RacGAP1 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. Cell Proliferation
2.4. Cell Migration
2.5. Cell Invasion
2.6. Top Flash Assay
2.7. RNA Purification and Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.8. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Protein Extraction
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
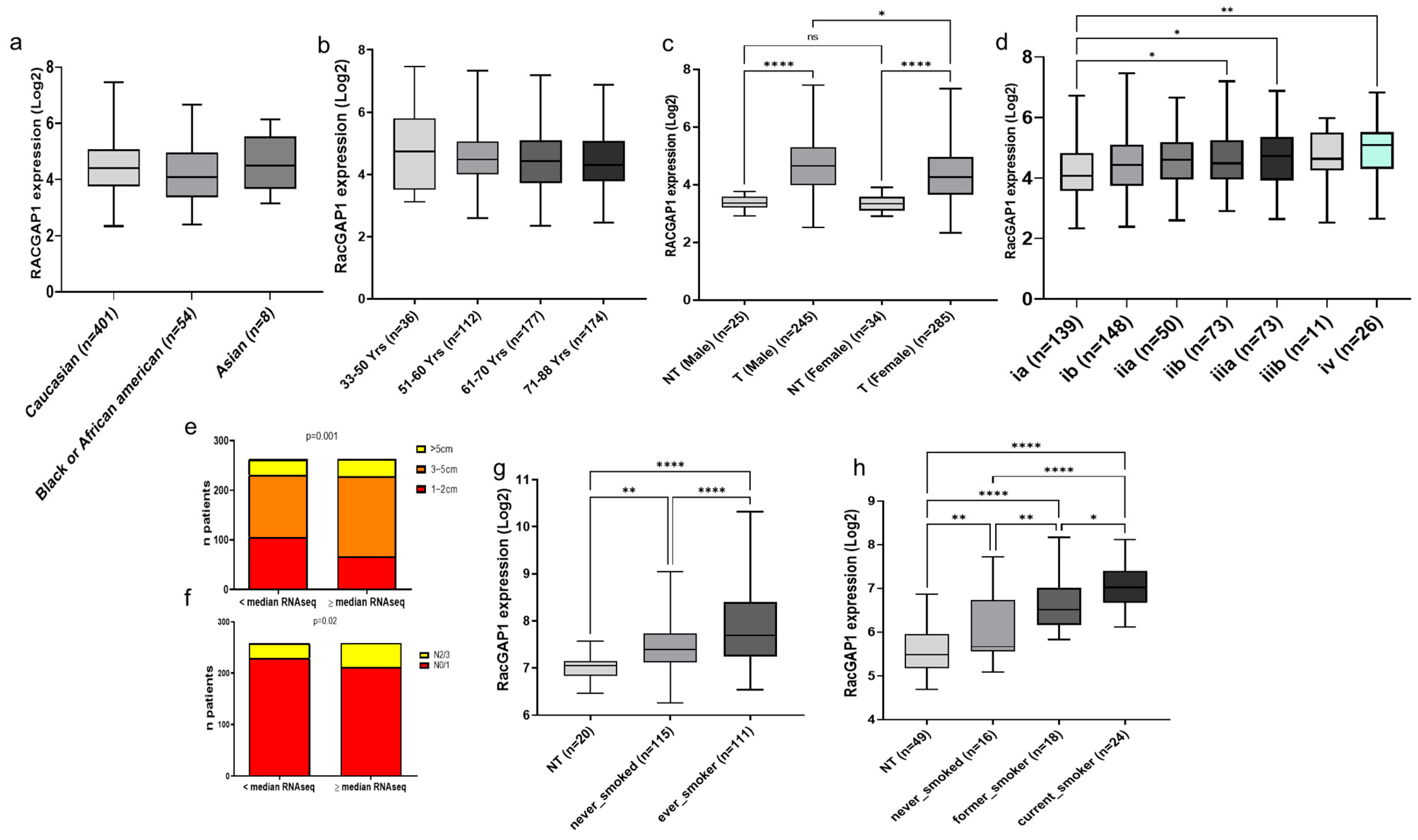
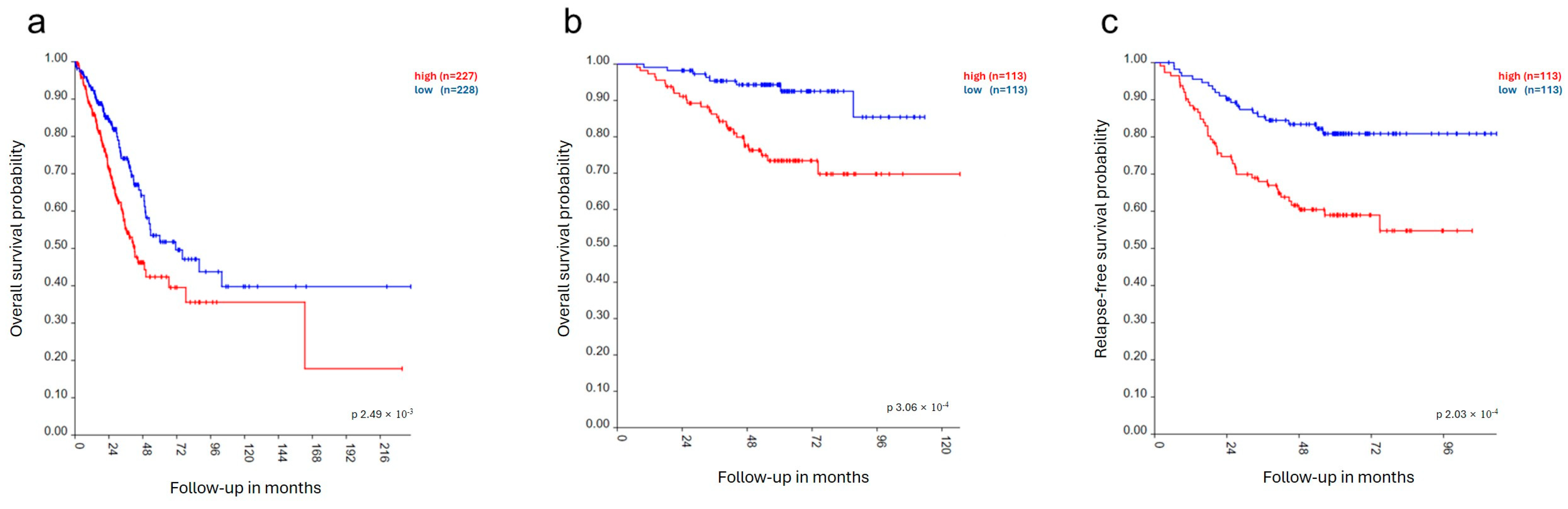
3.1. RacGAP1 in Patients
3.2. Effects of RacGAP1 Silencing on Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion
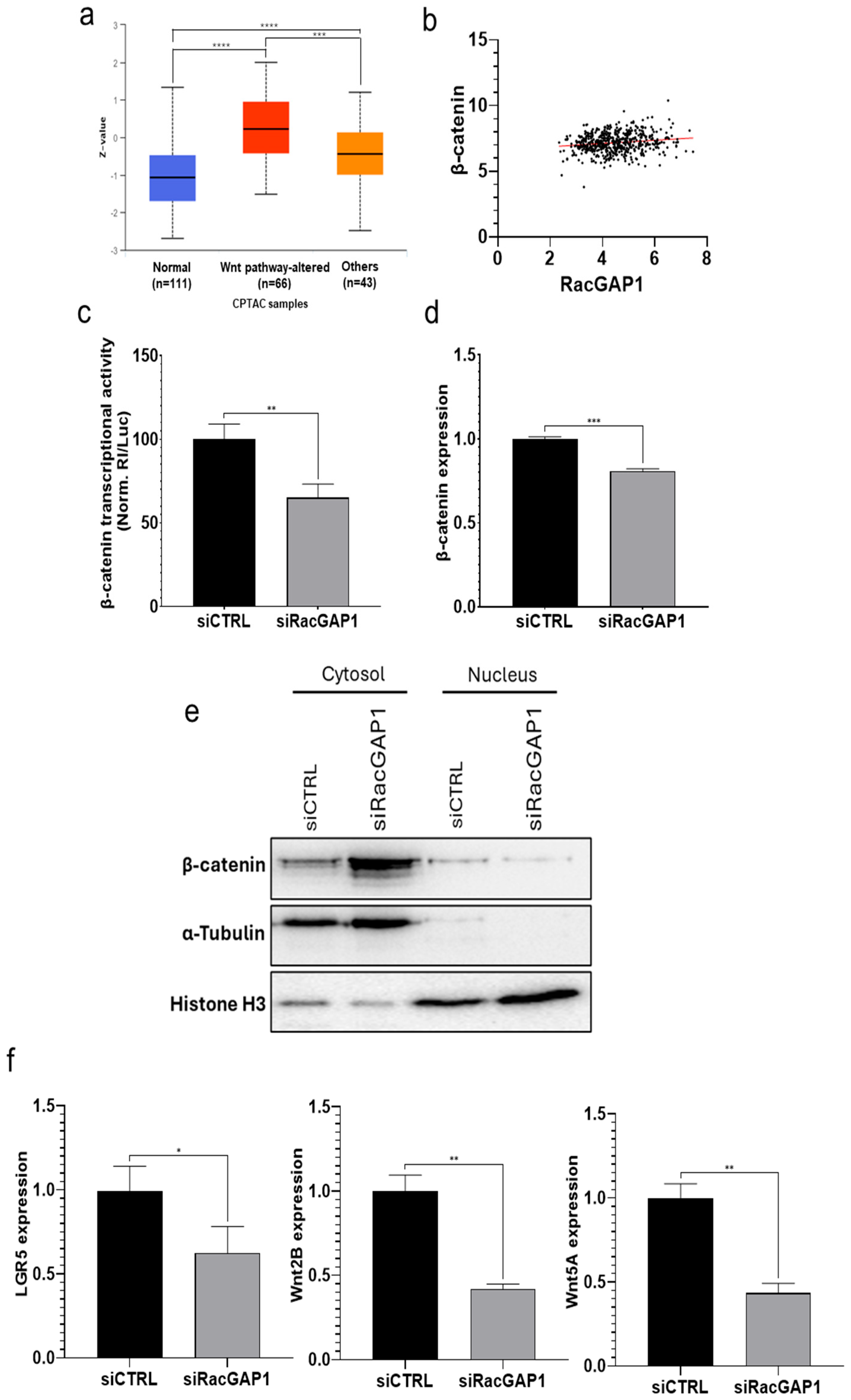
3.3. RacGAP1 Exerts Its Oncogenic Effect by Regulating the Wnt Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RacGAP1 | Rac GTPase activating protein 1 |
| LC | lung cancer |
| SCLC | small cell lung cancer |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| LUAD | lung adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| Rho GAPs | Rho GTPase-activating proteins |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| WRE | Wnt response element |
| TCF | T-cell factor |
| LRG5 | Leucine Rich Repeat Containing G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5 |
| FZD/LRP5 | Frizzleds/Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein |
| RPPH1 | ribonuclease P RNA component H1 |
| DDX56 | DEAD-Box Helicase 56 |
| PST | 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase |
| ATF4 | Activating transcription factor 4 |
| RSPO | R-spondin |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Page, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Read, W.; Tierney, R.; Vlahiotis, A.; Spitznagel, E.L.; Piccirillo, J. Changing Epidemiology of Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States over the Last 30 Years: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiologic, and End Results Database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4539–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nooreldeen, R.; Bach, H. Current and Future Development in Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, A.A.; Solomon, B.J.; Sequist, L.V.; Gainor, J.F.; Heist, R.S. Lung Cancer. Lancet 2021, 398, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Forjaz, G.; Mooradian, M.J.; Meza, R.; Kong, C.Y.; Cronin, K.A.; Mariotto, A.B.; Lowy, D.R.; Feuer, E.J. The Effect of Advances in Lung-Cancer Treatment on Population Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.H.; Stoeber, K. The Cell Cycle and Cancer. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, P.; Villalonga, P.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases and Cell Cycle Control. Growth Factors 2006, 24, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, R.B.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases: Regulation and Roles in Cancer Cell Biology. Small GTPases 2016, 7, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touré, A.; Dorseuil, O.; Morin, L.; Timmons, P.; Jégou, B.; Reibel, L.; Gacon, G. MgcRacGAP, a New Human GTPase-Activating Protein for Rac and Cdc42 Similar to Drosophila rotundRacGAP Gene Product, Is Expressed in Male Germ Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 6019–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Fang, G. MgcRacGAP Controls the Assembly of the Contractile Ring and the Initiation of Cytokinesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13158–13163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPase Signalling in Cell Migration. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-M.; Cao, X.-Y.; He, P.; Li, J.; Feng, M.-X.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-H.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, L.; et al. Overexpression of Rac GTPase Activating Protein 1 Contributes to Proliferation of Cancer Cells by Reducing Hippo Signaling to Promote Cytokinesis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1233–1249.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, D.; Pan, X.; Chu, Y.; Yin, J. FOXM1 Transcriptional Regulation of RacGAP1 Activates the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway to Promote the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 29, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Toiyama, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Shigemori, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Ide, S.; Kitajima, T.; Fujikawa, H.; Yasuda, H.; Okita, Y.; et al. Rac GTPase-Activating Protein 1 (RACGAP1) as an Oncogenic Enhancer in Esophageal Carcinoma. Oncology 2019, 97, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Jiang, Y.; Huan, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Cao, Z.; He, X.; et al. Rac GTPase Activating Protein 1 Promotes the Glioma Growth by Regulating the Expression of MCM3. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 37, 101756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yong, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H. Rac GTPase Activating Protein 1 Promotes Oncogenic Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, A.; Bosch, L.J.W.; Martens-de Kemp, S.R.; Carvalho, B.; Sillars-Hardebol, A.H.; Dobson, R.J.; de Rinaldis, E.; Meijer, G.A.; Abeln, S.; Heringa, J.; et al. Aurora Kinase A (AURKA) Interaction with Wnt and Ras-MAPK Signalling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornschein, J.; Nielitz, J.; Drozdov, I.; Selgrad, M.; Wex, T.; Jechorek, D.; Link, A.; Vieth, M.; Malfertheiner, P. Expression of Aurora Kinase A Correlates with the Wnt-Modulator RACGAP1 in Gastric Cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Cancers and Targeted Therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Nuerlan, S.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, C. YY1/circCTNNB1/miR-186-5p/YY1 Positive Loop Aggravates Lung Cancer Progression Through the Wnt Pathway. Epigenetics 2024, 19, 2369006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Feng, G.; Xing, Z.; Gao, X. Circ-EIF3I Facilitates Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Lung Cancer via Regulating the Activity of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Through the miR-1253/NOVA2 Axis. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 3133–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.; He, B.; Xu, Z.; Uematsu, K.; Mazieres, J.; Mikami, I.; Reguart, N.; Moody, T.W.; Kitajewski, J.; McCormick, F.; et al. Inhibition of Wnt-2-Mediated Signaling Induces Programmed Cell Death in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6170–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jiang, X.; Duan, L.; Xiong, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, P.; Jiang, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhao, S.; Yang, C.; et al. LncRNA PKMYT1AR Promotes Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Activating Wnt Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qi, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, H. MARVELD3 Inhibits the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cell Migration by Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sun, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Gu, Q.; Dong, X.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, J.; Cheng, R.; Qi, H.; et al. Overexpression of Wnt5a Promotes Angiogenesis in NSCLC. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 832562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Li, Y.; Wei, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, H. BZW2 Promotes Malignant Progression in Lung Adenocarcinoma Through Enhancing the Ubiquitination and Degradation of GSK3β. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, S.; Tu, J.; Wang, M.; Liang, W.; Cheng, J.; Guan, J.; Xu, J. RACGAP1 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation Through the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Han, T.; Miao, R.; Zhou, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, J.; Hu, D. RACGAP1 Promotes the Progression and Poor Prognosis of Lung Adenocarcinoma Through Its Effects on the Cell Cycle and Tumor Stemness. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Zuo, Y.; He, K.; Zhang, T.; Peng, D.; Wang, W. Elevated RACGAP1 Expression Enhances Malignant Potential in Lung Adenocarcinoma and Serves as a Prognostic Factor. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 4244–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korinek, V.; Barker, N.; Morin, P.J.; van Wichen, D.; de Weger, R.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Clevers, H. Constitutive Transcriptional Activation by a Beta-Catenin-Tcf Complex in APC−/− Colon Carcinoma. Science 1997, 275, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosca, N.; Khoubai, F.Z.; Fedou, S.; Carrillo-Reixach, J.; Caruso, S.; Del Rio-Alvarez, A.; Dubois, E.; Avignon, C.; Dugot-Senant, N.; Guettier, C.; et al. LIM Homeobox-2 Suppresses Hallmarks of Adult and Pediatric Liver Cancers by Inactivating MAPK/ERK and Wnt/Beta-Catenin Pathways. Liver Cancer 2022, 11, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A New Mathematical Model for Relative Quantification in Real-Time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Huang, W.; Xia, H.; Mi, J.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhou, L.; Lu, Z.; Wu, F. Oncogenic and Immunological Roles of RACGAP1 in Pan-Cancer and Its Potential Value in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Ooi, L.L.P.J.; Hui, K.M. Upregulation of Rac GTPase-Activating Protein 1 Is Significantly Associated with the Early Recurrence of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6040–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt Signaling in Cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottardi, C.J.; Wong, E.; Gumbiner, B.M. E-Cadherin Suppresses Cellular Transformation by Inhibiting β-Catenin Signaling in an Adhesion-Independent Manner. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, B.; Guo, D.; Pan, L.; Luo, X.; Tang, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; et al. Up-Regulation of RACGAP1 Promotes Progressions of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Regulated by GABPA via PI3K/AKT Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, e3034150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Westover, D.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Zhou, S.; Hesilaiti, N.; et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in the Development and Therapeutic Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Luo, X.; Terp, M.G.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Shen, L.; Chen, Y.; Jacobsen, K.; Bivona, T.G.; Chen, H.; et al. DDX56 Modulates Post-Transcriptional Wnt Signaling Through miRNAs and Is Associated with Early Recurrence in Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, K.; Liang, W.; Wang, X. lncRNA RPPH1 Promotes Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression Through the miR-326/WNT2B Axis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Zhou, C.; He, J.; Meng, X. LncRNA AL139294.1 Can Be Transported by Extracellular Vesicles to Promote the Oncogenic Behaviour of Recipient Cells Through Activation of the Wnt and NF-κB2 Pathways in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Han, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Divisi, D.; Capobianco, E.; Zhang, L.; Dong, W. PTS Is Activated by ATF4 and Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Development via the Wnt Pathway. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 1912–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dai, Q.; Fu, X.; Chen, Q.; Tang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhou, Q. CircVAPA Exerts Oncogenic Property in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by the miR-876-5p/WNT5A Axis. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Liu, H.; Mao, X.; Qin, Y.; Fan, C. ATF4 Promotes Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion Partially Through Regulating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, N.; Pezzullo, M.; De Leo, I.; Truda, A.; Marchese, G.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. A Novel ceRNET Relying on the lncRNA JPX, miR-378a-3p, and Its mRNA Targets in Lung Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lokman, N.A.; Barry, S.C.; Oehler, M.K.; Ricciardelli, C. LGR5: An Emerging Therapeutic Target for Cancer Metastasis and Chemotherapy Resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025, 44, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mosca, N.; Pezzullo, M.; De Leo, I.; Truda, A.; Marchese, G.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. RacGAP1 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cells 2025, 14, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110773
Mosca N, Pezzullo M, De Leo I, Truda A, Marchese G, Russo A, Potenza N. RacGAP1 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cells. 2025; 14(11):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110773
Chicago/Turabian StyleMosca, Nicola, Mariaceleste Pezzullo, Ilenia De Leo, Anna Truda, Giovanna Marchese, Aniello Russo, and Nicoletta Potenza. 2025. "RacGAP1 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway" Cells 14, no. 11: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110773
APA StyleMosca, N., Pezzullo, M., De Leo, I., Truda, A., Marchese, G., Russo, A., & Potenza, N. (2025). RacGAP1 Plays an Oncogenic Role in Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Cells, 14(11), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14110773









