Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
2.2. Inhibitors
2.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
2.4. RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Viability and Apoptosis Assays
2.6. Colony-Forming Cell (CFC) and Re-Plating Assay
2.7. Long-Term Culture-Initiating Cell (LTC-IC) Assay
2.8. Lentiviral-Mediated SMO shRNA Knockdown in CD34+ CML Patient Samples
2.9. Xenotransplantation Experiments Using PDX Models
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HH-Associated Genes, SMO and GLI2, Are Highly Elevated in CD34+ CML Cells, Particularly in IM-Nonresponders
3.2. A Selective SMO Inhibitor, Glasdegib, Is More Effective at Targeting CD34+ CML Cells from IM-Nonresponders In Vitro
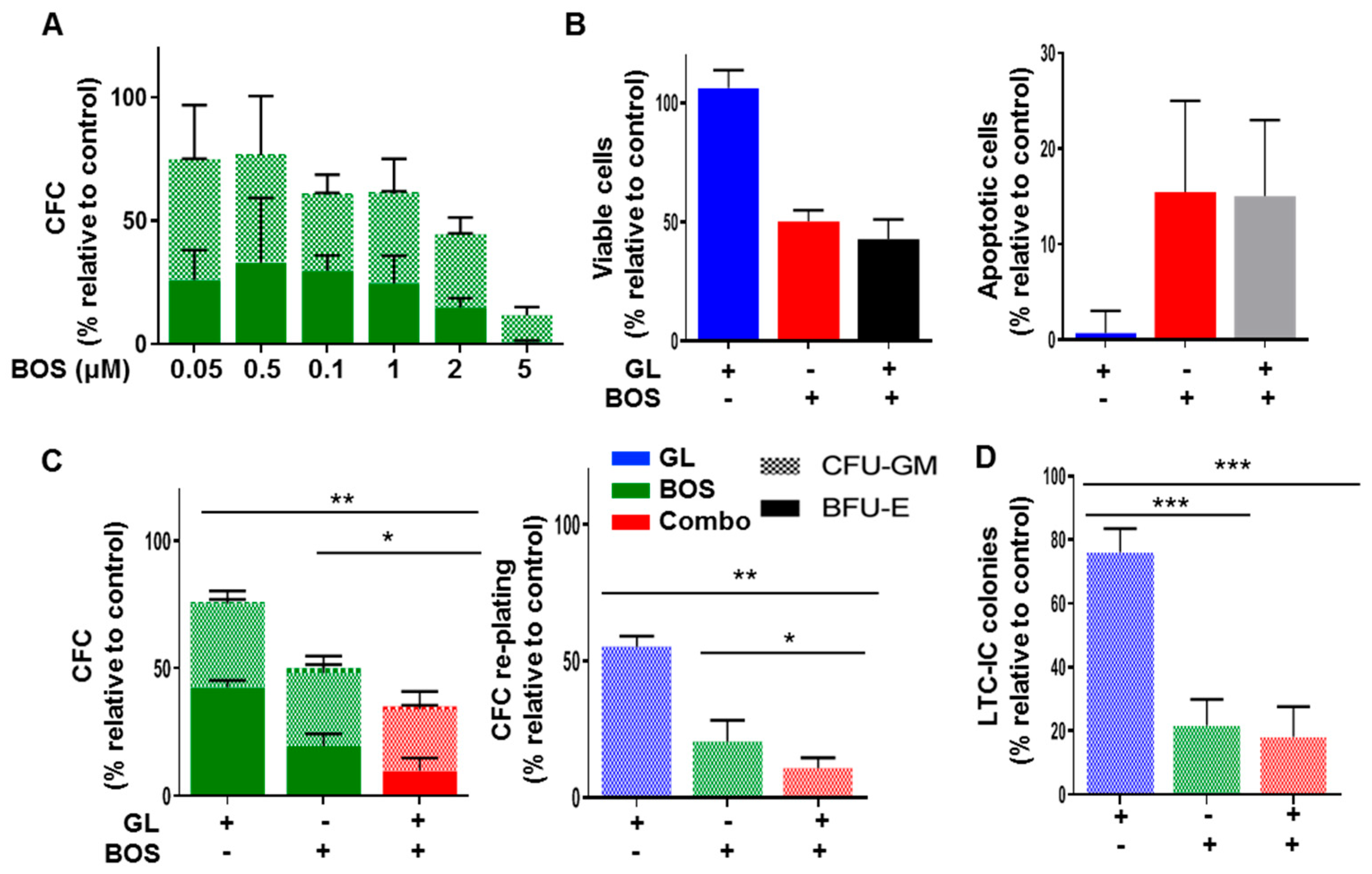
3.3. Dual Inhibition of SMO and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Inhibits Proliferation and Long-Term Clonogenic Activities of CML Stem/Progenitor Cells In Vitro
3.4. Glasdegib Treatment Results in the Decreased Expression of GLI2 Selectively in Stem Cell-Enriched CML Cells
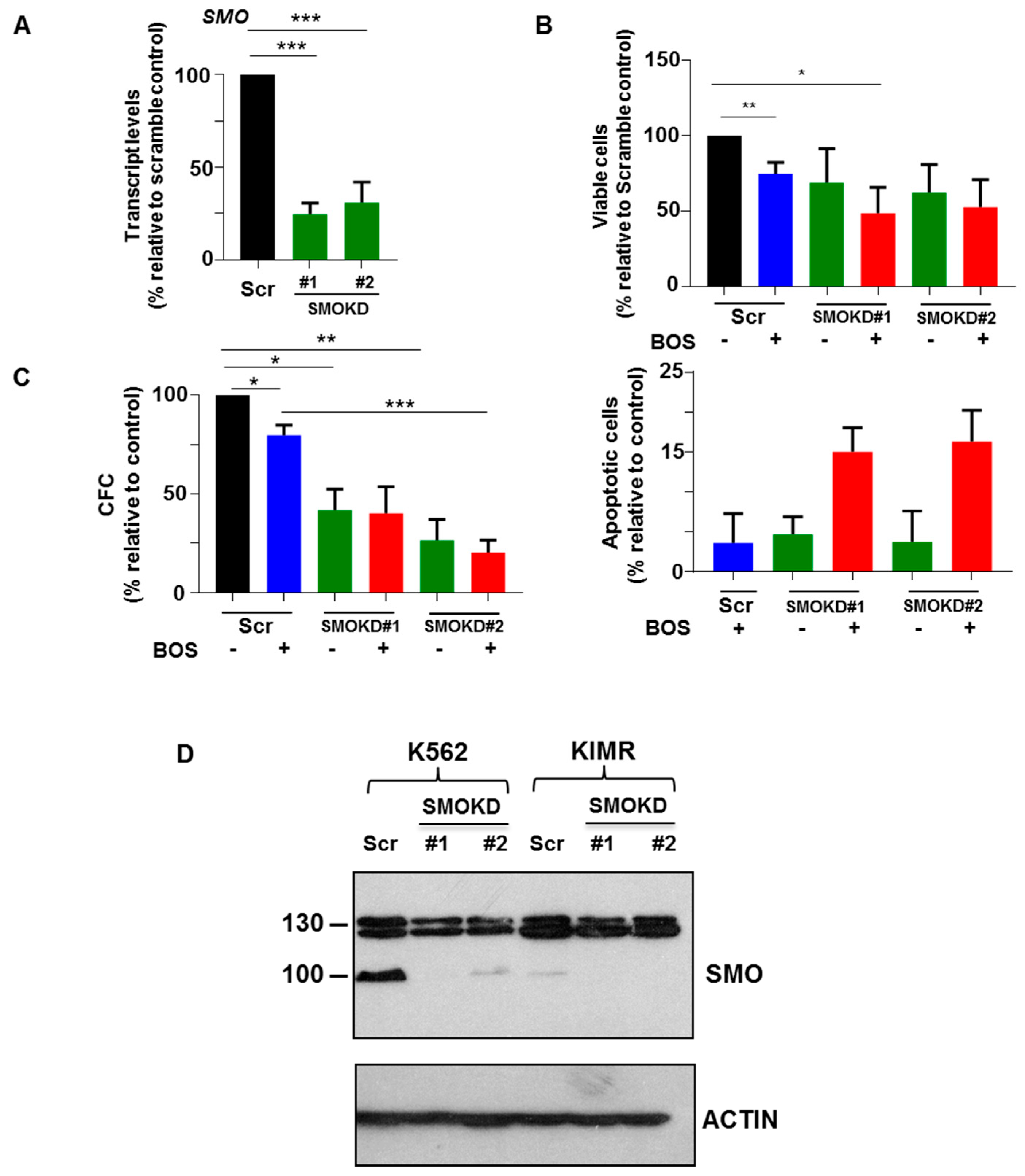
3.5. Knockdown of SMO in CD34+ CML Stem/Progenitor Cells Sensitizes Their Responses to BOS
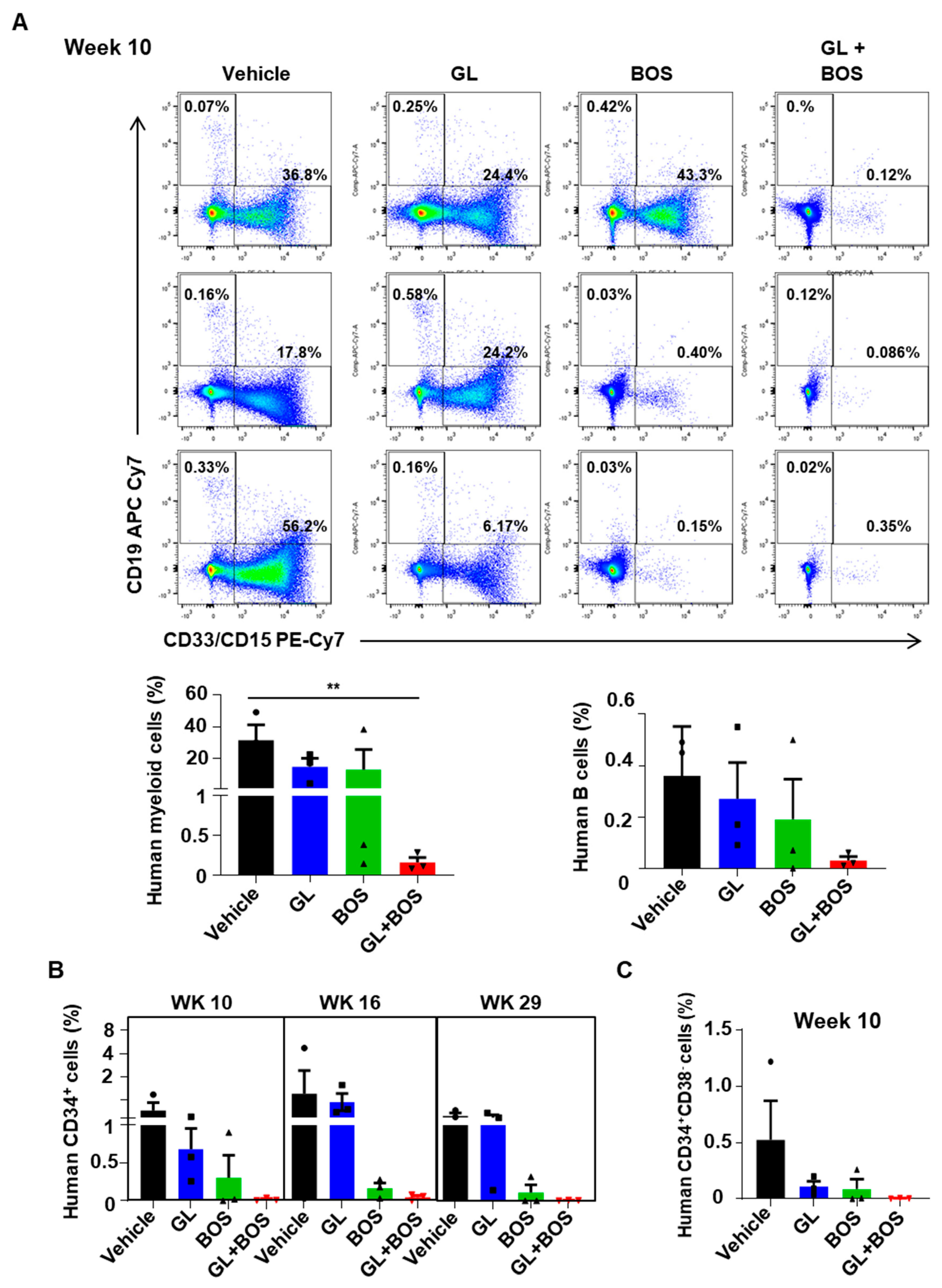
3.6. Dual Inhibition of SMO and BCR-ABL1 in CD34+ Stem/Progenitor Cells Resulted in Reduced Engraftment of Leukemic Cells in a Patient-Derived Xenotransplantation (PDX) Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowley, J.D. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature 1973, 243, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyers, C.L. Chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druker, B.J.; Tamura, S.; Buchdunger, E.; Ohno, S.; Segal, G.M.; Fanning, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Lydon, N.B. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druker, B.J.; Guilhot, F.; O'Brien, S.G.; Gathmann, I.; Kantarjian, H.; Gattermann, N.; Deininger, M.W.; Silver, R.T.; Goldman, J.M.; Stone, R.M.; et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Larson, R.A.; Guilhot, F.; Radich, J.P.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Cervantes, F.; Fujihara, S.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.P.; Eide, C.A.; Druker, B.J. Response and Resistance to BCR-ABL1-Targeted Therapies. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpaz, M.; Silver, R.T.; Druker, B.J.; Goldman, J.M.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Guilhot, F.; Schiffer, C.A.; Fischer, T.; Deininger, M.W.; Lennard, A.L.; et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2002, 99, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyers, C.L.; Hochhaus, A.; Feldman, E.; Goldman, J.M.; Miller, C.B.; Ottmann, O.G.; Schiffer, C.A.; Talpaz, M.; Guilhot, F.; Deininger, M.W.; et al. Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in myeloid blast crisis: Results of a phase II study. Blood 2002, 99, 3530–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Liu, X.; Fruhstorfer, C.; Jiang, X. Clinical Insights into Structure, Regulation, and Targeting of ABL Kinases in Human Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorre, M.E.; Mohammed, M.; Ellwood, K.; Hsu, N.; Paquette, R.; Rao, P.N.; Sawyers, C.L. Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 2001, 293, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Giannoudis, A.; Lane, S.; Williamson, P.; Pirmohamed, M.; Clark, R.E. Expression of the uptake drug transporter hOCT1 is an important clinical determinant of the response to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 83, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierks, C.; Beigi, R.; Guo, G.R.; Zirlik, K.; Stegert, M.R.; Manley, P.; Trussell, C.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Landwerlin, K.; Veelken, H.; et al. Expansion of Bcr-Abl-positive leukemic stem cells is dependent on Hedgehog pathway activation. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, A.; Jamieson, C.H.; Fereshteh, M.; Abrahamsson, A.; Blum, J.; Kwon, H.Y.; Kim, J.; Chute, J.P.; Rizzieri, D.; et al. Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2009, 458, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, K.; Babaian, A.; Nakamichi, N.; Chen, M.; Chafe, S.C.; Watanabe, A.; Forrest, D.L.; Mager, D.L.; Eaves, C.J.; Dedhar, S.; et al. Integrin-Linked Kinase Mediates Therapeutic Resistance of Quiescent CML Stem Cells to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cell Stem. Cell 2020, 27, 110–124.e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, A.S.; Agarwal, A.; Loriaux, M.; Cortes, J.; Deininger, M.W.; Druker, B.J. Human chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are insensitive to imatinib despite inhibition of BCR-ABL activity. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.; Helgason, G.V.; Schemionek, M.; Zhang, B.; Myssina, S.; Allan, E.K.; Nicolini, F.E.; Muller-Tidow, C.; Bhatia, R.; Brunton, V.G.; et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells are not dependent on Bcr-Abl kinase activity for their survival. Blood 2012, 119, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, R.; Joyner, A.L. Roles for Hedgehog signaling in adult organ homeostasis and repair. Development 2014, 141, 3445–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, E.; Belloni, E.; Gaudenz, K.; Jay, P.; Berta, P.; Scherer, S.W.; Tsui, L.C.; Muenke, M. Mutations in the human Sonic Hedgehog gene cause holoprosencephaly. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, S.P.; di Magliano, M.P.; Heiser, P.W.; Nielsen, C.M.; Roberts, D.J.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Qi, Y.P.; Gysin, S.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Yajnik, V.; et al. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 2003, 425, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Nakamura, M.; Tasaki, A.; Yamanaka, N.; Nakashima, H.; Nomura, M.; Kuroki, S.; Katano, M. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a new therapeutic target for patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6071–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellbrock, J.; Latuske, E.; Kohler, J.; Wagner, K.; Stamm, H.; Vettorazzi, E.; Vohwinkel, G.; Klokow, M.; Uibeleisen, R.; Ehm, P.; et al. Expression of Hedgehog Pathway Mediator GLI Represents a Negative Prognostic Marker in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Inhibition Exerts Antileukemic Effects. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2388–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Turner, K.A.; Woolfson, A.; Jiang, X. The Hedgehog Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyaz, M.; Khan, M.S.; Mudassar, S. Hedgehog Signaling: An Achilles' Heel in Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Matsui, W. Hedgehog pathway as a drug target: Smoothened inhibitors in development. OncoTargets Ther. 2012, 5, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munchhof, M.J.; Li, Q.; Shavnya, A.; Borzillo, G.V.; Boyden, T.L.; Jones, C.S.; LaGreca, S.D.; Martinez-Alsina, L.; Patel, N.; Pelletier, K.; et al. Discovery of PF-04449913, a Potent and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of Smoothened. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolska-Washer, A.; Robak, T. Glasdegib in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 3219–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, N.; Minami, Y.; Kakiuchi, S.; Kuwatsuka, Y.; Hayakawa, F.; Jamieson, C.; Kiyoi, H.; Naoe, T. Small-molecule Hedgehog inhibitor attenuates the leukemia-initiation potential of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1422–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Baccarani, M.; Silver, R.T.; Schiffer, C.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Deininger, M.W.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2020, 34, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Rothe, K.; Chen, M.; Wu, A.; Babaian, A.; Yen, R.; Zeng, J.; Ruschmann, J.; Petriv, O.I.; O’Neill, K.; et al. The miR-185/PAK6 axis predicts therapy response and regulates survival of drug-resistant leukemic stem cells in CML. Blood 2020, 136, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogge, D.E.; Lansdorp, P.M.; Reid, D.; Gerhard, B.; Eaves, C.J. Enhanced detection, maintenance, and differentiation of primitive human hematopoietic cells in cultures containing murine fibroblasts engineered to produce human steel factor, interleukin-3, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 1996, 88, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Chen, M.; Phoa, A.; Yang, Z.; Forrest, D.L.; Jiang, X. Identification of a PAK6-Mediated MDM2/p21 Axis That Modulates Survival and Cell Cycle Control of Drug-Resistant Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, J.; Therond, P.P. The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahon, F.X.; Rea, D.; Guilhot, J.; Guilhot, F.; Huguet, F.; Nicolini, F.E.; Rousselot, P. Discontinuation of imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who have maintained complete molecular response: Update results of the STIM study. Blood 2011, 118, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; McDonald, T.; Lin, A.; Chakraborty, S.; Huang, Q.; Snyder, D.S.; Bhatia, R. Persistence of leukemia stem cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients in prolonged remission with imatinib treatment. Blood 2011, 118, 5565–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadarangani, A.; Pineda, G.; Lennon, K.M.; Chun, H.J.; Shih, A.; Schairer, A.E.; Court, A.C.; Goff, D.J.; Prashad, S.L.; Geron, I.; et al. GLI2 inhibition abrogates human leukemia stem cell dormancy. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha; Dalal, H.; Subramanian, S.; V, P.S.; Gowda, D.A.; H, K.; Damodar, S.; Vyas, N. Exovesicular-Shh confers Imatinib resistance by upregulating Bcl2 expression in chronic myeloid leukemia with variant chromosomes. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahreddine, H.A.; Culjkovic-Kraljacic, B.; Assouline, S.; Gendron, P.; Romeo, A.A.; Morris, S.J.; Cormack, G.; Jaquith, J.B.; Cerchietti, L.; Cocolakis, E.; et al. The sonic hedgehog factor GLI1 imparts drug resistance through inducible glucuronidation. Nature 2014, 511, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainez-Gonzalez, D.; Serrano-Lopez, J.; Alonso-Dominguez, J.M. Understanding the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells: A Necessary Step toward a Cure. Biology 2021, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicurella, M.; De Chiara, M.; Neri, L.M. Hedgehog and PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathways Involvement in Leukemic Malignancies: Crosstalk and Role in Cell Death. Cells 2025, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, R.; Grasedieck, S.; Wu, A.; Lin, H.; Su, J.; Rothe, K.; Nakamoto, H.; Forrest, D.L.; Eaves, C.J.; Jiang, X. Identification of key microRNAs as predictive biomarkers of Nilotinib response in chronic myeloid leukemia: A sub-analysis of the ENESTxtnd clinical trial. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2443–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Yen, R.; Grasedieck, S.; Lin, H.; Nakamoto, H.; Forrest, D.L.; Eaves, C.J.; Jiang, X. Identification of multivariable microRNA and clinical biomarker panels to predict imatinib response in chronic myeloid leukemia at diagnosis. Leukemia 2023, 37, 2426–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, D.A.; Zhang, B.; Kinstrie, R.; Tarafdar, A.; Morrison, H.; Campbell, V.L.; Moka, H.A.; Ho, Y.; Nixon, C.; Manley, P.W.; et al. Deregulated hedgehog pathway signaling is inhibited by the smoothened antagonist LDE225 (Sonidegib) in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukaemia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.; Cho, J. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors as Targeted Cancer Therapy and Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Dick, J.E. Cancer stem cells: Lessons from leukemia. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreso, A.; Dick, J.E. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem. Cell 2014, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, G.; Oehler, V.G.; Papayannidis, C.; Courtney, R.; Shaik, M.N.; Zhang, X.; O'Connell, A.; McLachlan, K.R.; Zheng, X.; Radich, J.; et al. Treatment with PF-04449913, an oral smoothened antagonist, in patients with myeloid malignancies: A phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetics study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e339–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.; Matsui, W. Hedgehog Signaling in Myeloid Malignancies. Cancers 2021, 13, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.P.; Cortes, J.E.; Martinelli, G.; Smith, B.D.; Clarke, E.; Copland, M.; Talpaz, M. Dasatinib Plus Smoothened(SMO) Inhibitor BMA_833923 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) with Resistance or Suboptimal Response to a Prior Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI): Phase I Study CA180323. In Proceedings of the ASH, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 December 2014; p. 4539. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turner, K.A.; Chen, M.; Rothe, K.; Forrest, D.L.; Jiang, X. Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cells 2025, 14, 1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191565
Turner KA, Chen M, Rothe K, Forrest DL, Jiang X. Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cells. 2025; 14(19):1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191565
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurner, Kelly A., Min Chen, Katharina Rothe, Donna L. Forrest, and Xiaoyan Jiang. 2025. "Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" Cells 14, no. 19: 1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191565
APA StyleTurner, K. A., Chen, M., Rothe, K., Forrest, D. L., & Jiang, X. (2025). Dual Targeting of Smoothened, a Key Regulator in the Hedgehog Pathway, and BCR-ABL1 Effectively Eradicates Drug-Insensitive Stem/Progenitor Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cells, 14(19), 1565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191565






