Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Literature Review
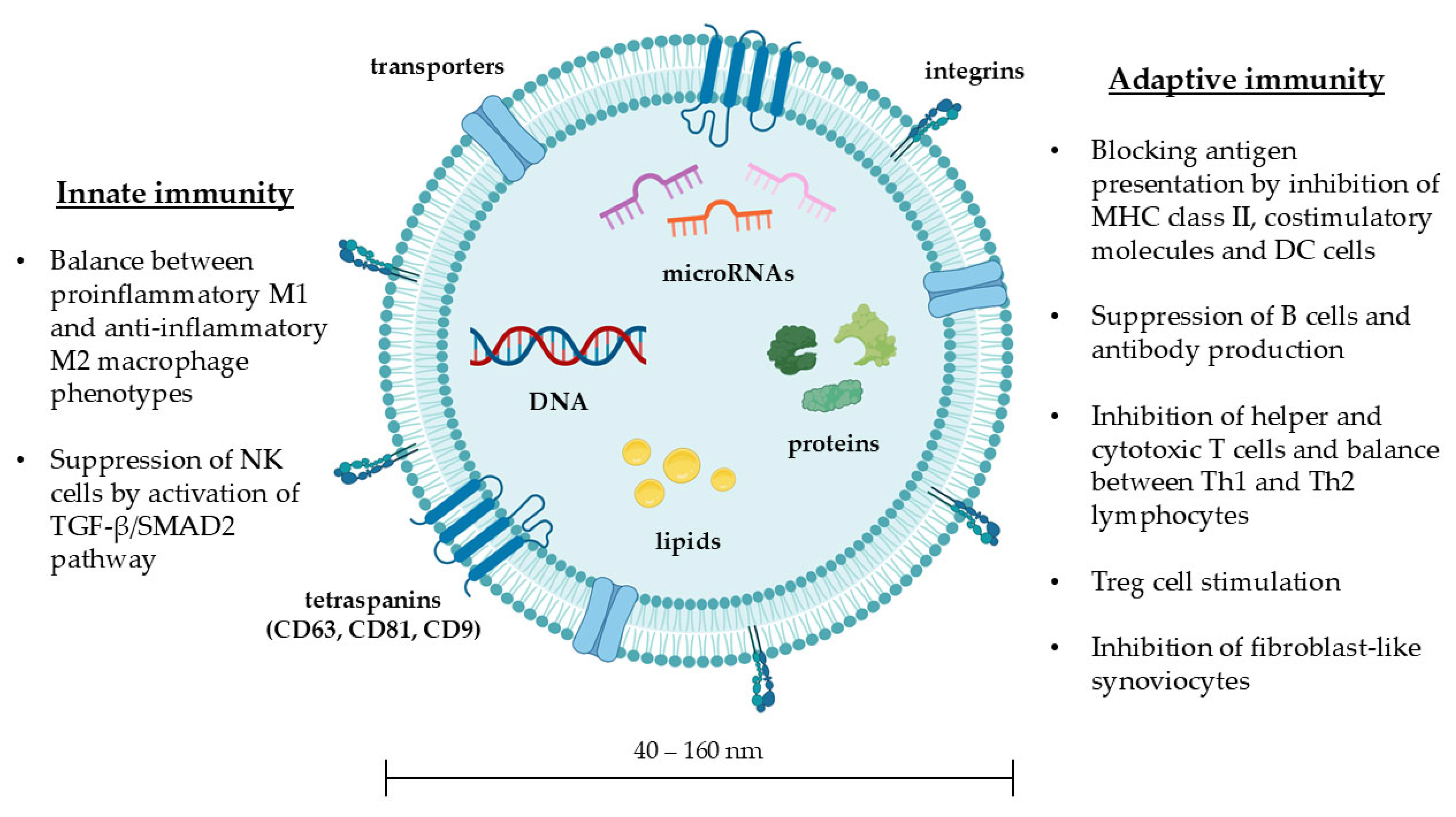
3.1. Structure and Biological Functions of Exosomes
3.2. MSC-Exos: Immunoregulation
3.3. MSC-Exos’ Antifibrotic Properties
3.4. Exosomal Content: microRNAs
3.5. Exosomal microRNAs’ Antifibrotic Properties
3.6. MSC-Exos and microRNAs: Pulmonary Hypertension
4. Discussion: MSC-Exos Transplantation as a Cell-Free Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASC | Adipose-derived stem cell |
| BLM | Bleomycin |
| BMSC | Bone-Marrow-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| HIF | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor |
| hUCMSC | human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IRF | Interferon Regulatory Factor |
| IL ISEV | Interleukin International Society for Extracellular Vesicles |
| FGF | Fibroblast Growth Factor |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| miR | microRNA |
| MCP-1 MISEV | Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| MSC MSC-Exos | Mesenchymal stem cell Mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomes |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| PAH | Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension |
| PDGF | Platelet-Derived Growth Factor |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3 kinases |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor γ |
| SMA | Smooth Muscle Actin |
| SMAD | Small Mother Against Decapentaplegic |
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| TGF | Transforming Growth Factor |
| Th | T helper |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| Treg | T regulatory |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Dumoitier, N.; Lofek, S.; Mouthon, L. Pathophysiology of Systemic Sclerosis: State of the Art in 2014. La Presse Médicale 2014, 43, e267–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.R.; Hare, J.M. Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, P.; Robey, P.G.; Simmons, P.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Revisiting History, Concepts, and Assays. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 2, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squillaro, T.; Peluso, G.; Galderisi, U. Clinical Trials with Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An Update. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 829–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, D.G.; Pittenger, M.F. Concise Review: MSC-Derived Exosomes for Cell-Free Therapy. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cras, A.; Farge, D.; Carmoi, T.; Lataillade, J.-J.; Wang, D.D.; Sun, L. Update on Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy in Lupus and Scleroderma. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiducci, S.; Porta, F.; Saccardi, R.; Guidi, S.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Manetti, M.; Mazzanti, B.; Dal Pozzo, S.; Milia, A.F.; Bellando-Randone, S.; et al. Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Foster Revascularization of Ischemic Limbs in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigatsubo, Y.; Ihata, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Hama, M.; Kirino, Y.; Ueda, A.; Takeno, M.; Shirai, A.; Ohno, S. Therapeutic Angiogenesis in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis by Autologous Transplantation of Bone-Marrow-Derived Cells. Mod. Rheumatol. 2010, 20, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Papa, N.; Di Luca, G.; Sambataro, D.; Zaccara, E.; Maglione, W.; Gabrielli, A.; Fraticelli, P.; Moroncini, G.; Beretta, L.; Santaniello, A.; et al. Regional Implantation of Autologous Adipose Tissue-Derived Cells Induces a Prompt Healing of Long-Lasting Indolent Digital Ulcers in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, K.; Yanishi, K.; Yoshimi, R.; Hamada, N.; Kondo, K.; Fujimoto, K.; Nakajima, H.; Kuwahara, K.; Higashi, Y.; Fukumoto, Y.; et al. Impact of Therapeutic Angiogenesis Using Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Mononuclear Cells Implantation in Critical Limb Ischemia With Scleroderma―Subanalysis of the Long-Term Clinical Outcomes Survey. Circ. J. 2019, 83, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehbe, T.; Abi Saab, M.; Abi Chahine, N.; Margossian, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Refractory Scleroderma: A Report of 2 Cases. Stem Cell Investig. 2016, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopeit, M.; Schendel, M.; Föll, J.; Müller, L.P.; Keysser, G.; Behre, G. Marked Improvement of Severe Progressive Systemic Sclerosis after Transplantation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from an Allogeneic Haploidentical-Related Donor Mediated by Ligation of CD137L. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, G.; Miyamoto, M.; Tara, S.; Kirinoki-Ichikawa, S.; Kubota, Y.; Hada, T.; Takagi, I.; Mizuno, K. Therapeutic Vascular Angiogenesis for Intractable Macroangiopathy-Related Digital Ulcer in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Pilot Study. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyszer, G.; Christopeit, M.; Fick, S.; Schendel, M.; Taute, B.M.; Behre, G.; Müller, L.P.; Schmoll, H. Treatment of Severe Progressive Systemic Sclerosis with Transplantation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Allogeneic Related Donors: Report of Five Cases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2540–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, J.; Tang, X.; Wang, D.; Feng, X.; Wang, F.; Hua, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, L. Sustained Benefit from Combined Plasmapheresis and Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, Y.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, J. Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis. Beijing Da Xue Xue bao. Yi Xue Ban = J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 2018, 50, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, R.; Guo, W.; Zhu, M.; Xing, W.; Jiang, D.; Liu, C.; Xu, X. Serum IFN-γ Levels Predict the Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar-Soto, C.-H.; Mejia-Romero, R.; Aguilera, N.; Alzate-Granados, J.P.; Mendoza-Pinto, C.; Munguía-Realpozo, P.; Méndez-Martínez, S.; García-Carrasco, M.; Rojas-Villarraga, A. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Management of Systemic Sclerosis. Systematic Review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.P.; Ismail, N.; Zhang, X.; Aguda, B.D.; Lee, E.J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, T.; Schafer, J.; Lee, M.-L.T.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Detection of MicroRNA Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, T.L.; Sánchez-Abarca, L.I.; Muntión, S.; Preciado, S.; Puig, N.; López-Ruano, G.; Hernández-Hernández, Á.; Redondo, A.; Ortega, R.; Rodríguez, C.; et al. MSC Surface Markers (CD44, CD73, and CD90) Can Identify Human MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles by Conventional Flow Cytometry. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic Comparison Defines Novel Markers to Characterize Heterogeneous Populations of Extracellular Vesicle Subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeria, C.; Weiss, R.; Roy, M.; Tripisciano, C.; Kasper, C.; Weber, V.; Egger, D. Hypoxia Conditioned Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Induce Increased Vascular Tube Formation in Vitro. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Shen, L.; Xie, X.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, M. The Therapeutic Effects of Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Scleroderma. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 19, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Herr, F.; Vernochet, A.; Mennesson, B.; Oberlin, E.; Durrbach, A. Human Fetal Liver Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Impair Natural Killer Cell Function. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, M.; Mavin, E.; Nicholson, L.; Green, K.; Dickinson, A.M.; Wang, X. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Dendritic Cell Maturation and Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, A.; Brandi, J.; Caligola, S.; Delfino, P.; Bazzoni, R.; Carusone, R.; Cecconi, D.; Giugno, R.; Manfredi, M.; Robotti, E.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Dependent Regulation of B Cell PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway and Actin Cytoskeleton. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Miura, Y.; Fujishiro, A.; Shindo, T.; Shimazu, Y.; Hirai, H.; Tahara, H.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Ichinohe, T.; Maekawa, T. Graft-Versus-Host Disease Amelioration by Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Associated with Peripheral Preservation of Naive T Cell Populations. Stem Cells 2018, 36, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-G.; Xie, Q.-L.; Li, B.-B.; Zhou, L.; Yan, D. Exosomes Derived from IDO1-Overexpressing Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Immunotolerance of Cardiac Allografts. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1657–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarnath, S.; Foley, J.E.; Farthing, D.E.; Gress, R.E.; Laurence, A.; Eckhaus, M.A.; Métais, J.-Y.; Rose, J.J.; Hakim, F.T.; Felizardo, T.C.; et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Harness Purinergenic Signaling to Tolerize Human Th1 Cells In Vivo. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Su, C.; Wei, Q.; Sun, H.; Xie, J.; Nong, G. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Mice by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization via the MicroRNA-146a-5p/NOTCH1 Axis. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 1975–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, M.; Tian, D.; Yuan, Z. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Biswas, S.K.; Fisher, E.A.; Gilroy, D.W.; Goerdt, S.; Gordon, S.; Hamilton, J.A.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Lawrence, T.; et al. Macrophage Activation and Polarization: Nomenclature and Experimental Guidelines. Immunity 2014, 41, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, B.; He, J.; Hua, H. Labial Gland Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes-Mediated MiRNA-125b Attenuates Experimental Sjogren’s Syndrome by Targeting PRDM1 and Suppressing Plasma Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 871096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xing, Y.; Gan, Y.; He, J.; Hua, H. Labial Gland-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Exosomes Ameliorate Murine Sjögren’s Syndrome by Modulating the Balance of Treg and Th17 Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; He, X.; Yang, X.; Shan, F.; Feng, J. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Inflammation and Demyelination of the Central Nervous System in EAE Rats by Regulating the Polarization of Microglia. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 67, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Jeong, M.; Kim, S.; Jang, K.; Kang, B.-K.; Lee, D.Y.; Bae, S.-C.; Kim, K.S.; Youn, J. Infusion of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Autoimmune Nephritis in a Lupus Model by Suppressing Follicular Helper T-Cell Development. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojehdehi, S.; Soudi, S.; Hesampour, A.; Rasouli, S.; Soleimani, M.; Hashemi, S.M. Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Experimental Type-1 Autoimmune Diabetes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 9433–9443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdipour, E.; Salmasi, Z.; Sabeti, N. Potential of Stem Cell-derived Exosomes to Regenerate β Islets through Pdx-1 Dependent Mechanism in a Rat Model of Type 1 Diabetes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 20310–20321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Tang, F.; Xiao, L.; Han, S.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J. MiR-205-5p in Exosomes Divided from Chondrogenic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviated Rheumatoid Arthritis via Regulating MDM2 in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2022, 22, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Yan, F.; Lu, Y. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell–Derived MiRNA-150-5p–Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Qiu, B. Exosomal MicroRNA-320a Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Regulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Activation by Suppressing CXCL9 Expression. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Gao, J.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, K. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Loaded MiR-451a Targets ATF2 to Improve Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 127, 111365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Q. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022, 42, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemoto-Kuroda, T.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, T.W.; An, S.Y.; Prockop, D.J.; et al. MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Immune Responses in Two Autoimmune Murine Models: Type 1 Diabetes and Uveoretinitis. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 1214–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yuan, J.; Cai, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Yan, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; et al. HucMSC-exosomes Carrying MiR-326 Inhibit Neddylation to Relieve Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Tian, H.; Xu, J.-Y.; Gao, F.; Hu, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. BMSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Intervened the Pathogenic Changes of Scleroderma in Mice through MiRNAs. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozier, P.; Maumus, M.; Maria, A.T.J.; Toupet, K.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Jorgensen, C.; Guilpain, P.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Systemic Sclerosis via MiR-29a-3p. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 121, 102660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Xue, Y.; Wan, W.; Zou, H.; et al. Exosomes Carrying Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Function Alleviate Scleroderma Skin Fibrosis by Inhibiting the TGF-Β1/Smad3 Axis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Long, X.; Mo, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Long, M.; Li, M. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Skin Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis by Inhibiting the IL-33/ST2 Axis via the Delivery of MicroRNA-214. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 157, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, D.; Moshaverinia, A.; Liu, D.; Kou, X.; Yu, W.; Yang, R.; Sun, L.; Shi, S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Tight-Skin Mice Identifies MiR-151-5p as a Therapeutic Target for Systemic Sclerosis. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozier, P.; Maumus, M.; Bony, C.; Maria, A.T.J.; Sabatier, F.; Jorgensen, C.; Guilpain, P.; Noël, D. Extracellular Vesicles Are More Potent Than Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Exert an Anti-Fibrotic Effect in an In Vitro Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Benedetto, P.; Ruscitti, P.; Berardicurti, O.; Vomero, M.; Navarini, L.; Dolo, V.; Cipriani, P.; Giacomelli, R. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Clark, A.G. Impact of MicroRNA Regulation on Variation in Human Gene Expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares, C.V.; Evangelista, A.F.; Xavier, D.J.; Rassi, D.M.; Arns, T.; Foss-Freitas, M.C.; Foss, M.C.; Puthier, D.; Sakamoto-Hojo, E.T.; Passos, G.A.; et al. Identifying Common and Specific MicroRNAs Expressed in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell of Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Patients. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkerman, L.; Casas, R.; Ludvigsson, J.; Tavira, B.; Skoglund, C. Serum MiRNA Levels Are Related to Glucose Homeostasis and Islet Autoantibodies in Children with High Risk for Type 1 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Lin, J.; Xie, L.; Chen, S.; Liang, J.; Xu, J. Downregulation of MiR-633 Activated AKT/MTOR Pathway by Targeting AKT1 in Lupus CD4+ T Cells. Lupus 2019, 28, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari Ghods, F.; Topal Sarikaya, A.; Arda, N.; Hamuryudan, V. MiRNA and MRNA Profiling in Systemic Lupus Reveals a Novel Set of Cytokine-Related MiRNAs and Their Target Genes in Cases With and Without Renal Involvement. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Ye, L.; Wu, K.; Lin, K.; Ye, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Q.; et al. NovelmiRNA-25 Inhibits AMPD2 in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Represents a Promising Novel Biomarker. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q.-J. MiR-17-92 Cluster Targets Phosphatase and Tensin Homology and Ikaros Family Zinc Finger 4 to Promote TH17-Mediated Inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12446–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesha, S.H.; Dudics, S.; Song, Y.; Mahurkar, A.; Moudgil, K.D. The MiRNA Expression Profile of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Reveals Novel Potential Disease Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossato, M.; Affandi, A.J.; Thordardottir, S.; Wichers, C.G.K.; Cossu, M.; Broen, J.C.A.; Moret, F.M.; Bossini-Castillo, L.; Chouri, E.; van Bon, L.; et al. Association of MicroRNA-618 Expression With Altered Frequency and Activation of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, B.; Xiao, X.; Zuo, X. MicroRNA-130b Regulates Scleroderma Fibrosis by Targeting Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouri, E.; Servaas, N.H.; Bekker, C.P.J.; Affandi, A.J.; Cossu, M.; Hillen, M.R.; Angiolilli, C.; Mertens, J.S.; van den Hoogen, L.L.; Silva-Cardoso, S.; et al. Serum MicroRNA Screening and Functional Studies Reveal MiR-483-5p as a Potential Driver of Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 89, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artlett, C.M.; Sassi-Gaha, S.; Hope, J.L.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Katsikis, P.D. Mir-155 Is Overexpressed in Systemic Sclerosis Fibroblasts and Is Required for NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Collagen Synthesis during Fibrosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhu, H.; Luo, H.; Gao, S.; Dai, X.; Li, Y.; Zuo, X. MicroRNA-202-3p Regulates Scleroderma Fibrosis by Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinase 1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Choi, D.-Y.; Yun, S.J.; Choi, S.-M.; Kang, J.W.; Jung, J.W.; Hwang, D.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, D.-W. Proteomic Analysis of Microvesicles Derived from Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Proteome. Res. 2012, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.W.; Wang, J.; Lee, C.J.; Liu, M.; Neelamegham, S.; Canty, J.M.; Nguyen, J. The MicroRNA Regulatory Landscape of MSC-Derived Exosomes: A Systems View. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
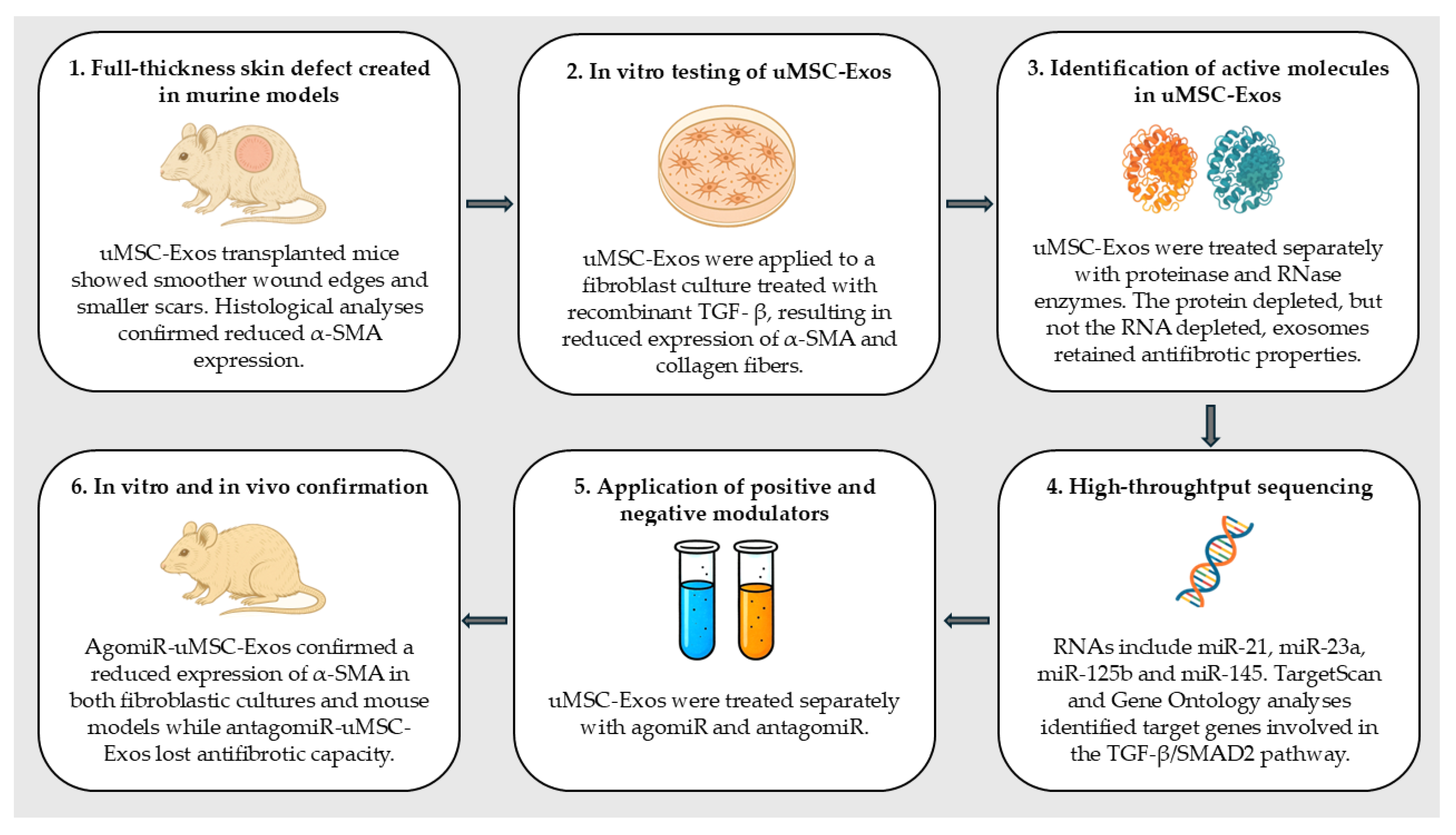
- Fang, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Yang, C.; Bi, H.; Qian, X.; Wu, M.; Ji, K.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, H.; Uchiyama, A.; Yokoyama, Y.; Sekiguchi, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Amalia, S.N.; Inoue, Y.; Ogino, S.; Torii, R.; Hosoi, M.; et al. Antifibrotic Effects and Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in a Systemic Sclerosis Mouse Model: Possible Contribution of MiR-196b-5p. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 104, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dichev, V.; Mehterov, N.H.; Kazakova, M.H.; Karalilova, R.V.; Batalov, A.Z.; Sarafian, V.S. Serum Protein Levels of YKL-40 and Plasma MiR-214 Expression in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Jung, J.-H.; Ahn, K.-J.; Jang, A.Y.; Byun, K.; Yang, P.C.; Chung, W.-J. Stem Cell and Exosome Therapy in Pulmonary Hypertension. Korean Circ. J. 2022, 52, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Aslam, M.; Vitali, S.H.; Vergadi, E.; Konstantinou, G.; Sdrimas, K.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Kourembanas, S. Exosomes Mediate the Cytoprotective Action of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2012, 126, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Ge, L.L.; Li, K.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes Improve Pulmonary Hypertension through Inhibition of Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, J.M.; Pereira, M.; Wen, S.; Dooner, M.S.; Del Tatto, M.; Papa, E.; Goldberg, L.R.; Baird, G.L.; Ventetuolo, C.E.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. Exosomes Induce and Reverse Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cansu, D.Ü.; Korkmaz, C. Pulmonary Hypertension in Connective Tissue Diseases: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanelli, L.; Buratta, S.; Sagini, K.; Ferrara, G.; Lanni, M.; Emiliani, C. Exosome-Based Strategies for Diagnosis and Therapy. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakr, R.; Pavan, T.; Siqueira, I.; Zanchet, D.; Calegaro, N.; Andrade, N.; Neto, G.; Neves, M.; Bredemeier, M.; Palominos, P.; et al. AB0505 Case Report of Allogeneic Unrelated-Donor Mesenchymal Stem Cells (Msc) Infusion in Systemic Sclerosis (Ssc). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, A943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, D.; Ugurlucan, M.; Ong, L.; Bieback, K.; Pittermann, E.; Westien, I.; Wang, W.; Yerebakan, C.; Li, W.; Gaebel, R.; et al. Is the Intravascular Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Safe? Microvasc. Res. 2009, 77, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-O.; Han, J.W.; Kim, J.-M.; Cho, H.-J.; Park, C.; Lee, N.; Kim, D.-W.; Yoon, Y.-S. Malignant Tumor Formation After Transplantation of Short-Term Cultured Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Experimental Myocardial Infarction and Diabetic Neuropathy. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xunian, Z.; Kalluri, R. Biology and Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3100–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendt, M.; Kamerkar, S.; Sugimoto, H.; McAndrews, K.M.; Wu, C.-C.; Gagea, M.; Yang, S.; Blanko, E.V.R.; Peng, Q.; Ma, X.; et al. Generation and Testing of Clinical-Grade Exosomes for Pancreatic Cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, S.; Ridinger, J.; Rupp, A.-K.; Janssen, J.W.; Altevogt, P. Body Fluid Derived Exosomes as a Novel Template for Clinical Diagnostics. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, W.; El-Ansary, M.; Sabry, D.; Mostafa, M.A.; Fayad, T.; Kotb, E.; Temraz, M.; Saad, A.-N.; Essa, W.; Adel, H. Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Extracellular Vesicles Can Safely Ameliorate the Progression of Chronic Kidney Diseases. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, S.; Mohammadzadeh, D.; Norooznezhad, A.H.; Payandeh, M.; Hassaninia, D.; Pournazari, M.; Soufivand, P.; Yarani, R.; Mansouri, K. Improvement in the Clinical Manifestations of Interstitial Lung Disease Following Treatment with Placental Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Extracellular Vesicles in a Patient with Systemic Sclerosis: A Case Report. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2023, 46, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nishida, H.; An, S.Y.; Shetty, A.K.; Bartosh, T.J.; Prockop, D.J. Chromatographically Isolated CD63+ CD81+ Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Rescue Cognitive Impairments after TBI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevillet, J.R.; Kang, Q.; Ruf, I.K.; Briggs, H.A.; Vojtech, L.N.; Hughes, S.M.; Cheng, H.H.; Arroyo, J.D.; Meredith, E.K.; Gallichotte, E.N.; et al. Quantitative and Stoichiometric Analysis of the MicroRNA Content of Exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14888–14893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Mardini, O.; Ericsson, M.; Prabhakar, S.; Maguire, C.A.; Chen, J.W.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Dynamic Biodistribution of Extracellular Vesicles in Vivo Using a Multimodal Imaging Reporter. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y.; Du, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhao, W.; Han, Z.; Kong, D.; et al. Enhanced Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes with an Injectable Hydrogel for Hindlimb Ischemia Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30081–30091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, P.; Tang, S.; Chen, A.; Li, M.; Peng, G.; Gao, H.; Weng, H.; et al. Combination of Lyophilized Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Concentrated Conditioned Medium and Polysaccharide Hydrogel in the Inhibition of Hypertrophic Scarring. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozier, P.; Maumus, M.; Maria, A.T.J.; Toupet, K.; Jorgensen, C.; Guilpain, P.; Noël, D. Lung Fibrosis Is Improved by Extracellular Vesicles from IFNγ-Primed Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Murine Systemic Sclerosis. Cells 2021, 10, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, D.G.; Lim, G.T.; Kwon, S.; Um, W.; Oh, B.H.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.; Jo, D.-G.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, J.H. Metabolically Engineered Stem Cell–Derived Exosomes to Regulate Macrophage Heterogeneity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, T.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, Z.; Li, Y.; Xue, T.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, W.; Lin, Z.; et al. Engineered Cell Membrane Vesicles Expressing CD40 Alleviate System Lupus Nephritis by Intervening B Cell Activation. Small Methods 2023, 7, e2200925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Differences | BLM Group | MSC-Exos Group | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Macroscopic | Thickened skin layer, reduced subcutaneous adipose tissue | Skin and subcutaneous tissue of normal thickness | [25,48] |
| Histological | Macrophages and CD4+/CD8+ T lymphocytes inflammatory infiltrate, abundant ECM, collagen fibers and hydroxyproline | Significant reduction in inflammatory infiltrate, collagen fiber deposition and hydroxyproline content | [25,48] |
| Molecular | High levels of tissue fibrosis markers (TGF-β1, collagen 1, and fibronectin 1) | Reduced tissue fibrosis markers (TGF-β1, collagen 1, and fibronectin 1) | [25,48] |
| EMT | High levels of vimentin and α-SMA (high differentiation of endothelial cells into mesenchymal cells with fibroblastic activity) | Low values of fibroblast markers (vimentin and α-SMA), suggesting inhibition of the EMT process | [25] |
| microRNAs | Target Pathways | Biologic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-214 | IL-33/ST2 | Alleviates skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by blocking the IL33/ST2 axis | [51] |
| miR-23a-3p | P53, PI3K | Cell cycle regulation | [69] |
| miR-424-5p | VEGF | Angiogenesis stimulation | [69] |
| miR-144-3p | PDGF | Cell survival, anti-apoptosis | [69] |
| miR-130a-3p | HOXA5 | Angiogenesis stimulation | [69] |
| miR-145-5p | TGF-β | Inhibition of fibroblast proliferation | [69] |
| miR-29a/b-3p | COL1A1, FBN1 | Reduction in collagen synthesis | [69] |
| miR-221-5p | Wnt | Endothelial proliferation | [69] |
| miR-21-5p | Crim1 | Cardiomyocyte survival | [69] |
| miR-125b-5p | TP53, BAK1 | Apoptosis inhibition | [69] |
| miR-22-3p | TGF-β, PI3K | Protection from oxidative stress | [69] |
| miR-199a-3p | ADAMTS3, p53 | Regulation of energy metabolism | [69] |
| miR-191-5p | BDNF | Cellular differentiation | [69] |
| let-7a/b/i | COL1A1, HMGA2 | Reduction in fibroblast proliferation | [69] |
| miR21,miR-125b, miR-145 | TGFβ/SMAD2 pathway | Suppression of myofibroblast differentiation, Reduction in scar formation | [70] |
| miR-196b-5p | COL1A2 | Reduction in collagen synthesis | [71] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbetta, C.; Bonomi, F.; Lepri, G.; Furst, D.E.; Randone, S.B.; Guiducci, S. Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis. Cells 2025, 14, 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131018
Barbetta C, Bonomi F, Lepri G, Furst DE, Randone SB, Guiducci S. Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis. Cells. 2025; 14(13):1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131018
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbetta, Cristiano, Francesco Bonomi, Gemma Lepri, Daniel E. Furst, Silvia Bellando Randone, and Serena Guiducci. 2025. "Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis" Cells 14, no. 13: 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131018
APA StyleBarbetta, C., Bonomi, F., Lepri, G., Furst, D. E., Randone, S. B., & Guiducci, S. (2025). Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes and MicroRNAs: Advancing Cell-Free Therapy in Systemic Sclerosis. Cells, 14(13), 1018. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14131018





