The cGAS/STING Pathway: Friend or Foe in Regulating Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
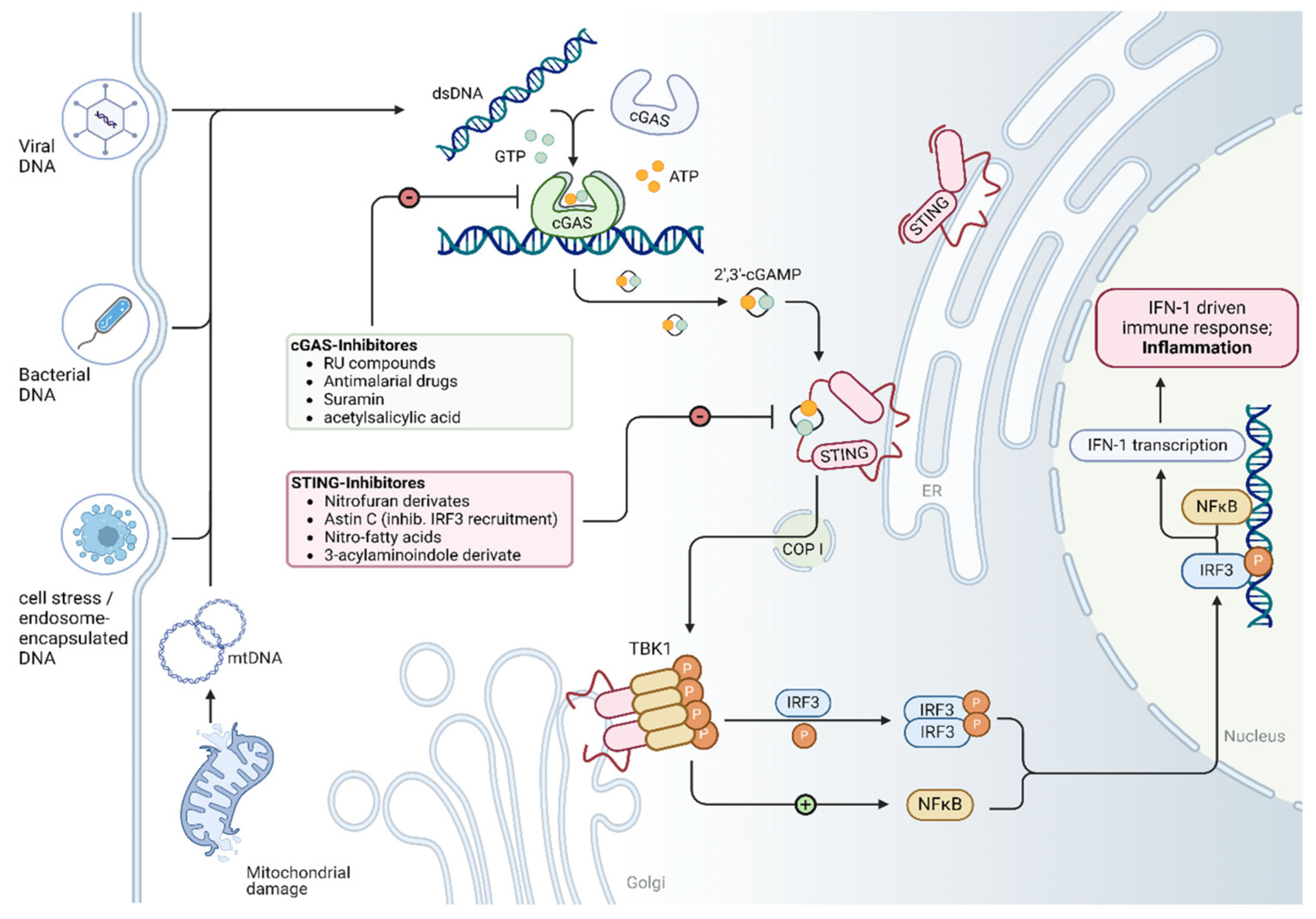
2. Overview of the cGAS/STING Signaling Pathway
3. Activation of the cGAS/STING Pathway in Different Cardiomyopathies
3.1. Dilated Cardiomyopathy
3.1.1. Lamin A/C (LMNA) Cardiomyopathy
3.1.2. LEM Domain-Containing Protein 2 (LEMD2)-Associated Cardiomyopathy
3.2. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
3.3. Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy
3.4. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy
3.5. Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy
3.6. Other Cardiomyopathies
4. Molecular Interventions and Potential Targets Within the cGAS/STING Pathway in Cardiomyopathy
4.1. Molecular Intervention in the cGAS/STING Pathway in Cardiomyopathy
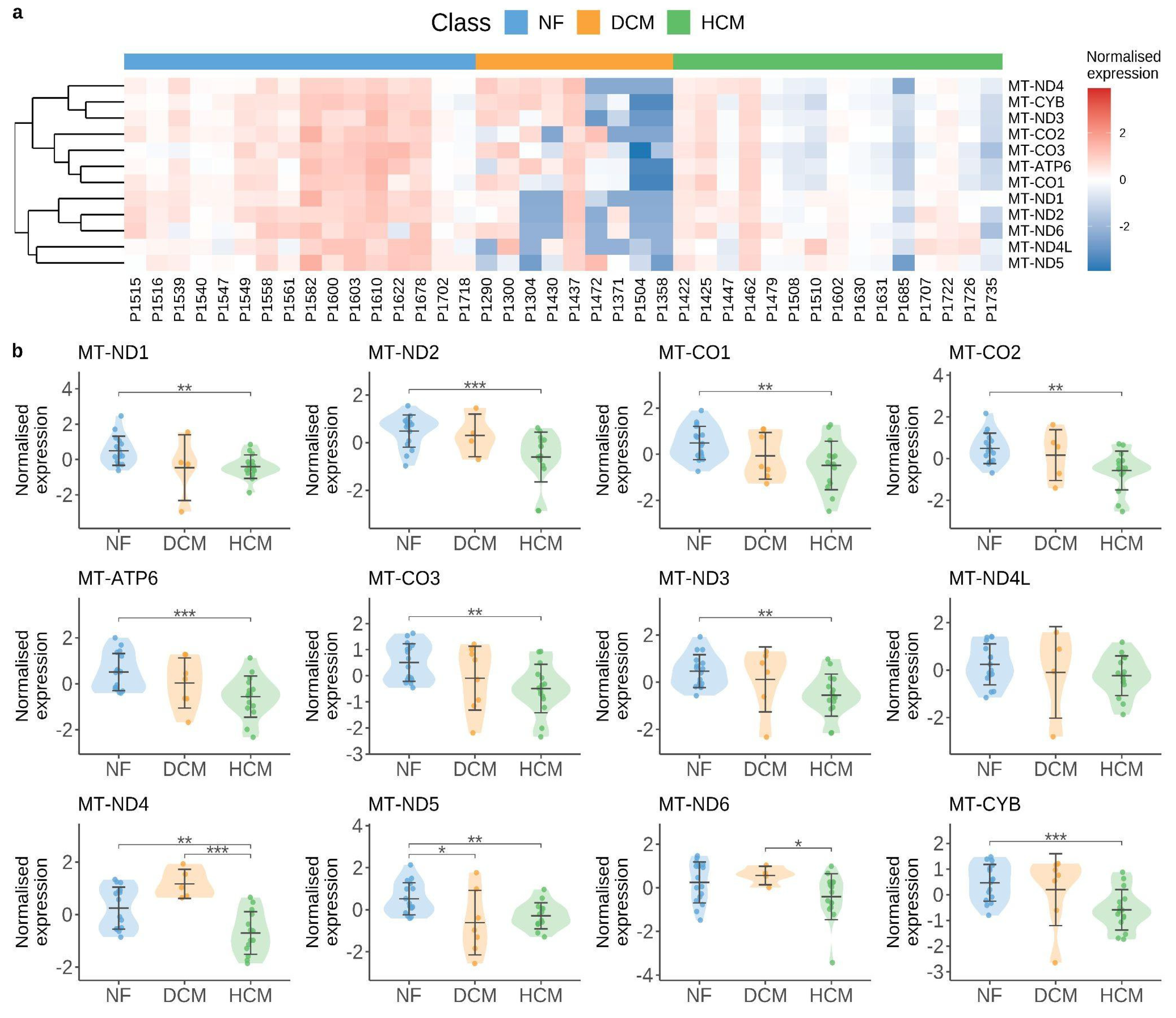
4.2. Mitochondrial Alteration as a Hotspot for cGAS/STING Pathway Activation
4.3. Future Perspectives in Understanding the cGAS/STING Pathway in Cardiomyopathy
- (i)
- Does DNA damage directly contribute to disease progression, or is it merely a byproduct of late-stage damage to cardiomyocytes and progressive cell loss?
- (ii)
- How is the cGAS/STING pathway activated and regulated in myocytes compared to non-myocyte populations during cardiomyopathy (e.g., macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells)? What are the specific downstream targets of cGAS in degenerating cardiac muscle cells?
- (iii)
- Given that mtDNA has been shown to activate cGAS/STING signaling during cardiomyopathy [117], it is crucial to elucidate the mechanisms governing mtDNA release into the cytosol. Furthermore, can cytosolic mtDNA be selectively targeted as a therapeutic strategy to mitigate cardiac dysfunction?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACM | arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy |
| AIM2 | Absent In Melanoma 2 |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ARVC/D | arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BRG1/SMARCA4 | Brahma-related gene 1 |
| CaM-kinase | Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase |
| CDH2 | cadherin-2 |
| cGAMP | cyclic GMP–AMP |
| cGAS | cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
| CRAT | Carnitine acetyltransferase |
| DAMPs | damage-associated molecular patterns |
| DCM | Dilated cardiomyopathy |
| DIC | Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy |
| DSC2 | Desmocollin-2 |
| dsDNA | double-stranded DNA |
| DSG2 | Desmoglein-2 |
| DSP | Desmoplakin |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| GTP | Guanosine-5′-triphosphate |
| HCM | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| ICA69 | islet cell autoantigen 69 |
| IFI16 | interferon-gamma-inducible protein 16 |
| IFN | interferon |
| IRF3 | interferon regulatory factor 3 |
| ISGs | interferon-stimulated genes |
| JUP | Junction Plakoglobin |
| LEMD2 | LEM domain-containing protein 2 |
| LMNA | Gene encoding Lamin A/C |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK/ERK | mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| METRNL | Meteorin-like hormone |
| MITOL/MARCH5 | Mitochondrial E3 Ubiquitin Ligase |
| mPTP | mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| mtDNA | mitochondrial DNA |
| NAD⁺ | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NARP | Neuropathy-ataxia-retinitis pigmentosa |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 |
| PGC1α | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1-alpha |
| PKP2 | Plakophilin-2 |
| PLN | phospholamban |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SASP | senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| SASP | senescence-associated secretory phenotype |
| SIC | Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin-1 |
| snRNA-seq | single-nucleus RNA-sequencing |
| STING | Stimulator of interferon genes |
| TBK1 | TANK-binding Kinase 1 |
| TLR9 | Toll-like receptor 9 |
| TMEM43 | transmembrane protein 43 |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TRAF2 | tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 |
| ULK1 | Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1 |
| γ-H2AX | phosphorylated histone H2AX |
References
- Brieler, J.; Breeden, M.A.; Tucker, J. Cardiomyopathy: An Overview. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ciarambino, T.; Menna, G.; Sansone, G.; Giordano, M. Cardiomyopathies: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, W.J.; Maron, B.J.; Thiene, G. Classification, Epidemiology, and Global Burden of Cardiomyopathies. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ommen, S.R.; Ho, C.Y.; Asif, I.M.; Balaji, S.; Burke, M.A.; Day, S.M.; Dearani, J.A.; Epps, K.C.; Evanovich, L.; Ferrari, V.A.; et al. 2024 AHA/ACC/AMSSM/HRS/PACES/SCMR Guideline for the Management of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2024, 149, e1239–e1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, K.M.; Trembley, M.A.; Chandler, S.F.; Sanders, S.P.; Saffitz, J.E.; Abrams, D.J.; Pu, W.T. Molecular Mechanisms of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Berlo, J.H.; Maillet, M.; Molkentin, J.D. Signaling Effectors Underlying Pathologic Growth and Remodeling of the Heart. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafian, H.; McKenna, W.J.; Watkins, H. Disease Pathways and Novel Therapeutic Targets in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla-Vera, M.; Hahn, V.S.; Kass, D.A. Leveraging Signaling Pathways to Treat Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1618–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Du, F.; Shi, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP Is an Endogenous Second Messenger in Innate Immune Signaling by Cytosolic DNA. Science 2013, 339, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Is a Cytosolic DNA Sensor That Activates the Type I Interferon Pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Regulation and Function of the cGAS-STING Pathway of Cytosolic DNA Sensing. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-D.; Wu, J.; Gao, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Pivotal Roles of cGAS-cGAMP Signaling in Antiviral Defense and Immune Adjuvant Effects. Science 2013, 341, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decout, A.; Katz, J.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Ablasser, A. The cGAS-STING Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Xu, H.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.; Brautigam, C.A.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.J. The Cytosolic DNA Sensor cGAS Forms an Oligomeric Complex with DNA and Undergoes Switch-like Conformational Changes in the Activation Loop. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Chen, Z.J. STING Specifies IRF3 Phosphorylation by TBK1 in the Cytosolic DNA Signaling Pathway. Sci. Signal 2012, 5, ra20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, G.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.-C.; Chen, Z.J. Structural Basis of STING Binding with and Phosphorylation by TBK1. Nature 2019, 567, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Otsu, K. Inflammation and Metabolic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Nie, G.; Dai, Y. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation-Related Signaling Pathways in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, D.; Chong, M.H.A.; Lahoti, N.; Bigogno, C.M.; Prema, R.; Mohiddin, S.A.; Marelli-Berg, F. Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Chronic Cardiac Inflammation: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapy. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 293, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.P.S.; de Roda, V.M.P.; Andrieux, P.; Kalil, J.; Chevillard, C.; Cunha-Neto, E. Inflammation and Mitochondria in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Chagas Disease Cardiomyopathy. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 2062–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zou, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Weng, X.; Pei, Z.; Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, Z.; Gao, R.; et al. Critical Role of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, e223–e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; VanPortfliet, J.J.; Chen, Y.-F.; Bryant, J.D.; Li, Y.; Fails, D.; Torres-Odio, S.; Ragan, K.B.; Deng, J.; Mohan, A.; et al. Cooperative Sensing of Mitochondrial DNA by ZBP1 and cGAS Promotes Cardiotoxicity. Cell 2023, 186, 3013–3032.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, C.; Tan, Y.; Ni, D.; Peng, J.; Yi, G. cGAS-STING Signaling in Ischemic Diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 531, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Wu, H.; Wu, Q.; Duan, M.; Deng, W.; Tang, Q. STING-IRF3 Contributes to Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction, Inflammation, Apoptosis and Pyroptosis by Activating NLRP3. Redox Biol. 2019, 24, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Ni, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, F.; Li, S.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yao, X.; et al. ICA69 Aggravates Ferroptosis Causing Septic Cardiac Dysfunction via STING Trafficking. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, Q.; Ren, K.; Wu, P.; Wang, Y.; Lv, C. ALDH2 Mitigates LPS-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction, Inflammation, and Apoptosis through the cGAS/STING Pathway. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Angelini, A.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Patterson, C.; Pi, X.; Xie, L. CRAT Links Cholesterol Metabolism to Innate Immune Responses in the Heart. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, L.; Cheedipudi, S.M.; Cathcart, B.; Gurha, P.; Marian, A.J. Cytosolic DNA Sensing Protein Pathway Is Activated in Human Hearts with Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J. Cardiovasc. Aging 2023, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheedipudi, S.M.; Asghar, S.; Marian, A.J. Genetic Ablation of the DNA Damage Response Pathway Attenuates Lamin-Associated Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Mice. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2022, 7, 1232–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- En, A.; Bogireddi, H.; Thomas, B.; Stutzman, A.V.; Ikegami, S.; LaForest, B.; Almakki, O.; Pytel, P.; Moskowitz, I.P.; Ikegami, K. Pervasive Nuclear Envelope Ruptures Precede ECM Signaling and Disease Onset without Activating cGAS-STING in Lamin-Cardiomyopathy Mice. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.M.; Geng, K.; Law, B.Y.-K.; Wang, P.; Pu, Y.L.; Chen, Q.; Xu, H.W.; Tan, X.Z.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Xu, Y. Lipotoxicity-Induced mtDNA Release Promotes Diabetic Cardiomyopathy by Activating the cGAS-STING Pathway in Obesity-Related Diabetes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2023, 39, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zeng, W.; Shao, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, H.; et al. Mitochondrial Damage and Activation of the Cytosolic DNA Sensor cGAS-STING Pathway Lead to Cardiac Pyroptosis and Hypertrophy in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mice. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.-B.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.-C.; Wu, Y.-J.; Niu, K.-M.; Li, K.-X.; Zhang, J.-R.; Sun, H.-J. Metrnl Ameliorates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via Inactivation of cGAS/STING Signaling Dependent on LKB1/AMPK/ULK1-Mediated Autophagy. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 51, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lai, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kang, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Hou, N.; et al. BRG1 Deficiency Promotes Cardiomyocyte Inflammation and Apoptosis by Activating the cGAS-STING Signaling in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Inflammation 2024, 48, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, T.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, H.; Yu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Shen, X.; Sun, T.; Shi, H.; et al. IL-37 Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis by Regulating mtDNA-Enriched Vesicle Release in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy Mice. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Shao, Y.; Xiong, X.; Ma, J.; Zhai, M.; Lu, G.; Jiang, L.; Jin, P.; Tang, J.; Yang, J.; et al. Irisin Improves Diabetic Cardiomyopathy-Induced Cardiac Remodeling by Regulating GSDMD-Mediated Pyroptosis through MITOL/STING Signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, L.; Cheedipudi, S.M.; Chen, S.N.; Fan, S.; Lombardi, R.; Chen, X.; Coarfa, C.; Robertson, M.J.; Gurha, P.; Marian, A.J. Haploinsufficiency of Tmem43 in Cardiac Myocytes Activates the DNA Damage Response Pathway Leading to a Late-Onset Senescence-Associated pro-Fibrotic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhuri, S.; Garg, N.J. PARP1-cGAS-NF-κB Pathway of Proinflammatory Macrophage Activation by Extracellular Vesicles Released during Trypanosoma Cruzi Infection and Chagas Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, P.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T. Ginsenoside Rb1 Mitigates Acute Catecholamine Surge-Induced Myocardial Injuries in Part by Suppressing STING-Mediated Macrophage Activation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Buchmann, S.; Kroth, A.; Arias-Loza, A.-P.; Kohlhaas, M.; Wagner, N.; Grüner, G.; Nickel, A.; Cirnu, A.; Williams, T.; et al. Mechanistic Insights of the LEMD2 p.L13R Mutation and Its Role in Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, e43–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yu, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, R.; Su, Y. GAS-STING Signaling Plays an Essential Pathogenetic Role in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 24, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymans, S.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Tschöpe, C.; Klingel, K. Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Causes, Mechanisms, and Current and Future Treatment Approaches. Lancet 2023, 402, 998–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichart, D.; Magnussen, C.; Zeller, T.; Blankenberg, S. Dilated Cardiomyopathy: From Epidemiologic to Genetic Phenotypes: A Translational Review of Current Literature. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 286, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, R.G.; Semsarian, C.; Macdonald, P. Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2017, 390, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Johnson, R.; Birch, S.; Zentner, D.; Hershberger, R.E.; Fatkin, D. Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, E.M.; Mestroni, L. Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Genetic Determinants and Mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.N.; Sbaizero, O.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Mestroni, L. Lamin A/C Cardiomyopathy: Implications for Treatment. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, S.; Chandran, S.; Rajasekaran, N.S.; Melkani, G.C. Genetic and Pathophysiological Basis of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Laminopathies. Genes 2024, 15, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnaloja, F.; Carnevali, F.; Jacchetti, E.; Raimondi, M.T. Lamin A/C Mechanotransduction in Laminopathies. Cells 2020, 9, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray-Nerger, L.A.; Cristea, I.M. Lamin Post-Translational Modifications: Emerging Toggles of Nuclear Organization and Function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ji, J.Y. Understanding Lamin Proteins and Their Roles in Aging and Cardiovascular Diseases. Life Sci. 2018, 212, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, X.; Melendez-Perez, A.J.; Reddy, K.L. The Nuclear Lamina. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2022, 14, a040113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, T.; Su, J.; Shen, J.; Zhou, J.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Meng, X.; et al. Lamin A/C Deficiency-Mediated ROS Elevation Contributes to Pathogenic Phenotypes of Dilated Cardiomyopathy in iPSC Model. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Captur, G.; Arbustini, E.; Bonne, G.; Syrris, P.; Mills, K.; Wahbi, K.; Mohiddin, S.A.; McKenna, W.J.; Pettit, S.; Ho, C.Y.; et al. Lamin and the Heart. Heart 2018, 104, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Patel, P.N.; Gorham, J.M.; McDonough, B.; DePalma, S.R.; Adler, E.E.; Lam, L.; MacRae, C.A.; Mohiuddin, S.M.; Fatkin, D.; et al. Identification of Pathogenic Gene Mutations in LMNA and MYBPC3 That Alter RNA Splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7689–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Elsherbiny, A.; Kessler, L.; Cordero, J.; Shi, H.; Serke, H.; Lityagina, O.; Trogisch, F.A.; Mohammadi, M.M.; El-Battrawy, I.; et al. Lamin A/C-Dependent Chromatin Architecture Safeguards Naïve Pluripotency to Prevent Aberrant Cardiovascular Cell Fate and Function. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuela-Sopilniak, N.; Morival, J.; Lammerding, J. Multi-Level Transcriptomic Analysis of LMNA -Related Dilated Cardiomyopathy Identifies Disease-Driving Processes. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feurle, P.; Abentung, A.; Cera, I.; Wahl, N.; Ablinger, C.; Bucher, M.; Stefan, E.; Sprenger, S.; Teis, D.; Fischer, A.; et al. SATB2-LEMD2 Interaction Links Nuclear Shape Plasticity to Regulation of Cognition-Related Genes. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanisch, K.; Song, C.; Engelkamp, D.; Koch, J.; Wang, A.; Hallberg, E.; Foisner, R.; Leonhardt, H.; Stewart, C.L.; Joffe, B.; et al. Nuclear Envelope Localization of LEMD2 Is Developmentally Dynamic and Lamin A/C Dependent yet Insufficient for Heterochromatin Tethering. Differentiation 2017, 94, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.D. The Role of the LEMD2 p.L13R Mutation in Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 185–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravia, X.M.; Ramirez-Martinez, A.; Gan, P.; Wang, F.; McAnally, J.R.; Xu, L.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Liu, N.; Olson, E.N. Loss of Function of the Nuclear Envelope Protein LEMD2 Causes DNA Damage-Dependent Cardiomyopathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e158897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah, N.; Chen, R.; Duff, H.J.; Seifer, C.M.; Buffo, I.; Huculak, C.; Clarke, S.; Clegg, R.; Jassal, D.S.; Gordon, P.M.K.; et al. Characterization of a Unique Form of Arrhythmic Cardiomyopathy Caused by Recessive Mutation in LEMD2. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2019, 4, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo-Almorós, A.; Cepeda-Rodrigo, J.M.; Lorenzo, Ó. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2022, 222, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillmann, W.H. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1160–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Pang, P.; Yang, Q.; Lin, J.; Deng, S.; Wu, S.; Fan, G.; et al. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Clinical Phenotype and Practice. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1032268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ahmad, S.S.; Kamal, M.A. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: From Mechanism to Management in a Nutshell. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, L.R.; Gropler, R.J. Metabolic and Molecular Imaging of the Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1628–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrado, D.; Basso, C.; Judge, D.P. Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 784–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.D.; Lakdawala, N.K.; Papoutsidakis, N.; Aubert, G.; Mazzanti, A.; McCanta, A.C.; Agarwal, P.P.; Arscott, P.; Dellefave-Castillo, L.M.; Vorovich, E.E.; et al. Desmoplakin Cardiomyopathy, a Fibrotic and Inflammatory Form of Cardiomyopathy Distinct from Typical Dilated or Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2020, 141, 1872–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacita, A.M.; McNally, E.M. Genetic Spectrum of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Heart Fail. 2019, 12, e005850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, R.; Marian, A.J. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Is a Disease of Cardiac Stem Cells. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2010, 25, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, Y.B.; Parikh, V.N. Genetic Risk Stratification in Arrhythmogenic Left Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Card. Electrophysiol. Clin. 2023, 15, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Lee, C.J. Transmembrane Proteins with Unknown Function (TMEMs) as Ion Channels: Electrophysiological Properties, Structure, and Pathophysiological Roles. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, J.; Helle, E.; Care, M.; Moayedi, Y.; Gollob, M.H.; Thavendiranathan, P.; Spears, D.; Hanneman, K. Cardiac MRI and Clinical Outcomes in TMEM43 Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaginging 2023, 5, e230155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almajidi, Y.Q.; Kadhim, M.M.; Alsaikhan, F.; Turki Jalil, A.; Hassan Sayyid, N.; Alexis Ramírez-Coronel, A.; Hassan Jawhar, Z.; Gupta, J.; Nabavi, N.; Yu, W.; et al. Doxorubicin-Loaded Micelles in Tumor Cell-Specific Chemotherapy. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Santos, R.X.; Cardoso, S.; Correia, S.; Oliveira, P.J.; Santos, M.S.; Moreira, P.I. Doxorubicin: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly Effect. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3267–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheibani, M.; Azizi, Y.; Shayan, M.; Nezamoleslami, S.; Eslami, F.; Farjoo, M.H.; Dehpour, A.R. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: An Overview on Pre-Clinical Therapeutic Approaches. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2022, 22, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.-Y.; Guo, Z.; Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.-P.; Teng, T.; Yan, L.; Tang, Q.-Z. Underlying the Mechanisms of Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity: Oxidative Stress and Cell Death. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.S.; Jaiswal, A.; Khurana, A.; Bhatti, J.S.; Navik, U. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: An Update on the Molecular Mechanism and Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Effective Management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, K.B.; Sardão, V.A.; Oliveira, P.J. Mitochondrial Determinants of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, S.; Dai, Y. Research Progress of Therapeutic Drugs for Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Baat, E.C.; Mulder, R.L.; Armenian, S.; Feijen, E.A.; Grotenhuis, H.; Hudson, M.M.; Mavinkurve-Groothuis, A.M.; Kremer, L.C.; van Dalen, E.C. Dexrazoxane for Preventing or Reducing Cardiotoxicity in Adults and Children with Cancer Receiving Anthracyclines. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 9, CD014638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, P.; Barootkoob, B.; ElHashash, A.; Nair, A. Efficacy of Dexrazoxane in Cardiac Protection in Pediatric Patients Treated with Anthracyclines. Cureus 2023, 15, e37308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Bawa-Khalfe, T.; Lu, L.-S.; Lyu, Y.L.; Liu, L.F.; Yeh, E.T.H. Identification of the Molecular Basis of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srzić, I.; Nesek Adam, V.; Tunjić Pejak, D. SEPSIS DEFINITION: WHAT’S NEW IN THE TREATMENT GUIDELINES. Acta Clin. Croat. 2022, 61, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, J. The Pathophysiology of Sepsis—2021 Update: Part 2, Organ Dysfunction and Assessment. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2022, 79, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleakley, G.; Cole, M. Recognition and Management of Sepsis: The Nurse’s Role. Br. J. Nurs. 2020, 29, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Singer, M. Pathophysiology of Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Heureux, M.; Sternberg, M.; Brath, L.; Turlington, J.; Kashiouris, M.G. Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, J. Carnitine--Metabolism and Functions. Physiol. Rev. 1983, 63, 1420–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholte, H.R.; Rodrigues Pereira, R.; de Jonge, P.C.; Luyt-Houwen, I.E.; Hedwig, M.; Verduin, M.; Ross, J.D. Primary Carnitine Deficiency. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1990, 28, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berg, S.M.; Beck-Nielsen, H.; Færgeman, N.J.; Gaster, M. Carnitine Acetyltransferase: A New Player in Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance? Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 9, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.J.; Park, C.-H.; Kim, H.; Han, S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; Chung, J.H. Carnitine Acetyltransferase Deficiency Mediates Mitochondrial Dysfunction-Induced Cellular Senescence in Dermal Fibroblasts. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarría, N.G.; Echeverría, L.E.; Stewart, M.; Gallego, C.; Saldarriaga, C. Chagas Disease: Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, É.; Menezes Falcão, L. Chagas Cardiomyopathy and Heart Failure: From Epidemiology to Treatment. Rev. Port. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 39, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.C.P.; Beaton, A.; Acquatella, H.; Bern, C.; Bolger, A.F.; Echeverría, L.E.; Dutra, W.O.; Gascon, J.; Morillo, C.A.; Oliveira-Filho, J.; et al. Chagas Cardiomyopathy: An Update of Current Clinical Knowledge and Management: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 138, e169–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina de Chazal, H.; Del Buono, M.G.; Keyser-Marcus, L.; Ma, L.; Moeller, F.G.; Berrocal, D.; Abbate, A. Stress Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis and Treatment: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 1955–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.Z.; Amin, L.Z.; Pradipta, A. Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy: A Brief Review. J. Med. Life 2020, 13, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, D.K. Acute Stress-Induced (Takotsubo) Cardiomyopathy. Heart 2018, 104, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, J.; Brieger, D. Clinical Perspectives: Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy. Intern. Med. J. 2024, 54, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Woodward, J.J.; Sasaki, T.; Minie, M.; Elkon, K.B. Cutting Edge: Antimalarial Drugs Inhibit IFN-β Production through Blockade of Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-DNA Interaction. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4089–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skopelja-Gardner, S.; An, J.; Tai, J.; Tanaka, L.; Sun, X.; Hermanson, P.; Baum, R.; Kawasumi, M.; Green, R.; Gale, M.; et al. The Early Local and Systemic Type I Interferon Responses to Ultraviolet B Light Exposure Are cGAS Dependent. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Sooreshjani, M.A.; Mikek, C.; Opoku-Temeng, C.; Sintim, H.O. Suramin Potently Inhibits cGAMP Synthase, cGAS, in THP1 Cells to Modulate IFN-β Levels. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 1301–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Huang, Y.-J.; He, X.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.-S.; Xue, W.; Cai, H.; Zhan, X.-Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; et al. Acetylation Blocks cGAS Activity and Inhibits Self-DNA-Induced Autoimmunity. Cell 2019, 176, 1447–1460.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Mei, J.; Huang, L.; Lou, X.; Zhao, S.; Song, L.; Chen, W.; et al. The Cyclopeptide Astin C Specifically Inhibits the Innate Immune CDN Sensor STING. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3405–3421.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, F.; Shmuel-Galia, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, J.Y.; Barasa, L.; Mondal, S.; Wilson, R.; Sultana, N.; Shaffer, S.A.; Ng, S.-L.; et al. Targeting STING Oligomerization with Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2305420120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobritz, M.; Borjas, T.; Patel, V.; Coppa, G.; Aziz, M.; Wang, P. H151, A SMALL MOLECULE INHIBITOR OF STING AS A NOVEL THERAPEUTIC IN INTESTINAL ISCHEMIA-REPERFUSION INJURY. Shock 2022, 58, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, M.; Papangeli, I.; Simonson, B.; Akkad, A.-D.; Hill, M.C.; Arduini, A.; Fleming, S.J.; Melanson, M.; Hayat, S.; Kost-Alimova, M.; et al. Single-Nucleus Profiling of Human Dilated and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Nature 2022, 608, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraste, M. Oxidative Phosphorylation at the Fin de Siècle. Science 1999, 283, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Transcriptional Paradigms in Mammalian Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 611–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, P.; Khan, N.A.; Rani, B.; Rani, D.S.; Selvaraj, P.; Jyothi, V.; Bahl, A.; Narasimhan, C.; Rakshak, D.; Premkumar, K.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA Variations Associated with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Mitochondrion 2014, 16, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreu, A.L.; Checcarelli, N.; Iwata, S.; Shanske, S.; DiMauro, S. A Missense Mutation in the Mitochondrial Cytochrome b Gene in a Revisited Case with Histiocytoid Cardiomyopathy. Pediatr. Res. 2000, 48, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rak, M.; Bénit, P.; Chrétien, D.; Bouchereau, J.; Schiff, M.; El-Khoury, R.; Tzagoloff, A.; Rustin, P. Mitochondrial Cytochrome c Oxidase Deficiency. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatuch, Y.; Christodoulou, J.; Feigenbaum, A.; Clarke, J.T.; Wherret, J.; Smith, C.; Rudd, N.; Petrova-Benedict, R.; Robinson, B.H. Heteroplasmic mtDNA Mutation (T----G) at 8993 Can Cause Leigh Disease When the Percentage of Abnormal mtDNA Is High. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1992, 50, 852–858. [Google Scholar]
- Ahuja, P.; Wanagat, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liem, D.A.; Ping, P.; Antoshechkin, I.A.; Margulies, K.B.; Maclellan, W.R. Divergent Mitochondrial Biogenesis Responses in Human Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2013, 127, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanlidis, G.; Nascimben, L.; Couper, G.S.; Shekar, P.S.; del Monte, F.; Tian, R. Defective DNA Replication Impairs Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Human Failing Hearts. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenson, J.M.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ea, C.-K.; Chen, Z.J. Ubiquitin-like Conjugation by Bacterial cGAS Enhances Anti-Phage Defence. Nature 2023, 616, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, J.L.; Jones, J.; Bolleddu, S.I.; Vanthenapalli, S.; Rodgers, L.E.; Shah, K.; Karia, K.; Panguluri, S.K. Cardiovascular Risks Associated with Gender and Aging. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2019, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahsili-Fahadan, P.; Geocadin, R.G. Heart-Brain Axis: Effects of Neurologic Injury on Cardiovascular Function. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cardiomyopathy Type | Model (In Vivo–In Vitro) | Key Findings | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (SIC) | LPS-injected mice; H9C2 cells, neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) | STING knockdown suppresses IRF3 activation, reduces inflammation, apoptosis, and pyroptosis | [24] |
| Human blood; LPS-injected mice; RAW264.7 macrophages; H9C2 cells | Islet cell autoantigen of 69 kDa (ICA69) deletion inhibits STING-mediated inflammation and ferroptosis | [25] | |
| LPS-injected mice; H9C2 cells | cGAS knockdown or ALDH2 treatment reduces STING pathway activation | [26] | |
| Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) | Myh6-Cre:LmnaF/F: Crat-/- mice; Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes (NRVMs) | cGAS knockdown reduces IFN-stimulated gene expression | [27] |
| Human DCM hearts | Elevated cGAS in human primary DCM samples; STING unchanged | [28] | |
| LMNA-DCM mice (with/without cGAS) | cGAS deletion improves survival and cardiac function | [29] | |
| LMNA-DCM mice: (Myh6-MerCreMer:LmnaF/F) | No activation of cGAS/STING in cardiomyocytes, cGAS or STING knockout does not rescue the phenotypes of LMNA-DCM | [30] | |
| Diabetic cardiomyopathy | Diabetic (db/db) mice; Palmitic acid (PA)-treated H9C2 cells (rat cardiomyocytes) | Mitochondrial mtDNA activates cGAS/STING; STING inhibition in H9C2 cardiomyocytes (by C176) reduces inflammation and apoptosis | [31] |
| PA-treated H9C2 cells | Cytosolic mtDNA activates cGAS/STING; knockdown inhibits pyroptosis | [32] | |
| Streptozotocin (STZ)-treated (db/db) mice; NRCMs | Meteorin-like hormone (Metrnl) inhibits cGAS/STING in cardiomyocytes and activates the autophagy pathway | [33] | |
| STZ-treated and high-fat-diet (HFD)-fed mice; NRCMs | BRG1 loss activates STING, worsening inflammation and apoptosis induced by hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia | [34] | |
| STZ-treated and HFD-fed mice; human blood | Fibroblasts engulf mtDNA vesicles, activating cGAS/STING | [35] | |
| STZ-treated and HFD-fed mice; H9C2 cells | Irisin and mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase (MITOL) inhibit cGAS/STING, improving cardiac function | [36] | |
| Other Types: TMEM43 arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy | Tmem43 mutant mice: Myh6-Cre: Tmem43W/F mice | STING activated at later stages; related to DNA damage signals | [37] |
| Chagas cardiomyopathy | T. cruzi-infected mice; Murine bone marrow cells, macrophages | cGAS/STING senses T. cruzi vesicles, promotes inflammation | [38] |
| Stress cardiomyopathy | Ovariectomized mice treated with isoproterenol; RAW264.7 macrophages | Ginsenoside Rb1 suppresses STING-mediated macrophage inflammation | [39] |
| LEMD2 arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy | Lemd2 mutant mice (Lemd2 p.L13R knock-in); HeLa LEMD2 p.L13R KI cells | Nuclear envelope rupture recruits cGAS, activates STING/IFN signaling | [40] |
| Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy | Doxorubicin-treated mice (acute injury) | STING knockdown reduces vacuolization and myofibril loss and improves function | [41] |
| Low-dose Doxorubicin-treated mice (chronic injury); human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells (HCMECs) | Global and endothelial-cell-specific STING deletion ameliorates cardiotoxicity and endothelial dysfunction | [21] |
| Target | Compound/Drug | Mode of Action | Effects on Signaling Cascades and in Animal Models | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| cGAS | RU-compounds (RU.365, RU.521) | Catalytic site inhibitor | Reduced expression levels of Ifnb1 mRNA in Trex knockout mice (which constitutively activate cGAS) ↓ IL-1β, ↓ cleaved caspase-3 ↓ Apoptosis | [34] |
| Antimalarial drugs (i.e., Hydroxychloroquine, Quinacrine) | Disrupting dsDNA binding | Hydroxychloroquine and Quinacrine inhibit dsDNA binding to cGAS In vitro: ↓ IFN-β expression In vivo: ↓ Early IFN-1 response in Hydroxycloroquine-treated mice | [101,102] | |
| Suramin | Disrupting dsDNA binding | Suramin inhibits dsDNA binding to cGAS in vitro (THP1-Dual cells) ↓ IFN-β expression (mRNA and protein) | [103] | |
| Acetylsalicylic acid | cGAS acetylation and inhibition | ↓ IFN-production in vitro (THP-1 cells) ↓ Expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISG) Trex1–/– bone marrow cells ↓ ISG expression in the hearts of Trex1–/– mice | [104] | |
| STING and TBK1 | Astin C | STING inhibition—targeting the cyclic dinucleotide binding site | ↓ Expression of Ifnb, Cxcl10, Isg15, Isg56 and Tnf mRNA in the heart of Trex1-/- mice (in vivo) ↓ Expression of type 1 interferone in Trex1-/- Bone marrow cells (in vitro) | [105] |
| Nitrofuran derivatives - C176 and C178 | STING inhibition—covalent binding to cysteine residue 91, inhibiting palmitoylation and activation of STING | ↓ Serum levels of type I interferons and IL-6 in Trex1−/− mice | [106] | |
| ↓ Phosphorylation of p65 ↑ Improves diastolic cardiac function ↑ Partially improve myocardial hypertrophy | [31] | |||
| ↓ Cardiac IRF3 phosphorylation, IRF3 nuclear translocation, and CD38 expression ↑ Cardiomyocyte NAD levels, mitochondrial function, and ↑ left ventricular systolic function ↓ Cardiomyocyte apoptosis ↓ Antitumor effects of doxorubicin | [21] | |||
| ↓ IL-1β, cleaved caspase-3 No effect on γ-H2AX ↓ Apoptosis | [34] | |||
| Amlexanox | TBK1 inhibitor | Same effect as C176 | [21] | |
| 3-acylaminoindole derivative - H-151 | STING inhibition—blocking the activation-induced palmitoylation and clustering of STING | ↓ Calf thymus DNA-induced production of TNF in a dose-dependent manner | [39] | |
| ↓ Reduces IFN-β levels in a dose-dependent manner | [107] | |||
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | Major chemical constituent of ginseng; suppressing the activation of STING | ↓ STING-mediated proinflammatory activation of macrophages ↓ Myocardial fibrosis and inflammatory responses in the heart ↓ DNA-triggered proinflammatory activation of macrophages ↓ DNA-triggered whole-genome gene expression alterations in macrophages | [39] | |
| DMXAA | STING agonist | ↑ STING phosphorylation. ↑ TNF, IL6, CCL2, IFN-β | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Gao, Y.; Lee, H.K.; Yu, A.C.-H.; Kipp, M.; Kaddatz, H.; Zhan, J. The cGAS/STING Pathway: Friend or Foe in Regulating Cardiomyopathy. Cells 2025, 14, 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110778
Wang W, Gao Y, Lee HK, Yu AC-H, Kipp M, Kaddatz H, Zhan J. The cGAS/STING Pathway: Friend or Foe in Regulating Cardiomyopathy. Cells. 2025; 14(11):778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110778
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Weiyue, Yuanxu Gao, Hyun Kyoung Lee, Albert Cheung-Hoi Yu, Markus Kipp, Hannes Kaddatz, and Jiangshan Zhan. 2025. "The cGAS/STING Pathway: Friend or Foe in Regulating Cardiomyopathy" Cells 14, no. 11: 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110778
APA StyleWang, W., Gao, Y., Lee, H. K., Yu, A. C.-H., Kipp, M., Kaddatz, H., & Zhan, J. (2025). The cGAS/STING Pathway: Friend or Foe in Regulating Cardiomyopathy. Cells, 14(11), 778. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110778






