Pathological Mechanisms Involved in HIV-Associated Lymphomagenesis: Novel Targeted Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Main Text
2.1. Chronic Inflammation Is Proposed as an Initiator of the Indirect Pathway
2.2. Upregulation of miRNA-99 and miRNA-146a in HIV-Infected Macrophages
2.3. Suppression of Immune Responses Mediated by Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase and NK Cell Receptors
2.4. Co-Infection with Oncogenic Virus
2.5. Tumor Immune Microenvironment Therapeutic Approaches
2.6. B Cell Activation and Expansion
2.7. Immune Dysfunction Conditioned by Dysregulated BAFF Levels
2.8. Abnormal CD40L Incorporation in HIV and Its Consequences
2.9. Proto-Oncogenes Mutations Caused by AID Overexpression
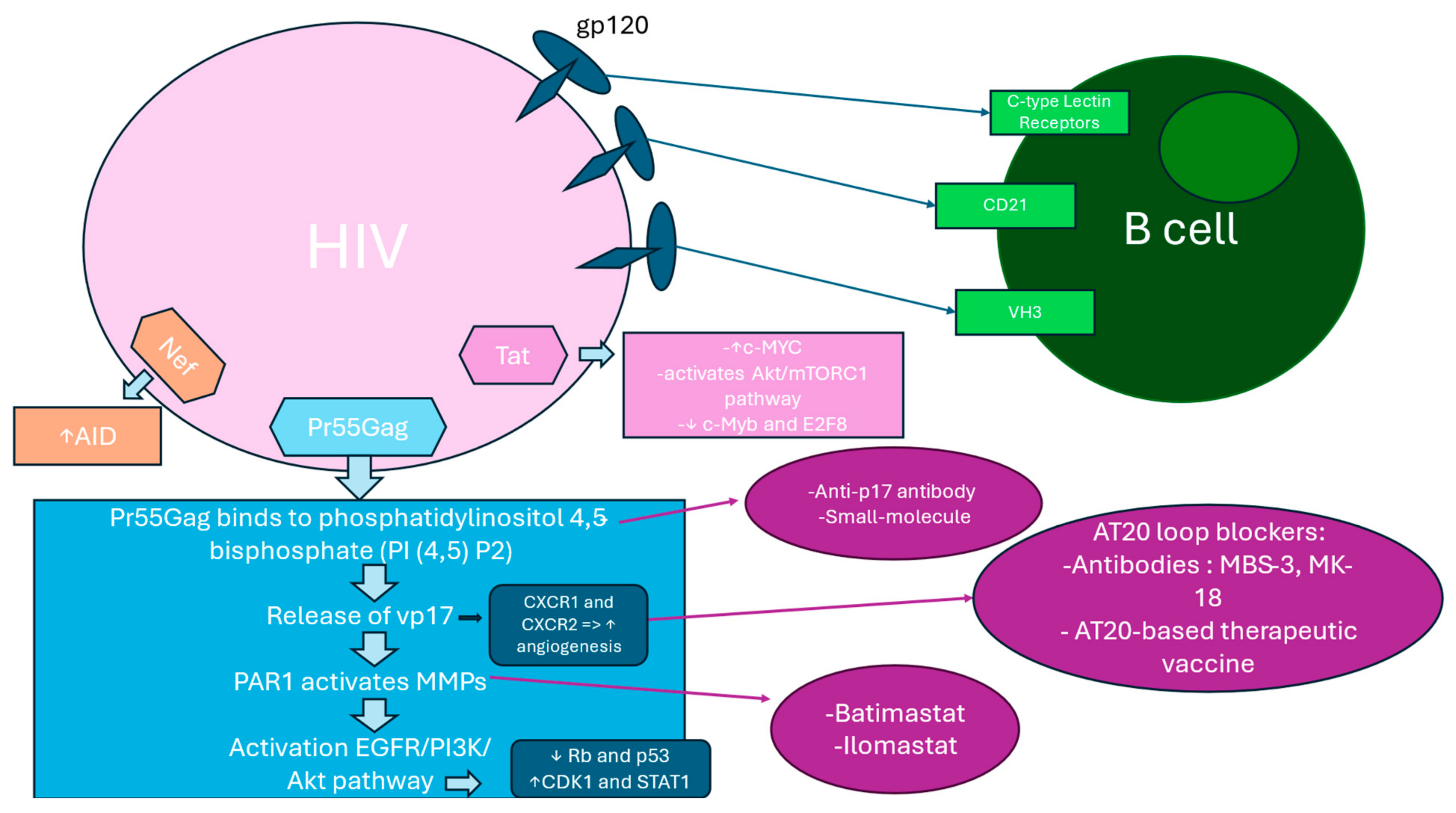
2.10. Hyperactivation of B Cell Surface Markers
2.11. HIV Binding to B Cells Through Alternative Surface Molecules
2.12. p17 Variants Induced PAR1/EGFR/PI3K/Akt Pathway Activation
2.13. Pr55Gag Binding to PI (4,5) P2 at the Plasma Membrane Induce vp17s Release
2.14. The PAR1/EGFR/PI3K/Akt Pathway
2.15. Akt Activation Effect on CDK1, Rb, p53, and Other Players in Cancer Cell Growth and Survival
2.16. PI3K Additional Pathways in Cancer Progression
2.17. AT20 Seen as a Target for Neutralizing Antibodies or Small Molecules
2.18. Tat and Nef Implication in B-Cell Transformation via c-MYC
3. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1-MT | 1-Methyl-Tryptophan |
| ABL | Abelson tyrosine kinase 1 |
| AICDA | Activation-induced cytidine deaminase |
| AID | Activation-induced cytidine deaminase |
| AIDS | Acquired immune deficiency syndrome |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| BL | Burkitt’s lymphoma |
| Breg | B regulatory cells |
| cART | Combined antiretroviral therapies |
| CAR-T | Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy |
| CCL5 | C–C Motif Chemokine Ligand 5 |
| CD40L | CD40 Ligand |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| CHEK1 | Checkpoint Kinase 1 |
| c-MYC | Cellular MYC |
| CR2 | Complement receptor 2 |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 |
| CXCR | C–X–C Motif Chemokine Receptor |
| DHE | Dihydroergotamine |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| E2F8 | E2F transcription factor 8 |
| EBNA2 | EBV-encoded nuclear antigen 2 |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| HALs | HIV-associated lymphomas |
| HC-AT20 | Hydrophobic cluster at amino terminal 20 |
| HL | Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| hMSH2 | Human mutS homolog 2 |
| IDO | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase |
| IgH | Immunoglobulin heavy chain |
| IL | Interleukin |
| KLH | Keyhole limpet hemocyanin |
| KS | Kaposi’s sarcoma |
| LMP1 | Latent membrane protein 1 |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibody |
| MAPK8 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| NCR | Natural cytotoxicity receptors |
| NF-kB | Nuclear factor kappa–light–chain–enhancer of activated B cells |
| NHL | Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| NK | Natural killer cells |
| NKG2D | NK receptor group 2 member D |
| PAR-1 | Protease-activated receptor 1 |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| PDK1 | Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand-1 |
| PI (4,5) P2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate |
| PLWHIV | People living with HIV |
| PTP-1B | Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B |
| RAC1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| Rb | Retinoblastoma protein |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| TGF | Transforming growth factor |
| TIME | Tumor immune microenvironment |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TNF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| Tregs | Regulatory T cells |
| Trp16 | Tryptophan at position 16 |
| Tyr29 | Tyrosine at position 29 |
| VH3 | Variable heavy chain 3 |
| Vp17 | p17 variants |
References
- Yarchoan, R.; Uldrick, T.S. HIV-Associated Cancers and Related Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, S.M.; Painschab, M.S.; Horner, M.J.; Muchengeti, M.; Fedoriw, Y.; Shiels, M.S.; Gopal, S. Epi-demiology of haematological malignancies in people living with HIV. Lancet HIV 2020, 7, e641–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, E.P.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Engels, E.A. Cumulative Incidence of Cancer Among Individuals with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome in the United States. Cancer 2011, 117, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübel, K.; Bower, M.; Aurer, I.; Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Besson, C.; Brunnberg, U.; Cattaneo, C.; Collins, S.; Cwynarski, K.; Dalla Pria, A.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated lymphomas: EHA-ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 840–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, Q.; He, S.; Fu, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y. Immune Characteristics and Immunotherapy of HIV-Associated Lymphoma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 9984–9997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevin, A.S.; McKinnon, L.; Burgener, A.; Klatt, N.R. Microbial translocation and microbiome dysbiosis in HIV-associated immune activation. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Serrano-Villar, S.; Latorre, A.; Artacho, A.; Ferrús, M.L.; Madrid, N.; Vallejo, A.; Sainz, T.; Martínez-Botas, J.; Ferrando-Martínez, S.; et al. Altered metabolism of gut microbiota contributes to chronic immune activation in HIV-infected individuals. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epeldegui, M.; Magpantay, L.; Guo, Y.; Halec, G.; Cumberland, W.G.; Yen, P.K.; Macatangay, B.; Margolick, J.B.; Rositch, A.F.; Wolinsky, S.; et al. A prospective study of serum microbial translocation biomarkers and risk of AIDS-related non-Hodgkin lymphoma. AIDS 2018, 32, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Smith, A.J.; Wietgrefe, S.W.; Southern, P.J.; Schacker, T.W.; Reilly, C.S.; Estes, J.D.; Burton, G.F.; Silvestri, G.; Lifson, J.D.; et al. Cumulative mechanisms of lymphoid tissue fibrosis and t cell depletion in HIV-1 and SIV infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, J.; Patel, M.; Suchard, M.; Gededzha, M.; Ranchod, H.; Howard, W.; Snyman, T.; Wiggill, T. Derangements of immunological proteins in HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: The frequency and prognostic impact. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1340096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandera, A.; Ferrario, G.; Saresella, M.; Marventano, I.; Soria, A.; Zanini, F.; Sabbatini, F.; Airoldi, M.; Marchetti, G.; Franzetti, F.; et al. CD4+ T cell depletion, immune activation and increased production of regulatory T cells in the thymus of HIV-infected individuals. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVoeght, A.; Martens, H.; Renard, C.; Vaira, D.; Debruche, M.; Simonet, J.; Geenen, V.; Moutschen, M.; Darcis, G. Exploring the link between innate immune activation and thymic function by measuring scd14 and trecs in hiv patients living in belgium. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185761. [Google Scholar]
- Makgoeng, S.B.; Bolanos, R.S.; Jeon, C.Y.; Weiss, R.E.; Arah, O.A.; Breen, E.C.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Hussain, S.K. Markers of Immune Activation and Inflammation, and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2018, 2, pky082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, G.; Yao, Z.Q.; Moorman, J.P.; Ning, S. MicroRNA regulation of viral immunity, latency, and carcinogenesis of selected tumor viruses and HIV. Rev. Med. Virol. 2015, 25, 320–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.; Wiggill, T.; Mia, Z.; Patel, M. Tumour-associated macrophages in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: The prognostic and therapeutic impact in a South African centre with high HIV seroprevalence. Immunol. Res. 2024, 72, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adu-Gyamfi, C.G.; Savulescu, D.; George, J.A.; Suchard, M.S. Indoleamine 2, 3-Dioxygenase-Mediated Tryptophan Catabolism: A Leading Star or Supporting Act in the Tuberculosis and HIV Pas-de-Deux? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planès, R.; Bahraoui, E. HIV-1 Tat protein induces the production of IDO in human monocyte derived-dendritic cells through a direct mechanism: Effect on T cells proliferation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, D.; Mold, J.; Hunt, P.W.; Kanwar, B.; Loke, P.; Seu, L.; Barbour, J.D.; Lowe, M.M.; Jayawardene, A.; Aweeka, F.; et al. Tryptophan catabolism by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 alters the balance of TH17 to regulatory T cells in HIV disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 32ra36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, H.C.; Chinnadurai, R.; Bosinger, S.E.; Galipeau, J. The IDO inhibitor 1-methyl tryptophan activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor response in mesenchymal stromal cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91914–91927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochems, C.; Fantini, M.; Fernando, R.I.; Kwilas, A.R.; Donahue, R.N.; Lepone, L.M.; Grenga, I.; Kim, Y.S.; Brechbiel, M.W.; Gulley, J.L.; et al. The IDO1 selective inhibitor epacadostat enhances dendritic cell immunogenicity and lytic ability of tumor antigen-specific T cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 37762–37772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.F.; Hu, H.Y.; Xu, X.Q.; Fu, G.F. Changes in NK Cell Subsets and Receptor Expressions in HIV-1 Infected Chronic Patients and HIV Controllers. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 792775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, O.; O’Connor, S. Therapeutic Potential of IL-15 and N-803 in HIV/SIV Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Ding, X.; Jin, Y.; Qin, R.; Xia, B.; Liao, Q.; Hu, H.; Song, W.; Wang, Z.; et al. Pathologically complete remission to combination of invariant NK T cells and anti-CD20 an-tibody in a refractory HIV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patient. Immunotherapy 2022, 14, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurain, K.; Ramaswami, R.; Yarchoan, R. The role of viruses in HIV-associated lymphomas. Semin. Hematol. 2022, 59, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, J.; Yasui, T.; Takaoka-Shichijo, Y.; Muraoka, M.; Kulwichit, W.; Raab Traub, N.; Kikutani, H. Mimicry of CD40 Signals by Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 in B Lymphocyte Responses. Science 1999, 286, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, B.N.; Edelstein, L.C.; Pegman, P.M.; Smith, S.M.; Loughran, S.T.; Clarke, A.; Mehl, A.; Rowe, M.; Gélinas, C.; Walls, D. Nuclear Factor kb-Dependent Activation of the Antiapoptotic Bfl-1 Gene by the Epstein-Barr Virus Latent Membrane Protein 1 and Activated Cd40 Receptor. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1800–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Hur, D.Y. LMP1 and 2A Induce the Expression of Nrf2 Through Akt Signaling Pathway in Epstein-Barr Virus–Transformed B Cells. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, W.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Ryu, K.J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, C. Epstein-Barr Virus Ebna2 Directs Doxorubicin Resistance of B Cell Lymphoma Through CCL3 and CCL4-mediated Activation of NF-kb andBtk. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5361–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Armani-Tourret, M.; Bone, B.; Tan, T.S.; Sun, W.; Bellefroid, M.; Struyve, T.; Louella, M.; Yu, X.G.; Lichterfeld, M. Immune targeting of HIV-1 reservoir cells: A path to elimination strategies and cure. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. Targeting the tumor microenvironment in B-cell lymphoma: Challenges and opportunities. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarova, M.; Steinle, A. Impairment of NKG2D-Mediated Tumor Immunity by TGF-β. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantziou, A.; Brenna, C.; Ioannidou, K.; Chen, O.Y.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Antoniadou, A.; Psichogiou, M.; Papaioannou, M.; Tsirigotis, P.; Foukas, P.G.; et al. HIV infection is associated with compromised tumor microenvironment adaptive immune reactivity in Hodgkin lym-phoma. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 6215–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsburg, D.J.; Koike, A.; Nasta, S.D.; Svoboda, J.; Schuster, S.J.; Wasik, M.A.; Caponetti, G.C. Patterns of immune checkpoint protein expression in MYC-overexpressing aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabatanzi, R.; Cose, S.; Joloba, M.; Jones, S.R.; Nakanjako, D. Effects of HIV infection and ART on phenotype and function of circulating monocytes, natural killer, and innate lymphoid cells. AIDS Res. Ther. 2018, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. A Review of Human Carcinogens. Part B: Biological Agents; IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans: Lyon, France, 2012; Volume 100. [Google Scholar]
- Vendrame, E.; Hussain, S.K.; Breen, E.C.; Magpantay, L.I.; Widney, D.P.; Jacobson, L.P.; Variakojis, D.; Knowlton, E.R.; Bream, J.H.; Ambinder, R.F.; et al. Serum levels of cytokines and biomarkers for inflammation and immune activation, and HIV associated non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcetti, R.; Gloghini, A.; Caruso, A.; Carbone, A. A lymphomagenic role for HIV beyond immune suppression? Blood 2016, 127, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyon-Laliberté, K.; Aranguren, M.; Byrns, M.; Chagnon-Choquet, J.; Paniconi, M.; Routy, J.P.; Tremblay, C.; Quintal, M.C.; Brassard, N.; Kaufmann, D.E.; et al. Excess BAFF Alters NR4As Expression Levels and Breg Function of Human Precursor-like Marginal Zone B-Cells in the Context of HIV-1 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odagiu, L.; May, J.; Boulet, S.; Baldwin, T.A.; Labrecque, N. Role of the Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A Family in T-Cell Biology. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 11, 624122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Roy, J.; Barat, C.; Ouellet, M.; Gilbert, C.; Tremblay, M.J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated CD40 ligand transactivates B lymphocytes and promotes infection of CD41 T cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5872–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.P.; Arcipowski, K.M.; Bishop, G.A. Differential B-lymphocyte regulation by CD40 and its viral mimic, latent membrane protein 1. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualucci, L.; Neumeister, P.; Goossens, T.; Nanjangud, G.; Chaganti, R.S.K.; Küppers, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Hypermutation of Multiple Proto-Oncogenes in B-cell Diffuse Large-Cell Lymphomas. Nature 2001, 412, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbiani, D.F.; Bunting, S.; Feldhahn, N.; Bothmer, A.; Camps, J.; Deroubaix, S.; McBride, K.M.; Klein, I.A.; Stone, G.; Eisenreich, T.R.; et al. AID produces DNA double-strand breaks in non-Ig genes and mature B cell lymphomas with reciprocal chromosome translocations. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, T.G.; Dyer, M.J.S. The Role of Immunoglobulin Translocations in the Pathogenesis of B-cell Malignancies. Blood 2000, 96, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, R.R.; Shah, R.K.; Frazer, J.K. Molecular Genetics of Childhood, Adolescent and Young Adult non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoraro, L.; Palumbo, A.; Erikson, J.; Falda, M.; Giovanazzo, B.; Emanuel, B.S.; Rovera, G.; Nowell, P.C.; Croce, C.M. A 14;18 and an 8;14 Chromosome Translocation in a Cell Line Derived From an Acute B-Cell Leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 7166–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, B.W.; Nucifora, G.; McCabe, N.; Espinosa, R.; Le Beau, M.M.; McKeithan, T.W. Identification of the Gene Associated With the Recurring Chromosomal Translocations T(3;14)(q27;q32) and T(3;22)(q27;q11) in B-cell Lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5262–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxer, L.M.; Dang, C.V. Translocations Involving C-Myc and C-Myc Function. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5595–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.C.; Masur, H.; Edgar, L.C.; Whalen, G.; Rook, A.H.; Fauci, A.S. Abnormalities of B-Cell Activation and Immunoregulation in Patients With the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, P.S.; Leal, F.E.; Soares, M.A. Clinical and Molecular Properties of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Related Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 675353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaspina, A.; Moir, S.; Kottilil, S.; Hallahan, C.W.; Ehler, L.A.; Liu, S.; Planta, M.A.; Chun, T.-W.; Fauci, A.S. Deleterious Effect of HIV-1 Plasma Viremia on B Cell Costimulatory Function. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5965–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybel, T.E.; Vase, M.Ø.; Lauridsen, K.L.; Enemark, M.B.; Møller, M.B.; Pedersen, C.; Pedersen, G.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Obel, N.; Schade Larsen, C.; et al. CD38 is a potential treatment target in lymphoma patients concurrently infected with human immunodeficiency virus. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breen, E.C.; van der Meijden, M.; Cumberland, W.; Kishimoto, T.; Detels, R.; Martínez-Maza, O. The development of AIDS-associated Burkitt’s/small noncleaved cell lymphoma is preceded by elevated serum levels of interleukin 6. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 92, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. Irreversible Phenotypic Perturbation and Functional Impairment of B Cells During Hiv-1 Infection. Front. Med. 2017, 11, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berberian, L.; Goodglick, L.; Kipps, T.J.; Braun, J. Immunoglobulin VH3 Gene Products: Natural Ligands for HIV Gp120. Science 1993, 261, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Qiao, X.; Klasse, P.J.; Chiu, A.; Chadburn, A.; Knowles, D.M.; Moore, J.P.; Cerutti, A. Hiv-1 Envelope Triggers Polyclonal Ig Class Switch Recombination Through a CD40-Independent Mechanism Involving BAFF and C-Type Lectin Receptors. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3931–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moir, S.; Malaspina, A.; Li, Y.; Chun, T.W.; Lowe, T.; Adelsberger, J.; Baseler, M.; Ehler, L.A.; Liu, S.; Davey, R.T.; et al. B Cells of HIV-1-infected Patients Bind Virions Through CD21-Complement Interactions and Transmit Infectious Virus to Activated T Cells. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorarinsdottir, K.; Camponeschi, A.; Gjertsson, I.; Mårtensson, I.L. Cd21-/Low B Cells: A Snapshot of a Unique B Cell Subset in Health and Disease. Scand. J. Immunol. 2015, 82, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaguliants, M.; Bayurova, E.; Avdoshina, D.; Kondrashova, A.; Chiodi, F.; Palefsky, J.M. Oncogenic Effects of HIV-1 Proteins, Mechanisms Behind. Cancers 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.A.; Mahajan, S.; Ritz, J. B lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia contain signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 1 and STAT3 constitutively phosphorylated on serine residues. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 3140–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugatti, A.; Caccuri, F.; Filippini, F.; Ravelli, C.; Caruso, A. Binding to PI(4,5)P2 is indispensable for secretion of B-cell clonogenic HIV-1 matrix protein p17 variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomishige, N.; Bin Nasim, M.; Murate, M.; Pollet, B.; Didier, P.; Godet, J.; Richert, L.; Sako, Y.; Mély, Y.; Kobayashi, T. HIV-1 Gag targeting to the plasma membrane reorganizes sphingomyelin-rich and cholesterol-rich lipid domains. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccuri, F.; Iaria, M.L.; Campilongo, F.; Varney, K.; Rossi, A.; Mitola, S.; Schiarea, S.; Bugatti, A.; Mazzuca, P.; Giagulli, C.; et al. Cellular aspartyl proteases promote the unconventional secretion of biologically active HIV-1 matrix protein p17. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagulli, C.; Caccuri, F.; Zorzan, S.; Bugatti, A.; Zani, A.; Filippini, F.; Manocha, E.; D’ursi, P.; Orro, A.; Dolcetti, R.; et al. B-cell clonogenic activity of HIV-1 p17 variants is driven by PAR1-mediated EGF transactivation. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, D.; Notkins, A.L.; Zhou, P. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication in primary human T cells transduced with an intracellular anti-HIV-1 p17 antibody gene. J. Gene Med. 2003, 5, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenter, I.; Sierra, L.; Fraser, A.K.; Maciunas, L.; Mankowski, M.K.; Vinnik, A.; Fedichev, P.; Ptak, R.G.; Martin-Garcia, J.; Cockln, S. Identification of a small-molecule inhibitor of HIV-1 assembly that targets the phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate binding site of the HIV-1 matrix protein. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Lao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gillespie, D.A. Akt: A double-edged sword in cell proliferation and genome stability. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 951724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtivelman, E.; Sussman, J.; Stokoe, D. A role for PI 3-kinase and PKB activity in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, E.; Wang, L.; Okada, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Okada, N. Abnormal expression of Rb pathway-related proteins in salivary gland acinic cell carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, N.; Tremblay, M.L. Involvement of the small protein tyrosine phosphatases TC-PTP and PTP1B in signal transduction and diseases: From diabetes, obesity to cell cycle, and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1754, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Marine, J.C.; Danovi, D.; Falini, B.; Pelicci, P.G. Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Ramaswamy, N.T.; Hong, X.; Pelling, J.C. Association of JNK1 with p21waf1 and p53: Modulation of JNK1 activity. Mol. Carcinog. 2003, 36, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattler, M.; Salgia, R.; Okuda, K.; Uemura, N.; Durstin, M.A.; Pisick, E.; Xu, G.; Li, J.L.; Prasad, K.V.; Griffin, J.D. The proto-oncogene product p120CBL and the adaptor proteins CRKL and c-CRK link c-ABL, p190BCR/ABL and p210BCR/ABL to the phosphatidylinositol-3’ kinase pathway. Oncogene 1996, 12, 839–846. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Carpenter, E.S.; Takeuchi, K.K.; Halbrook, C.J.; Peverley, L.V.; Bien, H.; Hall, J.C.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Pal, D.; Song, Y.; et al. PI3K regulation of RAC1 is required for KRAS-induced pancreatic tumorigenesis in mice. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1405–1416.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliouat-Denis, C.M.; Dendouga, N.; Van den Wyngaert, I.; Goehlmann, H.; Steller, U.; van de Weyer, I.; Van Slycken, N.; Andries, L.; Kass, S.; Luyten, W.; et al. p53-independent reg ulation of p21Waf1/Cip1 expression and senescence by Chk2. Mol. Cancer Res. 2005, 3, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.H.; Contractor, T.; Clausen, R.; Klimstra, D.S.; Du, Y.C.; Allen, P.J.; Brennan, M.F.; Levine, A.J.; Harris, C.R. Attenuation of the retinoblastoma pathway in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors due to increased cdk4/cdk6. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4612–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, N.N.; Losman, J.A.; Lu, T.; Yip, N.; Krisnan, K.; Krolewski, J.; Goff, S.P.; Wang, J.Y.J.; Rothman, P.B. Direct interaction of Jak1 and v-Abl is required for v-Abl induced activation of STATs and proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 6795–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ursi, P.; Rondina, A.; Zani, A.; Uggeri, M.; Messali, S.; Caruso, A.; Caccuri, F. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the B Cell Growth and Clonogenic Activity of HIV-1 Matrix Protein p17 Variants. Viruses 2024, 16, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccuri, F.; Rueckert, C.; Giagulli, C.; Schulze, K.; Basta, D.; Zicari, S.; Marsico, S.; Cervi, E.; Fiorentini, S.; Slevin, M.; et al. HIV-1 matrix protein p17 promotes lymphangiogenesis and activates the endothelin-1/endothelin B receptor axis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giagulli, C.; Marsico, S.; Magiera, A.K.; Bruno, R.; Caccuri, F.; Barone, I.; Fiorentini, S.; Andò, S.; Caruso, A. Opposite effects of HIV-1 p17 variants on PTEN activation and cell growth in B cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaria, M.L.; Fiorentini, S.; Focà, E.; Zicari, S.; Giagulli, C.; Caccuri, F.; Francisci, D.; Di Perri, G.; Castelli, F.; Baldelli, F.; et al. Synthetic HIV-1 matrix protein p17-based AT20-KLH therapeutic immunization in HIV-1-infected patients receiving antiretroviral treatment: A phase I safety and immunogenicity study. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Focà, E.; Iaria, M.L.; Caccuri, F.; Fiorentini, S.; Motta, D.; Giagulli, C.; Castelli, F.; Caruso, A. Long-lasting humoral immune response induced in HIV-1-infected patients by a synthetic peptide (AT20) derived from the HIV-1 matrix protein p17 functional epitope. HIV Clin. Trials 2015, 16, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves de Souza Rios, L.; Mapekula, L.; Mdletshe, N.; Chetty, D.; Mowla, S. HIV-1 Transactivator of Transcription (Tat) Co-operates with AP-1 Factors to Enhance c-MYC Transcription. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 693706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valyaeva, A.A.; Tikhomirova, M.A.; Potashnikova, D.M.; Bogomazova, A.N.; Snigiryova, G.P.; Penin, A.A.; Logacheva, M.D.; Arifulin, E.A.; Shmakova, A.A.; Germini, D.; et al. Ectopic expression of HIV-1 Tat modifies gene expression in cultured B cells: Implications for the development of B-cell lymphomas in HIV-1-infected patients. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germini, D.; Tsfasman, T.; Klibi, M.; El-Amine, R.; Pichugin, A.; Iarovaia, O.V.; Bilhou-Nabera, C.; Subra, F.; Bou Saada, Y.; Sukhanova, A.; et al. HIV Tat induces a prolonged MYC relocalization next to IGH in circulating B-cells. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbay, B.; Germini, D.; Bissenbaev, A.K.; Musinova, Y.R.; Sheval, E.V.; Vassetzky, Y.; Dokudovskaya, S. HIV-1 Tat Activates Akt/mTORC1Pathway and AICDAExpression by Downregulating Its Transcriptional Inhibitors in B Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mdletshe, N.; Nel, A.; Shires, K.; Mowla, S. HIV Nef enhances the expression of oncogenic c-MYC and activation-induced cytidine deaminase in Burkitt lymphoma cells, promoting genomic instability. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Straista, M.; Caccuri, F.; Arnaut, N.; Caruso, A.; Slevin, M. Pathological Mechanisms Involved in HIV-Associated Lymphomagenesis: Novel Targeted Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2025, 14, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100705
Straista M, Caccuri F, Arnaut N, Caruso A, Slevin M. Pathological Mechanisms Involved in HIV-Associated Lymphomagenesis: Novel Targeted Therapeutic Approaches. Cells. 2025; 14(10):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100705
Chicago/Turabian StyleStraista, Mihaela, Francesca Caccuri, Nicoleta Arnaut, Arnaldo Caruso, and Mark Slevin. 2025. "Pathological Mechanisms Involved in HIV-Associated Lymphomagenesis: Novel Targeted Therapeutic Approaches" Cells 14, no. 10: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100705
APA StyleStraista, M., Caccuri, F., Arnaut, N., Caruso, A., & Slevin, M. (2025). Pathological Mechanisms Involved in HIV-Associated Lymphomagenesis: Novel Targeted Therapeutic Approaches. Cells, 14(10), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100705





