Krüppel-like Factors in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Abstract
Highlights
- The Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) occupy nodal positions at the intersection of transcriptional regulation, metabolism, stress response, and cell fate determination in both normal gastrointestinal (GI) physiology and disease
- The functions of the KLFs within the GI tract are highly context-dependent.
- Understanding specific KLF functions in the GI tract is essential.
- The KLFs can potentially be targeted for GI diseases.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Expression of KLFs in Gastrointestinal Tract
3. KLFs in Gastrointestinal Inflammation and Injury
4. KLFs in Gastrointestinal Cancer
5. KLFs in Esophagus
5.1. Squamous Epithelium
5.2. Barrett’s Esophagus
6. KLFs in Stomach
7. KLFs in Intestine
8. KLFs in Pancreas and Liver
8.1. Pancreas
8.2. Liver
9. KLFs in Signaling Pathways of the Gastrointestinal Tract
9.1. PI3K/AKT Signaling
9.2. NF-kB Signaling
9.3. Wnt Signaling
9.4. Notch Signaling
9.5. MAPK Signaling
9.6. TGFβ Signaling
10. Current Advancements and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bieker, J.J. Krüppel-like factors: Three fingers in many pies. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 34355–34358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, B.B.; Yang, V.W. Mammalian Kruppel-like factors in health and diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1337–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetreault, M.P.; Yang, Y.; Katz, J.P. Krüppel-like factors in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, N.M.; Hoffman, M.; Goldberg, I.J.; Drosatos, K. Krüppel-like factors: Crippling and un-crippling metabolic pathways. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, R.A.; Ekwall, K. Sin3: A flexible regulator of global gene expression and genome stability. Curr. Genet. 2005, 47, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presnell, J.S.; Schnitzler, C.E.; Browne, W.E. KLF/SP Transcription Factor Family Evolution: Expansion, Diversification, and Innovation in Eukaryotes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 2289–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, M.J.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, L. Krupsilonppel-like factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Bhargava, D.; Chen, X.; Zhou, T.; Dursuk, G.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Zong, Z.; Katz, S.I.; Lomberk, G.A.; et al. KLF5 and p53 comprise an incoherent feed-forward loop directing cell-fate decisions following stress. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomberk, G.; Urrutia, R. The family feud: Turning off Sp1 by Sp1-like KLF proteins. Biochem. J. 2005, 392, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-K.; He, P.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. SP and KLF Transcription Factors in Digestive Physiology and Diseases. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1845–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Nino, W.R.; Zazueta, C. New insights of Kruppel-like transcription factors in adipogenesis and the role of their regulatory neighbors. Life Sci 2021, 265, 118763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, B.B.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Nandan, M.O.; Yang, V.W. The diverse functions of Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5 in epithelial biology and pathobiology. Bioessays 2007, 29, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Yang, J.W.; Yang, V.W.; Bialkowska, A.B. Krüppel-like Factor 5, Increased in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma, Promotes Proliferation, Acinar-to-Ductal Metaplasia, Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia, and Tumor Growth in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1494–1508.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Jia, Z.; Gagea, M.; Li, Z.; Zuo, X.; Kong, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, K. KLF4 Is Essential for Induction of Cellular Identity Change and Acinar-to-Ductal Reprogramming during Early Pancreatic Carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinn, J.; Hallou, A.; Han, S.; Krizic, K.; Ulyanchenko, S.; Iglesias-Bartolome, R.; England, F.J.; Verstreken, C.; Chalut, K.J.; Jensen, K.B.; et al. A biomechanical switch regulates the transition towards homeostasis in oesophageal epithelium. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, J.; Opitz, O.G.; Nakagawa, H.; Jenkins, T.D.; Friedman, S.L.; Rustgi, A.K. The Krüppel-like transcriptional factors Zf9 and GKLF coactivate the human keratin 4 promoter and physically interact. FEBS Lett. 2000, 473, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, M.P.; Yang, Y.; Travis, J.; Yu, Q.C.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Tobias, J.W.; Katz, J.P. Esophageal squamous cell dysplasia and delayed differentiation with deletion of krüppel-like factor 4 in murine esophagus. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 171–181.e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Lin, T.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, M.; Napier, D.L.; et al. KLF4 deletion alters gastric cell lineage and induces MUC2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Kong, X.; Li, Q.; Guo, K.; Tan, D.; Le, X.; Wei, D.; Huang, S.; et al. Disruption of Klf4 in villin-positive gastric progenitor cells promotes formation and progression of tumors of the antrum in mice. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.P.; Perreault, N.; Goldstein, B.G.; Actman, L.; McNally, S.R.; Silberg, D.G.; Furth, E.E.; Kaestner, K.H. Loss of Klf4 in mice causes altered proliferation and differentiation and precancerous changes in the adult stomach. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flandez, M.; Guilmeau, S.; Blache, P.; Augenlicht, L.H. KLF4 regulation in intestinal epithelial cell maturation. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, T.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. KLF4 Regulates Goblet Cell Differentiation in BMI1(+) Reserve Intestinal Stem Cell Lineage during Homeostasis. Int. J. Stem. Cells 2020, 13, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; McConnell, B.B.; Kaestner, K.H.; Yang, V.W. Altered intestinal epithelial homeostasis in mice with intestine-specific deletion of the Krüppel-like factor 4 gene. Dev. Biol. 2011, 349, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacher, E.; Tsai, C.; Litichevskiy, L.; Shipony, Z.; Iweka, C.A.; Schneider, K.M.; Chuluun, B.; Heller, H.C.; Menon, V.; Thaiss, C.A.; et al. Aging disrupts circadian gene regulation and function in macrophages. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.K.; Saxena, M.; Maharjan, K.; Song, J.J.; Shroyer, K.R.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like Factor 5 Regulates Stemness, Lineage Specification, and Regeneration of Intestinal Epithelial Stem Cells. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 9, 587–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, T.; Ogawa, S.; Manabe, I.; Tanaka, M.; Sanada, M.; Sato, T.; Taketo, M.M.; Nakao, K.; Clevers, H.; Fukayama, M.; et al. KLF5 regulates the integrity and oncogenicity of intestinal stem cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2882–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, M.O.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like factor 5 is essential for proliferation and survival of mouse intestinal epithelial stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 14, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A.; Wan Mohamad Nazarie, W.F.; Low, T.Y. Two Sides of the Same Coin: The Roles of KLF6 in Physiology and Pathophysiology. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miele, L.; Beale, G.; Patman, G.; Nobili, V.; Leathart, J.; Grieco, A.; Abate, M.; Friedman, S.L.; Narla, G.; Bugianesi, E.; et al. The Kruppel-like factor 6 genotype is associated with fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 282–291.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.-W.; Bernstein, D.E. Risk Factors for the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, Including Genetics. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, W.A.; Omenetti, S.; Date, D.; Di Martino, L.; De Salvo, C.; Kim, G.D.; Chowdhry, S.; Bamias, G.; Cominelli, F.; Pizarro, T.T.; et al. KLF6 contributes to myeloid cell plasticity in the pathogenesis of intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydor, S.; Manka, P.; Best, J.; Jafoui, S.; Sowa, J.P.; Zoubek, M.E.; Hernandez-Gea, V.; Cubero, F.J.; Kälsch, J.; Vetter, D.; et al. Krüppel-like factor 6 is a transcriptional activator of autophagy in acute liver injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarrizzo, M.; LaComb, J.F.; Bialkowska, A.B. The Role of Krüppel-like Factors in Pancreatic Physiology and Pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakis, K.A.; Krempski, J.; Svingen, P.; Xiong, Y.; Sarmento, O.F.; Lomberk, G.A.; Urrutia, R.A.; Faubion, W.A. Krüppel-like factor KLF10 deficiency predisposes to colitis through colonic macrophage dysregulation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G900–G909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Sun, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ng, M.; Liu, Z.; He, L.; et al. MAP3K2-regulated intestinal stromal cells define a distinct stem cell niche. Nature 2021, 592, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittner, J.; Schulz, S.R.; Steinmetz, T.D.; Berges, J.; Hauke, M.; Channell, W.M.; Cunningham, A.F.; Hauser, A.E.; Hutloff, A.; Mielenz, D.; et al. Krüppel-like factor 2 controls IgA plasma cell compartmentalization and IgA responses. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmen, F.A.; Xiao, R.; Velarde, M.C.; Nicholson, R.D.; Bowman, M.T.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y.; Oh, S.P.; Simmen, R.C. Dysregulation of intestinal crypt cell proliferation and villus cell migration in mice lacking Kruppel-like factor 9. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1757–G1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhang, R.; Jain, R.; Shi, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, G.; Sangwung, P.; Tugal, D.; Atkins, G.B.; Prosdocimo, D.A.; et al. Circadian control of bile acid synthesis by a KLF15-Fgf15 axis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bakheet, R.; Parhar, R.S.; Huang, C.H.; Hussain, M.M.; Pan, X.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Hashmi, S. Regulation of fat storage and reproduction by Krüppel-like transcription factor KLF3 and fat-associated genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 411, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, J.; Parhar, R.S.; Huang, C.H.; Brey, C.; Gaugler, R. A Krüppel-like factor in Caenorhabditis elegans with essential roles in fat regulation, cell death, and phagocytosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2008, 27, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrano, A.C.; Dillin, A.; Hunter, T. A Krüppel-like factor downstream of the E3 ligase WWP-1 mediates dietary-restriction-induced longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Guarino, M.; Hernández-Bule, M.L.; Bacci, S. Cellular and Molecular Processes in Wound Healing. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.M.; Barreda, D.R. Acute Inflammation in Tissue Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eming, S.A.; Krieg, T.; Davidson, J.M. Inflammation in Wound Repair: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.; Bhagat, S.; Paul, S.; Katz, J.P.; Sengupta, D.; Bhargava, D. Neutrophils in Cancer and Potential Therapeutic Strategies Using Neutrophil-Derived Exosomes. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpaev, K.T. Transcription Factor KLF2 and Its Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Processes. Biochemistry 2020, 85, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, R.J.; Boon, R.A.; Rondaij, M.G.; Kragt, A.; Volger, O.L.; Elderkamp, Y.W.; Meijers, J.C.; Voorberg, J.; Pannekoek, H.; Horrevoets, A.J. KLF2 provokes a gene expression pattern that establishes functional quiescent differentiation of the endothelium. Blood 2006, 107, 4354–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Watanabe, I.; Chang, E.; Vinayachandran, V.; Nayak, L.; Lapping, S.; Liao, S.; Madera, A.; et al. KLF2 regulates neutrophil activation and thrombosis in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e147191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.M.; Nambudiri, V.; Dai, G.; Larman, H.B.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Garcia-Cardena, G. Statins exert endothelial atheroprotective effects via the KLF2 transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26714–26719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen-Banerjee, S.; Mir, S.; Lin, Z.; Hamik, A.; Atkins, G.B.; Das, H.; Banerjee, P.; Kumar, A.; Jain, M.K. Kruppel-like factor 2 as a novel mediator of statin effects in endothelial cells. Circulation 2005, 112, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, M.W.; Cao, Z.; Wara, A.K.; Lebedeva, M.A.; Senbanerjee, S.; Jain, M.K. Kruppel-like factor 4 is a mediator of proinflammatory signaling in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 38247–38258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, M.P.; Wang, M.L.; Yang, Y.; Travis, J.; Yu, Q.C.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Katz, J.P. Klf4 overexpression activates epithelial cytokines and inflammation-mediated esophageal squamous cell cancer in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 2124–2134.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Laroui, H.; Merlin, D.; Yang, V.W. Genetic deletion of Klf4 in the mouse intestinal epithelium ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis by modulating the NF-kappaB pathway inflammatory response. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Smith, R.S., Jr.; Hsu, Y.T.; Chao, L.; Chao, J. Kruppel-like factor 4 is a novel mediator of Kallistatin in inhibiting endothelial inflammation via increased endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35471–35478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.O.; Doty, R.T.; Hicks, J.S.; Willerford, D.M. Regulation of T-cell receptor D beta 1 promoter by KLF5 through reiterated GC-rich motifs. Blood 2003, 101, 4492–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Ren, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, K.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Tang, H.; Deng, Q.; et al. FBW7 regulates endothelial functions by targeting KLF2 for ubiquitination and degradation. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Li, A.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T.; Shen, Q.; Cui, Q.; Qin, X. Key role of microRNA-15a in the KLF4 suppressions of proliferation and angiogenesis in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, A.T.; Tian, H.; Anih, E.; Recio, F.O., 3rd; Shatat, M.A.; Johnson, T.; Liao, X.; Ramirez-Bergeron, D.L.; Proweller, A.; Ishikawa, M.; et al. Endothelial Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates angiogenesis and the Notch signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12016–12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Du, C.; Shi, Q.; Xu, S.; Jia, J.; Tang, X.; Li, F.; et al. Beyond proliferation: KLF5 promotes angiogenesis of bladder cancer through directly regulating VEGFA transcription. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 43791–43805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, S.; Tan, Y.; He, P.; Xu, J.; Proud, C.G.; et al. Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase promotes angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via PI3K/Akt and STAT3. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shi, Y.; Wen, Y.; Li, W.; Feng, J.; Chen, C. The roles of TNFAIP2 in cancers and infectious diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5188–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.; Shi, Y.; Dong, W.; Liu, C.; Schmidt, T.J.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M.; Fan, D.; Ai, W. Kruppel-like factor KLF4 facilitates cutaneous wound healing by promoting fibrocyte generation from myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranjapye, A.; NandyMazumdar, M.; Browne, J.A.; Leir, S.H.; Harris, A. Kruppel-like factor 5 regulates wound repair and the innate immune response in human airway epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Nandan, M.O.; Chanchevalap, S.; Dalton, W.B.; Hisamuddin, I.M.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like factors 4 and 5: The yin and yang regulators of cellular proliferation. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinke, J.M.; Sorg, H. Wound repair and regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuce, K.; Ozkan, A.I. The kruppel-like factor (KLF) family, diseases, and physiological events. Gene 2024, 895, 148027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, J.; Takeuchi, Y.; Kanazawa, S.; Nomir, A.G.; Kito, A.; Elkhashab, E.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Yang, V.W.; Akiyama, S.; Morisaki, I.; et al. Kruppel-like factor 4 regulates matrix metalloproteinase and aggrecanase gene expression in chondrocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 370, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.; Lee, W.K. KLF10 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene and Its TGF-beta Signaling. Cancers 2018, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bailey, D.; Yang, P.; Kim, E.; Que, J. The development and stem cells of the esophagus. Development 2021, 148, dev193839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, C.H.; Iyer, P.G.; Vela, M.F.; Katzka, D.A. The Esophageal Epithelial Barrier in Health and Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Q.; Deng, M.; Xue, N.N.; Li, T.X.; Guo, Y.X.; Gao, L.; Zhao, D.; Fan, R.T. lncRNA KLF3-AS1 Suppresses Cell Migration and Invasion in ESCC by Impairing miR-185-5p-Targeted KLF3 Inhibition. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, B.G.; Chao, H.H.; Yang, Y.; Yermolina, Y.A.; Tobias, J.W.; Katz, J.P. Overexpression of Kruppel-like factor 5 in esophageal epithelia in vivo leads to increased proliferation in basal but not suprabasal cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1784–G1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, M.P.; Weinblatt, D.; Shaverdashvili, K.; Yang, Y.; Katz, J.P. KLF4 transcriptionally activates non-canonical WNT5A to control epithelial stratification. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaverdashvili, K.; Padlo, J.; Weinblatt, D.; Jia, Y.; Jiang, W.; Rao, D.; Laczkó, D.; Whelan, K.A.; Lynch, J.P.; Muir, A.B.; et al. KLF4 activates NFκB signaling and esophageal epithelial inflammation via the Rho-related GTP-binding protein RHOF. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Katz, J.P. KLF4 is downregulated but not mutated during human esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis and has tumor stage-specific functions. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, D.; Rusakow, D.; Zheng, W.; Awad, S.; Katz, J.P. KLF5 inhibition initiates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-transformed human squamous epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Tetreault, M.P.; Billig, J.; Victor, N.; Goyal, A.; Sepulveda, A.R.; Katz, J.P. Loss of transcription factor KLF5 in the context of p53 ablation drives invasive progression of human squamous cell cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6475–6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tetreault, M.P.; Yermolina, Y.A.; Goldstein, B.G.; Katz, J.P. Krüppel-like factor 5 controls keratinocyte migration via the integrin-linked kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18812–18820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yan, X. Current knowledge of Kruppel-like factor 5 and vascular remodeling: Providing insights for therapeutic strategies. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 13, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tarapore, R.S.; Jarmel, M.H.; Tetreault, M.P.; Katz, J.P. p53 mutation alters the effect of the esophageal tumor suppressor KLF5 on keratinocyte proliferation. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 4033–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Ying, K.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Ji, M.; Sun, Y. NEDD4L affects KLF5 stability through ubiquitination to control ferroptosis and radiotherapy resistance in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarapore, R.S.; Yang, Y.; Katz, J.P. Restoring KLF5 in esophageal squamous cell cancer cells activates the JNK pathway leading to apoptosis and reduced cell survival. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Gopalan, V.; Law, S.; Tang, J.C.; Chan, K.W.; Lam, A.K. MiR-498 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Clinicopathological impacts and functional interactions. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 62, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Du, S.; Gao, S.; Lu, L. MiR-4262 inhibits the development of esophageal cancer by negatively regulating KLF6 level. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2020, 115, 104476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Yao, F.; Chen, L.; Lu, C.; Ni, Y.; Fang, W.; Jin, H. Krüppel-like factor 9 was down-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and negatively regulated beta-catenin/TCF signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Gu, J.; Yao, X.; Sun, X. Hypoxic tumour cell-derived exosomal miR-340-5p promotes radioresistance of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma via KLF10. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Xue, L.; Tian, X.; Deng, H.; Xue, Q.; Gao, S.; Gao, Y.; et al. KLF12 interacts with TRIM27 to affect cisplatin resistance and cancer metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating L1CAM expression. Drug Resist. Updates 2024, 76, 101096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, B.; Cui, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Kong, L.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, S. KLF13 promotes esophageal cancer progression and regulates triacylglyceride and free fatty acid metabolism through GPIHBP1. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spechler, S.J.; Souza, R.F. Barrett’s esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, C.; Ogden, S.; Britton, E.; Consortium, O.; Ang, Y.; Sharrocks, A.D. Repurposing of KLF5 activates a cell cycle signature during the progression from a precursor state to oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Elife 2020, 9, e57189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazumori, H.; Ishihara, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Amano, Y.; Kinoshita, Y. Roles of Kruppel-like factor 4 in oesophageal epithelial cells in Barrett’s epithelium development. Gut 2011, 60, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttar, N.S.; DeMars, C.J.; Lomberk, G.; Ilyas, S.I.; Bonilla-Velez, J.; Achra, S.; Rashtak, S.; Wang, K.K.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; Urrutia, R. Distinct role of Kruppel-like factor 11 in the regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 11433–11444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Sheta, E.A.; Powell, S.M.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Washington, K.; Goldknopf, I.L.; El-Rifai, W. Alterations in Barrett’s-related adenocarcinomas: A proteomic approach. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, J.C.; Shivdasani, R.A. Gastric epithelial stem cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenring, J.R.; Mills, J.C. Cellular Plasticity, Reprogramming, and Regeneration: Metaplasia in the Stomach and Beyond. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, I.; Nagata, T.; Sekine, S.; Moriyama, M.; Shibuya, K.; Hojo, S.; Matsui, K.; Yoshioka, I.; Okumura, T.; Hori, T.; et al. Prognostic significance of KLF4 expression in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Gong, W.; Kanai, M.; Schlunk, C.; Wang, L.; Yao, J.C.; Wu, T.T.; Huang, S.; Xie, K. Drastic down-regulation of Krüppel-like factor 4 expression is critical in human gastric cancer development and progression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, L.S.; Chan, C.P.; Chen, C.J.; Lin, S.H.; Lai, M.T.; Hsu, J.D.; Yeh, K.T.; Soon, M.S. Decreased Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) expression may correlate with poor survival in gastric adenocarcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Gao, S.; Song, D.; Feng, Y. MiR-135b-5p promotes viability, proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4). Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 16, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noto, J.M.; Khizanishvili, T.; Chaturvedi, R.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Delgado, A.G.; Khurana, S.S.; Sierra, J.C.; Krishna, U.S.; Suarez, G.; et al. Helicobacter pylori promotes the expression of Krüppel-like factor 5, a mediator of carcinogenesis, in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H.; Hou, X.; Su, Q.; He, Y.; Yang, D. KLF5 Is Activated by Gene Amplification in Gastric Cancer and Is Essential for Gastric Cell Proliferation. Cells 2021, 10, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Goldstein, B.G.; Chao, H.H.; Katz, J.P. KLF4 and KLF5 regulate proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in esophageal cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 1216–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Qian, X.K.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, X.G.; Shi, X.J.; Gao, Y.S. KLF5 promotes proliferation in gastric cancer via regulating p21 and CDK4. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 4224–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Chen, Q.H.; Jian, R.; Zhou, J.R.; Xu, Y.; Lu, F.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, H. The Partial Role of KLF4 and KLF5 in Gastrointestinal Tumors. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 2425356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangodkar, J.; Shi, J.; DiFeo, A.; Schwartz, R.; Bromberg, R.; Choudhri, A.; McClinch, K.; Hatami, R.; Scheer, E.; Kremer-Tal, S.; et al. Functional role of the KLF6 tumour suppressor gene in gastric cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tan, X.P.; Yuan, Y.S.; Hu, C.M.; He, C.H.; Wang, W.Z.; Li, J.C.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, N.Z. Decreased expression of KLF6 and its significance in gastric carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2010, 27, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.P.; Tian, Y.F.; Lin, C.C.; Hung, S.T.; Uen, Y.H.; Hseu, Y.C.; Chou, C.L.; Cheng, L.C.; Wang, W.C.; Kuang, Y.Y.; et al. A novel mechanism driving poor-prognostic gastric cancer: Overexpression of the transcription factor Kruppel-like factor 16 promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer through regulating the Notch pathway. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 2717–2735. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Hu, S.J.; Liu, J.F.; Ma, M.J.; Du, L.M.; Bai, F.H. Kruppel-Like Factor 2 Is a Gastric Cancer Suppressor and Prognostic Biomarker. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2023, 2023, 2360149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, Y.; Kan, W.; Li, F.; Ji, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. microRNA-32-5p targets KLF2 to promote gastric cancer by activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 4895–4908. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; He, H.; Qiu, F.; Qian, H. Expression and Prognosis Value of the KLF Family Members in Colorectal Cancer. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 6571272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Tan, B.; An, Z. Kruppel-like factor 1 serves as a facilitator in gastric cancer progression via activating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2021, 68, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, F. KLF3 Transcription Activates WNT1 and Promotes the Growth and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via Activation of the WNT/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Lab. Investig. 2023, 103, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Ramnarayanan, K.; Sundar, R.; Padmanabhan, N.; Srivastava, S.; Koiwa, M.; Yasuda, T.; Koh, V.; Huang, K.K.; Tay, S.T.; et al. Single-Cell Atlas of Lineage States, Tumor Microenvironment, and Subtype-Specific Expression Programs in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 670–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yu, T.; Fan, Z.; Yang, H.; Lin, X. Krüppel-Like Factor 7 is a Marker of Aggressive Gastric Cancer and Poor Prognosis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, H.; Zhou, J.; Qian, P.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H. Krüppel-like factor 8 involved in hypoxia promotes the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer via epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, A.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, J.; Miao, A.; Pan, G. KLF8 is associated with poor prognosis and regulates glycolysis by targeting GLUT4 in gastric cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 5087–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Xie, R.; Liu, C.; Xiao, X.; Wu, K.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. KLF8 involves in TGF-beta-induced EMT and promotes invasion and migration in gastric cancer cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Xiao, X.; Xie, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L. Krüppel-like factor 8 contributes to hypoxia-induced MDR in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z.; Guo, D.; Gu, T.; Wang, B.; Xiao, L.; et al. KLF9 suppresses gastric cancer cell invasion and metastasis through transcriptional inhibition of MMP28. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 7915–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Lin, H.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, H.; Wang, P.; Tan, H.; Fu, Y. Integrative multiomics analysis reveals the subtypes and key mechanisms of platinum resistance in gastric cancer: Identification of KLF9 as a promising therapeutic target. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.M.; Yeh, K.T.; Yeh, C.M.; Soon, M.S.; Hsu, L.S. KLF10 Functions as an Independent Prognosis Factor for Gastric Cancer. Medicina 2022, 58, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.Q.; Tan, B.B.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhao, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Jia, N. KLF11 promotes gastric cancer invasion and migration by increasing Twist1 expression. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Migita, T.; Hosoda, F.; Okada, N.; Gotoh, M.; Arai, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Ohki, M.; Miyata, S.; Takeuchi, K.; et al. Krüppel-like factor 12 plays a significant role in poorly differentiated gastric cancer progression. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Feng, Z.; Yan, R.; Liu, F.; Yin, L.; Shen, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L. Kruppel-like Factors 3 Regulates Migration and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells Through NF-κB Pathway. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2023, 29, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Ma, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; et al. KLF15 Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Gastric Cancer Cells via Up-Regulating CDKN1A/p21 and CDKN1C/p57 Expression. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1518–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalu, S.; Abdelhamid, A.M.; Saber, S.; Elmorsy, E.A.; Hamad, R.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; Yahya, G.; Salama, M.M. Cell cycle machinery in oncology: A comprehensive review of therapeutic targets. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; You, J.; Hong, Q.; Ye, F. Transcription factor KLF15 inhibits the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells via regulating the TFAP2A-AS1/NISCH axis. Biol. Direct 2021, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.J.; Li, Y.; Tan, B.B.; Zhao, Q.; Fan, L.Q.; Zhang, Z.D.; Zhao, X.F.; Li, S.Y. Up-regulation of KLF17 expression increases the sensitivity of gastric cancer to 5-fluorouracil. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2021, 35, 20587384211010925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beumer, J.; Clevers, H. Cell fate specification and differentiation in the adult mammalian intestine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palikuqi, B.; Rispal, J.; Klein, O. Good Neighbors: The Niche that Fine Tunes Mammalian Intestinal Regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2022, 14, a040865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.J.M.; Lo, Y.H.; Mah, A.T.; Kuo, C.J. The Intestinal Stem Cell Niche: Homeostasis and Adaptations. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, B.B.; Kim, S.S.; Yu, K.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Takeda, N.; Manabe, I.; Nusrat, A.; Nagai, R.; Yang, V.W. Krüppel-like factor 5 is important for maintenance of crypt architecture and barrier function in mouse intestine. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1302–1313.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandan, M.O.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Bialkowska, A.B.; McConnell, B.B.; Shroyer, K.R.; Robine, S.; Yang, V.W. Inducible intestine-specific deletion of Krüppel-like factor 5 is characterized by a regenerative response in adult mouse colon. Dev. Biol. 2014, 387, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chidgey, M.; Yang, V.W.; Bialkowska, A.B. Krüppel-like factor 5 is essential for maintenance of barrier function in mouse colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2017, 313, G478–G491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.P.; Perreault, N.; Goldstein, B.G.; Lee, C.S.; Labosky, P.A.; Yang, V.W.; Kaestner, K.H. The zinc-finger transcription factor Klf4 is required for terminal differentiation of goblet cells in the colon. Development 2002, 129, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Chen, X.; Yang, V.W. Kruppel-like factor 4 mediates p53-dependent G1/S cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xie, X.; Yao, J.; Jin, X.; Jiang, H.; Ji, C. Transcription factor Krüppel-like factor 4 upregulated G protein-coupled receptor 30 alleviates intestinal inflammation and apoptosis, and protects intestinal integrity from intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Aggarwal, G.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Nandan, M.O.; Yang, V.W. Notch inhibits expression of the Krüppel-like factor 4 tumor suppressor in the intestinal epithelium. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzi, J.P.; Guo, L.; Chang, S.M.; Cousins, R.J. Krüppel-like factor 4 regulates adaptive expression of the zinc transporter Zip4 in mouse small intestine. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G517–G523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W. Decreased Expression of KLF4 Leading to Functional Deficit in Pediatric Patients with Intestinal Failure and Potential Therapeutic Strategy Using Decanoic Acid. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidling, J.C.; Nabokina, S.M.; Said, H.M. Molecular mechanisms involved in the adaptive regulation of human intestinal biotin uptake: A study of the hSMVT system. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G275–G281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; McConnell, B.B.; Nandan, M.O.; Katz, J.P.; Kaestner, K.H.; Yang, V.W. Haploinsufficiency of Krüppel-like factor 4 promotes adenomatous polyposis coli dependent intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7147–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yue, H.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; Shen, K.; Yang, K.; Leng, X.; et al. Downregulated KLF4, induced by m6A modification, aggravates intestinal barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.M.; Elkarim, E.A.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. KLF4 Suppresses Tumor Formation in Genetic and Pharmacological Mouse Models of Colonic Tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, D.T.; Chen, X.; Feng, J.; Torbenson, M.; Dang, L.H.; Yang, V.W. Overexpression of Krüppel-like factor 4 in the human colon cancer cell line RKO leads to reduced tumorigenecity. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3424–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lan, X.; Song, F.; Sun, J.; Zhou, K.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-25-3p promotes pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, J.; Chu, T.H.; Liu, Y.; Kim, J.; Ruiz de Sabando, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Zee, S.Y.; Sheridan, B.S.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. KLF5 protects the intestinal epithelium against Th17 immune response in a murine colitis model. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e153488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetreault, M.P.; Alrabaa, R.; McGeehan, M.; Katz, J.P. Krüppel-like factor 5 protects against murine colitis and activates JAK-STAT signaling in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Kweon, S.S.; Tanikawa, C.; Jia, W.H.; Xiang, Y.B.; Cai, Q.; Zeng, C.; Schmit, S.L.; Shin, A.; Matsuo, K.; et al. Large-Scale Genome-Wide Association Study of East Asians Identifies Loci Associated With Risk for Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1455–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialkowska, A.B.; Liu, Y.; Nandan, M.O.; Yang, V.W. A Colon Cancer-derived Mutant of Kruppel-like Factor 5 (KLF5) Is Resistant to Degradation by Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β (GSK3β) and the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase F-box and WD Repeat Domain-containing 7α (FBW7α) *. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5997–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, M.O.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Yang, V.W. KLF5 mediates the hyper-proliferative phenotype of the intestinal epithelium in mice with intestine-specific endogenous K-Ras(G12D) expression. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, M.; Wu, F.; Li, G. Ketogenesis attenuated KLF5 disrupts iron homeostasis via LIF to confer oxaliplatin vulnerability in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Gao, H.; Feng, W.; Li, W.; Miao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zong, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. KLF5 inhibition overcomes oxaliplatin resistance in patient-derived colorectal cancer organoids by restoring apoptotic response. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhou, Y.; Li, C.; Rychahou, P.; Zhang, S.; Titlow, W.B.; Bauman, G.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Ketogenesis Attenuates KLF5-Dependent Production of CXCL12 to Overcome the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Sun, D.; Han, Q.; Yan, H.; Dai, G. microRNA-425 promoted the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells by targeting KLF3 through the PI3K/AKT pathway. Minerva Med. 2021, 112, 537–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fesneau, O.; Thevin, V.; Pinet, V.; Goldsmith, C.; Vieille, B.; M’Homa Soudja, S.; Lattanzio, R.; Hahne, M.; Dardalhon, V.; Hernandez-Vargas, H.; et al. An intestinal T(H)17 cell-derived subset can initiate cancer. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 1637–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Han, J.; Tian, Z.; Meng, Q.; Niu, W. KLF7 enhances the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer cells via the miR-139-5p/TPD52 axis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2024, 25, 2385172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Li, K.; Qiao, S.; Li, M.; Mei, Y.; Ding, L.; Lv, Q.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. KLF7 promotes colon adenocarcinoma progression through the PDGFB signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, M.; Shi, X.; Zhao, J.; Nan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. KLF8 promotes tumorigenesis, invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by transcriptional activation of FHL2. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25402–25417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Simmen, R.C.; Raj, V.R.; Van, T.T.; MacLeod, S.L.; Simmen, F.A. Krüppel-like factor 9 (KLF9) prevents colorectal cancer through inhibition of interferon-related signaling. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Lü, B.; Xu, J.; Hu, H.; Lai, M. Downregulation of Krüppel-like factor 9 in human colorectal cancer. Pathol. Int. 2008, 58, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Bile Acids as Hormones: The FXR-FGF15/19 Pathway. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Du, C.Y.; Sheng, S.F.; Wang, W.; Fan, Y.T.; et al. Transcription factor Klf9 controls bile acid reabsorption and enterohepatic circulation in mice via promoting intestinal Asbt expression. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2362–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Wei, F.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, F.; Huang, F.; Qian, L. Correction: KLF12 as a potential biomarker for lateral pelvic lymph node metastases in advanced rectal cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2025, 74, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Sun, L.; Shan, P.; Zhang, X.; Huan, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, T.; Wei, T.; Zhang, X.; et al. Loss of KLF14 triggers centrosome amplification and tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Fan, Q.; Dong, H.; Ye, F.; Li, J.; Zhu, X. The KLF14 Transcription Factor Regulates Glycolysis by Downregulating LDHB in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerra, V.G.; Drosatos, K. Specificity Proteins (SP) and Krüppel-like Factors (KLF) in Liver Physiology and Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, P.N.; Fan, L.; Sweet, D.R.; Jain, M.K. The Krüppel-Like Factors and Control of Energy Homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 2019, 40, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Fang, H.; Du, Y.; Liang, Y. KLF15 transcriptionally activates LINC00689 to inhibit colorectal cancer development. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.D.; Xu, S.D.; Hao, S.H.; Han, K.; Chen, J.W.; Ling, H.; Chen, R.X.; Jin, X.H.; Cao, J.H.; Lin, J.L.; et al. KLF16 enhances stress tolerance of colorectal carcinomas by modulating nucleolar homeostasis and translational reprogramming. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2828–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.L.; Zhou, N.; Sun, Z.; Dou, X.L.; Guan, M.; Bai, C.M. KLF17 Expression in Colorectal Carcinoma and Its Clinical Significance. Acta Acad. Med. Sin. 2016, 38, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Shen, T.Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, Z.; Qin, H.; Wang, F. Clinical significance and biological role of KLF17 as a tumour suppressor in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 2117–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Luo, M.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D. Anti-oncogenic mechanism of KLF17 in colon cancer by repressing cell migration and invasion via FHL1 upregulation. Chin. J. Physiol. 2023, 66, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lin, F.; Zhang, P.; Ni, W.; Bi, L.; Wu, J.; Jiang, L. Thioredoxin-1 inhibitor, 1-methylpropyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide, inhibits the growth, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyeva, L.G.; Chernov, I.P.; Zinovyeva, M.V.; Kopantzev, E.P.; Sverdlov, E.D. Expression of master regulatory genes of embryonic development in pancreatic tumors. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 475, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumayne, C.; Tarussio, D.; Sanchez-Archidona, A.R.; Picard, A.; Basco, D.; Berney, X.P.; Ibberson, M.; Thorens, B. Klf6 protects β-cells against insulin resistance-induced dedifferentiation. Mol. Metab. 2020, 35, 100958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhuang, R.; Song, L.; Chang, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, J.; Xu, X.; et al. METRNL represses beta-to-alpha cell trans-differentiation to maintain beta cell function under diabetic metabolic stress in mice. Diabetologia 2025, 68, 1769–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, F.C.; Gu, F.M.; Yuan, S.X.; Huang, J.; Pan, Z.Y.; Wang, W.J. Circulating Tumor Cells Expressing Krüppel-Like Factor 8 and Vimentin as Predictors of Poor Prognosis in Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Cancer Control 2021, 28, 10732748211027163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.J.; Wu, W.C.; Chang, H.W.; Lai, Y.T.; Lin, C.H.; Yu, W.C.; Chang, V.H. KLF10 affects pancreatic function via the SEI-1/p21Cip1 pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 60, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Zapico, M.E.; van Velkinburgh, J.C.; Gutiérrez-Aguilar, R.; Neve, B.; Froguel, P.; Urrutia, R.; Stein, R. MODY7 gene, KLF11, is a novel p300-dependent regulator of Pdx-1 (MODY4) transcription in pancreatic islet beta cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 36482–36490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.K.; Subramaniam, M.; Kari, V.; Pitel, K.S.; Baumgart, S.J.; Naylor, R.M.; Nagarajan, S.; Wegwitz, F.; Ellenrieder, V.; Hawse, J.R.; et al. Krüppel-like Transcription Factor KLF10 Suppresses TGFβ-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via a Negative Feedback Mechanism. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2387–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berasain, C.; Arechederra, M.; Argemí, J.; Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; Avila, M.A. Loss of liver function in chronic liver disease: An identity crisis. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, C.M.; Downs, K.M.; Bieker, J.J. Erythroid Kruppel-like factor exhibits an early and sequentially localized pattern of expression during mammalian erythroid ontogeny. Dev. Dyn. 1996, 206, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guixé-Muntet, S.; de Mesquita, F.C.; Vila, S.; Hernández-Gea, V.; Peralta, C.; García-Pagán, J.C.; Bosch, J.; Gracia-Sancho, J. Cross-talk between autophagy and KLF2 determines endothelial cell phenotype and microvascular function in acute liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lai, C.H.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Huang, X.; Qi, X.; Wang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Xiaoli, F.; Li, L.; et al. Simvastatin ameliorates total liver ischemia/reperfusion injury via KLF2-mediated mechanism in rats. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavski, Y.; Abel, T.; Hu, J.; Kleinlützum, D.; Buchholz, C.J.; Belz, C.; Augustin, H.G.; Boon, R.A.; Dimmeler, S. Endothelial transcription factor KLF2 negatively regulates liver regeneration via induction of activin A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3993–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Ruan, X.Z.; Lau, C.W.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y. The role of KLF2 in regulating hepatic lipogenesis and blood cholesterol homeostasis via the SCAP/SREBP pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell-Anderson, K.S.; Funnell, A.P.; Williams, H.; Mat Jusoh, H.; Scully, T.; Lim, W.F.; Burdach, J.G.; Mak, K.S.; Knights, A.J.; Hoy, A.J.; et al. Loss of Krüppel-like factor 3 (KLF3/BKLF) leads to upregulation of the insulin-sensitizing factor adipolin (FAM132A/CTRP12/C1qdc2). Diabetes 2013, 62, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sue, N.; Jack, B.H.; Eaton, S.A.; Pearson, R.C.; Funnell, A.P.; Turner, J.; Czolij, R.; Denyer, G.; Bao, S.; Molero-Navajas, J.C.; et al. Targeted disruption of the basic Krüppel-like factor gene (Klf3) reveals a role in adipogenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 3967–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishida, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Hishida-Nozaki, Y.; Shao, C.; Huang, L.; Wang, C.; Shojima, K.; Xue, Y.; Hang, Y.; Shokhirev, M.; et al. In vivo partial cellular reprogramming enhances liver plasticity and regeneration. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Yamada, M.; Kamimoto, K.; Kok, C.Y.; Kaneko, K.; Ema, M.; Miyajima, A.; Itoh, T. The transcription factor Klf5 is essential for intrahepatic biliary epithelial tissue remodeling after cholestatic liver injury. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6214–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, N.; Kubo, A.; Liu, H.; Akita, K.; Laub, F.; Ramirez, F.; Keller, G.; Friedman, S.L. Developmental regulation of yolk sac hematopoiesis by Kruppel-like factor 6. Blood 2006, 107, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Monson, C.; Gao, C.; Gouon-Evans, V.; Matsumoto, N.; Sadler, K.C.; Friedman, S.L. Klf6/copeb is required for hepatic outgrowth in zebrafish and for hepatocyte specification in mouse ES cells. Dev. Biol. 2010, 344, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, D.; He, C.; Yu, Q.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S. KLF6 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, X.; Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, S.; Xie, A.; Shi, J.; et al. Crosstalk between macrophage-derived PGE(2) and tumor UHRF1 drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3776–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.; Duan, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, M.; et al. HMGB1-mediated elevation of KLF7 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through upregulating TLR4 and PTK2. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4042–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaumond, F.; Gréchez-Cassiau, A.; Subramaniam, M.; Brangolo, S.; Peteri-Brünback, B.; Staels, B.; Fiévet, C.; Spelsberg, T.C.; Delaunay, F.; Teboul, M. Kruppel-like factor KLF10 is a link between the circadian clock and metabolism in liver. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 3059–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, T.; Cui, A.; Sun, X.; Fang, W.; Xie, L.; Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Chang, Y. Involvement of KLF11 in hepatic glucose metabolism in mice via suppressing of PEPCK-C expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iizuka, K.; Takeda, J.; Horikawa, Y. Krüppel-like factor-10 is directly regulated by carbohydrate response element-binding protein in rat primary hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Yahagi, N.; Aita, Y.; Murayama, Y.; Sawada, Y.; Piao, X.; Toya, N.; Oya, Y.; Shikama, A.; Takarada, A.; et al. KLF15 Enables Rapid Switching between Lipogenesis and Gluconeogenesis during Fasting. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 2373–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Wang, B.; Orihuela, Y.; Hong, E.G.; Fisch, S.; Haldar, S.; Cline, G.W.; Kim, J.K.; Peroni, O.D.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. Regulation of gluconeogenesis by Krüppel-like factor 15. Cell Metab. 2007, 5, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Nomura, K.; Senga, Y.; Okada, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Okamoto, S.; Minokoshi, Y.; Imamura, M.; Takeda, S.; Hosooka, T.; et al. Hyperglycemia induces skeletal muscle atrophy via a WWP1/KLF15 axis. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Cai, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, D.; Gao, C. The ubiquitination degradation of KLF15 mediated by WSB2 promotes lipogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibiting PDLIM2 expression. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 40, 192–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.S.; Cui, W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development 2016, 143, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, J.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Lu, W.Q. KLF2 inhibits colorectal cancer progression and metastasis by inducing ferroptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2023, 9, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Z.; Ding, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, T. Resveratrol improves uric acid-induced pancreatic beta-cells injury and dysfunction through regulation of miR-126. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cui, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Han, S.; Yang, C.; Yin, H. MiRNA-21-5p induces chicken hepatic lipogenesis by targeting NFIB and KLF3 to suppress the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Anim. Sci. 2024, 102, skae055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Huang, H.J.; Gong, Y.; Yue, S.; Tang, L.M.; Cheng, S.Y. MicroRNA-206 suppresses gastric cancer cell growth and metastasis. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, T.; Dong, T.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X. The transcription factor Kruppel-like factor 5 promotes cell growth and metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT/Snail signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 508, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Qian, J.; Xia, P.; Liu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Yao, X.; Jiao, Q.; Wei, M. Targeting the KLF5/PI3K/AKT axis as a therapeutic strategy to overcome neoadjuvant chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1593639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Li, K.; Hu, B.; Cai, Z.; Li, J.; Tao, H.; Cao, J. Fatty acid binding protein 5 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by degradation of Kruppel-like factor 9 mediated by miR-889-5p via cAMP-response element binding protein. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltimore, D. Discovering NF-kappaB. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2009, 1, a000026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, S.W.; Moerman, A.M.; Mao, X. Molecular mechanisms of cytokine-induced neuroprotection: NFkappaB and neuroplasticity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2005, 11, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, V.; Jacque, E. [The alternative NF-kB activation pathway and cancer: Friend or foe?]. Med. Sci. 2008, 24, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, W.; Ling, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xia, P. Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis via microRNA-1. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Shen, G.; Wang, Y.; Hong, F.; Tang, X.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Elevated Kallistatin promotes the occurrence and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.J.; Zeng, S.; Xie, R.; Hu, C.J.; Wang, S.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Xiao, Y.F.; Yang, S.M. hTERT promotes gastric intestinal metaplasia by upregulating CDX2 via NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 26969–26978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, K.; Wang, D.; Zou, H.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qu, C. TRAF7 enhances ubiquitin-degradation of KLF4 to promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Lett. 2020, 469, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchevalap, S.; Nandan, M.O.; McConnell, B.B.; Charrier, L.; Merlin, D.; Katz, J.P.; Yang, V.W. Kruppel-like factor 5 is an important mediator for lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory response in intestinal epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Jiang, H.; Tan, X.; Lu, J.; Baiyun, R.; Zhang, Z. Activation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway Involving KLF9 Plays a Critical Role in Allicin Resisting Against Arsenic Trioxide-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 176, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Chen, S.L.; Peng, S.L.; Tsai, Y.L.; Chang, Z.M.; Chang, V.H.; Ch’ang, H.J. Upregulating sirtuin 6 ameliorates glycolysis, EMT and distant metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma with kruppel-like factor 10 deficiency. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, R.; Manzoor, M.; Hussain, A. Wnt signaling pathway: A comprehensive review. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Deng, Z.L.; Luo, X.; Song, W.X.; Sharff, K.A.; Tang, N.; Haydon, R.C.; Luu, H.H.; He, T.C. Wnt signaling and human diseases: What are the therapeutic implications? Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, A.D.; Moon, R.T. Wnt and calcium signaling: Beta-catenin-independent pathways. Cell Calcium. 2005, 38, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A. Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway: A brief overview. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2011, 43, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Yuan, L.; Hao, B.; Xiang, J.; Cheng, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, X. KLF3 promotes colorectal cancer growth by activating WNT1. Aging 2024, 16, 2475–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Ye, S.; Ruiz, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ying, Q.L. Klf2 and Tfcp2l1, Two Wnt/beta-Catenin Targets, Act Synergistically to Induce and Maintain Naive Pluripotency. Stem Cell Rep. 2015, 5, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Huang, W.; Hu, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.; Yuan, D.; Li, M. Kruppel-like factor 2 mediated anti-proliferative and anti-metastasis effects of simvastatin in p53 mutant colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 511, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.M.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C. KLF4 interacts with beta-catenin/TCF4 and blocks p300/CBP recruitment by beta-catenin. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 30, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Kato, Y.; Evans, P.M.; Yuan, S.; Yang, J.; Rychahou, P.G.; Yang, V.W.; He, X.; Evers, B.M.; et al. Novel cross talk of Kruppel-like factor 4 and beta-catenin regulates normal intestinal homeostasis and tumor repression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J.; Li, L.F.; Yang, G.D.; Xia, S.S.; Wang, R.; Leng, Z.W.; Liu, Z.L.; Tian, H.P.; He, Y.; Meng, C.Y.; et al. MiR-92a promotes stem cell-like properties by activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101760–101770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, B.B.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Nandan, M.O.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Gordon, F.J.; Yang, V.W. Haploinsufficiency of Kruppel-like factor 5 rescues the tumor-initiating effect of the Apc(Min) mutation in the intestine. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4125–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.; Xiol, J.; Dill, M.T.; Yuan, W.C.; Panero, R.; Roper, J.; Osorio, F.G.; Maglic, D.; Li, Q.; Gurung, B.; et al. Regenerative Reprogramming of the Intestinal Stem Cell State via Hippo Signaling Suppresses Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 590–604.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Qi, T.; Lin, J.; Zhai, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Deng, X. KLF6-mediated recruitment of the p300 complex enhances H3K23su and cooperatively upregulates SEMA3C with FOSL2 to drive 5-FU resistance in colon cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2025, 57, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Cai, S.Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.H.; Lin, C.; Zhai, J.; Wu, M.C.; Shen, F. Kruppel-like factor 8 is a new Wnt/beta-catenin signaling target gene and regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.N.; He, H.G.; Shi, Y.; Cao, J.; Yuan, J.Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Shi, C.F.; Zhu, N.; Wei, Y.P.; Liu, F.; et al. Kruppel-like factor 8 promotes cancer stem cell-like traits in hepatocellular carcinoma through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Fan, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Z. Kruppel-like factor 9 suppressed tumorigenicity of the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by negatively regulating frizzled-5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Ye, C.; Liao, X.; Zhou, F.; Shi, Y.; Zhong, H.; Huang, J. KMT2A maintains stemness of gastric cancer cells through regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling-activated transcriptional factor KLF11. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, S.; Zhu, C.; Chen, S.; Yu, C.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. MicroRNA-137 reduces stemness features of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting KLF12. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Xue, C.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Li, L. Notch signaling pathway in cancer: From mechanistic insights to targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopan, R.; Ilagan, M.X. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: Unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 2009, 137, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Assoro, A.B.; Leon-Ferre, R.; Braune, E.B.; Lendahl, U. Roles of Notch Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrinet, L.; Rodilla, V.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Koch, U.; Espinosa, L.; Kaestner, K.H.; Kopan, R.; Lewis, J.; Radtke, F. Dll1- and dll4-mediated notch signaling are required for homeostasis of intestinal stem cells. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1230–1240.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Pritchard, D.M.; Yang, X.; Bennett, E.; Liu, G.; Liu, C.; Ai, W. KLF4 gene expression is inhibited by the notch signaling pathway that controls goblet cell differentiation in mouse gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 296, G490–G498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, M.E.; Giroux, V.; Natsuizaka, M.; Liu, M.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Stairs, D.B.; Nakagawa, H.; Wang, K.K.; Wang, T.C.; Lynch, J.P.; et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling enhances transdifferentiation of the esophageal squamous epithelium towards a Barrett’s-like metaplasia via KLF4. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3857–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Madrid, P.; Barbachano, A.; Albandea-Rodriguez, D.; Rodriguez-Cobos, J.; Rodriguez-Salas, N.; Prieto, I.; Burgos, A.; Martinez de Villarreal, J.; Real, F.X.; Gonzalez-Sancho, J.M.; et al. Vitamin D opposes multilineage cell differentiation induced by Notch inhibition and BMP4 pathway activation in human colon organoids. Cell Death Dis 2024, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Rauch, J.; Kolch, W. Targeting MAPK Signaling in Cancer: Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Sensitivity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Chen, J.; Quan, M.; Li, Q.; Gao, Y. KLF4-mediated upregulation of CD9 and CD81 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma development via JNK signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, X.; Lv, K.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Luo, X.; Liu, T.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; et al. KLF4 downregulates hTERT expression and telomerase activity to inhibit lung carcinoma growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52870–52887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, L.; Mai, C.; Mu, T.; Zeng, Y. KLF4 down-regulation resulting from TLR4 promotion of ERK1/2 phosphorylation underpins inflammatory response in sepsis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Goldstein, B.G.; Nakagawa, H.; Katz, J.P. Kruppel-like factor 5 activates MEK/ERK signaling via EGFR in primary squamous epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, J.K.; Dong, L.H.; Zheng, B.; Han, M. Kruppel-like factor (KLF) 5 mediates cyclin D1 expression and cell proliferation via interaction with c-Jun in Ang II-induced VSMCs. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, M.O.; McConnell, B.B.; Ghaleb, A.M.; Bialkowska, A.B.; Sheng, H.; Shao, J.; Babbin, B.A.; Robine, S.; Yang, V.W. Kruppel-like factor 5 mediates cellular transformation during oncogenic KRAS-induced intestinal tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, A.; Moser, C.; Lang, S.A.; Hackl, C.; Gottfried, E.; Kreutz, M.; Schlitt, H.J.; Geissler, E.K.; Stoeltzing, O. Up-regulation of Kruppel-like factor 5 in pancreatic cancer is promoted by interleukin-1beta signaling and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zheng, B.; Han, M.; Miao, S.B.; Wen, J.K. Synthetic retinoid Am80 inhibits interaction of KLF5 with RAR alpha through inducing KLF5 dephosphorylation mediated by the PI3K/Akt signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yea, S.; Narla, G.; Zhao, X.; Garg, R.; Tal-Kremer, S.; Hod, E.; Villanueva, A.; Loke, J.; Tarocchi, M.; Akita, K.; et al. Ras promotes growth by alternative splicing-mediated inactivation of the KLF6 tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, U.; Puche, J.E.; Hannivoort, R.; Lang, U.E.; Cohen-Naftaly, M.; Friedman, S.L. Hepatocyte growth factor enhances alternative splicing of the Kruppel-like factor 6 (KLF6) tumor suppressor to promote growth through SRSF1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.L.; Blobe, G.C. Role of transforming growth factor Beta in human cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2078–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, M.A.; Sheppard, D. TGF-beta activation and function in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 51–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. Signaling Receptors for TGF-beta Family Members. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a022053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlle, E.; Massague, J. Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, X.F. Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Baker, D.; Ten Dijke, P. TGF-beta-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.E.; Iyemere, V.P.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4/GKLF) is a target of bone morphogenetic proteins and transforming growth factor beta 1 in the regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11661–11669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yori, J.L.; Johnson, E.; Zhou, G.; Jain, M.K.; Keri, R.A. Kruppel-like factor 4 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulation of E-cadherin gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16854–16863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbalakshmi, A.R.; Sahoo, S.; McMullen, I.; Saxena, A.N.; Venugopal, S.K.; Somarelli, J.A.; Jolly, M.K. KLF4 Induces Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition (MET) by Suppressing Multiple EMT-Inducing Transcription Factors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Xie, L.; Barwick, B.; Fu, C.; Li, X.; Wu, D.; Xia, S.; Chen, J.; et al. Acetylation of KLF5 maintains EMT and tumorigenicity to cause chemoresistant bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, L.; Xia, S.; Kucuk, O.; Deng, X.; Boise, L.H.; Dong, J.T. TGF-beta causes Docetaxel resistance in Prostate Cancer via the induction of Bcl-2 by acetylated KLF5 and Protein Stabilization. Theranostics 2020, 10, 7656–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Miao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, F.; Lv, Z.; Huo, J.; et al. CCL7 and TGF-beta secreted by MSCs play opposite roles in regulating CRC metastasis in a KLF5/CXCL5-dependent manner. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2327–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tong, X.; Li, C.; Jin, E.; Su, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, H.T. Quaking 5 suppresses TGF-beta-induced EMT and cell invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e52079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.D.; Xie, W.; Song, W.; Ma, Y.Y.; Liu, G.; Liang, M.L.; Da, X.W.; Yao, G.Q.; Zhang, B.X.; Gao, C.J.; et al. Platelet releasates promote the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by suppressing the expression of KLF6. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Wu, X. Targeting Transcription Factors in Cancer: From “Undruggable” to “Druggable”. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2594, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz de Sabando, A.; Wang, C.; He, Y.; García-Barros, M.; Kim, J.; Shroyer, K.R.; Bannister, T.D.; Yang, V.W.; Bialkowska, A.B. ML264, A Novel Small-Molecule Compound That Potently Inhibits Growth of Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangodkar, J.; Dhawan, N.S.; Melville, H.; Singh, V.J.; Yuan, E.; Rana, H.; Izadmehr, S.; Farrington, C.; Mazhar, S.; Katz, S.; et al. Targeting the FOXO1/KLF6 axis regulates EGFR signaling and treatment response. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Békés, M.; Langley, D.R.; Crews, C.M. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
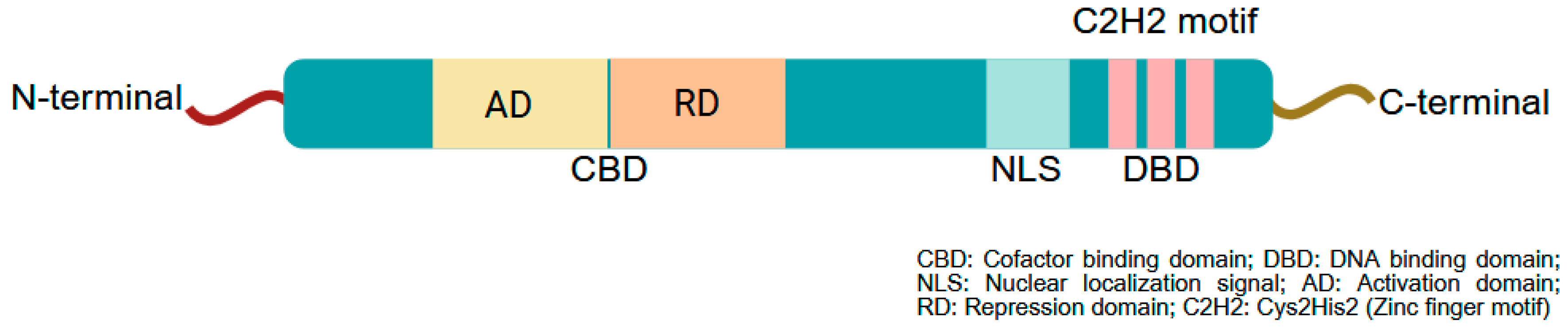
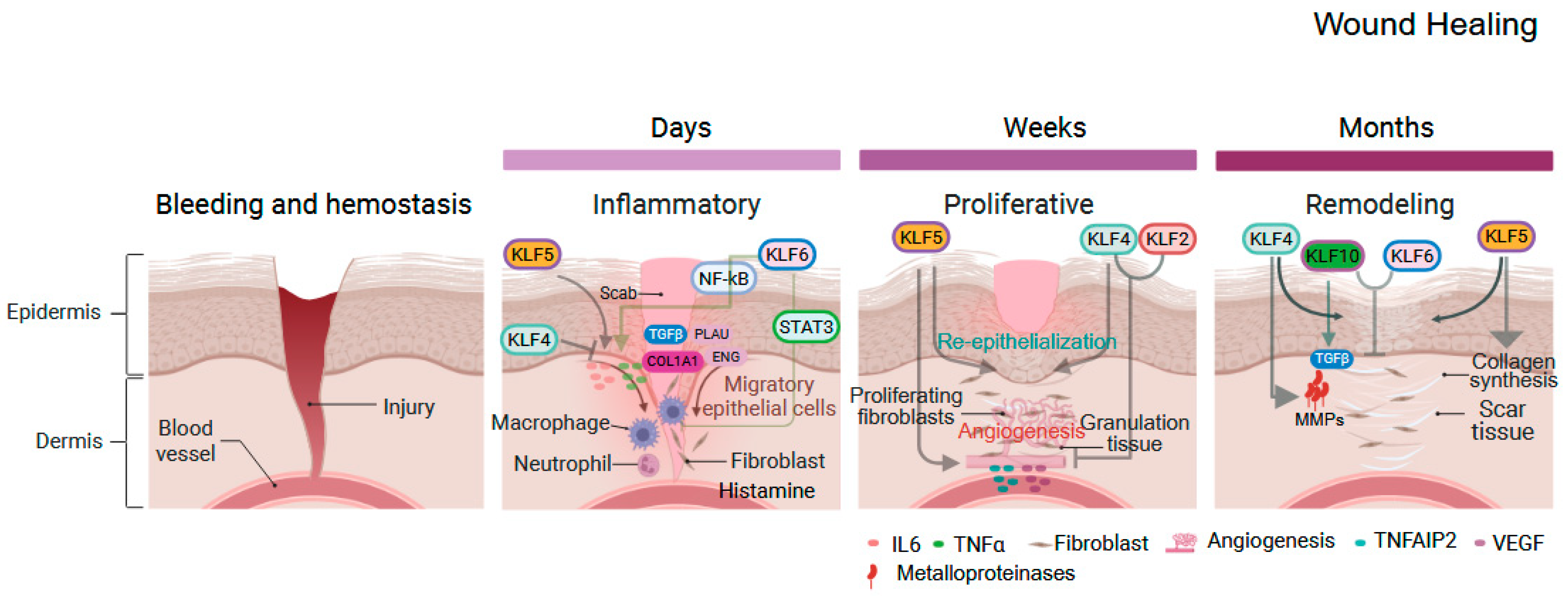
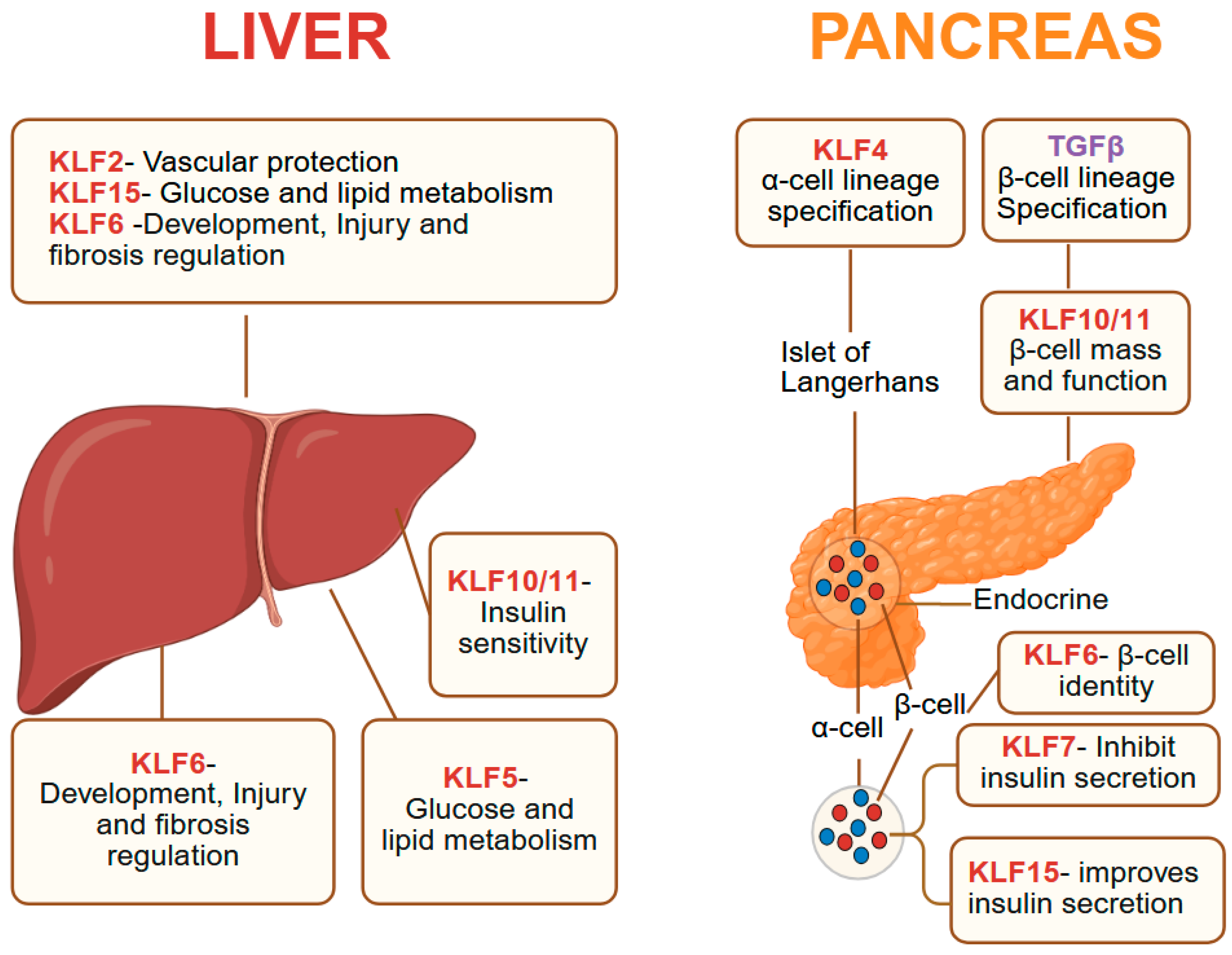

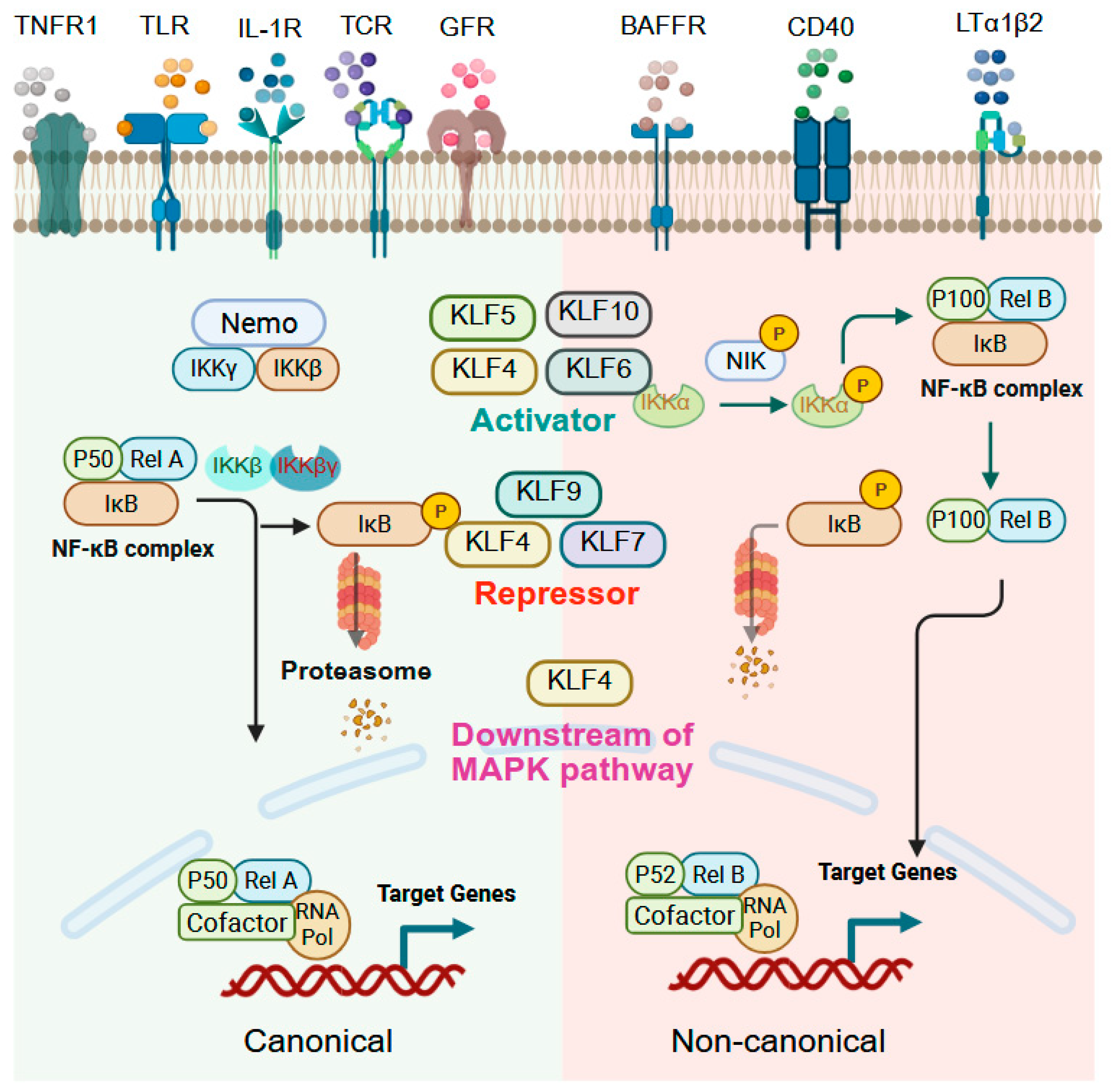
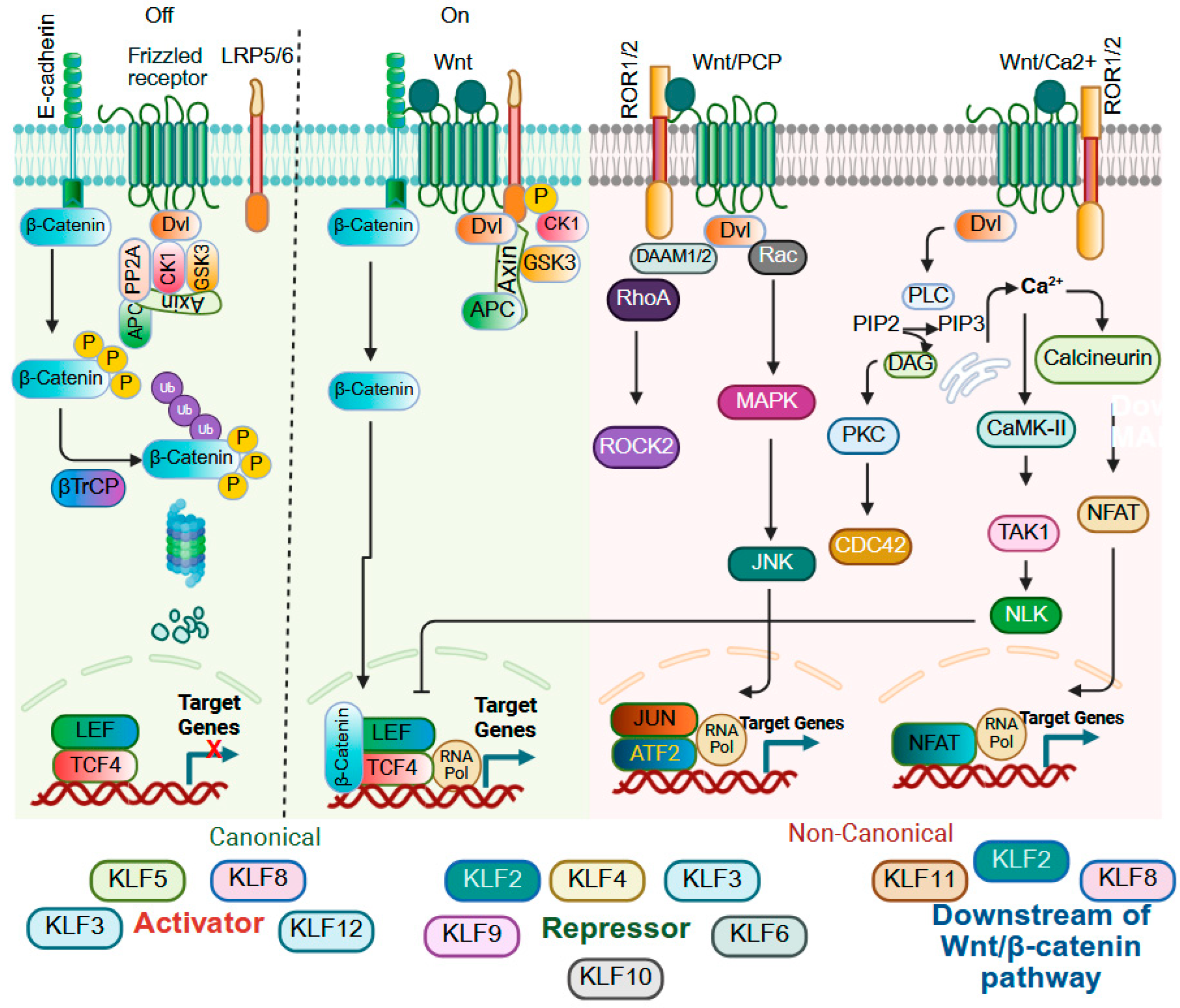
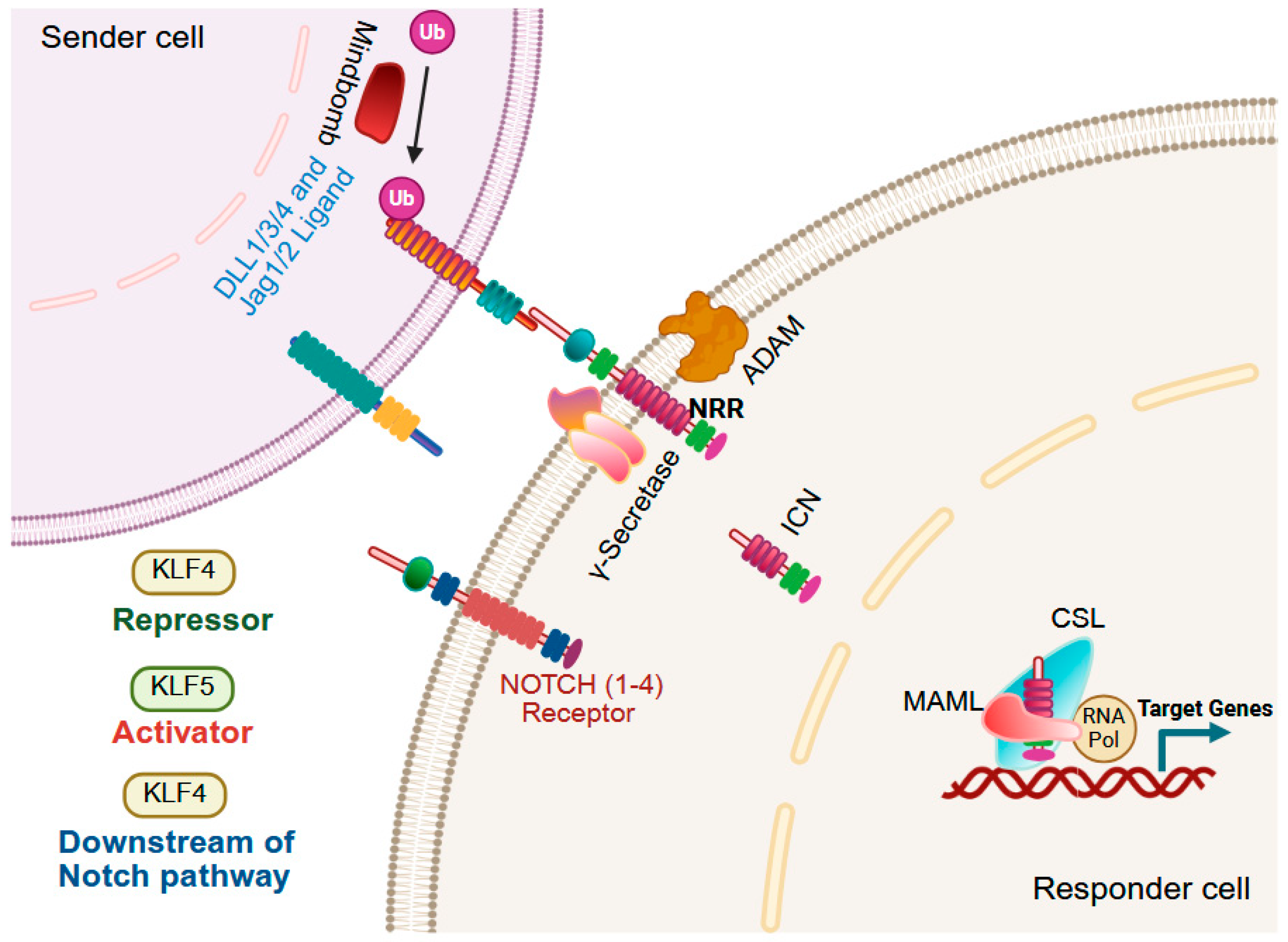
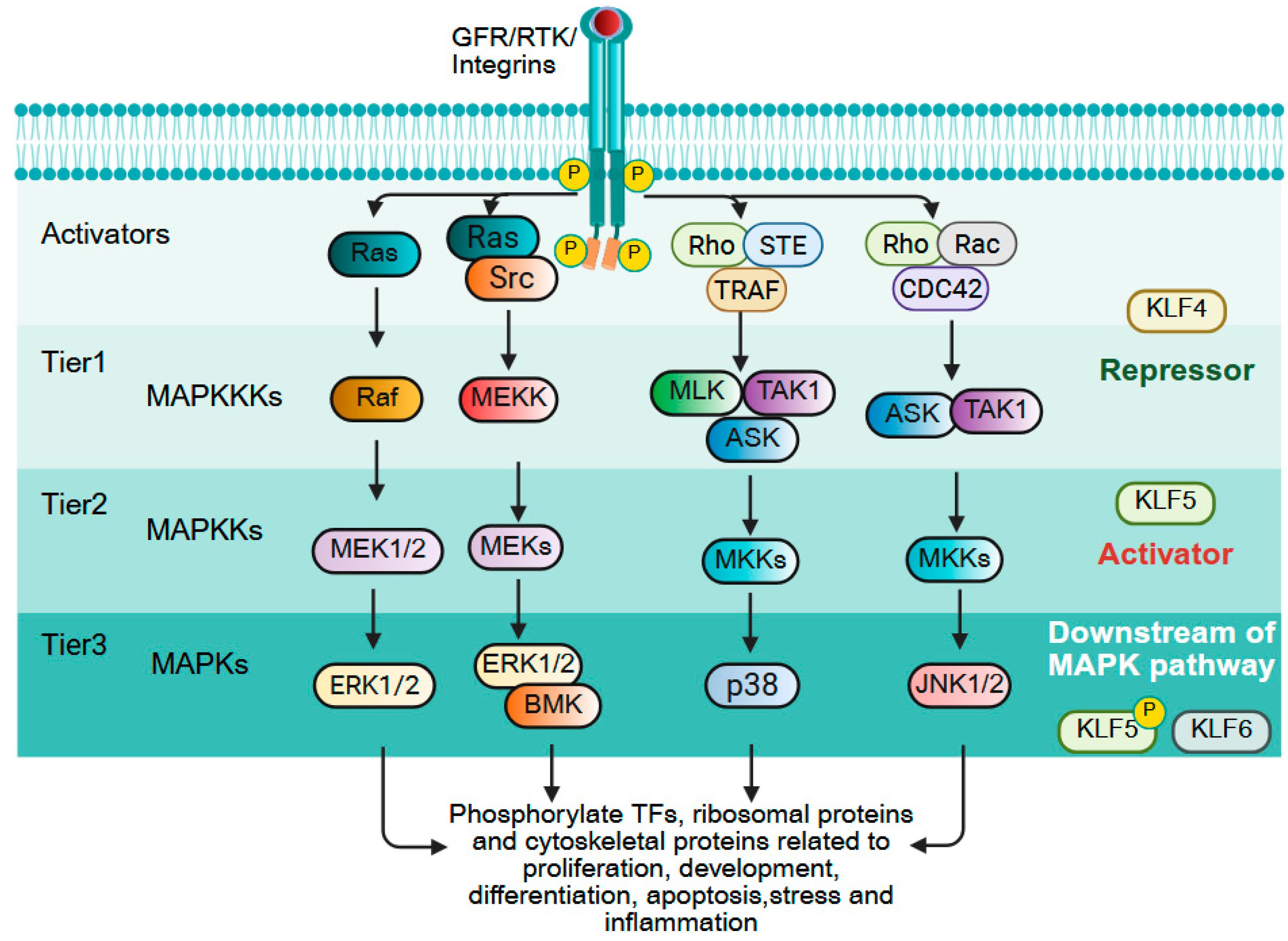
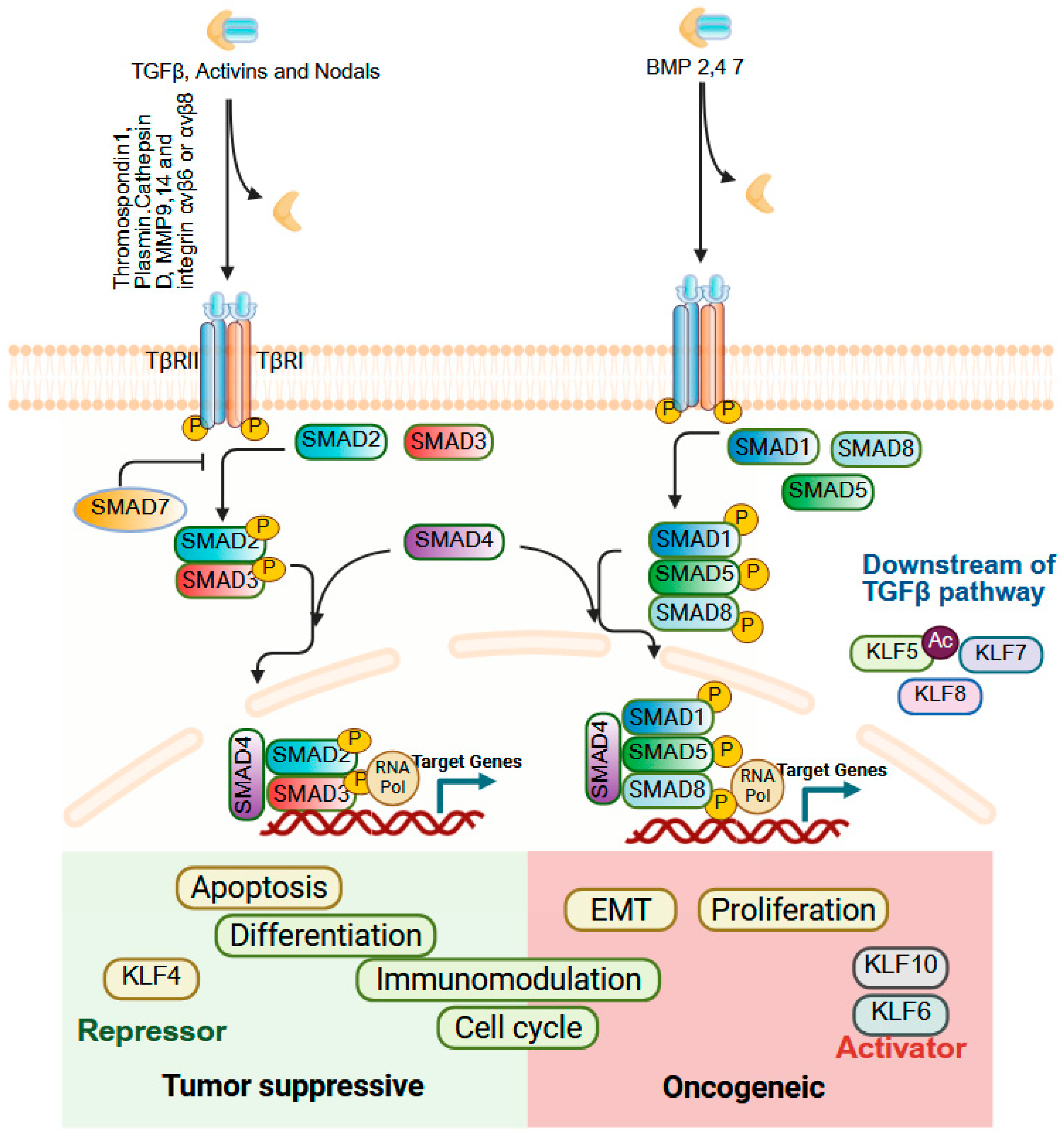
| Gene Symbol | Human Chromosome | Expression in Adult Tissues | Interacting Co-Regulators Based on Experiments and/or STRING Prediction # |
|---|---|---|---|
| KLF1 | chr19:12,884,422-12,887,201 | Erythroid | CREBBP, UBA52, UBB, UBC, RPS27A |
| KLF2 | chr19:16,324,826-16,328,685 | Lung, blood vessels, lymphocytes | FOXO1, p300, KAT2B, WWP1, FBXW7 |
| KLF3 | chr4:38,664,197-38,701,517 | Adipocytes, brain and erythroid tissue | CTBP2, FHL3, LHX8, UBE2I |
| KLF4 | chr9:107,484,852-107,490,482 | Gut, skin, cornea, several other epithelial tissues | Sp1, p300, HUWE1, HDAC2, CREBBP |
| KLF5 | chr13:73,054,976-73,077,541 | Gut, skin, lung, cornea, several other epithelial tissues | RARA, NFkB1, p300, WWP1, FBXW7 |
| KLF6 | chr10:3,775,996-3,785,281 | Ubiquitous | RELA, SP1, TAF9, NFKBIA, HDAC3 |
| KLF7 | chr2:207,074,137-207,173,856 | Ubiquitous | FBXO38 |
| KLF8 | chrX:55,908,123-56,291,531 | Ubiquitous | CTBP1, p300, CREBBP, KAT2B |
| KLF9 | chr9:70,384,604-70,414,657 | Ubiquitous | Sin3A, PGR |
| KLF10 | chr8:102,648,784-102,655,725 | Ubiquitous | SIAH1, KAT2B, Sin3A, SP1, FOXP3 |
| KLF11 | chr2:10,042,849-10,054,836 | Ubiquitous | SIN3A, p300, CBX5 |
| KLF12 | chr13:73,686,089-74,306,045 | Bone, brain, kidney, liver and lung | CTBP1, IDO2, DNMT3L, EHMT2 |
| KLF13 | chr15:31,326,835-31,435,665 | Ubiquitous | SIN3A, HDAC1, CREBBP, KAT2B, MMP28 |
| KLF14 | chr7:130,415,525-130,418,967 | Ubiquitous | SP1, PAX3, GATA1, Pou3F1,RXRB, ZEB1 |
| KLF15 | chr3:126,288,125-126,357,408 | Ubiquitous | STAT3, p300, ANKS1A, ZBTB24, PRKAB2 |
| KLF16 | chr19:1,852,399-1,876,536 | Ubiquitous | BPGM, H4C6, p300, SIN3A and Sin3B |
| KLF17 | chr1:44,043,927-44,135,140 | Ubiquitous | CIB3 |
| KLF18 | chr1: 44,137,821-44,141,631 | Testis, upper leg skin | AQP1, ATG, BTN2A, BTN2A2, CCM2 |
| Gene Symbol | Role | Cancer Types | Main Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| KLF1 | Oncogene | Gastric, CRC | Drives proliferation |
| KLF2 | Tumor suppressor | CRC, PDAC | Regulates angiogenesis and HIF-1α, Notch-1, GPX4 pathways |
| KLF3 | Tumor suppressor | Gastric, ESCC, Pancreatic | Transcriptional repressor; KLF3-AS1 (lncRNA) suppresses tumors |
| KLF4 | Dual* (mainly tumor suppressor in GI) | Gastric, CRC, PDAC | Regulates p21/p27/p53; inhibits EMT; suppresses proliferation and invasion |
| KLF5 | Dual* (oncogene/tumor suppressor) | ESCC, CRC, Gastric | Oncogenic TP63/SOX2 complex; drives metabolism; suppresses ferroptosis |
| KLF6 | Dual* (oncogene/tumor suppressor) | Gastric, Intestinal, HCC | Tumor-suppressive via p21; silenced by the TAM–UHRF1 axis in HCC |
| KLF7 | Oncogene | CRC, HCC, Gastric | Activates PDGFB leading to MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT3; promotes invasion |
| KLF8 | Oncogene | Gastric, CRC, PDAC | Induced by TGFβ1/hypoxia; promotes EMT, invasion, drug resistance |
| KLF9 | Tumor suppressor | ESCC, Gastric, CRC | Represses β-catenin/TCF and MMP28; reduces metastasis and drug resistance |
| KLF10 | Tumor suppressor | Gastric, ESCC | Effector of TGFβ/SMAD; represses SLUG; loss leads to poor prognosis and radioresistance |
| KLF11 | Oncogene | Gastric | Promotes invasion via Twist1 |
| KLF12 | Dual* (oncogene/tumor suppressor) | ESCC, Gastric, Rectal | Oncogenic in gastric; suppressor in rectal (regulates L1CAM, metastasis) |
| KLF13 | Oncogene | Esophageal, Gastric | Promotes EMT and invasion via NF-κB and GPIHBP1 |
| KLF14 | Tumor suppressor | CRC | Represses glycolysis (LDHB) and centrosome amplification (Plk4) |
| KLF15 | Tumor suppressor | Gastric, CRC | Regulates p21/p57; lncRNAs (TFAP2A-AS1, LINC00689) suppress YAP1/β-catenin |
| KLF16 | Oncogene | CRC | Supports stress tolerance via ATF4 translational reprogramming |
| KLF17 | Tumor suppressor | CRC, Gastric | Activates FHL1; inhibits EMT and chemoresistance; silenced via hypermethylation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhargava, D.; Bhargava, A.N.; Katz, J.P. Krüppel-like Factors in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Cells 2025, 14, 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191513
Bhargava D, Bhargava AN, Katz JP. Krüppel-like Factors in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Cells. 2025; 14(19):1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191513
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhargava, Dharmendra, Anchal Neha Bhargava, and Jonathan P. Katz. 2025. "Krüppel-like Factors in the Gastrointestinal Tract" Cells 14, no. 19: 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191513
APA StyleBhargava, D., Bhargava, A. N., & Katz, J. P. (2025). Krüppel-like Factors in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Cells, 14(19), 1513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14191513







