Novel BCR-Targeting Fusion Proteins for Antigen-Specific Depletion of Alloreactive B Cells in Antibody-Mediated Rejection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Samples
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Fusion Protein Construction
| Primer | Sequences |
| 1F | GGACTCTAGAGCTATGGGCCTG |
| 1R | ACTTCCTCCTCCTCCACTCCCACCCCCACCGGAGCCGCCACCACCCCATCTCAGTGTCAGGGG |
| 2F | GGTGGTGGCGGCTCCGGTGGGGGTGGGAGTGGAGGAGGAGGAAGTACTCACACATGCCCACCG |
| 2R | ACTAACCGGTTTATTTCCCGGGAGACAG |
| 3F | GGACTCTAGAGCCATGGGCCTG |
| 3R | ACTTCCTCCTCCTCCACTCCCACCCCCACCGGAGCCGCCACCACCCCATCTCAGGGT |
| 4F | GGTGGTGGCGGCTCCGGTGGGGGTGGGAGTGGAGGAGGAGGAAGTACTCACACATGCCCAC |
| 4R | ACTAACCGGTCTATTTCCCGGGAGACAG |
2.4. Protein Expression and Purification
2.5. Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. ELISA for Functional Validation of Recombinant Proteins
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis of BCR Binding
2.9. Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC) Assay
2.10. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
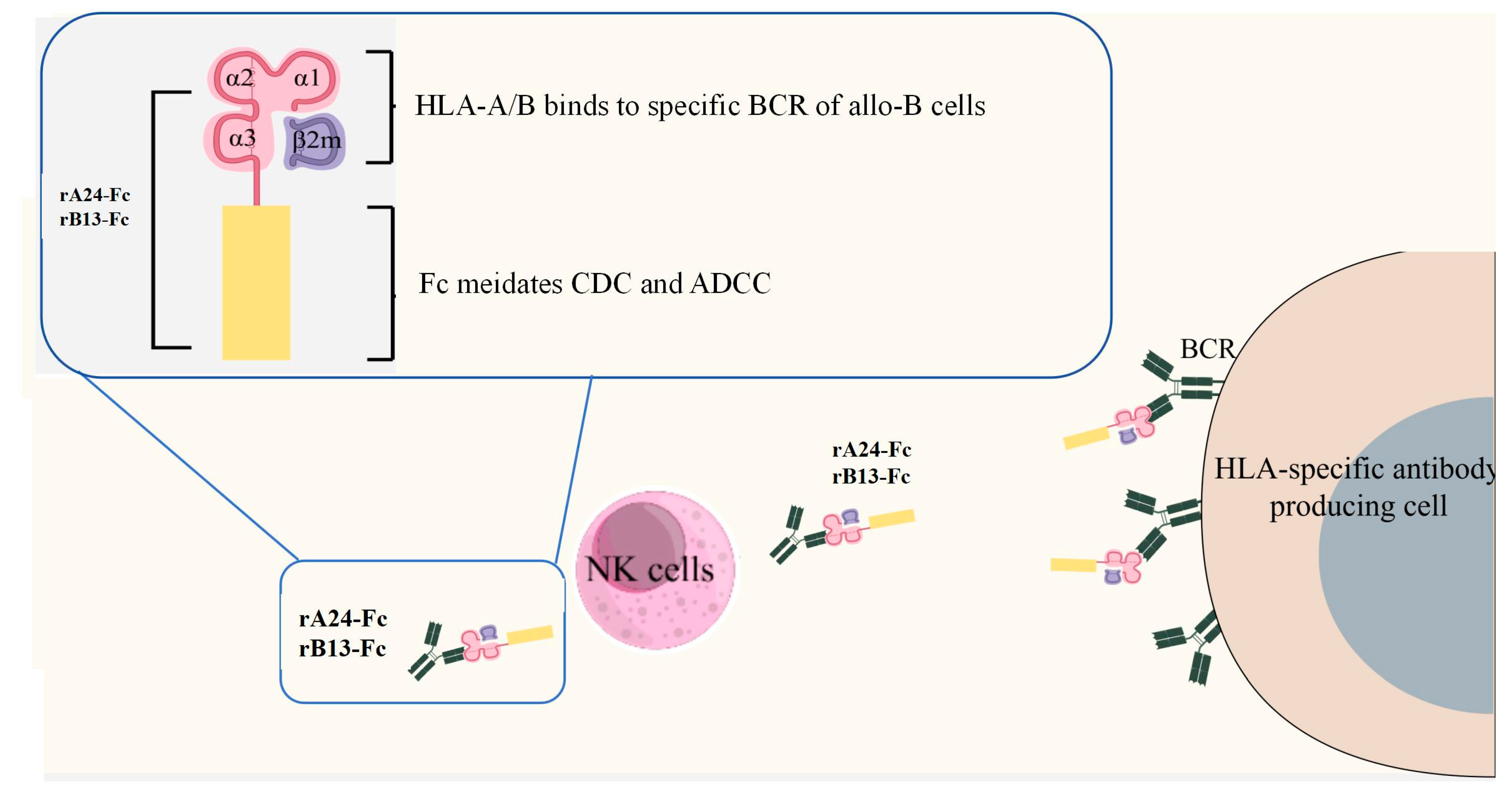
3.1. Design and Production of HLA-Fc Proteins
3.2. The rA24-Fc and rB13-Fc Exhibits Binding Affinity for Both W6/32 Hybridoma Cells and Their Secreted Antibodies
3.3. BCR-Targeting Fusion Protein rA24-Fc and rB13-Fc Mediates Specific Hybridoma Cell Lysis via Complement Activation
3.4. BCR-Targeting Fusion Proteins Mediates NK Cell-Dependent Lysis of W6/32 Hybridoma Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruzado, J.M. Antibody-Mediated Rejection of Solid-Organ Allografts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2579–2580. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Dumortier, J.; Conti, F.; Hiriart, J.B.; Dharancy, S.; Duvoux, C.; Besch, C.; Houssel-Debry, P.; Latournerie, M.; Chermak, F.; Meszaros, M.; et al. Treatment of donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies-mediated rejection after liver transplantation: A French nationwide retrospective study. Liver Transpl. 2023, 29, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Acevedo, A.; Pathoulas, C.L.; Murphy, P.A.; Valenzuela, N.M. The Transplant Bellwether: Endothelial Cells in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. J. Immunol. 2023, 211, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, M.M.; Cook, J.L.; Chang, P.; Francis, G.; Hsu, D.T.; Kiernan, M.S.; Kobashigawa, J.A.; Lindenfeld, J.; Masri, S.C.; Miller, D.; et al. Antibody-mediated rejection in cardiac transplantation: Emerging knowledge in diagnosis and management: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, 1608–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.; Singh, D.; Brown, S.J.; Wang, J.H.; Kasiske, B.L. Incidence, risk factors, treatment, and consequences of antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection: A systematic review. Clin. Transplant. 2021, 35, e14320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levine, D.J.; Glanville, A.R.; Aboyoun, C.; Belperio, J.; Benden, C.; Berry, G.J.; Hachem, R.; Hayes, D., Jr.; Neil, D.; Reinsmoen, N.L.; et al. Antibody-mediated rejection of the lung: A consensus report of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2016, 35, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhao, D.; Sa, R.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhu, L.; Chen, G. A modified perioperative regimen for deceased donor kidney transplantation in presensitized recipients without prior desensitization therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1223567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Luo, G.; Xu, C.; Sun, Z.; Mei, H. Role of MICA antibodies in solid organ transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2014, 28, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragun, D.; Müller, D.N.; Bräsen, J.H.; Fritsche, L.; Nieminen-Kelhä, M.; Dechend, R.; Kintscher, U.; Rudolph, B.; Hoebeke, J.; Eckert, D.; et al. Angiotensin II type 1-receptor activating antibodies in renal-allograft rejection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 558–569. [Google Scholar]
- Abuzeineh, M.; Kyeso, Y.; Philogene, M.C.; Alachkar, N.; Alasfar, S. Presentation and Outcomes of Antibody-Mediated Rejection Associated with Angiotensin II Receptor 1 Antibodies Among Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 1501–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverson, L.P.; Hachem, R.R. Antibody-mediated rejection: Diagnosis and treatment. Clin. Chest Med. 2023, 44, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasfar, S.; Kodali, L.; Schinstock, C.A. Current therapies in kidney transplant rejection. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuazzam, F.; Dubrawka, C.; Abdulhadi, T.; Amurao, G.; Alrata, L.; Alsabbagh, D.Y.; Alomar, O.; Alhamad, T. Emerging therapies for antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Hu, J.; Luo, W.; Luo, Q.; Guo, J.; Tian, F.; Ming, Y.; Zou, Y. Analysis of sera of recipients with allograft rejection indicates that keratin 1 is the target of anti-endothelial antibodies. J. Immunol. Res. 2017, 2017, 8679841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodsky, F.M.; Parham, P.; Barnstable, C.J.; Crumpton, M.J.; Bodmer, W.F. Monoclonal antibodies for analysis of the HLA system. Immunol. Rev. 1979, 47, 3–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN)/Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR). Annu. Data Rep. 2015, 15, 1–28. Available online: https://www.srtr.org/reports-tools/srtroptn-annual-data-report/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Gupta, G.; Jawdeh, B.G.A.; Racusen, L.C.; Bhasin, B.; Arend, L.J.; Trollinger, B.; Kraus, E.; Rabb, H.; Zachary, A.A.; Montgomery, R.A.; et al. Late antibody-mediated rejection in renal allografts: Outcome after conventional and novel therapies. Transplantation 2014, 97, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, Y.; Mirioglu, S.; Dirim, A.B.; Ozluk, Y.; Yegit, O.; Aksoy, E.; Safak, S.; Guller, N.; Demir, E.; Artan, A.S.; et al. A comparison of methods of plasmapheresis for the treatment of late antibody mediated rejection in kidney transplant recipients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2023, 27, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.A.; Amir, N.; Asbury, A.; Lange, A.; Hardinger, K.L. Treatment of antibody-mediated rejection in renal transplant patients: A clinical practice survey. Clin. Transplant. 2015, 29, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, R.A.; Zachary, A.A.; Racusen, L.C.; Leffell, M.S.; King, K.E.; Burdick, J.; Maley, W.R.; Ratner, L.E. Plasmapheresis and intravenous immune globulin provides effective rescue therapy for refractory humoral rejection and allows kidneys to be successfully transplanted into cross-match-positive recipients. Transplantation 2000, 70, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, P.N.; Butterly, D.W.; Greenberg, A.; Reddan, D.N.; Tuttle-Newhall, J.; Collins, B.H.; Kuo, P.C.; Reinsmoen, N.; Fields, T.; Howell, D.N.; et al. Beneficial effect of plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin on renal allograft survival of patients with acute humoral rejection. Transplantation 2003, 75, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchet, A.; Muller, B.; Olagne, J.; Barba, T.; Joly, M.; Obrecht, A.; Rabeyrin, M.; Dijoud, F.; Picard, C.; Mezaache, S.; et al. Evolution of humoral lesions on follow-up biopsy stratifies the risk for renal graft loss after antibody-mediated rejection treatment. Am. J. Transpl. 2022, 22, 2652–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ye, Y.; Hu, X. A non-invasive piTreg-related gene signature for spontaneous tolerance in renal transplantation. Gene 2023, 887, 147724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhmig, G.A.; Wahrmann, M.; Regele, H.; Exner, M.; Robl, B.; Derfler, K.; Soliman, T.; Bauer, P.; Müllner, M.; Druml, W. Immunoadsorption in severe C4d-positive acute kidney allograft rejection: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Transpl. 2007, 7, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, C.; Nochy, D.; Andrade, J.; Verine, J.; Gautreau, C.; Charron, D.; Hill, G.S.; Glotz, D.; Suberbielle-Boissel, C. Comparison of combination plasmapheresis/IVIg/anti-CD20 versus high-dose IVIg in the treatment of antibody-mediated rejection. Am. J. Transpl. 2009, 9, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautenet, B.; Blancho, G.; Büchler, M.; Morelon, E.; Toupance, O.; Barrou, B.; Ducloux, D.; Chatelet, V.; Moulin, B.; Freguin, C.; et al. One-year results of the effects of rituximab on acute antibody-mediated rejection in renal transplantation: RITUX ERAH, a multicenter double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Transplantation 2016, 100, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandary, F.; Regele, H.; Baumann, L.; Bond, G.; Kozakowski, N.; Wahrmann, M.; Hidalgo, L.G.; Haslacher, H.; Kaltenecker, C.C.; Aretin, M.B.; et al. A randomized trial of bortezomib in late antibody-mediated kidney transplant rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreeb, K.; Culme-Seymour, E.; Ridha, E.; Dumont, C.; Atkinson, G.; Hsu, B.; Reinke, P. Study design: Human leukocyte antigen class I molecule A∗02-chimeric antigen receptor regulatory T cells in renal transplantation. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, K.G.; Hoeppli, R.E.; Huang, Q.; Gillies, J.; Luciani, D.S.; Orban, P.C.; Broady, R.; Levings, M.K. Alloantigen-specific regulatory T cells generated with a chimeric antigen receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betriu, S.; Rovira, J.; Arana, C.; García-Busquets, A.; Matilla-Martinez, M.; Ramirez-Bajo, M.J.; Bañon-Maneus, E.; Lazo-Rodriguez, M.; Bartoló-Ibars, A.; Claas, F.H.J.; et al. Chimeric HLA antibody receptor T cells for targeted therapy of antibody-mediated rejection in transplantation. HLA 2023, 102, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchia, J.; Weiskopf, K.; Levy, R. Targeting lymphoma with precision using semisynthetic anti-idiotype peptibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 5376–5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Song, L.; Lu, X.; Tan, L.; Li, X.; Fu, L.; Luo, Q.; Xie, X.; Zou, Y. Novel BCR-Targeting Fusion Proteins for Antigen-Specific Depletion of Alloreactive B Cells in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Cells 2025, 14, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181410
Zhang J, Wei L, Song L, Lu X, Tan L, Li X, Fu L, Luo Q, Xie X, Zou Y. Novel BCR-Targeting Fusion Proteins for Antigen-Specific Depletion of Alloreactive B Cells in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Cells. 2025; 14(18):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181410
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jing, Leiyan Wei, Lei Song, Xiaofang Lu, Liang Tan, Xin Li, Li Fu, Qizhi Luo, Xubiao Xie, and Yizhou Zou. 2025. "Novel BCR-Targeting Fusion Proteins for Antigen-Specific Depletion of Alloreactive B Cells in Antibody-Mediated Rejection" Cells 14, no. 18: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181410
APA StyleZhang, J., Wei, L., Song, L., Lu, X., Tan, L., Li, X., Fu, L., Luo, Q., Xie, X., & Zou, Y. (2025). Novel BCR-Targeting Fusion Proteins for Antigen-Specific Depletion of Alloreactive B Cells in Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Cells, 14(18), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14181410







