Pathogenesis of Autoimmunity/Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Abstract
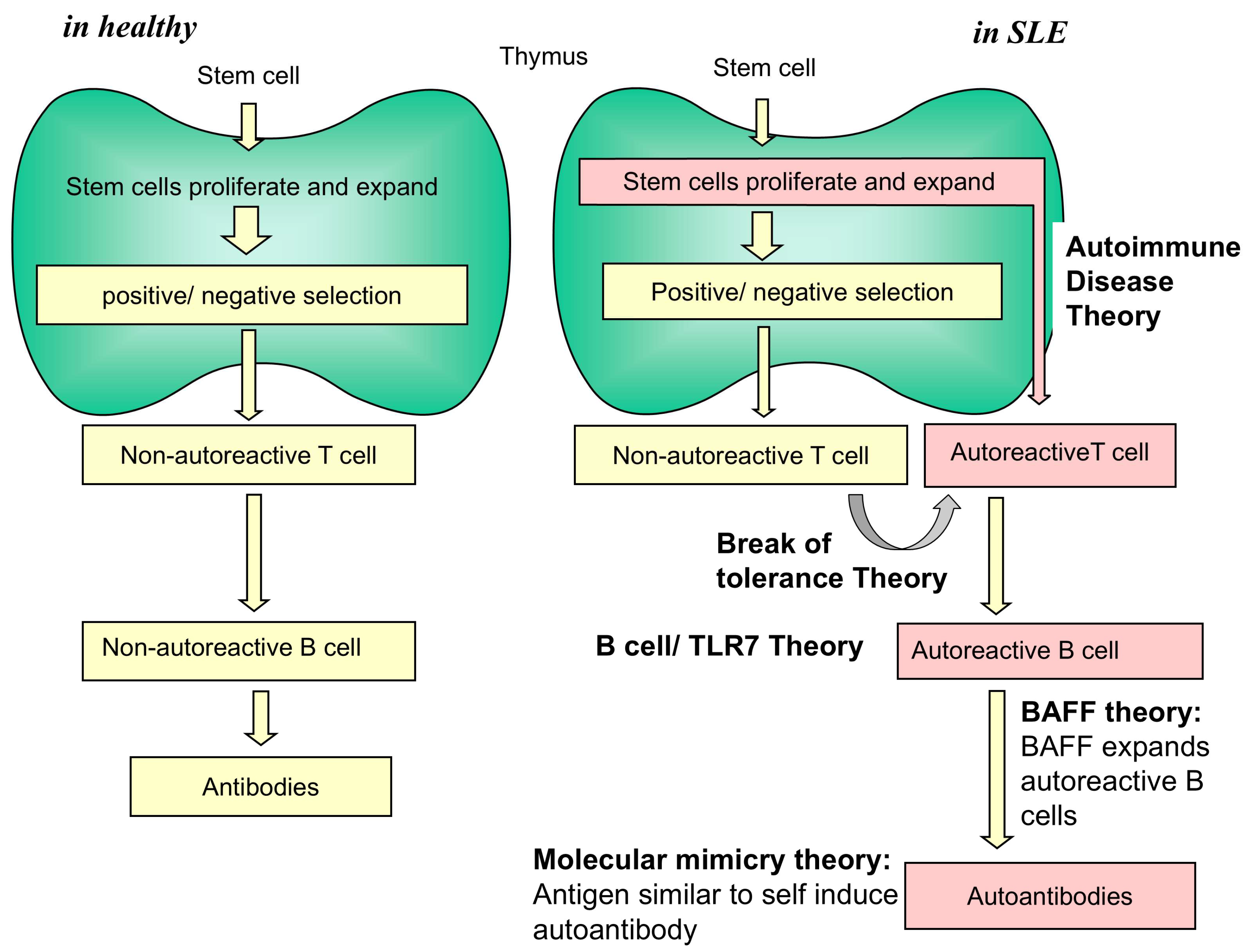
1. Introduction
2. Studies on B Cells, TLR7, TLR9, MyD88, BAFF, and IL-21
3. Autoantibody Studies
4. T Cell Studies
5. Studies on Interferon α
6. Self-Organized Criticality Theory of Autoimmunity; Infection Causes SLE
7. Concluding Remarks
8. Patents
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGS | Aicardi-Goutières syndrome |
| Ab | Antibody |
| BAFF | B cell activating factor of the TNF family |
| BXSB/MpJ mice | A recombinant inbred mouse line produced from an intercross between C57BL/6J (B6) and SB/Le mice |
| CCR7 | Chemokine receptor 7 |
| CTL | Cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
| CXCR5 | Chemokine receptor 5 |
| DC | Dendritic cell |
| DOCK8 | Dedicator of cytokinesis 8 |
| GC | Germinal center |
| gld | Generalized lymphoproliferative disease gene |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| ICOS | Inducible co-stimulator |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IRF | IFN regulatory factor |
| IL | Interleukin |
| lpr | Lymphoproliferation gene |
| MtV-8 | Mouse mammary tumor virus-8 |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| NZW mice | New Zealand White mice |
| NZB mice | New Zealand Black mice |
| OX | Orexin receptor |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome Corona virus 2 |
| strain SB/Le | Strain of mice homozygous for the mutant genes beige (bg), satin (sa), and white-bellied agouti (Aw) |
| Slam | Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule gene |
| STAT4 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 4 |
| TACI | Transmembrane activator and CAML (calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand) interactor |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| Tfh cell | T follicular helper cell |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| TNFSF4 | Tumor necrosis factor superfamily, member 4 |
| Tyk | Tyrosine kinase |
| yaa | Y chromosome-linked autoimmune acceleration gene |
References
- Fanouriakis, A.; Tziolos, N.; Bertsias, G.; Boumpas, D.T. Update οn the diagnosis and management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, D.A.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Schwartz, R.S. Multiple serologic reactions and their relationship to clinical activity in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1984, 27, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, J.E.; Niewold, T.B. A successful trial for lupus—How good Is good enough? N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaniv, G.; Twig, G.; Shor, D.B.; Furer, A.; Sherer, Y.; Mozes, O.; Komisar, O.; Slonimsky, E.; Klang, E.; Lotan, E.; et al. Volcanic explosion of autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: A diversity of 180 different antibodies found in SLE patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, I.R. Autoimmunity since the 1957 clonal selection theory: A little acorn to a large oak. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2008, 86, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dameshek, W.; Witebsky, E.; Milgrom, F. Autoimmunity: Experimental and clinical aspects. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1965, 124, 916–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, I.R. Travels and travails of autoimmunity: A historical journey from discovery to rediscovery. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, A251–A258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumiyama, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Shiozawa, S. Self-organized criticality theory of autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, S.; Tsumiyama, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Uto, K.; Sakurai, K.; Nakashima, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Doi, A.; Tarui, M.; Izumikawa, M.; et al. DOCK8-Expressing T follicular helper cells newly generated beyond self-organized criticality cause systemic lupus erythematosus. iScience 2022, 25, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Bayry, J. High risk of autoimmune diseases after COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.; Chen, T.Y.-T.; Wang, S.-I.; Hung, Y.-M.; Chen, H.-Y.; James, C.C. Risk of autoimmune diseases in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 56, 101783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diani, S.; Leonardi, E.; Cavezzi, A.; Bouslenko, Z.; Ferrari, S.; Iacono, O.; Limoli, A.; Natalini, D.; Conti, S.; Mantovani, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2—The role of natural immunity: An narrative review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouranloo, K.; Mrinalini Dey, M.; Elwell, H.; Nune, A. A systematic review of the incidence, management and prognosis of new-onset autoimmune connective tissue diseases after COVID-19. Rheumatol. Int. 2023, 43, 1221–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Woo, J.S.; Jhun, J.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, A.R.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, H.; Park, S.H.; Cho, M.L. SARS-CoV-2 spike aggravates lupus nephritis and lung fibrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2024, 11, e001104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Prak, E.L.; Weigert, M. Editing Disease-Associated Autoantibodies. Immunity 1997, 6, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berland, R.; Fernandez, L.; Kari, E.; Han, J.-H.; Lomakin, I.; Akira, S.; Wortis, H.H.; Kearney, J.F.; Ucci, A.A.; Imanishi-Kari, T. Toll-like receptor 7-dependent loss of B cell tolerance in pathogenic autoantibody knockin mice. Immunity 2006, 25, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izui, S.; Iwamoto, M.; Fossati, L.; Merino, R.; Takahashi, S.; Ibnou-Zekri, N. The Yaa gene model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunol. Rev. 1995, 144, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisitkun, P.; Deane, J.A.; Difilippantonio, M.J.; Tarasenko, T.; Satterthwaite, A.B.; Bolland, S. Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 2006, 312, 1669–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossati, L.; Sobel, E.S.; Iwamoto, M.; Cohen, P.L.; Eisenberg, R.A.; Izui, S. The Yaa gene-mediated acceleration of murine lupus: Yaa- T cells from non-autoimmune mice collaborate with Yaa + B cells to produce lupus autoantibodies in vivo. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 3412–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudgins, C.C.; Steinberg, R.T.; Klinman, D.M.; Patton Reeves, M.J.; Steinberg, A.D. Studies of consomic mice bearing the Y chromosome of the BXSB mouse. J. Immunol. 1985, 134, 3849–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, S.; Fossati-Jimack, L.; Moll, T.; Amano, H.; Amano, E.; Ida, A.; Ibnou-Zekri, N.; Laporte, C.; Santiago-Raber, M.-L.; Rozzo, S.J.; et al. Differential role of three major New Zealand Black-derived loci linked with Yaa-induced murine lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, S.; Tus, K.; Li, Q.-Z.; Wang, A.; Tian, X.-H.; Zhou, J.; Liang, C.; Bartov, G.; McDaniel, L.D.; Zhou, X.J.; et al. A Tlr7 translocation accelerates systemic autoimmunity in murine lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9970–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S.R.; Kashgarian, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Flavell, R.A.; Akira, S.; Shlomchik, M.J. Toll-like receptor 9 controls anti-DNA autoantibody production in murine lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, K.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Shupe, J.; Kashgarian, M.; Kim, D.; Keith Elkon, K.; Shlomchik, M.J. TLR9 Regulates TLR7-and MyD88-Dependent Autoantibody Production and Disease in a Murine Model of Lupus. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilstra, J.S.; Kim, M.; Gordon, R.A.; Leibler, C.; Cosgrove, H.A.; Bastacky, S.; Nickerson, K.M.; Schlomchik, M.J. B cell-specific Myd88 regulates disease progression in murine lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20230263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichmann, L.L.; Schenten, D.; Medzhitov, R.; Kashgarian, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Signals via the adaptor MyD88 in B cells and DCs make distinct and synergistic contributions to immune activation and tissue damage in lupus. Immunity 2013, 38, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fike, A.J.; Bricker, K.N.; Gonzalez, M.V.; Maharjan, A.; Bui, T.; Nuon, K.; Emrich, S.M.; Weber, J.L.; Luckenbill, S.A.; Choi, N.M.; et al. IRF7 controls spontaneous autoimmune germinal center and plasma cell checkpoints. J. Exp. Med. 2025, 222, e20231882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, H.A.; Gingras, S.; Kim, M.; Bastacky, S.; Tilstra, J.S.; Shlomchik, M.J. B cell-intrinsic TLR7 expression drives severe lupus in TLR9-deficient mice. JCI Insight. 2023, 8, e172219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.J.; Cañete, P.F.; Wang, H.; Medhavy, A.; Bones, J.; Roco, J.A.; He, Y.; Qin, Y.; Cappello, J.; Ellyard, J.I.; et al. TLR7 gain-of-function genetic variation causes human lupus. Nature 2022, 605, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, F.; Woodcock, S.A.; Lawton, P.; Ambrose, C.; Baetscher, M.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J.; Browning, J.L. Mice transgenic for BAFF develop lymphocytic disorders along with autoimmune manifestations. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1697–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.A.; Johnston, J.; Mudri, S.; Enselman, R.; Dillon, S.R.; Madden, K.; Xu, W.; Parrish-Novak, J.; Don Foster, J.; Lofton-Day, C.; et al. TACI and BCMA are receptors for a TNF homologue implicated in B-cell autoimmune disease. Nature 2000, 404, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groom, J.R.; Fletcher, C.A.; Walters, S.N.; Grey, S.T.; Watt, S.V.; Sweet, M.J.; Smyth, M.J.; Mackay, C.R.; Mackay, F. BAFF and MyD88 signals promote a lupuslike disease independent of T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, H.M.; Thouvenel, C.D.; Leach, S.; Arkatkar, T.; Metzler, G.; Scharping, N.E.; Kolhatkar, N.S.; Rawlings, D.J.; Jackson, S.W. BAFF promotes autoantibody production via TACI-dependent activation of transitional B cells. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3525–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mockel, T.; Basta, F.; Weinmann-Menke, J.; Schwarting, A. B cell activating factor (BAFF): Structure, functions, autoimmunity and clinical implicatiions in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheema, G.S.; Roschke, V.; Hilbert, D.M.; Stohl, W. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune–based rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Roschke, V.; Baker, K.P.; Wang, Z.; Alarco’n, A.G.; Fessler, B.J.; Bastian, H.; Kimberly, R.P.; Zhou, T. A role for B lymphocyte stimulator in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atisha-Fregoso, Y.; Malkiel, S.; Harris, K.M.; Byron, M.; Ding, L.; Kanaparthi, S.; Barry, W.T.; Gao, W.; Ryker, K.; Tosta, P.; et al. Phase II randomized trial of rituximab plus cyclophosphamide followed by belimumab for the treatment of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.W.; Davidson, A. BAFF inhibition in SLE-its tolerance restored? Immunol. Rev. 2019, 292, 102–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urowitz, M.B.; Ohsfeldt, R.L.; Wielage, R.C.; Kelton, K.A.; Asukai, Y.; Ramachandran, S. Organ damage in patients treated with belimumab versus standard of care: A propensity score-matched com parative analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Petri, M.; Zamani, O.; Cervera, R.; Wallace, D.J.; Tegzova, D.; Sanchez-Guerrero, J.; Schwarting, A.; Merrill, J.T.; Chatham, W.W.; et al. A phase III, randomized, placebo-controlled study of belimumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits B lymphocyte stimulator, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3918–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarra, S.V.; Guzman, R.M.; Gallacher, A.E.; Hall, S.; Levy, R.A.; Jimenez, R.E.; Li, E.K.-M.; Thomas, M.; Kim, H.-M.; León, M.G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 377, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odegard, J.M.; Marks, B.R.; DiPlacido, L.D.; Poholek, A.C.; Kono, D.H.; Dong, C.; Flavell, R.A.; Craft, J. ICOS-dependent extrafollicular helper T cells elicit IgG production via IL-21 in systemic autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2873–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubier, J.A.; Sproule, T.J.; Foreman, O.; Spolski, R.; Shaffer, D.J.; Morse, H.C., III; Leonard, W.J.; Roopenian, D.C. A critical role for IL-21 receptor signaling in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus in BXSB-Yaa mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhee, C.G.; Bubier, J.A.; Sproule, T.J.; Park, G.; Steinbuck, M.P.; Schott, W.H.; Christianson, G.J.; Morse, H.C., III; Roopenian, D.C. IL-21 Is a Double-Edged Sword in the Systemic Lupus Erythematosus–like Disease of BXSB.Yaa Mice. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4581–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, P.; Ma, L.; Shan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y. Increased interleukin 21 and follicular helper T-like cells and reduced interleukin 10+ B cells in patients with new-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2014, 41, 1781–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.R.; Spolski, R.; Ettinger, R.; Kim, H.-P.; Wang, G.; Qi, C.-F.; Hwu, P.; Shaffer, D.J.; Akilesh, S.; Roopenian, D.C.; et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5361–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, T.N.; Bothwell, A.L.M.; Briles, D.E.; Janeway, C.A. IgG anti-DNA autoantibodies within an individual autoimmune mouse are the products of clonal selection. J. Immunol. 1989, 142, 4269–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, A.; Manheimer-Lory, A.; Aranow, C.; Peterson, R.; Hannigan, N.; Diamond, B. Molecular Characterization of a Somatically Mutated Anti-DNA Antibody Bearing Two Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-related Idiotypes. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, B.; Katz, J.B.; Paul, E.; Aranow, C.; Lustgarten, D.; Scharff, M.D. The role of somatic mutation in the pathogenic anti-DNA response. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 1992, 10, 731–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.K.; Putterman, C.; Diamond, B. Pathogenic autoantibodies are routinely generated during the response to foreign antigen: A paradigm for autoimmune disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2019–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unni, K.K.; Holley, K.E.; McDuffie, F.C.; Titus, J.L. Comparative study of NZB mice under germfree and conventional conditions. J. Rheumatol. 1975, 2, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiller, J.; Habicht, G.; Weigle, W. Kinetic differences in unresponsiveness of thymus and bone marrow cells. Science 1971, 171, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigle, W.O. Termination of acquired immunological tolerance to protein antigens following immunization with alterted proteinantigens. J. Exp. Med. 1962, 116, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.-H.; Mamura, M.J.; Hardin, J.A.; Janeway, C.A., Jr. Induction of autoreactive B cells allows priming of autoreactive T cells. J. Exp. Med. 1991, 173, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spolski, R.; Leonard, W.J. Interlelukin-21: Basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, P.; Ueno, H.; Schmitt, N. T follicular helper (Tfh) cells in lupus: Activation and involvement in SLE pathogenesis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Ho, J.H.; Pasoto, S.G.; Bunin, V.; Kim, S.T.; Carrasco, S.; Borba, E.F.; Goncalves, C.R.; Costa, P.R.; Kallas, E.G.; et al. Circulating follicular helper-like T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with disease activity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Tsai, L.M.; Leong, Y.A.; Hu, X.; Ma, C.S.; Chevalier, N.; Sun, X.; Vandenberg, K.; Rockman, S.; Ding, Y.; et al. Circulating precursor CCR7loPD-1hiCXCR5+CD4+ T cells indicate Tfh cell activity and promote antibody responses upon antigen reexposure. Immunity 2013, 39, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauveau, S.; Pirgova, G.; Cheng, H.-W.; De Martin, A.; Zhou, F.Y.; Wideman, S.; Rittscher, J.; Ludewig, B.; Amon, T.I. Visualization of T cell migration in the spleen reveals a network of perivascular pathways that guide entry into T zones. Immunity 2020, 52, 794–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- William, J.; Euler, C.; Christensen, S.; Shlomchik, M.J. Evolution of autoantibody responses via somatic hypermutation outside of germinal centers. Science 2002, 297, 2066–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, N.; Gatenby, P.A.; Wilson, A.; Malik, S.; Fulsher, D.A.; Tangye, S.G.; Harinder Manku, H.; Vyse, T.J.; Roncador, G.; Huttley, G.A.; et al. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akama-Garren, E.H.; Yin, X.; Prestwood, T.R.; Ma, M.; Utz, P.J.; Carroll, M.C. T cell help shapes B cell tolerance. Sci. Immunol. 2024, 9, eadj7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellford, S.A.; Schwartzberg, P.L. Help me help you: Emerging concepts in T follicular helper cell differentiation, identity, and function. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2024, 87, 102421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinuesa, C.G.; Cook, M.; Angelucci, C.; Athanasopoulos, V.; Rui, L.; Hill, K.M.; Yu, D.; Domaschenz, H.; Whittle, B.; Lambe, T.; et al. A RING-type ubiquitin ligase family member required to repress follicular helper T cells and autoimmunity. Nature 2005, 435, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, H.; Abe, M.; Hirose, S.; Tsushima, F.; Tezuka, K.; Akiba, H.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Kohsaka, H.; Miyasaka, N.; et al. Involvement of Inducible Costimulator-B7 Homologous Protein Costimulatory Pathway in Murine Lupus Nephritis. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2848–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutloff, A.; Buchner, K.; Reiter, K.; Baelde, H.J.; Odendahl, M.; Jacobi, A.; Dorner, T.; Kroczek, R.A. Involvement of Inducible Costimulator in the Exaggerated Memory B Cell and Plasma Cell Generation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, M.K.; Olferiew, M.; Kirou, K.A. Standing on shoulders: Interferon research from viral inference to lupus pathogenesis and treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gresser, I.; Maury, C.; Tovey, M.; Morel-Maroger, L.; Pontillon, F. Progressive glomerulonephritis in mice treated with interferon preparations at birth. Nature 1976, 263, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, C.; Thoua, Y.; Ronco, P.; Verroust, P.; Tovey, M.; Morel-Maroger, L. The effect of exogenous interferon: Acceleration of autoimmune and renal diseases in (NZB/W) F1 mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1980, 40, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, C.; Tsumiyama, K.; Uchimura, C.; Honda, E.; Miyazaki, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Miura, Y.; Hashiramoto, A.; Felsher, D.W.; Shiozawa, S. Conditional upregulation of IFNα alone is sufficient to induce systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, S.; Kuroki, Y.; Kim, M.; Hirohata, S.; Ogino, T. Interferon-alpha in lupus psychosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozawa, S.; Chihara, K.; Shiozawa, K.; Fujita, T.; Ikegami, H.; Koyama, S.; Kurimoto, M. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for alpha-interferon: Circulating α-interferon-like substance in the plasma of healthy individuals and rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1986, 66, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, C.; Zhu, J.; Kreska, D.; Morel, L.; Mohan, C.; Zhu, J.; Kreska, D.; Morel, L.; et al. Deficiency of type I interferon contributes to Sle2-associated component lupus phenotypes. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3063–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hron, J.D.; Peng, S.L. Type I IFN Protects Against Murine Lupus. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 2134–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccala, R.; Gonzalez-Quintial Schreiber, R.D.; Lawson, B.R.; Kono, D.H.; Theofilopoulos, A.N. Anti-IFN-α/β receptor antibody treatment ameliorates disease in lupus-predisposed mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5976–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, Y.J.; Lebon, P.; Casanova, J.-L.; Gresser, I. A brief historical perspective on the pathological consequences of excessive type I interferon exposure in vivo. J. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 38, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okanoue, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Itoh, Y.; Minami, M.; Yasui, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Nishioji, K.; Katagishi, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tada, T.; et al. Side effects of high dose interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 1996, 25, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronnblom, L.E.; Alm, G.V.; Oberg, K.E. Autoimmunity after alpha-interferron therapy for malignant carcinoid tumors. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 115, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandl, U.B.; Nagel-Hiemke, M.; May, D.; Kreuzfelder, E.; Kloke, O.; Kranzhoff, M.; Seeber, S.; Niederle, N. Lupus-like autoimmune disease induced by interferon therapy for myeloproliferative disorders. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1992, 65, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrenstein, M.R.; McSweeney, E.; Swane, M.; Worman, C.P.; Goldstone, A.H.; Isenberg, D.A. Appearance of anti-DNA antibodies in patients treated with interferon-alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1993, 36, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathian, A.; Weinberg, A.; Gallegos, M.; Banchereau, J.; Koutouzov, S. IFN-α induces early lethal lupus in preautoimmune (New Zealand Black x New Zealand White) F1 but not in BALB/c mice. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairhurst, A.-M.; Mathian, A.; Connolly, J.E.; Wang, A.; Gray, H.F.; George, T.A.; Boudreaux, C.D.; Zhou, X.J.; Li, Q.-Z.; Koutouzov, S.; et al. Systemic IFN alpha drives kidney nephritis in B6.Sle123 mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanujam, M.; Kahn, P.; Huang, W.; Tao, H.; Madaio, M.P.; Factor, S.M.; Davidson, A. Interferon-alpha treatment of female (NZW x BXSB)F(1) mice mimics some but not all features associated with the Yaa mutation. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Schnitzer, T.J. Serum interferon levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982, 25, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preble, O.T.; Black, R.J.; Friedman, R.M.; Klippel, J.H.; Vilcek, J. Systemic lupus erythematosus: Presence in human serum of an unusual acid-labile leukocyte interferon. Science 1982, 216, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Wussow, P.; Jakschies, D.; Hartung, K.; Deicher, H. Presence of interferon and anti-interferon in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 1988, 8, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggs, J.M.; Hanna, R.N.; Rajan, B.; Zerrouki, K.; Karnell, J.L.; Sagar, D.; Vainshtein, I.; Farmer, E.; Rosenthal, K.; Morehouse, C.; et al. Characterisation of anifrolumab, a fully human anti interferon receptor antagonist antibody for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2018, 5, e000261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Khamashta, M.; Merrill, J.T.; Werth, V.P.; Kalunian, K.; Brohawn, P.; Illei, G.G.; Drappa, J.; Wang, L.; Yoo, S.; et al. Anifrolumab, an anti-interferon-α receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate-to-severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.A.; Morand, E.F.; Bruce, I.N.; Manzi, S.; Kalunian, K.C.; Vital, E.M.; Ford, T.L.; Gupta, R.; Hiepe, F.; Santiago, M.; et al. Type I interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus (TULIP-1): A randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Rheumatol. 2019, 1, e208–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Bruce, I.N.; Askanase, A.D.; Richez, C.; Bae, S.-C.; Brohawn, P.Z.; Pineda, L.; Berglind, A.; et al. TULIP-2 trial investigators Trial of anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Morand, E.F.; Askanase, A.D.; Vital, E.M.; Merrill, J.T.; Kalyani, R.N.; Abreu, G.; Pineda, L.; Tummala, R. Anifrolumab reduces flare rates in patients with moderate to severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aicardi, J.; Goutieres, F. A progressive familial encephalopathy in infancy with calcifications of the basal ganglia and chronic cerebrospinal fluid lymphocytosis. Ann. Neurol. 1984, 15, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, Y.J.; Manel, N. Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome and the type I interferonopathies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deapen, D.; Escalante, A.; Weinrib, L.; Horwitz, D.; Bachman, B.; Roy-Burman, P.; Walker, A.; Mack, T.M. A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglia, M.; Merlott, G.; De Andrea, M.; Borgogna, C.; Cantaluppi, V. Viral infections and systemic lupus erythematosus: New players in an old story. Viruses 2021, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumiyama, K.; Hashiramoto, A.; Takimoto, M.; Tsuji-Kawahara, S.; Miyazawa, M.; Shiozawa, S. IFNγ–producing effector CD8 T lymphocytes cause immune glomerular injury by recognizing antigen presented as immune complex on target tissue. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- St Rose, M.-C.; Qui, H.Z.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Mihalyo, M.A.; Hagymasi, A.T.; Clark, R.B.; Adler, A.J. The E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b regulates expansion but not functional activity of self-reactive CD4 T cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4975–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higdon, L.E.; Deets, K.A.; Friesen, T.J.; Sze, K.-Y.; Fink, P.J. Receptor revision in CD4 T cells is influenced byfollicular helper T cell formation andgerminal-center interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5652–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.; Angelosanto, J.M.; Kao, C.; Doering, T.A.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Barnett, B.E.; Wherry, E.J. Molecular and transcriptional basis of CD4+ T Cell dysfunction during chronic infection. Immunity 2014, 40, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vella, L.A.; Herati, R.S.; Wherry, E.J. CD4+T cell differentiation in chronic viral Infections: The Tfh Perspective. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 1072–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinkernagel, R.M. Immunology taught by viruses. Science 1996, 271, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Schneider, D.A.; Soares, M.P. Disease tolerance as a defense strategy. Science 2012, 335, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guga, S.; Wang, Y.; Graham, D.C.; Vyse, T.J. A review of genetic risk in systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Fang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, P.; Ge, M.; Xu, Y.Q.; Gao, Z.X.; Wang, P.; Wang, D.G.; et al. Human Papillomavirus Infection and Autoimmune Diseases: A Two-Sample Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 27, e15430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Carrasco, M.; Mendoza-Pinto, C.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Molano-González, N.; Vallejo-Ruiz, V.; Munguía-Realpozo, P.; Colombo, A.L.; Cervera, R. Prevalence of Cervical HPV Infection in Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2019, 18, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnon, T.I.; Horton, R.M.; Grigorova, L.L.; Cyster, J.G. Visualization of splenic marginal zone B-cell suttling and follicular B-cell egress. Nature 2013, 493, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebegg, M.; Kumar, S.D.; Silva-Cayetano, A.; Fonceca, V.R.; Linterman, M.A.; Graca, L. Regulation of the germinal center response. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiel, S.; Barlev, A.N.; Atishafregoso, Y.; Suurmond, J.; Diamond, B. Plasma cell differentiation pathways in systemic lupus erythematosus. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suurmond, J.; Atisha-Fregoso, Y.; Barlev, A.N.; Calderon, S.A.; Mackay, M.C.; Aranow, C.; Diamond, B. Patterns of ANA+ B cells for SLE patient stratification. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e127885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enders, M.; Franken, L.; Philipp, M.-S.; Kessler, N.; Baumgart, A.K.; Eichler, M.; Wiertz, E.J.H.; Garbi, N.; Kurts, C. Splenic red pulp macrophages cross-prime early effector CTL that provide rapid defense against viral infections. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldstone, M.B. Molecular mimicry: Its evolution from concept to mechanism as a cause of autoimmune disease. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2014, 33, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, N.R. Negative selection, epitope mimicry and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, N.J.; Choi, M.Y.; Fritzler, M.J. Emerging technologies in autoantibody testing for rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischinger, S.; Boudreau, C.M.; Butler, A.L.; Streeck, H.; Galit, A.G. Sex differences in vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Sem. Immunopathol. 2019, 41, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Ellingson, M.K.; Wong, P.; Israelow, B.; Lucas, C.; Klein, J.; Silva, J.; Mao, T.; Eun, J.; Tokuyama, M.; et al. Sex differences in immune responses that underlie COVID-19 disease outcomes. Nature 2020, 588, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiozawa, S. Pathogenesis of Autoimmunity/Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Cells 2025, 14, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141080
Shiozawa S. Pathogenesis of Autoimmunity/Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Cells. 2025; 14(14):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141080
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiozawa, Shunichi. 2025. "Pathogenesis of Autoimmunity/Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)" Cells 14, no. 14: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141080
APA StyleShiozawa, S. (2025). Pathogenesis of Autoimmunity/Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Cells, 14(14), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14141080




