ZEB1 and Neural Stem Cells: Insights into Microglia-Conditioned Medium-Driven Neuroinflammation
Abstract
Highlights
- ZEB1 knockdown in neural stem cells (NSCs) significantly reduced neurosphere formation, cell migration, reactive oxygen species generation, and cytokine produc-tion under both non-inflammatory conditions and inflammation induced by condi-tioned medium from LPS-activated microglia.
- ZEB1 is a regulator of NSC behavior, modulating their responses to a neuroinflam-matory milieu.
- Targeting ZEB1 may offer a novel therapeutic approach for controlling neuroinflam-mation and preserving neurogenesis in central nervous system disorders.
- Modulation of ZEB1 could help protect NSC function during inflammatory challenges.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. NSC Culture
2.2. Primary Microglia Culture
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Apoptosis Assay Using Flow Cytometry
2.5. Transfection of ZEB1 siRNA
2.6. ICC Assay
2.7. Colony Formation Assay
2.8. Wound Healing Assay
2.9. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) Assessment
2.10. ROS Assessment
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
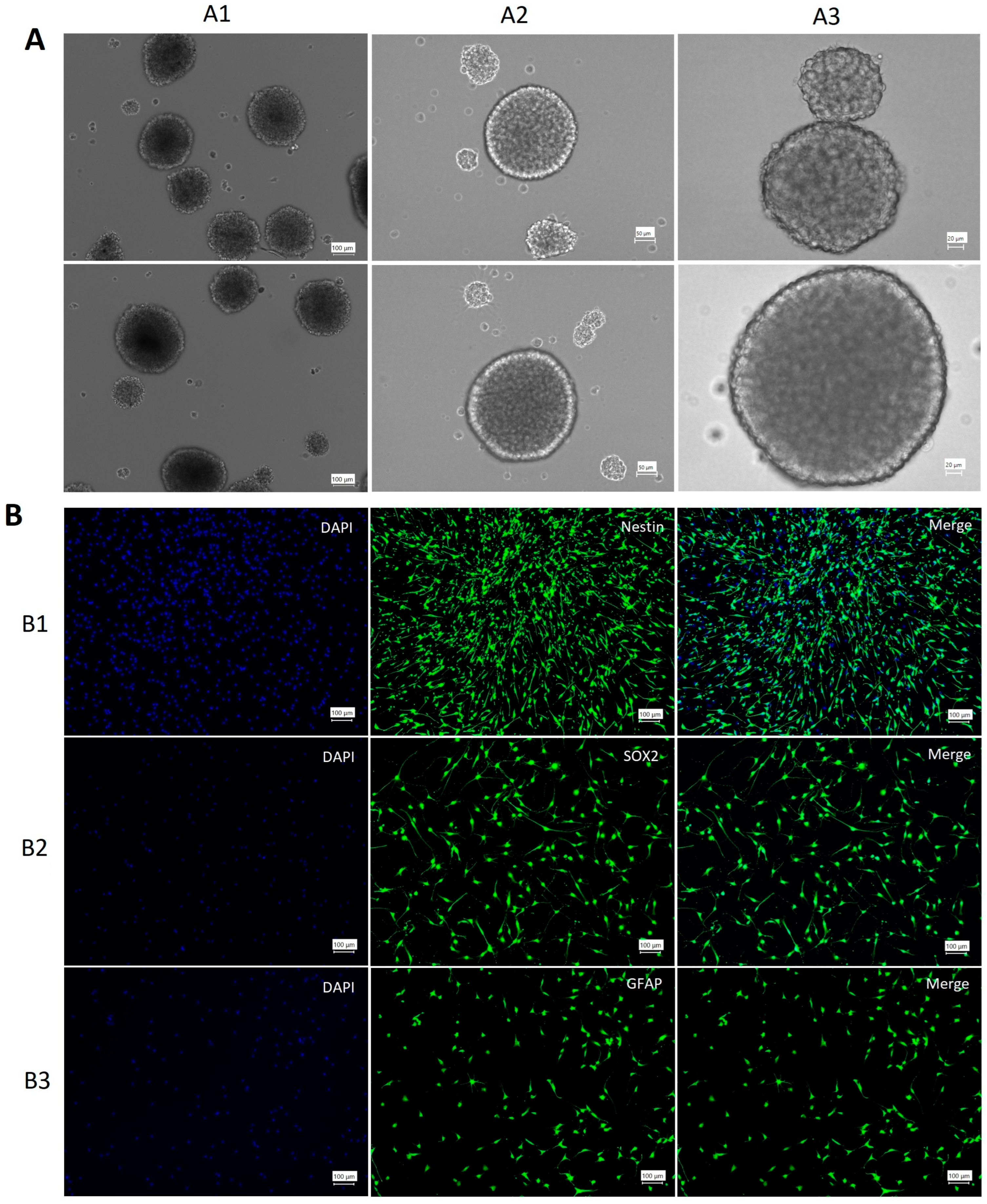
3.1. NSCs Characterization
3.2. Microglial Activation and NSC Inflammatory Response
3.3. Evaluation of ZEB1 Expression in NSCs
3.4. Modulatory Effect of ZEB1 on NSC Colony Formation
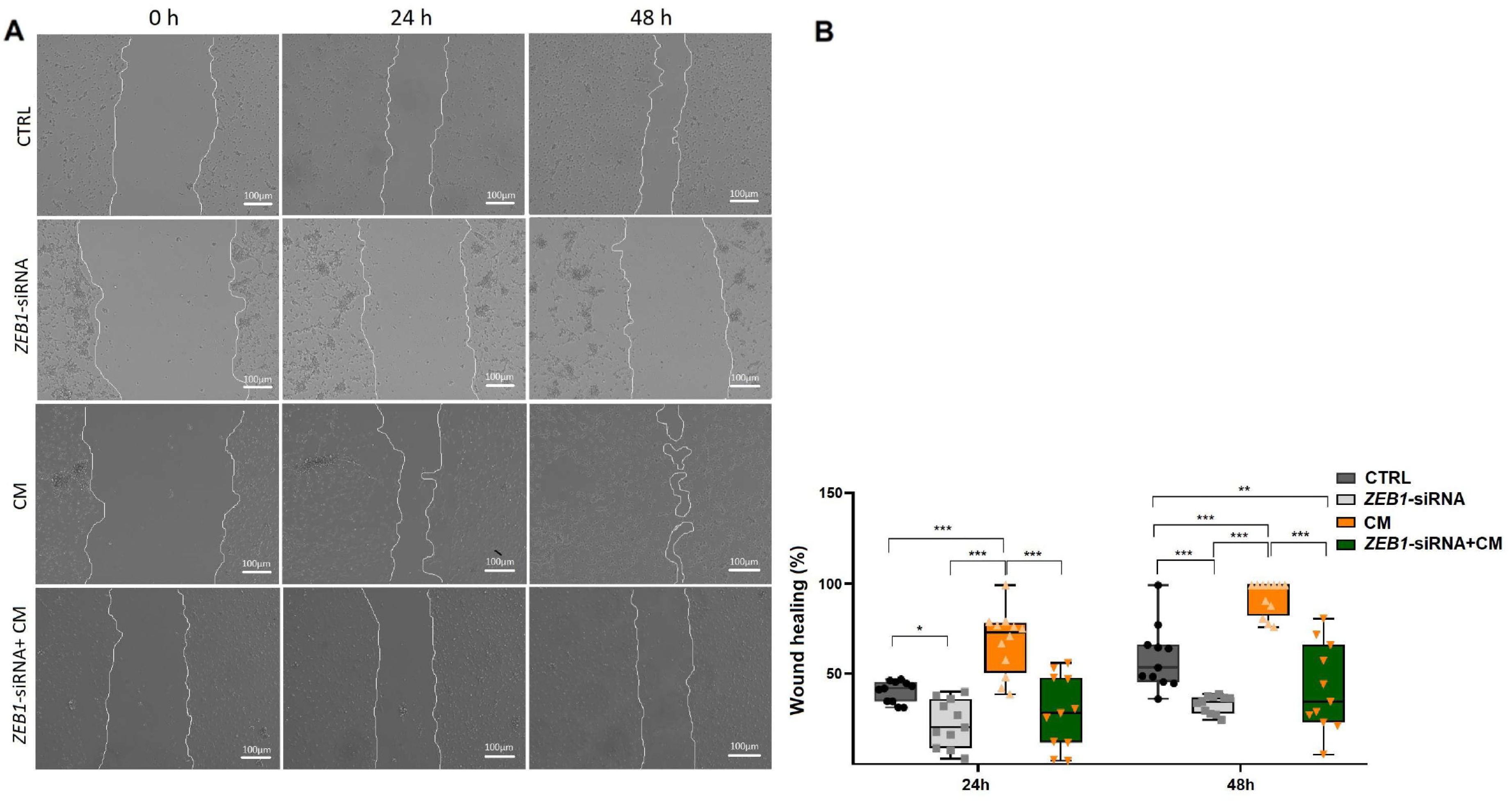
3.5. The Impact of ZEB1 on NSC Migration
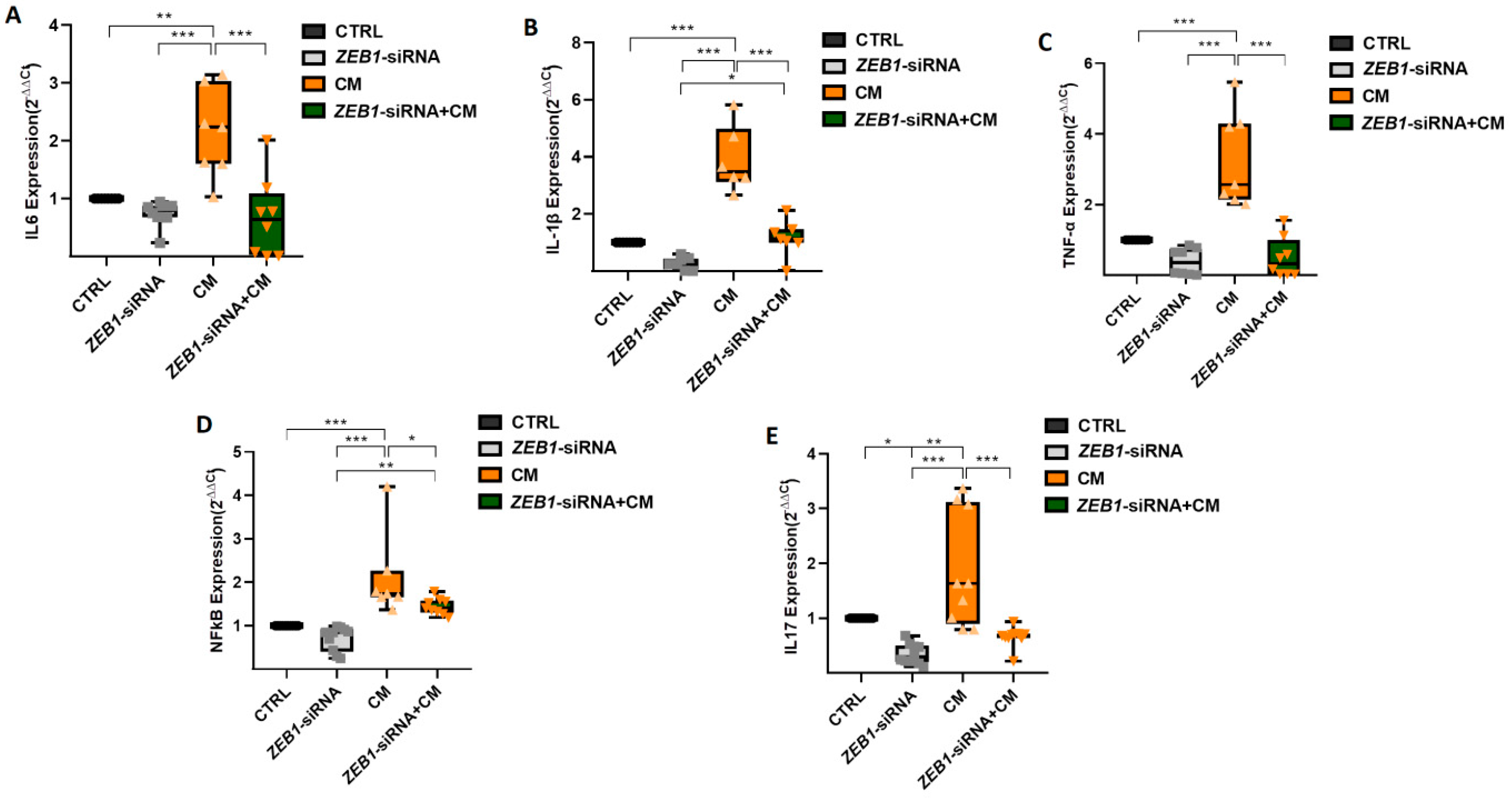
3.6. The Impact of ZEB1 on Cytokine Levels
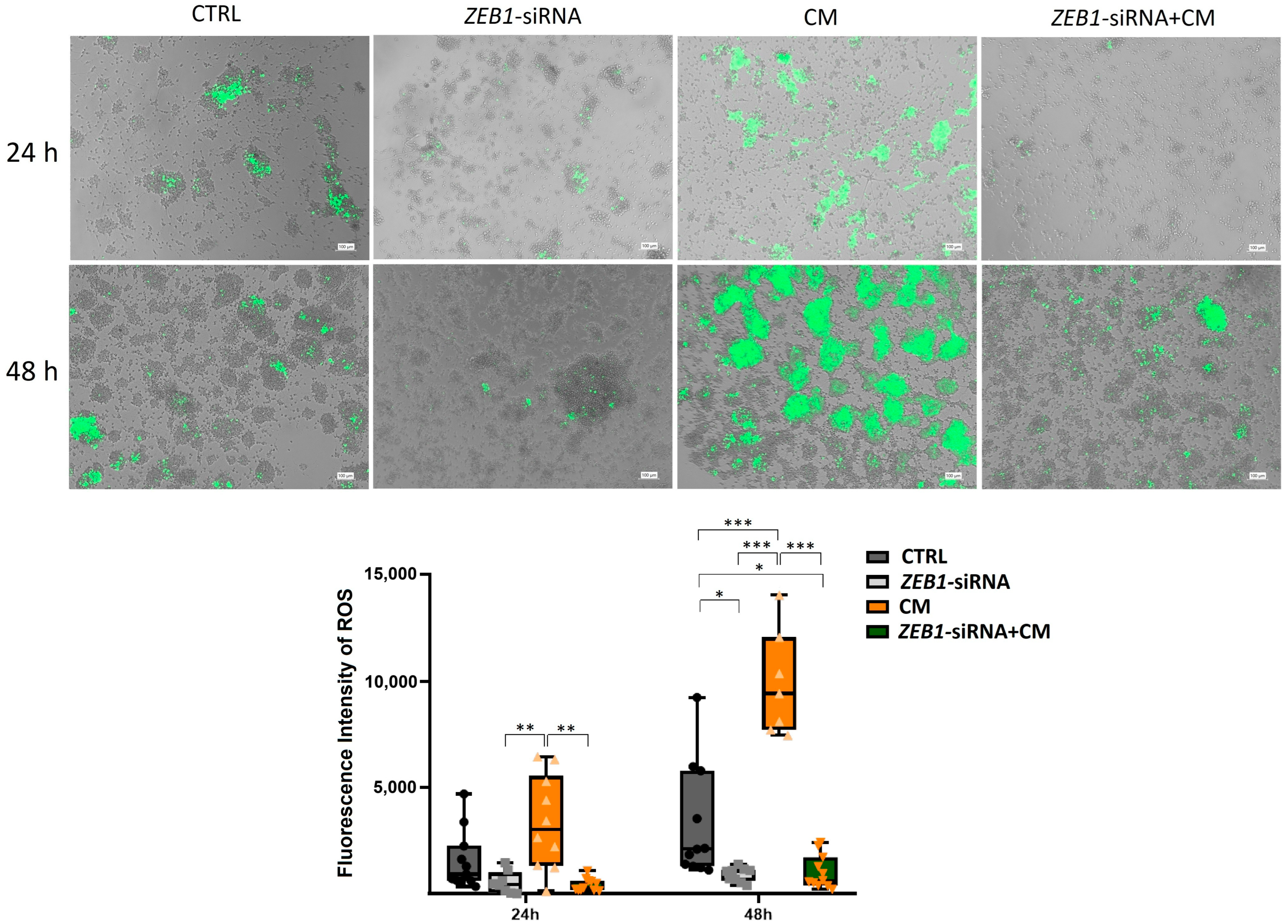
3.7. The Impact of ZEB1 on ROS
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Göbel, K.; Ruck, T.; Meuth, S.G. Cytokine signaling in multiple sclerosis: Lost in translation. Mult. Scler. J. 2018, 24, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a common feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, A. Neuroinflammation: The pathogenic mechanism of neurological disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, C.T.; Claasen, J.H.; Bonde, S.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in the adult brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13632–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakol-Afshari, J.; Boroumand, A.R.; Farkhad, N.K.; Moghadam, A.A.; Sahab-Negah, S.; Gorji, A. Safety and efficacy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L. Neural stem cells promote neuroplasticity: A promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaquian, D.; Delgado Ocaña, S.; Perez, C.; Banchio, C. Phosphatidylcholine restores neuronal plasticity of neural stem cells under inflammatory stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.A.B.; Lakshman, N.; Lau, K.S.K.; Morshead, C.M. Regulating endogenous neural stem cell activation to promote spinal cord injury repair. Cells 2022, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Lian, D.; Wu, J.; He, D.; Sun, K.; Li, L. Regulation of the p75 neurotrophin receptor attenuates neuroinflammation and stimulates hippocampal neurogenesis in experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae meningitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daviaud, N.; Garbayo, E.; Sindji, L.; Martínez-Serrano, A.; Schiller, P.C.; Montero-Menei, C.N. Survival, differentiation, and neuroprotective mechanisms of human stem cells complexed with neurotrophin-3-releasing pharmacologically active microcarriers in an ex vivo model of Parkinson’s disease. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottoboni, L.; von Wunster, B.; Martino, G. Therapeutic plasticity of neural stem cells. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamri, M.S.; McClellan, B.L.; Hartlage, M.S.; Haase, S.; Faisal, S.M.; Thalla, R.; Dabaja, A.; Banerjee, K.; Carney, S.V.; Mujeeb, A.A.; et al. Targeting neuroinflammation in brain cancer: Uncovering mechanisms, pharmacological targets, and neuropharmaceutical developments. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, S.W.; Jeon, H.Y.; Jin, X.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.K.; Shin, Y.J.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Seo, S.; et al. TP53 gain-of-function mutation promotes inflammation in glioblastoma. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonaki, E.; Kahlert, U.D.; Meuth, S.G.; Gorji, A. The role of the ZEB1–neuroinflammation axis in CNS disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yan, L.; Xia, L.; Lu, X.; Zhu, W.; Ding, D.; Du, M.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Hu, B. Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) is required for neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 19317–19329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, X.L.; Yang, X.; Shen, Q. ZEB1 represses neural differentiation and cooperates with CTBP2 to dynamically regulate cell migration during neocortex development. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2335–2353.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonaki, E.; Ariakia, F.; Jalili-Nik, M.; Shafiee Ardestani, M.; Tondro, G.; Samini, F.; Ghasemi, S.; Sahab-Negah, S.; Gorji, A. Targeting BMI-1 with PLGA–PEG nanoparticle-containing PTC209 modulates the behavior of human glioblastoma stem cells and cancer cells. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, A.; Han, X. The roles of ZEB1 in tumorigenic progression and epigenetic modifications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barrios, O.; Sanchez-Moral, L.; Cortés, M.; Ninfali, C.; Profitós-Pelejà, N.; Martínez-Campanario, M.C.; Siles, L.; Del Campo, R.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J.; Darling, D.S.; et al. ZEB1 promotes inflammation and progression towards inflammation-driven carcinoma through repression of the DNA repair glycosylase MPG in epithelial cells. Gut 2019, 68, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ismaeel, Q.; Neal, C.P.; Al-Mahmoodi, H.; Almutairi, Z.; Al-Shamarti, I.; Straatman, K.; Jaunbocus, N.; Irvine, A.; Issa, E.; Moreman, C.; et al. ZEB1 and IL-6/11-STAT3 signalling cooperate to define invasive potential of pancreatic cancer cells via differential regulation of the expression of S100 proteins. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Z. MicroRNA-128-3p alleviates neuropathic pain through targeting ZEB1. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 729, 134946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiernan, E.A.; Bata, A.; Gerstein, R.M.; Schafer, D.P. Mechanisms of microglial activation in models of inflammation and hypoxia: Implications for chronic intermittent hypoxia. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, R.; Wang, L.; He, Y.; Yue, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; Lei, X. Dermal fibroblast migration and proliferation upon wounding or lipopolysaccharide exposure is mediated by stathmin. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 781282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Shen, H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. Minocycline inhibited the pro-apoptotic effect of microglia on neural progenitor cells and protected their neuronal differentiation in vitro. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 542, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, M.T.; Saso, L.; Farina, M. LPS-activated microglial cell-derived conditioned medium protects HT22 neuronal cells against glutamate-induced ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöberl, N.; Maguire, E.; Salis, E.; Shaw, B.; Hall-Roberts, H. Human iPSC-derived glia models for the study of neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodburn, S.C.; Bollinger, J.L.; Wohleb, E.S. The semantics of microglia activation: Neuroinflammation, homeostasis, and stress. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lois, C.; Alvarez-Buylla, A. Long-distance neuronal migration in the adult mammalian brain. Science 1994, 264, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Campbell, L.; Zheng, B.; Fan, L.; Cai, Z.; Rhodes, P. Lipopolysaccharide-activated microglia induce death of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and impede their development. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, J.; Swan, P.; Shaikh, R.; Cregan, S.P. Microglia-derived IL-1β triggers p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in neural precursor cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagno, J.; Xu, X.; Karajgikar, M.; Brown, A.; Cregan, S.P. Microglia-derived TNFα induces apoptosis in neural precursor cells via transcriptional activation of the Bcl-2 family member Puma. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, V.W.; Mazucanti, C.H.; de Sá Lima, L.; de Mello, P.S.; de Souza Port’s, N.M.; Kinoshita, P.F.; Leite, J.A.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Scavone, C. Neuroprotective action of α-Klotho against LPS-activated glia conditioned medium in primary neuronal culture. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Deng, P.; Li, L.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Hao, D.; Yang, H. Advances in genetically modified neural stem cell therapy for central nervous system injury and neurological diseases. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawbeh, A.; Gondcaille, C.; Saih, F.E.; Raas, Q.; Loichot, D.; Hamon, Y.; Keime, C.; Benani, A.; Di Cara, F.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M.; et al. Impaired peroxisomal beta-oxidation in microglia triggers oxidative stress and impacts neurons and oligodendrocytes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2025, 18, 1542938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Wei, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. Neuroprotective effects of natural compounds on LPS-induced inflammatory responses in microglia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, Z. Cyclooxygenase-2 contributes to the hypoxia-induced aggravation of the neuroinflammation response stimulated by lipopolysaccharide in microglia. Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyarce, M.P.; Iturriaga, R. Contribution of oxidative stress and inflammation to the neurogenic hypertension induced by intermittent hypoxia. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evilsizor, M.N.; Park, J.S.; Hermann, B.P.; Scimemi, A. Microglia in experimental brain injury: Implications on neuronal injury and circuit remodeling. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 317. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Siebzehnrubl, F.A.; Martinez-Garay, I. Transcriptional control of embryonic and adult neural progenitor activity. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1217596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Errington, A.C.; Jimenez-Pascual, A.; Eftychidis, V.; Brabletz, S.; Stemmler, M.P.; Brabletz, T.; Petrik, D.; Siebzehnrubl, F.A. The transcription factor ZEB1 regulates stem cell self-renewal and cell fate in the adult hippocampus. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.M.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Trang, H.T.; Kim, Y.M.; Cho, Y.H.; Park, D.; Hong, S. Smad3 regulates E-cadherin via miRNA-200 pathway. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3051–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Pappan, L.; Galliher-Beckley, A.; Shi, J. IL-1β promotes stemness and invasiveness of colon cancer cells through ZEB1 activation. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial–mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Arellano, G.; Ifergan, I.; Lin, J.; Snowden, C.; Kim, T.; Thomas, J.J.; Law, C.; Guan, T.; Balabanov, R.D.; et al. ZEB1 promotes pathogenic Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation in multiple sclerosis. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lu, X.; Finn, M.E.; Wang, W.; Shao, H.; Dean, D.C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. ZEB1 regulation of wound-healing-induced inflammation in alkali-damaged corneas. iScience 2022, 25, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, K.K.; Wang, F.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, W.; Liu, J.Y.; Jiang, D.Y.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; et al. Conditional deletion of Zeb1 in Csf1r⁺ cells reduces inflammatory response of the cornea to alkali burn. iScience 2024, 27, 108460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.T.; Schafer, S.T.; Gage, F.H. Adult neurogenesis in the hippocampus: From stem cells to behavior. Cell 2016, 167, 897–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-Y.; Chi, C.-Y.; Zheng, C.-W.; Wang, C.-H.; Chiu, I.-M. Coordinated Actions of Neurogenesis and Gliogenesis in Nerve Injury Repair and Neuroregeneration. Int. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 4, 810–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, Y.; Qin, L.; Shen, H.; Xie, Y.; Xia, W.; Gao, W.Q. Zeb1 is important for proper cleavage plane orientation of dividing progenitors and neuronal migration in the mouse neocortex. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2479–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Howell, D.; Trivedi, N.; Kessler, K.; Ong, T.; Rosmaninho, P.; Raposo, A.A.; Robinson, G.; Roussel, M.F.; Castro, D.S.; et al. Zeb1 controls neuron differentiation and germinal zone exit by a mesenchymal-epithelial-like transition. eLife 2016, 5, e12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Moinuddin; Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S.; et al. Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carelli, S.; Rey, F.; Maghraby, E.; Cereda, C. Insights on ZEB1-AS1: Emerging roles from cancer to neurodegeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 1187–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; Lan, J.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium inhibits microglial activation to ameliorate neuroinflammation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice and cell models. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 202, 110760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.T.; Lu, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J. XIST accelerates neuropathic pain progression through regulation of miR-150 and ZEB1 in CCI rat models. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6098–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Stream | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ZEB1 | Forward | GCCCATCGAGCTTCCTGTAA |
| Reverse | TGGAAACATGGCTCCTGTGC | |
| IL-1β | Forward | GGGTGGTTCAAGGCATAACA |
| Reverse | GTCGAGATGCTGCTGTGAGA | |
| IL6 | Forward | TCCTACCCCAACTTCCAATGCTC |
| Reverse | TTGGATGGTCTTGGTCCTTAGCC | |
| IL17 | Forward | GGGAAGTTGGACCACCACAT |
| Reverse | CGCCTTCTTTTCAGGGTGGA | |
| NFkB | Forward | ACACAGGACCAGGGACAG |
| Reverse | AGGGGTTGTTGTTGGTCTGG | |
| TNF-α | Forward | AAATGGGCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTC |
| Reverse | TCTGCTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poonaki, E.; Kahlert, U.D.; Stummer, W.; Meuth, S.G.; Gorji, A. ZEB1 and Neural Stem Cells: Insights into Microglia-Conditioned Medium-Driven Neuroinflammation. Cells 2025, 14, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201587
Poonaki E, Kahlert UD, Stummer W, Meuth SG, Gorji A. ZEB1 and Neural Stem Cells: Insights into Microglia-Conditioned Medium-Driven Neuroinflammation. Cells. 2025; 14(20):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201587
Chicago/Turabian StylePoonaki, Elham, Ulf Dietrich Kahlert, Walter Stummer, Sven G. Meuth, and Ali Gorji. 2025. "ZEB1 and Neural Stem Cells: Insights into Microglia-Conditioned Medium-Driven Neuroinflammation" Cells 14, no. 20: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201587
APA StylePoonaki, E., Kahlert, U. D., Stummer, W., Meuth, S. G., & Gorji, A. (2025). ZEB1 and Neural Stem Cells: Insights into Microglia-Conditioned Medium-Driven Neuroinflammation. Cells, 14(20), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14201587









