Regulation of WDFY1 Expression by miRNAs, Transcription Factors, and IL-6 in Murine Mesangial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. PCR Cloning of Wdfy1 Promoter and 5′ UTR
2.3. PCR Cloning of Wdfy1 3′ UTR
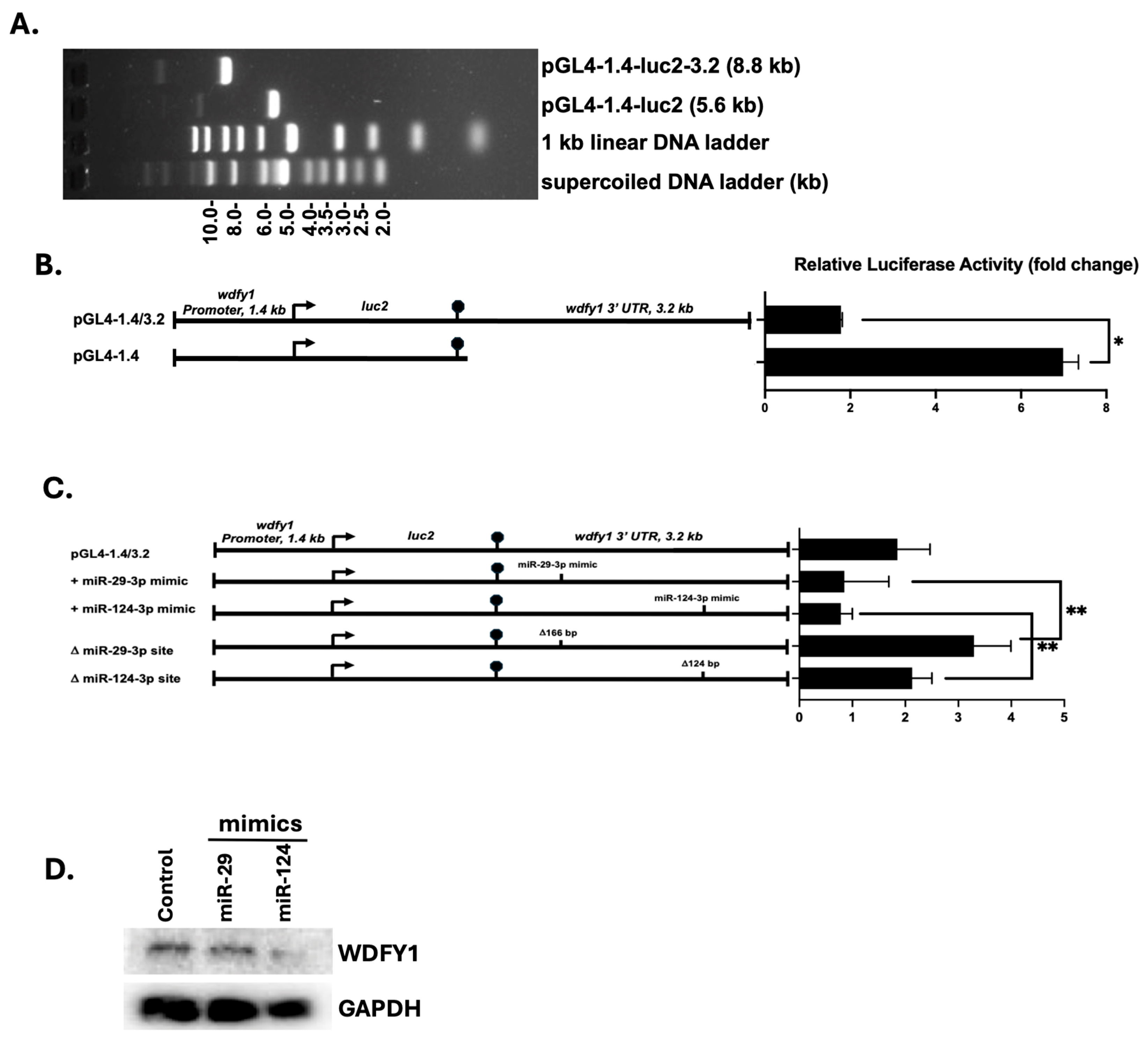
2.4. Generation of Luciferase Reporter Constructs
2.5. Luciferase Assay
2.6. Manipulation of Wdfy1 Expression Using miRNA Mimics and siRNAs in HeLa Cells
2.7. Mesangial Cell Culture, siRNA Treatment, and IL-6 Stimulation
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
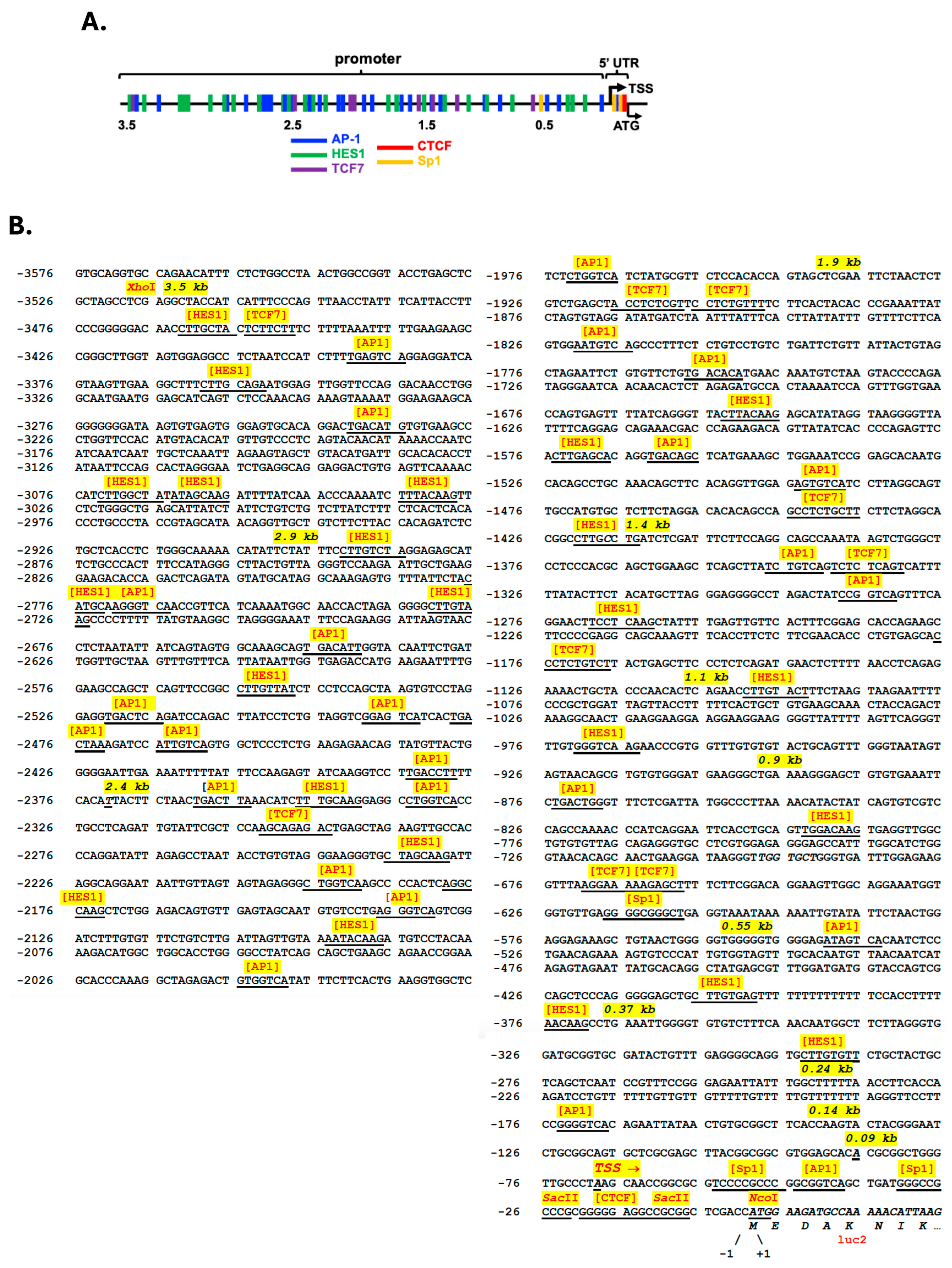
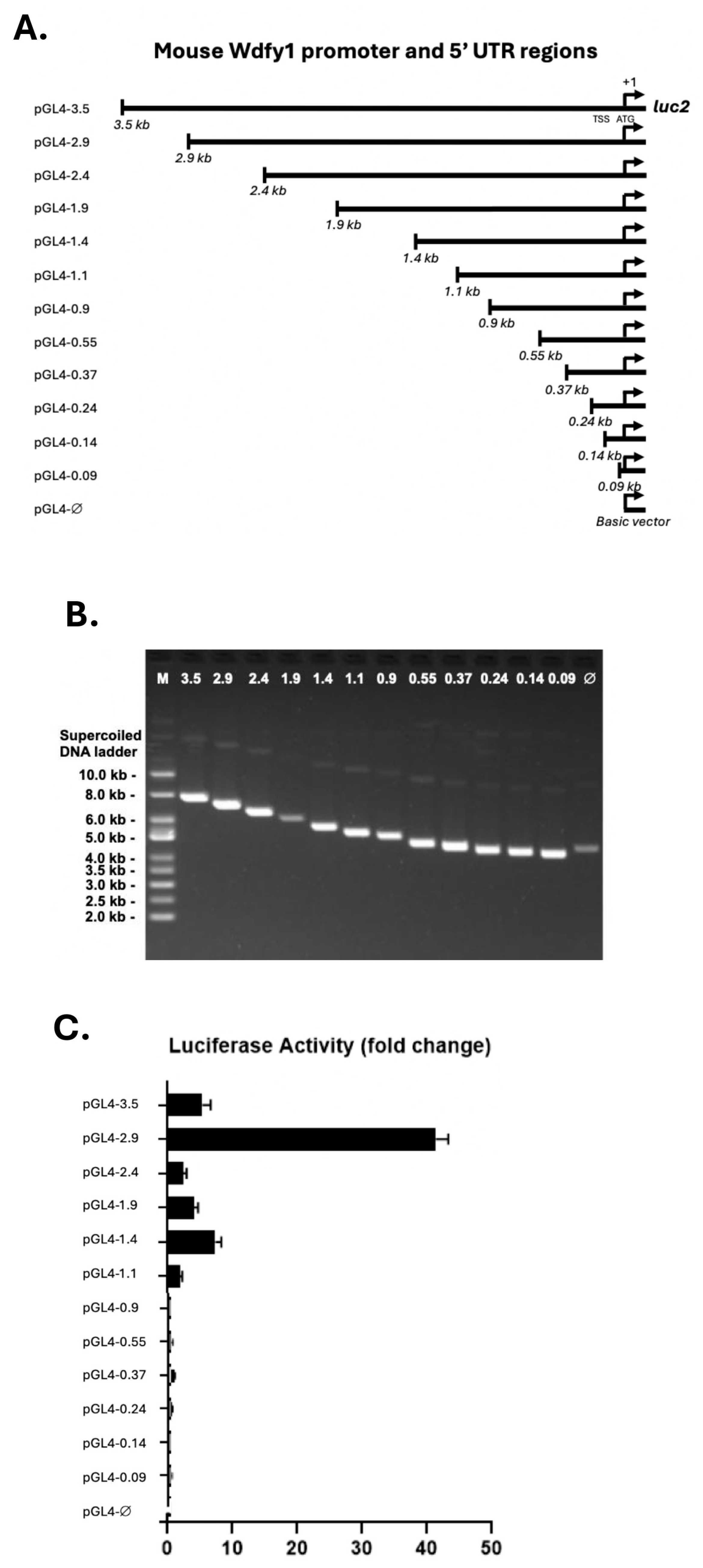
3.1. Cloning and Identification of Putative Regulatory Elements Within the Wdfy1 Promoter and 5′-UTR Regions
3.2. Multiple TF Regulated WDFY1 Expression in Mesangial Cells
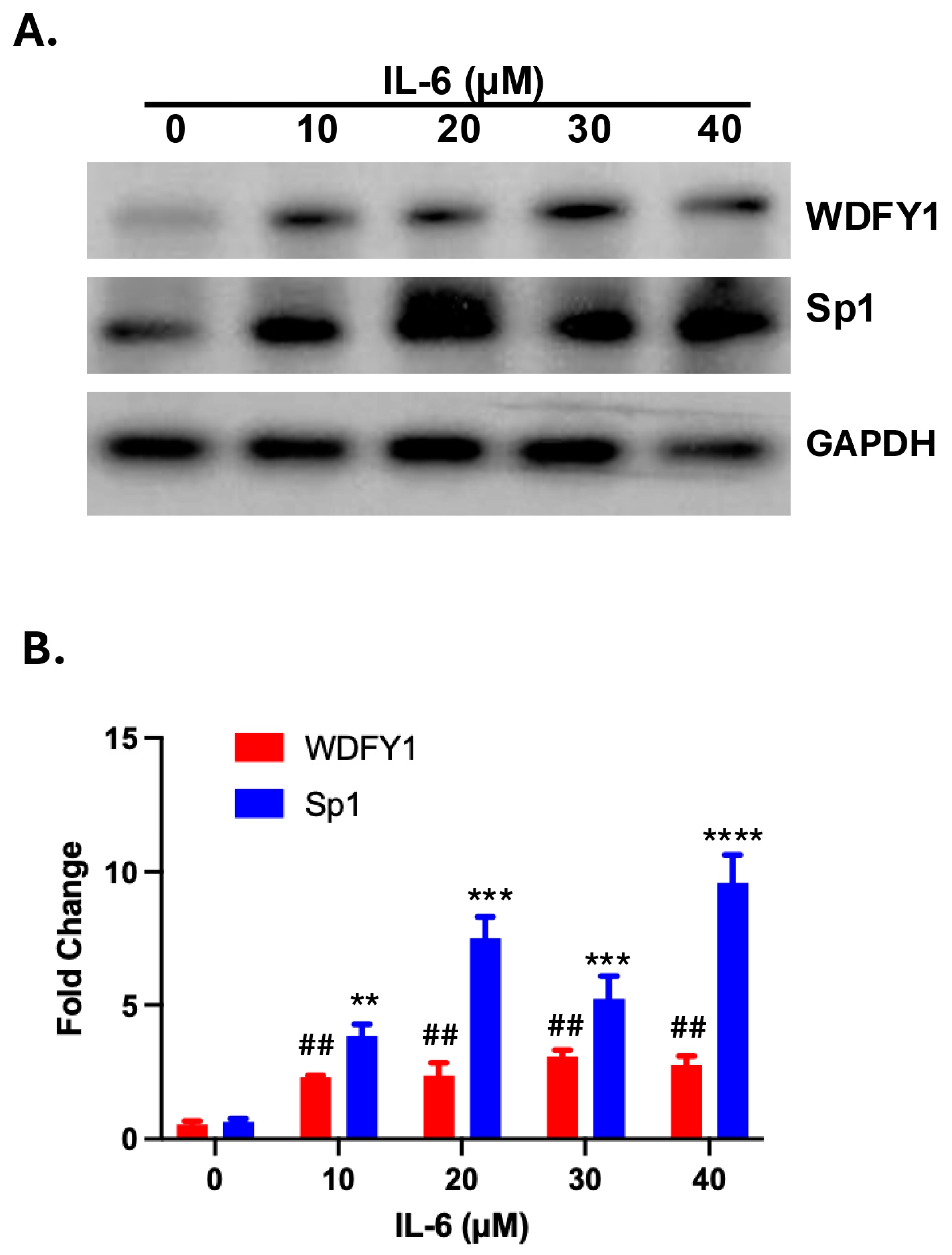
3.3. IL-6-Induced WDFY1 Upregulation Is Associated with Decreased Sp1 Expression
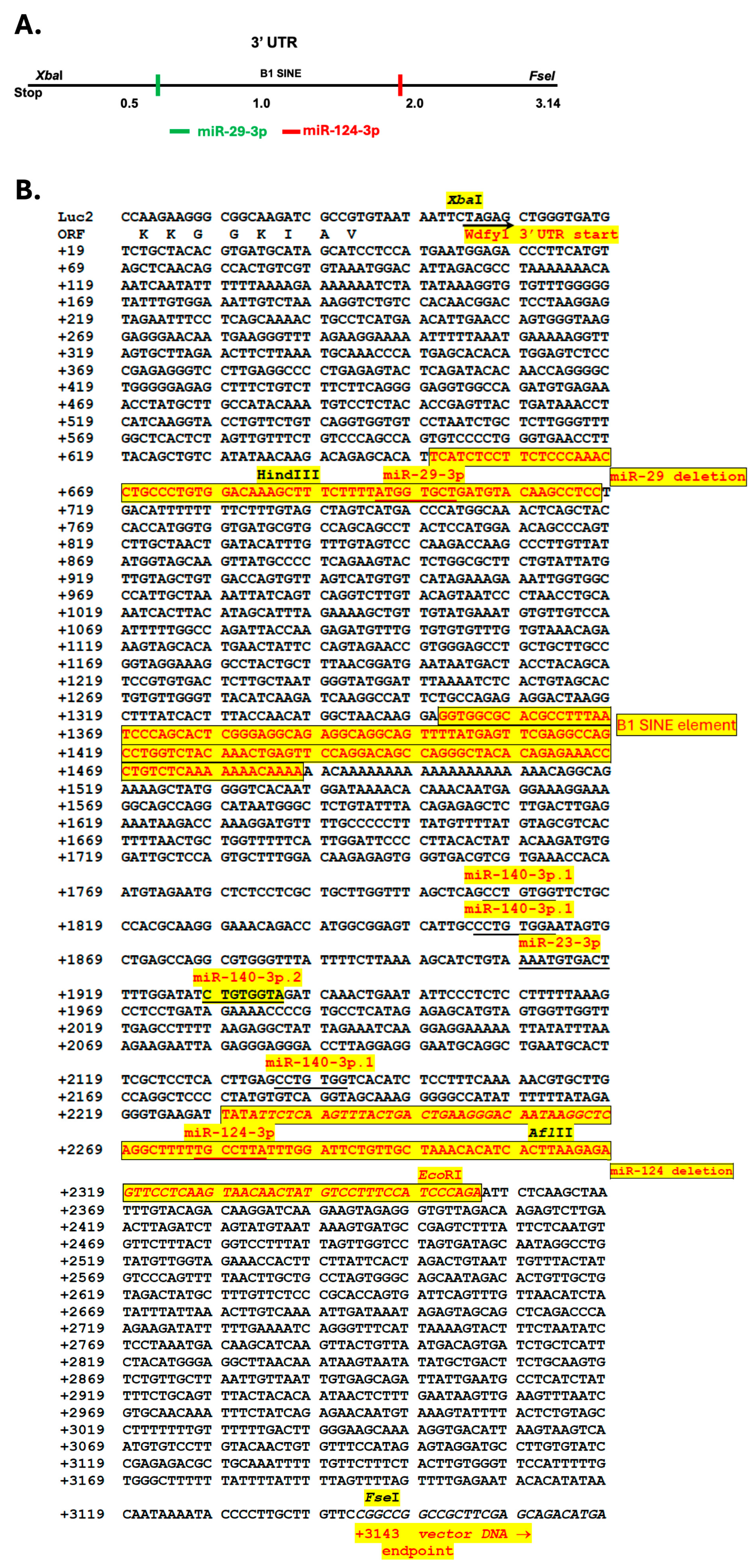
3.4. 3′-UTR Binding by miRNAs Inhibits WDFY1 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blatner, N.R.; Stahelin, R.V.; Diraviyam, K.; Hawkins, P.T.; Hong, W.; Murray, D.; Cho, W. The Molecular Basis of the Differential Subcellular Localization of FYVE Domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 53818–53827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenmark, H.; Aasland, R.; Driscoll, P.C. The phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate-binding FYVE finger. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, S.H.; Ktistakis, N.; Davidson, K.; Anderson, K.E.; Manifava, M.; Ellson, C.D.; Lipp, P.; Bootman, M.; Coadwell, J.; Nazarian, A.; et al. FENS-1 and DFCP1 are FYVE domain-containing proteins with distinct functions in the endosomal and Golgi compartments. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3991–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Vora, M.; Haney, R.M.; Filonov, G.S.; Musselman, C.A.; Burd, C.G.; Kutateladze, A.G.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Stahelin, R.V.; Kutateladze, T.G. Membrane insertion of the FYVE domain is modulated by pH. Proteins 2009, 76, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.J.; Gu, R.; Sarin, R.; Zavodovskaya, R.; Chen, C.-P.; Christiansen, B.A.; Adamopoulos, I.E. Autophagy-linked FYVE containing protein WDFY3 interacts with TRAF6 and modulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 73, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.Q.; Wang, S.; Lei, C.Q.; Sun, M.S.; Shu, H.B.; Liu, Y. WDFY1 mediates TLR3/4 signaling by recruiting TRIF. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, R.; Paludan, S.R. Catching the adaptor-WDFY1, a new player in the TLR-TRIF pathway. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y. Wdfy1 deficiency impairs Tlr3-mediated immune responses in vivo. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, M.H.W.; Rhee, S.H.; Perkins, D.J.; Medvedev, A.E.; Piao, W.; Fenton, M.J.; Vogel, S.N. TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions regulate TLR4 signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teranishi, H.; Tabata, K.; Saeki, M.; Umemoto, T.; Hatta, T.; Otomo, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Natsume, T.; Yoshimori, T.; Hamasaki, M. Identification of CUL4A-DDB1-WDFY1 as an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex involved in initiation of lysophagy. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Xiong, M.; Guo, S.; Gui, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Feng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. WDFY1, a WD40 repeat protein, is not essential for spermatogenesis and male fertility in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 596, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giralt, A.; Brito, V.; Pardo, M.; Rubio, S.E.; Marion-Poll, L.; Martín-Ibáñez, R.; Zamora-Moratalla, A.; Bosch, C.; Ballesteros, J.J.; Blasco, E.; et al. Helios modulates the maturation of a CA1 neuronal subpopulation required for spatial memory formation. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 323, 113095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Balsells, A.; Brito, V.; Fernández, B.; Pardo, M.; Straccia, M.; Ginés, S.; Alberch, J.; Hernández, I.; Arranz, B.; Canals, J.M.; et al. Lack of Helios During Neural Development Induces Adult Schizophrenia-Like Behaviors Associated with Aberrant Levels of the TRIF-Recruiter Protein WDFY1. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisi, I.; D’Onofrio, M.; Brandi, R.; Felsani, A.; Capsoni, S.; Drovandi, G.; Felici, G.; Weitschek, E.; Bertolazzi, P.; Cattaneo, A. Gene expression biomarkers in the brain of a mouse model for alzheimer’s disease: Mining of microarray data by logic classification and feature selection. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 24, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Shao, W.-H. WDFY1-expressing follicular dendritic cells play a critical role in lupus development in cGVHD mouse model. J. Immunol. 2025, vkaf017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Davie, J.R. The role of Sp1 and Sp3 in normal and cancer cell biology. Ann. Anat.-Anat. Anz. 2010, 192, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Datta, P.K.; Bagchi, S. Stability of the Sp3-DNA complex is promoter-specific: Sp3 efficiently competes with Sp1 for binding to promoters containing multiple Sp-sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5368–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.E.; Zhen, Y.; Qi, X.; Shao, W.-H. Axl Expression in Renal Mesangial Cells Is Regulated by Sp1, Ap1, MZF1, and Ep300, and the IL-6/miR-34a Pathway. Cells 2022, 11, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Lei, C.-T.; Zhang, C. Interleukin-6 Signaling Pathway and Its Role in Kidney Disease: An Update. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.M.; Shao, W.-H. Transcription Factors in the Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis and Their Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Schatten, H.; Ray, B.K. Activation of Sp1 and its functional co-operation with serum amyloid a-activating sequence binding factor in synoviocyte cells trigger synergistic action of interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 in serum amyloid a gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 4300–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Si, F. MicroRNA-124 represents a novel diagnostic marker in human lupus nephritis and plays an inhibitory effect on the growth and inflammation of renal mesangial cells by targeting TRAF6. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 1578–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelsalam, M.; Zaki, M.E.S.; El-Kheir, N.Y.A.; Salama, M.F.; Osman, A.O.B.S. Study of MicroRNA-124 in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. Endocrine, Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2024, 24, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassani, M.; Dehani, M.; Rafie, M.Z.; Esmaeilzadeh, E.; Davar, S.; Pakzad, B.; Mosallaei, M.; Hoseini, S.M.; Bayat, H.; Soosanabadi, M. Investigation of rs531564 Polymorphism in the Primary MicroRNA-124 Gene in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Disease Susceptibility and Clinical Characteristics. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 20, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.C.; Eler, E.S.; e Silva, C.E.F.; da Silva, M.N.F.; Araújo, N.P.; Svartman, M.; Feldberg, E. LINE-1 and SINE-B1 mapping and genome diversification in Proechimys species (Rodentia: Echimyidae). Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Hua, M.; Li, N.; Yao, H.; Cao, X. The microRNA miR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses to intracellular bacterial infection by targeting interferon-γ. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ye, L.; Xu, S.; Guo, G.; Zuo, Z.; Ye, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, B.; Xue, X.; Lin, Q.; et al. Downregulated miR-29a promotes B cell overactivation by upregulating Crk-like protein in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Peng, J.; Gan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, F.; Ji, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, C.; Bao, J. Jieduquyuziyin prescription enhances CD11a and CD70 DNA methylation of CD4+ T cells via miR-29b-sp1/DNMT1 pathway in MRL/lpr mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 317, 116776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, M.; Farquharson, C.; Stephen, L.A. The role of miR-29 family in disease. J. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 122, 696–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, S.; Shen, R.; Liu, S.; You, Y. HOXA11-OS participates in lupus nephritis by targeting miR-124-3p mediating Cyr61 to regulate podocyte autophagy. Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, A.C.; Gonzalez-Rico, F.J.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.M. B1-SINE retrotransposons: Establishing genomic insulatory networks. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2011, 1, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbarbary, R.A.; Lucas, B.A.; Maquat, L.E. Retrotransposons as regulators of gene expression. Science 2016, 351, aac7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, R.; MacLeod, B.L.; Nelson, M.M.; Ibrahim, M.M.H.; Borges, B.C.; Jaradat, N.W.; Finneran, M.C.; Giger, R.J.; Corfas, G. Identification of in vivo roles of ErbB4-JMa and its direct nuclear signaling using a novel isoform-specific knock out mouse. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wright, M.; Gogol, M.M.; Bradford, W.D.; Zhang, N.; Bazzini, A.A. Translation of small downstream ORFs enhances translation of canonical main open reading frames. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuveni, E.; Getselter, D.; Oron, O.; Elliott, E. Differential contribution of cis and trans gene transcription regulatory mechanisms in amygdala and prefrontal cortex and modulation by social stress. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adams, D.E.; Li, S.; Zhen, Y.; Kaynak, A.; Qi, X.; Yu, J.J.; Shao, W.-H. Regulation of WDFY1 Expression by miRNAs, Transcription Factors, and IL-6 in Murine Mesangial Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110798
Adams DE, Li S, Zhen Y, Kaynak A, Qi X, Yu JJ, Shao W-H. Regulation of WDFY1 Expression by miRNAs, Transcription Factors, and IL-6 in Murine Mesangial Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(11):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110798
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdams, David E., Siru Li, Yuxuan Zhen, Ahmet Kaynak, Xiaoyang Qi, Jane J. Yu, and Wen-Hai Shao. 2025. "Regulation of WDFY1 Expression by miRNAs, Transcription Factors, and IL-6 in Murine Mesangial Cells" Cells 14, no. 11: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110798
APA StyleAdams, D. E., Li, S., Zhen, Y., Kaynak, A., Qi, X., Yu, J. J., & Shao, W.-H. (2025). Regulation of WDFY1 Expression by miRNAs, Transcription Factors, and IL-6 in Murine Mesangial Cells. Cells, 14(11), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110798







