Xu, B.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic hallmarks of poorly differentiated and anaplastic thyroid cancers. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1052–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic analyses of ovarian carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singeisen, H.; Renzulli, M.M.; Pavlicek, V.; Probst, P.; Hauswirth, F.; Muller, M.K.; Adamczyk, M.; Weber, A.; Kaderli, R.M.; Renzulli, P. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 4: A new member of the MEN family. Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e220411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Thakuria, M.; Chen, T.; Marcelus, C.; Cheng, J.; Nomburg, J.; Thorner, A.R.; Slevin, M.K.; Powers, W.; Burns, R.T.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of virus-positive and virus-negative Merkel cell carcinoma. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, L.; Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Claret, F.X.; Yang, H. Jab1/CSN5 negatively regulates p27 and plays a role in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1890–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.A.; Gindin, Y.; Lu, C.; Griffith, O.L.; Griffith, M.; Shen, D.; Hoog, J.; Li, T.; Larson, D.E.; Watson, M.; et al. Aromatase inhibition remodels the clonal architecture of estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, M.J.; Ding, L.; Shen, D.; Luo, J.; Suman, V.J.; Wallis, J.W.; Van Tine, B.A.; Hoog, J.; Goiffon, R.J.; Goldstein, T.C.; et al. Whole-genome analysis informs breast cancer response to aromatase inhibition. Nature 2012, 486, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbolo, M.; Vicentini, C.; Mafficini, A.; Fassan, M.; Pedron, S.; Corbo, V.; Mastracci, L.; Rusev, B.; Pedrazzani, C.; Landoni, L.; et al. Mutational and copy number asset of primary sporadic neuroendocrine tumors of the small intestine. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovisa, S.; Citro, S.; Sonego, M.; Dall’Acqua, A.; Ranzuglia, V.; Berton, S.; Colombatti, A.; Belletti, B.; Chiocca, S.; Schiappacassi, M.; et al. SUMOylation regulates p27Kip1 stability and localization in response to TGFβ. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirane, M.; Harumiya, Y.; Ishida, N.; Hirai, A.; Miyamoto, C.; Hatakeyama, S.; Nakayama, K.; Kitagawa, M. Down-regulation of p27(Kip1) by two mechanisms, ubiquitin-mediated degradation and proteolytic processing. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13886–13893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surjit, M.; Lal, S.K. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 phosphorylates and regulates the stability of p27kip1 protein. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machacek, M.; Hodgson, L.; Welch, C.; Elliott, H.; Pertz, O.; Nalbant, P.; Abell, A.; Johnson, G.L.; Hahn, K.M.; Danuser, G. Coordination of Rho GTPase activities during cell protrusion. Nature 2009, 461, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, A.H.; Ou, L.; Gay, A.; Besson, A.; Kriwacki, R.W. Mapping Interactions between p27 and RhoA that Stimulate Cell Migration. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, S.S.; Becker-Hapak, M.; Pintucci, G.; Pagano, M.; Dowdy, S.F. Novel p27(kip1) C-terminal scatter domain mediates Rac-dependent cell migration independent of cell cycle arrest functions. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besson, A.; Gurian-West, M.; Schmidt, A.; Hall, A.; Roberts, J.M. p27Kip1 modulates cell migration through the regulation of RhoA activation. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serres, M.P.; Kossatz, U.; Chi, Y.; Roberts, J.M.; Malek, N.P.; Besson, A. p27(Kip1) controls cytokinesis via the regulation of citron kinase activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iancu-Rubin, C.; Atweh, G.F. p27(Kip1) and stathmin share the stage for the first time. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 346–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiappacassi, M.; Lovat, F.; Canzonieri, V.; Belletti, B.; Berton, S.; Di Stefano, D.; Vecchione, A.; Colombatti, A.; Baldassarre, G. p27Kip1 expression inhibits glioblastoma growth, invasion, and tumor-induced neoangiogenesis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton, S.; Belletti, B.; Wolf, K.; Canzonieri, V.; Lovat, F.; Vecchione, A.; Colombatti, A.; Friedl, P.; Baldassarre, G. The tumor suppressor functions of p27(kip1) include control of the mesenchymal/amoeboid transition. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 5031–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belletti, B.; Baldassarre, G. New light on p27(kip1) in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3701–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pellizzari, I.; Fabris, L.; Berton, S.; Segatto, I.; Citron, F.; D’Andrea, S.; Cusan, M.; Benevol, S.; Perin, T.; Massarut, S.; et al. p27kip1 expression limits H-Ras-driven transformation and tumorigenesis by both canonical and non-canonical mechanisms. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64560–64574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liang, J.; Zubovitz, J.; Petrocelli, T.; Kotchetkov, R.; Connor, M.K.; Han, K.; Lee, J.H.; Ciarallo, S.; Catzavelos, C.; Beniston, R.; et al. PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.H.; Cheong, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Eom, J.I.; Lee, S.T.; Hahn, J.S.; Ko, Y.W.; Lee, M.H. Cytoplasmic mislocalization of p27Kip1 protein is associated with constitutive phosphorylation of Akt or protein kinase B and poor prognosis in acute myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5225–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrea, M.D.; Liang, J.; Da Silva, T.; Hong, F.; Shao, S.H.; Han, K.; Dumont, D.; Slingerland, J.M. Phosphorylation of p27Kip1 regulates assembly and activation of cyclin D1-Cdk4. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 6462–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, N.; Kitagawa, M.; Hatakeyama, S.; Nakayama, K. Phosphorylation at serine 10, a major phosphorylation site of p27(Kip1), increases its protein stability. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25146–25154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nakka, M.; Kelly, A.J.; Lau, C.C.; Krailo, M.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Hicks, J.M.; Man, T.K. p27 Is a Candidate Prognostic Biomarker and Metastatic Promoter in Osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4002–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, J.J.; González, J.M.; Edo, M.D.; Viana, R.; Boya, P.; Cervera, J.; Verges, M.; Rivera, J.; Andrés, V. Tumor suppressor p27(Kip1) undergoes endolysosomal degradation through its interaction with sorting nexin 6. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2998–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.W.; Leong, K.W.; Ng, Y.M.; Kwong, Y.L.; Tse, E. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase PIN1 relieves cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) inhibition by the CDK inhibitor p27. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 21431–21441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bencivenga, D.; Stampone, E.; Azhar, J.; Parente, D.; Ali, W.; Del Vecchio, V.; Della Ragione, F.; Borriello, A. p27Kip1 and Tumors: Characterization of CDKN1B Variants Identified in MEN4 and Breast Cancer. Cells 2025, 14, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030188
Bencivenga D, Stampone E, Azhar J, Parente D, Ali W, Del Vecchio V, Della Ragione F, Borriello A. p27Kip1 and Tumors: Characterization of CDKN1B Variants Identified in MEN4 and Breast Cancer. Cells. 2025; 14(3):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030188
Chicago/Turabian StyleBencivenga, Debora, Emanuela Stampone, Jahanzaib Azhar, Daniela Parente, Waqar Ali, Vitale Del Vecchio, Fulvio Della Ragione, and Adriana Borriello. 2025. "p27Kip1 and Tumors: Characterization of CDKN1B Variants Identified in MEN4 and Breast Cancer" Cells 14, no. 3: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030188
APA StyleBencivenga, D., Stampone, E., Azhar, J., Parente, D., Ali, W., Del Vecchio, V., Della Ragione, F., & Borriello, A. (2025). p27Kip1 and Tumors: Characterization of CDKN1B Variants Identified in MEN4 and Breast Cancer. Cells, 14(3), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14030188








