Beyond Support Cells: Astrocytic Autophagy as a Central Regulator of CNS Homeostasis and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Insights of Autophagy in the CNS
2.1. Molecular Mechanisms of Autophagy
Macroautophagy
2.2. CNS-Specific Features and Physiological Relevance of Autophagy
2.2.1. Functional Distinctions from Autophagy in Peripheral Tissues
2.2.2. Neuronal Vulnerability and the Need for Basal Autophagy
2.2.3. Autophagy in Synaptic Function and Plasticity
2.3. Astrocytic Autophagy as a Central Regulator of Physiological CNS Homeostasis
2.3.1. Energetic Adaptation and Lipid Homeostasis
2.3.2. Redox Homeostasis and ROS Regulation
2.3.3. Regulation of Neurotransmitter Transport and Membrane Protein Availability
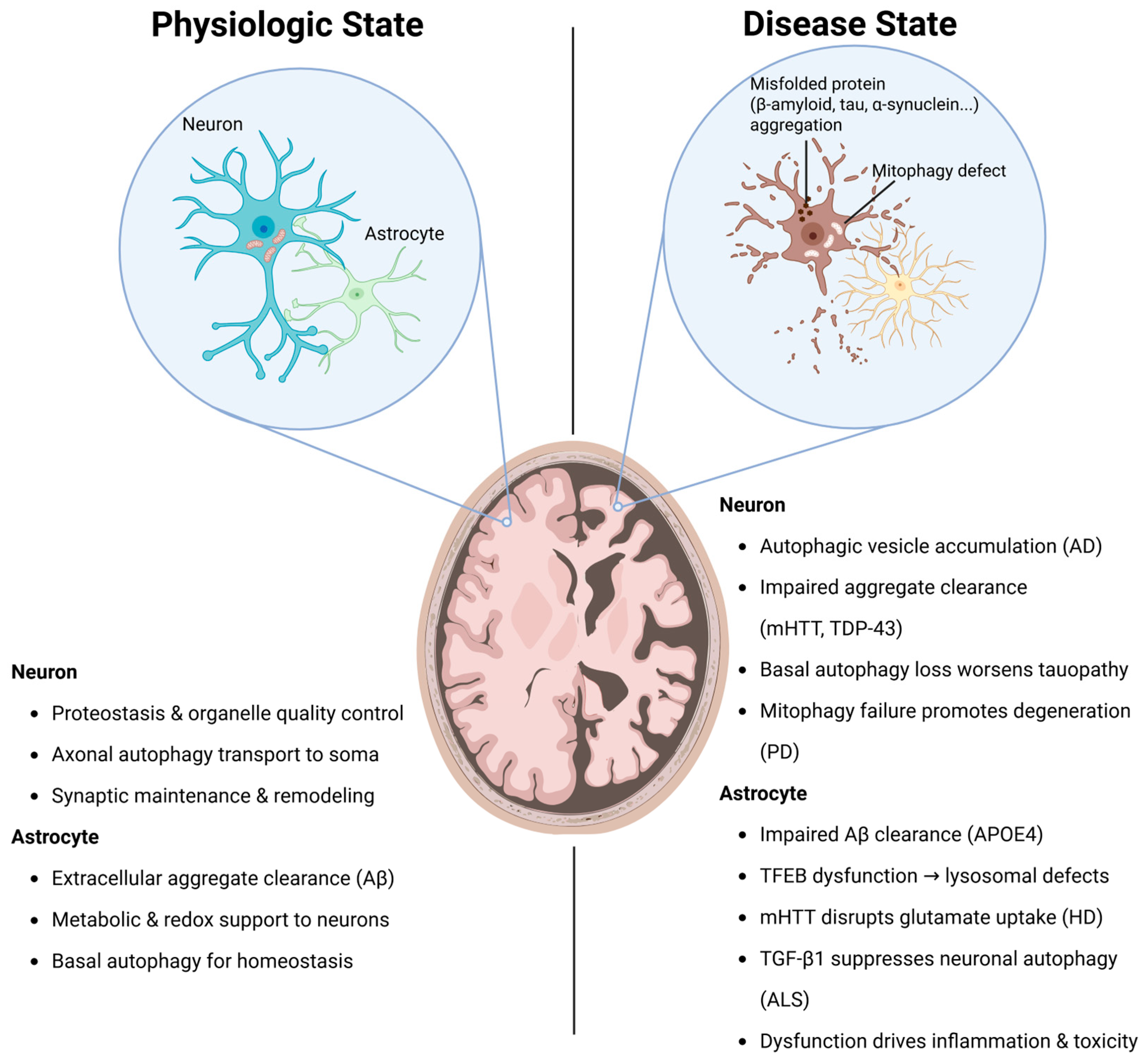
2.4. Autophagy Dysfunction in Neurons and Astrocytes in Neurodegenerative Diseases
2.4.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
2.4.2. Parkinson’s Disease
2.4.3. Huntington’s Disease
2.4.4. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
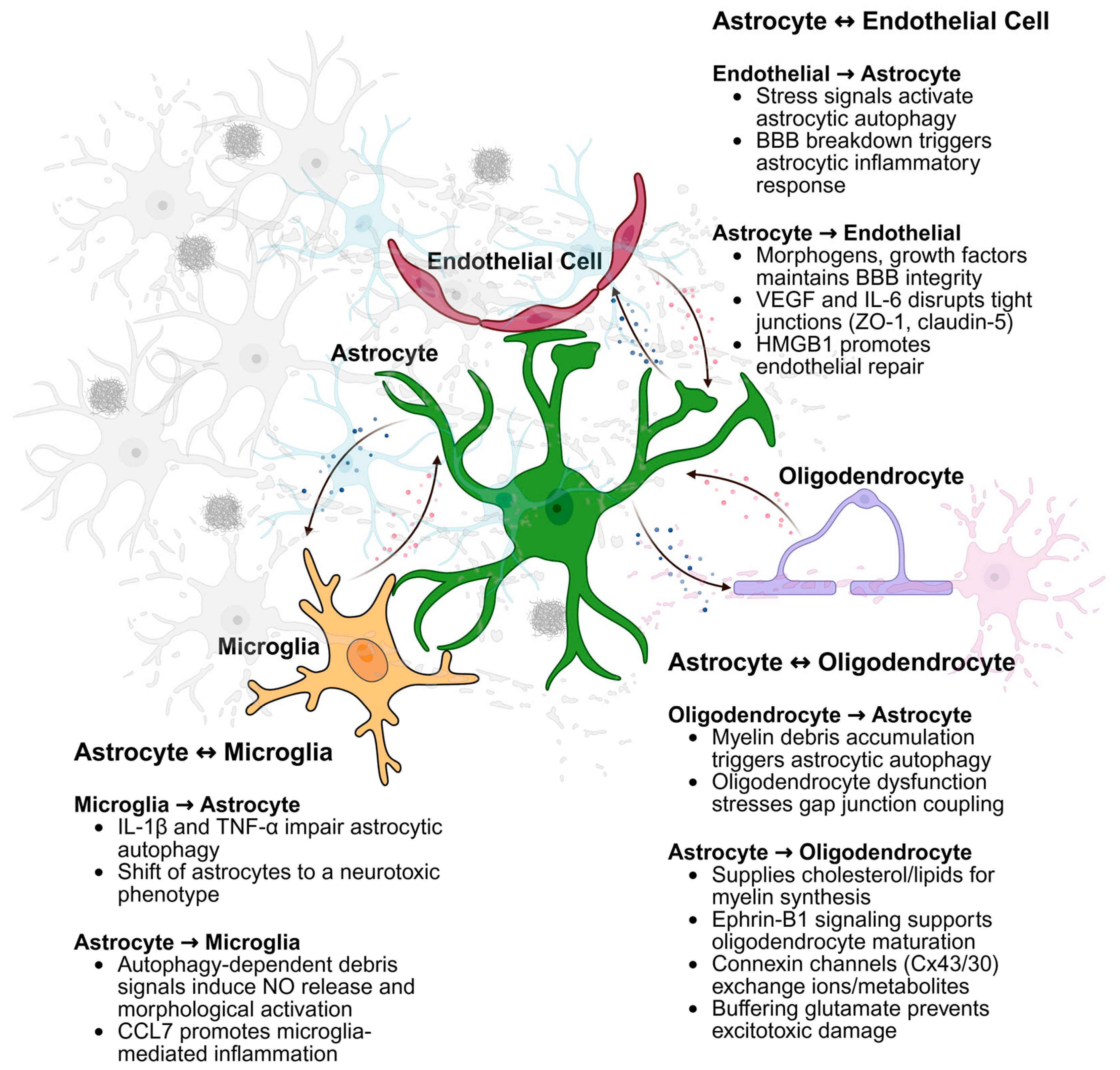
3. Autophagy in Astrocytes and the Crosstalk with Other Cell Types
3.1. Astrocyte-Neuronal Crosstalk
3.2. Astrocyte-Endothelial Crosstalk
3.3. Astrocyte-Microglial Crosstalk
3.4. Astrocyte-Oligodendrocyte Crosstalk
4. Astrocytic Autophagy-Targeted Drug Development Progress
4.1. Pharmacological Agents Targeting Astrocytic Autophagy
4.2. Regulation of Astrocytic Autophagy in Specific Neurological Disorders
4.2.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
4.2.2. Parkinson’s Disease
4.2.3. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
4.3. Autophagy-Modulating Drugs in Clinical Development for Neurodegenerative Diseases
4.3.1. Blarcamesine (ANAVEX®2-73)—Alzheimer’s Disease
4.3.2. Rapamycin (Sirolimus)—Alzheimer’s Disease
4.3.3. Felodipine—Huntington’s Disease
4.3.4. AT-1501 (Tegoprubart)—Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
| Neurological Disorder | Pharmacological Agent | Mechanism of Modulation in Astrocytes (If Known) | Key Preclinical Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s Disease | LC3B Overexpression (Genetic) | Enhanced autophagy | Reduced Aβ aggregates, improved cognition in mouse models [155] |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Rapamycin | mTOR inhibition | Promotes Aβ clearance [173] |
| Alzheimer’s Disease | Resveratrol, Metformin | Caloric restriction mimetics | Modulates autophagy, potential Aβ clearance [174] |
| Parkinson’s Disease | Lithium | Inhibition of inositol monophosphatase | Protective effects against MPP+-induced injury [139] |
| Huntington’s Disease | Rapamycin | mTOR inhibition | Reduced mHTT accumulation [175] |
| ALS | IADB | Autophagy promotion | Reduced mutant SOD1 aggregates, alleviated astrocyte activation in mouse models [148] |
| Mood Disorders | Amitriptyline, Citalopram | PI3 kinase-dependent pathways, ASM inhibition (potential) | Induction of autophagy in astrocytes [145] |
| Drug Name | Primary Neurodegenerative Disease(s) | Primary Autophagy-Related Mechanism | Current/Latest Clinical Trial Phase | Relevant ClinicalTrials.gov/ISRCTN ID(s) | Key Clinical Outcome (Brief) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blarcamesine (ANAVEX®2-73) | AD, PD | SIGMAR1 activation (autophagy enhancement) | AD: Phase 2b/3 completed; PD: Phase 2 PoC completed | NCT03790709, NCT04314934 | AD: Significantly slowed clinical progression (ADAS-Cog13, CDR-SB), improved biomarkers (plasma Aβ42/40-ratio, brain volume) |
| Rapamycin (Sirolimus) | AD | mTOR inhibition (autophagy induction) | AD: Phase 2 recruiting (NCT04629495), Phase 1 completed (NCT04200911) | NCT04629495, NCT04200911 1 | AD: Phase 1 showed rapamycin not detectable in CSF, but changes in AD/inflammatory biomarkers; Phase 2 ongoing for safety, tolerability, feasibility |
| Felodipine | HD | L-type Calcium Channel Blocker (autophagy induction) | HD: Phase 2 (dose-finding) | ISRCTN56240656, EudraCT-2021-000897-27 | HD: Primary outcome is safety and tolerability; exploratory outcomes include motor/cognitive function, biomarkers |
| AT-1501 (Tegoprubart) | ALS | CD40L antagonism (indirect link via inflammation/immune modulation) | ALS: Phase 2a completed | NCT04322149 | ALS: Safe and well-tolerated, demonstrated dose-dependent target engagement, reduced inflammatory biomarkers |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vargas, J.N.S.; Hamasaki, M.; Kawabata, T.; Youle, R.J.; Yoshimori, T. The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy in mammals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Matsui, T. Molecular Mechanisms of Macroautophagy, Microautophagy, and Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2024, 91, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-D.; Lv, C.-L.; Feng, L.; Guo, J.-X.; Zhao, S.-Y.; Jiang, P. The role of autophagy in brain health and disease: Insights into exosome and autophagy interactions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Butt, A.; Li, B.; Illes, P.; Zorec, R.; Semyanov, A.; Tang, Y.; Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocytes in human central nervous system diseases: A frontier for new therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, J.D.; Seeher, K.M.; Schiess, N.; Nichols, E.; Cao, B.; Servili, C.; Cavallera, V.; Cousin, E.; Hagins, H.; Moberg, M.E.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of disorders affecting the nervous system, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 344–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potokar, M.; Jorgačevski, J. Targeting autophagy in astrocytes: A potential for neurodegenerative disease intervention. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2025, 19, 1584767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valori, C.F.; Possenti, A.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Challenges and Opportunities of Targeting Astrocytes to Halt Neurodegenerative Disorders. Cells 2021, 10, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Klionsky, D.J. Mammalian autophagy: Core molecular machinery and signaling regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatogawa, H. Mechanisms governing autophagosome biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Cuervo, A.M. The coming of age of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejlvang, J.; Olsvik, H.; Svenning, S.; Bruun, J.A.; Abudu, Y.P.; Larsen, K.B.; Brech, A.; Hansen, T.E.; Brenne, H.; Hansen, T.; et al. Starvation induces rapid degradation of selective autophagy receptors by endosomal microautophagy. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 3640–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Troya, S.; Perez-Perez, M.E.; Florencio, F.J.; Crespo, J.L. The role of TOR in autophagy regulation from yeast to plants and mammals. Autophagy 2008, 4, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, Y.; Sekito, T.; Ohsumi, Y. Autophagy in yeast: A TOR-mediated response to nutrient starvation. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 279, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K.L. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganley, I.G.; Lam, D.H.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, S.; Jiang, X. ULK1.ATG13.FIP200 complex mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12297–12305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funderburk, S.F.; Wang, Q.J.; Yue, Z. The Beclin 1-VPS34 complex--at the crossroads of autophagy and beyond. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, C.; Metlagel, Z.; Takaesu, G.; Otomo, T. Structure of the human ATG12~ATG5 conjugate required for LC3 lipidation in autophagy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, J.; Walczak, M.; Ibiricu, I.; Schuchner, S.; Ogris, E.; Kraft, C.; Martens, S. Mechanism and functions of membrane binding by the Atg5-Atg12/Atg16 complex during autophagosome formation. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4304–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeya, Y.; Mizushima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Oshitani-Okamoto, S.; Ohsumi, Y.; Yoshimori, T. LC3, GABARAP and GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II formation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 2805–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankiv, S.; Clausen, T.H.; Lamark, T.; Brech, A.; Bruun, J.A.; Outzen, H.; Overvatn, A.; Bjorkoy, G.; Johansen, T. p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24131–24145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Song, J.C.; Cho, S.J.; Yun, S.M.; Koh, Y.H.; Song, J.; Johnson, G.V.; Jo, C. NDP52 associates with phosphorylated tau in brains of an Alzheimer disease mouse model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenknop, A.; Rogov, V.V.; Rogova, N.Y.; Lohr, F.; Guntert, P.; Dikic, I.; Dotsch, V. Characterization of the interaction of GABARAPL-1 with the LIR motif of NBR1. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 410, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Noda, T.; Yoshimori, T. Dynein-dependent movement of autophagosomes mediates efficient encounters with lysosomes. Cell Struct. Funct. 2008, 33, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huotari, J.; Helenius, A. Endosome maturation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 3481–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ney, P.A. Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B. Critical roles of FAM134B in ER-phagy and diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Muhlinen, N.; Thurston, T.; Ryzhakov, G.; Bloor, S.; Randow, F. NDP52, a novel autophagy receptor for ubiquitin-decorated cytosolic bacteria. Autophagy 2010, 6, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Lao, U.; Edgar, B.A. TOR-mediated autophagy regulates cell death in Drosophila neurodegenerative disease. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 186, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Nakamura, K.; Matsui, M.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakahara, Y.; Suzuki-Migishima, R.; Yokoyama, M.; Mishima, K.; Saito, I.; Okano, H.; et al. Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 2006, 441, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Waguri, S.; Chiba, T.; Murata, S.; Iwata, J.; Tanida, I.; Ueno, T.; Koike, M.; Uchiyama, Y.; Kominami, E.; et al. Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes neurodegeneration in mice. Nature 2006, 441, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.C.; Wang, C.; Peng, X.; Gan, B.; Guan, J.L. Neural-specific deletion of FIP200 leads to cerebellar degeneration caused by increased neuronal death and axon degeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 3499–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononenko, N.L.; Classen, G.A.; Kuijpers, M.; Puchkov, D.; Maritzen, T.; Tempes, A.; Malik, A.R.; Skalecka, A.; Bera, S.; Jaworski, J.; et al. Retrograde transport of TrkB-containing autophagosomes via the adaptor AP-2 mediates neuronal complexity and prevents neurodegeneration. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitomo, A.; Yukitake, H.; Hirai, K.; Horike, K.; Ueta, K.; Chung, Y.; Warabi, E.; Yanagawa, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Furuyashiki, T.; et al. Ulk2 controls cortical excitatory-inhibitory balance via autophagic regulation of p62 and GABAA receptor trafficking in pyramidal neurons. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3165–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehata, M.; Matsumura, H.; Okubo-Suzuki, R.; Ohkawa, N.; Inokuchi, K. Neuronal stimulation induces autophagy in hippocampal neurons that is involved in AMPA receptor degradation after chemical long-term depression. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 10413–10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Z.; Du, W.; Que, H.; Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Jian, F.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, Y.; Tian, R.; et al. Recycling of autophagosomal components from autolysosomes by the recycler complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoletopoulou, V.; Sidiropoulou, K.; Kallergi, E.; Dalezios, Y.; Tavernarakis, N. Modulation of Autophagy by BDNF Underlies Synaptic Plasticity. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraz, M.M.; Guha, P.; Kang, I.G.; Semenza, E.R.; Malla, A.P.; Song, Y.J.; Reilly, L.; Treisman, I.; Cortes, P.; Coggiano, M.A.; et al. Cocaine-induced locomotor stimulation involves autophagic degradation of the dopamine transporter. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, V.V.; Anand, A.; Herr, J.B.; Miranda, C.; Vogel, M.C.; Maday, S. Synaptic activity controls autophagic vacuole motility and function in dendrites. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202002084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, I.; Keyser, C.; Zhang, Z.; Rosolia, B.; Hwang, J.Y.; Zukin, R.S.; Yan, J. Epigenetic regulation of autophagy in neuroinflammation and synaptic plasticity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1322842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpova, A.; Hiesinger, P.R.; Kuijpers, M.; Albrecht, A.; Kirstein, J.; Andres-Alonso, M.; Biermeier, A.; Eickholt, B.J.; Mikhaylova, M.; Maglione, M.; et al. Neuronal autophagy in the control of synapse function. Neuron 2025, 113, 974–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Smedlund, K.; Zhou, Q.G.; Cai, W.; Hill, J.W. Astrocyte involvement in metabolic regulation and disease. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 36, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Long, C.; Peng, X.; Tao, J.; Pu, Y.; Yue, R. Bridging metabolic syndrome and cognitive dysfunction: Role of astrocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1393253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Fu, J.T.; Tzeng, S.F. Exposure to lipid mixture induces intracellular lipid droplet formation and impairs mitochondrial functions in astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 178, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preeti, K.; Sood, A.; Fernandes, V. Metabolic Regulation of Glia and Their Neuroinflammatory Role in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 2527–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cho, S.; Kim, M.J.; Park, Y.J.; Cho, E.; Jo, Y.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Thoudam, T.; Woo, S.H.; et al. ApoE4-dependent lysosomal cholesterol accumulation impairs mitochondrial homeostasis and oxidative phosphorylation in human astrocytes. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolič, T.; Tavčar, P.; Horvat, A.; Černe, U.; Halužan Vasle, A.; Tratnjek, L.; Kreft, M.E.; Scholz, N.; Matis, M.; Petan, T.; et al. Astrocytes in stress accumulate lipid droplets. Glia 2021, 69, 1540–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Qi, G.; Vitali, F.; Shang, Y.; Raikes, A.C.; Wang, T.; Jin, Y.; Brinton, R.D.; Gu, H.; Yin, F. Loss of fatty acid degradation by astrocytic mitochondria triggers neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolaños, J.P. Bioenergetics and redox adaptations of astrocytes to neuronal activity. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. S2), 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, C.; Huang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, K.; Xu, J.; Guo, G.; Tong, A.; Zhou, L. The role of astrocytes in oxidative stress of central nervous system: A mixed blessing. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Fabuel, I.; Le Douce, J.; Logan, A.; James, A.M.; Bonvento, G.; Murphy, M.P.; Almeida, A.; Bolaños, J.P. Complex I assembly into supercomplexes determines differential mitochondrial ROS production in neurons and astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13063–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, H.; Almeida, A.; Figueiredo-Pereira, C.; Queiroga, C. Carbon monoxide targeting mitochondria in astrocytes: Modulation of cell metabolism, redox response and cell death. Springerplus 2015, 4, L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-Pereira, C.; Villarejo-Zori, B.; Cipriano, P.C.; Tavares, D.; Ramírez-Pardo, I.; Boya, P.; Vieira, H.L.A. Carbon Monoxide Stimulates Both Mitophagy And Mitochondrial Biogenesis to Mediate Protection Against Oxidative Stress in Astrocytes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.A.; Liu, J.; Miller, J.W.; Rothstein, J.D.; Farrell, K.; Stein, B.A.; Longuemare, M.C. Neuronal regulation of glutamate transporter subtype expression in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnewald, U.; Westergaard, N.; Schousboe, A. Glutamate transport and metabolism in astrocytes. Glia 1997, 21, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camandola, S. Astrocytes, emerging stars of energy homeostasis. Cell Stress 2018, 2, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petr, G.T.; Sun, Y.; Frederick, N.M.; Zhou, Y.; Dhamne, S.C.; Hameed, M.Q.; Miranda, C.; Bedoya, E.A.; Fischer, K.D.; Armsen, W.; et al. Conditional deletion of the glutamate transporter GLT-1 reveals that astrocytic GLT-1 protects against fatal epilepsy while neuronal GLT-1 contributes significantly to glutamate uptake into synaptosomes. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 5187–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoletopoulou, V.; Papandreou, M.E.; Tavernarakis, N. Autophagy in the physiology and pathology of the central nervous system. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, F.M.; Fleming, A.; Caricasole, A.; Bento, C.F.; Andrews, S.P.; Ashkenazi, A.; Fullgrabe, J.; Jackson, A.; Jimenez Sanchez, M.; Karabiyik, C.; et al. Autophagy and Neurodegeneration: Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Neuron 2017, 93, 1015–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, K.; Jimenez-Sanchez, M. Autophagy in Astrocytes and its Implications in Neurodegeneration. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 2605–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.H.; Cuervo, A.M.; Kumar, A.; Peterhoff, C.M.; Schmidt, S.D.; Lee, J.H.; Mohan, P.S.; Mercken, M.; Farmery, M.R.; Tjernberg, L.O.; et al. Macroautophagy--a novel Beta-amyloid peptide-generating pathway activated in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickford, F.; Masliah, E.; Britschgi, M.; Lucin, K.; Narasimhan, R.; Jaeger, P.A.; Small, S.; Spencer, B.; Rockenstein, E.; Levine, B.; et al. The autophagy-related protein beclin 1 shows reduced expression in early Alzheimer disease and regulates amyloid β accumulation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2190–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal-Garcia, A.; Branca, R.M.; Francis, P.T.; Ballard, C.; Winblad, B.; Lehtiö, J.; Nilsson, P.; Aarsland, D.; Pereira, J.B.; Bereczki, E. Proteomic signatures of Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementias: A comparative analysis. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Seo, J.; Gao, F.; Feldman, H.M.; Wen, H.L.; Penney, J.; Cam, H.P.; Gjoneska, E.; Raja, W.K.; Cheng, J.; et al. APOE4 Causes Widespread Molecular and Cellular Alterations Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease Phenotypes in Human iPSC-Derived Brain Cell Types. Neuron 2018, 98, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, P.B.; Castellano, J.M.; Garai, K.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Shah, A.; Bu, G.; Frieden, C.; Holtzman, D.M. ApoE influences amyloid-beta (Abeta) clearance despite minimal apoE/Abeta association in physiological conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E1807–E1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, R.A.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Mechanisms of autophagy-lysosome dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 926–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.E.; Wilson, N.; Son, S.M.; Obrocki, P.; Wrobel, L.; Rob, M.; Takla, M.; Korolchuk, V.I.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Autophagy, aging, and age-related neurodegeneration. Neuron 2025, 113, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibinski, G.; Parkinson, N.J.; Brown, J.M.; Chakrabarti, L.; Lloyd, S.L.; Hummerich, H.; Nielsen, J.E.; Hodges, J.R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Thusgaard, T.; et al. Mutations in the endosomal ESCRTIII-complex subunit CHMP2B in frontotemporal dementia. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendra, D.P.; Jin, S.M.; Tanaka, A.; Suen, D.F.; Gautier, C.A.; Shen, J.; Cookson, M.R.; Youle, R.J. PINK1 is selectively stabilized on impaired mitochondria to activate Parkin. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, H.D.E.; Hirst, W.D.; Wade-Martins, R. The Role of Astrocyte Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Trends Neurosci. 2017, 40, 358–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilariño-Güell, C.; Rajput, A.; Milnerwood, A.J.; Shah, B.; Szu-Tu, C.; Trinh, J.; Yu, I.; Encarnacion, M.; Munsie, L.N.; Tapia, L.; et al. DNAJC13 mutations in Parkinson disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 23, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Qin, Z.H.; Sheng, R. The Multiple Roles of Autophagy in Neural Function and Diseases. Neurosci. Bull. 2024, 40, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, J.; Shin, J.Y.; Roberts, M.; Wang, C.E.; Sheng, G.; Li, S.; Li, X.J. Mutant huntingtin in glial cells exacerbates neurological symptoms of Huntington disease mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10653–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmaki, H.; Nourazarian, A.; Shademan, B.; Khaki-Khatibi, F. The autophagy paradox: A new hypothesis in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem. Int. 2024, 179, 105827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, T.B.; Hogarth, P.; Kruer, M.C.; Gregory, A.; Wieland, T.; Schwarzmayr, T.; Graf, E.; Sanford, L.; Meyer, E.; Kara, E.; et al. Exome Sequencing Reveals De Novo WDR45 Mutations Causing a Phenotypically Distinct, X-Linked Dominant Form of NBIA. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, K.; Chun, S.J.; Boillee, S.; Fujimori-Tonou, N.; Yamashita, H.; Gutmann, D.H.; Takahashi, R.; Misawa, H.; Cleveland, D.W. Astrocytes as determinants of disease progression in inherited amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, P.; Rodriguez-Muela, N.; Klim, J.R.; de Boer, A.S.; Agrawal, S.; Sandoe, J.; Lopes, C.S.; Ogliari, K.S.; Williams, L.A.; Shear, M.; et al. Reactive Astrocytes Promote ALS-like Degeneration and Intracellular Protein Aggregation in Human Motor Neurons by Disrupting Autophagy through TGF-beta1. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, L.; Rubinsztein, D.C. The autophagy of stress granules. FEBS Lett. 2024, 598, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freischmidt, A.; Wieland, T.; Richter, B.; Ruf, W.; Schaeffer, V.; Müller, K.; Marroquin, N.; Nordin, F.; Hübers, A.; Weydt, P.; et al. Haploinsufficiency of TBK1 causes familial ALS and fronto-temporal dementia. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecto, F.; Yan, J.; Vemula, S.P.; Liu, E.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J.G.; Shi, Y.; Siddique, N.; Arrat, H.; et al. SQSTM1 Mutations in Familial and Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 1440–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, H.; Morino, H.; Ito, H.; Izumi, Y.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kamada, M.; Nodera, H.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Mutations of optineurin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 2010, 465, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M.; Hertz, L. Why are astrocytes important? Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, H.; Dai, Z.; He, C.; Qin, S.; Su, Z. From Physiology to Pathology of Astrocytes: Highlighting Their Potential as Therapeutic Targets for CNS Injury. Neurosci. Bull. 2025, 41, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, N.J.; Lyons, D.A. Glia as architects of central nervous system formation and function. Science 2018, 362, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakh, B.S. Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions in the Striatum: Insights on Identity, Form, and Function. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Dong, A.; Kulkarni, V.V.; Chen, J.; Laxton, O.; Anand, A.; Maday, S. Differential regulation of autophagy during metabolic stress in astrocytes and neurons. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsztein, D.C.; Codogno, P.; Levine, B. Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, F.; Hughes, L.; Fu, Y.; Bardy, C.; Halliday, G.M.; Dzamko, N. Astrocytes contribute to toll-like receptor 2-mediated neurodegeneration and alpha-synuclein pathology in a human midbrain Parkinson’s model. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linda, K.; Schuurmans, I.M.E.; Smeenk, H.; Vints, K.; Negwer, M.; Peredo, N.; Lewerissa, E.I.; Swerts, J.; Hoekstra, M.; Mordelt, A.; et al. Neuronal autophagosomes are transported to astrocytes for degradation. bioRxiv 2024. [CrossRef]
- Palumbos, S.D.; Popolow, J.; Goldsmith, J.; Holzbaur, E.L.F. Autophagic stress activates distinct compensatory secretory pathways in neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2421886122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Shin, D.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, Y.J.; Rajanikant, G.K.; Majid, A.; Baek, S.H.; Bae, O.N. Role of Autophagy in Endothelial Damage and Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption in Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wei, J.Y.; Li, Y.; Ban, M.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.J.; Zhao, D.; Tong, P.G.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.J.; et al. Endothelial depletion of Atg7 triggers astrocyte-microvascular disassociation at blood-brain barrier. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 222, e202103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoriūnas, A.; Verkhratsky, A. Astrocyte-Endotheliocyte Axis in the Regulation of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2538–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Autophagy Protects the Blood-Brain Barrier Through Regulating the Dynamic of Claudin-5 in Short-Term Starvation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guérit, S.; Fidan, E.; Macas, J.; Czupalla, C.J.; Figueiredo, R.; Vijikumar, A.; Yalcin, B.H.; Thom, S.; Winter, P.; Gerhardt, H.; et al. Astrocyte-derived Wnt growth factors are required for endothelial blood-brain barrier maintenance. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 199, 101937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Kovac, A.; Morofuji, Y. Neurovascular unit crosstalk: Pericytes and astrocytes modify cytokine secretion patterns of brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2018, 38, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulica, P.; Grünewald, A.; Pereira, S.L. Astrocyte-Neuron Metabolic Crosstalk in Neurodegeneration: A Mitochondrial Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 668517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Li, J.R.; Chen, W.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Wu, C.C.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.J. Disruption of in vitro endothelial barrier integrity by Japanese encephalitis virus-Infected astrocytes. Glia 2015, 63, 1915–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, K.; Pham, L.D.; Katusic, Z.S.; Arai, K.; Lo, E.H. Astrocytic high-mobility group box 1 promotes endothelial progenitor cell-mediated neurovascular remodeling during stroke recovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7505–7510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, M.K.; Jo, M.; Kim, J.H.; Suk, K. Microglia-Astrocyte Crosstalk: An Intimate Molecular Conversation. Neuroscientist 2019, 25, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Rao, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, D.; Xu, Z.; et al. Microglial debris is cleared by astrocytes via C4b-facilitated phagocytosis and degraded via RUBICON-dependent noncanonical autophagy in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lv, Q.; Su, J. Astrocyte-derived CCL7 promotes microglia-mediated inflammation following traumatic brain injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafatti, M.; Cocozza, G.; Limatola, C.; Garofalo, S. Microglial crosstalk with astrocytes and immune cells in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1223096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhusal, A.; Afridi, R.; Lee, W.H.; Suk, K. Bidirectional Communication Between Microglia and Astrocytes in Neuroinflammation. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, D.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, H.I. Decoding hippocampal subfield and glial responses in ischemia using single-cell transcriptomics. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Feng, J. Cross talk between activation of microglia and astrocytes in pathological conditions in the central nervous system. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhl, C.; Sievers, J. Microglia is activated by astrocytes in trimethyltin intoxication. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Zong, Y.; Cao, X.P.; Tan, L.; Tan, L. Microglial priming in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, V.H.; Holmes, C. Microglial priming in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.R.; Liu, J.C.; Bao, J.S.; Bai, Q.Q.; Wang, G.Q. Interaction of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Neurovascular Unit. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.V.; Hanson, J.E.; Sheng, M. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litwiniuk, A.; Juszczak, G.R.; Stankiewicz, A.M.; Urbańska, K. The role of glial autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 4528–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani Shabestari, S.; Morabito, S.; Danhash, E.P.; McQuade, A.; Sanchez, J.R.; Miyoshi, E.; Chadarevian, J.P.; Claes, C.; Coburn, M.A.; Hasselmann, J.; et al. Absence of microglia promotes diverse pathologies and early lethality in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajbakhsh, A.; Read, M.; Barreto, G.E.; Ávila-Rodriguez, M.; Gheibi-Hayat, S.M.; Sahebkar, A. Apoptotic neurons and amyloid-beta clearance by phagocytosis in Alzheimer’s disease: Pathological mechanisms and therapeutic outlooks. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 895, 173873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Nam, H.; Kim, L.E.; Jeon, Y.; Min, H.; Ha, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, E.K.; et al. TLR4 (toll-like receptor 4) activation suppresses autophagy through inhibition of FOXO3 and impairs phagocytic capacity of microglia. Autophagy 2019, 15, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomilio, C.; Gorojod, R.M.; Riudavets, M.; Vinuesa, A.; Presa, J.; Gregosa, A.; Bentivegna, M.; Alaimo, A.; Alcon, S.P.; Sevlever, G.; et al. Microglial autophagy is impaired by prolonged exposure to β-amyloid peptides: Evidence from experimental models and Alzheimer’s disease patients. Geroscience 2020, 42, 613–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, J.; Mothes, T.; Kolahdouzan, M.; Eriksson, O.; Moslem, M.; Bergström, J.; Ingelsson, M.; O’Callaghan, P.; Healy, L.M.; Falk, A.; et al. Crosstalk between astrocytes and microglia results in increased degradation of α-synuclein and amyloid-β aggregates. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Litvinchuk, A.; Chiang, A.C.; Aithmitti, N.; Jankowsky, J.L.; Zheng, H. Astrocyte-Microglia Cross Talk through Complement Activation Modulates Amyloid Pathology in Mouse Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Tao, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Duan, Y. Iron accumulation and microglia activation contribute to substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in the 6-OHDA-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 36, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Mendívil, C.; Luengo, E.; Trigo-Alonso, P.; García-Magro, N.; Negredo, P.; López, M.G. Protective role of microglial HO-1 blockade in aging: Implication of iron metabolism. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.P.; Kam, T.I.; Panicker, N.; Kim, S.; Oh, Y.; Park, J.S.; Kwon, S.H.; Park, Y.J.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Park, H.; et al. Block of A1 astrocyte conversion by microglia is neuroprotective in models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Song, N.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Xie, J. New Progress on the Role of Glia in Iron Metabolism and Iron-Induced Degeneration of Dopamine Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouali Alami, N.; Schurr, C.; Olde Heuvel, F.; Tang, L.; Li, Q.; Tasdogan, A.; Kimbara, A.; Nettekoven, M.; Ottaviani, G.; Raposo, C.; et al. NF-κB activation in astrocytes drives a stage-specific beneficial neuroimmunological response in ALS. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e98697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Pina-Crespo, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, W.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Yu, H.; et al. Membralin deficiency dysregulates astrocytic glutamate homeostasis leading to ALS-like impairment. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 3103–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttenplan, K.A.; Weigel, M.K.; Adler, D.I.; Couthouis, J.; Liddelow, S.A.; Gitler, A.D.; Barres, B.A. Knockout of reactive astrocyte activating factors slows disease progression in an ALS mouse model. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, D. The evolving landscape of neurotoxicity by unconjugated bilirubin: Role of glial cells and inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Même, W.; Calvo, C.F.; Froger, N.; Ezan, P.; Amigou, E.; Koulakoff, A.; Giaume, C. Proinflammatory cytokines released from microglia inhibit gap junctions in astrocytes: Potentiation by beta-amyloid. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 494–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, H.S.; Portugal, C.C.; Socodato, R.; Relvas, J.B. Oligodendrocyte, Astrocyte, and Microglia Crosstalk in Myelin Development, Damage, and Repair. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Gonzalez, I.; Holloway, R.K.; Jiwaji, Z.; Dando, O.; Kent, S.A.; Emelianova, K.; Lloyd, A.F.; Forbes, L.H.; Mahmood, A.; Skripuletz, T.; et al. Astrocyte-oligodendrocyte interaction regulates central nervous system regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, G.; Xu, D.-E.; Du, Y.-t.; Zhu, C.; Hu, H.; Luo, L.; Feng, L.; Huang, W.; Sun, Y.-Y.; et al. Autophagy in Oligodendrocyte Lineage Cells Controls Oligodendrocyte Numbers and Myelin Integrity in an Age-dependent Manner. Neurosci. Bull. 2025, 41, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognatta, R.; Karl, M.T.; Fyffe-Maricich, S.L.; Popratiloff, A.; Garrison, E.D.; Schenck, J.K.; Abu-Rub, M.; Miller, R.H. Astrocytes Are Required for Oligodendrocyte Survival and Maintenance of Myelin Compaction and Integrity. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutley-Koury, S.N.; Anderson, A.; Taitano-Johnson, C.; Ajayi, M.; Kulinich, A.O.; Contreras, K.; Regalado, J.; Tiwari-Woodruff, S.K.; Ethell, I.M. Astrocytic Ephrin-B1 Regulates Oligodendrocyte Development and Myelination. ASN Neuro 2024, 16, 2401753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.R.; Johnson, D.A.; Sirkis, D.W.; Messing, A.; Johnson, J.A. Nrf2 activation in astrocytes protects against neurodegeneration in mouse models of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 13574–13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, V.; Tyagi, S.; Dey, D.; Singh, A.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Sinha, S.; Sharma, J.B.; Seth, P.; Sen, S. Glial cholesterol redistribution in hypoxic injury in vitro influences oligodendrocyte maturation and myelination. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, S.E.; Zhao, Y.; Gulinello, M.; Lee, S.C.; Raine, C.S.; Brosnan, C.F. Deletion of astrocyte connexins 43 and 30 leads to a dysmyelinating phenotype and hippocampal CA1 vacuolation. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 7743–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnow, A.M.; Attwell, D. NMDA Receptors: Power Switches for Oligodendrocytes. Neuron 2016, 91, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamen, Y.; Evans, K.A.; Sitnikov, S.; Spitzer, S.O.; de Faria, O.; Yucel, M.; Káradóttir, R.T. Clemastine and metformin extend the window of NMDA receptor surface expression in ageing oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Xian, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Pei, Z. Potential protective effects of autophagy activated in MPP+ treated astrocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishwarya, R.; Abdullah, C.S.; Morshed, M.; Remex, N.S.; Bhuiyan, M.S. Sigmar1’s Molecular, Cellular, and Biological Functions in Regulating Cellular Pathophysiology. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 705575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C. Autophagy in brain tumors: Molecular mechanisms, challenges, and therapeutic opportunities. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, A.A.; Gao, A.; Coombs, K.M. Autophagy Modulators Profoundly Alter the Astrocyte Cellular Proteome. Cells 2020, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Yosef, T.; Damri, O.; Agam, G. Dual Role of Autophagy in Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Bang, Y.; Moon, S.H.; Kim, A.; Choi, H.J. Amitriptyline interferes with autophagy-mediated clearance of protein aggregates via inhibiting autophagosome maturation in neuronal cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-W.; Zhu, X.-X.; Tang, D.-S.; Lu, J.-H. Targeting autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease: Animal models and mechanisms. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, G.; Beard, D.J.; Couch, Y.; Neuhaus, A.A.; Adriaanse, B.A.; DeLuca, G.C.; Sutherland, B.A.; Buchan, A.M. Rapamycin in ischemic stroke: Old drug, new tricks? J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Yan, X.; Yacipi, N.; Duan, W.; Li, C.; Thompson, M.; Shan, Z.; Bi, L. Pharmacological Modulation of Autophagy Prevents Mutant SOD1G93A Induced Neurotoxicity in Experimental Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Cai, H.; Le, W. Autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: Pathogenesis and therapy. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Afshar, S.; Lorzadeh, S.; Adlimoghaddam, A.; Rezvani Jalal, N.; West, R.; Dastghaib, S.; Igder, S.; Torshizi, S.R.N.; et al. Enhancing autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease through drug repositioning. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 237, 108171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.P.; Shacka, J.J. Autophagy Modulation in Disease Therapy: Where Do We Stand? Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2013, 1, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Hao, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, X.; Song, L. The dual roles of autophagy and the GPCRs-mediating autophagy signaling pathway after cerebral ischemic stroke. Mol. Brain 2022, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.; Cuttino, L.; Gewirtz, D.A. Autophagy is not uniformly cytoprotective: A personalized medicine approach for autophagy inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—General. Subj. 2016, 1860, 2130–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chun, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, U.; Chu, J.; Bhalla, M.; Choi, S.H.; Yousefian-Jazi, A.; Kim, S.; et al. Astrocytic autophagy plasticity modulates Aβ clearance and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Shrestha, Y.; Jayatunga, D.P.W.; Rea, S.; Martins, R.; Bharadwaj, P. Activate or Inhibit? Implications of Autophagy Modulation as a Therapeutic Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Levine, B.; Green, D.R.; Kroemer, G. Pharmacological modulation of autophagy: Therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 487–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izrael, M.; Slutsky, S.G.; Revel, M. Rising Stars: Astrocytes as a Therapeutic Target for ALS Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, W.E.; Sprouse, J.; Rebowe, N.; Hanania, T.; Klamer, D.; Missling, C.U. ANAVEX®2-73 (blarcamesine), a Sigma-1 receptor agonist, ameliorates neurologic impairments in a mouse model of Rett syndrome. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 187, 172796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Song, Y.-Q.; Tu, J. Autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis: Therapeutic potential and future perspectives. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 72, 101464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.H.; Ye, Y.; Wan, B.B.; Yu, Y.D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.J. Emerging Benefits: Pathophysiological Functions and Target Drugs of the Sigma-1 Receptor in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5649–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, C.; Zhen, X. Sigma-1 Receptor-Modulated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane, S.; Grimmer, T.; Teo, K.; O’Brien, T.J.; Woodward, M.; Grunfeld, J.; Mander, A.; Brodtmann, A.; Brew, B.J.; Morris, P.; et al. Blarcamesine for the treatment of Early Alzheimer’s Disease: Results from the ANAVEX2-73-AD-004 Phase IIB/III trial. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 12, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.M.; Mayer, J.; Nilsson, P.; Shimozawa, M. How close is autophagy-targeting therapy for Alzheimer’s disease to clinical use? A summary of autophagy modulators in clinical studies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1520949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, M.M.; Garbarino, V.R.; Kautz, T.F.; Song, X.; Lopez-Cruzan, M.; Linehan, L.; Van Skike, C.E.; De Erausquin, G.A.; Galvan, V.; Orr, M.E.; et al. Rapamycin treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias: A pilot phase 1 clinical trial. Commun. Med. 2025, 5, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, P.A.; Faulds, D. Felodipine. A review of the pharmacology and therapeutic use of the extended release formulation in cardiovascular disorders. Drugs 1992, 44, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, F.H.; Menzies, F.M.; Lopez, A.; Stamatakou, E.; Karabiyik, C.; Ureshino, R.; Ricketts, T.; Jimenez-Sanchez, M.; Esteban, M.A.; Lai, L.; et al. Felodipine induces autophagy in mouse brains with pharmacokinetics amenable to repurposing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, K.; Cutting, E.; Apostolopoulos, D.; Evans, A.H.; Oakley, L.; Dayimu, A.; Demiris, N.; Bongaerts, K.; Staples, R.; Gooding, W.; et al. Trial to assess the tolerability of using felodipine to upregulate autophagy as a treatment of Huntington’s disease (FELL-HD): A phase II, single-centre, open-label, dose-finding trial protocol. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e087983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, I.J.; Berman, D.M.; DeLaura, I.; Gao, Q.; Willman, M.A.; Miller, A.; Gill, A.; Gill, C.; Perrin, S.; Ricordi, C.; et al. The anti-CD40L monoclonal antibody AT-1501 promotes islet and kidney allograft survival and function in nonhuman primates. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eadf6376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincecum, J.M.; Vieira, F.G.; Wang, M.Z.; Thompson, K.; De Zutter, G.S.; Kidd, J.; Moreno, A.; Sanchez, R.; Carrion, I.J.; Levine, B.A.; et al. From transcriptome analysis to therapeutic anti-CD40L treatment in the SOD1 model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarev, E.D.; Shriver, L.P.; Dittel, B.N. CD40 expression by microglial cells is required for their completion of a two-step activation process during central nervous system autoimmune inflammation. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonninen, T.M.; Goldsteins, G.; Laham-Karam, N.; Koistinaho, J.; Lehtonen, Š. Proteostasis Disturbances and Inflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, S.; Ladha, S.; Maragakis, N.; Rivner, M.H.; Katz, J.; Genge, A.; Olney, N.; Lange, D.; Heitzman, D.; Bodkin, C.; et al. Safety and tolerability of tegoprubart in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A Phase 2A clinical trial. PLoS Med. 2024, 21, e1004469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Juan, M.; Ordóñez-Gutiérrez, L.; Wandosell, F. Clearance of β-amyloid mediated by autophagy is enhanced by MTORC1 inhibition but not AMPK activation in APP/PSEN1 astrocytes. Glia 2024, 72, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.J.T.; Frendo-Cumbo, S.; MacPherson, R.E.K. Resveratrol and Metformin Recover Prefrontal Cortex AMPK Activation in Diet-Induced Obese Mice but Reduce BDNF and Synaptophysin Protein Content. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 71, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.R.; de Moraes, R.C.M.; Xu, B.P.; Crawley, S.R.; Khan, M.A.; Melkani, G.C. Rapamycin reduces neuronal mutant huntingtin aggregation and ameliorates locomotor performance in Drosophila. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1223911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Chang, W.; Min, S.S.; Song, D.Y.; Yoo, H.I. Beyond Support Cells: Astrocytic Autophagy as a Central Regulator of CNS Homeostasis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells 2025, 14, 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171342
Lee JH, Chang W, Min SS, Song DY, Yoo HI. Beyond Support Cells: Astrocytic Autophagy as a Central Regulator of CNS Homeostasis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171342
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jung Ho, Wonseok Chang, Sun Seek Min, Dae Yong Song, and Hong Il Yoo. 2025. "Beyond Support Cells: Astrocytic Autophagy as a Central Regulator of CNS Homeostasis and Neurodegenerative Diseases" Cells 14, no. 17: 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171342
APA StyleLee, J. H., Chang, W., Min, S. S., Song, D. Y., & Yoo, H. I. (2025). Beyond Support Cells: Astrocytic Autophagy as a Central Regulator of CNS Homeostasis and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cells, 14(17), 1342. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171342






