Red Cell Death in Renal Disease: The Role of Eryptosis in CKD and Dialysis Patients
Abstract
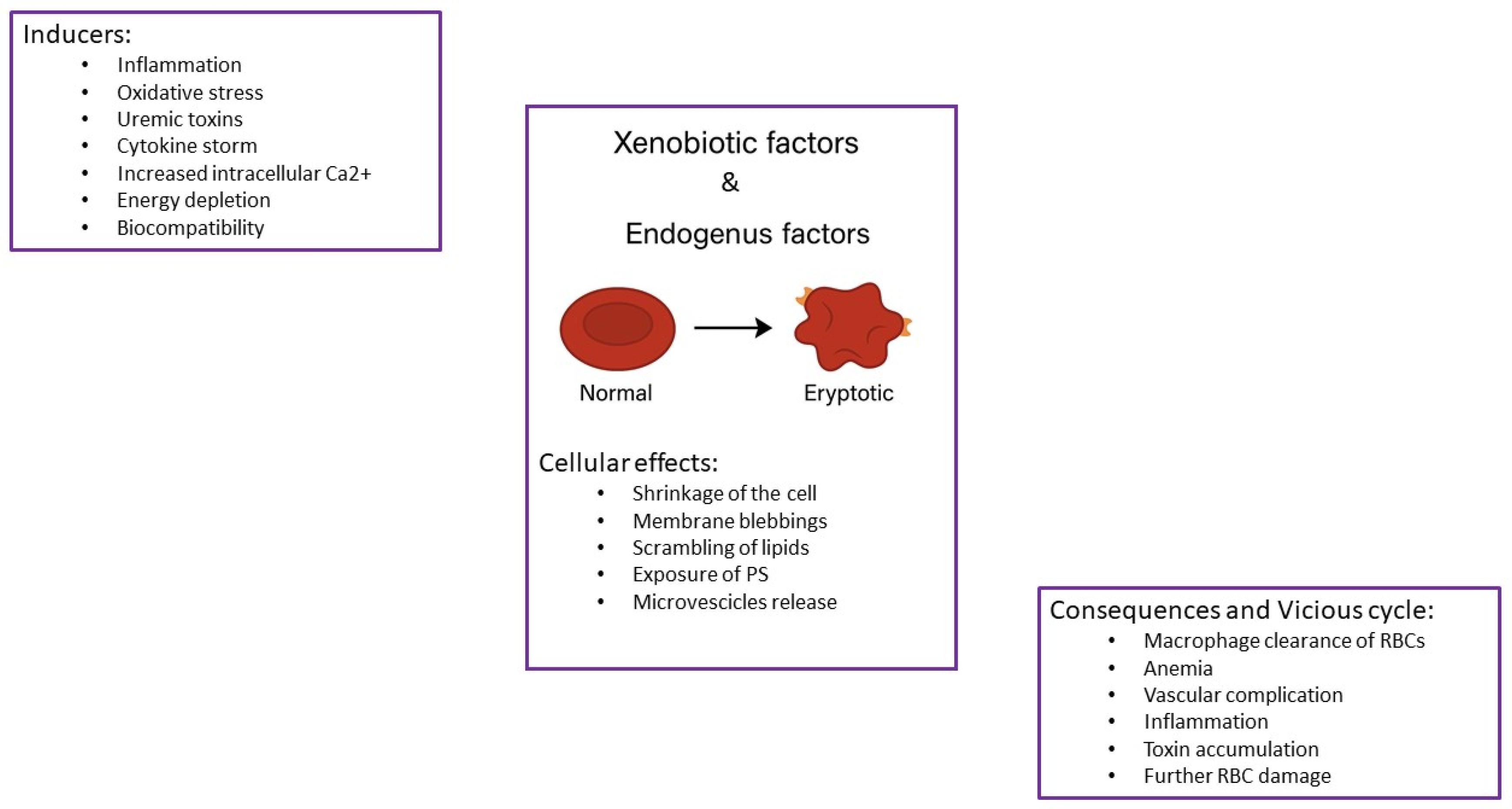
1. Introduction
1.1. The Aim of This Study
1.2. Literature Search Tools
2. Bibliographic Research Results
3. Chronic Kidney Disease Setting
End-Stage Renal Disease: Hemodialysis (HD) and Peritoneal Dialysis (PD)
4. Translational and Clinical Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liang, X.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y. Red Blood Cells-Derived Components as Biomimetic Functional Materials: Matching Versatile Delivery Strategies Based on Structure and Function. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 47, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi Barhaghtalab, R.; Tanimowo Aiyelabegan, H.; Maleki, H.; Mirzavi, F.; Gholizadeh Navashenaq, J.; Abdi, F.; Ghaffari, F.; Vakili-Ghartavol, R. Recent Advances with Erythrocytes as Therapeutics Carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 665, 124658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Red Blood Cells in Biology and Translational Medicine: Natural Vehicle Inspires New Biomedical Applications. Theranostics 2024, 14, 220–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.D.; Ghosh, J.; Ghosh, S.; Eswarappa, S.M. Emerging Concepts in the Molecular Cell Biology and Functions of Mammalian Erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; du Plooy, J.N.; Bester, J. A Comprehensive Review on Eryptosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 1977–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, E.; Lang, F. Triggers, Inhibitors, Mechanisms, and Significance of Eryptosis: The Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 513518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.S.; Lang, P.A.; Bauer, C.; Duranton, C.; Wieder, T.; Huber, S.M.; Lang, F. Mechanisms of Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 15, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Ghaffari, S. Erythroid Enucleation: A Gateway into a “Bloody” World. Exp. Hematol. 2021, 95, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, X. New Insights into the Mechanisms of Red Blood Cell Enucleation: From Basics to Clinical Applications. EJHaem 2024, 5, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Ghaffari, S. Advances in Understanding the Mechanisms of Erythropoiesis in Homeostasis and Disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiftsoglou, A.S.; Vizirianakis, I.S.; Strouboulis, J. Erythropoiesis: Model Systems, Molecular Regulators, and Developmental Programs. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 800–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulier, A.; Sankaran, V.G. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms That Regulate Human Erythropoiesis. Blood 2022, 140, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, S.C.; Derganc, J.; Shevkoplyas, S.S.; Yoshida, T.; Bitensky, M.W. A Detailed Study of Time-Dependent Changes in Human Red Blood Cells: From Reticulocyte Maturation to Erythrocyte Senescence. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 135, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, H.U.; Bogdanova, A. Mechanisms Tagging Senescent Red Blood Cells for Clearance in Healthy Humans. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, G.J.C.G.M.; Willekens, F.L.A.; Werre, J.M. Erythrocyte Aging: A More than Superficial Resemblance to Apoptosis? Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachenko, A.; Havranek, O. Cell Death Signaling in Human Erythron: Erythrocytes Lose the Complexity of Cell Death Machinery upon Maturation. Apoptosis 2025, 30, 652–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Abed, M.; Lang, E.; Föller, M. Oxidative Stress and Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Lang, K.S.; Lang, P.A.; Huber, S.M.; Wieder, T. Osmotic Shock-Induced Suicidal Death of Erythrocytes. Acta Physiol. 2006, 187, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Gulbins, E.; Lang, P.A.; Zappulla, D.; Föller, M. Ceramide in Suicidal Death of Erythrocytes. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Gulbins, E.; Lerche, H.; Huber, S.M.; Kempe, D.S.; Foller, M. Eryptosis, a Window to Systemic Disease. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 22, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Lang, E.; Föller, M. Physiology and Pathophysiology of Eryptosis. Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2012, 39, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, N.B.; Steiner, T.M.; Kuntsevich, V.; Virzì, G.M.; Azevedo, M.; Nakao, L.S.; Barreto, F.C.; Ronco, C.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P.; et al. Uremic Toxicity-Induced Eryptosis and Monocyte Modulation: The Erythrophagocytosis as a Novel Pathway to Renal Anemia. Blood Purif. 2016, 41, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.B.; Wagner-Britz, L.; Maia, S.; Steffen, P.; Wagner, C.; Kaestner, L.; Bernhardt, I. Regulation of Phosphatidylserine Exposure in Red Blood Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Killing Me Softly-Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, B. Influence of Hemolysis on Nucleated Red Blood Cells Count. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2023, 45, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghareeb, S.A.; Alfhili, M.A.; Fatima, S. Molecular Mechanisms and Pathophysiological Significance of Eryptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujais, S.K.; Story, K.; Brouillette, J.; Takano, T.; Soroka, S.; Franek, C.; Mendelssohn, D.; Finkelstein, F.O. Health-Related Quality of Life in CKD Patients: Correlates and Evolution over Time. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstratiadis, G.; Konstantinou, D.; Chytas, I.; Vergoulas, G. Cardio-Renal Anemia Syndrome. Hippokratia 2008, 12, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Staples, A.O.; Wong, C.S.; Smith, J.M.; Gipson, D.S.; Filler, G.; Warady, B.A.; Martz, K.; Greenbaum, L.A. Anemia and Risk of Hospitalization in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurella Tamura, M.; Vittinghoff, E.; Yang, J.; Go, A.S.; Seliger, S.L.; Kusek, J.W.; Lash, J.; Cohen, D.L.; Simon, J.; Batuman, V.; et al. Anemia and Risk for Cognitive Decline in Chronic Kidney Disease. BMC Nephrol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.N.; Parfrey, P.S.; Harnett, J.D.; Kent, G.M.; Murray, D.C.; Barre, P.E. The Impact of Anemia on Cardiomyopathy, Morbidity, and and Mortality in End-Stage Renal Disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1996, 28, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, H.W.; Claussner, A.; Erbes, P.M.; Scheuermann, E.H.; Schoeppe, W.; Koch, K.M. Serum Erythropoietin Concentration in Chronic Renal Failure: Relationship to Degree of Anemia and Excretory Renal Function. Blood 1979, 54, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelkl, J.; Alzoubi, K.; Mamar, A.-K.; Ahmed, M.S.E.; Abed, M.; Lang, F. Stimulation of Suicidal Erythrocyte Death by Increased Extracellular Phosphate Concentrations. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 38, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Yin, Y.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, M.; Wang, X. What Should Be Responsible for Eryptosis in Chronic Kidney Disease? Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2022, 47, 375–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.; Qadri, S.M. Mechanisms and Significance of Eryptosis, the Suicidal Death of Erythrocytes. Blood Purif. 2012, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.L.; Buddington, B.; Alfrey, A.C. Urinary Albumin, Transferrin and Iron Excretion in Diabetic Patients. Kidney Int. 1991, 40, 923–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, R.; Nemkov, T.; D’Alessandro, A.; Grau, M.; Dietz, T.; Bohnert, B.N.; Essigke, D.; Wörn, M.; Schaefer, L.; Xiao, M.; et al. Proteinuric Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Altered Red Blood Cell Lifespan, Deformability and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, R.; Qadri, S.M.; Artunc, F. Eryptosis: A Driver of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2024, 33, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, U.; Kaya, S.; Cim, A.; Büyükbayram, H.; Gökalp, O.; Dal, M.S.; Tamer, M.N. Increased Caspase-3 Immunoreactivity of Erythrocytes in STZ Diabetic Rats. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 316384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, S.; Strauch, P.; Maktabi, M.; Pybus, B.S.; Reichard, G.; Walker, L.A.; Rochford, R. Mechanisms of 8-Aminoquinoline Induced Haemolytic Toxicity in a G6PDd Humanized Mouse Model. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.E.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. Triggering of Suicidal Erythrocyte Death by Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.S.E.; Langer, H.; Abed, M.; Voelkl, J.; Lang, F. The Uremic Toxin Acrolein Promotes Suicidal Erythrocyte Death. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2013, 37, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabe, J.E.; Echegoyen, L.A.; Pastrana, B.; Martínez-Maldonado, M. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glycolysis by Vanadate. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9555–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Ji, S.; Dong, W.; Qi, Y.; Song, W.; Cui, D.; Shi, J. Indolic Uremic Solutes Enhance Procoagulant Activity of Red Blood Cells through Phosphatidylserine Exposure and Microparticle Release. Toxins 2015, 7, 4390–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Mattiotti, M.; Clementi, A.; Milan Manani, S.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. In Vitro Induction of Eryptosis by Uremic Toxins and Inflammation Mediators in Healthy Red Blood Cells. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.F.; Bonan, N.B.; Steiner, T.M.; Tozoni, S.S.; Rodrigues, S.; Nakao, L.S.; Kuntsevich, V.; Pecoits Filho, R.; Kotanko, P.; Moreno-Amaral, A.N. Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, Stimulates Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Erythrocyte Cell Death Supposedly by an Organic Anion Transporter 2 (OAT2) and NADPH Oxidase Activity-Dependent Pathways. Toxins 2018, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.; Towhid, S.T.; Schmid, E.; Hoffmann, S.M.; Abed, M.; Münzer, P.; Vogel, S.; Neis, F.; Brucker, S.; Gawaz, M.; et al. Dynamic Adhesion of Eryptotic Erythrocytes to Immobilized Platelets via Platelet Phosphatidylserine Receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2014, 306, C291-7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikisz, P.; Jacenik, D. The Tobacco Smoke Component, Acrolein, as a Major Culprit in Lung Diseases and Respiratory Cancers: Molecular Mechanisms of Acrolein Cytotoxic Activity. Cells 2023, 12, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Jiang, K.; Shi, L.; Fei, J.; Zheng, J.; Ou, S.; Ou, J. Formation of Di-Cysteine Acrolein Adduct Decreases Cytotoxicity of Acrolein by ROS Alleviation and Apoptosis Intervention. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Zheng, J.; Huang, J.; Ho, C.-T.; Ou, S. Interaction of Acrylamide, Acrolein, and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural with Amino Acids and DNA. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 5039–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopera, M.; Gwozdzinski, K.; Pieniazek, A. Acrolein Induces Changes in Cell Membrane and Cytosol Proteins of Erythrocytes. Molecules 2024, 29, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monden, Y.; Nakahara, K.; Nanjo, S.; Fujii, Y.; Matsumura, A.; Masaoka, A.; Kawashima, Y. Invasive Thymoma with Myasthenia Gravis. Cancer 1984, 54, 2513–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abed, M.; Artunc, F.; Alzoubi, K.; Honisch, S.; Baumann, D.; Föller, M.; Lang, F. Suicidal Erythrocyte Death in End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyring-Wösten, A.; Kuntsevich, V.; Campos, I.; Williams, S.; Ma, J.; Patel, S.; Ornillo, C.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Erythrocyte Sodium Sensitivity and Eryptosis in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprara, C.; Virzì, G.M.; Chieregato, K.; Marchionna, N.; Corradi, V.; Brendolan, A.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. Immunomodulation Driven by Theranova Filter during a Single HD Session. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcello, M.; Virzi, G.M.; Cantaluppi, V.; Marengo, M.; Brendolan, A.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. #1573 Effects of Haemodialysis Coupled with Hemadsorption on Uremic Toxins Removal, Oxidative Stress and Cellular Death. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, gfae069-1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, R.; Artunc, F.; Qadri, S.M.; Lang, F. Reduced Erythrocyte Survival in Uremic Patients Under Hemodialysis or Peritoneal Dialysis. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2016, 41, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, F.E.; Schollum, J.B.; Coulter, C.V.; Doyle, T.C.A.; Duffull, S.B.; Walker, R.J. Red Blood Cell Survival in Long-Term Dialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2011, 58, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomini, M.; Sirolli, V.; Settefrati, N.; Dottori, S.; Di Liberato, L.; Arduini, A. Increased Erythrocyte Phosphatidylserine Exposure in Chronic Renal Failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Milan Manani, S.; Clementi, A.; Castegnaro, S.; Brocca, A.; Riello, C.; de Cal, M.; Giuliani, A.; Battaglia, G.G.; Crepaldi, C.; et al. Eryptosis Is Altered in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 2019, 48, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Milan Manani, S.; Marturano, D.; Clementi, A.; Lerco, S.; Tantillo, I.; Giuliani, A.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. Eryptosis in Peritoneal Dialysis-Related Peritonitis: The Potential Role of Inflammation in Mediating the Increase in Eryptosis in PD. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, J.; Pretorius, E. Effects of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 on Erythrocytes, Platelets and Clot Viscoelasticity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.; Thiel, C.; Towhid, S.T.; Alzoubi, K.; Honisch, S.; Lang, F.; Königsrainer, A. Stimulation of Erythrocyte Cell Membrane Scrambling by C-Reactive Protein. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzì, G.M.; Morisi, N.; Marturano, D.; Milan Manani, S.; Tantillo, I.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. Peritoneal Inflammation in PD-Related Peritonitis Induces Systemic Eryptosis: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgatzakou, H.T.; Tzounakas, V.L.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Velentzas, A.D.; Papageorgiou, E.G.; Voulgaridou, A.I.; Kokkalis, A.C.; Antonelou, M.H.; Papassideri, I.S. Pathophysiological aspects of red blood cells in end-stage renal disease patients resistant to recombinant human erythropoietin therapy. Eur. J. Haematol. 2017, 98, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgatzakou, H.T.; Tzounakas, V.L.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Velentzas, A.D.; Kokkalis, A.C.; Antonelou, M.H.; Papassideri, I.S. Short-term effects of hemodiafiltration versus conventional hemodialysis on erythrocyte performance. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 96, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwozdzinski, K.; Pieniazek, A.; Gwozdzinski, L. Reactive Oxygen Species and Their Involvement in Red Blood Cell Damage in Chronic Kidney Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6639199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Rocha, S.; Rocha-Pereira, P.; Castro, E.; Miranda, V.; do Sameiro Faria, M.; Loureiro, A.; Quintanilha, A.; Belo, L.; Santos-Silva, A. Altered erythrocyte membrane protein composition in chronic kidney disease stage 5 patients under haemodialysis and recombinant human erythropoietin therapy. Blood Purif. 2008, 26, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgatzakou, H.T.; Antonelou, M.H.; Papassideri, I.S.; Kriebardis, A.G. Red blood cell abnormalities and the pathogenesis of anemia in end-stage renal disease. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2016, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Qian, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, D.; You, H.; Hou, B.; Han, F.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, F.; Lam, S.M.; et al. Combinatorial lipidomics and proteomics underscore erythrocyte lipid membrane aberrations in the development of adverse cardio-cerebrovascular complications in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Redox Biol. 2024, 78, 103389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldreich, T.; Nowak, C.; Fall, T.; Carlsson, A.C.; Carrero, J.J.; Ripsweden, J.; Qureshi, A.R.; Heimbürger, O.; Barany, P.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Circulating proteins as predictors of cardiovascular mortality in end-stage renal disease. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Search String | Papers | |
|---|---|---|
| Eryptosis OR RBC apoptosis | Renal disease | 48 |
| CKD | 16 | |
| Dialysis | 18 | |
| HD | 17 | |
| PD | 6 |
| Uremic Toxin | Precursor(s) | Site of Production | Enzymes Involved | Mechanism of Action in Eryptosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoxyl sulfate | Tryptophan | Colon → Liver | Bacterial tryptophanase, cytochrome P450, SULTs | Increases ROS and intracellular Ca2+; promotes PS exposure and cell shrinkage |
| p-Cresyl sulfate | Tyrosine, Phenylalanine | Colon → Liver | Bacterial fermentation, sulfotransferases | Induces oxidative stress; enhances membrane damage and eryptosis signaling |
| Acrolein | Lipids, Polyamines, Threonine | Endogenous (various tissues) | Amine oxidases, lipid peroxidation pathways | Alters membrane structure; increases Ca2+ and ceramide; triggers PS externalization |
| Uremic Toxin | Molecular Pathways Activated | Mechanism Summary in Eryptosis |
|---|---|---|
| Indoxyl Sulfate |
| Increases oxidative stress and intracellular Ca2+, promoting membrane PS exposure. |
| Acrolein |
| Alters membrane fluidity and integrity, triggering eryptosis signaling. |
| Vanadate |
| Induces eryptosis by causing energy failure in RBCs. |
| p-Cresol |
| Promotes Ca2+ influx and phosphatidylserine exposure on the erythrocyte surface. |
| Homocysteine |
| Weakens antioxidant defenses, sensitizing cells to eryptosis. |
| Methylglyoxal |
| Causes membrane dysfunction and promotes eryptotic signaling. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Virzì, G.M.; Clementi, A.; Ronco, C.; Zanella, M. Red Cell Death in Renal Disease: The Role of Eryptosis in CKD and Dialysis Patients. Cells 2025, 14, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130967
Virzì GM, Clementi A, Ronco C, Zanella M. Red Cell Death in Renal Disease: The Role of Eryptosis in CKD and Dialysis Patients. Cells. 2025; 14(13):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130967
Chicago/Turabian StyleVirzì, Grazia Maria, Anna Clementi, Claudio Ronco, and Monica Zanella. 2025. "Red Cell Death in Renal Disease: The Role of Eryptosis in CKD and Dialysis Patients" Cells 14, no. 13: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130967
APA StyleVirzì, G. M., Clementi, A., Ronco, C., & Zanella, M. (2025). Red Cell Death in Renal Disease: The Role of Eryptosis in CKD and Dialysis Patients. Cells, 14(13), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130967








