Inverse Bicontinuous and Discontinuous Phases of Lipids, and Membrane Curvature
Abstract
1. Introduction
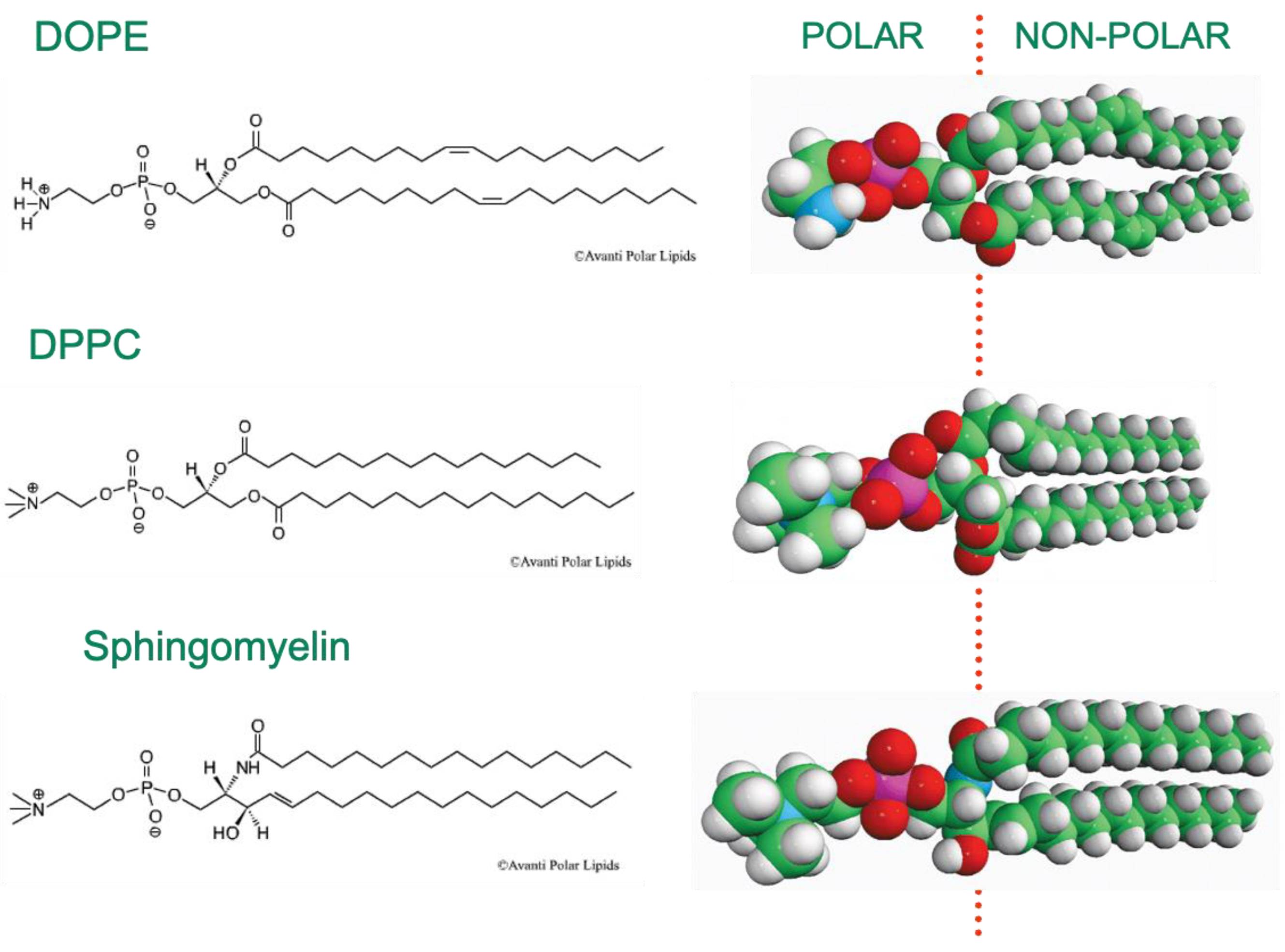
2. Amphiphiles and Lipid Membrane Self-Assembly
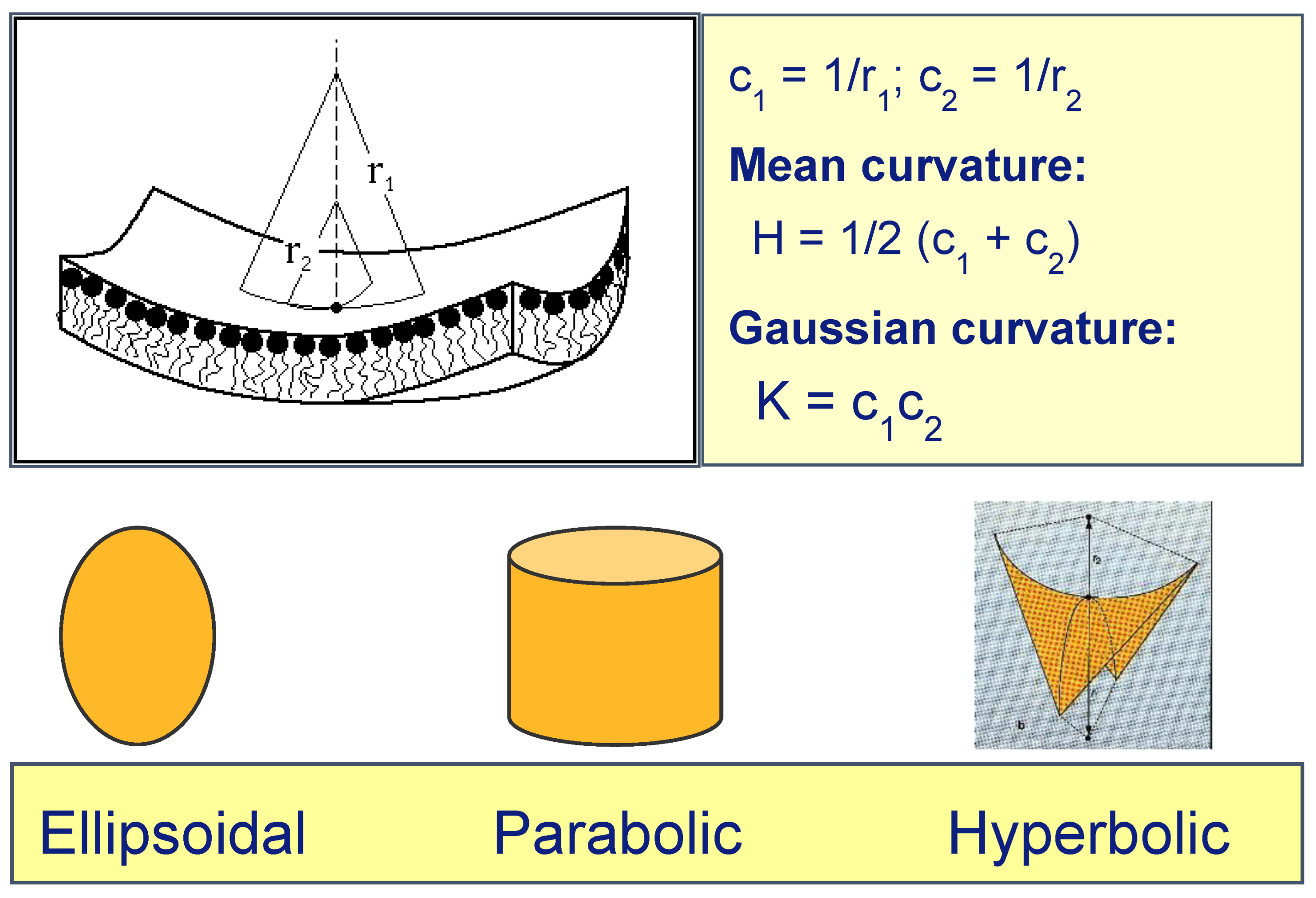
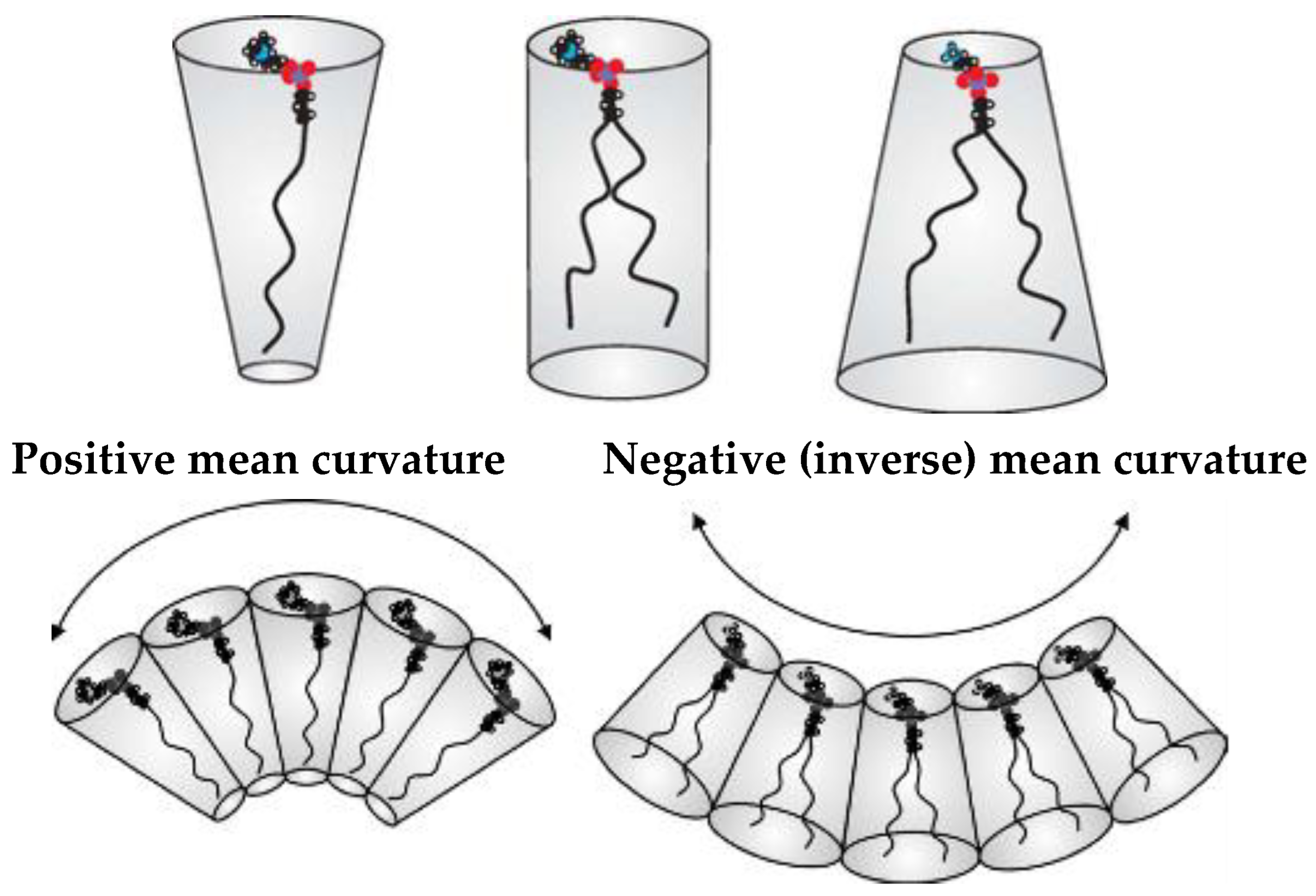
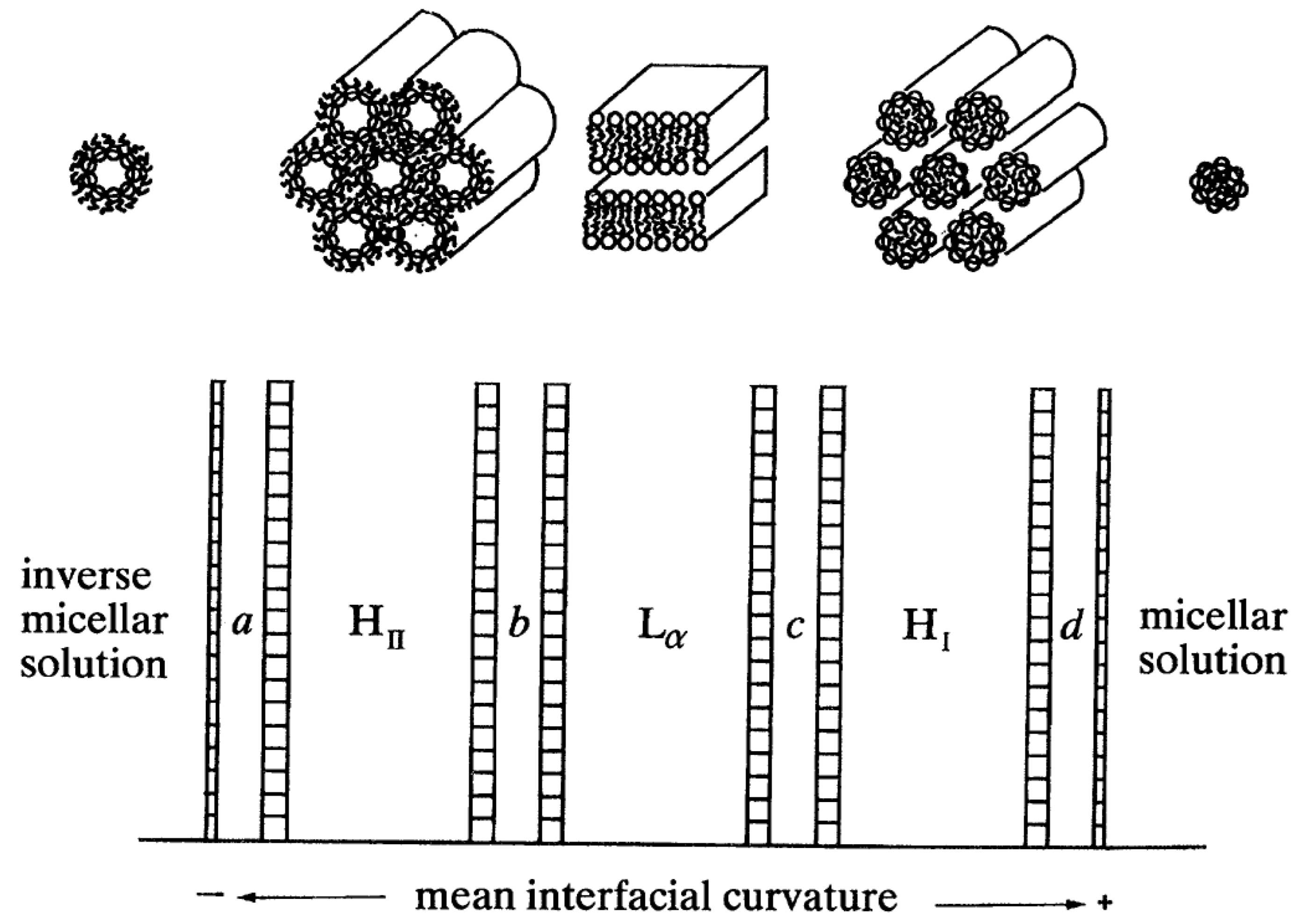
3. Interfacial Curvature and Lyotropic Phase Diagrams
- When c1 and c2 have the same sign (both positive or both negative), K > 0, and the interface is elliptic (e.g., a spherical lipid vesicle).
- When either c1 or c2 is zero, K = 0, and the interface is parabolic (e.g., flat bilayers, or cylinders as in the inverse hexagonal HII phase.)
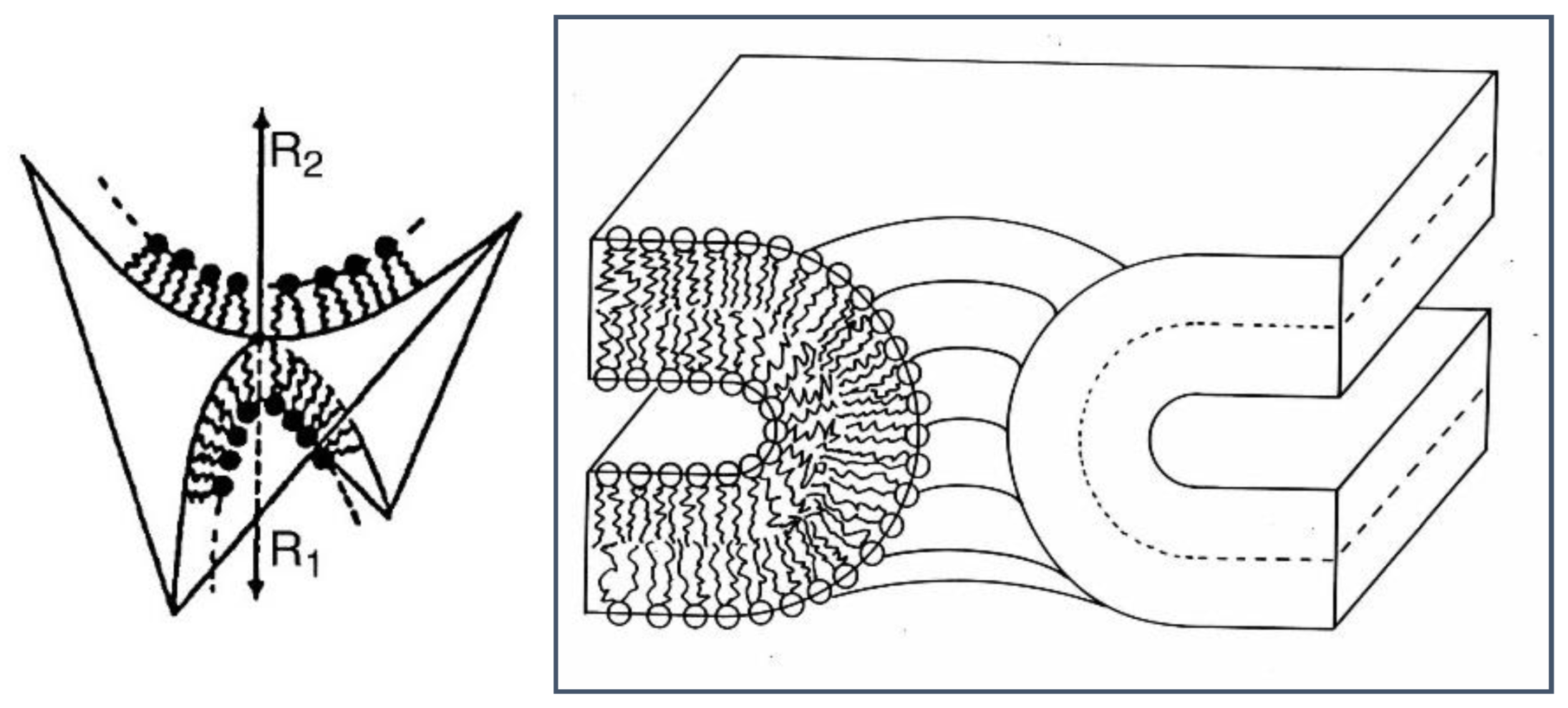
- When c1 and c2 have opposite signs, K < 0, and the interface is hyperbolic (e.g., a saddle-surface), as found transiently in membrane fusion channels, and stably within bicontinuous cubic phases.
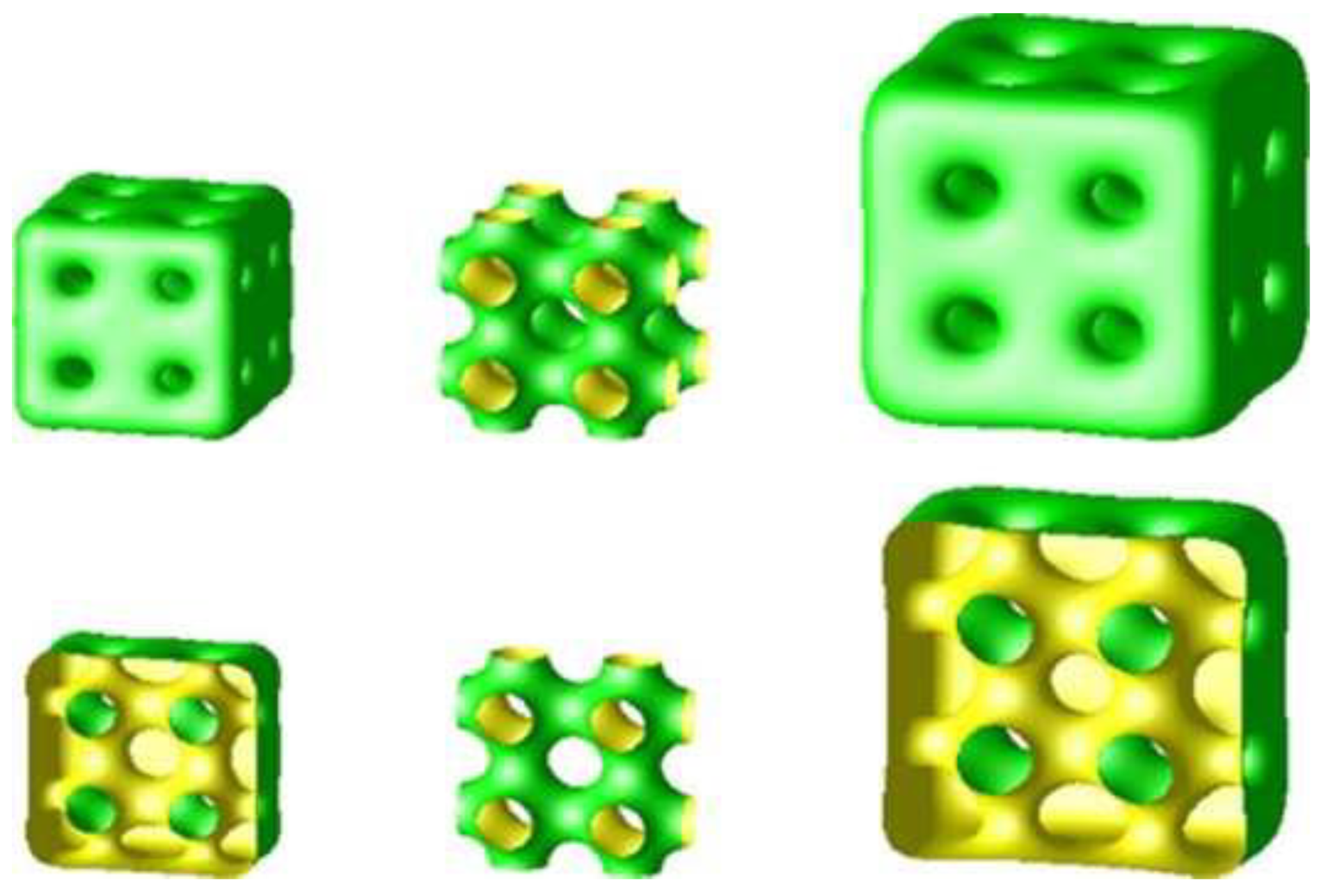
4. Inverse Bicontinuous Cubic Phases of Lipids
5. Relationship Between Membrane Curvature and Membrane Fusion
6. In Cubo Crystallisation of Membrane Proteins
7. Complex Membrane Morphologies in Biological Systems
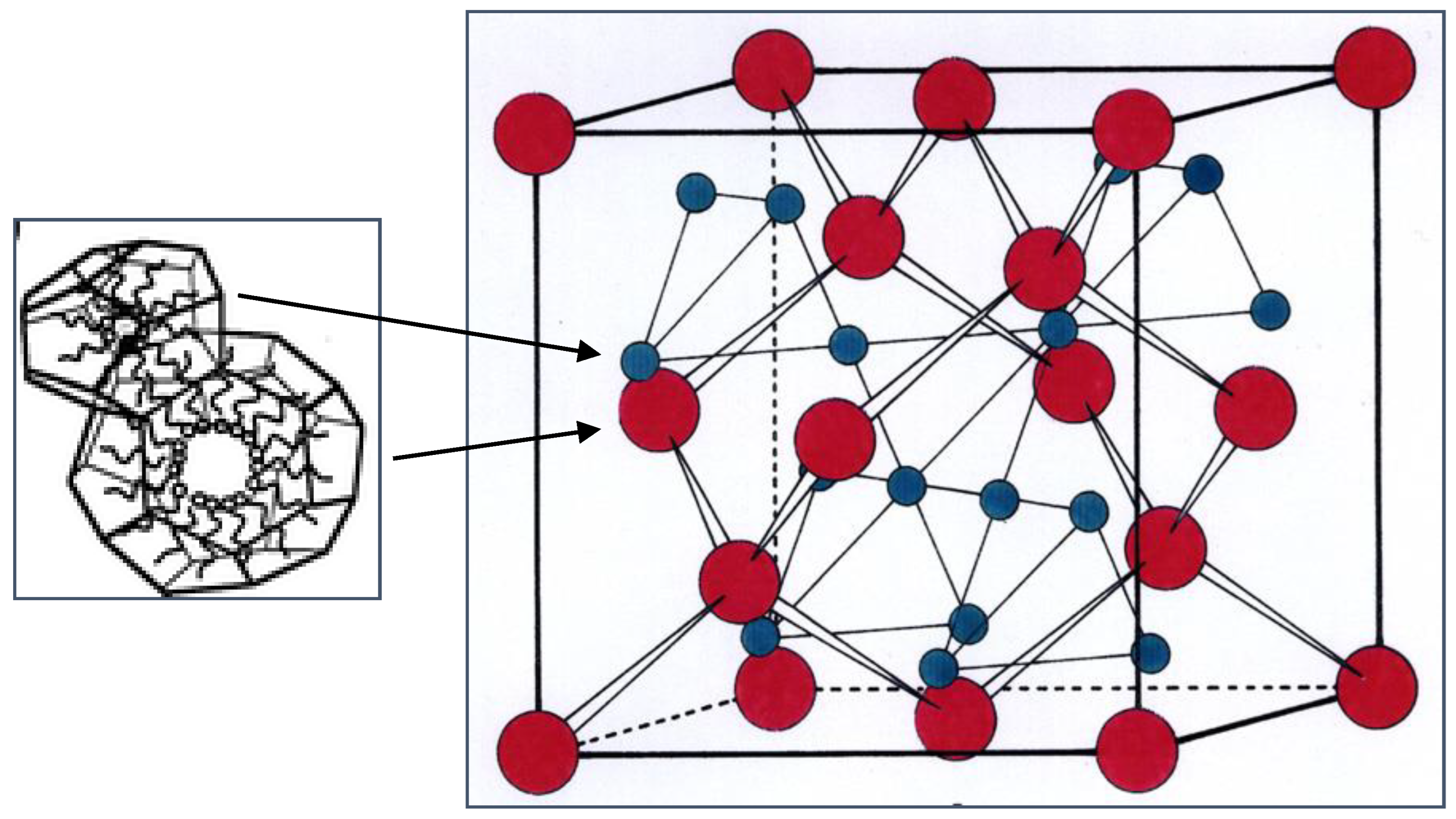
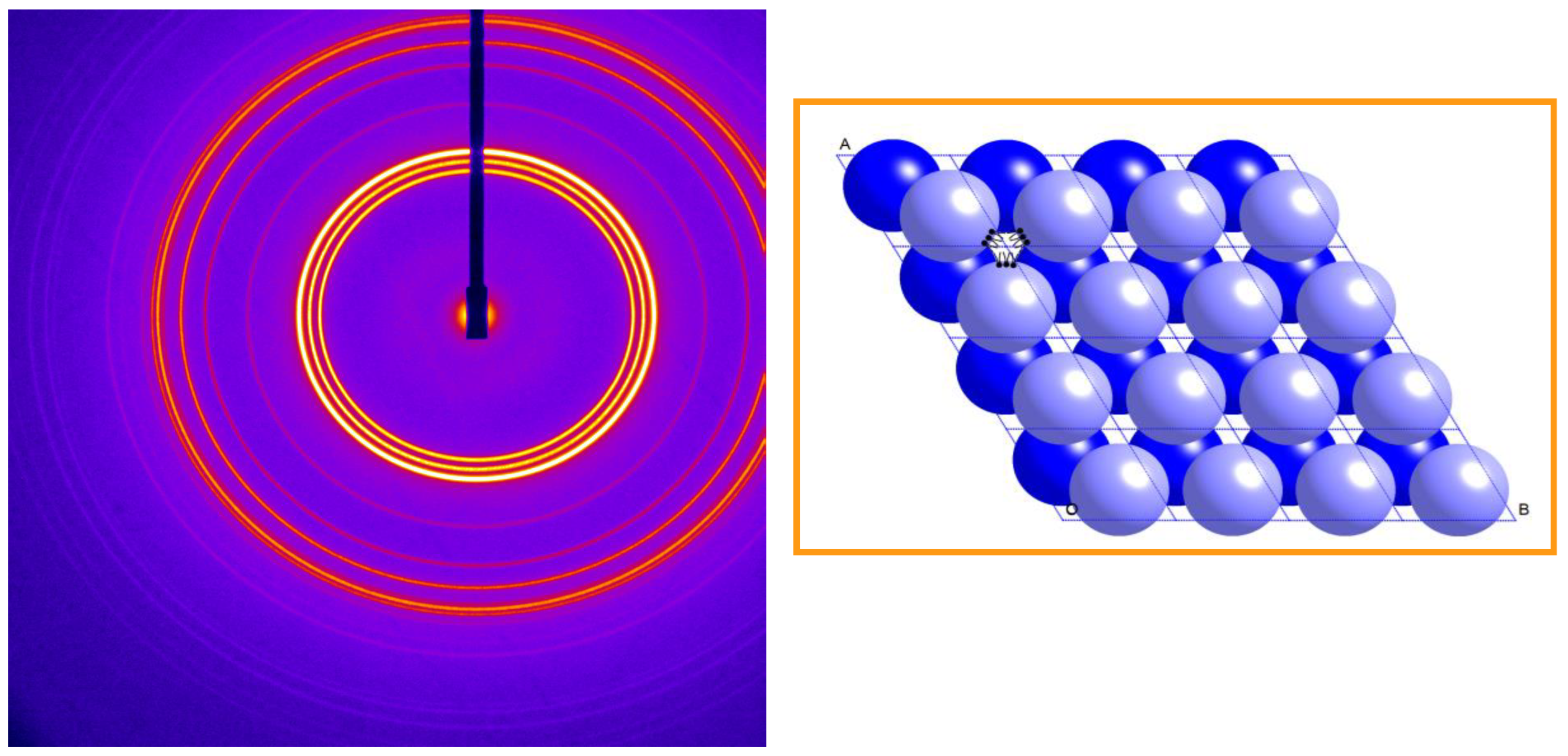
8. Inverse Discontinuous Lipid Phases
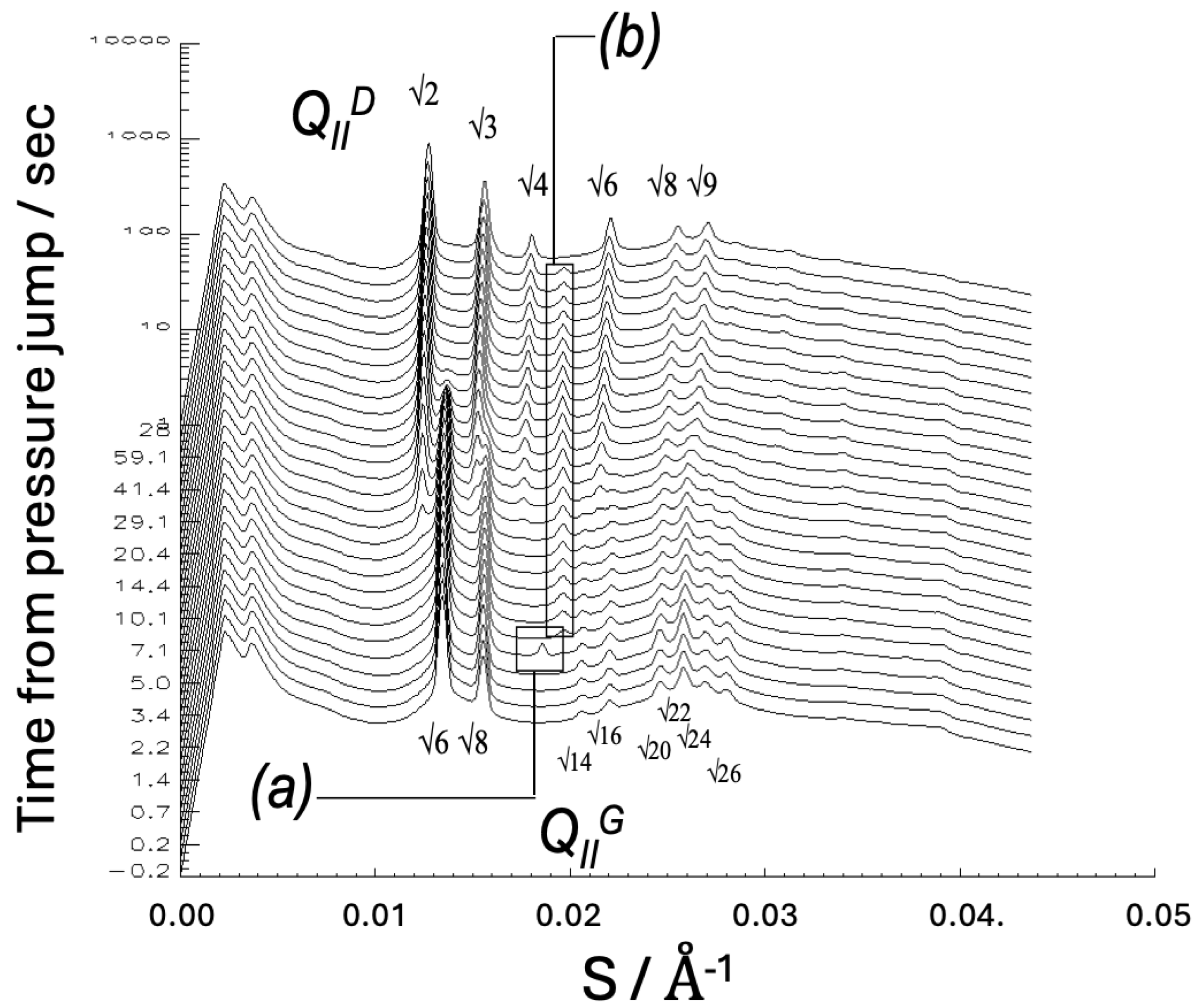
9. Hydrostatic Pressure Effects on Lipid Phase Behaviour
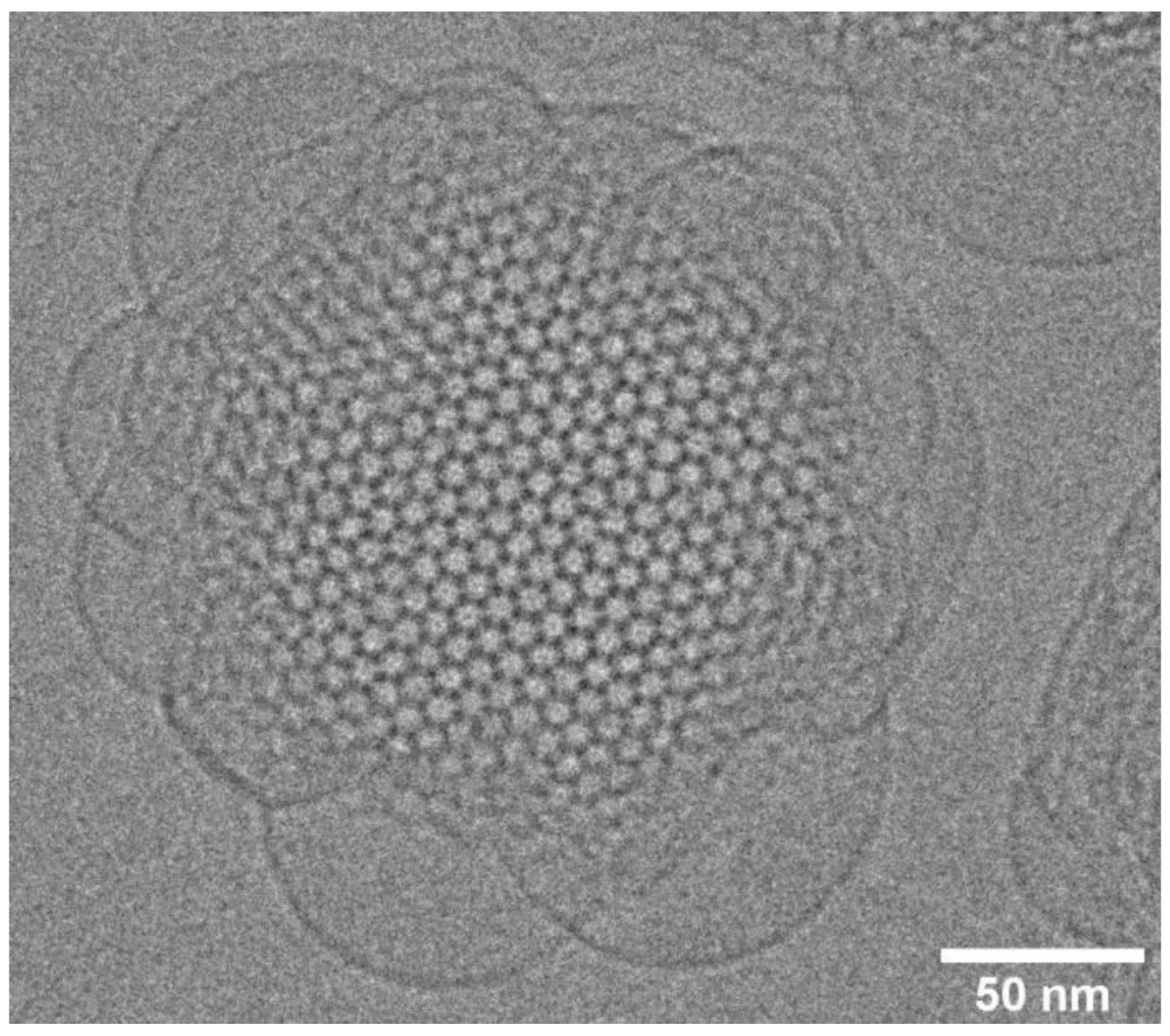
10. Lipid Nanoparticles: Cubosomes, Hexosomes, and Micellosomes
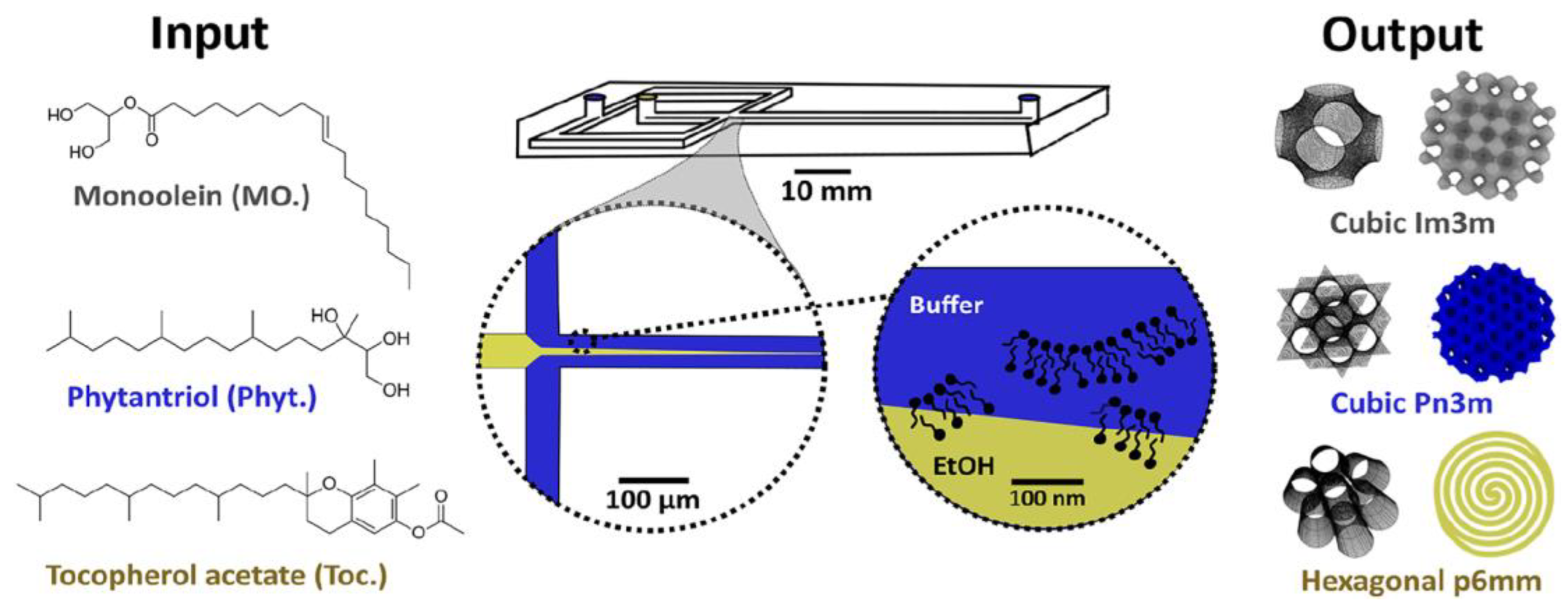
11. Microfluidic Platforms for Production of Lipid Nanoparticles
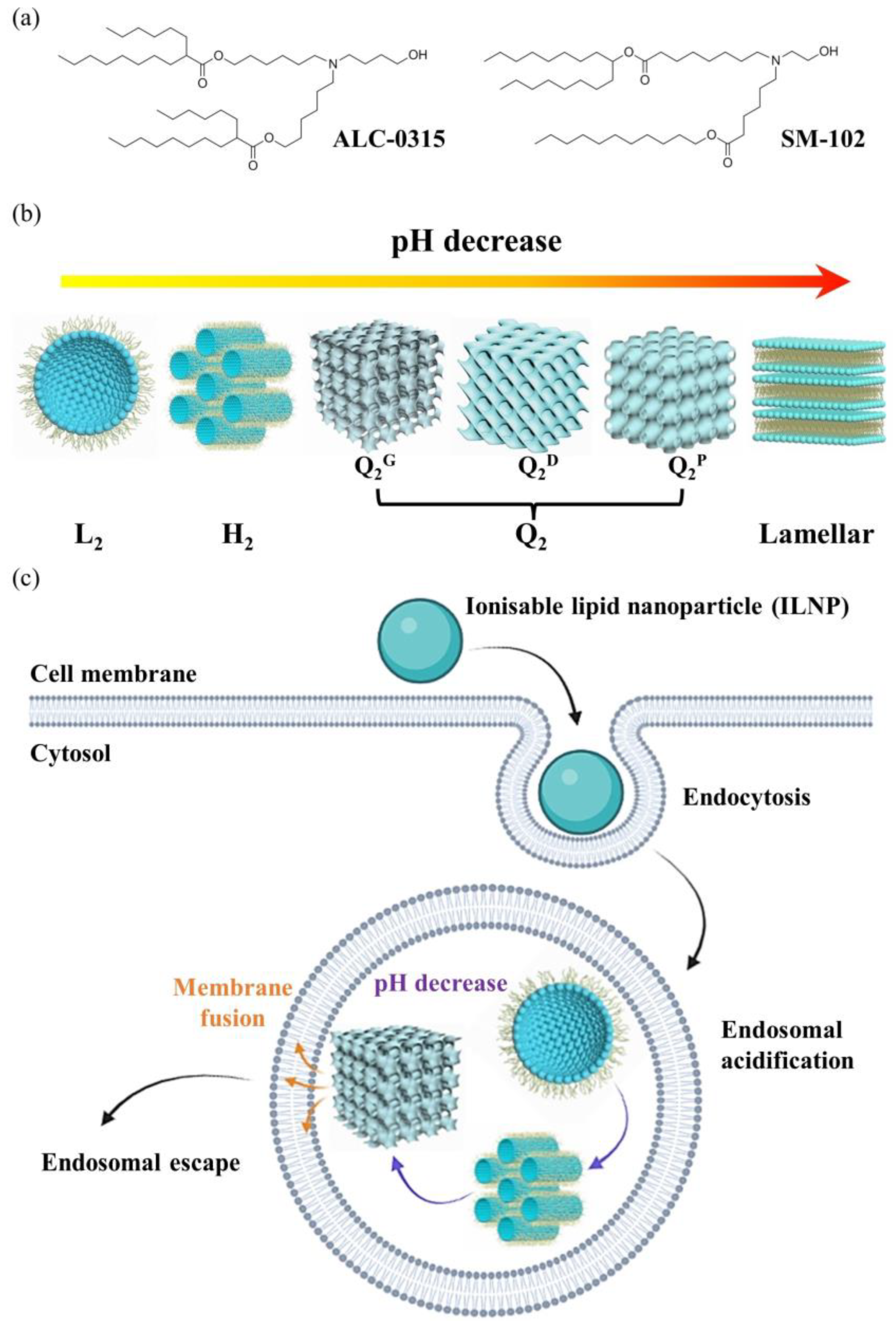
12. pH-Triggered Changes in Connectivity Within Lipid Nanoparticles
13. pH-Dependent Phase Transitions in Cationic Ionizable Lipid/Cholesterol Mixtures
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bassereau, P.; Jin, R.; Baumgart, T.; Deserno, M.; Dimova, R.; Frolov, V.A.; Bashkirov, P.V.; Grubmuller, H.; Jahn, R.; Risselada, H.J.; et al. The 2018 biomembrane curvature and remodeling roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 343001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozelli, J.C., Jr.; Epand, R.M. Membrane Shape and the Regulation of Biological Processes. J. Mol. Biol. 2020, 432, 5124–5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Baumgart, T. Membrane reshaping by protein condensates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2023, 1865, 184121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D. Elastic curvature constants of lipid monolayers and bilayers. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2006, 144, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campelo, F.; Arnarez, C.; Marrink, S.J.; Kozlov, M.M. Helfrich model of membrane bending: From Gibbs theory of liquid interfaces to membranes as thick anisotropic elastic layers. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 208, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deserno, M. Fluid lipid membranes: From differential geometry to curvature stresses. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 185, 11–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalutskii, M.A.; Galimzyanov, T.R.; Pinigin, K.V. Determination of elastic parameters of lipid membranes from simulation under varied external pressure. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, 024414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzati, V. Biological significance of lipid polymorphism: The cubic phases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1997, 7, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzenga, R.; Seddon, J.M.; Drummond, C.J.; Boyd, B.J.; Schroder-Turk, G.E.; Sagalowicz, L. Nature-Inspired Design and Application of Lipidic Lyotropic Liquid Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1900818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, P.; Luzzati, V.; Delacroix, H. Cubic phases of lipid-containing systems. Structure analysis and biological implications. J. Mol. Biol. 1988, 204, 165–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzati, V.; Vargas, R.; Mariani, P.; Gulik, A.; Delacroix, H. Cubic phases of lipid-containing systems. Elements of a theory and biological connotations. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 229, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, J.M. Structure of the inverted hexagonal (HII) phase, and non-lamellar phase transitions of lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1031, 1–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancuylenberg, G.; Sadeghpour, A.; Tyler, A.I.I.; Rappolt, M. From angular to round: In depth interfacial analysis of binary phosphatidylethanolamine mixtures in the inverse hexagonal phase. Soft Matter 2023, 19, 8519–8530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golani, G.; Schwarz, U.S. High curvature promotes fusion of lipid membranes: Predictions from continuum elastic theory. Biophys. J. 2023, 122, 1868–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, J.; LjusbergWahren, H.; Almgren, M.; Larsson, K. Cubic lipid-water phase dispersed into submicron particles. Langmuir 1996, 12, 4611–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K. Bicontinuous cubic lipid-water particles and cubosomal dispersions. Mesoporous Cryst. Relat. Nano-Struct. Mater. 2004, 148, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Akinc, A.; Maier, M.A.; Manoharan, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Jayaraman, M.; Barros, S.; Ansell, S.; Du, X.; Hope, M.J.; Madden, T.D.; et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, G.C.; Ces, O.; Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M. Inverse lyotropic phases of lipids and membrane curvature. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, S1105–S1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobierski, J.; Wnetrzak, A.; Chachaj-Brekiesz, A.; Dynarowicz-Latka, P. Predicting the packing parameter for lipids in monolayers with the use of molecular dynamics. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 211, 112298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M.; Templer, R.H. Cubic Phases of Self-Assembled Amphiphilic Aggregates. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A-Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1993, 344, 377–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Hyde, S.T.; Larsson, K.; Lidin, S. Minimal-Surfaces and Structures—From Inorganic and Metal Crystals to Cell-Membranes and Bio-Polymers. Chem. Rev. 1988, 88, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M.; Duesing, P.M.; Winter, R.; Erbes, J. Modeling the phase behavior of the inverse hexagonal and inverse bicontinuous cubic phases in 2:1 fatty acid phosphatidylcholine mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7262–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M.; Warrender, N.A.; Syrykh, A.; Huang, Z.; Winter, R.; Erbes, J. Inverse bicontinuous cubic phases in 2:1 fatty acid phosphatidylcholine mixtures. The effects of chain length, hydration, and temperature. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7251–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, C.E.; Drummond, C.J. Nanostructured bicontinuous cubic lipid self-assembly materials as matrices for protein encapsulation. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3449–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, A.I.; Barriga, H.M.; Parsons, E.S.; McCarthy, N.L.; Ces, O.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J. Electrostatic swelling of bicontinuous cubic lipid phases. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 3279–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriga, H.M.; Tyler, A.I.; McCarthy, N.L.; Parsons, E.S.; Ces, O.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J. Temperature and pressure tuneable swollen bicontinuous cubic phases approaching nature’s length scales. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.S.W.; Leal, C. The stabilization of primitive bicontinuous cubic phases with tunable swelling over a wide composition range. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherezov, V.; Clogston, J.; Misquitta, Y.; Abdel-Gawad, W.; Caffrey, M. Membrane protein crystallization in meso: Lipid type-tailoring of the cubic phase. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, B.G.; MacDonald, R.C.; Siegel, D.P. Cubic phases in phosphatidylcholine-cholesterol mixtures: Cholesterol as membrane “fusogen”. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.P.; Kozlov, M.M. The Gaussian curvature elastic modulus of N-monomethylated dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine: Relevance to membrane fusion and lipid phase behavior. Biophys. J. 2004, 87, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltenegger, M.; Kremser, J.; Frewein, M.P.K.; Ziherl, P.; Bonthuis, D.J.; Pabst, G. Intrinsic lipid curvatures of mammalian plasma membrane outer leaflet lipids and ceramides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, E.M.; Rosenbusch, J.P. Lipidic cubic phases: A novel concept for the crystallization of membrane proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 14532–14535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, M. A comprehensive review of the lipid cubic phase or in meso method for crystallizing membrane and soluble proteins and complexes. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2015, 71, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.G.; DeVree, B.T.; Zou, Y.; Kruse, A.C.; Chung, K.Y.; Kobilka, T.S.; Thian, F.S.; Chae, P.S.; Pardon, E.; Calinski, D.; et al. Crystal structure of the beta2 adrenergic receptor-Gs protein complex. Nature 2011, 477, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shah, S.T.; Caffrey, M. Host Lipid and Temperature as Important Screening Variables for Crystallizing Integral Membrane Proteins in Lipidic Mesophases. Trials with Diacylglycerol Kinase. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 2846–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Marko, M.; Buttle, K.F.; Leith, A.; Mieczkowski, M.; Mannella, C.A. Cubic membrane structure in amoeba (Chaos carolinensis) mitochondria determined by electron microscopic tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 1999, 127, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almsherqi, Z.; Margadant, F.; Deng, Y. A look through ‘lens’ cubic mitochondria. Interface Focus. 2012, 2, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Angelova, A. Coronavirus-Induced Host Cubic Membranes and Lipid-Related Antiviral Therapies: A Focus on Bioactive Plasmalogens. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 630242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranathan, V.; Osuji, C.O.; Mochrie, S.G.; Noh, H.; Narayanan, S.; Sandy, A.; Dufresne, E.R.; Prum, R.O. Structure, function, and self-assembly of single network gyroid (I4132) photonic crystals in butterfly wing scales. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11676–11681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielsen, K.; De Raedt, H.; Stavenga, D.G. Reflectivity of the gyroid biophotonic crystals in the ventral wing scales of the Green Hairstreak butterfly, Callophrys rubi. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilts, B.D.; Apeleo Zubiri, B.; Klatt, M.A.; Butz, B.; Fischer, M.G.; Kelly, S.T.; Spiecker, E.; Steiner, U.; Schroder-Turk, G.E. Butterfly gyroid nanostructures as a time-frozen glimpse of intracellular membrane development. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, A.L.; Pirih, P.; Wang, L.; Patel, N.H.; Clode, P.L.; Schroder-Turk, G.E.; Wilts, B.D. Elucidating nanostructural organization and photonic properties of butterfly wing scales using hyperspectral microscopy. J. R. Soc. Interface 2024, 21, 20240185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, A.L.; Millsteed, A.J.; Kirkensgaard, J.J.K.; Shaw, J.; Clode, P.L.; Schroder-Turk, G.E. Composite material in the sea urchin Cidaris rugosa: Ordered and disordered micrometre-scale bicontinuous geometries. J. R. Soc. Interface 2024, 21, 20230597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, J.M.; Robins, J.; Gulik-Krzywicki, T.; Delacroix, H. Inverse micellar phases of phospholipids and glycolipids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, G.C.; Tyler, A.I.I.; Brooks, N.J.; Templer, R.H.; Ces, O.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M. Ordered micellar and inverse micellar lyotropic phases. Liq. Cryst. 2010, 37, 679–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M. An inverse face-centered cubic phase formed by diacylglycerol-phosphatidylcholine mixtures. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7997–8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, A.I.; Shearman, G.C.; Brooks, N.J.; Delacroix, H.; Law, R.V.; Templer, R.H.; Ces, O.; Seddon, J.M. Hydrostatic pressure effects on a hydrated lipid inverse micellar Fd3m cubic phase. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 3033–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzati, V.; Vargas, R.; Gulik, A.; Mariani, P.; Seddon, J.M.; Rivas, E. Lipid polymorphism: A correction. The structure of the cubic phase of extinction symbol Fd-- consists of two types of disjointed reverse micelles embedded in a three-dimensional hydrocarbon matrix. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delacroix, H.; Gulik-Krzywicki, T.; Seddon, J.M. Freeze fracture electron microscopy of lyotropic lipid systems: Quantitative analysis of the inverse micellar cubic phase of space group Fd3m (Q227). J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 258, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duesing, P.M.; Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M. Quantifying packing frustration energy in inverse lyotropic mesophases. Langmuir 1997, 13, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappolt, M.; Cacho-Nerin, F.; Morello, C.; Yaghmur, A. How the chain configuration governs the packing of inverted micelles in the cubic Fd3m-phase. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 6291–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M.; Zeb, N.; Templer, R.H.; McElhaney, R.N.; Mannock, D.A. An Fd3m lyotropic cubic phase in a binary glycolipid/water system. Langmuir 1996, 12, 5250–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiel, I.; Sagalowicz, L.; Mezzenga, R. A Reverse Micellar Mesophase of Face-Centered Cubic Fm(3)over-barm Symmetry in Phosphatidylcholine/Water/Organic Solvent Ternary Systems. Langmuir 2013, 29, 15805–15812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearman, G.C.; Tyler, A.I.; Brooks, N.J.; Templer, R.H.; Ces, O.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M. A 3-D hexagonal inverse micellar lyotropic phase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1678–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, J.A. Fast flip-flop of cholesterol and fatty acids in membranes: Implications for membrane transport proteins. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.X.; Baoukina, S.; Tieleman, D.P. Cholesterol Flip-Flop in Heterogeneous Membranes. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 2064–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, R.; Erbes, J.; Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M.; Syrykh, A.; Warrender, N.A.; Rapp, G. Inverse bicontinuous cubic phases in fatty acid/phosphatidylcholine mixtures: The effects of pressure and lipid composition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N.J.; Seddon, J.M. High Pressure X-ray Studies of Lipid Membranes and Lipid Phase Transitions. Z. Für Phys. Chem. 2014, 228, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, J.M.; Squires, A.M.; Conn, C.E.; Ces, O.; Heron, A.J.; Mulet, X.; Shearman, G.C.; Templer, R.H. Pressure-jump X-ray studies of liquid crystal transitions in lipids. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 2635–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, C.E.; Ces, O.; Mulet, X.; Finet, S.; Winter, R.; Seddon, J.M.; Templer, R.H. Dynamics of structural transformations between lamellar and inverse bicontinuous cubic lyotropic phases. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 108102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, A.M.; Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M.; Woenkhaus, J.; Winter, R.; Narayanan, T.; Finet, S. Kinetics and mechanism of the interconversion of inverse bicontinuous cubic mesophases. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2005, 72, 011502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, C.E.; Ces, O.; Squires, A.M.; Mulet, X.; Winter, R.; Finet, S.M.; Templer, R.H.; Seddon, J.M. A pressure-jump time-resolved X-ray diffraction study of cubic-cubic transition kinetics in monoolein. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, A.M.; Conn, C.E.; Seddon, J.M.; Templer, R.H. Quantitative model for the kinetics of lyotropic phase transitions involving changes in monolayer curvature. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A.E.; Zhou, Q. Lipid Nanoparticles horizontal line From Liposomes to mRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barriga, H.M.G.; Holme, M.N.; Stevens, M.M. Cubosomes: The Next Generation of Smart Lipid Nanoparticles? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 2958–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozdz, W.T. Cubosome Topologies at Various Particle Sizes and Crystallographic Symmetries. Langmuir 2015, 31, 13321–13326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
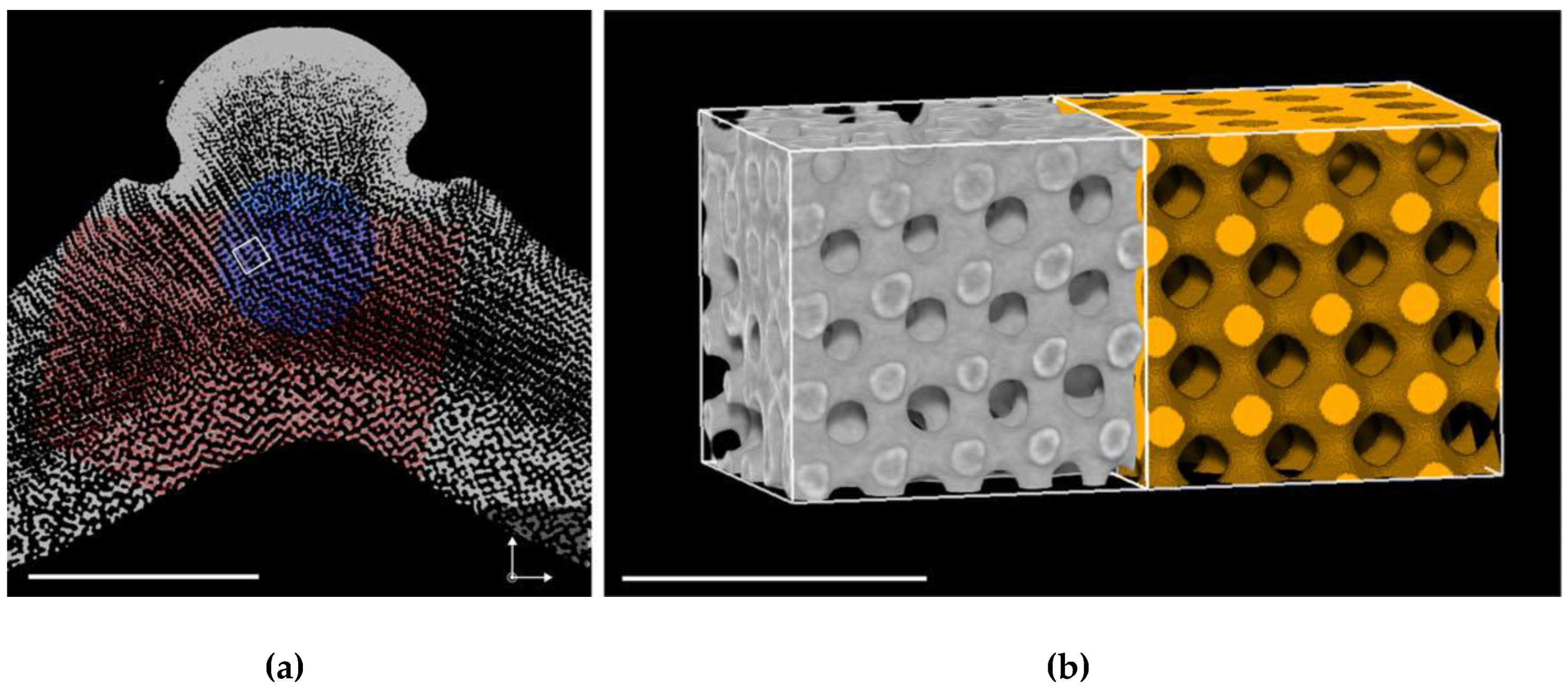
- Demurtas, D.; Guichard, P.; Martiel, I.; Mezzenga, R.; Hebert, C.; Sagalowicz, L. Direct visualization of dispersed lipid bicontinuous cubic phases by cryo-electron tomography. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
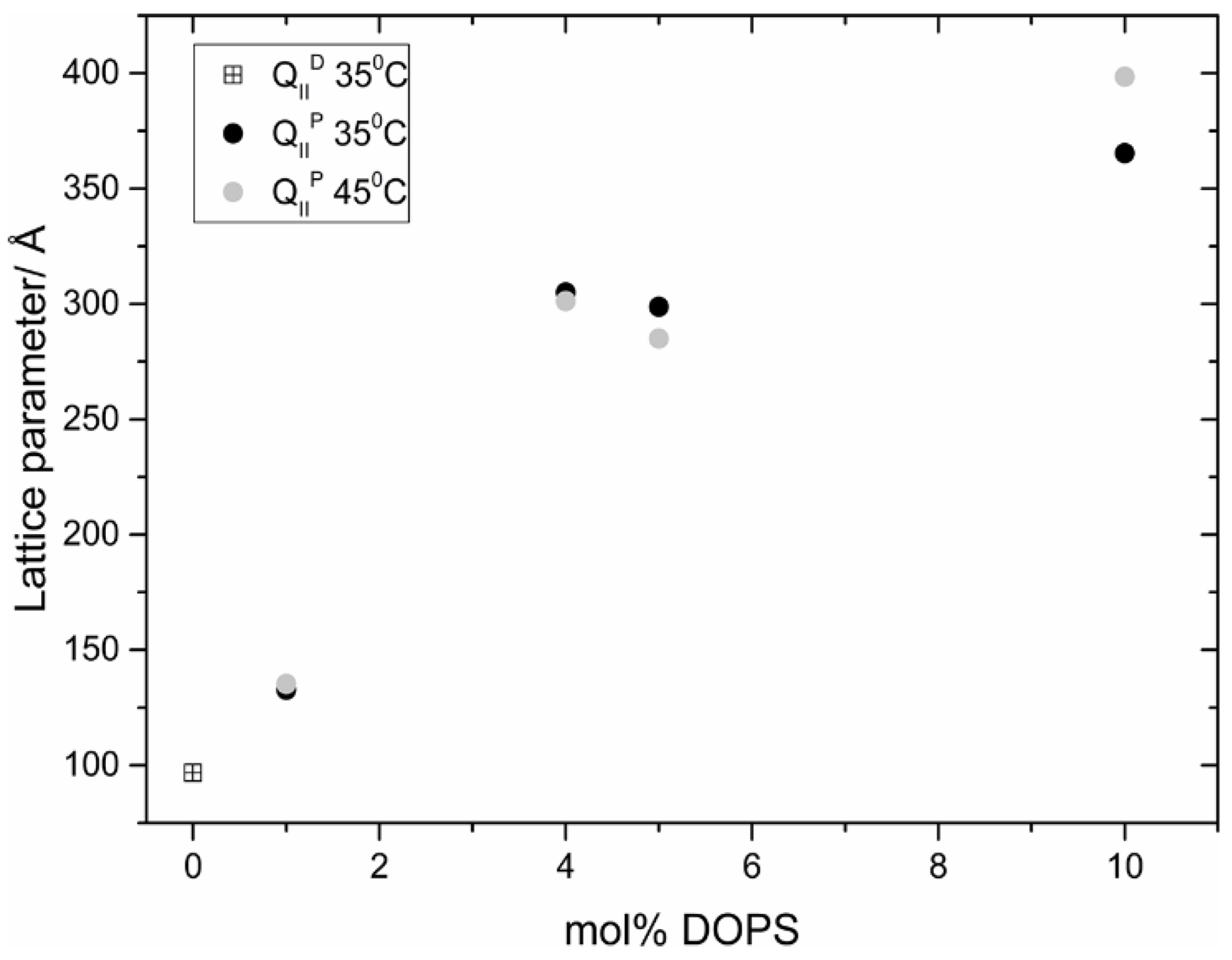
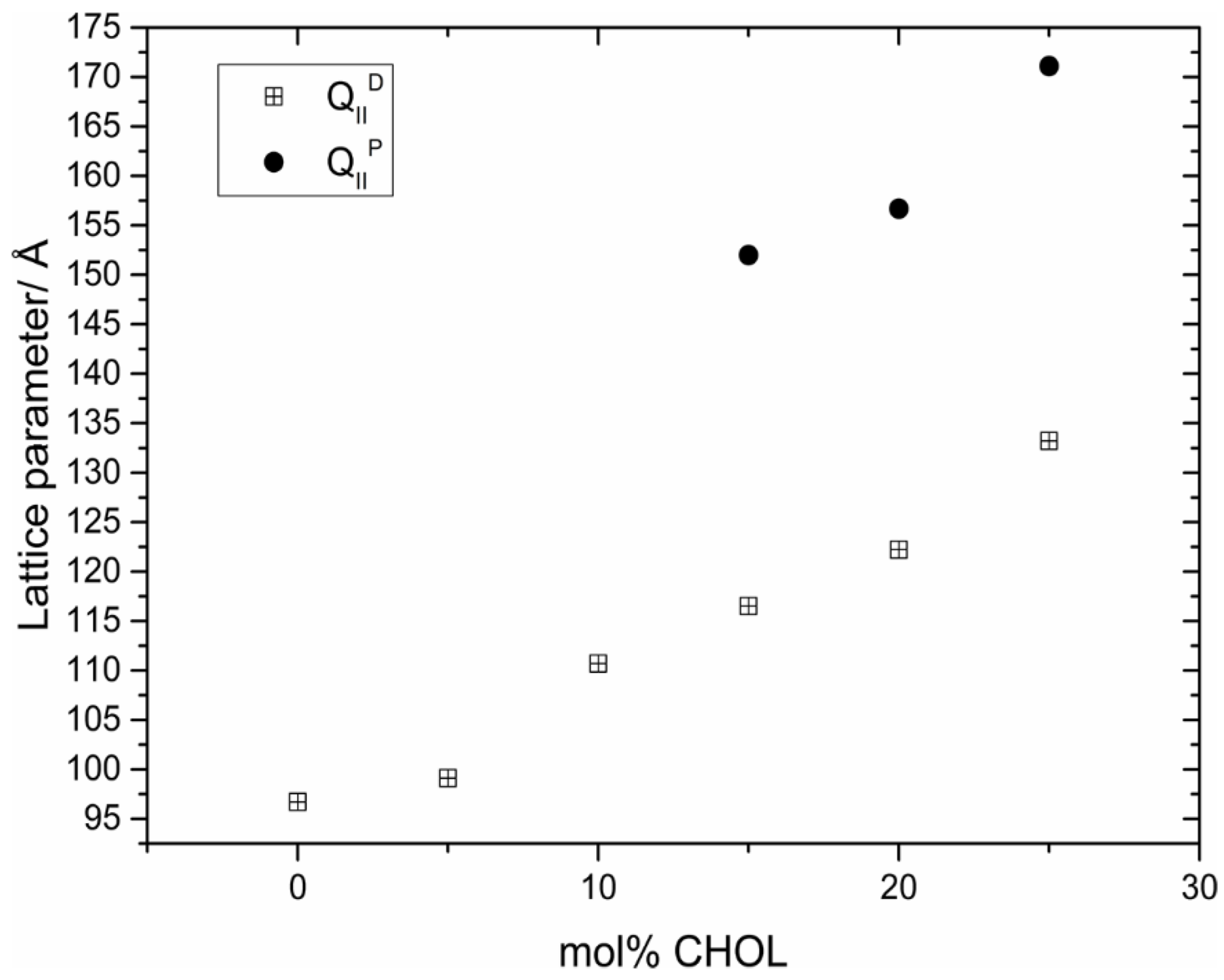
- Barriga, H.M.G.; Ces, O.; Law, R.V.; Seddon, J.M.; Brooks, N.J. Engineering Swollen Cubosomes Using Cholesterol and Anionic Lipids. Langmuir 2019, 35, 16521–16527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, C.; Bouxsein, N.F.; Ewert, K.K.; Safinya, C.R. Highly efficient gene silencing activity of siRNA embedded in a nanostructured gyroid cubic lipid matrix. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16841–16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Leal, C. Cuboplexes: Topologically Active siRNA Delivery. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10214–10226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Booth, A.; Rappolt, M.; Peckham, M.; Tyler, A.I.I.; Beales, P.A. Topological and Morphological Membrane Dynamics in Giant Lipid Vesicles Driven by Monoolein Cubosomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2025, 64, e202414970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, A.C.; Clulow, A.J.; Boyd, B.J. Formation of Self-Assembled Mesophases During Lipid Digestion. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 657886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadsater, M.; Barauskas, J.; Nylander, T.; Tiberg, F. Formation of Highly Structured Cubic Micellar Lipid Nanoparticles of Soy Phosphatidylcholine and Glycerol Dioleate and Their Degradation by Triacylglycerol Lipase. Acs Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 7063–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkington, C.P.; Seddon, J.M.; Elani, Y. Microfluidic technologies for the synthesis and manipulation of biomimetic membranous nano-assemblies. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 3693–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sung, J.; Chang, Y.; Alfeche, A.; Leal, C. Microfluidics Synthesis of Gene Silencing Cubosomes. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9196–9205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkington, C.P.; Contini, C.; Barritt, J.D.; Simpson, P.A.; Seddon, J.M.; Elani, Y. A microfluidic platform for the controlled synthesis of architecturally complex liquid crystalline nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Dyett, B.P.; Zhai, J.; Strachan, J.B.; Drummond, C.J.; Conn, C.E. Formation of particulate lipid lyotropic liquid crystalline nanocarriers using a microfluidic platform. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2023, 634, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.X.; Seddon, J.M.; Beales, P.A.; Rappolt, M.; Tyler, A.I.I. Breaking Isolation to Form New Networks: pH-Triggered Changes in Connectivity inside Lipid Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 16556–16565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipp, J.; Dabkowska, A.; Reiser, A.; Frank, K.; Krzyszton, R.; Brummer, C.; Nickel, B.; Blanchet, C.E.; Sudarsan, A.; Ibrahim, M.; et al. pH-dependent structural transitions in cationic ionizable lipid mesophases are critical for lipid nanoparticle function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2310491120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carucci, C.; Philipp, J.; Muller, J.A.; Sudarsan, A.; Kostyurina, E.; Blanchet, C.E.; Schwierz, N.; Parsons, D.F.; Salis, A.; Radler, J.O. Buffer Specificity of Ionizable Lipid Nanoparticle Transfection Efficiency and Bulk Phase Transition. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 10829–10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Angelova, A.; Angelov, B.; Dyett, B.; Matthews, L.; Zhang, Y.; El Mohamad, M.; Cai, X.; Valimehr, S.; Drummond, C.J.; et al. Real-Time pH-Dependent Self-Assembly of Ionisable Lipids from COVID-19 Vaccines and In Situ Nucleic Acid Complexation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202304977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Bandara, S.R.; Tan, Z.; Leal, C. Lipid nanoparticle topology regulates endosomal escape and delivery of RNA to the cytoplasm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2301067120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seddon, J.M. Inverse Bicontinuous and Discontinuous Phases of Lipids, and Membrane Curvature. Cells 2025, 14, 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100716
Seddon JM. Inverse Bicontinuous and Discontinuous Phases of Lipids, and Membrane Curvature. Cells. 2025; 14(10):716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100716
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeddon, John M. 2025. "Inverse Bicontinuous and Discontinuous Phases of Lipids, and Membrane Curvature" Cells 14, no. 10: 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100716
APA StyleSeddon, J. M. (2025). Inverse Bicontinuous and Discontinuous Phases of Lipids, and Membrane Curvature. Cells, 14(10), 716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100716







