MMP-12 Inhibitors Inverse Eosinophilic Inflammation-Mediated Bronchial Fibrosis in Murine Models of Pulmonary Airway Obstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Mouse Treatments
2.3. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Collagen Staining and Quantification
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. ELISA Analysis
2.7. Airway Resistance Measurement
2.8. MMP-12 Inhibitors
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
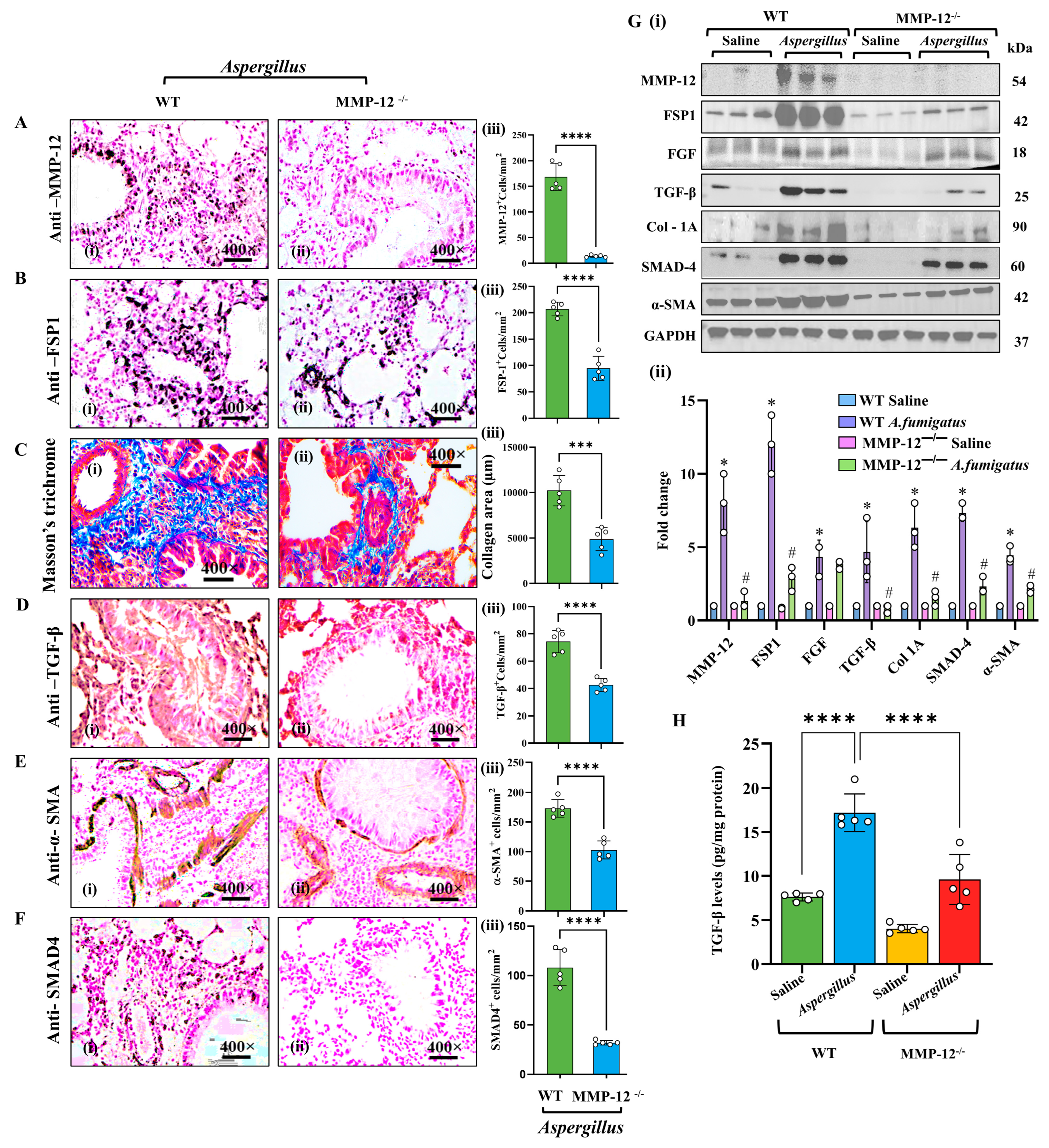
3.1. MMP-12 Regulates Eosinophil-Responsive Proinflammatory Cytokines and Promotes Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Aspergillus fumigatus Extract-Challenged Mice
3.2. MMP-12 Drives Fibroblast Accumulation and Fibrosis in Aspergillus fumigatus Extract Allergic Airway Inflammation
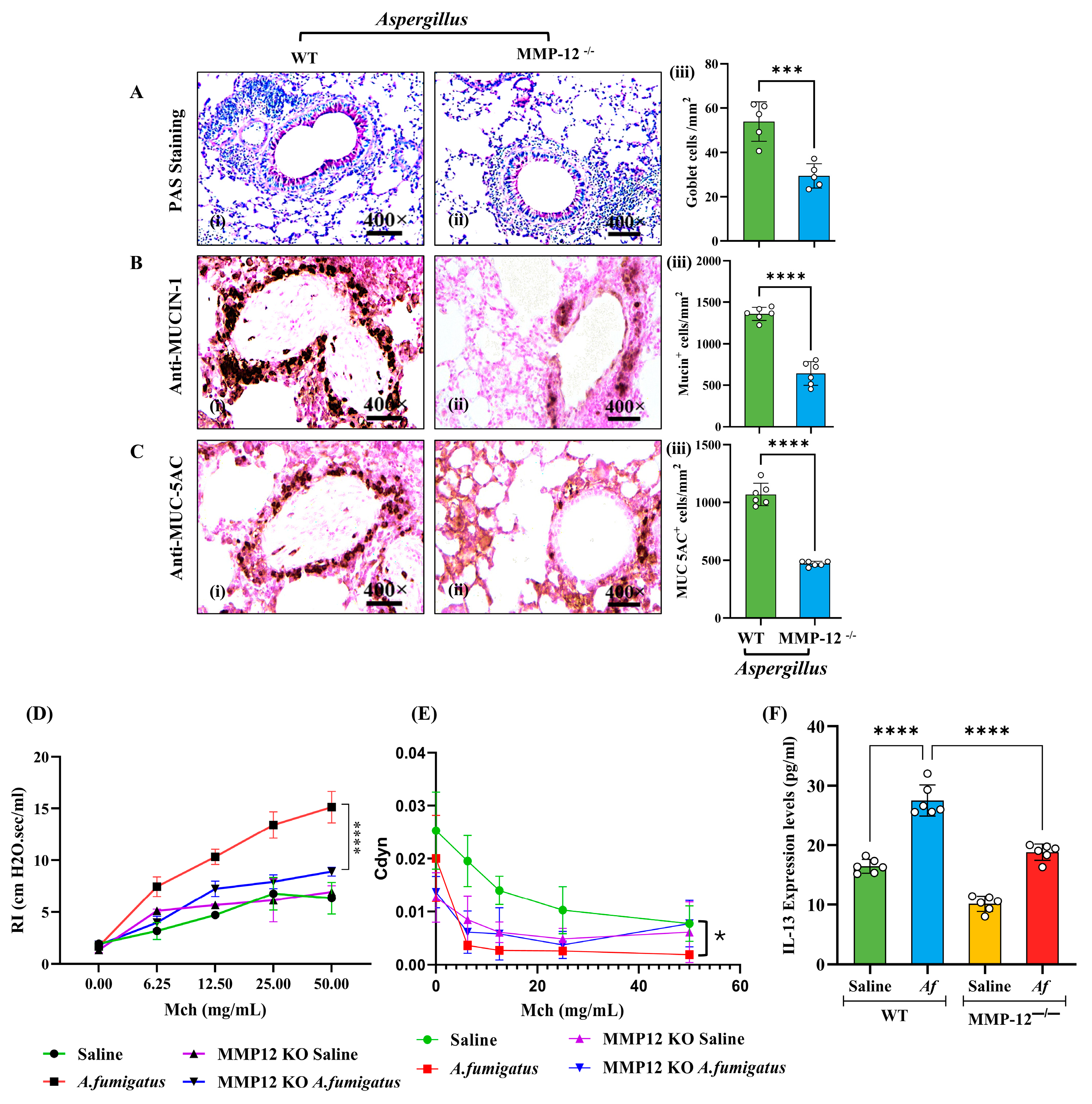
3.3. MMP-12 Deficiency Improves Airway Functional Abnormalities in Aspergillus fumigatus-Challenged Mice
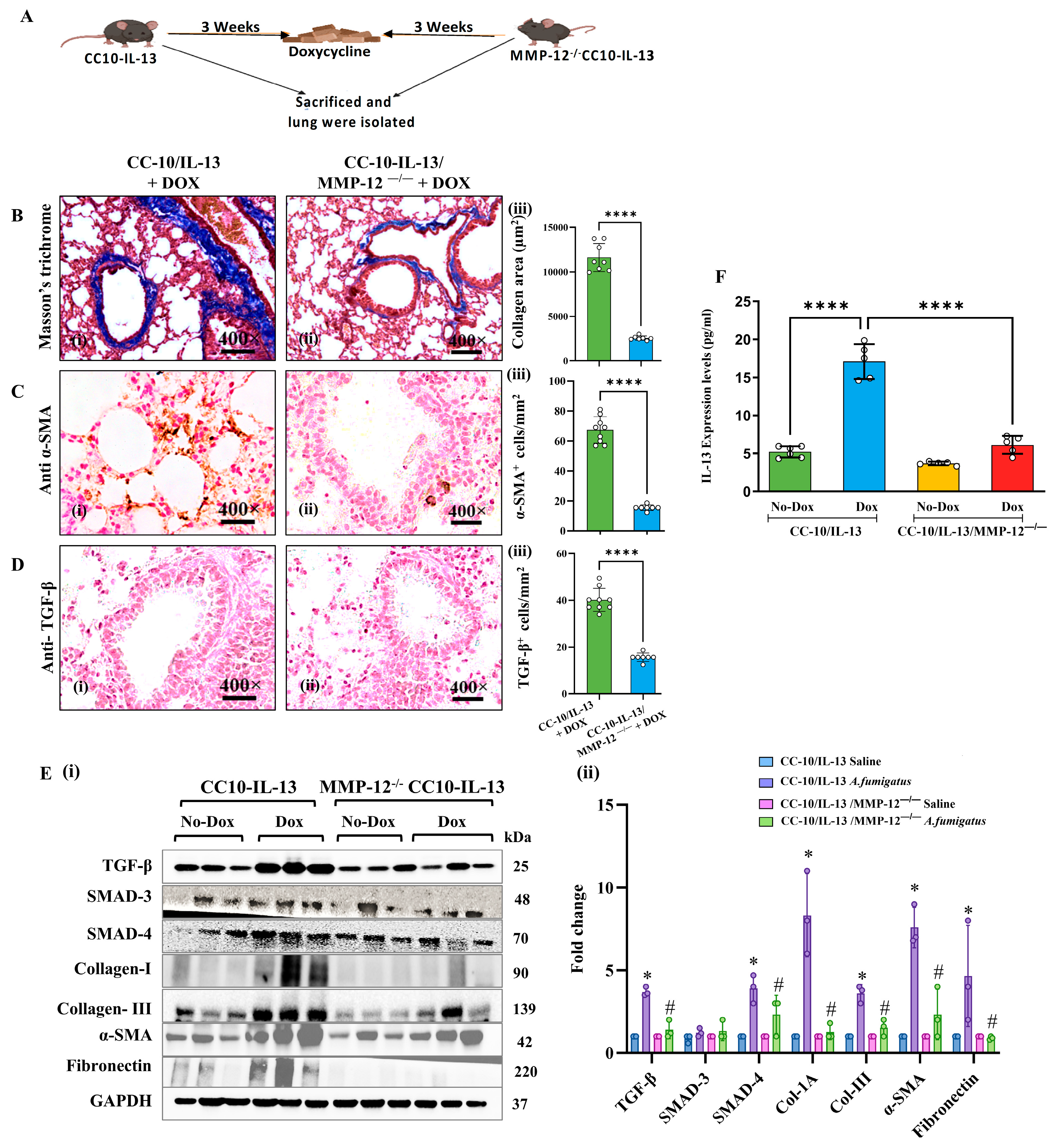
3.4. MMP-12 Regulates IL-13 Overexpression-Induced Bronchial Fibrosis
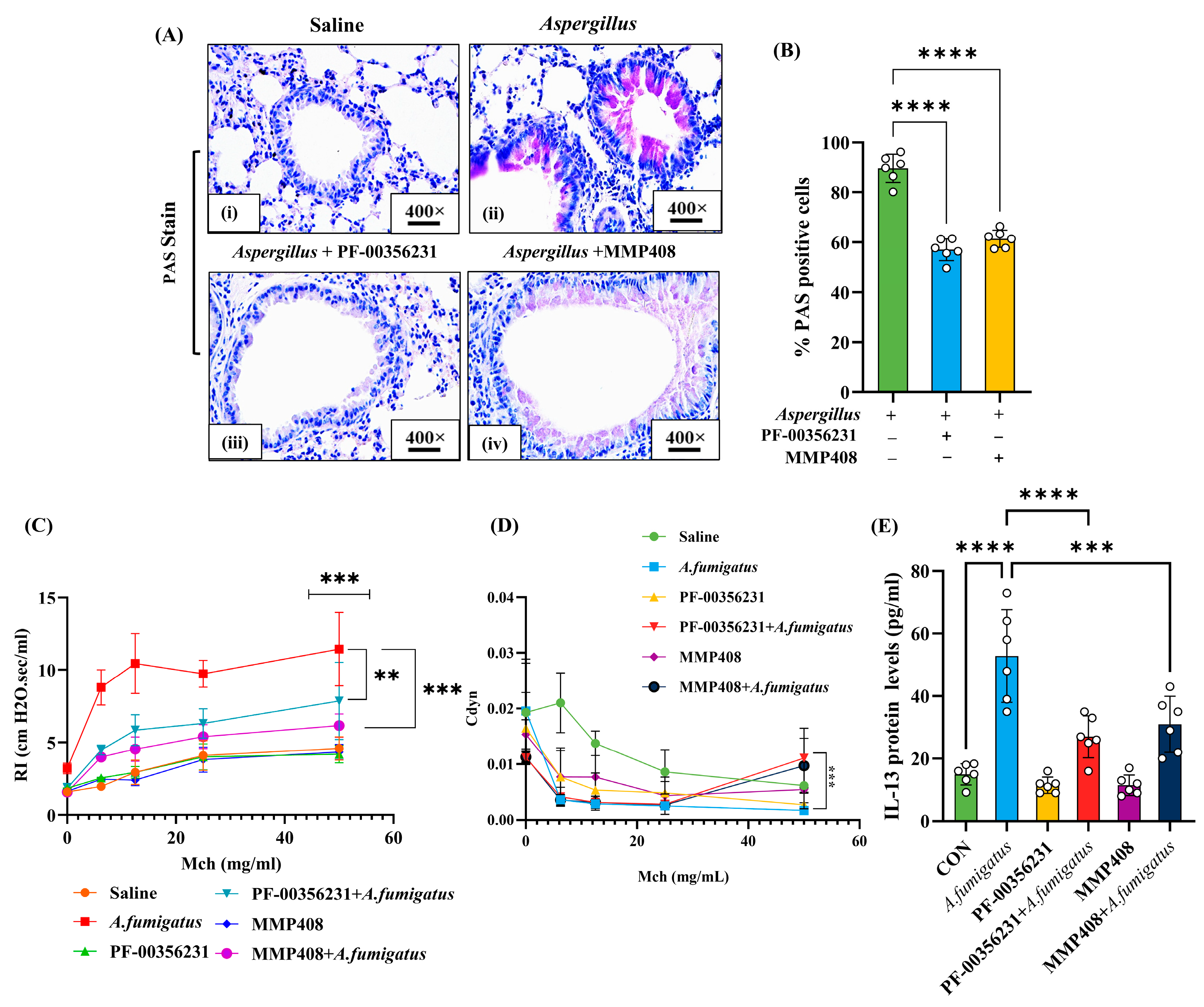
3.5. Pharmacological Inhibition of MMP-12 Reduces Allergen-Induced Fibrosis
3.6. Mucus Cell Hyperplasia and Airway Obstruction in Aspergillus fumigatus Extract-Challenged and MMP-12 Inhibitor-Treated Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The roles of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkington, P.T.; Friedland, J.S. Matrix metalloproteinases in destructive pulmonary pathology. Thorax 2006, 61, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulou, M.-E.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Stolz, D. Matrix metalloproteinases in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, S.J.; Atsuta, R.; McIntyre, J.O.; Hackett, T.-L.; Singhera, G.K.; Dorscheid, D.R. IL-13 and TH2 cytokine exposure triggers matrix metalloproteinase 7–mediated Fas ligand cleavage from bronchial epithelial cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 366–374.e368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, J.A.; Kang, M.J.; Crouthers, K.; Homer, R.; Lee, C.G. State of the art. Mechanistic heterogeneity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Insights from transgenic mice. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2006, 3, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.A.; Jarjour, N.N. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in asthma. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2003, 9, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, N.; Temma, T.; Aita, K.; Shimochi, S.; Koshino, K.; Senda, M.; Iida, H. Development of matrix metalloproteinase-targeted probes for lung inflammation detection with positron emission tomography. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thickett, D.R.; Perkins, G.D.; O’Kane, C.; McKeown, S.; McAuley, D. Does MMP-12 play a role in human lung fibrosis? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2008, 38, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanone, S.; Zheng, T.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, W.; Lee, C.G.; Ma, B.; Chen, Q.; Homer, R.J.; Wang, J.; Rabach, L.A.; et al. Overlapping and enzyme-specific contributions of matrix metalloproteinases-9 and -12 in IL-13-induced inflammation and remodeling. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronski, T.J., Jr.; Martin, R.L.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Walsh, B.C.; Holman, M.C.; Huber, M.; Van Wart, H.E.; Shapiro, S.D. Hydrolysis of a broad spectrum of extracellular matrix proteins by human macrophage elastase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 12189–12194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Homer, R.J.; Ma, B.; Riese, R.J., Jr.; Chapman, H.A., Jr.; Shapiro, S.D.; Elias, J.A. Inducible targeting of IL-13 to the adult lung causes matrix metalloproteinase- and cathepsin-dependent emphysema. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadavalli, C.S.; Upparahalli Venkateshaiah, S.; Kumar, S.; Kandikattu, H.K.; Oruganti, L.; Kathera, C.S.; Mishra, A. Allergen-induced NLRP3/caspase1/IL-18 signaling initiate eosinophilic esophagitis and respective inhibitors protect disease pathogenesis. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandikattu, H.K.; Manohar, M.; Verma, A.K.; Kumar, S.; Yadavalli, C.S.; Venkateshaiah, S.U.; Mishra, A. Macrophages-induced IL-18–mediated eosinophilia promotes characteristics of pancreatic malignancy. Life Sci. Alliance 2021, 4, e202000979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Majid, D.; Kandikattu, H.K.; Yadavalli, C.S.; Upparahalli Venkateshaiah, S. Role of IL-18-transformed CD274-expressing eosinophils in promoting airway obstruction in experimental asthma. Allergy 2022, 77, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Hotchandani, R.; Cunningham, K.; McFadyen, I.; Bard, J.; Morgan, P.; Schlerman, F. A selective matrix metalloprotease 12 inhibitor for potential treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Discovery of (S)-2-(8-(methoxycarbonylamino) dibenzo [b, d] furan-3-sulfonamido)-3-methylbutanoic acid (MMP408). J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 1799–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aristorena, M.; Gallardo-Vara, E.; Vicen, M.; de Las Casas-Engel, M.; Ojeda-Fernandez, L.; Nieto, C.; Blanco, F.J.; Valbuena-Diez, A.C.; Botella, L.M.; Nachtigal, P. MMP-12, secreted by pro-inflammatory macrophages, targets endoglin in human macrophages and endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahnoon, L.; Bajbouj, K.; Mahboub, B.; Hamoudi, R.; Hamid, Q. Targeting il-13 and il-4 in asthma: Therapeutic implications on airway remodeling in severe asthma. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 68, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar-Garcia, E.A.; Vargas-Guerrero, B.; Gasca-Lozano, L.E.; Gurrola-Diaz, C.M. Molecular changes underlying pulmonary emphysema and chronic bronchitis in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: An updated review. Histol. Histopathol. 2024, 39, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, X.H.; Huang, Q.P.; Chen, M.L.; Xie, Z.F. Association of the MMP-3, MMP-9 and MMP-12 gene polymorphisms with COPD risk: A meta-analysis. Arch. Med. Sci. 2024, 20, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Foster, P.S.; Yang, M. The role of macrophages in asthma-related fibrosis and remodelling. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 269, 108820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Dalal, S.S.; Chen, E.S.; Downey, R.; Schulman, L.L.; Ginsburg, M.; D’Armiento, J. Human collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1) expression in the lungs of patients with emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, K.; Takagi, M.; Kurokawa, Y.; Satomi, S.; Konttinen, Y.T. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated extracellular matrix protein degradation in human pulmonary emphysema. Lab. Investig. 1998, 78, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Betsuyaku, T.; Nishimura, M.; Takeyabu, K.; Tanino, M.; Venge, P.; Xu, S.; Kawakami, Y. Neutrophil granule proteins in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from subjects with subclinical emphysema. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1985–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demedts, I.K.; Brusselle, G.G.; Bracke, K.R.; Vermaelen, K.Y.; Pauwels, R.A. Matrix metalloproteinases in asthma and COPD. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Valdez, L.; Pardo, A.; Gaxiola, M.; Uhal, B.D.; Becerril, C.; Selman, M. Upregulation of gelatinases A and B, collagenases 1 and 2, and increased parenchymal cell death in COPD. Chest 2000, 117, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.D. Elastolytic metalloproteinases produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. Potential roles in destructive lung disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 150, S160–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babusyte, A.; Stravinskaite, K.; Jeroch, J.; Lotvall, J.; Sakalauskas, R.; Sitkauskiene, B. Patterns of airway inflammation and MMP-12 expression in smokers and ex-smokers with COPD. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunninghake, G.M.; Cho, M.H.; Tesfaigzi, Y.; Soto-Quiros, M.E.; Avila, L.; Lasky-Su, J.; Stidley, C.; Melén, E.; Söderhäll, C.; Hallberg, J. MMP12, lung function, and COPD in high-risk populations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Massague, J. TGF-beta in developmental and fibrogenic EMTs. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firszt, R.; Francisco, D.; Church, T.D.; Thomas, J.M.; Ingram, J.L.; Kraft, M. Interleukin-13 induces collagen type-1 expression through matrix metalloproteinase-2 and transforming growth factor-beta1 in airway fibroblasts in asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 43, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madala, S.K.; Pesce, J.T.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Wilson, M.S.; Minnicozzi, S.; Cheever, A.W.; Thompson, R.W.; Mentink-Kane, M.M.; Wynn, T.A. Matrix metalloproteinase 12-deficiency augments extracellular matrix degrading metalloproteinases and attenuates IL-13-dependent fibrosis. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3955–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouladi, M.A.; Robbins, C.S.; Swirski, F.K.; Cundall, M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Jordana, M.; Shapiro, S.D.; Stampfli, M.R. Interleukin-13-dependent expression of matrix metalloproteinase-12 is required for the development of airway eosinophilia in mice. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 30, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kathera, C.S.; Yadavalli, C.S.; Mishra, A. MMP-12 Inhibitors Inverse Eosinophilic Inflammation-Mediated Bronchial Fibrosis in Murine Models of Pulmonary Airway Obstruction. Cells 2025, 14, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171307
Kathera CS, Yadavalli CS, Mishra A. MMP-12 Inhibitors Inverse Eosinophilic Inflammation-Mediated Bronchial Fibrosis in Murine Models of Pulmonary Airway Obstruction. Cells. 2025; 14(17):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171307
Chicago/Turabian StyleKathera, Chandra Sekhar, Chandra Sekhar Yadavalli, and Anil Mishra. 2025. "MMP-12 Inhibitors Inverse Eosinophilic Inflammation-Mediated Bronchial Fibrosis in Murine Models of Pulmonary Airway Obstruction" Cells 14, no. 17: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171307
APA StyleKathera, C. S., Yadavalli, C. S., & Mishra, A. (2025). MMP-12 Inhibitors Inverse Eosinophilic Inflammation-Mediated Bronchial Fibrosis in Murine Models of Pulmonary Airway Obstruction. Cells, 14(17), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14171307






