Absence of Microglial Activation and Maintained Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Tissue Sample Preparation
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Scoring of Colitis Severity
2.5. Histological Quantification
2.6. RNA Isolation and qPCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Casp8ΔIEC Mice Develop Ileocolitis and Extraintestinal Inflammation
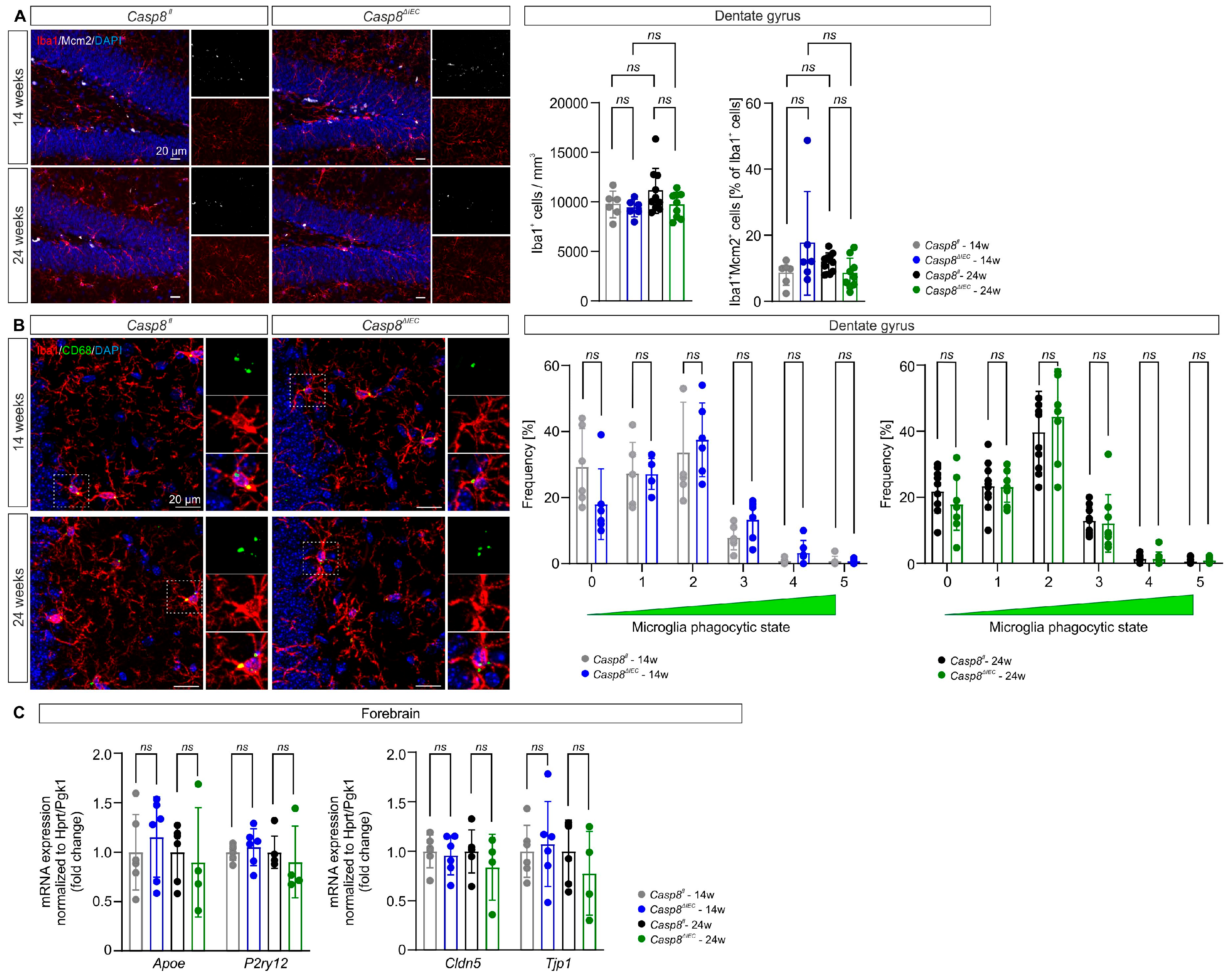
3.2. Microglial State in the Dentate Gyrus Is Maintained in Casp8ΔIEC Mice
3.3. Adult Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus Is Preserved Despite Ileocolitis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BRDU | 5-Bromo-2′-Desoxyuridine |
| CASP8 | Caspase 8 |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| CLDN5 | Claudin 5 |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride |
| DCX | Doublecortin |
| DG | Dentate gyrus |
| DSS | Dextran sodium sulfate |
| GCL | Granule cell layer |
| GDNF | Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| IBA1 | Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 |
| IBD | Inflammatory bowel disease |
| IEC | Intestinal epithelial cell |
| IGF1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| IL1B | Interleukin 1 beta |
| LCN2 | Lipocalin 2 |
| MCM2 | Minichromosome maintenance complex component 2 |
| P2RY12 | Purinergic receptor P2Y12 |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| QPCR | Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SOX2 | SRY-box transcription factor 2 |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| TJP1 | Tight junction protein 1 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated dUTP-X nick end labeling |
| UC | Ulcerative colitis |
| ZO-1 | Zona occludens 1 |
References
- Barberio, B.; Zamani, M.; Black, C.J.; Savarino, E.V.; Ford, A.C. Prevalence of symptoms of anxiety and depression in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairbrass, K.M.; Lovatt, J.; Barberio, B.; Yuan, Y.; Gracie, D.J.; Ford, A.C. Bidirectional brain–gut axis effects influence mood and prognosis in IBD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut 2022, 71, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.W.P.; Powell, N.; Norton, C.; Dumbrill, J.L.; Hayee, B.H.; Moulton, C.D. Cognitive Impairment in Adult Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Acad. Consult.-Liaison Psychiatry 2021, 62, 387–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masanetz, R.K.; Winkler, J.; Winner, B.; Günther, C.; Süß, P. The Gut–Immune–Brain Axis: An Important Route for Neuropsychiatric Morbidity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, T.; Parylak, S.L.; Linker, S.B.; Gage, F.H. The role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in brain health and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 67–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonafina, A.; Trinchero, M.F.; Ríos, A.S.; Bekinschtein, P.; Schinder, A.F.; Paratcha, G.; Ledda, F. GDNF and GFRα1 Are Required for Proper Integration of Adult-Born Hippocampal Neurons. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 4308–4319.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.F.; Xapelli, S. Intervention of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Other Neurotrophins in Adult Neurogenesis. In Recent Advances in NGF and Related Molecules: The Continuum of the NGF “Saga”; Calzà, L., Aloe, L., Giardino, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 95–115. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Chen, R.; Wu, L.; Chen, Q.; Hu, A.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X. The Regulatory Mechanism of Neurogenesis by IGF-1 in Adult Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, A.S.; Sahay, A.; Hen, R. Increasing Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis is Sufficient to Reduce Anxiety and Depression-Like Behaviors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.L.; Zhou, M.; Jhaveri, D.J. Dissecting the role of adult hippocampal neurogenesis towards resilience versus susceptibility to stress-related mood disorders. NPJ Sci. Learn. 2022, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyubova, G.; Kodali, M.; Upadhya, R.; Madhu, L.N.; Attaluri, S.; Somayaji, Y.; Shuai, B.; Rao, S.; Shankar, G.; Shetty, A.K. Extracellular vesicles from hiPSC-NSCs can prevent peripheral inflammation-induced cognitive dysfunction with inflammasome inhibition and improved neurogenesis in the hippocampus. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaro, B.; Lindvall, O.; Tesco, G.; Ekdahl, C.T.; Nitsch, R.M. Inhibition of Microglial Activation Protects Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Improves Cognitive Deficits in a Transgenic Mouse Model for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 9, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindvall, O.; Kokaia, Z. Neurogenesis following Stroke Affecting the Adult Brain. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a019034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, M.L.; Toda, H.; Palmer, T.D. Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 2003, 302, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekdahl, C.T.; Claasen, J.-H.; Bonde, S.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13632–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, C.T.; Kokaia, Z.; Lindvall, O. Brain inflammation and adult neurogenesis: The dual role of microglia. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Encinas, J.M.; Deudero, J.J.; Chancey, J.H.; Enikolopov, G.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.S.; Tsirka, S.E.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Microglia shape adult hippocampal neurogenesis through apoptosis-coupled phagocytosis. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukovic, J.; Colditz, M.J.; Blackmore, D.G.; Ruitenberg, M.J.; Bartlett, P.F. Microglia Modulate Hippocampal Neural Precursor Activity in Response to Exercise and Aging. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, C.; Martini, E.; Wittkopf, N.; Amann, K.; Weigmann, B.; Neumann, H.; Waldner, M.J.; Hedrick, S.M.; Tenzer, S.; Neurath, M.F.; et al. Caspase-8 regulates TNF-α-induced epithelial necroptosis and terminal ileitis. Nature 2011, 477, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzer, I.; Kaden-Volynets, V.; Ruder, B.; Letizia, M.; Bittel, M.; Rausch, P.; Basic, M.; Bleich, A.; Baines, J.F.; Neurath, M.F.; et al. Environmental Microbial Factors Determine the Pattern of Inflammatory Lesions in a Murine Model of Crohn’s Disease–Like Inflammation. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 26, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaden-Volynets, V.; Günther, C.; Zimmermann, J.; Beisner, J.; Becker, C.; Bischoff, S.C. Deletion of the Casp8 gene in mice results in ileocolitis, gut barrier dysfunction, and malassimilation, which can be partially attenuated by inulin or sodium butyrate. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G493–G507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masanetz, R.K.; Baum, W.; Schett, G.; Winkler, J.; Süß, P. Cellular plasticity and myeloid inflammation in the adult brain are independent of the transcriptional modulator DREAM. Neurosci. Lett. 2023, 796, 137061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefele, M.; Stolzer, I.; Ruder, B.; He, G.-W.; Mahapatro, M.; Wirtz, S.; Neurath, M.F.; Günther, C. Intestinal epithelial Caspase-8 signaling is essential to prevent necroptosis during Salmonella Typhimurium induced enteritis. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzer, I.; Schickedanz, L.; Chiriac, M.T.; López-Posadas, R.; Grassl, G.A.; Mattner, J.; Wirtz, S.; Winner, B.; Neurath, M.F.; Günther, C. STAT1 coordinates intestinal epithelial cell death during gastrointestinal infection upstream of Caspase-8. Mucosal Immunol. 2022, 15, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilton, D.K.; Mastro, K.; Heller, M.D.; Gergits, F.W.; Willing, C.R.; Fahey, J.B.; Frouin, A.; Daggett, A.; Gu, X.; Kim, Y.A.; et al. Microglia and complement mediate early corticostriatal synapse loss and cognitive dysfunction in Huntington’s disease. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2866–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motulsky, H.J.; Brown, R.E. Detecting outliers when fitting data with nonlinear regression—A new method based on robust nonlinear regression and the false discovery rate. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorner, H.; Stolzer, I.; Mattner, J.; Kaminski, S.; Leistl, S.; Edrich, L.-M.; Schwendner, R.; Hobauer, J.; Sebald, A.; Leikam, S.; et al. Gut Pathobiont–Derived Outer Membrane Vesicles Drive Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis–Associated Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 1183–1197.e1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampierakis, I.-A.; Koutmani, Y.; Semitekolou, M.; Morianos, I.; Polissidis, A.; Katsouda, A.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Xanthou, G.; Gravanis, A.; Karalis, K.P. Hippocampal neural stem cells and microglia response to experimental inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süß, P.; Hoffmann, A.; Rothe, T.; Ouyang, Z.; Baum, W.; Staszewski, O.; Schett, G.; Prinz, M.; Krönke, G.; Glass, C.K.; et al. Chronic Peripheral Inflammation Causes a Region-Specific Myeloid Response in the Central Nervous System. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4082–4095.e4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Ikegaya, Y.; Koyama, R. The effects of microglia- and astrocyte-derived factors on neurogenesis in health and disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 5880–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.G.; Windsor, J.W. The four epidemiological stages in the global evolution of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadad, J.; Schreiner, P.; Vavricka, S.R.; Greuter, T. The Genetics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2024, 28, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambu, R.; Warner, N.; Mulder, D.J.; Kotlarz, D.; McGovern, D.P.B.; Cho, J.; Klein, C.; Snapper, S.B.; Griffiths, A.M.; Iwama, I.; et al. A Systematic Review of Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, e653–e663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovani, D.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Lytras, T.; Bonovas, S. Environmental Risk Factors for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 647–659.e644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrom, M.; Long, M.; Dube, S.; Robbins, L.; Botwin, G.J.; Yang, S.; Mengesha, E.; Li, D.; Naito, T.; Bonthala, N.N.; et al. Comprehensive Association Analyses of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2024, 167, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, Y.; Kamal, S.; Jaffar, F.; Sriranganathan, D.; Quraishi, M.N.; Segal, J.P. Prevalence of Extraintestinal Manifestations in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 30, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, J.M.; Oliveira, S.N.; Correia, L. Neurologic manifestations of inflammatory bowel diseases. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Biller, J., Ferro, J.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 120, Chapter 40; pp. 595–605. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, C.V.; Radford-Smith, G.; Savage, E.; Robinson, C.; Cocchi, L.; Moran, R.J. Brain signatures of chronic gut inflammation. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1250268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Man, S.; Sun, B.; Ma, L.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.; Gao, W. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Kurokawa, K.; Hong, L.; Miyagawa, K.; Mochida-Saito, A.; Takeda, H.; Tsuji, M. Hippocampal and gut AMPK activation attenuates enterocolitis-like symptoms and co-occurring depressive-like behavior in ulcerative colitis model mice: Involvement of brain-gut autophagy. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 373, 114671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, R.; Prioreschi, C.; Lorenzo Rebenaque, L.; Colantoni, E.; Giovannini, D.; Frusciante, S.; Diretto, G.; Marco-Jiménez, F.; Mancuso, M.; Casciati, A.; et al. Gut–Brain Axis: Insights from Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Brain Tumor Development in a Mouse Model of Experimental Colitis Induced by Dextran Sodium Sulfate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanollahi, M.; Jameie, M.; Heidari, A.; Rezaei, N. The Dialogue Between Neuroinflammation and Adult Neurogenesis: Mechanisms Involved and Alterations in Neurological Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 923–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chausse, B.; Malorny, N.; Lewen, A.; Poschet, G.; Berndt, N.; Kann, O. Metabolic flexibility ensures proper neuronal network function in moderate neuroinflammation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabogal-Guáqueta, A.M.; Marmolejo-Garza, A.; Trombetta-Lima, M.; Oun, A.; Hunneman, J.; Chen, T.; Koistinaho, J.; Lehtonen, S.; Kortholt, A.; Wolters, J.C.; et al. Species-specific metabolic reprogramming in human and mouse microglia during inflammatory pathway induction. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T. Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawasai, O.; Yamada, K.; Takahashi, K.; Odaira, T.; Sakuma, W.; Ishizawa, D.; Takahashi, N.; Onuma, K.; Hozumi, C.; Nemoto, W.; et al. Liver hydrolysate prevents depressive-like behavior in an animal model of colitis: Involvement of hippocampal neurogenesis via the AMPK/BDNF pathway. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 390, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, S.E.; Zera, K.A.; Ivison, G.T.; Buckwalter, M.S.; Engleman, E.G. Brain profiling in murine colitis and human epilepsy reveals neutrophils and TNFα as mediators of neuronal hyperexcitability. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonis, S.; Pechnick, R.N.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Mahgerefteh, M.; Wawrowsky, K.; Michelsen, K.S.; Chesnokova, V. Chronic intestinal inflammation alters hippocampal neurogenesis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süß, P.; Kalinichenko, L.; Baum, W.; Reichel, M.; Kornhuber, J.; Loskarn, S.; Ettle, B.; Distler, J.H.W.; Schett, G.; Winkler, J.; et al. Hippocampal structure and function are maintained despite severe innate peripheral inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Sequence Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Sequence Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Apoe | GAACAACCCGCCTCGTGA | AGCTCCTTCCGAAACAAGTCC |
| Bdnf | GCTCATCTTTGCCAGAGCCC | AGCAGCTTTCTCAACGCCT |
| Cldn5 | GTTAAGGCACGGGTAGCACT | TACTTCTGTGACACCGGCAC |
| Gdnf | ACCCTGCTAGAAAACGCGAG | ACGGAGATCCGGGCAAAAG |
| Hprt | GTCATGTCGACCCTCAGTCC | GCAAGTCTTTCAGTCCTGTCC |
| Igf1 | ATACAGCCAACGGGAAACAG | CAACAAAGCTGGATGCCTGTC |
| Il1b | TGACAGTGATGAGAATGACCTG | CCACGGGAAAGACACAGGTA |
| Lcn2 | ACGGACTACAACCAGTTCGC | ATGCATTGGTCGGTGGGG |
| P2ry12 | AGTGCAAGAACACTCAAGGC | GACGGTGTACAGCAATGGGA |
| Pgk1 | GTCGTGATGAGGGTGGACTT | AACGGACTTGGCTCCATTGT |
| Tnf | TAGCCCACGTCGTAGCAAAC | GCAGCCTTGTCCCTTGAAGA |
| Tjp1 | GGAGATGTTTATGCGGACGG | CCATTGCTGTGCTCTTAGCG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masanetz, R.K.; Mundlos, H.; Stolzer, I.; Winkler, J.; Günther, C.; Süß, P. Absence of Microglial Activation and Maintained Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. Cells 2025, 14, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110841
Masanetz RK, Mundlos H, Stolzer I, Winkler J, Günther C, Süß P. Absence of Microglial Activation and Maintained Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. Cells. 2025; 14(11):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110841
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasanetz, Rebecca Katharina, Hanna Mundlos, Iris Stolzer, Jürgen Winkler, Claudia Günther, and Patrick Süß. 2025. "Absence of Microglial Activation and Maintained Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease" Cells 14, no. 11: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110841
APA StyleMasanetz, R. K., Mundlos, H., Stolzer, I., Winkler, J., Günther, C., & Süß, P. (2025). Absence of Microglial Activation and Maintained Hippocampal Neurogenesis in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Crohn’s Disease. Cells, 14(11), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110841







