The Effects of Neuronal Fyn Knockdown in the Hippocampus in the Rat Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
2.2. Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viral (rAAV) Vectors
2.3. Chemicals and Reagents
2.4. Experimental Design, Experimental Groups, and Kainate Exposure
2.5. In Vivo Vector Injections and Stereotaxic Surgery
2.6. SE Induction and Initial SE Severity Scoring
2.7. Euthanasia, Tissue Processing, Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Imaging, and Cell Quantification
2.8. Proximity Ligation Assay
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Initial SE Severity
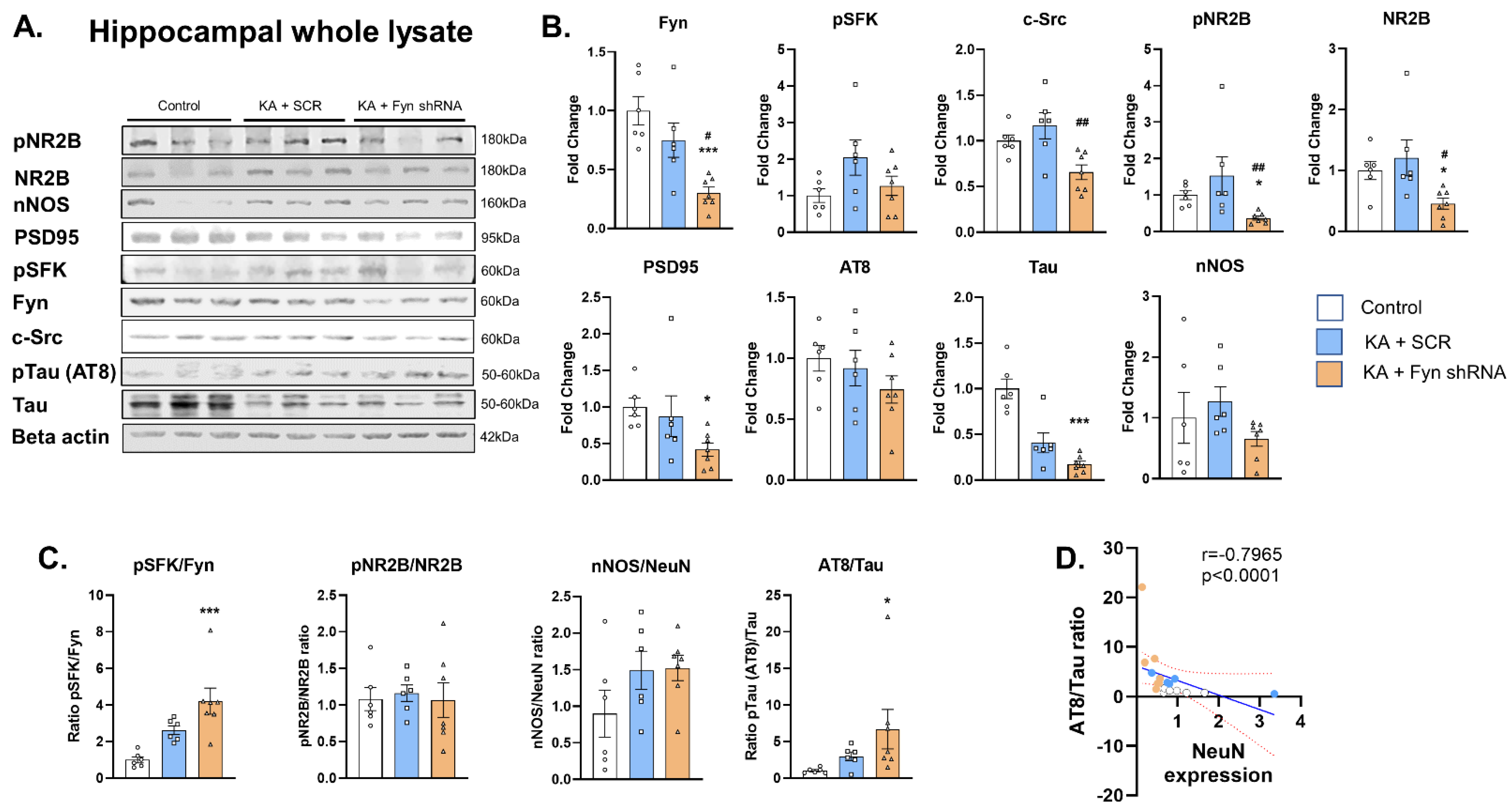
3.2. Fyn Knockdown Reduced Fyn but Increased pSFKY416 to Fyn Ratio in the Hippocampus at 8 Days Post-SE
3.3. The Effects of Fyn Knockdown on Fyn Interacting Molecules: Src, pNR2B, NR2B, PSD95, pTau (AT8), Total Tau, and nNOS Expression in the Hippocampus
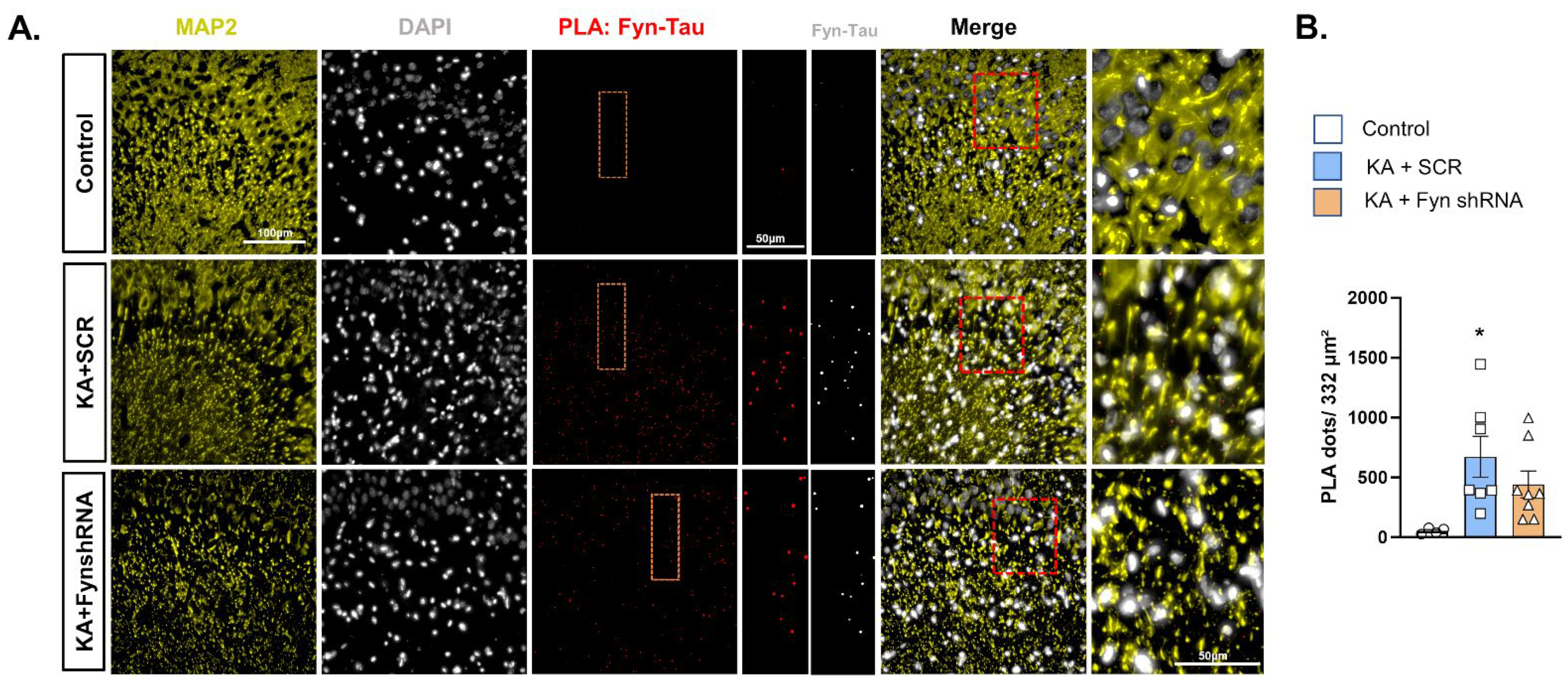
3.4. The Effects of Fyn Knockdown on Fyn–Tau Interactions
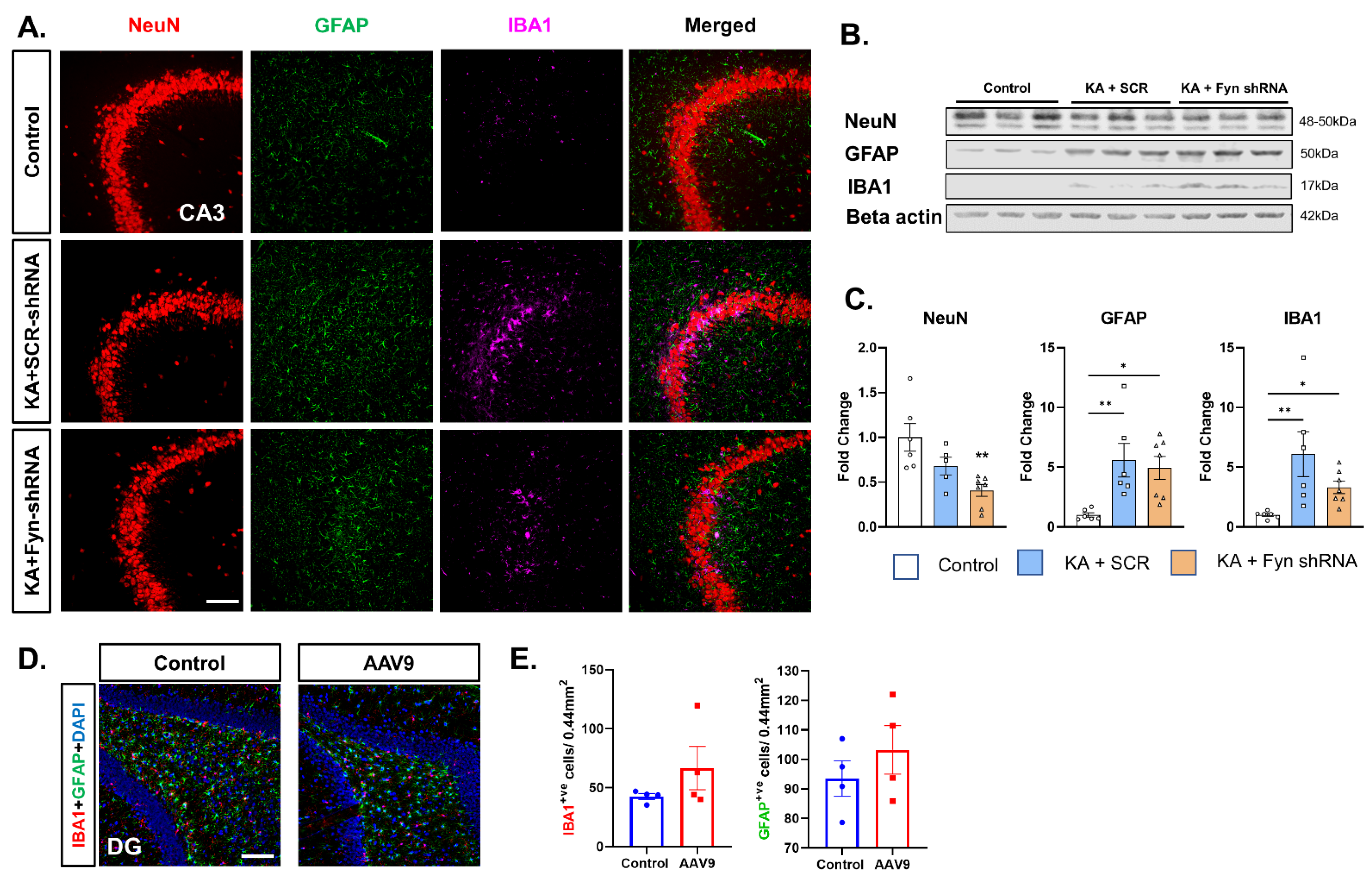
3.5. Hippocampal Neuronal Fyn Knockdown Did Not Prevent Neuronal Loss After SE and Also Had No Effect on SE-Induced Gliosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SFK | Src family kinase |
| KA | Kainate |
| SE | Status epilepticus |
| CaMKII | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| AAV | Adeno-associated viral vector |
| PLA | Proximity ligation assay |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NR2B | NMDA receptor subunit 2B |
| PSD95 | Post-synaptic density protein 95 |
| pSFKY416 | Phosphorylated Src family kinase at tyrosine 416 |
| pNR2BY1472 | Phosphorylated NR2B at tyrosine 1472 |
| NeuN | Neuronal Nuclear Protein |
| AT8 | Hyperphosphorylated tau at epitopes detected by AT8 antibody |
| SH3 | Src Homology 3 domain |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IBA1 | Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (microglial marker) |
| GFAP | Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (astrocytic marker) |
| rAAV | Recombinant adeno-associated viral vector |
| GC/mL | Genome copies per milliliter |
| SCR | Scramble (control vector) |
| miR30 | MicroRNA-30 |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus promoter |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| PTZ | Pentylenetetrazole |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| GPx-1 | Glutathione Peroxidase-1 |
| nNOS | Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| PKCδ | Protein Kinase C delta |
| Y18 | Tyrosine 18 (of tau) |
| eGFP | Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| ARRIVE | Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| NINDS | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke |
References
- CDC. Epilepsy Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/epilepsy/about/index.html (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Epilepsy. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Early Identification of Refractory Epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, P.; Brodie, M.J. Do the Third-Generation Antiseizure Medications Provide the “Magic Bullet” for Drug-Resistant Epilepsy? Focus on Cenobamate. Epilepsia 2025, 66, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Potschka, H.; Sisodiya, S.M.; Vezzani, A. Drug Resistance in Epilepsy: Clinical Impact, Potential Mechanisms, and New Innovative Treatment Options. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 606–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Schmidt, D. New Horizons in the Development of Antiepileptic Drugs: Innovative Strategies. Epilepsy Res. 2006, 69, 183–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Schmidt, D. Modern Antiepileptic Drug Development Has Failed to Deliver: Ways out of the Current Dilemma. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 657–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, M.C.; Thippeswamy, T. Inhibitors of Src Family Kinases, Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase, and NADPH Oxidase as Potential CNS Drug Targets for Neurological Diseases. CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; White, H.S. Animal Models of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy as Tools for Deciphering the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Pharmacoresistance and Discovering More Effective Treatments. Cells 2023, 12, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; French, J.; Bartfai, T.; Baram, T.Z. The Role of Inflammation in Epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, A.; Lukasiuk, K.; Dudek, F.E.; Staley, K.J. Epileptogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a022822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttachary, S.; Sharma, S.; Stark, S.; Thippeswamy, T. Seizure-Induced Oxidative Stress in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 745613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, N.; Saminathan, H.; Jin, H.; Neal, M.; Harischandra, D.S.; Gordon, R.; Kanthasamy, K.; Lawana, V.; Sarkar, S.; Luo, J.; et al. Fyn Kinase Regulates Microglial Neuroinflammatory Responses in Cell Culture and Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10058–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Carlson, S.; Puttachary, S.; Sarkar, S.; Showman, L.; Putra, M.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Thippeswamy, T. Role of the Fyn-PKCδ Signaling in SE-Induced Neuroinflammation and Epileptogenesis in Experimental Models of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 110, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, L.M.; Ke, Y.D.; Delerue, F.; Bi, M.; Gladbach, A.; van Eersel, J.; Wölfing, H.; Chieng, B.C.; Christie, M.J.; Napier, I.A.; et al. Dendritic Function of Tau Mediates Amyloid-Beta Toxicity in Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Models. Cell 2010, 142, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.; Rao, N.S.; Gardner, C.; Liu, G.; Trommater, J.; Bunney, M.; Gage, M.; Bassuk, A.G.; Hefti, M.; Lee, G.; et al. Enhanced Fyn-Tau and NR2B-PSD95 Interactions in Epileptic Foci in Experimental Models and Human Epilepsy. Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Thangavel, R.; Sharma, V.M.; Litersky, J.M.; Bhaskar, K.; Fang, S.M.; Do, L.H.; Andreadis, A.; Hoesen, G.V.; Ksiezak-Reding, H. Phosphorylation of Tau by Fyn: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.S.; Putra, M.; Meyer, C.; Almanza, A.; Thippeswamy, T. The Effects of Src Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Saracatinib, on the Markers of Epileptogenesis in a Mixed-Sex Cohort of Adult Rats in the Kainic Acid Model of Epilepsy. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1294514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of Seizure Activity by Electrical Stimulation: II. Motor Seizure. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.; Puttachary, S.; Liu, G.; Lee, G.; Thippeswamy, T. Fyn-Tau Ablation Modifies PTZ-Induced Seizures and Post-Seizure Hallmarks of Early Epileptogenesis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 592374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, M.; Vasanthi, S.S.; Rao, N.S.; Meyer, C.; Otterloo, M.V.; Thangi, L.; Thedens, D.R.; Kannurpatti, S.S.; Thippeswamy, T. Inhibiting Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase with 1400W Reduces Soman (GD)-Induced Ferroptosis in Long-Term Epilepsy-Associated Neuropathology: Structural and Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlations with Neurobehavior and Brain Pathology. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024, 388, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Carlson, S.; Gregory-Flores, A.; Hinojo-Perez, A.; Olson, A.; Thippeswamy, T. Mechanisms of Disease-Modifying Effect of Saracatinib (AZD0530), a Src/Fyn Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, in the Rat Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 156, 105410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, J.L.; de Jong, Y.P.; Terhorst, C.; Herzog, R.W. Immune Responses to Viral Gene Therapy Vectors. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Samulski, R.J. Engineering Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors for Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.L.; Dayton, R.D.; Diaczynsky, C.G.; Wang, D.B. Pronounced Microgliosis and Neurodegeneration in Aged Rats after Tau Gene Transfer. Neurobiol. Aging 2010, 31, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Drummond, E.S.; Muhling, J.; Martins, R.N.; Wijaya, L.K.; Ehlert, E.M.; Harvey, A.R. Pathology Associated with AAV Mediated Expression of Beta Amyloid or C100 in Adult Mouse Hippocampus and Cerebellum. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguore, W.A.; Domire, J.S.; Button, D.; Wang, Y.; Dufour, B.D.; Srinivasan, S.; McBride, J.L. AAV-PHP.B Administration Results in a Differential Pattern of CNS Biodistribution in Non-Human Primates Compared with Mice. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 2018–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, B.; Nho, B.; Seung, H.; Helmold, B.; Park, H.; Gözütok, Ö.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Ye, S.; Lee, H.; et al. Novel rAAV Vector Mediated Intrathecal HGF Delivery Has an Impact on Neuroimmune Modulation in the ALS Motor Cortex with TDP-43 Pathology. Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, F.; McDermott, E.; Mak, S.; Walsh, D.; Turnbull, M.; LeBeau, F.E.N.; Jackson, A.; Trevelyan, A.J.; Clowry, G.J. AAV8 Vector Induced Gliosis Following Neuronal Transgene Expression. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1287228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Liu, F.; Gong, C.-X.; Alonso, A.d.C.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Mechanisms of Tau-Induced Neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basheer, N.; Smolek, T.; Hassan, I.; Liu, F.; Iqbal, K.; Zilka, N.; Novak, P. Does Modulation of Tau Hyperphosphorylation Represent a Reasonable Therapeutic Strategy for Alzheimer’s Disease? From Preclinical Studies to the Clinical Trials. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2197–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, H.B. Targeting Fyn Kinase in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 83, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tang, B.; Fang, M.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, X. Altered Expression of C-Abl in Patients with Epilepsy and in a Rat Model. Synapse 2014, 68, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandía-Cristi, A.; Gutiérrez, D.A.; Dulcey, A.E.; Lara, M.; Vargas, L.; Lin, Y.-H.; Jimenez-Muñoz, P.; Larenas, G.; Xu, X.; Wang, A.; et al. Prophylactic Treatment with the C-Abl Inhibitor, Neurotinib, Diminishes Neuronal Damage and the Convulsive State in Pilocarpine-Induced Mice. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggon, T.J.; Eck, M.J. Structure and Regulation of Src Family Kinases. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7918–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scales, T.M.; Derkinderen, P.; Leung, K.-Y.; Byers, H.L.; Ward, M.A.; Price, C.; Bird, I.N.; Perera, T.; Kellie, S.; Williamson, R.; et al. Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Tau by the Src Family Kinases Lck and Fyn. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebouvier, T.; Scales, T.M.E.; Williamson, R.; Noble, W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Hanger, D.P.; Reynolds, C.H.; Anderton, B.H.; Derkinderen, P. The Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau Is Also Phosphorylated on Tyrosine. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2009, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Stein, L.; Thomas, R.; Djukic, B.; Taneja, P.; Knox, J.; Vossel, K.; Mucke, L. Phosphorylation of Tau at Y18, but Not Tau-Fyn Binding, Is Required for Tau to Modulate NMDA Receptor-Dependent Excitotoxicity in Primary Neuronal Culture. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Puttachary, S.; Thippeswamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G.; Thippeswamy, T. Status Epilepticus: Behavioral and Electroencephalography Seizure Correlates in Kainate Experimental Models. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, J.; Tezuka, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Sagara, H.; Yamamoto, T. Loss of Fyn Tyrosine Kinase on the C57BL/6 Genetic Background Causes Hydrocephalus with Defects in Oligodendrocyte Development. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 38, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, A.; Moyano, T.; Gutiérrez, D.A.; Carvajal, F.J.; Cerpa, W.; Hanley, J.G.; Gutiérrez, R.A.; Álvarez, A.R. C-Abl Regulates a Synaptic Plasticity-Related Transcriptional Program Involved in Memory and Learning. Prog. Neurobiol. 2021, 205, 102122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Denning, M.F. Fyn Is Induced by Ras/PI3K/Akt Signaling and Is Required for Enhanced Invasion/Migration. Mol. Carcinog. 2011, 50, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, G.; Basagni, F.; Rosini, M.; Minarini, A. Role of Fyn Kinase Inhibitors in Switching Neuroinflammatory Pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 4738–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Fu, Y. FYN: Emerging Biological Roles and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.E.; Colombo, G.; Schulz, R.; Siegert, S. Targeting Microglia with Lentivirus and AAV: Recent Advances and Remaining Challenges. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 707, 134310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Hosoi, N.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Fukai, Y.; Hiraga, A.; Nakai, J.; Nitta, K.; Shinohara, Y.; Konno, A.; Hirai, H. Development of Microglia-Targeting Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors as Tools to Study Microglial Behavior in Vivo. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamataki, M.; Rissiek, B.; Magnus, T.; Körbelin, J. Microglia Targeting by Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1425892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, D.R.; Leek, J.M.; Falduto, M.T.; Torres, K.E.O.; Sell, S.L.; Parsley, M.A.; Cowart, J.C.; Uchida, T.; Micci, M.-A.; DeWitt, D.S.; et al. Effects of AAV-Mediated Knockdown of nNOS and GPx-1 Gene Expression in Rat Hippocampus after Traumatic Brain Injury. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, T.; Roth, J.R.; Thompson, S.J.; Aldaher, A.R.; Cochran, J.N.; Roberson, E.D. A Peptide Inhibitor of Tau-SH3 Interactions Ameliorates Amyloid-β Toxicity. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

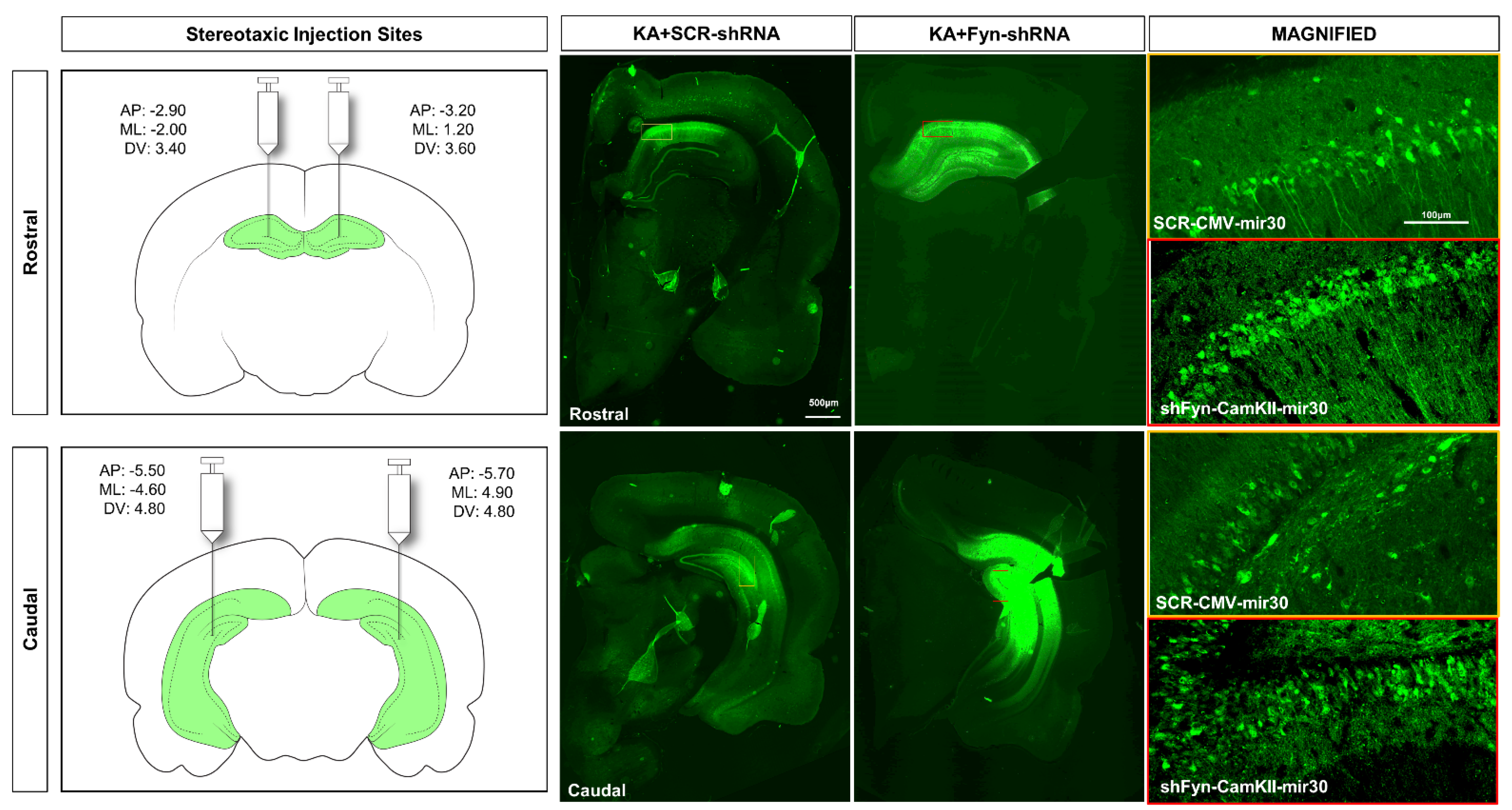
| Scramble | Fyn Knockdown | |
|---|---|---|
| Vector ID | VB010000-9397wgw | VB220605-1062nve |
| Vector Name | pAAV[miR30]-CMV>EGFP:Scramble_miR30-shRNA:WPRE | pAAV[2miR30]- Camk2a(short)>EGFP:{rFyn[shRNA#3]}: {rFyn[shRNA#2]}:WPRE |
| Vector Type | Mammalian miR30-shRNA Knockdown AAV Vector | Mammalian Dual miR30-shRNA Knockdown AAV Vector |
| Inserted Promoter | CMV | Camk2a(short) |
| Inserted shRNA | Scramble_miR30-shRNA | {rFyn[shRNA#3]}, {rFyn[shRNA#2]} |
| Target Sequence | ACCTAAGGTTAAGTCGCCCTCG | GTGAAGGACGGGCTCTGAAATT, CTGTGTGCAATGTAAGGATAAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, N.S.; Putra, M.; Meyer, C.; Parameswaran, S.; Thippeswamy, T. The Effects of Neuronal Fyn Knockdown in the Hippocampus in the Rat Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cells 2025, 14, 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100743
Rao NS, Putra M, Meyer C, Parameswaran S, Thippeswamy T. The Effects of Neuronal Fyn Knockdown in the Hippocampus in the Rat Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cells. 2025; 14(10):743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100743
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Nikhil S., Marson Putra, Christina Meyer, Sirisha Parameswaran, and Thimmasettappa Thippeswamy. 2025. "The Effects of Neuronal Fyn Knockdown in the Hippocampus in the Rat Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy" Cells 14, no. 10: 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100743
APA StyleRao, N. S., Putra, M., Meyer, C., Parameswaran, S., & Thippeswamy, T. (2025). The Effects of Neuronal Fyn Knockdown in the Hippocampus in the Rat Kainate Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Cells, 14(10), 743. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100743







