Astrocytes in Fear Memory Processing: Molecular Mechanisms Across the Amygdala–Hippocampus–Prefrontal Cortex Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
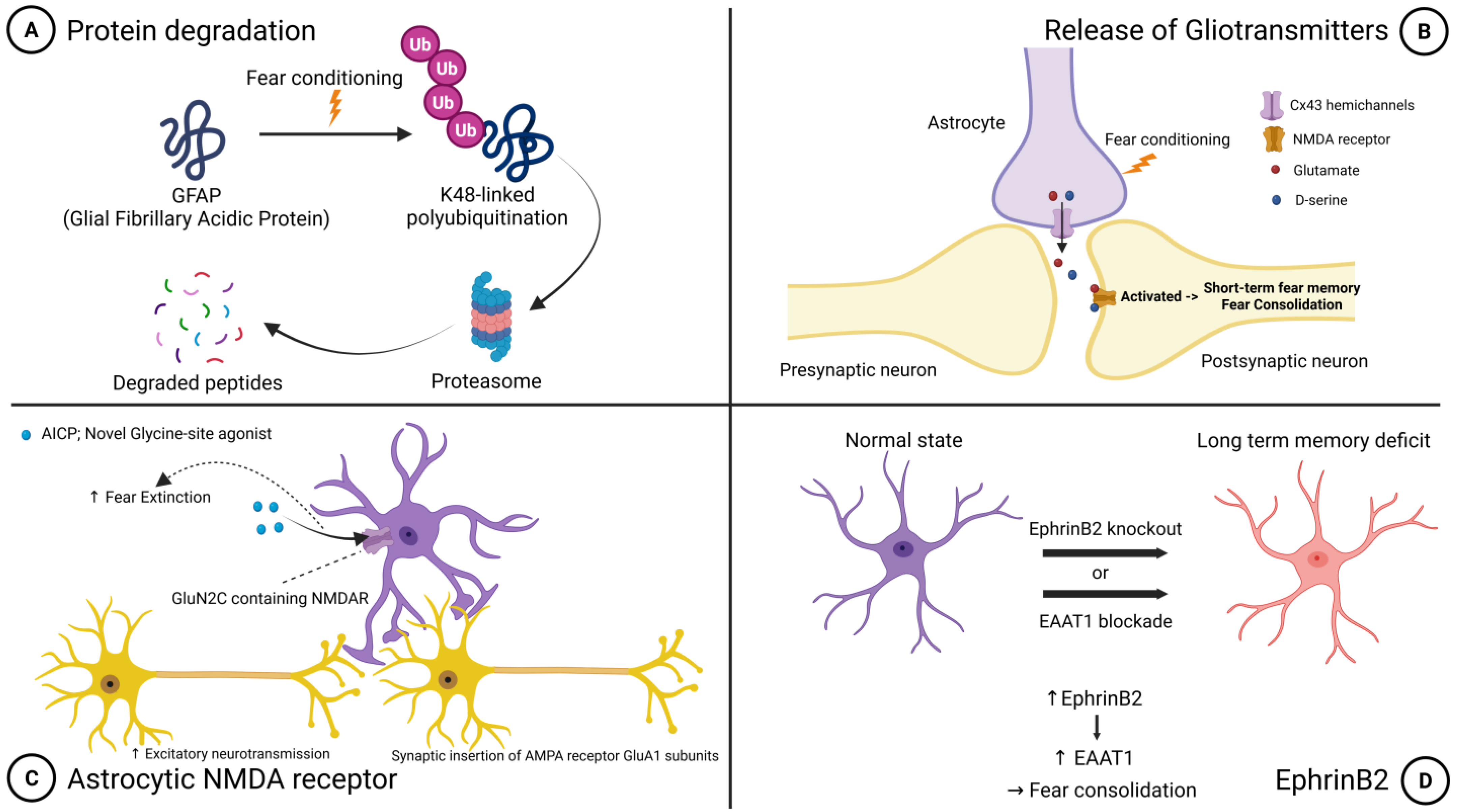
2. Astrocytes in the Amygdala: Orchestrating Fear Acquisition and Consolidation
2.1. Basolateral Amygdala Astrocytes in Fear Memory Formation
2.2. Molecular Mechanisms of Amygdala Astrocyte Function
3. Hippocampal Astrocytes: Guardians of Context and Extinction
3.1. Functional Roles of Hippocampal mPFC in Fear Memory
3.2. Molecular Mechanisms of Hippocampal Astrocyte Function
4. Prefrontal Cortex Astrocytes: Executives of Fear Regulation
4.1. Functional Roles of Hippocampal Astrocytes in Fear Memory
4.2. Molecular Mechanisms of mPFC Astrocytes
Astrocytic GABA Synthesis and Fear Extinction
5. Molecular Mechanisms of Astrocyte–Neuron Communication in Fear Memory
5.1. Gliotransmitter Systems
5.2. Calcium Signaling and Astrocyte Activation
5.3. Structural Plasticity and Synaptic Remodeling
5.4. Transcriptional Regulation
6. Modulating Factors of Astrocytic Function in Fear Memory
6.1. Early-Life Stress and Astrocyte Dysfunction
6.2. Trauma-Related Astrocyte Changes and Neuroinflammation
6.3. Sex Differences in Astrocytic Contributions to Fear Memory
6.4. Clinical Evidence of Astrocytic Dysfunction in Fear-Related Disorders
7. Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
7.1. Targeting Astrocytic Pathways for PTSD Treatment
7.2. Precision Medicine Approaches and Personalized Treatment
7.3. Targeting Neuroimmune Pathways in Fear-Related Disorders
7.4. Astrocyte Heterogeneity and Fear Memory Specificity
7.5. Astrocyte-Sleep-Fear Memory Axis
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AICP | (R)-2-amino-3-(4-(2-ethylphenyl)-1H-indole-2-carboxamido) propanoic acid |
| AMPA | α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BLA | Basolateral amygdala |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| ChR2 | Channelrhodopsin-2 |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| Cx43 | Connexin 43 |
| DREADD | Designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drugs |
| EAAT1 | Excitatory amino acid transporter 1 |
| eIF2α | Eukaryotic initiation factor 2α |
| FGF2 | Fibroblast growth factor 2 |
| GABA | γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| GR | Glucocorticoid receptor |
| LAA | Learning-associated astrocyte |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MDD | Major depressive disorder |
| MDMA | 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine |
| mPFC | Medial prefrontal cortex |
| nAChR | Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
| NFIA | Nuclear factor IA |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NMDAR | N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| OGT | O-GlcNAc transferase |
| PAP | Perisynaptic astrocytic process |
| pBF | Posterior basal forebrain |
| PTSD | Post-traumatic stress disorder |
| REM | Rapid eye movement |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
References
- Pan, S.; Mayoral, S.R.; Choi, H.S.; Chan, J.R.; Kheirbek, M.A. Preservation of a remote fear memory requires new myelin formation. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, I.; Humeau, Y.; Grenier, F.; Ciocchi, S.; Herry, C.; Luthi, A. Amygdala inhibitory circuits and the control of fear memory. Neuron 2009, 62, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixsaut, L.; Graff, J. The Medial Prefrontal Cortex and Fear Memory: Dynamics, Connectivity, and Engrams. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klavir, O.; Prigge, M.; Sarel, A.; Paz, R.; Yizhar, O. Manipulating fear associations via optogenetic modulation of amygdala inputs to prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, O.; Ulloa Severino, F.P.; Eroglu, C. The role of astrocyte structural plasticity in regulating neural circuit function and behavior. Glia 2022, 70, 1467–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Tao, Y.; Guo, X.; Cheng, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Ma, L. Fear Conditioning Downregulates Rac1 Activity in the Basolateral Amygdala Astrocytes to Facilitate the Formation of Fear Memory. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araque, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Haydon, P.G.; Oliet, S.H.; Robitaille, R.; Volterra, A. Gliotransmitters travel in time and space. Neuron 2014, 81, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, M.B.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.; Sudhof, T.C.; Quake, S.R. Spatial transcriptomics reveal neuron-astrocyte synergy in long-term memory. Nature 2024, 627, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Xie, L.; Li, C.H.; Lam, Y.Y.; Ramkrishnan, A.S.; Fu, Z.; Zeng, X.; Liu, S.; Iqbal, Z.; Li, Y. Chemogenetic Activation of Astrocytes in the Basolateral Amygdala Contributes to Fear Memory Formation by Modulating the Amygdala-Prefrontal Cortex Communication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamao, H.; Matsui, K. Astrocytic determinant of the fate of long-term memory. Glia 2025, 73, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabbe, S.; Grundemann, J.; Luthi, A. Amygdala Inhibitory Circuits Regulate Associative Fear Conditioning. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, X.; Qin, L.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; et al. Activation of astrocytes in hippocampus decreases fear memory through adenosine A(1) receptors. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.W.; Imhoff, B.R.; Sathi, Z.S.; Liu, W.Y.; Garza, K.M.; Dias, B.G. Contributions of glucocorticoid receptors in cortical astrocytes to memory recall. Learn. Mem. 2021, 28, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plas, S.L.; Tuna, T.; Bayer, H.; Juliano, V.A.L.; Sweck, S.O.; Arellano Perez, A.D.; Hassell, J.E.; Maren, S. Neural circuits for the adaptive regulation of fear and extinction memory. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1352797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, K.A.; Allen, N.J. From Synapses to Circuits, Astrocytes Regulate Behavior. Front. Neural Circuits 2022, 15, 786293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, M.R.; Argibay, L.M.; Molina, V.A.; Calfa, G.D.; Bender, C.L. Role of amygdala astrocytes in different phases of contextual fear memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 468, 115017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negron-Oyarzo, I.; Dib, T.; Chacana-Veliz, L.; Lopez-Quilodran, N.; Urrutia-Pinones, J. Large-scale coupling of prefrontal activity patterns as a mechanism for cognitive control in health and disease: Evidence from rodent models. Front. Neural Circuits 2024, 18, 1286111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, K.; McFadden, T.; Jarome, T.J. Neuronal and astrocytic protein degradation are critical for fear memory formation. Learn. Mem. 2023, 30, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, K.; Musaus, M.; Navabpour, S.; Martin, K.; Ray, W.K.; Helm, R.F.; Jarome, T.J. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Sex-Specific Protein Degradation Targets in the Amygdala During Fear Memory Formation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 716284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsambarth, S.; Carvajal, F.J.; Moraga-Amaro, R.; Mendez, L.; Tamburini, G.; Jimenez, I.; Verdugo, D.A.; Gomez, G.I.; Jury, N.; Martinez, P.; et al. Astroglial gliotransmitters released via Cx43 hemichannels regulate NMDAR-dependent transmission and short-term fear memory in the basolateral amygdala. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelkar, G.P.; Liu, J.; Dravid, S.M. Astrocytic NMDA Receptors in the Basolateral Amygdala Contribute to Facilitation of Fear Extinction. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 24, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, K.; Farhat, A.; Lamprecht, R. EphrinB2 in excitatory neurons and astrocytes in the basolateral amygdala controls long-term fear memory formation. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, X.; Li, L.; Fei, F.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Duan, S.; et al. Cholinergic signaling to CA1 astrocytes controls fear extinction. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eads7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.R.; Kwon, W.; Woo, J.; Ko, Y.; Maleki, E.; Yu, K.; Murali, S.; Sardar, D.; Deneen, B. Learning-associated astrocyte ensembles regulate memory recall. Nature 2025, 637, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Oliveira, M.M.; Sood, R.; Khlaifia, A.; Lou, D.; Hooshmandi, M.; Hung, T.Y.; Mahmood, N.; Reeves, M.; Ho-Tieng, D.; et al. mRNA translation in astrocytes controls hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2308671120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, D.; Kater, M.S.J.; Sakers, K.; Nygaard, K.R.; Liu, Y.; Koester, S.K.; Fass, S.B.; Lake, A.M.; Khazanchi, R.; Khankan, R.R.; et al. Activity-dependent translation dynamically alters the proteome of the perisynaptic astrocyte process. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazare, N.; Oudart, M.; Moulard, J.; Cheung, G.; Tortuyaux, R.; Mailly, P.; Mazaud, D.; Bemelmans, A.P.; Boulay, A.C.; Blugeon, C.; et al. Local Translation in Perisynaptic Astrocytic Processes Is Specific and Changes after Fear Conditioning. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, A.; Abramian, A.; Driessens, S.L.W.; Boers-Escuder, C.; van der Loo, R.J.; Smit, A.B.; van den Oever, M.C.; Verheijen, M.H.G. Activation of G(s) Signaling in Cortical Astrocytes Does Not Influence Formation of a Persistent Contextual Memory Engram. eNeuro 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Lun, W.Z.; Geng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, J.C.; Chen, G.H. Dynamic changes of media prefrontal cortex astrocytic activity in response to negative stimuli in male mice. Neurobiol. Stress 2024, 33, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiuk, M.Y.; Martirosyan, A.; Wahis, J.; de Vin, F.; Marneffe, C.; Kusserow, C.; Koeppen, J.; Viana, J.F.; Oliveira, J.F.; Voet, T.; et al. Identification of region-specific astrocyte subtypes at single cell resolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.B.; Jiang, X.; Quake, S.R.; Sudhof, T.C. Persistent transcriptional programmes are associated with remote memory. Nature 2020, 587, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Won, W.; Lee, S.; Han, K.; Ha, E.; Lee, J.; Hyeon, S.J.; Joo, Y.; Hong, H.; Lee, H.; et al. Astrocytic gamma-aminobutyric acid dysregulation as a therapeutic target for posttraumatic stress disorder. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, V.; Carreno-Munoz, M.I.; Chehrazi, P.; Michaud, J.L.; Chattopadhyaya, B.; Di Cristo, G. Developmental Syngap1 Haploinsufficiency in Medial Ganglionic Eminence-Derived Interneurons Impairs Auditory Cortex Activity, Social Behavior, and Extinction of Fear Memory. J. Neurosci. 2024, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.U.; Kim, S.; Sim, J.; Yang, S.; An, H.; Nam, M.H.; Jang, D.P.; Lee, C.J. Redefining differential roles of MAO-A in dopamine degradation and MAO-B in tonic GABA synthesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, J.; Timmermann, A.; Henning, L.; Muller, H.; Steinhauser, C.; Bedner, P. Astrocytic GABA Accumulation in Experimental Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 614923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, T.; Komano, K.; Tabaru, M.; Kofuji, T.; Saito, A.; Ugawa, Y.; Terao, Y. Repetitive pulsed-wave ultrasound stimulation suppresses neural activity by modulating ambient GABA levels via effects on astrocytes. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1361242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueberbach, T.; Simacek, C.A.; Tegeder, I.; Kirischuk, S.; Mittmann, T. Tonic activation of GABA(B) receptors via GAT-3 mediated GABA release reduces network activity in the developing somatosensory cortex in GAD67-GFP mice. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1198159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.G.; Lim, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, W.S.; Yoon, B.E.; Lee, C.J. Suppressing astrocytic GABA transaminase enhances tonic inhibition and weakens hippocampal spatial memory. Exp. Mol. Med. 2025, 57, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacagnina, A.F.; Brockway, E.T.; Crovetti, C.R.; Shue, F.; McCarty, M.J.; Sattler, K.P.; Lim, S.C.; Santos, S.L.; Denny, C.A.; Drew, M.R. Distinct hippocampal engrams control extinction and relapse of fear memory. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guayasamin, M.; Depaauw-Holt, L.R.; Adedipe, I.I.; Ghenissa, O.; Vaugeois, J.; Duquenne, M.; Rogers, B.; Latraverse-Arquilla, J.; Peyrard, S.; Bosson, A.; et al. Early-life stress induces persistent astrocyte dysfunction associated with fear generalisation. Elife 2025, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia-Soteras, A.; Heistek, T.S.; Kater, M.S.J.; Mak, A.; Negrean, A.; van den Oever, M.C.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Khakh, B.S.; Min, R.; Smit, A.B.; et al. Retraction of Astrocyte Leaflets From the Synapse Enhances Fear Memory. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostroff, L.E.; Manzur, M.K.; Cain, C.K.; Ledoux, J.E. Synapses lacking astrocyte appear in the amygdala during consolidation of Pavlovian threat conditioning. J. Comp. Neurol. 2014, 522, 2152–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Zhong, Q.L.; Mo, R.; Lu, C.L.; Ren, J.; Mo, J.W.; Guo, F.; Wen, Y.L.; Cao, X. Proteomic Profiling of Astrocytic O-GlcNAc Transferase-Related Proteins in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 729975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortola, R.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Carballo-Casla, A.; Cabello-Plan, S.; Koni, A.; Mustieles, V.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Artalejo, A.R.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Garcia-Esquinas, E. Role of Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as a Biomarker of Chronic Pain in Older Adults. Eur. J. Pain 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, G.; Muller, A.; Albrecht, A. Long-Term Impact of Early-Life Stress on Hippocampal Plasticity: Spotlight on Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, J.A.; Moraga-Amaro, R.; Diaz-Galarce, R.; Rojas, S.; Maturana, C.J.; Stehberg, J.; Saez, J.C. Restraint stress increases hemichannel activity in hippocampal glial cells and neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Cheng, Z.; Ali, A.I.; Wang, J.; Le, K.; Chibaatar, E.; Guo, Y. Chronic Unexpected Mild Stress Destroys Synaptic Plasticity of Neurons through a Glutamate Transporter, GLT-1, of Astrocytes in the Ischemic Stroke Rat. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 1615925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Cui, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Han, L.; Zhou, M.; Luo, J.; et al. Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing Reveals that Decorin Expression in the Amygdala Regulates Perineuronal Nets Expression and Fear Conditioning Response after Traumatic Brain Injury. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, M.; Facchinetti, R.; Torazza, C.; Ciarla, C.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Balbi, M.; Bonanno, G.; Popoli, M.; Steardo, L.; Milanese, M.; et al. Molecular signatures of astrocytes and microglia maladaptive responses to acute stress are rescued by a single administration of ketamine in a rodent model of PTSD. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fesharaki-Zadeh, A.; Miyauchi, J.T.; St Laurent-Arriot, K.; Tsirka, S.E.; Bergold, P.J. Increased Behavioral Deficits and Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Co-Morbid Traumatic Brain Injury and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. ASN Neuro 2020, 12, 1759091420979567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.N.; Lee, J.; Polonio, C.M.; Choi, J.; Akl, C.F.; Kilian, M.; Weiss, W.M.; Gunner, G.; Ye, M.; Heo, T.H.; et al. Psychedelic control of neuroimmune interactions governing fear. Nature 2025, 641, 1276–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, G.; Kritikos, M.; Kuan, P.F.; Carr, M.A.; Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Kotov, R.; Bromet, E.J.; Clouston, S.A.P.; Luft, B.J. Glial suppression and post-traumatic stress disorder: A cross-sectional study of 1,520 world trade center responders. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2023, 30, 100631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, M.E.; Hayes, J.; Huber, B.R.; Jeromin, A.; Fortier, C.B.; Fonda, J.R.; Lasseter, H.; Chaby, L.; McGlinchey, R.; Milberg, W. Plasma biomarkers associated with deployment trauma and its consequences in post-9/11 era veterans: Initial findings from the TRACTS longitudinal cohort. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.S.; Blissitt, G.; Zimmerman, K.; Orton, L.; Friedland, D.; Coady, E.; Laban, R.; Veleva, E.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Poor long-term outcomes and abnormal neurodegeneration biomarkers after military traumatic brain injury: The ADVANCE study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2025, 96, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sass, D.; Guedes, V.A.; Smith, E.G.; Vorn, R.; Devoto, C.; Edwards, K.A.; Mithani, S.; Hentig, J.; Lai, C.; Wagner, C.; et al. Sex Differences in Behavioral Symptoms and the Levels of Circulating GFAP, Tau, and NfL in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 746491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace-Schott, E.F.; Seo, J.; Bottary, R. The influence of sleep on fear extinction in trauma-related disorders. Neurobiol. Stress 2023, 22, 100500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace-Schott, E.F.; Germain, A.; Milad, M.R. Sleep and REM sleep disturbance in the pathophysiology of PTSD: The role of extinction memory. Biol. Mood Anxiety Disord. 2015, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhan, G.; Luo, X.; Zhou, Z. Role of astrocytes in sleep deprivation: Accomplices, resisters, or bystanders? Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1188306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kong, X.Y.; Hu, T.; Ge, Y.J.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.T.; He, S.; Zhang, P.; Chen, G.H. Aquaporin-4, Connexin-30, and Connexin-43 as Biomarkers for Decreased Objective Sleep Quality and/or Cognition Dysfunction in Patients With Chronic Insomnia Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 856867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Qin, J.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X. Large-Scale Integration of Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data Reveals Astrocyte Diversity and Transcriptomic Modules across Six Central Nervous System Disorders. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Munch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escartin, C.; Galea, E.; Lakatos, A.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Petzold, G.C.; Serrano-Pozo, A.; Steinhauser, C.; Volterra, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Agarwal, A.; et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pozo, A.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Munoz-Castro, C.; Jaisa-Aad, M.; Healey, M.A.; Welikovitch, L.A.; Jayakumar, R.; Bryant, A.G.; Noori, A.; et al. Astrocyte transcriptomic changes along the spatiotemporal progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 2384–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvonen, P.J.; Straus, L.D.; Acheson, D.; Gehrman, P. A Review of the Relationship Between Emotional Learning and Memory, Sleep, and PTSD. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Brain Region | Key Functions | Major Molecules/Pathways | Memory Phase | Experimental Evidence | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basolateral Amygdala (BLA) | Fear acquisition and consolidation; Amygdala-mPFC communication enhancement | Cx43 hemichannels (glutamate + D-serine release), EphrinB2-EAAT1 pathway, GFAP protein degradation, Astrocytic NMDA receptors (GluN2C) | Acquisition, Consolidation, Extinction | Chemogenetics (Gq-DREADD), Optogenetics (ChR2/ArchT), Spatial transcriptomics, Proteomic analysis | [8,9,10,18,19,20,21,22] |
| Hippocampus (CA1) | Contextual fear memory formation; Fear extinction regulation; Learning-associated astrocyte ensembles | Cholinergic signaling (α4/α7 nAChRs), ATP → Adenosine → A1 receptors, eIF2α protein synthesis regulation, NFIA transcription factor, PAPs local protein synthesis | Consolidation, Extinction, Recall | Optogenetics, Cholinergic modulation (donepezil), LAA ensemble manipulation, eIF2α genetic manipulation | [12,23,24,25,26,27] |
| Medial Prefrontal Cortex (mPFC) | Fear expression regulation; Extinction learning and recall; Remote memory maintenance; GABA-mediated tonic inhibition | Glucocorticoid receptors, Metabolic reprogramming (glucose/lipid metabolism), Structural plasticity, Sex-specific signaling, MAO-B-dependent GABA synthesis, GAT-3 mediated GABA release, Tonic GABA inhibition | Extinction, Recall, Remote memory | Chemogenetics (Gs-DREADD), Single-cell transcriptomics, GR knockout studies, Calcium imaging, Ultrasound stimulation | [13,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] |
| Aspect | Males | Females | Functional Implications | Experimental Evidence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein degradation targets (Amygdala) | Cytoskeleton proteins, ATP synthesis enzymes, cell signaling molecules | Vesicle transport proteins, microtubule-associated proteins | Different molecular mechanisms underlying fear memory formation | Proteomic analysis following fear conditioning | [19] |
| Astrocytic calcium event characteristics | Lower amplitude and smaller size calcium events | Higher amplitude and larger size calcium events | Greater fear discrimination sensitivity and more profound impairments following astrocyte manipulation in females | Calcium imaging in BLA astrocytes | [40] |
| Glucocorticoid receptor function (mPFC) | No extinction memory deficit with GR knockout | Impaired extinction memory recall with astrocytic GR knockout | Sex-specific therapeutic targeting needed for PTSD treatment | Astrocyte-specific GR knockout studies | [13] |
| Stress response effects | Stress exposure reduces sex differences | Stress exposure eliminates natural calcium signature advantages | Stress vulnerability and resilience mechanisms differ between sexes | Early-life stress paradigms with calcium imaging | [40] |
| BDNF-pain relationship | Lower BDNF linked to pain only in depression | Lower BDNF in severe pain regardless of depression status | Sex-specific biomarker potential for fear-related disorders | Serum BDNF analysis in chronic pain patients | [44] |
| PTSD susceptibility | Lower overall prevalence | Higher prevalence and different symptom profiles | Requires sex-specific precision medicine approaches | Clinical and epidemiological studies | [13] |
| Category | Target/ Population | Intervention/ Biomarker | Mechanism/ Finding | Key Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Therapeutic Targets | Fear/anxiety disorders | Donepezil | Acetylcholinesterase inhibition enhances astrocytic Ca2+ dynamics | Promotes fear extinction through α4/α7 nAChR activation | [23] |
| Therapeutic Targets | PTSD prevention | A1 receptor agonists | Mimic astrocyte-derived adenosine memory dampening | Selective consolidation interference without affecting acquisition/retrieval | [12] |
| Therapeutic Targets | PTSD | KDS2010 | Reversible MAO-B inhibition restores astrocytic GABA homeostasis | Corrects astrocytic dysfunction underlying PTSD symptoms | [32] |
| Therapeutic Targets | Fear memory disorders | Cx43 modulators | Enhance gliotransmitter release (glutamate + D-serine) | Rescue memory deficits through NMDAR activation | [20] |
| Therapeutic Targets | Long-term memory deficits | EAAT1 enhancers | Improve astrocytic glutamate uptake | Selective enhancement of memory consolidation | [22] |
| Therapeutic Targets | PTSD, anxiety disorders | Psilocybin/MDMA | Reverse meningeal monocyte accumulation, restore astrocyte–neuron communication | Target peripheral immune-brain interactions via EGFR-PTPRS | [51] |
| Clinical Biomarkers | WTC Responders (n = 1520) | Plasma GFAP | Reduced levels in severe PTSD | Glial suppression rather than activation | [52] |
| Clinical Biomarkers | Post-9/11 Veterans (n = 550) | Plasma GFAP | Lower levels with blast exposure and psychological symptoms | Astrocytic dysfunction in trauma | [53] |
| Clinical Biomarkers | UK Military Personnel | Plasma GFAP | Elevated levels 8 years post-TBI | Poor functional outcomes, unemployment | [54] |
| Clinical Biomarkers | TBI Patients | GFAP, Tau | Higher levels in females with more severe symptoms | Sex-specific glial responses to trauma | [55] |
| Clinical Biomarkers | Chronic Pain Patients | Serum BDNF | Sex-specific patterns with pain severity | Potential biomarker for fear-related disorders | [44] |
| Precision Medicine | Fear conditioning | Protein degradation patterns | Different targets in males vs. females | Sex-specific molecular mechanisms | [19] |
| Precision Medicine | Extinction memory | Astrocytic glucocorticoid receptors | Female-specific extinction memory deficits with GR knockout | Hormonal interventions may be sex-dependent | [13] |
| Precision Medicine | Sleep disruption | Astrocytic markers (AQP4, Cx30, Cx43) | Reduced levels in sleep-deprived individuals | Sleep restoration as adjunctive therapy | [59] |
| Future Directions | Memory-specific astrocytes | LAA ensemble modulation | Selective targeting of learning-associated astrocyte populations | Precision targeting without global effects | [24] |
| Future Directions | Memory recall | NFIA transcription factor | Essential transcriptional regulator in astrocytes | Critical for memory recall function | [24] |
| Future Directions | Energy metabolism | Gap junction modulators | Restore astrocytic connectivity and energy support | Support synaptic plasticity and memory | [58] |
| Future Directions | Remote memory | Metabolic reprogramming | Glucose/lipid metabolism support in astrocytes | Long-term memory maintenance | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, M.; Kim, M.S. Astrocytes in Fear Memory Processing: Molecular Mechanisms Across the Amygdala–Hippocampus–Prefrontal Cortex Network. Cells 2025, 14, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181444
Kim Y-R, Lee M, Kim MS. Astrocytes in Fear Memory Processing: Molecular Mechanisms Across the Amygdala–Hippocampus–Prefrontal Cortex Network. Cells. 2025; 14(18):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181444
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Young-Rae, Moonhyung Lee, and Man S. Kim. 2025. "Astrocytes in Fear Memory Processing: Molecular Mechanisms Across the Amygdala–Hippocampus–Prefrontal Cortex Network" Cells 14, no. 18: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181444
APA StyleKim, Y.-R., Lee, M., & Kim, M. S. (2025). Astrocytes in Fear Memory Processing: Molecular Mechanisms Across the Amygdala–Hippocampus–Prefrontal Cortex Network. Cells, 14(18), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181444





