Counter-Therapeutic Strategies for Resistance of FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Wild-Type FLT3 Signaling Pathways
3. Signaling Pathways Associated with FLT3 Mutations
4. Primary Resistance
5. Secondary On-Target Resistance
6. Secondary Off-Target Resistance
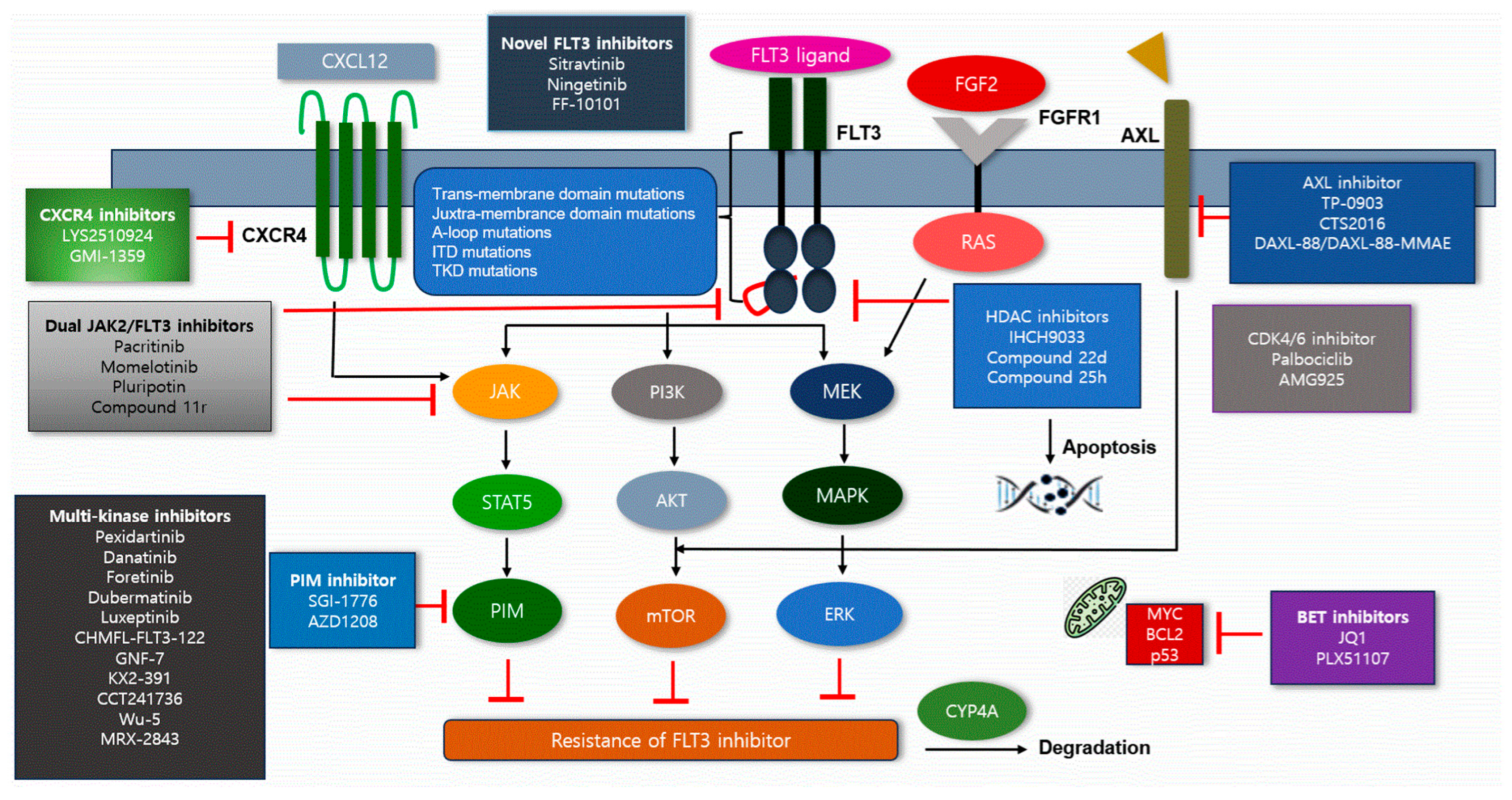
7. Strategies to Overcome Resistance to FLT3 Inhibitors
7.1. Novel FLT3 Inhibitors
| Novel Inhibitor | Action Mechanism | Clinical Impact of Inhibitors | Agents | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Novel FLT3 inhibitors | Secondary resistance mutations such as F691L, D835 and Y842C could activate downstream pathways such as AKT, ERK and STAT5 | Novel FLT3 inhibitors were effective against secondary resistance mutations of FLT3, thereby inhibiting downstream pathways | Sitravatinib Ningetinib FF-10101 | [32,33,34] |
| AXL inhibitors | AXL activates ERK/STAT5, increases AML cell survival and has bypassing effects of FLT3 inhibitions | AXL inhibitors bind to gatekeeper mutations such as F691L and overcome resistance | TP-0903 CTS2016 | [36] |
| HDAC inhibitors | HDAC8 downregulates p53 and increases leukemic cell survival; in addition, it reduces DNA repair defects in FLT3-ITD mutations | HDAC inhibitors selectively inhibit DNA repair in FLT3-ITD mutated cells, which induces HSP90 acetylation, FLT3 ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of FLT3, thereby inhibiting FLT3 downstream pathways | IHCH9033 Compound 22d Compound 25h | [37,38,39] |
| CDK4/6 inhibitors | CDKs—serine/threonine protein kinases—are crucial to regulate cell cycle; they activate after binding to cyclins and regulate DNA replication in leukemic cells | CDK4/6 inhibitors could inhibit DNA replication and induce leukemic cell arrest | Palbociclib Abemaciclib AMG925 | [40,41] |
| Dual JAK2 and FLT3 inhibitors | JAK2 mutation activates STAT5, MAPK and PI3K regardless of FLT3 action and activates bypass pathway of FLT3, thus achieving resistance to FLT3 inhibitors | Dual JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor -inhibits STAT5, MAPK and PI3K -suppress A-loop mutations (D835, D839, Y842) | Pacritinib Momelotinib Pluripontin Compound 11r | [42] |
| PIM inhibitor | PIM-1 upregulates downstream pathways of FLT3-ITD and promotes cell growth and survival, thus reducing sensitivity of FLT3 inhibitors | PIM inhibitors reduce replication of RNA and reduce Mcl-1 transcripts | SGI-1776 AZD1208duak JAK2 | [43] |
| CXCR4 inhibitor | CXCL12/CXCR4 axis influences cell migration, adhesion and survival in BM The axis activates downstream MAPK and ERK pathway | CXCR4 inhibitors could counteract activation of downstream pathway such as MAPK and ERK | LYS10924 GMI-1359 | [44] |
| BET inhibitor | BET associated with pro-survival factors MYC and BCL2 | BET inhibitors have inhibitory effect on MYC and BCL2 and could overcome mutations in F691L and D835 | JQ1 PLX51107 | [45] |
7.2. AXL Inhibitors
7.3. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
7.4. CDK4/6 Inhibitors
7.5. Dual JAK2 and FLT3 Inhibitors
7.6. PIM Inhibitor
7.7. CXCR4 Inhibitors
7.8. BET Inhibitors
7.9. Multi-Kinase Inhibitors
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazi, J.U.; Rönnstrand, L. FMS-like Tyrosine Kinase 3/FLT3: From Basic Science to Clinical Implications. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1433–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshinchi, S.; Appelbaum, F.R. Structural and functional alterations of FLT3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4263–4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhäll, A.; Heidel, F.; Fischer, T.; Rönnstrand, L. Internal tandem duplication mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of FLT3 display a higher oncogenic potential than the activation loop D835Y mutation. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S. Downstream molecular pathways of FLT3 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia: Biology and therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2011, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruglioni, M.; Crucitta, S.; Luculli, G.I.; Tancredi, G.; Giudice, M.L.D.; Mechelli, S.; Galimberti, S.; Danesi, R.; Marzia Re, M.D. Understanding mechanisms of resistance to FLT3 inhibitors in adult FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia to guide treatment strategy. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2024, 201, 104424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.K.; Park, B.B.; Uhm, J.E. Clinical Efficacies of FLT3 Inhibitors in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, M.; Minami, Y.; Kuzume, A.; Chi, S. Mechanisms Underlying Resistance to FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafone, T.; Palmisano, M.; Nicci, C.; Storti, S. An overview on the role of FLT3-tyrosine kinase receptor in acute myeloid leukemia: Biology and treatment. Oncol. Rev. 2012, 6, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, M.T.; Wang, H.G. Therapeutic targeting of FLT3 and associated drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, R.A.; Cordero, E.; Moharram, S.A.; Pietras, K.; Rönnstrand, L.; Kazi, J.U. Expression of GADS enhances FLT3-induced mitogenic signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14112–14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, D.; Corrêa, S.A.L.; Müller, J. Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4397–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocnik, J.R.; Okabe, R.; Yu, J.C.; Lee, B.H.; Giese, N.; Schenkein, D.P.; Gilliland, D.G. Roles of tyrosine 589 and 591 in STAT5 activation and transformation mediated by FLT3-ITD. Blood 2006, 108, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minieri, V.; Dominici, M.D.; Porazzi, P.; Mariani, S.A.; Spinelli, O.; Rambaldi, A.; Peterson, L.F.; Porcu, P.; Nevalainen, M.; Calabretta, B. Targeting STAT5 or STAT5-regulated pathways suppresses leukemogenesis of Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5793–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.-S.; Kim, H.-J. FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia: A review focusing on clinically applicable drugs. Blood Res. 2022, 57, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, S.P.; Daver, N.; DiNardo, C.; Kadia, T.; Konopleva, M.; Ravandi, F. Resistance to targeted therapies: Delving into FLT3 and IDH. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Yang, X.; Knapper, S.; White, P.; Smith, B.D.; Galkin, S.; Small, D.; Burnett, A.; Mark Levis, M. FLT3 ligand impedes the efficacy of FLT3 inhibitors in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2011, 117, 3286–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Ghosh, J.; Ramdas, B.; Liu, Y.; Chan, R.; Kapur, R.; Mali, R.S.; Martin, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Vemula, S.; et al. Regulation of Stat5 by FAK and PAK1 in Oncogenic FLT3- and KIT-Driven Leukemogenesis. Cell Rep. 2014, 9, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traer, E.; Javidi-Sharifi, N.; Agarwal, A.; Dunlap, J.B.; English, I.; Martinez, J.; Kovacsovics, T.J.; Tyner, J.W.; Wong, M.; Druker, B.J. FGF2 Promotes Resistance to Quizartinib In Vitro, and FGF2 Increases in the Marrow of Patients Prior to Resistance. Blood 2013, 122, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Hernandez, D.; Alonso, S.; Gao, M.; Su, M.; Ghiaur, G.; Levis, M.J.; Jones, R.J. Role of CYP3A4 in bone marrow microenvironment–mediated protection of FLT3/ITD AML from tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombouts, E.J.; Pavic, B.; Lowenberg, B.; Ploemacher, R.E. Relation between CXCR-4 expression, Flt3 mutations, and unfavorable prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004, 104, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, V.E.; Smith, C.C. FLT3 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Key Concepts and Emerging Controversies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 612880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cools, J.; Mentens, N.; Furet, P.; Fabbro, D.; Clark, J.J.; Griffin, J.D.; Marynen, P.; Gilliland, D.G. Prediction of resistance to small molecule FLT3 inhibitors: Implications for molecularly targeted therapy of acute leukemia. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6385–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.; Hernandez, D.; Rajkhowa, T.; Smith, S.C.; Raman, J.R.; Nguyen, B.; Small, D.; Levis, M. Preclinical studies of gilteritinib, a next-generation FLT3 inhibitor. Blood 2017, 129, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daver, N.; Cortes, J.; Ravandi, F.; Patel, K.P.; Burger, J.A.; Konopleva, M.; Kantarjian, H. Secondary mutations as mediators of resistance to targeted therapy in leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 3236–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.M.; Ferng, T.; Canaani, J.; Wang, E.S.; Morrissette, J.; Eastburn, D.J.; Pellegrino, M.; Durruthy-Durruthy, R.; Watt, C.D.; Asthana, S.; et al. Clonal selection with Ras pathway activation mediates secondary clinical resistance to selective FLT3 inhibition in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, C.; Janakakumara, J.V.; Liu, S.C.; Chng, W.J.; Tay, K.G.; Poon, L.F.; Xie, Z.; Palaniyandi, S.; Yu, H.; et al. Enhanced activation of STAT pathways and overexpression of survivin confer resistance to FLT3 inhibitors and could be therapeutic targets in AML. Blood 2009, 113, 4052–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette, M.A.; Côté, J.F. AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase as a Promising Therapeutic Target Directing Multiple Aspects of Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancers 2022, 14, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: Functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, M.M. The importance of FLT3 mutational analysis in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 10, 2273–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xiu, J.; Ren, C.; Yu, Z. Protein kinase PIM2: A simple PIM family kinase with complex functions in cancer metabolism and therapeutics. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y. Sitravatinib as a potent FLT3 inhibitor can overcome gilteritinib resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, P. Sitravatinib combined with venetoclax exerts effective synergy to eliminate acute myeloid leukemia cells with FLT3-ITD mutations. Transl. Oncol. 2025, 59, 102467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Deng, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, S.; Wang, P. Ningetinib, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, overcomes secondary drug resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levis, M.; Perl, A.; Schiller, G.; Fathi, A.T.; Roboz, G.; Wang, E.S.; Altman, J.; Rajkhowa, T.; Ando, M.; Suzuki, T.; et al. A phase 1 study of the irreversible FLT3 inhibitor FF-10101 in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2527–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferng, T.T.; Terada, D.; Ando, M.; Tarver, T.C.; Chaudhary, F.; Lin, K.C.; Logan, A.C.; Smith, C.C. The Irreversible FLT3 Inhibitor FF-10101 Is Active Against a Diversity of FLT3 Inhibitor Resistance Mechanisms. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, T.S.; Li, L.; Bruner, J.K.; Chou, M.; Nguyen, B.; Seo, J.; Zhu, R.; Levis, M.J.; Pratilas, C.A.; Small, D. Targeting rapid TKI-induced AXL upregulation overcomes adaptive ERK reactivation and exerts antileukemic effects in FLT3/ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Oncol. 2025, 19, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Jia, M.Y.; Fang, W.Y.; Chen, X.J.; Mu, L.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.; Xiang, R.F.; Wang, L.N.; Wang, L.; et al. FLT3 inhibition upregulates HDAC8 via FOXO to inactivate p53 and promote maintenance of FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, M.; Yan, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; et al. IHCH9033, a novel class I HDAC inhibitor, synergizes with FLT3 inhibitor and rescues quizartinib resistance in FLT3-ITD AML via enhancing DNA damage response. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, W.; Fang, H.; Hou, X. Simultaneous inhibition of FLT3 and HDAC by novel 6-ethylpyrazine-2-Carboxamide derivatives provides therapeutic advantages in acute myelocytic leukemia. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 279, 116847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, S.; Bergholz, J.S.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 356–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hsu, C.P.; Lu, J.F.; Kuchimanchi, M.; Sun, Y.N.; Ma, J.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Weidner, M.; et al. FLT3 and CDK4/6 inhibitors: Signaling mechanisms and tumor burden in subcutaneous and orthotopic mouse models of acute myeloid leukemia. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2014, 41, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Meng, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, C.; Gu, Y.C.; Han, L.; Wen, J.; Ton, M.; et al. 2-Aminopyrimidine derivatives as selective dual inhibitors of JAK2 and FLT3 for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 134, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Baird, K.; Ahn, J.Y.; Meltzer, P.; Lilly, M.; Levis, M.; Small, D. Pim-1 is up-regulated by constitutively activated FLT3 and plays a role in FLT3-mediated cell survival. Blood 2005, 105, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzapelle, R.; Leo, M.; Caprioglio, F.; Colley, L.S.; Lamarca, A.; Sabatino, L.; Colantuoni, V.; Crippa, M.P.; Bianchi, M.E. CXCR4/CXCL12 Activities in the Tumor Microenvironment and Implications for Tumor Immunotherapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Hizukuri, Y.; Severson, P.; Powell, B.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Narahara, M.; Sumi, H.; Hernandez, D.; Rajkhowa, T.; et al. A novel combination regimen of BET and FLT3 inhibition for FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Buelow, D.R.; Garrison, D.A.; Niu, M.; Eisenmann, E.D.; Huang, K.E.; Thomas, M.E.Z.; Weber, R.H.; Whatcott, C.J.; Warner, S.L.; et al. TP-0903 is active in models of drug-resistant acute myeloid leukemia. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Ouyang, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Mi, Y.; Wu, H. CTS2016, a novel AXL/FLT3 inhibitor for targeting AML/MDS and solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2023, 83 (Suppl. S7), 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, W.; Duan, Y.; Liu, D. Novel AXL-targeted agents overcome FLT3 inhibitor resistance in FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia cells. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Friedman, R. Combination strategies to overcome drug resistance in FLT+ acute myeloid leukaemia. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uras, I.Z.; Walter, G.J.; Scheicher, R.; Bellutti, F.; Prchal-Murphy, M.; Tigan, A.S.; Valent, P.; Heidel, F.H.; Kubicek, S.; Scholl, C.; et al. Palbociclib treatment of FLT3-ITD+ AML cells uncovers a kinase-dependent transcriptional regulation of FLT3 and PIM1 by CDK6. Blood 2016, 127, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Suh, Y.H.; Song, K.H.; Ryu, M.O.; Seo, K.W. Abemaciclib induces G1 arrest and lysosomal dysfunction in canine melanoma cells: Synergistic effects with fenbendazole. Front Vet Sci. 2025, 12, 1603686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.Y.; Talukder, M.; Cao, D.; Chen, C.W. Gilteritinib Enhances Anti-Tumor Efficacy of CDK4/6 Inhibitor, Abemaciclib in Lung Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 829759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Ly, C.; Mark, D.; Shah, N.P.; Konopleva, M.; Andreeff, M. AMG925, a Dual FLT3-CDK4/6 Inhibitor, Disrupts Survival Signaling and Triggers Apoptosis in AML Progenitor/Stem Cells. Blood 2016, 22, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Xia, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; McGee, L.R.; Newhall, K.; Sinclair, A.; Kamb, A.; et al. AMG 925 is a dual FLT3/CDK4 inhibitor with the potential to overcome FLT3 inhibitor resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummelt, C.; Gorantla, S.P.; Meggendorfer, M.; Charlet, A.; Endres, C.; Dohner, K.; Heidel, F.H.; Fischer, T.; Haferlach, T.; Duyster, J. Activating JAK-mutations confer resistance to FLT3 kinase inhibitors in FLT3-ITD positive AML in vitro and in vivo. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2017–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.; Goh, K.C.; Novotny-Diermayr, V.; Tan, Y.C.; Madan, B.; Amalini, C.; Ong, L.C.; Kheng, B.; Cheong, A.; Zhou, J.; et al. Pacritinib (SB1518), a JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2011, 1, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, Y.; Yang, K.; Long, C. Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 by pacritinib synergizes with chemotherapy in esophageal carcinoma. Toxicol. Vitr. 2025, 106, 106056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstovsek, S.; Odenike, O.; Singer, J.W.; Granston, T.; Al-Fayoumi, S.; Deeg, H.J. Phase 1/2 study of pacritinib, a next generation JAK2/FLT3 inhibitor, in myelofibrosis or other myeloid malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, M.; Kincaid, Z.; Kesarwani, M.; Ahmed, A.; Wunderlich, M.; Latif, T.; Starczynowski, D.; Azam, M. Momelotinib is a highly potent inhibitor of FLT3-mutant AML. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azhar, M.; Kincaid, Z.; Kesarwani, M.; Menke, J.; Schwieterman, J.; Ansari, S.; Reaves, A.; Ahmed, A.; Shehzad, R.; Khan, A.; et al. Rational polypharmacological targeting of FLT3, JAK2, ABL, and ERK1 suppresses the adaptive resistance to FLT3 inhibitors in AML. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 1460–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.S.; Redkar, S.; Taverna, P.; Cortes, K.E.; Gandhi, V. Mechanisms of cytotoxicity to Pim kinase inhibitor, SGI-1776, in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2011, 118, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, K.; Mathias, T.J.; Doshi, K.A.; Tron, A.E.; Kraus, M.; Trotta, R.; Perrotti, D.; Huszar, D.; Baer, M.R. The Pim Kinase Inhibitor AZD1208 Enhances Apoptosis Induction By Clinically Active FLT3 Inhibitors in FLT3-ITD Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells in Vitro and in Vivo through Synergistic Downregulation of Mcl-1 and of Bcl-xL. Blood 2014, 124, 3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, K.A.; Trotta, R.; Natarajan, K.; Rassool, F.V.; Tron, A.E.; Huszar, D.; Perrotti, D.; Baer, M.R. Pim kinase inhibition sensitizes FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia cells to topoisomerase 2 inhibitors through increased DNA damage and oxidative stress. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48280–48295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.; Natarajan, K.; Baldwin, P.R.; Doshi, K.A.; Lapidus, R.G.; Mathias, T.J.; Scarpa, M.; Trotta, R.; Davila, E.; Kraus, M.; et al. Concurrent Inhibition of Pim and FLT3 Kinases Enhances Apoptosis of FLT3-ITD Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells through Increased Mcl-1 Proteasomal Degradation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.R.; Jung, S.H.; Han, A.R.; Park, G.P.; Kim, H.J.; Yuan, B.; Battula, V.L.; Andreeff, M.; Konopleva, M.; Chung, Y.J.; et al. CXCR4 Inhibition Enhances Efficacy of FLT3 Inhibitors in FLT3-Mutated AML Augmented by Suppressed TGF-b Signaling. Cancers 2020, 12, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.S.; Zeng, Z.; Mu, H.; Wang, Z.; Konoplev, S.; McQueen, T.; Protopopova, M.; Cortes, J.; Marszalek, J.R.; Peng, S.B.; et al. Antileukemia activity of the novel peptidic CXCR4 antagonist LY2510924 as monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapy. Blood 2015, 126, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festuccia, C.; Mancini, A.; Gravina, G.L.; Colapietro, A.; Vetuschi, A.; Pompili, S.; Ventura, L.; Monache, S.D.; Iorio, R.; Fattore, A.D.; et al. Dual CXCR4 and E-Selectin Inhibitor, GMI-1359, Shows Anti-Bone Metastatic Effects and Synergizes with Docetaxel in Prostate Cancer Cell Intraosseous Growth. Cells 2019, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, K.H.; Basyal, M.; Jia, Y.; Ostermann, L.B.; Fogler, W.E.; John, L.; Magnani, J.L.; Zal, M.A.; Tomas, Z.; et al. Combined Blockage of E-Selectin and CXCR4 (GMI-1359) Enhances Anti-Leukemia Effect of FLT3 Inhibition (Sorafenib) and Protects Hematopoiesis in Pre-Clinical AML Models. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. S1), 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delrieu, L.; Hamaidia, S.; Montaut, E.; Garcia-Sandoval, A.C.; Teste, C.; Betton-Fraisse, P.; Bonnefoix, T.; Carras, S.; Gressin, R.; Lefebvre, C.; et al. BET inhibition revealed varying MYC dependency mechanisms independent of gene alterations in aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Clin. Epigenetics 2024, 16, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiskus, W.; Sharma, S.; Qi, J.; Shah, B.; Devaraj, S.G.T.; Leveque, C.; Portier, B.P.; Iyer, S.; Bradner, J.E.; Bhalla, K.N. BET protein antagonist JQ1 is synergistically lethal with FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and overcomes resistance to FLT3-TKI in AML cells expressing FLT-ITD. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2315–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .Benner, B.; Good, L.; Quiroga, D.; Schultz, T.E.; Kassem, M.; Carson, W.E.; Cherian, M.A.; Sardesai, S.; Wesolowski, R. Pexidartinib, a Novel Small Molecule CSF-1R Inhibitor in Use for Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumor: A Systematic Review of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Development. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.C.; Levis, M.J.; Frankfurt, O.; Pagel, J.M.; Roboz, G.J.; Stone, R.M.; Wang, E.S.; Severson, P.L.; West, B.L.; Le, M.H.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of the oral FLT3 inhibitor pexidartinib in relapsed/refractory FLT3-ITD-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavor, S.; Shalit, T.; Ilani, N.C.; Moskovitz, Y.; Livnat, N.; Groner, Y.; Barr, H.; Mark, D.; Minden, M.D.; Plotnikov, A.; et al. Dasatinib response in acute myeloid leukemia is correlated with FLT3/ITD, PTPN11 mutations and a unique gene expression signature. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Pomicter, A.D.; Yan, D.; Eiring, A.M.; Antelope, O.; Schumacher, J.A.; Kelley, T.W.; Tantravahi, S.K.; Kovacsovics, T.J.; Shami, P.J.; et al. Dasatinib overcomes stroma-based resistance to the FLT3 inhibitor quizartinib using multiple mechanisms. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2981–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zillhardt, M.; Park, S.M.; Romero, I.L.; Sawada, K.; Montag, A.; Krausz, T.; Yamada, S.D.; Peter, M.E.; Lengyel, E. Foretinib (GSK1363089), an orally available multi-kinase inhibitor of c-Met and VEGFR-2, blocks proliferation, induces anoikis, and impairs ovarian cancer metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, R.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Deng, T.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Xiao, X.; Wang, S. Foretinib Is Effective in Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Inhibiting FLT3 and Overcoming Secondary Mutations That Drive Resistance to Quizartinib and Gilteritinib. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.G.; Howell, S.B.; Zhang, H.; Rastgoo, N.; Local, A.; Kurtz, S.E.; Lo, P.; Bottomly, D.; Wilmot, B.; McWeeney, S.K.; et al. Luxeptinib (CG-806) Targets FLT3 and Clusters of Kinases Operative in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 1125–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, G.; Zhang, H.; Basyal, M.; Ly, C.; Yuan, B.; Ruvolo, V.; Piya, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Concomitant targeting of FLT3 and BTK overcomes FLT3 inhibitor resistance in acute myeloid leukemia through the inhibition of autophagy. Haematologica 2022, 108, 1500–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, A.; Yu, K.; Qi, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.; Wu, H.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Discovery of (R)-1-(3-(4-Amino-3-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-1H-pyrazolo [3,4-d] pyrimidin–1-yl) piperidin-1-yl)-2-(dimethylamino)ethanone (CHMFL-FLT3-122) as a Potent and Orally Available FLT3 Kinase Inhibitor for FLT3-ITD Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9625–9638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hu, C.; Chen, C.; Liang, X.; Wang, B.; Zou, F.; Yu, K.; Li, F.; Liu, Q.; Qi, Z.; et al. Selectively targeting FLT3-ITD mutants over FLT3-wt by a novel inhibitor for acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 106, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Ren, P.; Adrian, F.; Sun, F.; Lee, H.S.; Wang, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. A type-II kinase inhibitor capable of inhibiting the T315I “gatekeeper” mutant of Bcr-Abl. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5439–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Cai, M.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Shan, H. GNF-7, a novel FLT3 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance for the treatment of FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Xie, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Ren, R. A dual inhibitor overcomes drug-resistant FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, A.; Faisal, A.; Bavetsias, V.; Castro, D.G.; Sun, C.; Atrash, B.; Valenti, M.; Brandon, A.H.; Avery, S.; Pearson, A.; et al. The dual FLT3-Aurora inhibitor CCT241736 overcomes resistance to selective FLT3 inhibition driven by FLT3 ligand and FLT3 point mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10 (Suppl. S11), B74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Fang, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bu, Z.; Liu, M.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; et al. Wu-5, a novel USP10 inhibitor, enhances crenolanib-induced FLT3-ITD-positive AML cell death via inhibiting FLT3 and AMPK pathways. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 42, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Eisenman, K.M.; Sather, S.; McGranahan, A.; Armistead, P.M.; McGary, C.S.; Hunsucker, S.A.; Schlegel, J.; Martinson, H.; Cannon, C.; et al. Aberrant Mer receptor tyrosine kinase expression contributes to leukemogenesis in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5359–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minson, K.A.; Smith, C.C.; DeRyckere, D.; Libbrecht, C.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Huey, M.G.; Lasater, E.A.; Kirkpatrick, G.D.; Stashko, M.A.; Zhang, W.; et al. The MERTK/FLT3 inhibitor MRX-2843 overcomes resistance-conferring FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.-K. Counter-Therapeutic Strategies for Resistance of FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells 2025, 14, 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191526
Song M-K. Counter-Therapeutic Strategies for Resistance of FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells. 2025; 14(19):1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191526
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Moo-Kon. 2025. "Counter-Therapeutic Strategies for Resistance of FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia" Cells 14, no. 19: 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191526
APA StyleSong, M.-K. (2025). Counter-Therapeutic Strategies for Resistance of FLT3 Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cells, 14(19), 1526. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191526





