17β-Estradiol Promotes Tumorigenicity Through an Autocrine AREG/EGFR Loop in ER-α-Positive Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture Conditions
2.3. Generation of Stable AREG Knockdown Cells
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.6. Colony Formation Assay
2.7. Wound-Healing Assay
2.8. Cell Sphere Formation Assay
2.9. Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.10. Secretory Protein Array
2.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.12. Correlation Analysis
2.13. Approval of the Use of Human Breast Cancer Patient Serum Samples
2.14. Xenograft Study
2.15. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
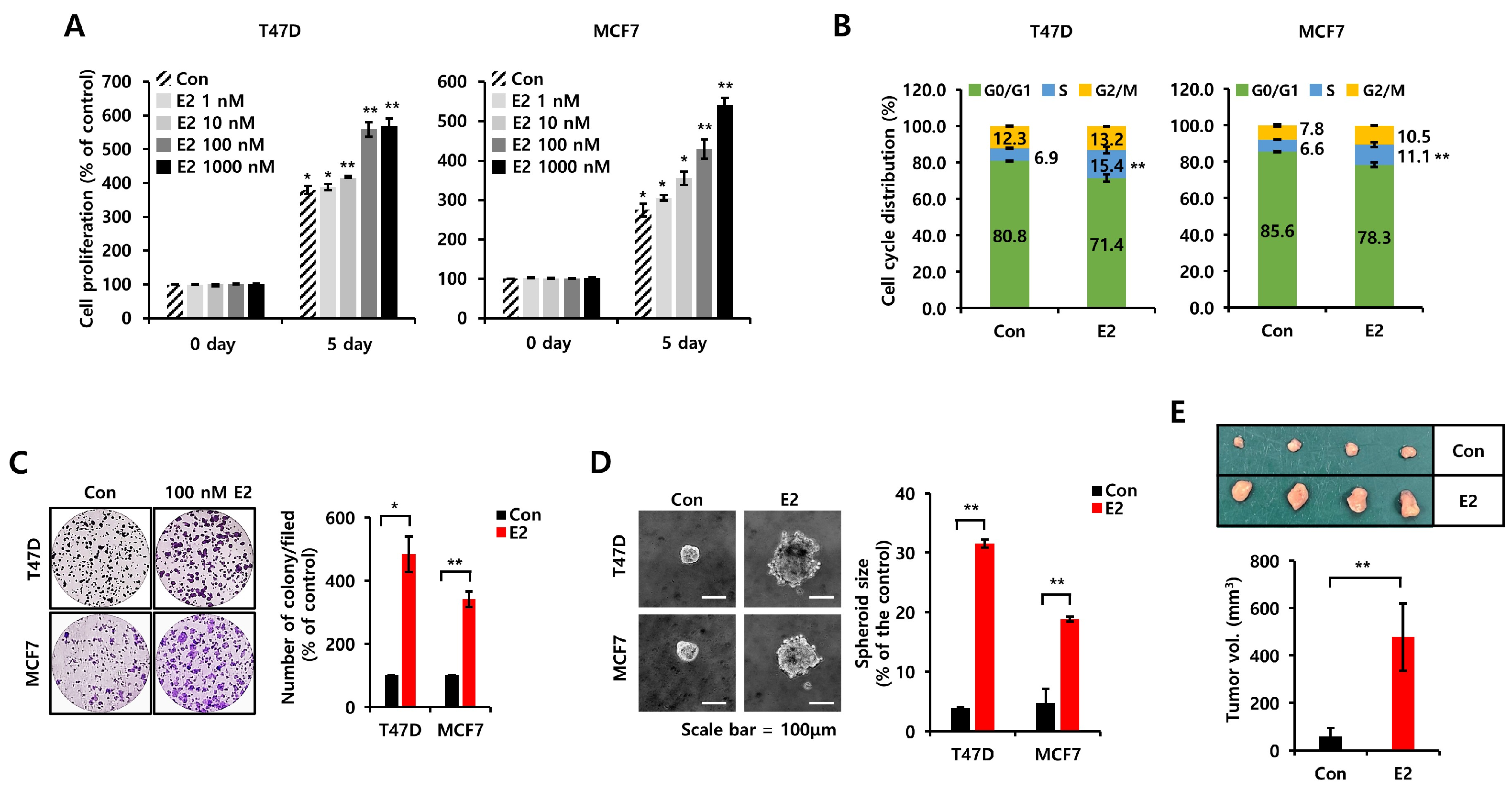
3.1. E2 Increases Cell Proliferation, Growth, and Tumorigenicity in ER+ Breast Cancer Cells
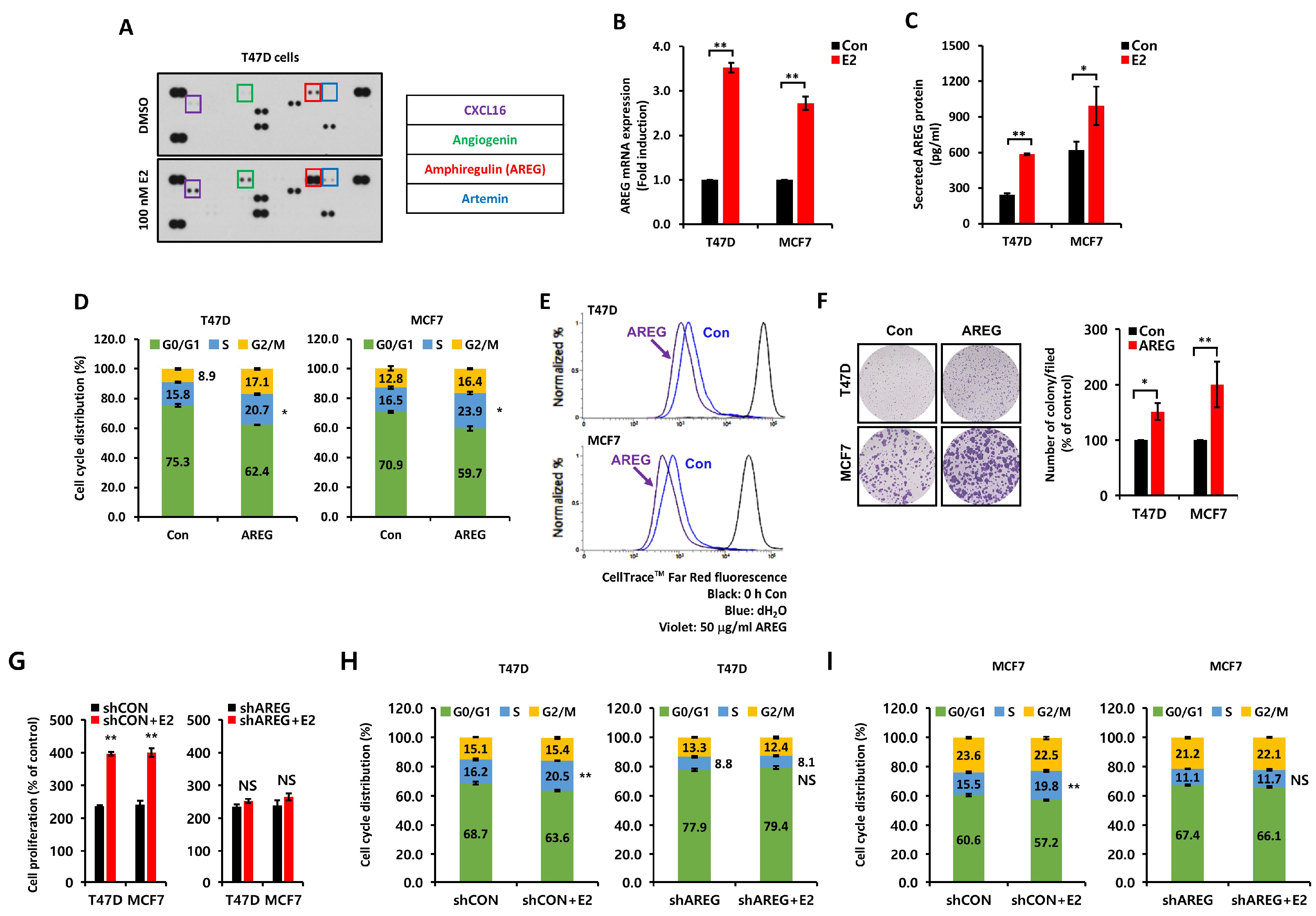
3.2. E2-Induced AREG Expression Stimulates Cell Proliferation
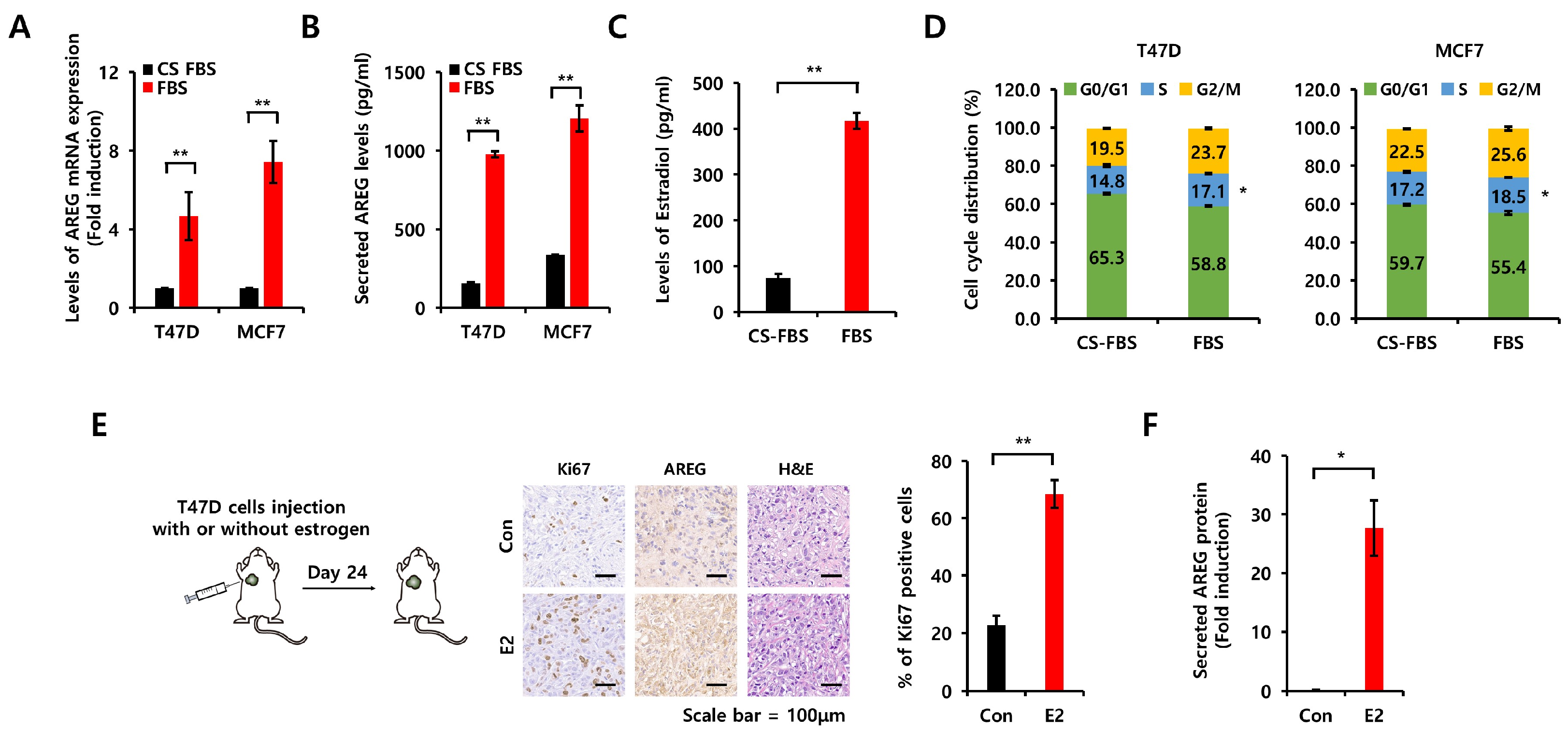
3.3. Comparison of Charcoal-Stripped Fetal Bovine Serum and Normal Fetal Bovine Serum on AREG Expression
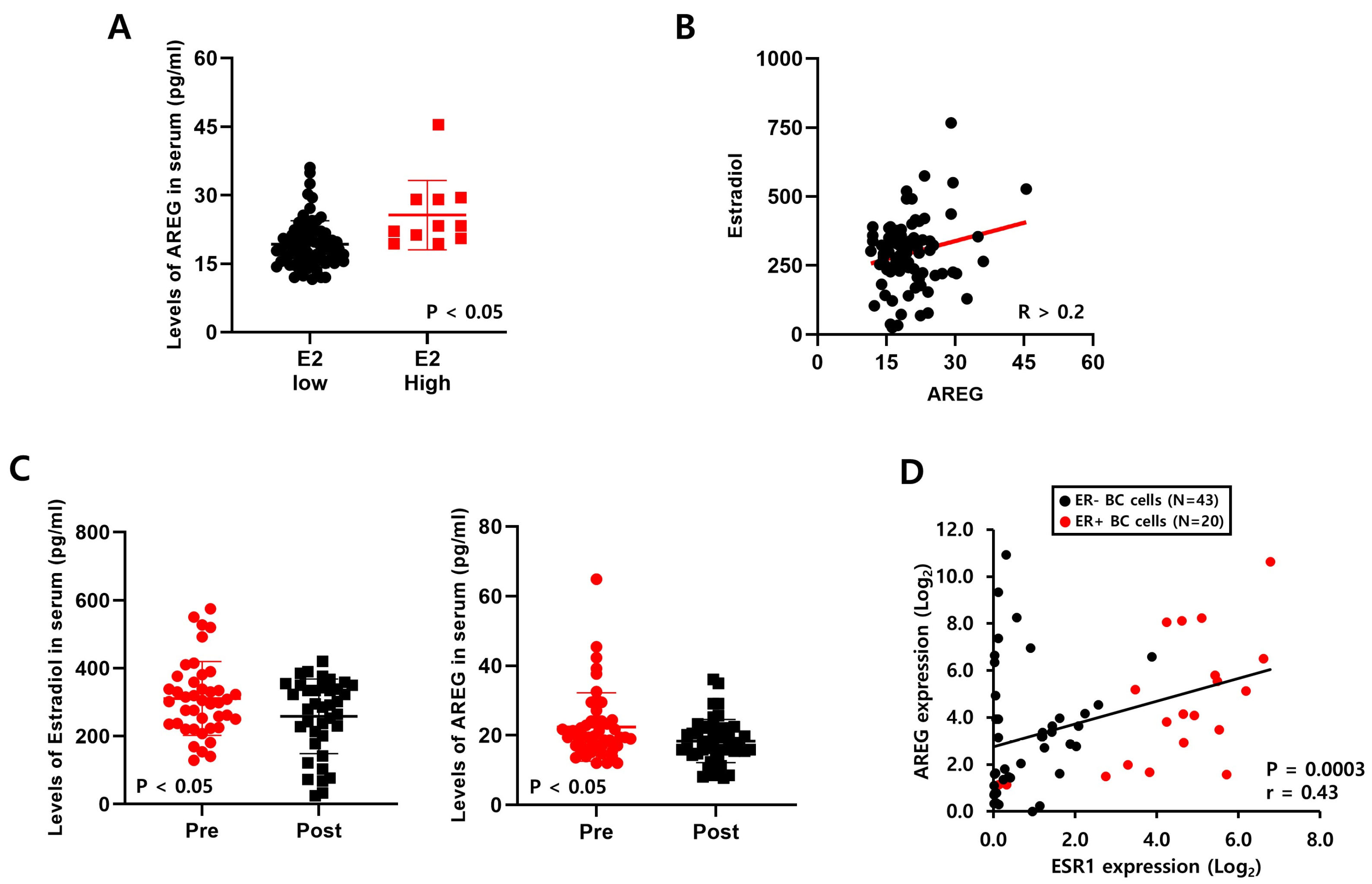
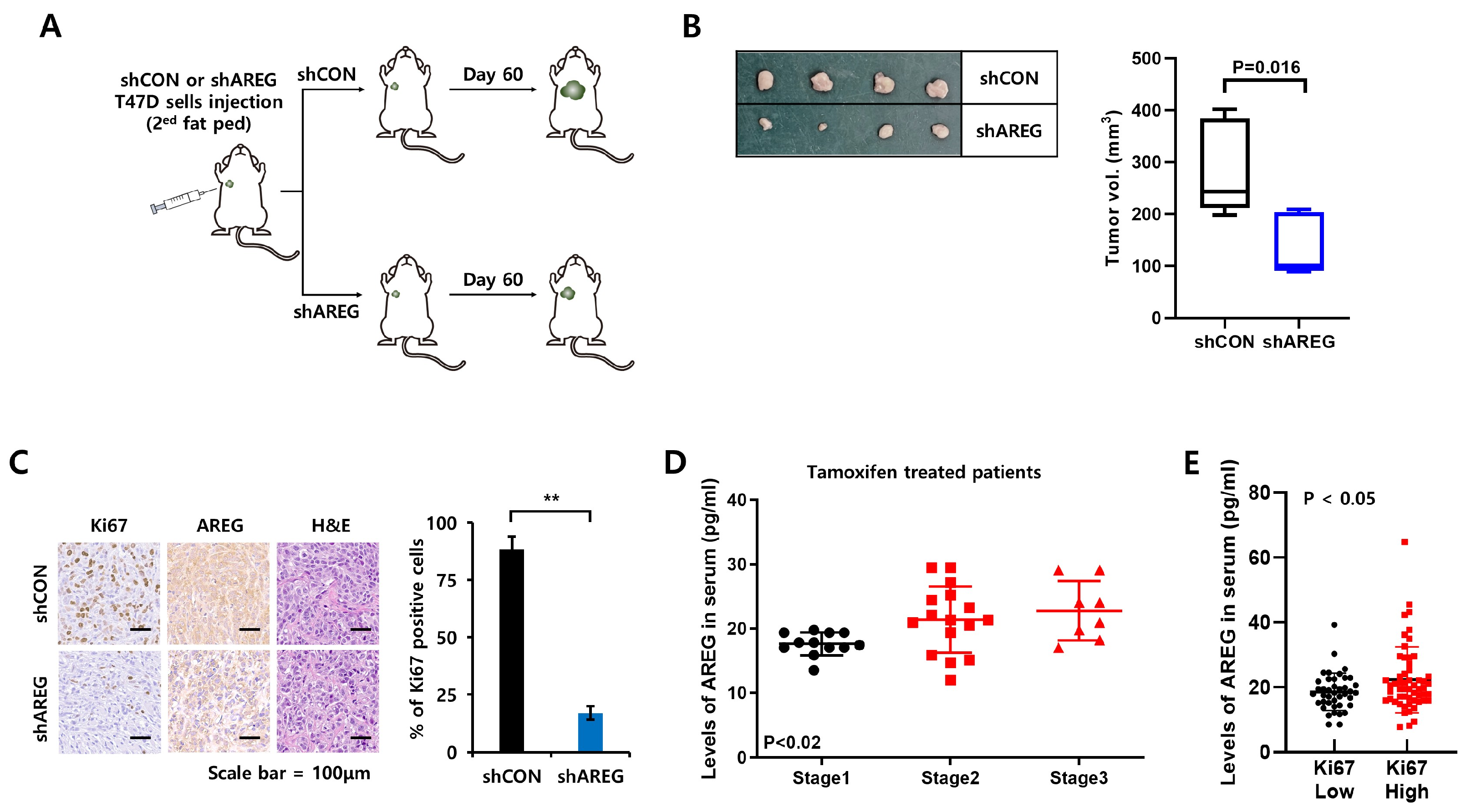
3.4. Levels of E2 Are Positively Correlated with AREG Expression in ER+ Breast Cancer Patient Serum
3.5. E2 Activates the EGFR Signaling Pathway via an Autocrine AREG Loop
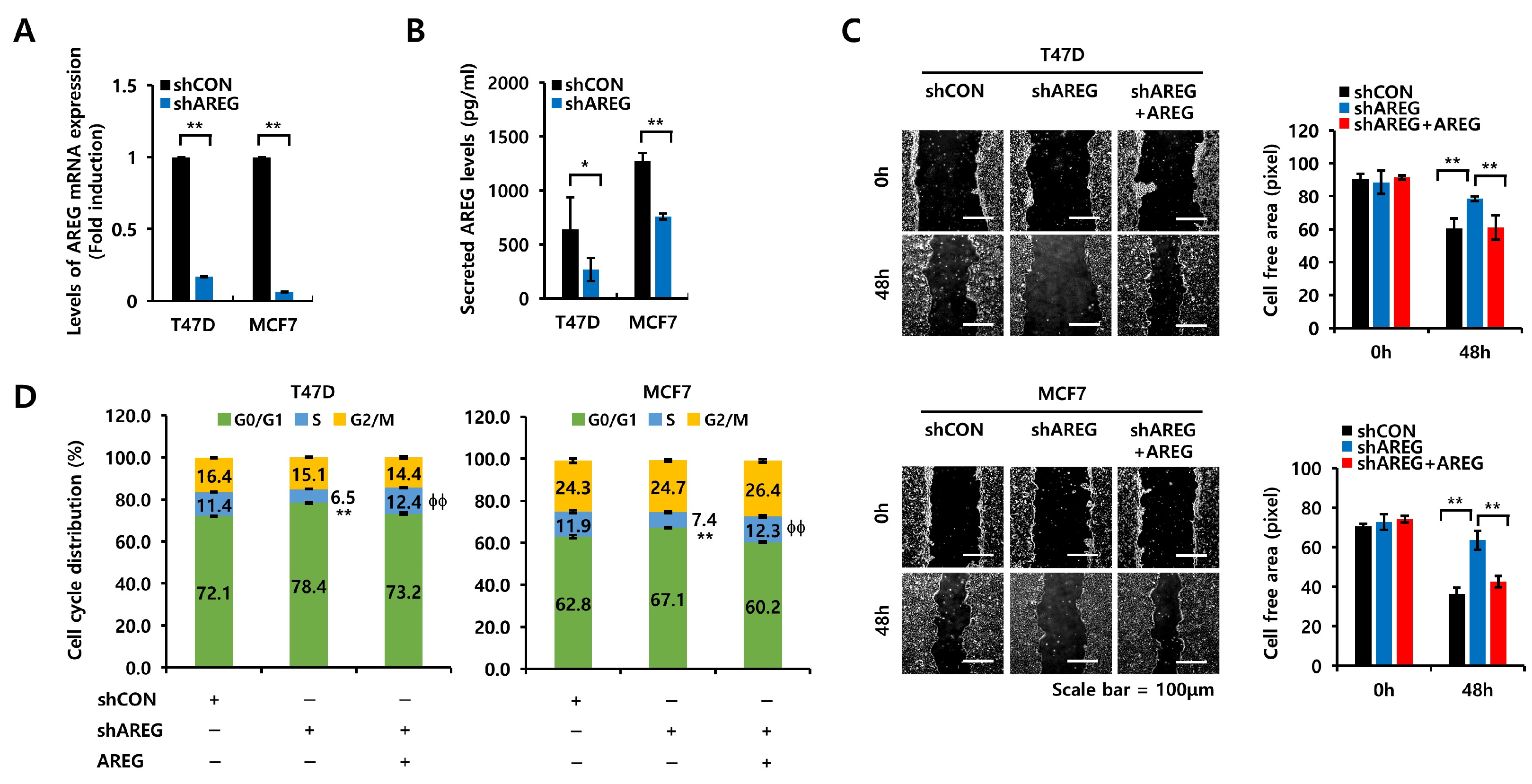
3.6. AREG Knockdown Suppresses S-Phase Entry and Cell Migration in ER+ Breast Cancer Cells
3.7. Diminished Expression of AREG Inhibits Tumorigenicity in an Orthotopic Xenograft Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clusan, L.; Ferrière, F.; Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F. A Basic Review on Estrogen Receptor Signaling Pathways in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sotiriou, C. Luminal breast cancer: From biology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Stebbing, J.; Giamas, G.; Murphy, J. Endocrine Resistance in Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer-From Mechanism to Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, S.; Syafruddin, S.E.; Mohtar, M.A. Impact of the Cancer Cell Secretome in Driving Breast Cancer Progression. Cancers 2023, 15, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaij-Visser, T.B.; de Wit, M.; Lam, S.W.; Jiménez, C.R. The cancer secretome, current status and opportunities in the lung, breast and colorectal cancer context. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2242–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miziak, P.; Baran, M.; Błaszczak, E.; Przybyszewska-Podstawka, A.; Kałafut, J.; Smok-Kalwat, J.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; Kiełbus, M.; Stepulak, A. Estrogen Receptor Signaling in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.A.; Herynk, M.H.; Cascone, T.; Saigal, B.; Nilsson, M.B.; Tran, H.; Ramachandran, S.; Diao, L.; Wang, J.; Le, X.; et al. Estrogen Promotes Resistance to Bevacizumab in Murine Models of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyder, S.M.; Nawaz, Z.; Chiappetta, C.; Stancel, G.M. Identification of functional estrogen response elements in the gene coding for the potent angiogenic factor vascular endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, Y.; Bae, S.Y.; You, D.; Jung, S.P.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, I.; Lee, S.K.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; et al. EGFR is a Therapeutic Target in Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 805–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.L.; Feng, P.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Sun, W.L.; Van Hiep, N.; Luo, C.S.; Wu, S.M. The Role of EREG/EGFR Pathway in Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, F.; Schaefer, L.; Wygrecka, M. EGFR Signaling in Lung Fibrosis. Cells 2022, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Sunnarborg, S.W. The ADAM17-amphiregulin-EGFR axis in mammary development and cancer. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2008, 13, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seefried, F.; Haller, L.; Fukuda, S.; Thongmao, A.; Schneider, N.; Utikal, J.; Higashiyama, S.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Kuphal, S. Nuclear AREG affects a low-proliferative phenotype and contributes to drug resistance of melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 2244–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Long, Q.; Zhu, D.; Fu, D.; Zhang, B.; Han, L.; Qian, M.; Guo, J.; Xu, J.; Cao, L.; et al. Targeting amphiregulin (AREG) derived from senescent stromal cells diminishes cancer resistance and averts programmed cell death 1 ligand (PD-L1)-mediated immunosuppression. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Cheng, H.; Bai, Z.; Li, J. Breast Cancer Cell Line Classification and Its Relevance with Breast Tumor Subtyping. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocca, D.R.; Fanelli, M.A. Estrogen receptors and cell proliferation in breast cancer. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 8, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.A.; Jenkins, E.C.; Lofgren, K.A.; Chandiramani, N.; Liu, H.; Aranda, E.; Barnett, M.; Kenny, P.A. Amphiregulin Is a Critical Downstream Effector of Estrogen Signaling in ERα-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.R.; Qu, L.H.; Ma, L.M. Differential impacts of charcoal-stripped fetal bovine serum on c-Myc among distinct subtypes of breast cancer cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Biological role of estrogen and estrogen receptors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzolek, I.; Sobieraj, J.; Domagala-Kulawik, J. Estrogens, Cancer and Immunity. Cancers 2022, 14, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkerd, E.J.; Dowsett, M. Influence of sex hormones on cancer progression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4038–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Fiandalo, M.V.; Pop, E.; Stocking, J.J.; Azabdaftari, G.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Ma, D.; Qu, J.; Mohler, J.L.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Charcoal-Stripped Fetal Bovine Serum Reveals Changes in the Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2963–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stossi, F.; Barnett, D.H.; Frasor, J.; Komm, B.; Lyttle, C.R.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S. Transcriptional profiling of estrogen-regulated gene expression via estrogen receptor (ER) alpha or ERbeta in human osteosarcoma cells: Distinct and common target genes for these receptors. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 3473–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Sunnarborg, S.W.; Kouros-Mehr, H.; Yu, Y.; Lee, D.C.; Werb, Z. Mammary ductal morphogenesis requires paracrine activation of stromal EGFR via ADAM17-dependent shedding of epithelial amphiregulin. Development 2005, 132, 3923–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeJeune, S.; Leek, R.; Horak, E.; Plowman, G.; Greenall, M.; Harris, A.L. Amphiregulin, epidermal growth factor receptor, and estrogen receptor expression in human primary breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 3597–3602. [Google Scholar]
- Chayangsu, C.; Khunsri, S.; Sriuranpong, V.; Tanasanvimon, S. The correlations between serum amphiregulin and other clinicopathological factors in colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2017, 8, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, E.A.; Pectasides, E.; Shabbeer, S.; Wiechmann, L.; Sparano, J.A.; Kenny, P.A. Evaluation of serum Amphiregulin levels in breast cancer patients and cancer-free controls. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardo, E.J.; Quinn, J.A.; Bland, K.I.; Frackelton, A.R., Jr. Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 1649–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrell, L.M.; Della Rocca, G.J.; van Biesen, T.; Luttrell, D.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Gβγ subunits mediate Src-dependent phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. A scaffold for G protein-coupled receptor-mediated Ras activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 4637–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillo, A.; Giroux, C.; Ethier, S.P. Knock-down of amphiregulin inhibits cellular invasion in inflammatory breast cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 2691–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ER+ Breast Cancer Patients | ||
|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | n = 100 | |
| Age | Pre | 41.76 (28–54) |
| Post | 57.02 (40–72) | |
| T stage | T1 | 36 |
| T2 | 45 | |
| T3 | 17 | |
| T4 | 2 | |
| N stage | N0 | 39 |
| N1 | 29 | |
| N2 | 18 | |
| N3 | 14 | |
| M stage | M0 | 96 |
| M1 | 4 | |
| EGFR | − | 88 |
| + | 12 | |
| PR | − | 21 |
| + | 78 | |
| HER2 | − | 74 |
| + | 26 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, S.Y.; Jeong, Y.; Ryu, J.M.; Lee, S.K.; Chae, B.J.; Yu, J.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.E. 17β-Estradiol Promotes Tumorigenicity Through an Autocrine AREG/EGFR Loop in ER-α-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. Cells 2025, 14, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100703
Yoon SY, Jeong Y, Ryu JM, Lee SK, Chae BJ, Yu J, Kim SW, Nam SJ, Kim S, Lee JE. 17β-Estradiol Promotes Tumorigenicity Through an Autocrine AREG/EGFR Loop in ER-α-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. Cells. 2025; 14(10):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100703
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Sun Young, Yisun Jeong, Jai Min Ryu, Se Kyung Lee, Byung Joo Chae, Jonghan Yu, Seok Won Kim, Seok Jin Nam, Sangmin Kim, and Jeong Eon Lee. 2025. "17β-Estradiol Promotes Tumorigenicity Through an Autocrine AREG/EGFR Loop in ER-α-Positive Breast Cancer Cells" Cells 14, no. 10: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100703
APA StyleYoon, S. Y., Jeong, Y., Ryu, J. M., Lee, S. K., Chae, B. J., Yu, J., Kim, S. W., Nam, S. J., Kim, S., & Lee, J. E. (2025). 17β-Estradiol Promotes Tumorigenicity Through an Autocrine AREG/EGFR Loop in ER-α-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. Cells, 14(10), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100703






