Bifidobacterium longum P77 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P72 and Their Mix—Live or Heat-Treated—Mitigate Sleeplessness and Depression in Mice: Involvement of Serotonergic and GABAergic Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture of B. longum P77 and L. plantarum P72
2.2. Culture of the SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cell Line
2.3. Animals
2.4. Preparation of Mice with Depression/Anxiety and Sleeplessness and Treatment with Test Agents
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.6. Whole Genome Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
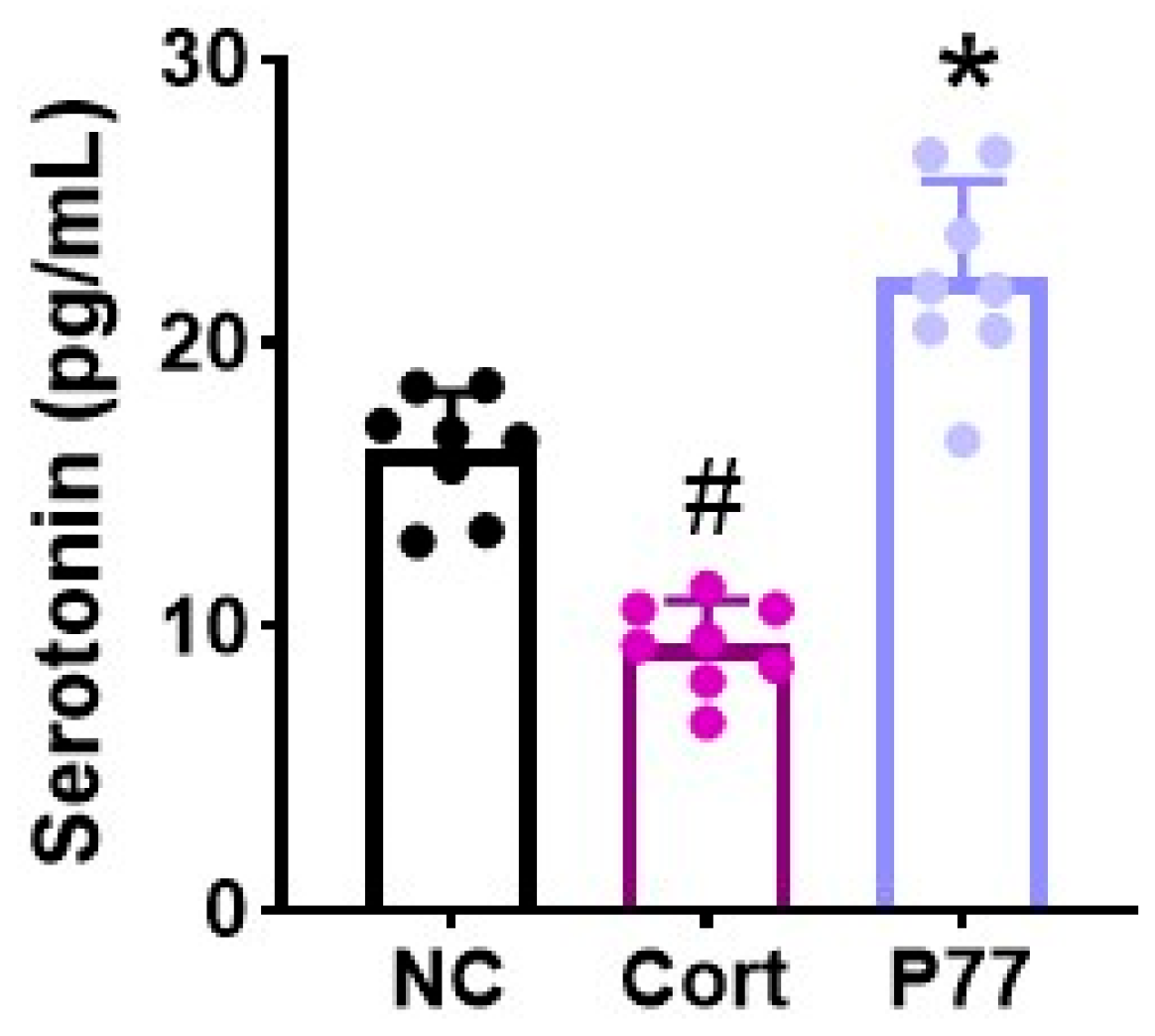
3.1. B. longum P77 Induced the Release of Serotonin in Corticosterone-Exposed SH-SY5Y Cells
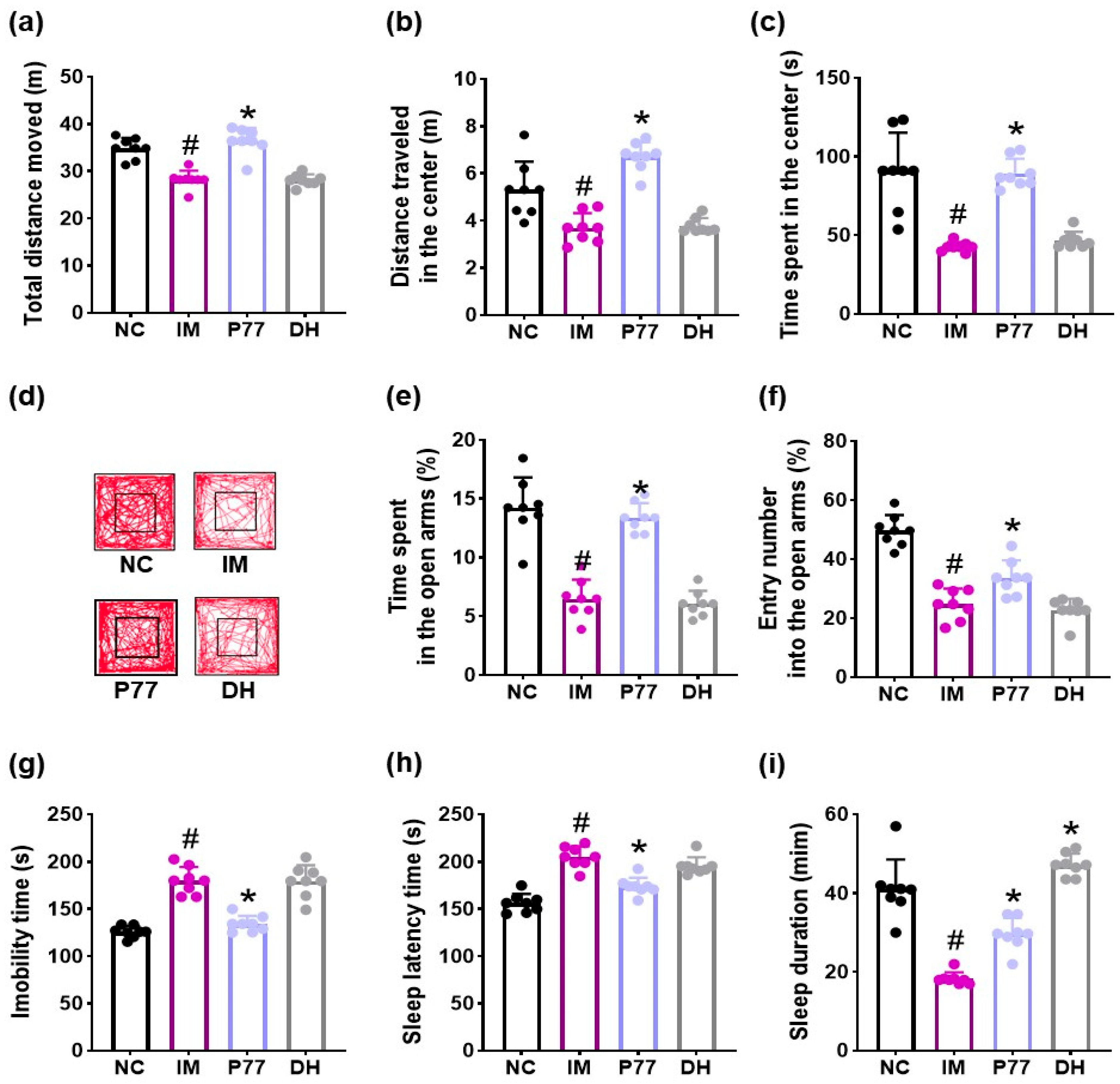
3.2. B. longum P77 Attenuated Depression/Anxiety- and Sleeplessness-Like Symptoms in Immobilization Stress-Exposed Mice
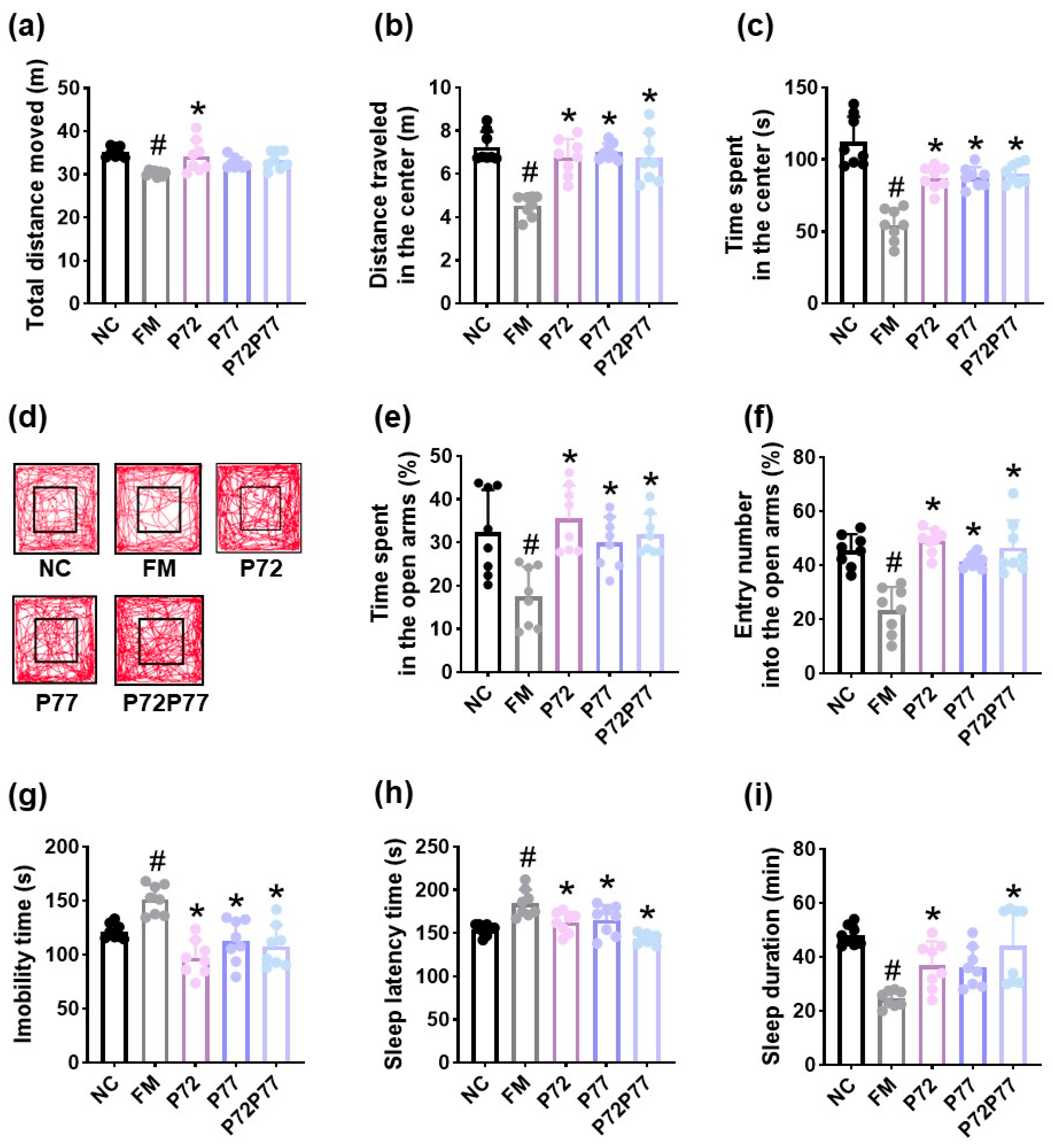
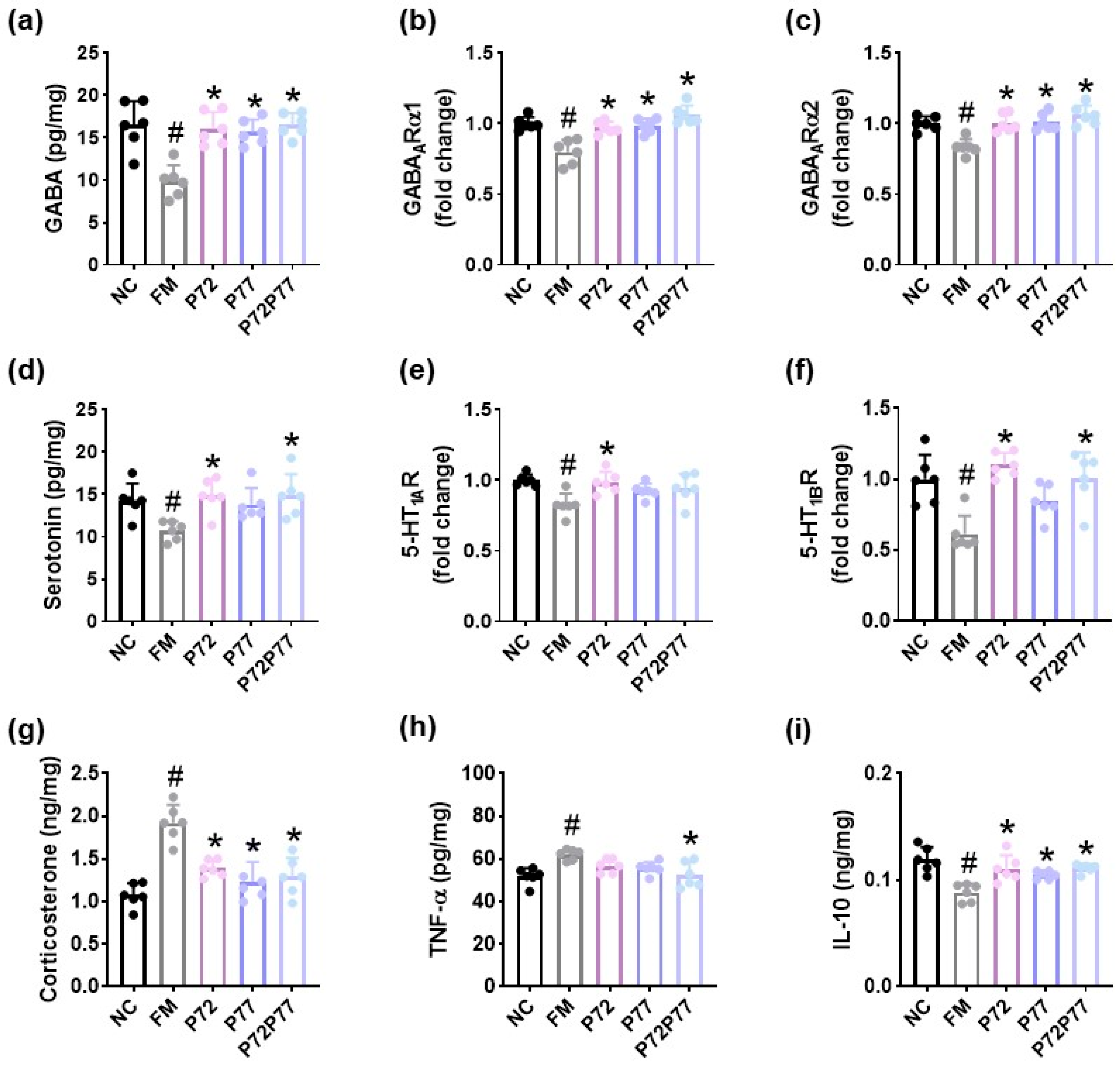
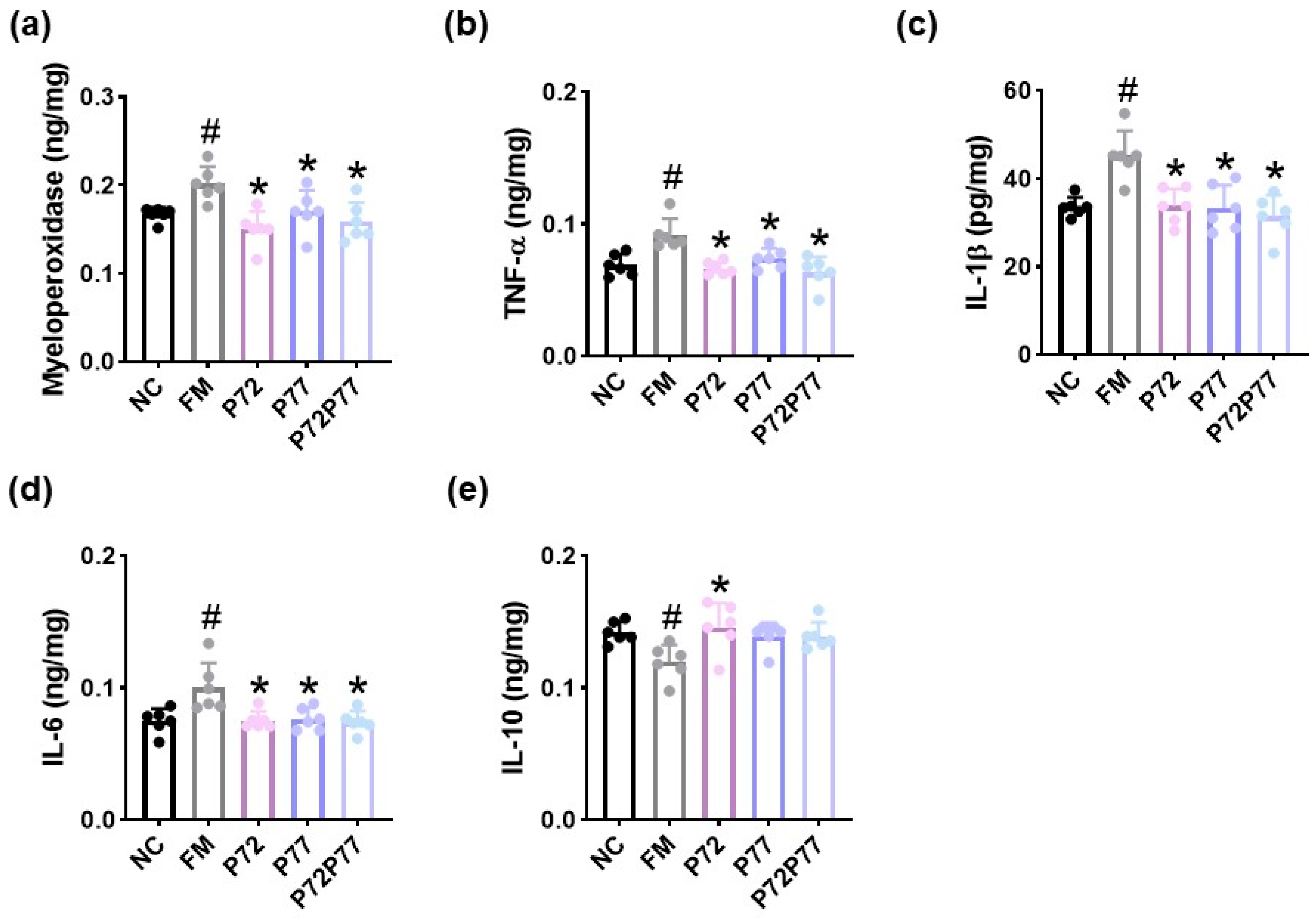
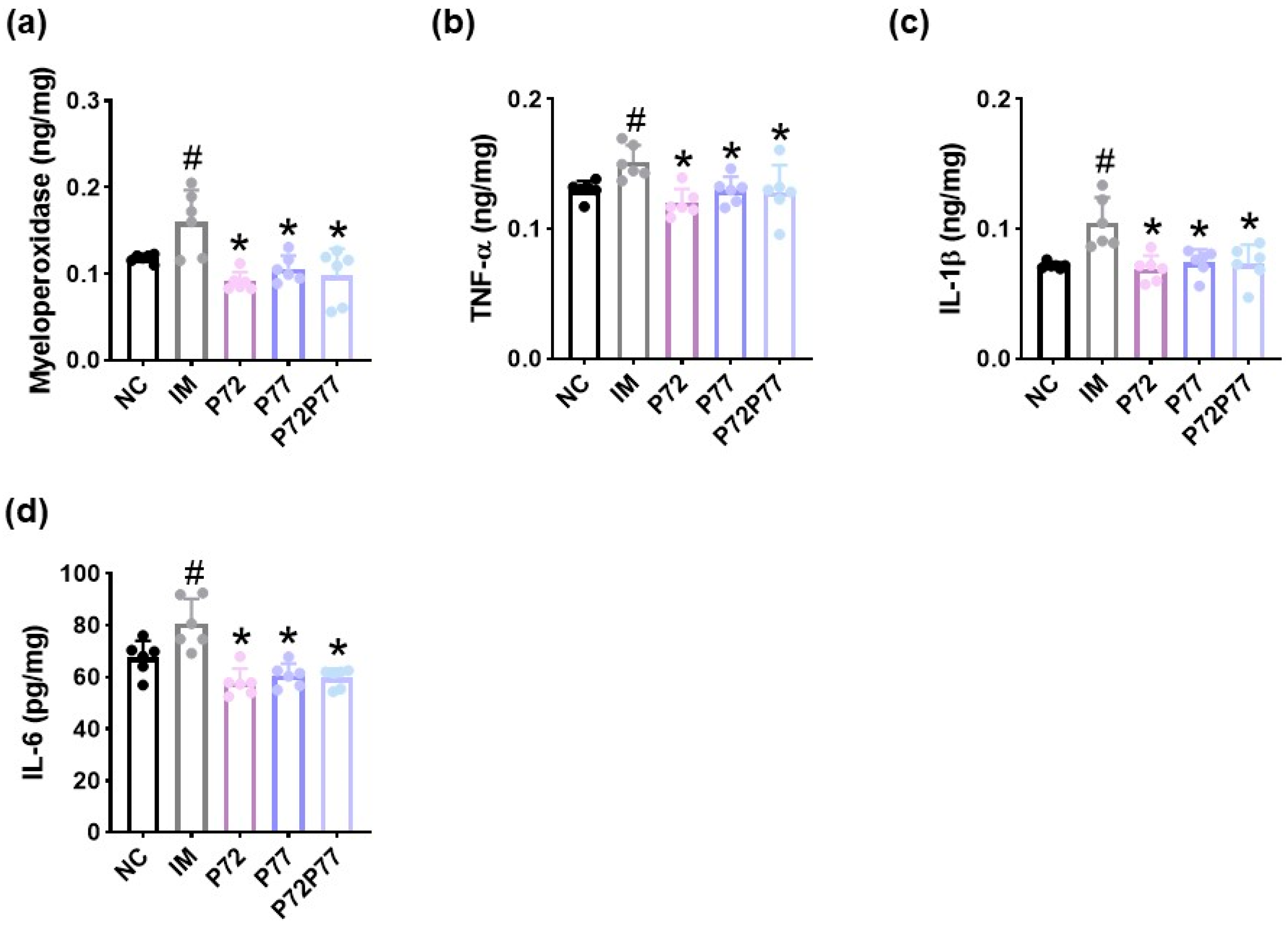
3.3. B. longum P77, L. plantarum P72, and P7277 Alleviated cFM Transplantation-Induced Depression/Anxiety- and Sleeplessness-Like Behaviors and Gut Inflammation in Mice
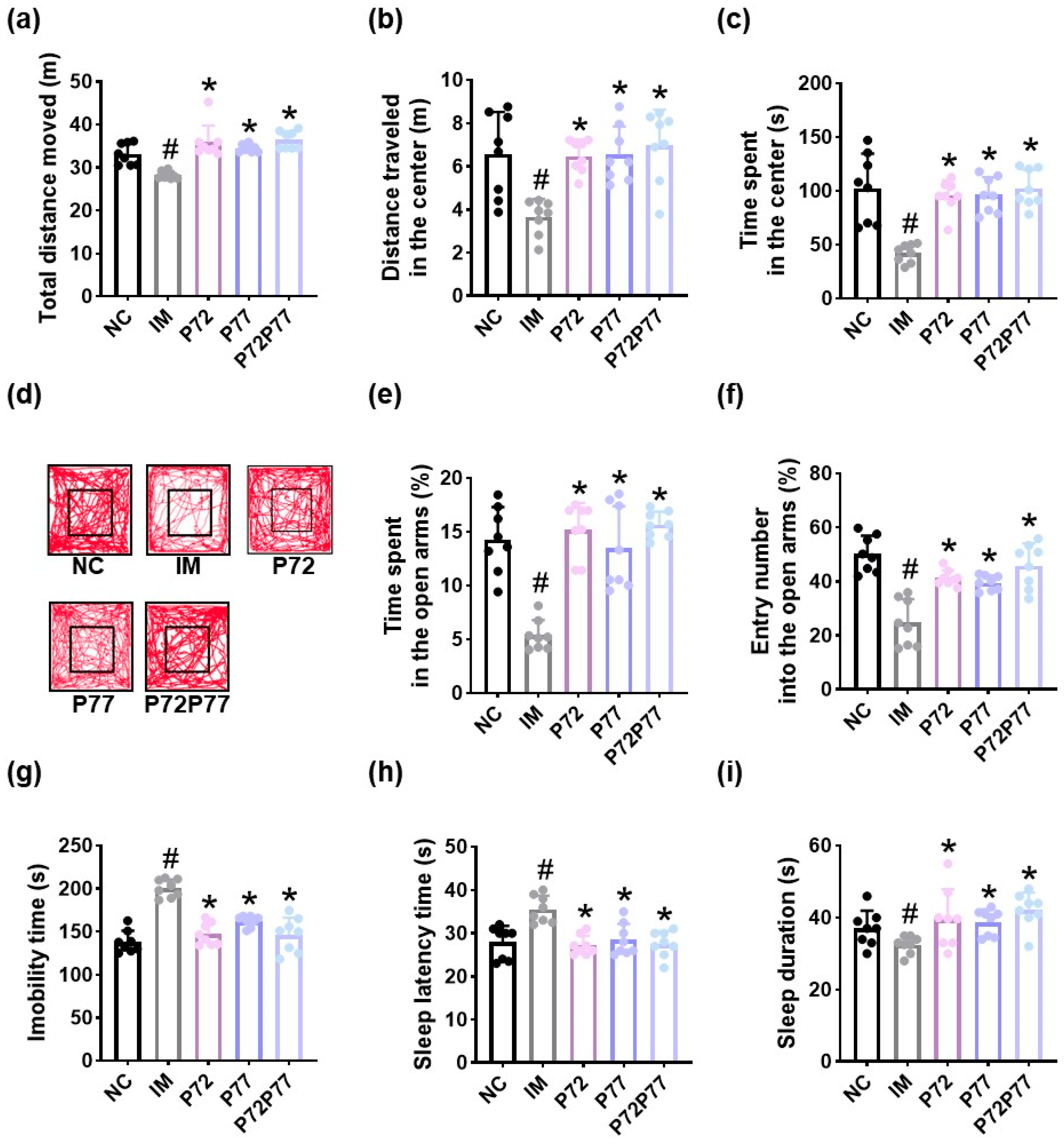
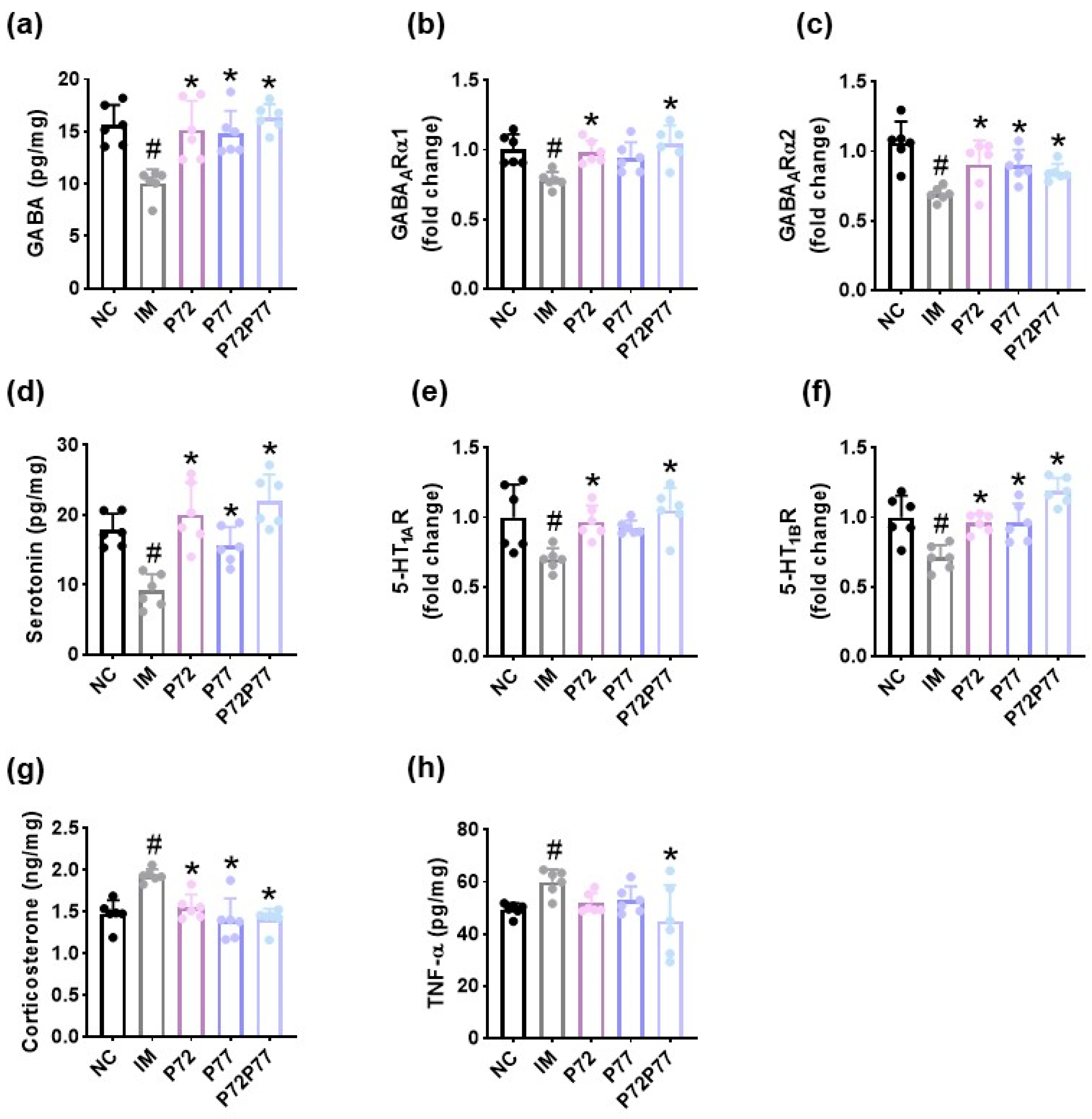
3.4. L. plantarum P72, B. longum P77, and P7277 Alleviated Immobilization Stress-Induced Depression/Anxiety- and Sleeplessness-Like Behavior and Systemic Inflammation in Mice
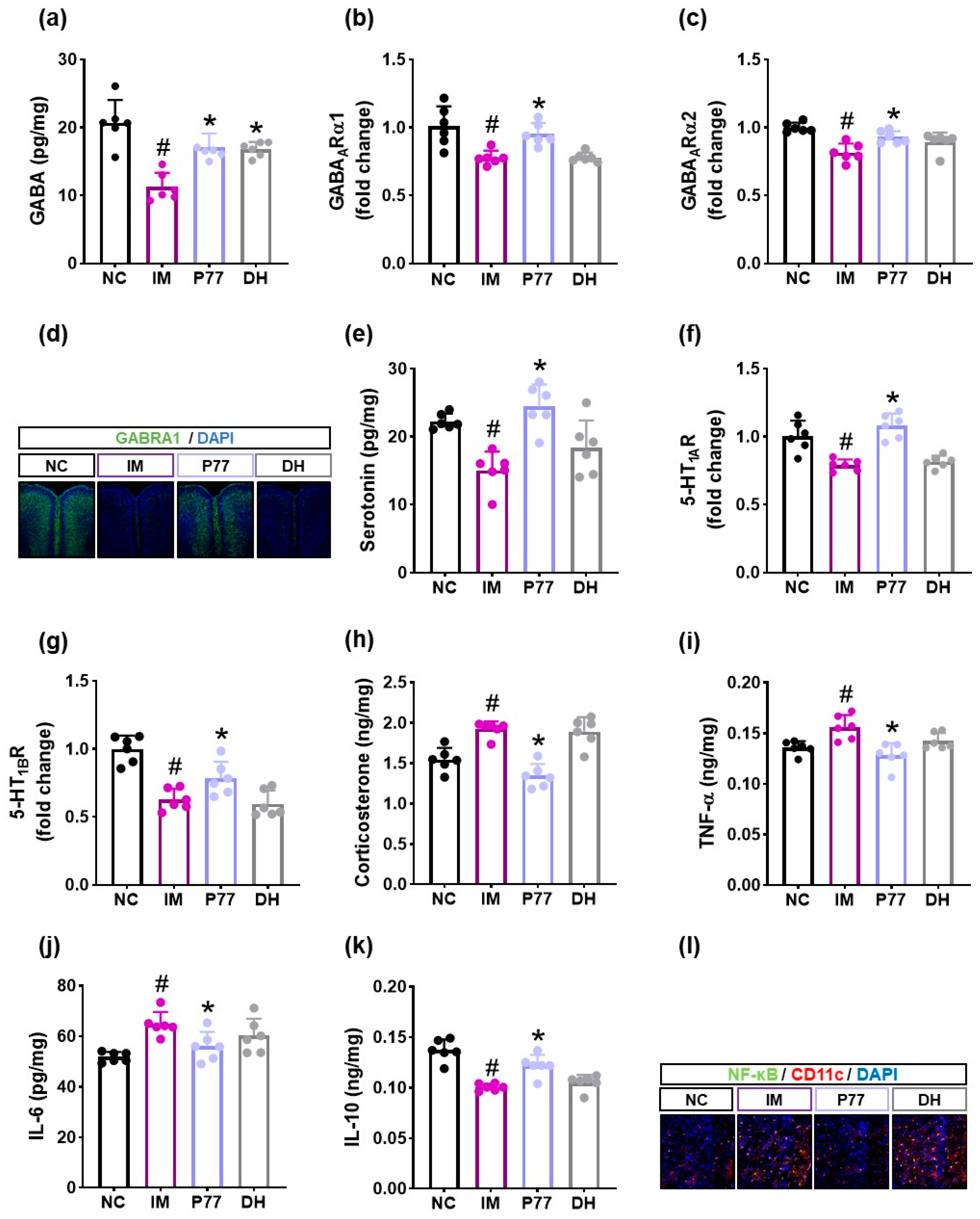
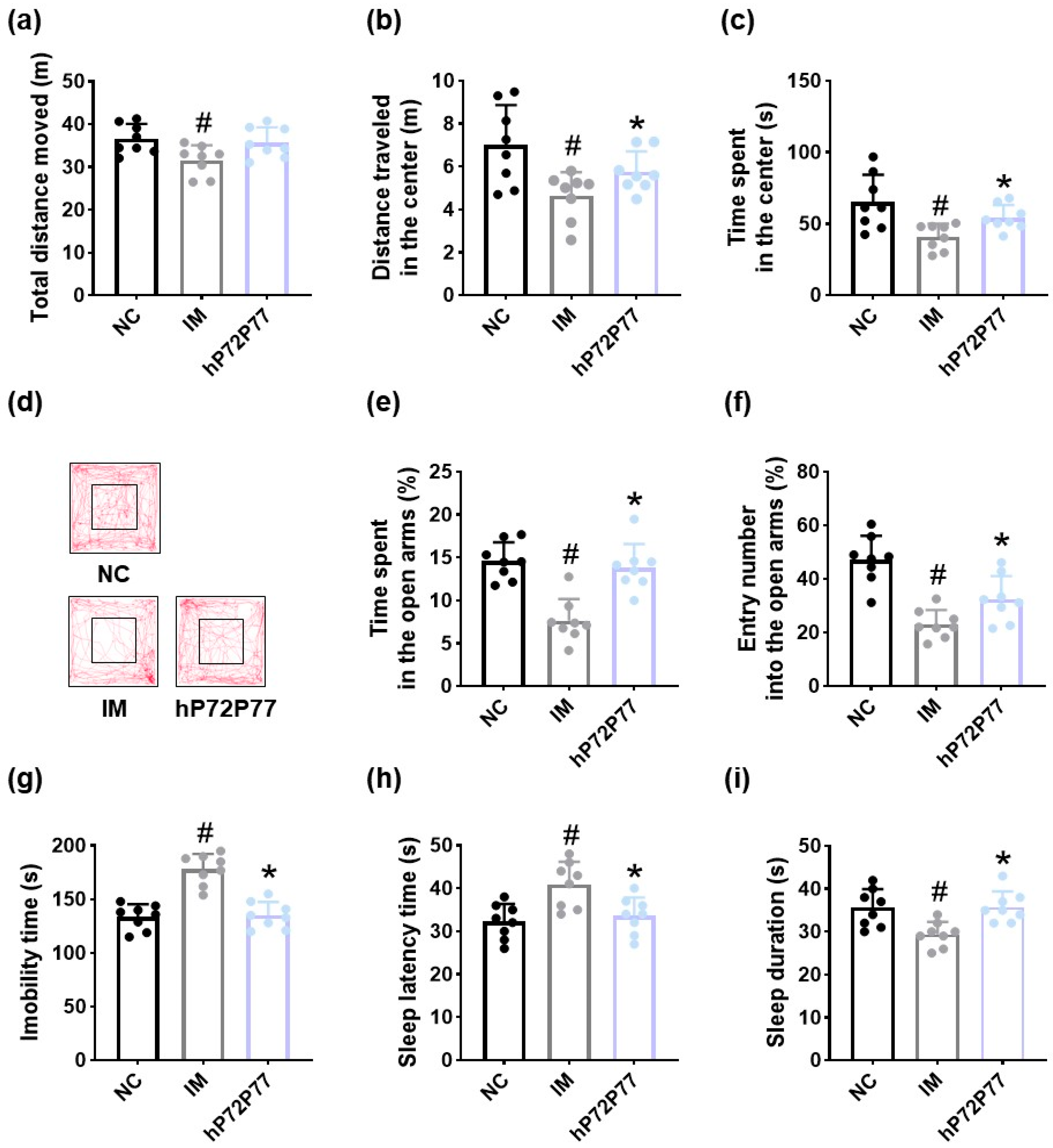
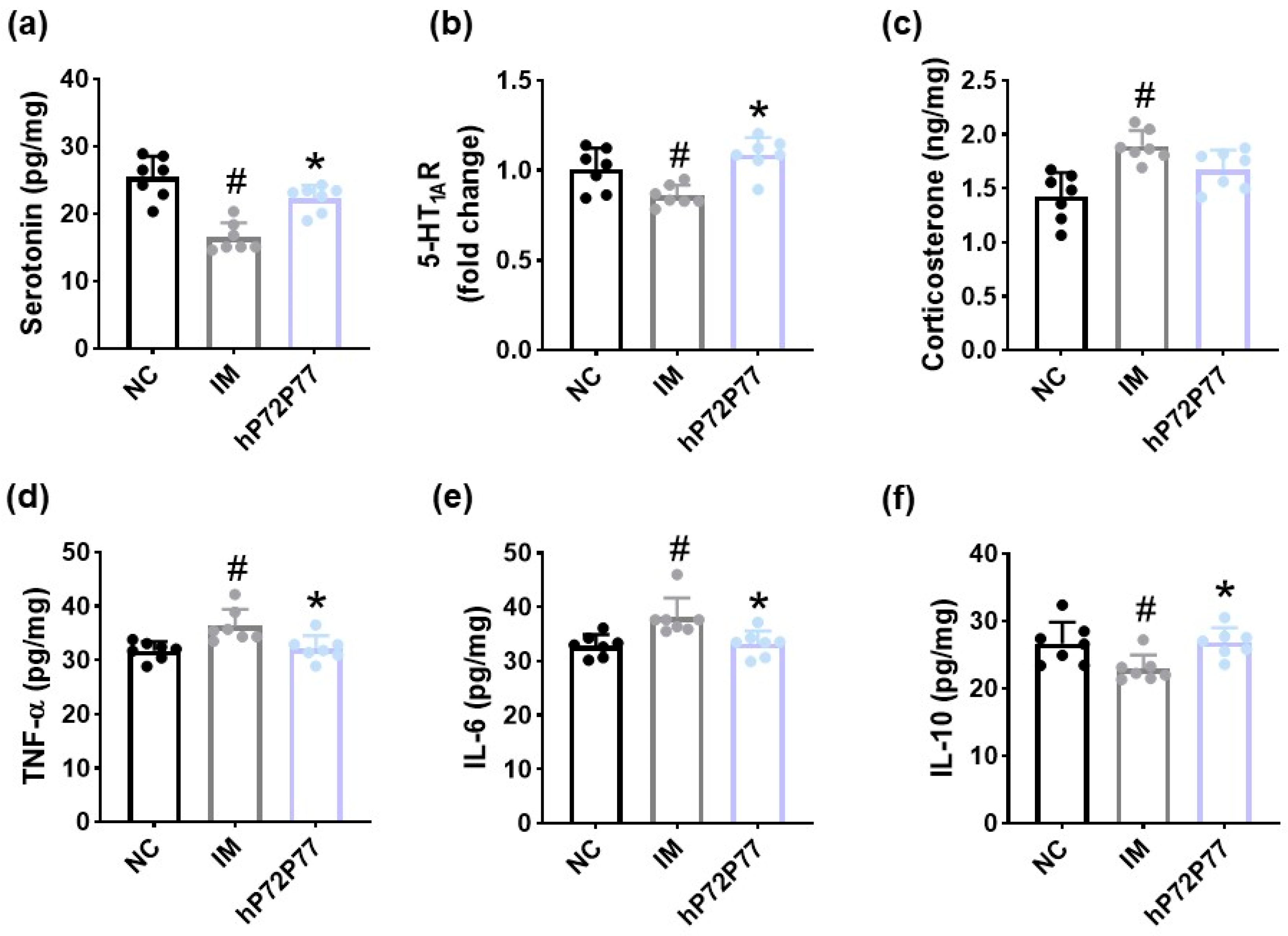
3.5. hP7277 Alleviated Immobilization Stress-Induced Depression/Anxiety- and Sleeplessness-Like Behavior and Neuroinflammation in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernstein, C.N. Psychological Stress and Depression: Risk Factors for IBD? Dig. Dis. 2016, 34, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigos, C.; Chrousos, G.P. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and stress. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 53, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Gu, W.; Lee, I.A.; Joh, E.H.; Kim, D.H. High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicks, L.M.T. Gut Bacteria and Neurotransmitters. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodo, T.W.; de Aquino, M.T.P.; Shimamoto, A.; Shanker, A. Critical Neurotransmitters in the Neuroimmune Network. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; Kupfer, D.J. Sleep research in affective illness: State of the art circa 1987. Sleep 1987, 10, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiji, K.; Sendani, A.A.; Ghavami, S.B.; Farmani, M.; Kazemifard, N.; Sadeghi, A.; Lotfali, E.; Aghdaei, H.A. The critical role of gut-brain axis microbiome in mental disorders. Metab. Brain Dis. 2023, 38, 2547–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, L.F.; Preda, A.; Blottière, H.M.; Clarke, G.; Albani, D.; Belcastro, V.; Carotenuto, M.; Cattaneo, A.; Citraro, R.; Ferraris, C.; et al. Microbiota-gut brain axis involvement in neuropsychiatric disorders. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.K.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus mucosae and Bifidobacterium longum Synergistically Alleviate Immobilization Stress-Induced Anxiety/Depression in Mice by Suppressing Gut Dysbiosis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zou, R.; Song, L.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, B.; Wang, G.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis strain CCFM687 regulated emotional behavior and the central BDNF pathway in chronic stress-induced depressive mice through reshaping the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7588–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, N.; Gorantla, V.R.; Chidambaram, S.B. The Role of Gut Dysbiosis in the Pathophysiology of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cells 2022, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Diaz, J.; Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Gil-Campos, M.; Gil, A. Mechanisms of Action of Probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S1), S49–S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.T. Probiotics. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2010, 67, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, A.T.; Selmi, C.; Meyers, F.J.; Keen, C.L.; Gershwin, M.E. Probiotics and immunity. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xiao, L.; Fu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Jing, Z.; Yuan, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Neuroprotective effects of probiotics on anxiety- and depression-like disorders in stressed mice by modulating tryptophan metabolism and the gut microbiota. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savignac, H.M.; Kiely, B.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Bifidobacteria exert strain-specific effects on stress-related behavior and physiology in BALB/c mice. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H.; Yeh, W.L.; Chou, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Lai, C.H.; Yeh, Y.T.; Liao, C.A.; Wu, C.C. Suppressive Effects of Lactobacillus on Depression through Regulating the Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in C57BL/6J Mice Induced by Ampicillin. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Lee, Y.K.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Cryan, J.F.; Chen, W. Towards a psychobiotic therapy for depression: Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 reverses chronic stress-induced depressive symptoms and gut microbial abnormalities in mice. Neurobiol. Stress 2020, 12, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Fang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Psychobiotic Lactobacillus plantarum JYLP-326 relieves anxiety, depression, and insomnia symptoms in test anxious college via modulating the gut microbiota and its metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1158137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Han, S.W.; Kim, D.H. A probiotic NVP1704 alleviates stress-induced sleeplessness/depression-like symptoms in mice by upregulating serotonergic and GABAergic systems and downregulating NF-κB activation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 77, ovae065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, L.C.; Hor, Y.Y.; Yusoff, N.A.A.; Choi, S.B.; Yusoff, M.S.B.; Roslan, N.S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohammad, J.A.M.; Abdullah, M.; Zakaria, N.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum P8 alleviated stress and anxiety while enhancing memory and cognition in stressed adults: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.T.; Tsai, Y.C.; Kuo, T.B.J.; Yang, C.C.H. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum PS128 on Depressive Symptoms and Sleep Quality in Self-Reported Insomniacs: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Pilot Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Zou, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Qian, L.; Wang, Q.; et al. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 attenuates major depression disorder via regulating gut microbiome and tryptophan metabolism: A randomized clinical trial. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 100, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Hong, J.K.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Jang, S.W.; Han, S.W.; Yoon, I.Y. Effects of Probiotic NVP-1704 on Mental Health and Sleep in Healthy Adults: An 8-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Lu, J.; Qiao, G.; Mao, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G.; Tian, P.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1025 Improves Sleep Quality via Regulating the Activity of the HPA Axis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Baek, J.S.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, D.H. Alleviation of Immobilization Stress or Fecal Microbiota-Induced Insomnia and Depression-like Behaviors in Mice by Lactobacillus plantarum and Its Supplement. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-W.; Shin, Y.-J.; Ma, X.; Son, Y.-H.; Jang, H.-M.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, D.-H. The Alleviation of Gut Microbiota-Induced Depression and Colitis in Mice by Anti-Inflammatory Probiotics NK151, NK173, and NK175. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, D.H. The Preventive and Curative Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri NK33 and Bifidobacterium adolescentis NK98 on Immobilization Stress-Induced Anxiety/Depression and Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Shin, Y.J.; Park, H.S.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Shim, J.J.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, D.H. Lactobacillus casei and Its Supplement Alleviate Stress-Induced Depression and Anxiety in Mice by the Regulation of BDNF Expression and NF-κB Activation. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, H.; Eun, J.S.; Nam, S.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Hong, J.T.; Lee, M.K.; Oh, K.W. Methanol extract of Longanae Arillus augments pentobarbital-induced sleep behaviors through the modification of GABAergic systems. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 122, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lach, G.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Anxiety, Depression, and the Microbiome: A Role for Gut Peptides. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porkka-Heiskanen, T.; Zitting, K.M.; Wigren, H.K. Sleep, its regulation and possible mechanisms of sleep disturbances. Acta Physiol. 2013, 208, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Oliveira, R.; Soares, R.; Barata, P. Influence of gut microbiota dysbiosis on brain function: A systematic review. Porto Biomed. J. 2020, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, A.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: Human-bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystal, A.D. New Developments in Insomnia Medications of Relevance to Mental Health Disorders. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 38, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemann, D.; Krone, L.B.; Wulff, K.; Nissen, C. Sleep, insomnia, and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidfar, M.; Kim, Y.K. Recent Developments on Future Antidepressant-related Serotonin Receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.M.; Kim, J.K.; Joo, M.K.; Shin, Y.J.; Lee, C.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.H. Transplantation of fecal microbiota from patients with inflammatory bowel disease and depression alters immune response and behavior in recipient mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K. Neuroinflammation through the vagus nerve-dependent gut-microbiota-brain axis in treatment-resistant depression. Prog. Brain Res. 2023, 278, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howland, R.H. Sleep interventions for the treatment of depression. J. Psychosoc. Nurs. Ment. Health Serv. 2011, 49, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blier, P.; Ward, N.M. Is there a role for 5-HT1A agonists in the treatment of depression? Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 53, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhamzeh, M.; Moravej, F.G.; Arabi, M.; Shahriari, E.; Mehrabi, S.; Ward, R.; Ahadi, R.; Joghataei, M.T. The Roles of Serotonin in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yohn, C.N.; Gergues, M.M.; Samuels, B.A. The role of 5-HT receptors in depression. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Tseng, H.W.; Hsieh, H.L.; Lee, C.W.; Wu, C.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces MMP-9 expression via p42/p44 MAPK, JNK, and nuclear factor-kappaB in A549 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 229, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Laurentiis, A.; Pisera, D.; Lasaga, M.; Díaz, M.; Theas, S.; Duvilanski, B.; Seilicovich, A. Effect of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on GABA release from mediobasal hypothalamus and posterior pituitary. Neuroimmunomodulation 2000, 7, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthold-Losleben, M.; Himmerich, H. The TNF-alpha system: Functional aspects in depression, narcolepsy and psychopharmacology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malynn, S.; Campos-Torres, A.; Moynagh, P.; Haase, J. The pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α regulates the activity and expression of the serotonin transporter (SERT) in astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 2013, 38, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, N.; Bode, C.; Duerschmied, D. The Effects of Serotonin in Immune Cells. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nau, F., Jr.; Yu, B.; Martin, D.; Nichols, C.D. Serotonin 5-HT2A receptor activation blocks TNF-α mediated inflammation in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Li, D.; Chitrakar, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Tian, H.; Luo, Y. Study on Lactiplantibacillus plantarum R6-3 from Sayram Ketteki to prevent chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression in mice through the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3304–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzen, P.L.; Buysse, D.J. Sleep disturbances and depression: Risk relationships for subsequent depression and therapeutic implications. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 10, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Tu, S.; Sheng, J.; Shao, A. Depression in sleep disturbance: A review on a bidirectional relationship, mechanisms and treatment. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2324–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, J.-S.; Ma, X.; Park, H.-S.; Lee, D.-Y.; Kim, D.-H. Bifidobacterium longum P77 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P72 and Their Mix—Live or Heat-Treated—Mitigate Sleeplessness and Depression in Mice: Involvement of Serotonergic and GABAergic Systems. Cells 2025, 14, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191547
Baek J-S, Ma X, Park H-S, Lee D-Y, Kim D-H. Bifidobacterium longum P77 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P72 and Their Mix—Live or Heat-Treated—Mitigate Sleeplessness and Depression in Mice: Involvement of Serotonergic and GABAergic Systems. Cells. 2025; 14(19):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191547
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Ji-Su, Xiaoyang Ma, Hee-Seo Park, Dong-Yun Lee, and Dong-Hyun Kim. 2025. "Bifidobacterium longum P77 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P72 and Their Mix—Live or Heat-Treated—Mitigate Sleeplessness and Depression in Mice: Involvement of Serotonergic and GABAergic Systems" Cells 14, no. 19: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191547
APA StyleBaek, J.-S., Ma, X., Park, H.-S., Lee, D.-Y., & Kim, D.-H. (2025). Bifidobacterium longum P77 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum P72 and Their Mix—Live or Heat-Treated—Mitigate Sleeplessness and Depression in Mice: Involvement of Serotonergic and GABAergic Systems. Cells, 14(19), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191547






