Structure of the Secretory Compartments in Goblet Cells in the Colon and Small Intestine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electron Tomography
2.2. Stereology
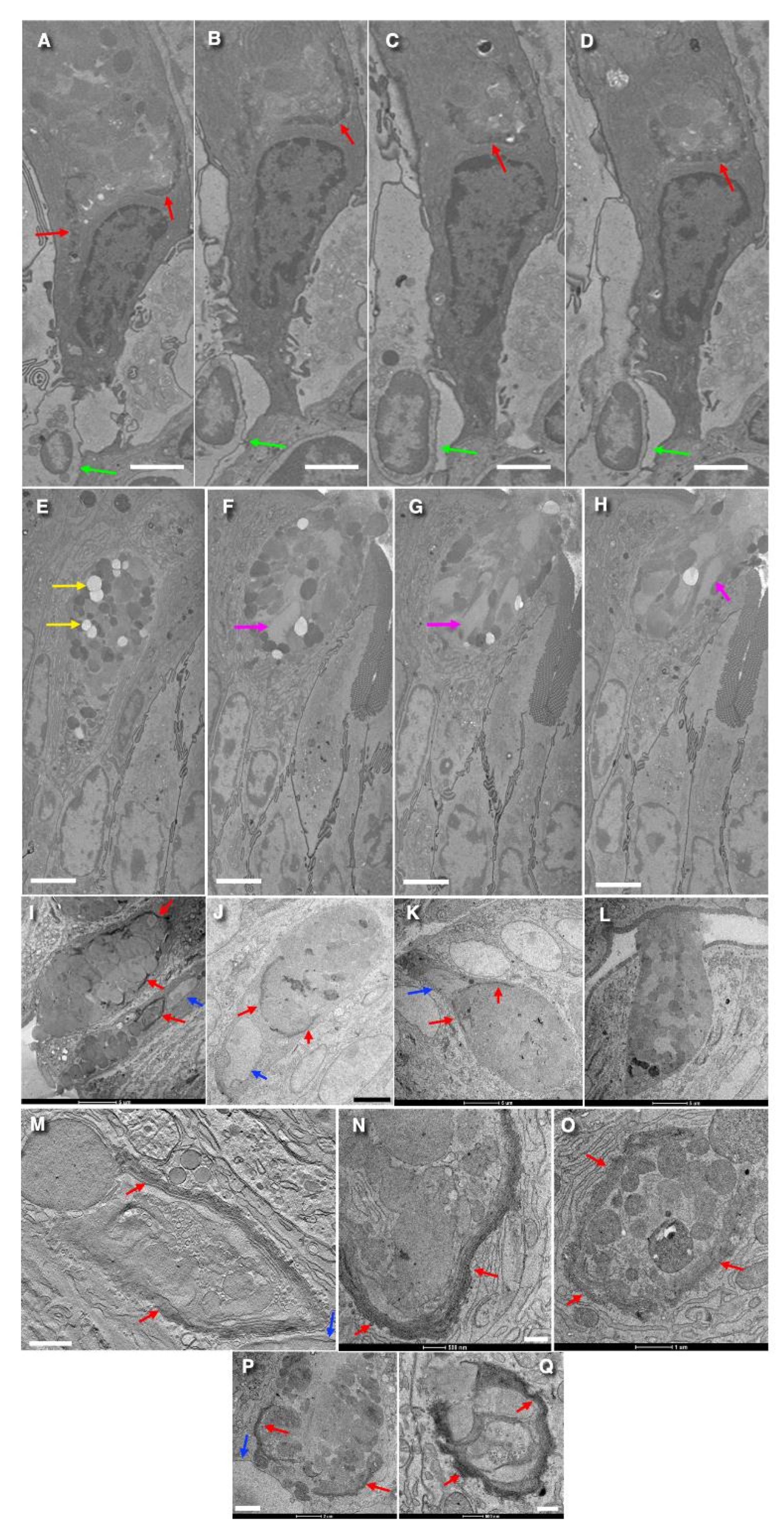
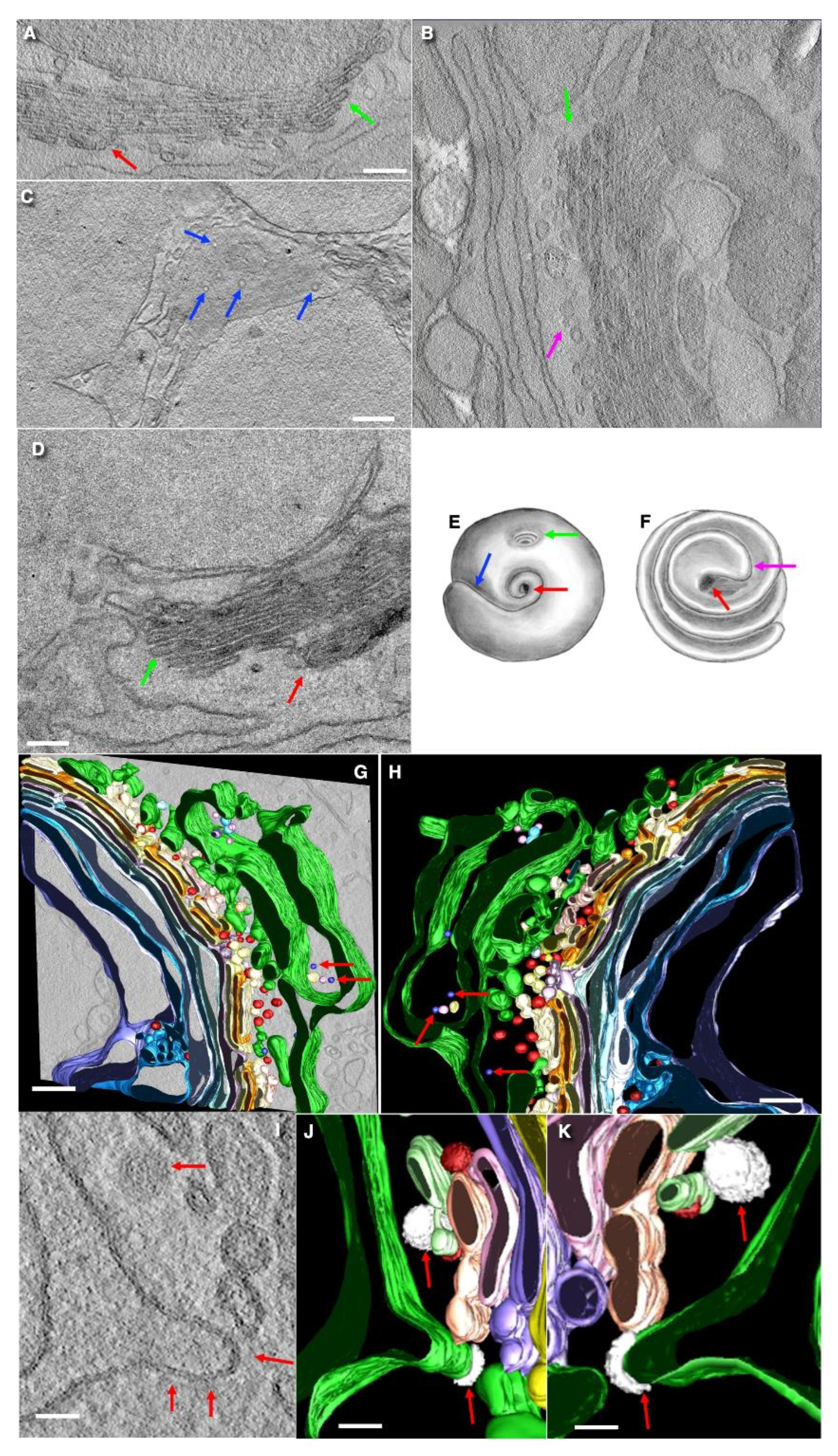
3. Results
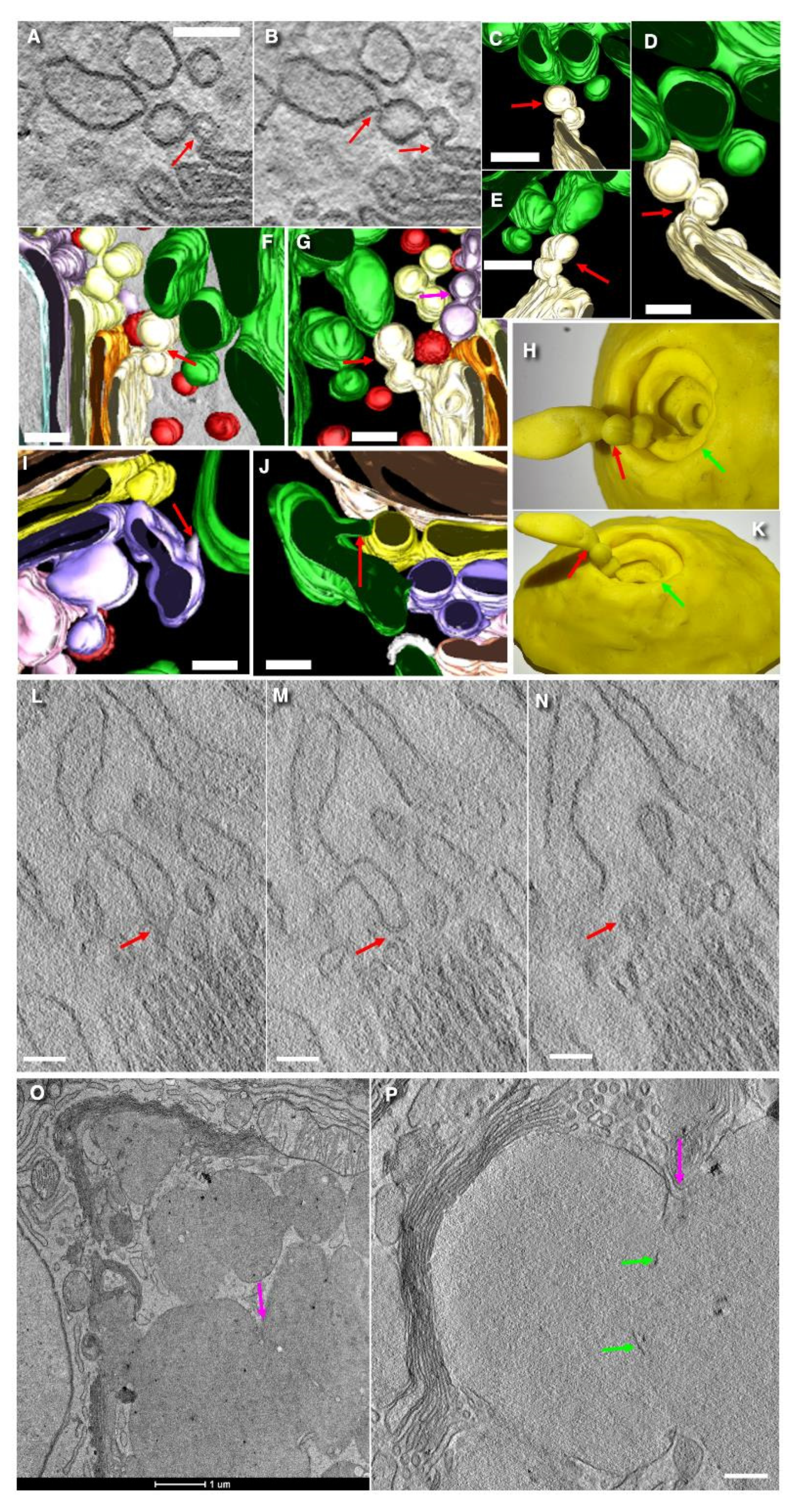
3.1. Structure of the Golgi
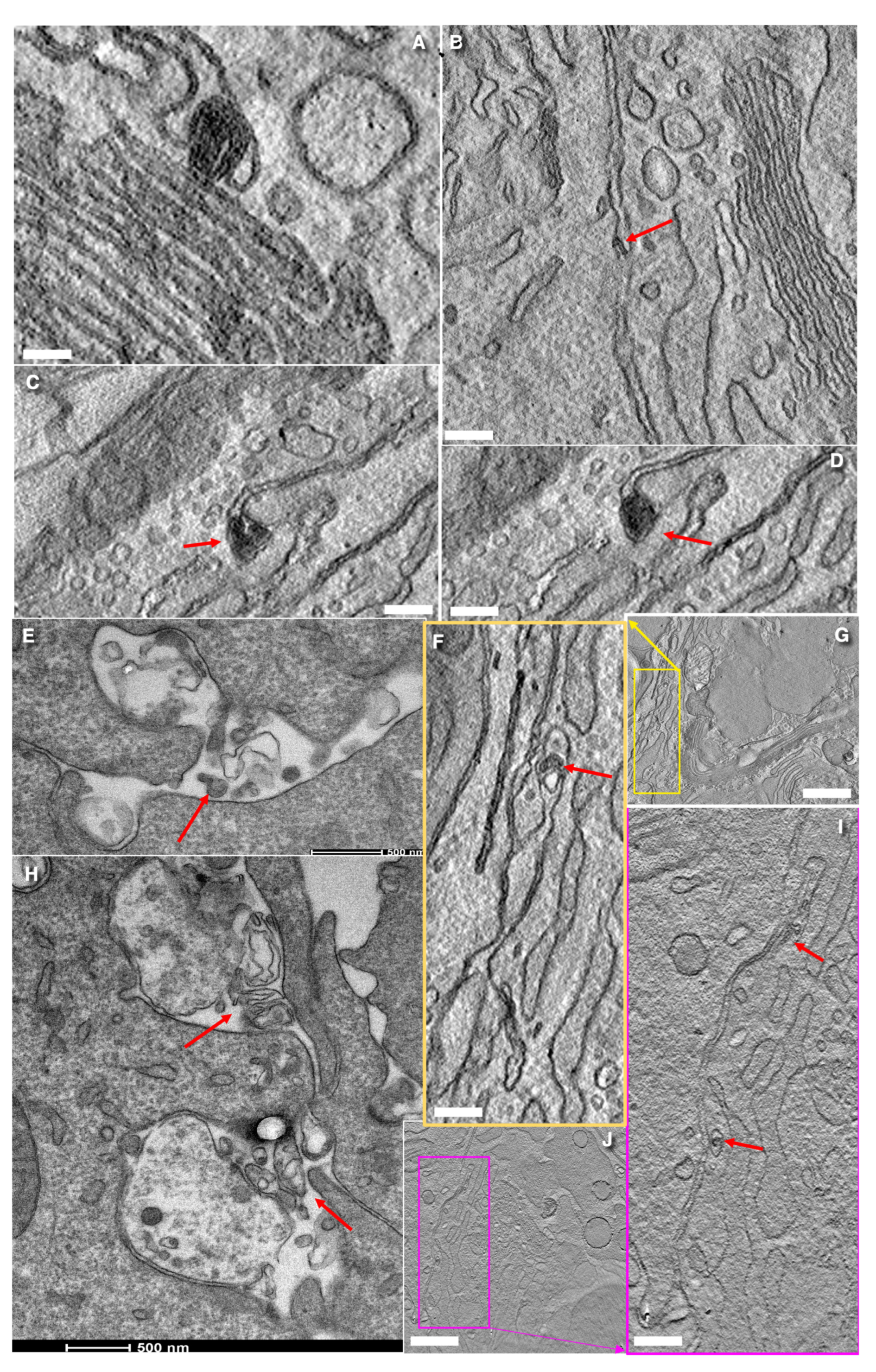
3.2. The Structure of the ER–Golgi Interface
3.3. Formation of Cisternal Distensions
3.4. The Problem of Cisternal Rims and Membrane Contacts
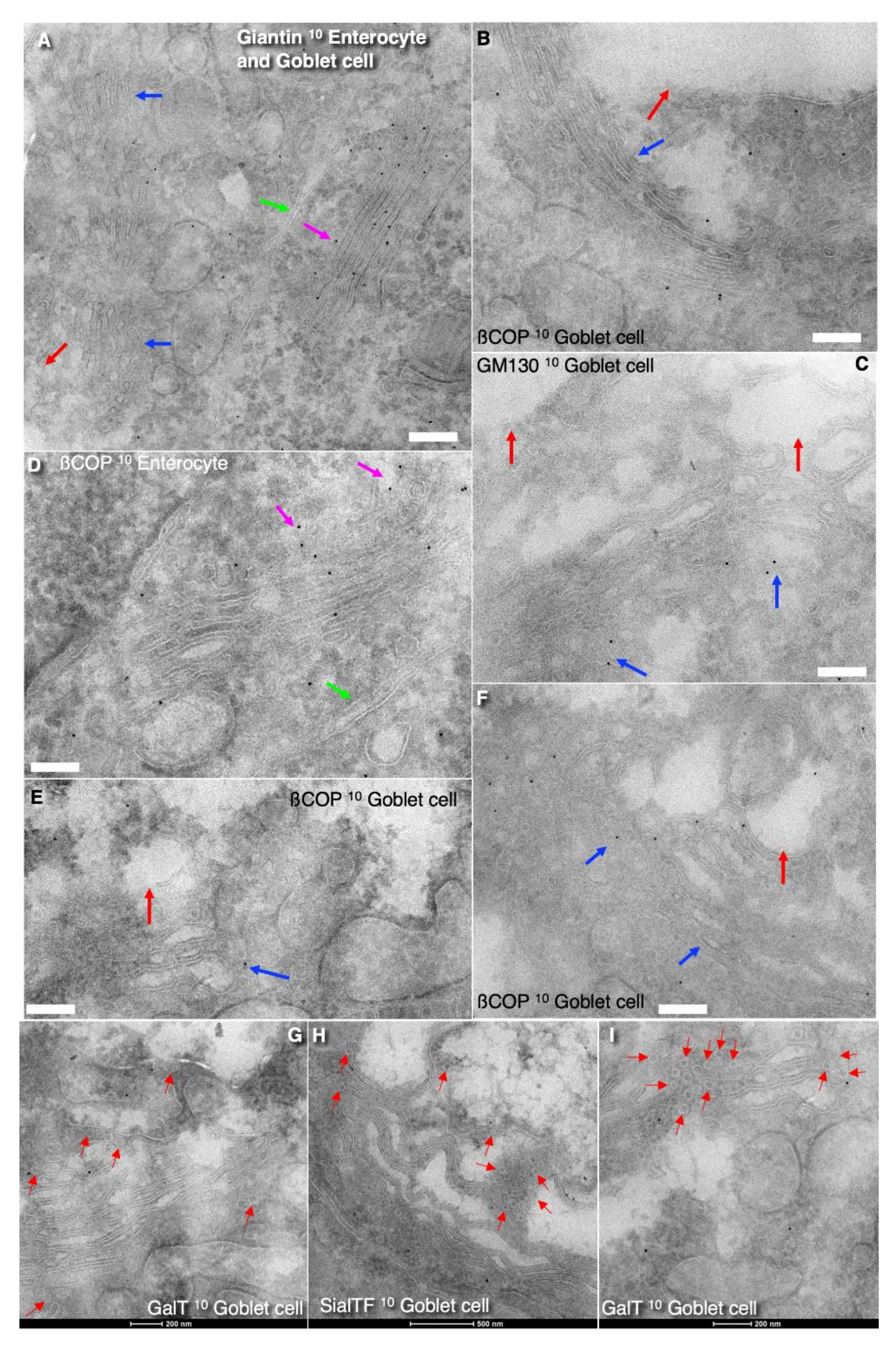
3.5. Immune Electron Microscopic Analysis
3.6. Structure of Secretory Granules
3.7. Turnover of Membranes of Secretory Granules
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Helicoids: A Brief Outline
Appendix A.1. Definition
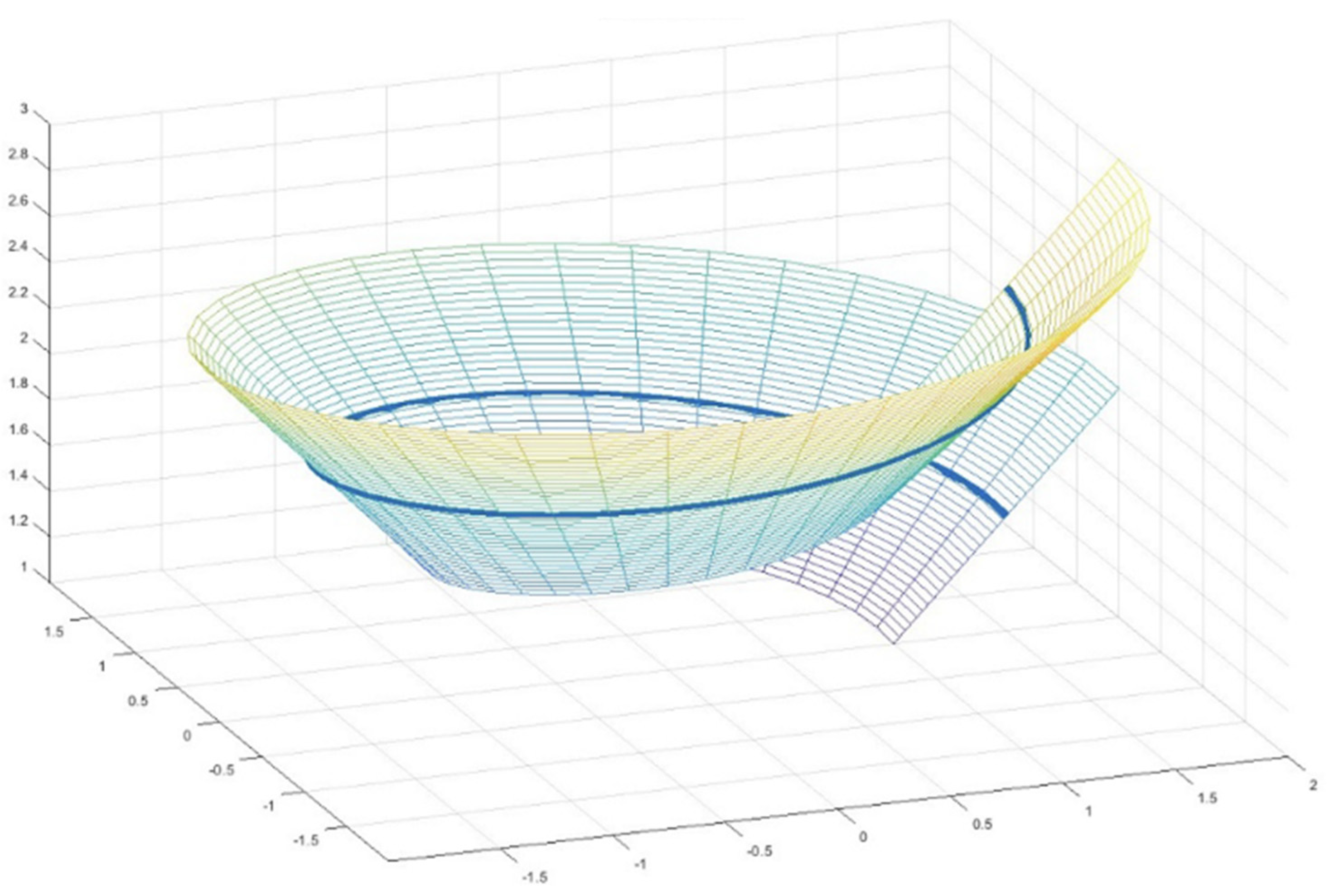
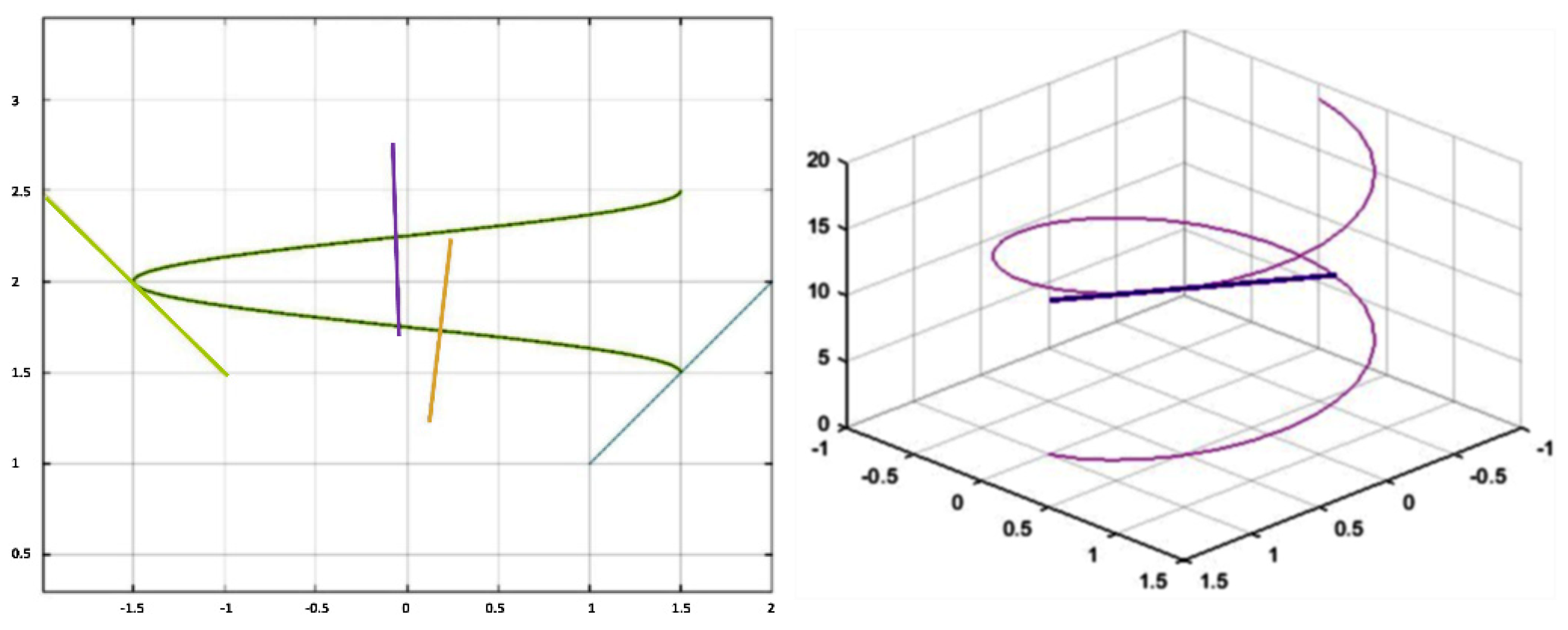
Appendix A.2. Features
Appendix A.3. Geometric Description
Appendix A.4. Perimeter
Appendix A.5. MATLAB Model (MATLAB Version 23.2.1, Also Known as MATLAB R2023b)
| clc clear all close all %%GEOMETRIC PARAMETERS rhomin=1; rhomax=2; turns=7; phi=pi/12*; h=0.5; %%GRAPHICAL PARAMETERS n=400; h=h/(2*pi); %%VECTORS rho=linspace(rhomin,rhomax,n); theta=linspace(0,2*pi*turns,n); [X,Y]=meshgrid(theta,rho); x=Y.*cos(X); y=Y.*sin(X); z=Y.*tan(phi)+h.*X; figure(1) mesh(x,y,z) axis equal angle=360/(2*pi/phi); filename=sprintf(‘min%.2f_max%.2f_turns%.0f_angle%.0f_pitch%.2f.pdf’,rhomin,rhomax,turns,angle,h*2*pi); filename2=sprintf(‘min%.2f max%.2f turns%.0f angle%.0f pitch%.2f.pdf’,rhomin,rhomax,turns,angle,h*2*pi); title (filename2) saveas(gcf,filename) filename=sprintf(‘min%.2f_max%.2f_turns_%.0f_angle%.0f_pitch%.2f.jpg’,rhomin,rhomax,turns,angle,h*2*pi); saveas(gcf,filename) |
References
- Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C. Is the intestinal goblet cell a major immune cell? Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Holmen-Larsson, J.; Jabbar, K.S.; Xia, L.; Xu, H.; Ghishan, F.K.; Carvalho, F.A.; Gewirtz, A.T.; Sjovall, H.; et al. Bacteria penetrate the normally impenetrable inner colon mucus layer in both murine colitis models and in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2014, 63, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Post, S.; Jabbar, K.S.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Arike, L.; Akhtar, N.; Sjovall, H.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C. Structural weakening of the colonic mucus barrier is an early event in ulcerative co- litis pathogenesis. Gut 2019, 68, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelaseyed, T.; Bergström, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Birchenough, G.M.; Schütte, A.; van der Post, S.; Svensson, F.; Rodríguez-Piñeiro, A.M.; Nyström, E.E.; et al. The mucus and mucins of the goblet cells and enterocytes provide the first defense line of the gastrointestinal tract and interact with the immune system. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birchenough, G.M.; Johansson, M.E.; Gustafsson, J.K.; Bergström, J.H.; Hansson, G.C. New developments in goblet cell mucus secretion and function. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchenough, G.M.H.; Nystrom, E.E.; Johansson, M.E.V.; Hansson, G.C. A sentinel goblet cell guards the colonic crypt by triggering Nlrp6-dependent Muc2 secretion. Science 2016, 352, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis, A.S.; Hansson, G.C. Intestinal mucus and their glycans: A habitat for thriving microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2023, 31, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Ho, S.B. Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: Recent insights and progress. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2010, 12, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.K.; Sjovall, H.; Hansson, G.C. Ex vivo measurements of mucus secretion by colon explants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 842, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson, J.K.; Ermund, A.; Johansson, M.E.; Schutte, A.; Hansson, G.C.; Sjovall, H. An Ex Vivo Method for Studying Mucus Formation, Properties, and Thickness in Human Colonic Biopsies and Mouse Small and Large Intestinal Explants. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G430–G438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, J.K.; Davis, J.E.; Rappai, T.; McDonald, K.G.; Kulkarni, D.H.; Knoop, K.A.; Hogan, S.P.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.; Lencer, W.I.; Newberry, R.D. Intestinal goblet cells sample and deliver lumenal antigens by regulated endocytic uptake and transcytosis. Elife 2021, 10, e67292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, J.K.; Johansson, M.E.V. The role of goblet cells and mucus in intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, J.D. The localization of acid mucopolysaccharides in the golgi complex of intestinal goblet cells. J. Cell Biol. 1967, 32, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, K.; Osakada, H.; Kojidani, T.; Waga, M.; Suda, Y.; Asakawa, H.; Haraguchi, T.; Nakano, A. Visualization of secretory cargo transport within the Golgi apparatus. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1602–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambraud, L.; Bernadac, A.; Gorvel, J.P.; Maroux, S. Renewal of goblet cell mucus granules during the cell migration along the crypt-villus axis in rabbit jejunum: An immunolabeling study. Biol. Cell 1989, 65, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, J.D.; Castle, A.M. Two regulated secretory pathways for newly synthesized parotid salivary proteins are distinguished by doses of secretagogues. J. Cell Sci. 1996, 109, 2591–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrianifahanana, M.; Moniaux, N.; Batra, S.K. Regulation of mucin expression: Mechanistic aspects and implications for cancer and inflammatory diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1765, 189–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonovo, B.; Ouwendijk, J.; Solimena, M. Biogenesis of secretory granules. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2006, 18, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, G.C.; Johansson, M.E. The Inner of the Two Muc2 Mucin-Dependent Mucus Layers in Colon is Devoid of Bacteria. Gut Microbes 2010, 1, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, K.B.; Tuvim, M.J.; Dickey, B.F. Regulated mucin secretion from airway epithelial cells. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonser, L.R.; Erle, D.J. Airway Mucus and Asthma: The Role of MUC5AC and MUC5B. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Liu, D.; Qin, M.; Chen, B.; Song, S.; Dai, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; He, B.; et al. Intestinal Mucin Induces More Endocytosis but Less Transcytosis of Nanoparticles across Enterocytes by Triggering Nanoclustering and Strengthening the Retrograde Pathway. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11443–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, R.L.S.; Correa, J.R.; Galera, P.D. Ultrastructural morphology of goblet cells of the conjunctiva of dogs. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2019, 22, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornick, S.; Kumar, M.; Moreau, F.; Gaisano, H.; Chadee, K. VAMP8-mediated MUC2 mucin exocytosis from colonic goblet cells maintains innate intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosini, Y.M.; Park, Y.; Jergens, A.E.; Shin, W.; Min, S.; Atherly, T.; Borcherding, D.C.; Jang, J.; Allenspach, K.; Mochel, J.P.; et al. Recapitulation of the accessible interface of biopsy-derived canine intestinal organoids to study epithelial-luminal interactions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Sheng, J.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Dong, R. Histological study of intestinal goblet cells, IgA, and CD3+ lymphocyte distribution in Huang-huai white goat. Folia Morphol. 2020, 79, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yu, M. Role of Goblet Cells in Intestinal Barrier and Mucosal Immunity. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, C. The relationship between intestinal goblet cells and the immune response. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20201471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C. Immunological aspects of intestinal mucus and mucins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, A.A.; Beznoussenko, G.V. The Regulated Secretion and Models of Intracellular Transport: The Goblet Cell as an Example. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briata, P.; Briata, P.; Mastracci, L.; Zapparoli, E.; Caputo, L.; Ferracci, E.; Silvestri, A.; Garuti, A.; Meriem Hamadou, M.H.; Inga, A.; et al. LncRNA EPR regulates intestinal mucus production and and tumorigenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 2023, gkad257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, G.; Leblond, C.P.; Haddad, A. Migration of glycoprotein from the Golgi apparatus to the surface of various cell types as shown by radioautography after labelled fucose injection into rats. J. Cell Biol. 1974, 60, 258–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, K.A.; Oliver, M.G.; Specian, R.D. Cytoarchitectural reorganization of rabbit colonic goblet cells during baseline secretion. Am. J. Anat. 1990, 189, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantero-Recasens, G.; Butnaru, C.M.; Valverde, M.A.; Naranjo, J.R.; Brouwers, N.; Malhotra, V. KChIP3 coupled to Ca2+ oscillations exerts a tonic brake on baseline mucin release in the colon. Elife 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.H.; Hasnain, S.Z. Mucus and Mucins: The Underappreciated Host Defence System. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 856962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, D.; Ushiki, T. Three-dimensional ultrastructure of the Golgi apparatus in different cells: High-resolution scanning electron microscopy of osmium-macerated tissues. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 2006, 69, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, D.; Kusumi, S.; Ushiki, T.; Watanabe, T. Integrative method for three-dimensional imaging of the entire Golgi apparatus by combining thiamine pyrophosphatase cytochemistry and array tomography using backscattered electron-mode scanning electron microscopy. Biomed. Res. 2017, 38, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, D.; Nakajima, M.; Ushiki, T. A useful method for observing intracellular structures of free and cultured cells by scanning electron microscopy. J. Electron. Microsc. 2012, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinger, A.; Pavelka, M. Localization of fucosyl residues in cellular compartments of rat duodenal absorptive enterocytes and goblet cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 47, 62–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger, A.; Pavelka, M. Subdomains of the rough endoplasmic reticulum in colon goblet cells of the rat: Lectin-cytochemical characterization. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1992, 40, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Spicer, S.S. Ultrastructural visualization of galactosyl residues in various alimentary epithelial cells with the peanut lectin-horseradish peroxidase procedure. Histochemistry 1982, 73, 607–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Spicer, S.S. Ultrastructural visualization of galactose in the glycoprotein of gastric surface cells with a peanut lectin conjugate. Histochem. J. 1982, 14, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taatjes, D.J.; Roth, J. Alteration in sialyltransferase and sialic acid expression accompanies cell differentiation in rat intestine. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 46, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, A.; Hendricks, L.; Moreman, K.W.; Tulsiani, D.R.P.; Touster, O.; Farquhar, M.G. Cell-type dependent variations in the subcellular distribution of a-mannosidase I and II. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentijn, J.A.; van Weeren, L.; Ultee, A.; Koster, A.J. Novel localization of Rab3D in rat intestinal goblet cells and Brunner’s gland acinar cells suggests a role in early Golgi trafficking. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G165–G177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, K.H. The cytomorphology of goblet cells of the fetal intestine. Studies of the large intestine of cattle (Bos primigenius taurus). Z. Mikrosk. Anat. Forsch. 1990, 104, 801–825. [Google Scholar]
- Neutra, M.; Leblond, C.P. Synthesis of the carbohydrate of mucus in the golgi complex as shown by electron microscope radioautography of goblet cells from rats injected with glucose-H3. J. Cell Biol. 1966, 30, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specian, R.D.; Neutra, M.R. Cytoskeleton of intestinal goblet cells in rabbit and monkey. The theca. Gastroenterology 1984, 87, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Specian, R.D.; Neutra, M.R. Regulation of intestinal goblet cell secretion. I. Role of parasympathetic stimulation. Am. J. Physiol. 1982, 242, G370–G379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.A.; Fusella, A.; Beznoussenko, G.V. The 50-nm Free Vesicles Visible in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Are Not COPII-Dependent. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabi, A.A.; Tsien, R.W. Perspectives on kiss-and-run: Role in exocytosis, endocytosis, and neurotransmission. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alés, E.; Tabares, L.; Poyato, J.M.; Valero, V.; Lindau, M.; Alvarez de Toledo, G. High calcium concentrations shift the mode of exocytosis to the kiss-and-run mechanism. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan-Bonnet, N.; Sougrat, R.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Molecular basis for Golgi maintenance and biogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, G.H.; Hirschberg, K.; Polishchuk, R.S.; Gerlich, D.; Phair, R.D.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Transport through the Golgi apparatus by rapid partitioning within a two-phase membrane system. Cell 2008, 133, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Parashuraman, S.; Rizzo, R.; Polishchuk, R.; Martella, O.; Di Giandomenico, D.; Fusella, A.; Spaar, A.; Sallese, M.; Capestrano, M.G.; et al. Transport of soluble proteins through the Golgi occurs by diffusion via continuities across cisternae. Elife 2014, 3, e02009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Adolf, F.; Herrmann, A.; Hellwig, A.; Beck, R.; Brügger, B.; Wieland, F.T. Scission of COPI and COPII vesicles is independent of GTP hydrolysis. Traffic 2013, 14, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolf, F.; Rhiel, M.; Reckmann, I.; Wieland, F.T. Sec24C/D-isoform-specific sorting of the preassembled ER-Golgi Q-SNARE complex. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2016, 27, 2697–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, A.V.; Chang, C.L.; Shtengel, G.; Xu, C.S.; Hoffman, D.P.; Freeman, M.; Iyer, N.; Aaron, J.; Khuon, S.; Bogovic, J.; et al. ER-to-Golgi protein delivery through an interwoven, tubular network extending from ER. Cell 2021, 184, 2412–2429.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Bejan, A.I.; Parashuraman, S.; Luini, A.; Kweon, H.-S.; Mironov, A.A. The Diffusion Model of Intra-Golgi Transport Has Limited Power. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, A., Jr.; Luini, A.; Mironov, A. A synthetic model of intra-Golgi traffic. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.A.; Beznoussenko, G.V. The kiss-and-run model of intra-Golgi transport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6800–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polishchuk, R.S.; Polishchuk, E.V.; Mironov, A.A. Coalescence of Golgi fragments in microtubule-deprived living cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 78, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Kweon, H.S.; Sesorova, I.S.; Mironov, A.A. Comparison of the Cisterna Maturation-Progression Model with the Kiss-and-Run Model of Intra-Golgi Transport: Role of Cisternal Pores and Cargo Domains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.A. Models of intracellular transport and evolution of the Golgi complex. Anat. Rec. 2002, 268, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Pilyugin, S.S.; Geerts, W.J.; Kozlov, M.M.; Burger, K.N.; Luini, A.; Derganc, J.; Mironov, A.A. Trans-membrane area asymmetry controls the shape of cellular organelles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5299–5333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beznoussenko, G.V.; Ragnini-Wilson, A.; Wilson, C.; Mironov, A.A. Three-dimensional and immune electron microscopic analysis of the secretory pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Histochem. Cell. Biol. 2016, 146, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannykh, S.I.; Rowe, T.; Balch, W.E. The organization of endoplasmic reticulum export complexes. J. Cell. Biol. 1996, 135, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironov, A.A.; Sesorova, I.S.; Seliverstova, E.V.; Beznoussenko, G.V. Different Golgi ultrastructure across species and tissues: Implications under functional and pathological conditions, and an attempt at classification. Tissue Cell. 2017, 49 Pt A, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, M.; Rotta, G.; Valzasina, B.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells shuttle microbes across gut epithelial monolayers. Immunobiology 2001, 204, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, M.; Urbano, M.; Valzasina, B.; Francolini, M.; Rotta, G.; Bonasio, R.; Granucci, F.; Kraehenbuhl, J.P.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells express tight junction proteins and penetrate gut epithelial monolayers to sample bacteria. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, M.; Valzasina, B.; Bonasio, R.; Urbano, M.; Ricciardi-Castagnoli, P. Dendritic cells, loaded with recombinant bacteria expressing tumor antigens, induce a protective tumor-specific response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7 (Suppl. S3), 865s–870s. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, D.P.; Shtengel, G.; Xu, C.S.; Campbell, K.R.; Freeman, M.; Wang, L.; Milkie, D.E.; Pasolli, H.A.; Iyer, N.; Bogovic, J.A.; et al. Correlative three-dimensional super-resolution and block-face electron microscopy of whole vitreously frozen cells. Science 2020, 367, eaaz5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.A., Jr.; Mironov, A.A. Estimation of subcellular organelle volume from ultrathin sections through centrioles with a discretized version of vertical rotator. J. Microsc. 1998, 192, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykov, Y.S.; Schaffer, M.; Dodonova, S.O.; Albert, S.; Plitzko, J.M.; Baumeister, W.; Engel, B.D.; Briggs, J.A. The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell. Elife 2017, 6, e32493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, R.; Rai, A.K.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Meyer, K.; Pelkmans, L. DYRK3 enables secretory trafficking by maintaining the liquid-like state of ER exit sites. Dev. Cell. 2023, 58, 1880–1897.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesorova, I.S.; Karelina, N.R.; Kazakova, T.E.; Parashuraman, S.; Zdorikova, M.A.; Dimov, I.D.; Seliverstova, E.V.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.A. Structure of the enterocyte transcytosis compartments during lipid absorption. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2020, 153, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusella, A.; Micaroni, M.; Di Giandomenico, D.; Mironov, A.A.; Beznoussenko, G.V. Segregation of the Qb-SNAREs GS27 and GS28 into Golgi vesicles regulates intra-Golgi transport. Traffic 2013, 14, 568–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaki, M.; Shemesh, T.; Kasthuri, N.; Klemm, R.W.; Schalek, R.; Hayworth, K.J.; Hand, A.R.; Yankova, M.; Huber, G.; Lichtman, J.W.; et al. Stacked endoplasmic reticulum sheets are connected by helicoidal membrane motifs. Cell 2013, 154, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.A.; Beznoussenko, G.V. Models of Intracellular Transport: Pros and Cons. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Rubin, B.K.; Voynow, J.A. Mucins, Mucus, and Goblet Cells. Chest 2018, 154, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, B.J.; Mastronarde, D.N.; McIntosh, J.R.; Howell, K.E. Structural evidence for multiple transport mechanisms through the Golgi in the pancreatic beta-cell line, HIT-T15. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2001, 29 Pt 4, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, B.J.; Volkmann, N.; McIntosh, J.R.; Howell, K.E. Direct continuities between cisternae at different levels of the Golgi complex in glucose-stimulated mouse islet beta cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5565–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satiat-Jeunemaitre, B. Spatial and temporal regulations in helicoidal extracellular matrices: Comparison between plant and animal systems. Tissue Cell 1992, 24, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.; Fuller, S.D.; Back, R.; Hollinshead, M.; Pfeiffer, S.; Simons, K. The dynamic nature of the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 108, 277–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G. Gut thoughts on the Golgi complex. Traffic 2000, 1, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.R. Entry at the trans-face of the Golgi. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippincott-Schwartz, J. An evolving paradigm for the secretory pathway? Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3929–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, G.; Uemura, T.; Chuang, C.C.; Polishchuk, E.; Santoro, M.; Ohvo-Rekilä, H.; Sato, T.; Di Tullio, G.; Varriale, A.; D’Auria, S.; et al. Vesicular and non-vesicular transport feed distinct glycosylation pathways in the Golgi. Nature 2013, 501, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Mitsushima, A.; Fukudome, H.; Kashima, Y. Three-dimensional architecture of the Golgi complex observed by high resolution scanning electron microscopy. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. 1986, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harada, A.; Kunii, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Sumi, T.; Kanda, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nadanaka, S.; Hirosawa, K.M.; Tokunaga, K.; Tojima, T.; et al. Dynamic movement of the Golgi unit and its glycosylation enzyme zones. Nat Commun. 2024, 15, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.W.; Lee, J.W. Linear Weingarten helicoidal surfaces in isotropic space. Symmetry 2016, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, Ö.G. Constructions of helicoidal surfaces in a 3-dimensional complete manifold with density. Mathematics 2018, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, B.B.; Babaarslan, M.; Küçükarikan, Y. Isometric Timelike Surfaces in 4—Dimensional Minkowski Space. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.14920. [Google Scholar]
- Bacia, K.; Futai, E.; Prinz, S.; Meister, A.; Daum, S.; Glatte, D.; Briggs, J.A.; Schekman, R. Multibudded tubules formed by COPII on artificial liposomes. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.P.; Frieboese, D.; Waltz, F.; Engel, B.D.; Bock, R. Identification and characterization of the COPII vesicle-forming GTPase Sar1 in Chlamydomonas. Plant Direct 2024, 8, e614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyle, E.; Miller, E.A.; Zanetti, G. Cryo-electron tomography reveals how COPII assembles on cargo-containing membranes. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2025, 32, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambourg, A.; Jackson, C.L.; Clermont, Y. Three dimensional configuration of the secretory pathway and segregation of secretion granules in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114 Pt 12, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambourg, A.; Clermont, Y.; Chrétien, M.; Olivier, L. Modulation of the Golgi apparatus in stimulated and nonstimulated prolactin cells of female rats. Anat. Rec. 1993, 235, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzola, J.J.; Russell, L.D. Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists; Jones and Bartlett: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; 542p. [Google Scholar]
- Trombetta, E.S.; Simons, J.F.; Helenius, A. Endoplasmic reticulum glucosidase II is composed of a catalytic subunit, conserved from yeast to mammals, and a tightly bound noncatalytic HDEL-containing subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 27509–27516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborský, P.; Koczula, K.M.; Gallotta, A.; Katrlík, J. Lectin-based lateral flow assay: Proof-of-concept. Analyst 2016, 141, 6444–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattrup, C.L.; Gendler, S.J. Structure and function of the cell surface (tethered) mucins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 431–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, P.; Singh, A.P.; Batra, S.K. Structure, evolution, and biology of the MUC4 mucin. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, H.C.; Sweeney, C.; Carraway, K.L., 3rd. The Membrane Mucin Muc4 Inhibits Apoptosis Induced by Multiple Insults via ErbB2-Dependent and ErbB2-Independent Mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2845–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W. SNAREs and traffic. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2005, 1744, 493–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karli, U.O.; Schäfer, T.; Burger, M.M. Fusion of neurotransmitter vesicles with target membrane is calcium independent in a cell-free system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5912–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, D.; Ushiki, T.; Watanabe, T. Novel scanning electron microscopy methods for analyzing the 3D structure of the Golgi apparatus. Anat. Sci. Int. 2017, 92, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrona, M.B.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Fusella, A.; Martella, O.; Moral, P.; Mironov, A.A. Silencing of the mammalian Sar1 isoforms reveals COPII-independent protein sorting and transport. Traffic 2013, 14, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepperkok, R.; Whitney, J.A.; Gomez, M.; Kreis, T.E. COPI vesicles accumulating in the presence of a GTP restricted arf1 mutant are depleted of anterograde and retrograde cargo. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113 Pt 1, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maszczak-Seneczko, D.; Sosicka, P.; Kaczmarek, B.; Majkowski, M.; Luzarowski, M.; Olczak, T.; Olczak, M. UDP-galactose (SLC35A2) and UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (SLC35A3) Transporters Form Glycosylation-related Complexes with Mannoside Acetylglucosaminyltransferases (Mgats). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15475–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maszczak-Seneczko, D.; Sosicka, P.; Majkowski, M.; Olczak, T.; Olczak, M. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine transporter and UDP-galactose transporter form heterologous complexes in the Golgi membrane. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 4082–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maszczak-Seneczko, D.; Wiktor, M.; Skurska, E.; Wiertelak, W.; Olczak, M. Delivery of Nucleotide Sugars to the Mammalian Golgi: A Very Well (un)Explained Story. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.L.; Newstead, S. Gateway to the Golgi: Molecular mechanisms of nucleotide sugar transporters. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 57, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasberg, W.; Luong, P.; Swift, K.A.; Audhya, A. Nutrient deprivation alters the rate of COPII subunit recruitment at ER subdomains to tune secretory protein transport. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Feng, Z.; Ke, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, T.; Dai, J.; Cui, W.; Pastor-Pareja, J.C.; Fukasawa, M.; Varlamov, O.; et al. Localization and activity of the SNARE Ykt6 determined by its regulatory domain and palmitoylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4815–4820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosumi, K.; Shibuichi, I.; Tosaka, H. Ultrastructural studies on the secretory mechanism of goblet cells in the rat jejunal epithelium. Arch. Histol. Jpn. 1981, 44, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mironov, A.A.; Luini, A.; Buccione, R. Constitutive transport between the trans-Golgi network and the plasma membrane according to the maturation model. A hypothesis. FEBS Lett. 1998, 440, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, E.E.L.; Martinez-Abad, B.; Arike, L.; Birchenough, G.M.H.; Nonnecke, E.B.; Castillo, P.A.; Svensson, F.; Bevins, C.L.; Hansson, G.C.; Johansson, M.E.V. An intercrypt subpopulation of goblet cells is essential for colonic mucus barrier function. Science 2021, 372, eabb1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailey, D.W.; Rambold, A.S.; Satpute-Krishnan, P.; Mitra, K.; Sougrat, R.; Kim, P.K.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Mitochondria supply membranes for autophagosome biogenesis during starvation. Cell 2010, 141, 656–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.K.; Miyoshi, H.; Beatty, W.L.; Head, R.D.; Malvin, N.P.; Cadwell, K.; Guan, J.-L.; Saitoh, T.; Akira, S.; Seglen, P.O.; et al. Autophagy proteins control goblet cell function by potentiating reactive oxygen species production. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 3130–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naama, M.; Telpaz, S.; Awad, A.; Ben-Simon, S.; Harshuk-Shabso, S.; Modilevsky, S.; Rubin, E.; Sawaed, J.; Zelik, L.; Zigdon, M.; et al. Autophagy controls mucus secretion from intestinal goblet cells by alleviating ER stress. Cell Host Microbe. 2023, 31, 433–446.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDole, J.R.; Wheeler, L.W.; McDonald, K.G.; Wang, B.; Konjufca, V.; Knoop, K.A.; Newberry, R.D.; Miller, M.J. Goblet cells deliver luminal antigen to CD103+ dendritic cells in the small intestine. Nature 2012, 483, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; Jensen, G.J.; McIntosh, J.R.; Björkman, P.J. FcRn-mediated antibody transport across epithelial cells revealed by electron tomography. Nature 2008, 455, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colony, P.C.; Specian, R.D. Endocytosis and vesicular traffic in fetal and adult colonic goblet cells. Anat. Rec. 1987, 218, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Abe, A.; Abedin, M.J.; Abeliovich, H.; Acevedo Arozena, A.; Adachi, H.; Adams, C.M.; Adams, P.D.; Adeli, K.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 2016, 12, 1–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Jensen, L.E.; Hurley, J.H. Autophagosome biogenesis comes out of the black box. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corfield, A.P. The interaction of the gut microbiota with the mucus barrier in health and disease in human. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameters ± SD (Number of Samples Is Equal to 6) | Colon | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rest. | Secr. | ||
| A. The percentage of goblet cells that have contacts with dendritic cells or their processes. | nd | 61 ± 7 | |
| B. The mean number of Golgi cisternae in stacks | 7.7 ± 2.4 | 7.1 ± 2.1 | |
| C. The mean volume of the Golgi ribbon (µm3) | nd | 49.1 ± 10 | |
| D. The mean surface area of Golgi cisternae (µm2) | nd | 1390 ± 134 | |
| E. Average diameter of secretory granules (µm) | 1.2 ± 0.2 * | 2.5 ± 0.31 * | |
| F. The ratio of the surface areas of the rims of the cisternae to the area of their flat zones in different cisternal layers | First layer | 0.33 ± 0.03 | nd |
| Second layers | 0.31 ± 0.09 | nd | |
| Third layer | 0.27 ± 0.07 | nd | |
| Fourth layer | 0.20 ± 0.05 | nd | |
| A. The ratio (%) between the LD for LC3 and Muc1 over MLOs versus background | LC3 | Muc1 |
| 4.1 ± 0.9 * | 4.6 ± 1.1 * | |
| B. The ratio (%) between the LD for Golgi enzymes (GalT and (SialTF) over the 52 nm vesicles versus the plane parts of cisternae | GalT | SialTF |
| 32 ± 14 ** | 41 ± 17 ** | |
| C. The ratio of the labeling density (LD) for ßCOP over the Golgi of neighboring enterocytes with microvilli to that of goblet cells | nd | 4.9 ± 1.5 ^ |
| D. The ratio of LD for giantin in the Golgi of the neighboring enterocytes with microvilli to the same parameter in goblet cells | nd | 5.2 ± 1.4 ^^ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mironov, A.A.; Sesorova, I.S.; Vavilov, P.S.; Longoni, R.; Briata, P.; Gherzi, R.; Beznoussenko, G.V. Structure of the Secretory Compartments in Goblet Cells in the Colon and Small Intestine. Cells 2025, 14, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151185
Mironov AA, Sesorova IS, Vavilov PS, Longoni R, Briata P, Gherzi R, Beznoussenko GV. Structure of the Secretory Compartments in Goblet Cells in the Colon and Small Intestine. Cells. 2025; 14(15):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151185
Chicago/Turabian StyleMironov, Alexander A., Irina S. Sesorova, Pavel S. Vavilov, Roberto Longoni, Paola Briata, Roberto Gherzi, and Galina V. Beznoussenko. 2025. "Structure of the Secretory Compartments in Goblet Cells in the Colon and Small Intestine" Cells 14, no. 15: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151185
APA StyleMironov, A. A., Sesorova, I. S., Vavilov, P. S., Longoni, R., Briata, P., Gherzi, R., & Beznoussenko, G. V. (2025). Structure of the Secretory Compartments in Goblet Cells in the Colon and Small Intestine. Cells, 14(15), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14151185







