Verapamil Restores β-Cell Mass and Function in Diabetogenic Stress Models via Proliferation and Mitochondrial Respiration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments and Viability Assays
2.2. Cell Survival Assessment and Inhibitory Concentration 50% Determination
2.3. Immunofluorescence Detection of Ki67
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Cell Viability Assays
2.7. Seahorse Assay (Metabolic Flux Analysis)
2.8. Transgenic Zebrafish Larvae Model Experiments
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
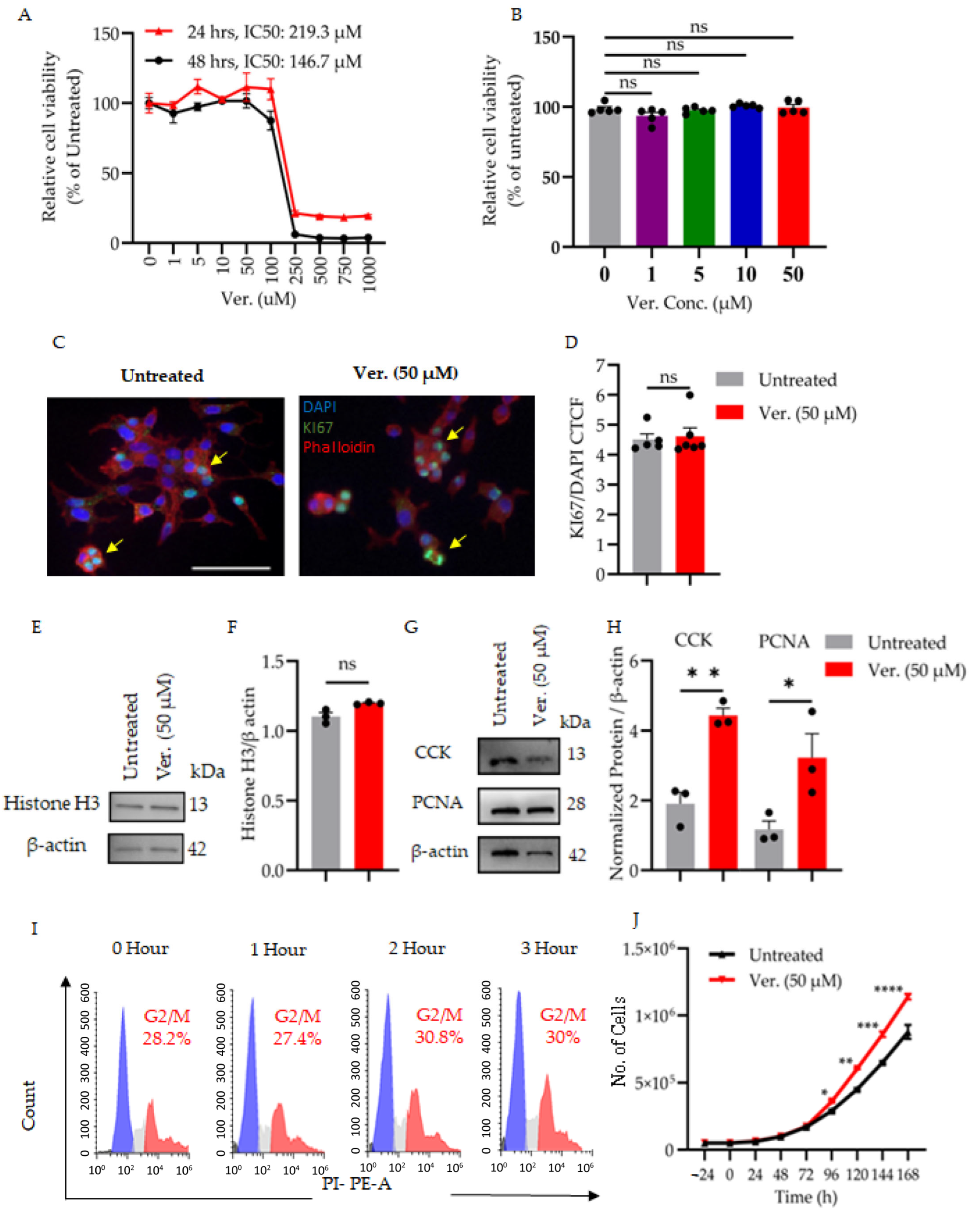
3.1. Verapamil Preserves β-Cell Integrity Under Diabetogenic Stress by Modulating Cytotoxicity, Proliferation, and Cell Cycle Progression
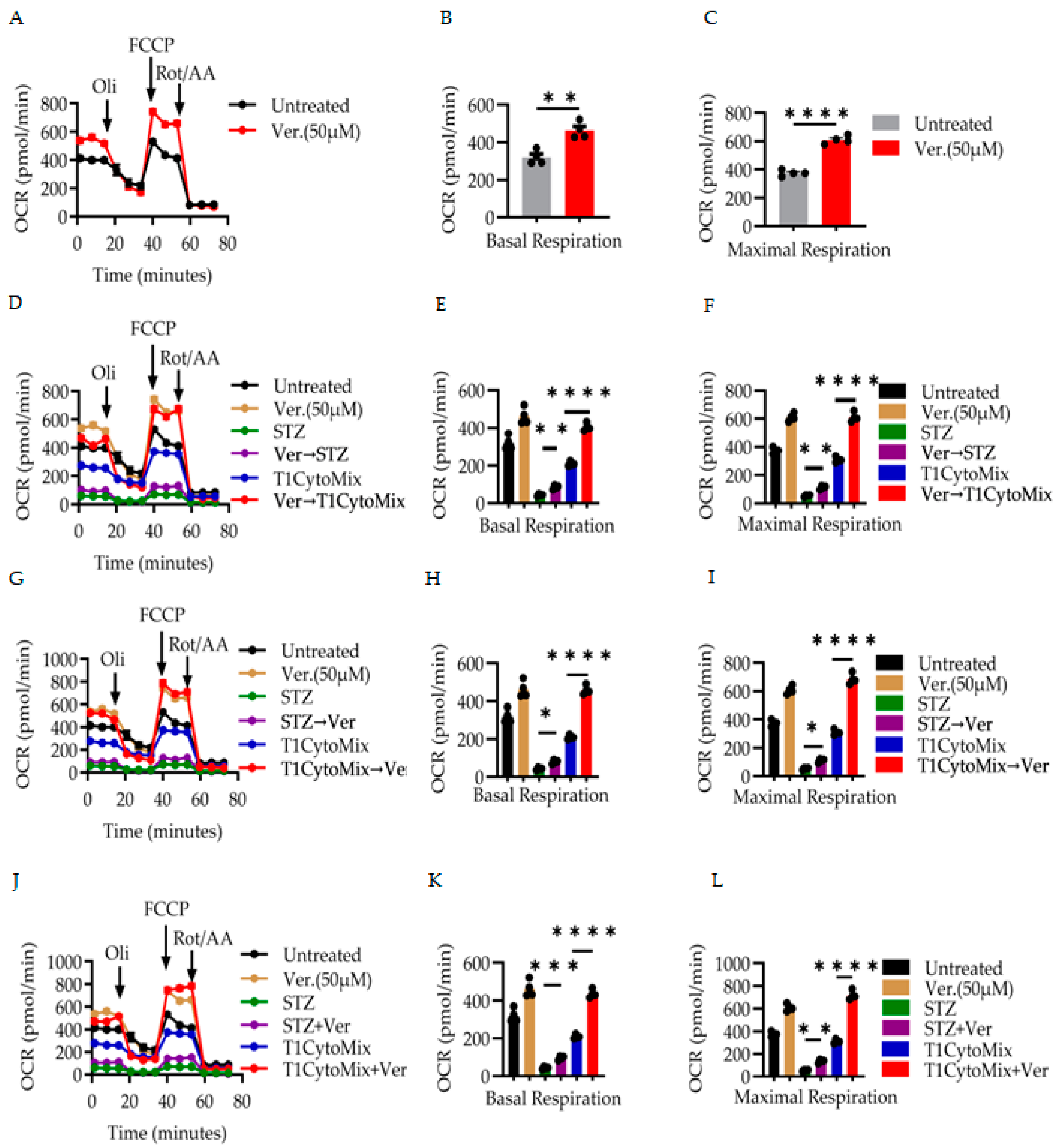
3.2. Verapamil Enhances Mitochondrial Respiration and Preserves Bioenergetic Function in β-Cells Under Diabetogenic Stress
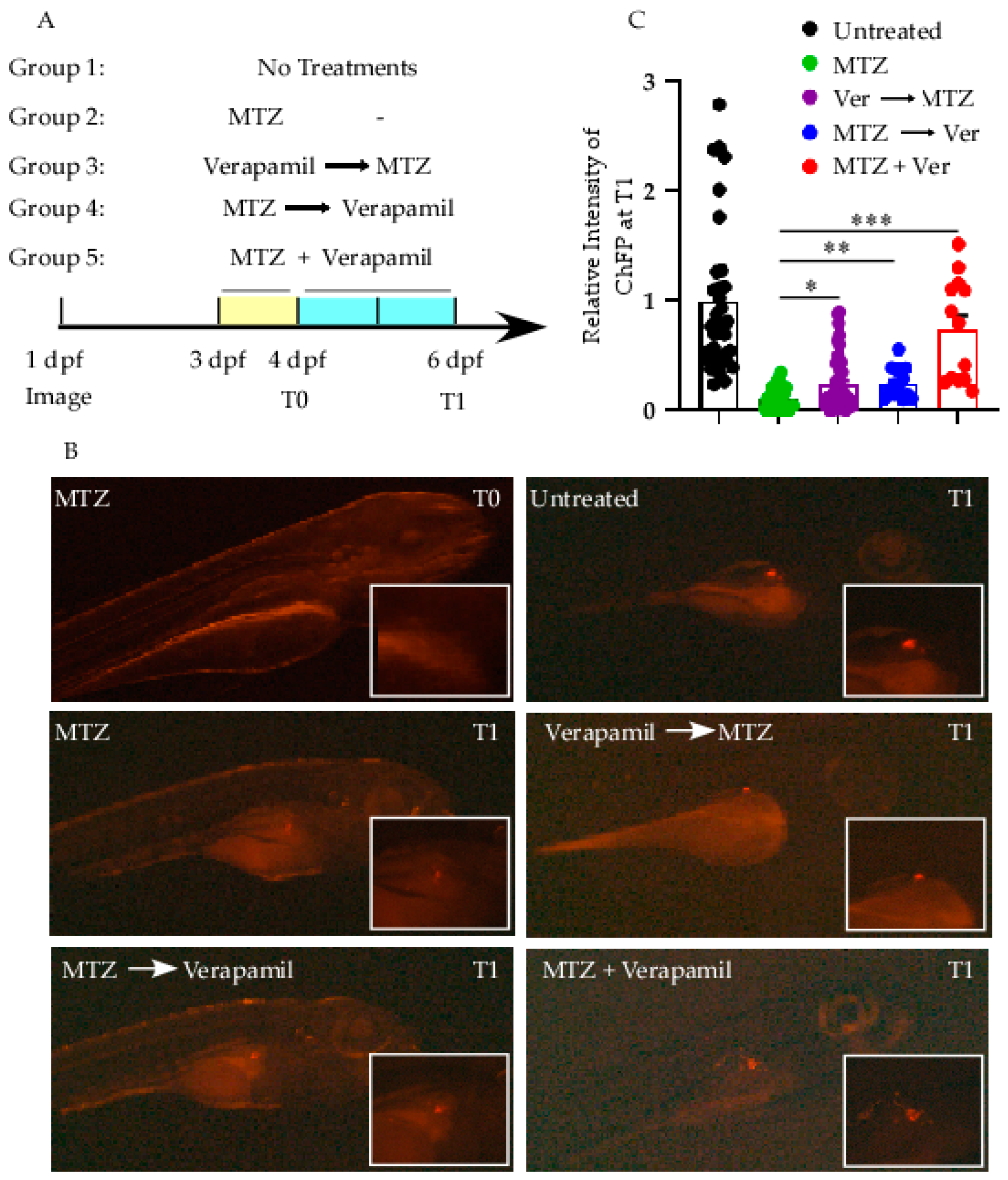
3.3. Verapamil Protects β-Cell in Zebrafish Model Against MTZ Stressor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022 Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin. Diabetes 2022, 40, 10–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahanovitz, L.; Sluss, P.M.; Russell, S.J. Type 1 Diabetes—A Clinical Perspective. Point Care 2017, 16, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galicia-Garcia, U.; Jebari, S.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Uribe, K.B.; Siddiqi, H.; Ostolaza, H.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Martin, C. Statin Treatment-Induced Development of Type 2 Diabetes: From Clinical Evidence to Mechanistic Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabakchieva, P.; Assyov, Y.; Gerasoudis, S.; Vasilev, G.; Peshevska-Sekulovska, M.; Sekulovski, M.; Lazova, S.; Miteva, D.G.; Gulinac, M.; Tomov, L.; et al. Islet transplantation-immunological challenges and current perspectives. World J. Transplant. 2023, 13, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-W.; Guan, B.-J.; Alzahrani, M.R.; Gao, Z.; Gao, L.; Bracey, S.; Wu, J.; Mbow, C.A.; Jobava, R.; Haataja, L.; et al. Adaptation to chronic ER stress enforces pancreatic β-cell plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, J.R.N.; Skyler, J.S. Challenges in Beta Cell Replacement for Type 1 Diabetes. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2024, 98, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forlenza, G.P.; McVean, J.; Beck, R.W.; Bauza, C.; Bailey, R.; Buckingham, B.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Sherr, J.L.; Clements, M.; Neyman, A.; et al. Effect of Verapamil on Pancreatic Beta Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2023, 329, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, S.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; He, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, Q. Effect of Verapamil on Blood Glucose in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Scholten, B.J.; Kreiner, F.F.; Gough, S.C.L.; von Herrath, M. Current and future therapies for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstock, R.S.; DuBose, S.N.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Chaytor, N.S.; Peterson, C.; Olson, B.A.; Munshi, M.N.; Perrin, A.J.; Miller, K.M.; Beck, R.W.; et al. Risk Factors Associated With Severe Hypoglycemia in Older Adults With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovalle, F.; Grimes, T.; Xu, G.; Patel, A.J.; Grayson, T.B.; Thielen, L.A.; Li, P.; Shalev, A. Verapamil and beta cell function in adults with recent-onset type 1 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Grimes, T.D.; Grayson, T.B.; Chen, J.; Thielen, L.A.; Tse, H.M.; Li, P.; Kanke, M.; Lin, T.T.; Schepmoes, A.A.; et al. Exploratory study reveals far reaching systemic and cellular effects of verapamil treatment in subjects with type 1 diabetes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effect of verapamil on mortality and major events after acute myocardial infarction (the Danish Verapamil Infarction Trial II--DAVIT II). Am. J. Cardiol. 1990, 66, 779–785. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secondary prevention with verapamil after myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 1990, 66, 33–40. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper-Dehoff, R.; Cohen, J.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Messerli, F.H.; Erdine, S.; Hewkin, A.C.; Kupfer, S.; Pepine, C.J.; INVEST Investigators. Predictors of development of diabetes mellitus in patients with coronary artery disease taking antihypertensive medications (findings from the INternational VErapamil SR-Trandolapril STudy [INVEST]). Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 890–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.J.; Yu, G.Z.; Zhang, G.F.; Yu, J.R. Protective effect of verapamil against alloxan-induced damage on pancreatic islet beta-cells in rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao 1992, 44, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Rho, H.W.; Park, B.H.; Park, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, U.H.; Chung, M.Y. Role of Ca2+ in alloxan-induced pancreatic beta-cell damage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1227, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefanian, H.; Al Madhoun, A.; Al-Rashed, F.; Alzaid, F.; Bahman, F.; Nizam, R.; Alhusayan, M.; John, S.; Jacob, S.; Williams, M.R.; et al. Unraveling Verapamil’s Multidimensional Role in Diabetes Therapy: From beta-Cell Regeneration to Cholecystokinin Induction in Zebrafish and MIN6 Cell-Line Models. Cells 2024, 13, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Muhammed, S.J.; Kessler, B.; Salehi, A. Mitochondrial proteome analysis reveals altered expression of voltage dependent anion channels in pancreatic beta-cells exposed to high glucose. Islets 2010, 2, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Meng, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; He, J.; He, Q.; Geng, Y. CaMKIV limits metabolic damage through induction of hepatic autophagy by CREB in obese mice. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 244, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumoto, K.; Yennek, S.; Chen, C.; Silva, L.F.D.; Traikov, S.; Sever, D.; Azad, A.; Shan, J.; Vainio, S.; Ninov, N.; et al. Wnt4 is heterogeneously activated in maturing β-cells to control calcium signaling, metabolism and function. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefanian, H.; Koti, L.; Sindhu, S.; Ahmad, R.; Al Madhoun, A.; Al-Mulla, F. Verapamil chronicles: Advances from cardiovascular to pancreatic beta-cell protection. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1322148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlenza, G.P.; Schamberger, M.S.; Buckingham, B.A. Verapamil and Pancreatic Beta Cell Function in Pediatric Type 1 Diabetes-Reply. Jama 2023, 330, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.E.; Röjdmark, S. Improvement of glucose tolerance by verapamil in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Acta Medica Scand. 1981, 210, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojdmark, S.; Andersson, D.E. Influence of verapamil on human glucose tolerance. Am. J. Cardiol. 1986, 57, 39D–43D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodneva, Y.; Shalev, A.; Frank, S.J.; Carson, A.P.; Safford, M.M. Calcium channel blocker use is associated with lower fasting serum glucose among adults with diabetes from the REGARDS study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 115, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnovale, C.; Dassano, A.; Mosini, G.; Mazhar, F.; D’Addio, F.; Pozzi, M.; Radice, S.; Fiorina, P.; Clementi, E. The β-cell effect of verapamil-based treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Gaxiola, E.; Messerli, F.H.; Mancia, G.; Erdine, S.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.; Pepine, C.J. Clinical outcomes in the diabetes cohort of the INternational VErapamil SR-Trandolapril study. Hypertension 2004, 44, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Huang, K.C.; Lu, C.W.; Chu, C.H.; Huang, C.N.; Chen, H.S.; Lee, I.T.; Chen, J.F.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, C.S.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial of R-Form Verapamil Added to Ongoing Metformin Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e4063–e4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degroote, L.; Martens, P.-J.; Viaene, M.; Heremans, Y.; Leuckx, G.; Geukens, N.; De Leu, N.; Staels, W.; Mathieu, C.; Gysemans, C. Verapamil and low-dose anti-mouse thymocyte globulin combination therapy stably reverses recent-onset type 1 diabetes in NOD mice by acting on the beta cell and immune axes. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 2263–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, J.I.; Araki, K.; Yamato, E.; Ikegami, H.; Asano, T.; Shibasaki, Y.; Oka, Y.; Yamamura, K.I. Establishment of a Pancreatic β Cell Line That Retains Glucose-Inducible Insulin Secretion: Special Reference to Expression of Glucose Transporter Isoforms*. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Guan, Y.; Yang, J. Cytokines in the Progression of Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 515136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Madhoun, A.; Haddad, D.; Kochumon, S.; Thomas, R.; Miranda, L.; George, P.; Abu-Khalaf, N.; Al-Mulla, F.; Ahmad, R. TNF-α/NF-κB mediated upregulation of Dectin-1 in hyperglycemic obesity: Implications for metabolic inflammation and diabetes. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozarowski, P.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Analysis of Cell Cycle by Flow Cytometry. In Checkpoint Controls and Cancer: Volume 2: Activation and Regulation Protocols; Schönthal, A.H., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 301–311. [Google Scholar]
- Pisharath, H.; Rhee, J.M.; Swanson, M.A.; Leach, S.D.; Parsons, M.J. Targeted ablation of beta cells in the embryonic zebrafish pancreas using E. coli nitroreductase. Mech. Dev. 2007, 124, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. The Zebrafish Book. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio), 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Alvarez-Perez, J.C.; Felsenfeld, D.P.; Liu, H.; Sivendran, S.; Bender, A.; Kumar, A.; Sanchez, R.; Scott, D.K.; Garcia-Ocaña, A.; et al. A high-throughput chemical screen reveals that harmine-mediated inhibition of DYRK1A increases human pancreatic beta cell replication. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, F.; Bouchi, R.; Kim-Muller, J.Y.; Ohmura, Y.; Sandoval, P.R.; Masini, M.; Marselli, L.; Suleiman, M.; Ratner, L.E.; Marchetti, P.; et al. Evidence of β-Cell Dedifferentiation in Human Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, P.; Lozano, P.; Ros, G.; Solano, F. Hyperglycemia and Oxidative Stress: An Integral, Updated and Critical Overview of Their Metabolic Interconnections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharroubi, I.; Ladrière, L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Dogusan, Z.; Cnop, M.; Eizirik, D.L. Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: Role of nuclear factor-kappaB and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5087–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Clark, A.; Rorsman, P. β-cell secretory dysfunction: A key cause of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Chen, J.; Lu, B.; Sethupathy, P.; Qian, W.J.; Shalev, A. Verapamil Prevents Decline of IGF-I in Subjects With Type 1 Diabetes and Promotes beta-Cell IGF-I Signaling. Diabetes 2023, 72, 1460–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnemann, A.K.; Neuman, J.C.; Battiola, T.J.; Wisinski, J.A.; Kimple, M.E.; Davis, D.B. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Regulates Cholecystokinin Production in β-Cells to Protect From Apoptosis. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavine, J.A.; Kibbe, C.R.; Baan, M.; Sirinvaravong, S.; Umhoefer, H.M.; Engler, K.A.; Meske, L.M.; Sacotte, K.A.; Erhardt, D.P.; Davis, D.B. Cholecystokinin expression in the β-cell leads to increased β-cell area in aged mice and protects from streptozotocin-induced diabetes and apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 309, E819–E828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hui, S.T.; Couto, F.M.; Mungrue, I.N.; Davis, D.B.; Attie, A.D.; Lusis, A.J.; Davis, R.A.; Shalev, A. Thioredoxin-interacting protein deficiency induces Akt/Bcl-xL signaling and pancreatic beta-cell mass and protects against diabetes. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 3581–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hamad, S.; Sivan, S.; Shoshan-Barmatz, V. The expression level of the voltage-dependent anion channel controls life and death of the cell. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5787–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, A.; Feige, J.N.; De Marchi, U. Mitochondrial Calcium Signaling in Pancreatic β-Cell. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Hernandez, A.; Verkhratsky, A. Calcium signalling in diabetes. Cell Calcium 2014, 56, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Ren, L.; Andersson, O. Leveraging zebrafish to investigate pancreatic development, regeneration, and diabetes. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 932–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, O.; Adams, B.A.; Yoo, D.; Ellis, G.C.; Gut, P.; Anderson, R.M.; German, M.S.; Stainier, D.Y. Adenosine signaling promotes regeneration of pancreatic β cells in vivo. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolovich-Rain, M.; Hija, A.; Grimsby, J.; Glaser, B.; Dor, Y. Pancreatic Beta Cells in Very Old Mice Retain Capacity for Compensatory Proliferation *. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27407–27414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; York Nathaniel, W.; Nichols Colin, G.; Remedi Maria, S. Pancreatic β Cell Dedifferentiation in Diabetes and Redifferentiation following Insulin Therapy. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollheim, C.B.; Maechler, P. β-Cell Mitochondria and Insulin Secretion: Messenger Role of Nucleotides and Metabolites. Diabetes 2002, 51 (Suppl. S1), S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, B.A.; Li, C.; Soleimanpour, S.A. Mitochondrial regulation of β-cell function: Maintaining the momentum for insulin release. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 42, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowiec, A.M.; Właszczuk, A.; Olakowska, E.; Lewin-Kowalik, J. TXNIP inhibition in the treatment of diabetes. Verapamil as a novel therapeutic modality in diabetic patients. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2022, 95, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismael, S.; Patrick, D.; Salman, M.; Parveen, A.; Stanfill, A.G.; Ishrat, T. Verapamil inhibits TXNIP-NLRP3 inflammasome activation and preserves functional recovery after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 161, 105423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devis, G.; Somers, G.; Van Obberghen, E.; Malaisse, W.J. Calcium antagonists and islet function. I. Inhibition of insulin release by verapamil. Diabetes 1975, 24, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, G.; Devis, G.; Van Obberghen, E.; Malaisse, W.J. Calcium Antagonists and Islet Function. II. Interaction of Theophylline and Verapamil. Endocrinology 1976, 99, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somers, G.; Devis, G.; Malaisse, W.J. Calcium antagonists and islet function. IX. Is extracellular calcium required for insulin release? Acta Diabetol. Lat. 1979, 16, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arefanian, H.; Al-Rashed, F.; Alzaid, F.; Bahman, F.; Abukhalaf, N.; Alsaeed, H.; Kochumon, S.; Williams, M.R.; Kidwai, S.M.; Alhamar, G.; et al. Verapamil Restores β-Cell Mass and Function in Diabetogenic Stress Models via Proliferation and Mitochondrial Respiration. Cells 2025, 14, 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211695
Arefanian H, Al-Rashed F, Alzaid F, Bahman F, Abukhalaf N, Alsaeed H, Kochumon S, Williams MR, Kidwai SM, Alhamar G, et al. Verapamil Restores β-Cell Mass and Function in Diabetogenic Stress Models via Proliferation and Mitochondrial Respiration. Cells. 2025; 14(21):1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211695
Chicago/Turabian StyleArefanian, Hossein, Fatema Al-Rashed, Fawaz Alzaid, Fatemah Bahman, Nermeen Abukhalaf, Halemah Alsaeed, Shihab Kochumon, Michayla R. Williams, Sarah M. Kidwai, Ghadeer Alhamar, and et al. 2025. "Verapamil Restores β-Cell Mass and Function in Diabetogenic Stress Models via Proliferation and Mitochondrial Respiration" Cells 14, no. 21: 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211695
APA StyleArefanian, H., Al-Rashed, F., Alzaid, F., Bahman, F., Abukhalaf, N., Alsaeed, H., Kochumon, S., Williams, M. R., Kidwai, S. M., Alhamar, G., Ahmad, R., Al-Mulla, F., & Al Madhoun, A. (2025). Verapamil Restores β-Cell Mass and Function in Diabetogenic Stress Models via Proliferation and Mitochondrial Respiration. Cells, 14(21), 1695. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14211695








