Neurofilament Light Chain in Serum and CSF as a Potential Biomarker for Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Healthy Controls
2.2. NfL Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients with Active PACNS
3.2. Patients with PACNS in Remission
3.3. Control Group
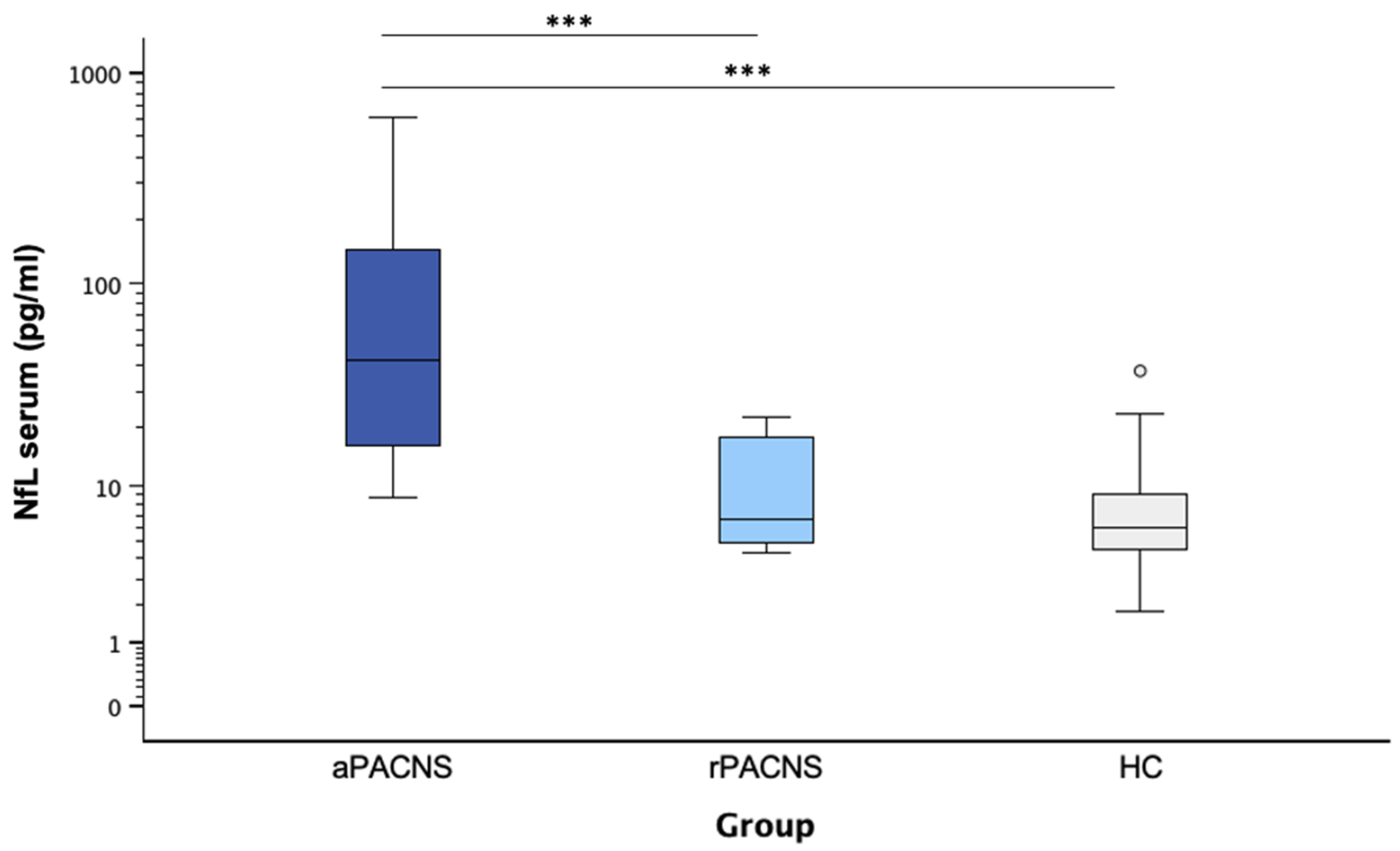
3.4. NfL Levels in Serum
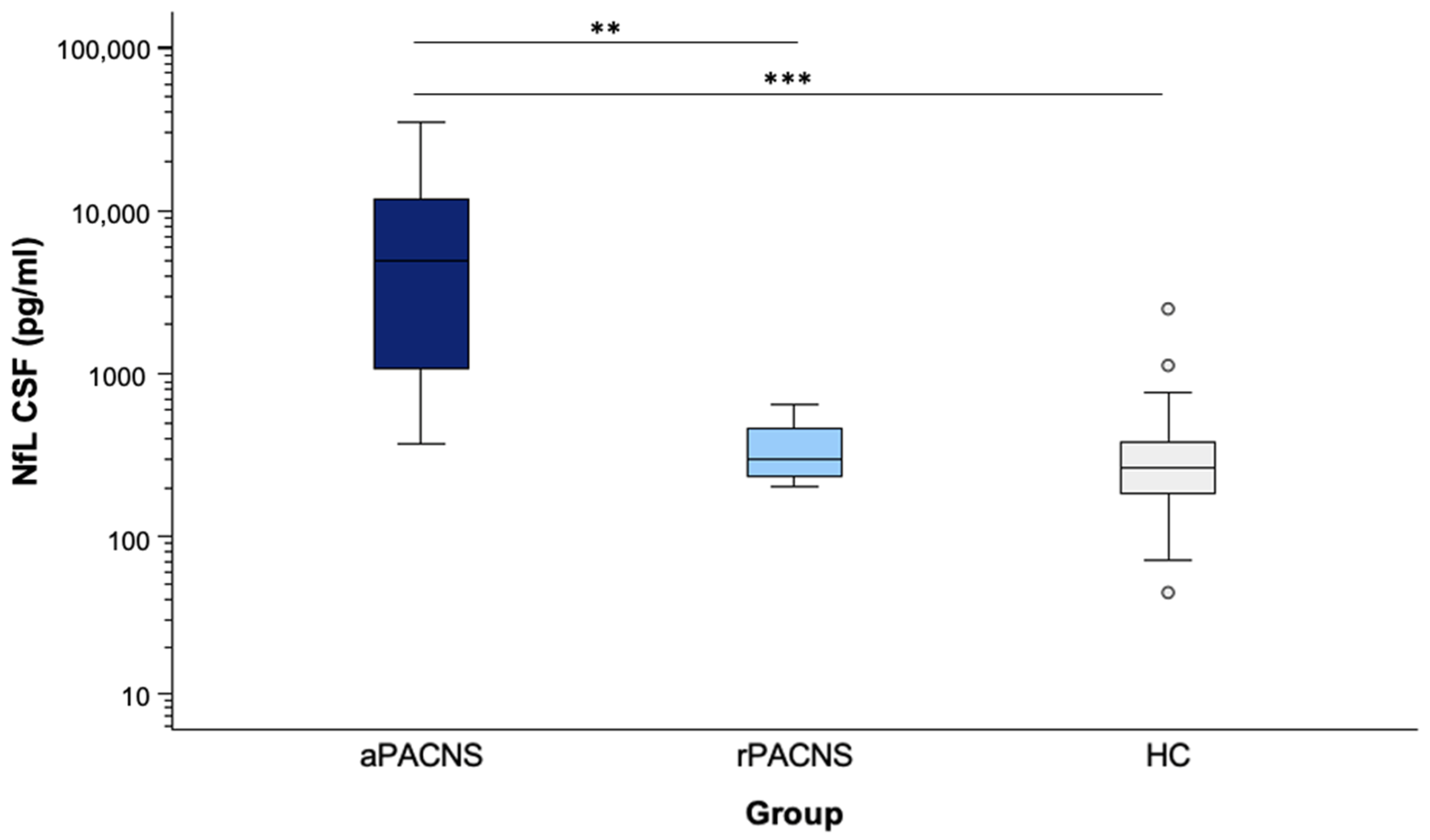
3.5. NfL Levels in CSF
3.6. Association Between Serum/CSF NfL Levels and Clinical Parameters in aPACNS
3.7. PACNS Patients Without Ischemic Stroke
4. Discussion
5. Limitations and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis |
| aPACNS | Active PACNS |
| CECs | Circulating Endothelial Cells |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal Fluid |
| DSA | Digital Subtraction Angiography |
| LSD | Least Significant Difference |
| MRA | Magnetic Resonance Angiography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NfL | Neurofilament Light Chain |
| OCBs | Oligoclonal Bands |
| PACNS | Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System |
| rPACNS | PACNS in Remission |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| TBI | Traumatic Brain Injury |
References
- Berlit, P. Diagnosis and Treatment of Cerebral Vasculitis. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2010, 3, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb-Chatterji, M.; Schuster, S.; Haeussler, V.; Gerloff, C.; Thomalla, G.; Magnus, T. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: New Potential Imaging Techniques and Biomarkers in Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb-Chatterji, M.; Magnus, T. Zerebrale Vaskulitis: Ein Update Zu Symptomen, Diagnostik Und Therapie. Neurol. Up2date 2021, 4, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, C.; Salvarani, C.; Hunder, G.; Brown, R.D. Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis: Pathology and Mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marini, C.; Totaro, R.; De Santis, F.; Ciancarelli, I.; Baldassarre, M.; Carolei, A. Stroke in Young Adults in the Community-Based L’Aquila Registry. Stroke 2001, 32, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilot Barlas, N.; Putaala, J.; Waje-Andreassen, U.; Vassilopoulou, S.; Nardi, K.; Odier, C.; Hofgart, G.; Engelter, S.; Burow, A.; Mihalka, L.; et al. Etiology of First-ever Ischaemic Stroke in European Young Adults: The 15 Cities Young Stroke Study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2013, 20, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.E. CNS Vasculitis. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuker, C.; Schmidt, A.; Strunk, D.; Sporns, P.B.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Minnerup, J. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: Diagnosis and Treatment. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418785071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, J.; Hellmann, D.B. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, D.S. Vasculitis of the Nervous System. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2004, 17, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferkorn, T.; Linn, J.; Habs, M.; Opherk, C.; Cyran, C.; Ottomeyer, C.; Straube, A.; Dichgans, M.; Nikolaou, K.; Saam, T. Black Blood MRI in Suspected Large Artery Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. J. Neuroimaging 2013, 23, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaerel, P.; De Ruyter, N.; Maes, F.; Velghe, B.; Wilms, G. Magnetic Resonance Angiography in Suspected Cerebral Vasculitis. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 14, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadkhodayan, Y.; Alreshaid, A.; Moran, C.J.; Cross, D.T.; Powers, W.J.; Derdeyn, C.P. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System at Conventional Angiography. Radiology 2004, 233, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Póvoa, P.; Costa, A.; Ducla-Soares, J. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Therapy of Isolated Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Stroke 1994, 25, 1693–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D.; Hunder, G.G. Adult Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis. Lancet 2012, 380, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D.; Christianson, T.; Miller, D.V.; Giannini, C.; Huston, J.; Hunder, G.G. An Update of the Mayo Clinic Cohort of Patients with Adult Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis: Description of 163 Patients. Medicine 2015, 94, e738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Khalil, M. Neurofilaments as Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2012, 18, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiottino, J.; Norgren, N.; Dobson, R.; Topping, J.; Nissim, A.; Malaspina, A.; Bestwick, J.P.; Monsch, A.U.; Regeniter, A.; Lindberg, R.L.; et al. Increased Neurofilament Light Chain Blood Levels in Neurodegenerative Neurological Diseases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Neurological Disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermunt, L.; Otte, M.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Killestein, J.; Lemstra, A.W.; van der Flier, W.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; Vijverberg, E.G.B.; Bouwman, F.H.; Gravesteijn, G.; et al. Age- and Disease-specific Reference Values for Neurofilament Light Presented in an Online Interactive Support Interface. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2022, 9, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb-Chatterji, M.; Pinnschmidt, H.O.; Duan, Y.; Haeussler, V.; Rissiek, B.; Gerloff, C.; Thomalla, G.; Magnus, T. Circulating Endothelial Cells as Promising Biomarkers in the Differential Diagnosis of Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiedt, S.; Duering, M.; Barro, C.; Kaya, A.G.; Boeck, J.; Bode, F.J.; Klein, M.; Dorn, F.; Gesierich, B.; Kellert, L.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light. Neurology 2018, 91, e1338–e1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattringer, T.; Pinter, D.; Enzinger, C.; Seifert-Held, T.; Kneihsl, M.; Fandler, S.; Pichler, A.; Barro, C.; Gröbke, S.; Voortman, M.; et al. Serum Neurofilament Light Is Sensitive to Active Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Neurology 2017, 89, 2108–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uphaus, T.; Bittner, S.; Gröschel, S.; Steffen, F.; Muthuraman, M.; Wasser, K.; Weber-Krüger, M.; Zipp, F.; Wachter, R.; Gröschel, K. NfL (Neurofilament Light Chain) Levels as a Predictive Marker for Long-Term Outcome After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2019, 50, 3077–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekny, M.; Wilhelmsson, U.; Stokowska, A.; Tatlisumak, T.; Jood, K.; Pekna, M. Neurofilament Light Chain (NfL) in Blood—A Biomarker Predicting Unfavourable Outcome in the Acute Phase and Improvement in the Late Phase after Stroke. Cells 2021, 10, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godasi, R.; Pang, G.; Chauhan, S.; Bollu, P.C. Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis; StatPearls Publishing: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Paramasivan, N.K.; Sharma, D.P.; Mohan, S.M.K.; Sundaram, S.; Sreedharan, S.E.; Sarma, P.S.; Sylaja, P.N. Primary Angiitis of the CNS: Differences in the Profile Between Subtypes and Outcomes From an Indian Cohort. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 11, e200262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krüger, C.; Pinnschmidt, H.; Wilmes, M.; Dargvainiene, J.; Leypoldt, F.; Seiler, A.; Berg, D.; Magnus, T.; Deb-Chatterji, M. Neurofilament Light Chain in Serum and CSF as a Potential Biomarker for Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Cells 2025, 14, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130966
Krüger C, Pinnschmidt H, Wilmes M, Dargvainiene J, Leypoldt F, Seiler A, Berg D, Magnus T, Deb-Chatterji M. Neurofilament Light Chain in Serum and CSF as a Potential Biomarker for Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Cells. 2025; 14(13):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130966
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrüger, Christina, Hans Pinnschmidt, Maximilian Wilmes, Justina Dargvainiene, Frank Leypoldt, Alexander Seiler, Daniela Berg, Tim Magnus, and Milani Deb-Chatterji. 2025. "Neurofilament Light Chain in Serum and CSF as a Potential Biomarker for Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System" Cells 14, no. 13: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130966
APA StyleKrüger, C., Pinnschmidt, H., Wilmes, M., Dargvainiene, J., Leypoldt, F., Seiler, A., Berg, D., Magnus, T., & Deb-Chatterji, M. (2025). Neurofilament Light Chain in Serum and CSF as a Potential Biomarker for Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System. Cells, 14(13), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14130966





