Dauricine Impedes the Tumorigenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Nrf2 and Reactive Oxygen Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
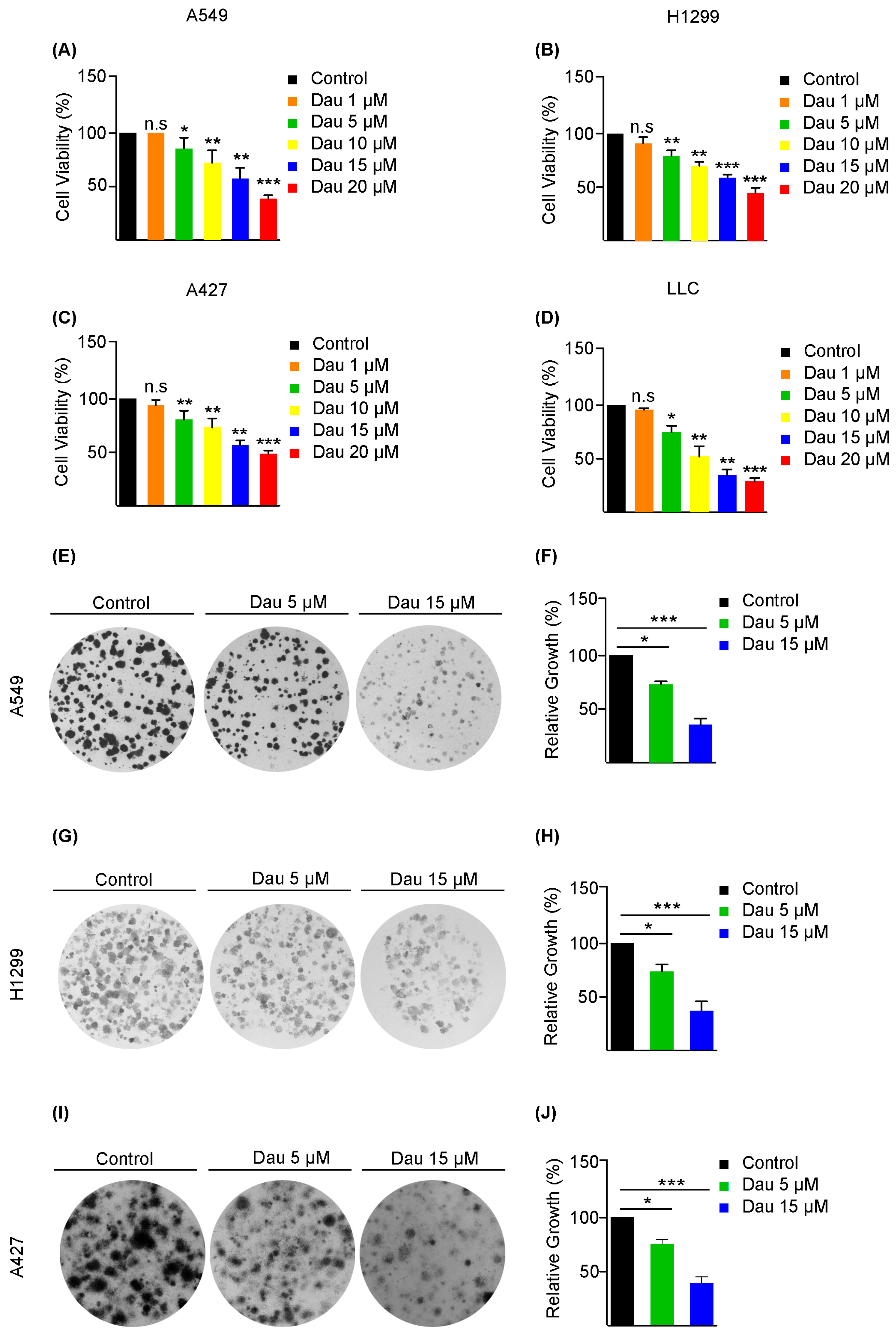
2.3. MTT
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
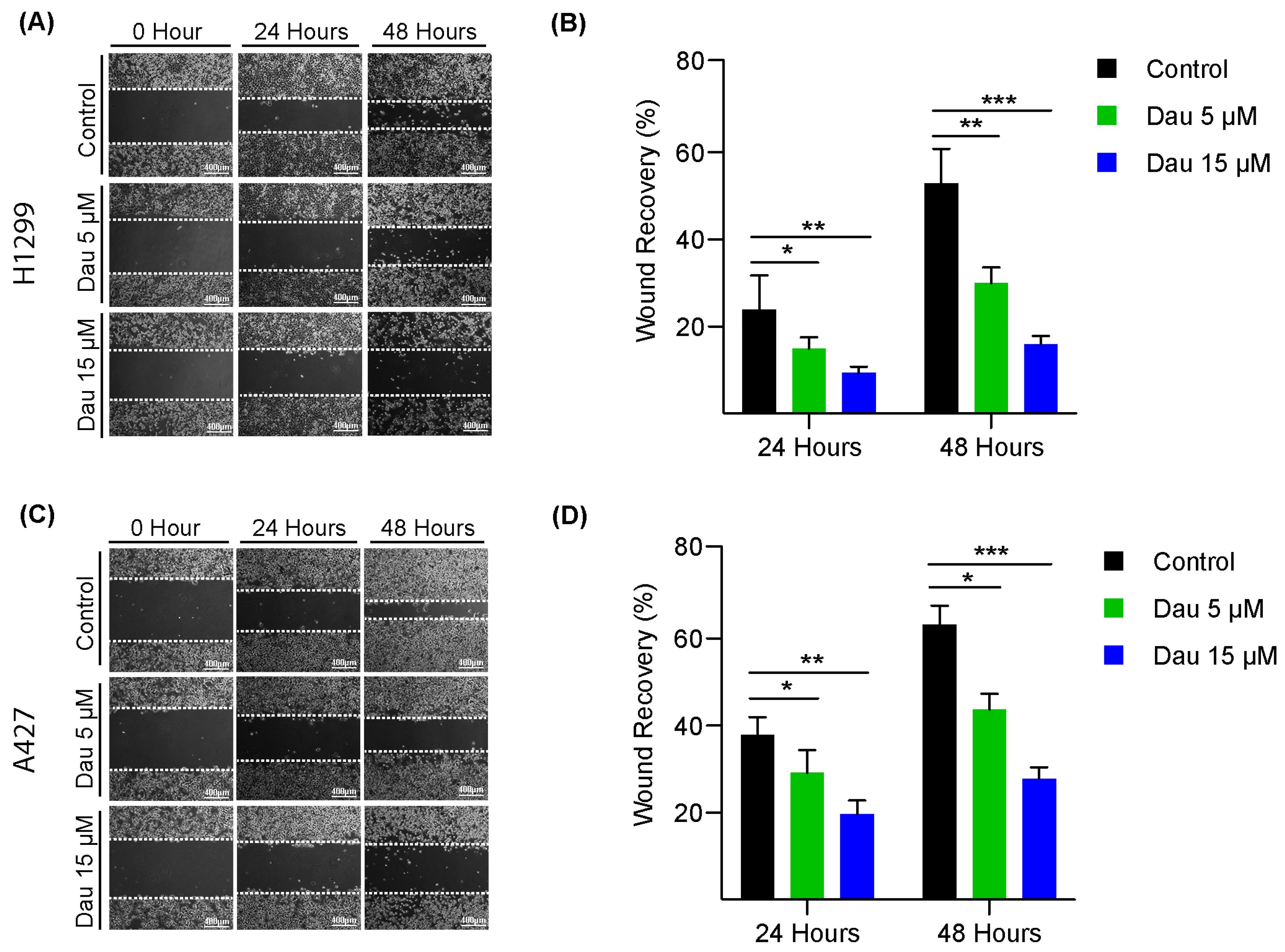
2.5. Wound Healing Assay
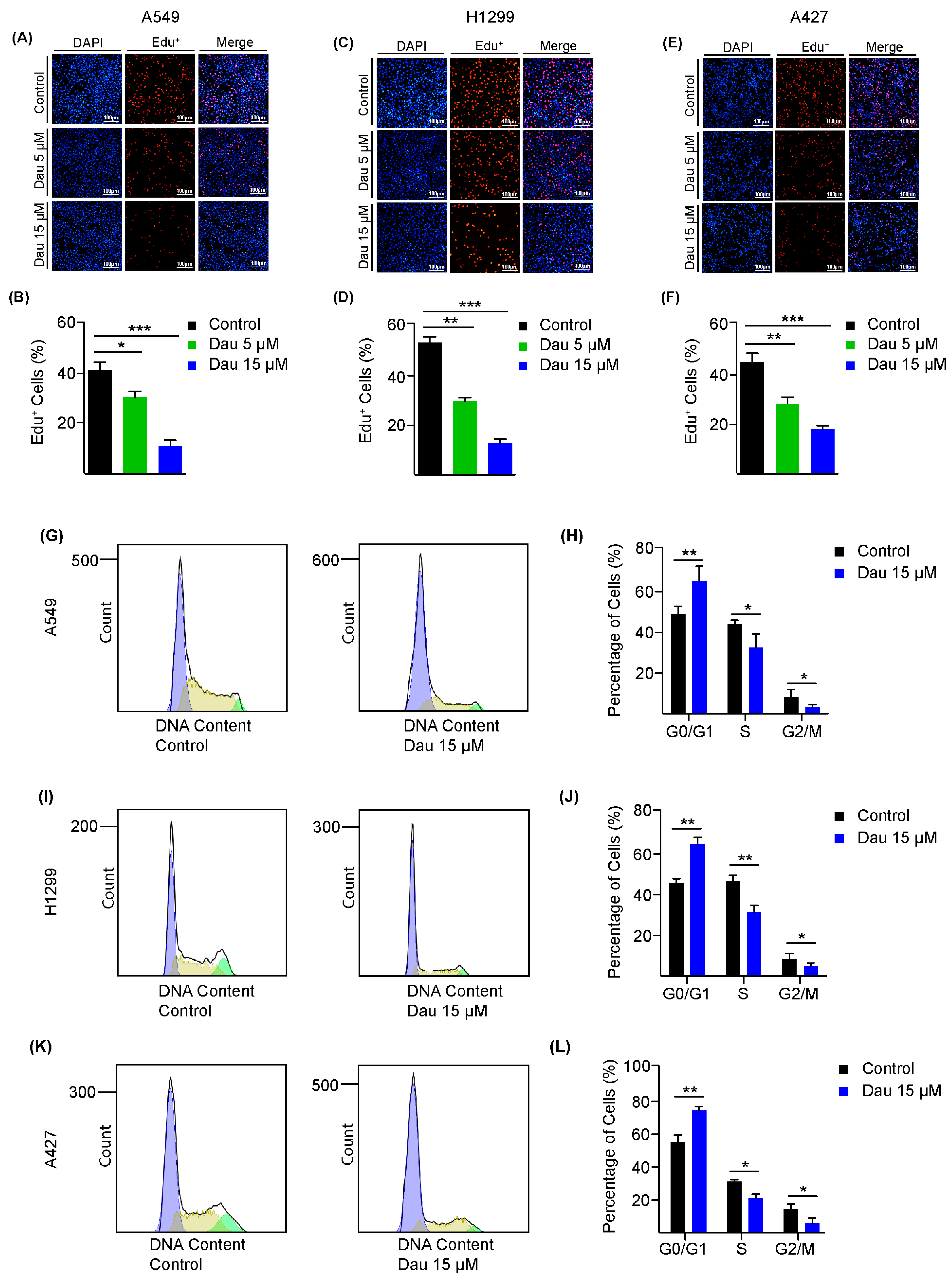
2.6. Edu Assay
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Mouse Syngeneic Model
2.9. Transgenic Mouse Lung Cancer Model
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
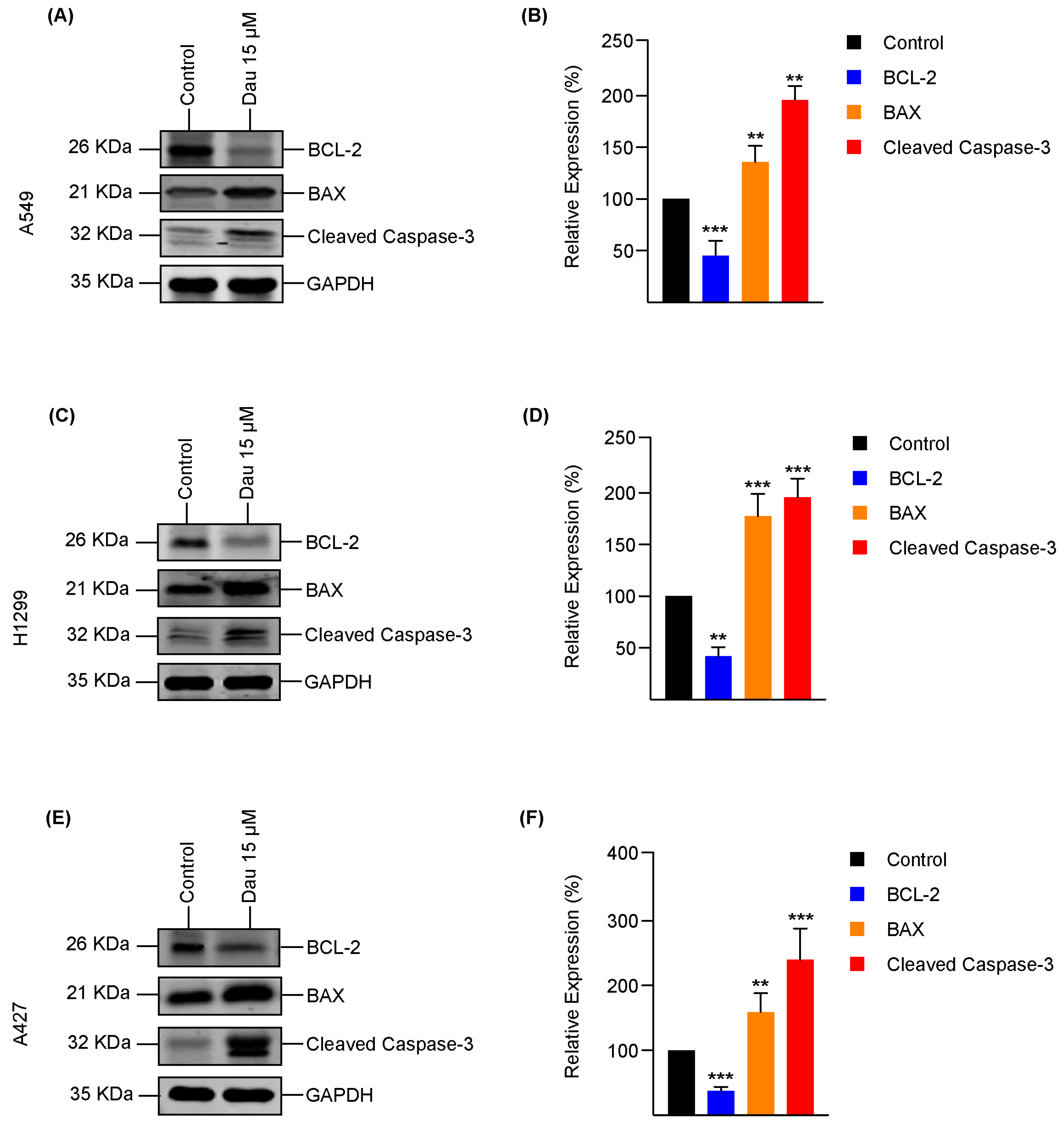
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dauricine Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of LUAD Cells
3.2. Dauricine Deters Cell Cycle Regulation and Growth of LUAD Cells
3.3. Dauricine Downregulates Nrf2 and Increases ROS Production
3.4. Dauricine Triggers Apoptosis in LUAD
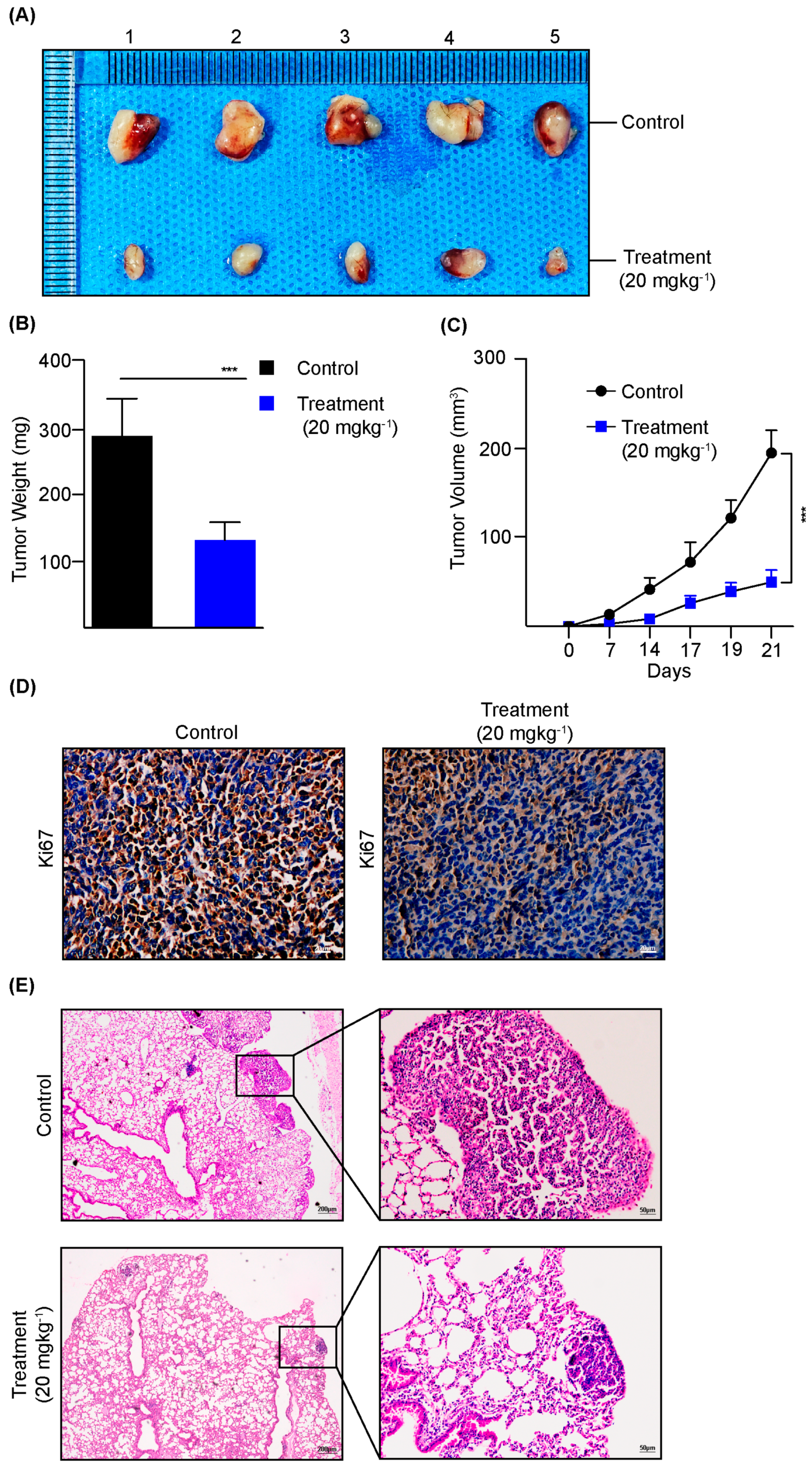
3.5. Dauricine Diminishes the Progression of LUAD In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kodaz, C.E. Lung Cancer Risk factors—A review article. Eurasian J. Med. Adv. 2022, 4, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.H. Lung cancer: A review. West Indian Med. J. 1975, 24, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, X.; Meng, D.; Zeng, L.; Zhuang, R.; Huang, S.; Lv, W.; Hu, J. Nrf2 Mediates Metabolic Reprogramming in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 578315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Azizi, A.R.J.; IIIzam, E.L.; Nazirah, A.; Sharifa, S.; Abbas, S.A. Lung Cancer: Risk Factors, Management, And Prognosis. IOSR J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2016, 15, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, S.V.S.; Sharma, J.; Kumar, S. GLOBOCAN 2020 Report on Global Cancer Burden: Challenges and Opportunities for Surgical Oncologists. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6497–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, P.M.; Wu, C.C.; Carter, B.W.; Munden, R.F. The epidemiology of lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gridelli, C.; Rossi, A.; Carbone, D.P.; Guarize, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Mok, T.; Petrella, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Rosell, R. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Daemen, A.; Nickles, D.; Jeon, S.-M.; Foreman, O.; Sudini, K.; Gnad, F.; Lajoie, S.; Gour, N.; Mitzner, W.; et al. NRF2 Activation promotes aggressive lung cancer and associates with poor clinical outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J.R.; Yang, P.; Cassivi, S.D.; Schild, S.E.; Adjei, A.A. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fujimoto, J.; Zhang, J.; Wedge, D.C.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Seth, S.; Chow, C.W.; Cao, Y.; Gumbs, C.; et al. Intratumor heterogeneity in localized lung adenocarcinomas delineated by multiregion sequencing. Science 2014, 346, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachgar, A.; Tazi, M.A.; Afif, M.; Er-Raki, A.; Kebdani, T.; Benjaafar, N. Le cancer du poumon: Incidence et survie à Rabat, Maroc. Rev. D’epidemiologie Et De Sante Publique 2016, 64, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Herbst, R.S.; Boshoff, C. Toward personalized treatment approaches for non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-S.; Gilligan, D.; Pacey, S. Treatment approaches for EGFR-inhibitor-resistant patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, e447–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachiglio, A.M.; Abate, R.E.; Sacco, A.; Pasquale, R.; Fenizia, F.; Lambiase, M.; Morabito, A.; Montanino, A.; Rocco, G.; Romano, C.; et al. Limits and potential of targeted sequencing analysis of liquid biopsy in patients with lung and colon carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66595–66605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelos, G.; Riester, M.; Pal, J.; Myacheva, K.; Moneke, I.; Rotondo, J.C.; Lübbert, M.; Diederichs, S. Fast proliferating and slowly migrating non-small cell lung cancer cells are vulnerable to decitabine and retinoic acid combinatorial treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 154, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukier, P.; Santini, F.C.; Scaranti, M.; Hoff, A.O. Endocrine side effects of cancer immunotherapy. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, T331–T347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroschinsky, F.; Stölzel, F.; von Bonin, S.; Beutel, G.; Kochanek, M.; Kiehl, M.; Schellongowski, P. New drugs, new toxicities: Severe side effects of modern targeted and immunotherapy of cancer and their management. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Ostrem, J.; Pellini, B.; Imbody, D.; Stern, Y.; Solanki, H.S.; Haura, E.B.; Villaruz, L.C. Overcoming KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer, American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book. American Society of Clinical Oncology. Annu. Meet. 2022, 42, 700–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.D.; Alexandrov, A.; Kim, J.; Wala, J.; Berger, A.H.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Shukla, S.A.; Guo, G.; Brooks, A.N.; Murray, B.A.; et al. Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canon, J.; Rex, K.; Saiki, A.Y.; Mohr, C.; Cooke, K.; Bagal, D.; Gaida, K.; Holt, T.; Knutson, C.G.; Koppada, N.; et al. The clinical KRAS(G12C) inhibitor AMG 510 drives anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2019, 575, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilly, J.; Hoffman, M.T.; Abbassi, L.; Li, Z.; Paradiso, F.; Parent, B.D.; Hennessey, C.J.; Jordan, A.C.; Morgado, M.; Dasgupta, S.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to oncogenic KRAS inhibition in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 2135–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, M.; Barbacid, M. Targeting KRAS mutant lung cancer: Light at the end of the tunnel. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Cancer metabolism: Looking forward, Nature Reviews. Cancer 2021, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; DeBerardinis, R.J. Understanding the Intersections between Metabolism and Cancer Biology. Cell 2017, 168, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chio, I.I.C.; Tuveson, D.A. ROS in Cancer: The Burning Question. Trends Mol. Med. 2017, 23, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.; Fenster, B.E.; Ito, H.; Takeda, K.; Bae, N.S.; Hirai, T.; Yu, Z.X.; Ferrans, V.J.; Howard, B.H.; Finkel, T. Ras proteins induce senescence by altering the intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 7936–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhu, H. Modulation of redox homeostasis: A strategy to overcome cancer drug resistance. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.S.; DeNicola, G.M. The Complex Interplay between Antioxidants and ROS in Cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Smolenski, R.; Harhun, M.; Patel, H.; Ahmed, S.; Wanisch, K.; Yáñez-Muñoz, R.; Baines, D. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)-dependent and -independent pathways regulate hypoxic inhibition of transepithelial Na+ transport across human airway epithelial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamari, S.; Menju, T.; Toyazaki, T.; Miyamoto, H.; Chiba, N.; Noguchi, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Miyata, R.; Kayawake, H.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Nrf2/p-Fyn/ABCB1 axis accompanied by p-Fyn nuclear accumulation plays pivotal roles in vinorelbine resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 48, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deen, A.J.; Adinolfi, S.; Härkönen, J.; Patinen, T.; Liu, X.; Laitinen, T.; Takabe, P.; Kainulainen, K.; Pasonen-Seppänen, S.; Gawriyski, L.M.; et al. Oncogenic KEAP1 mutations activate TRAF2-NFκB signaling to prevent apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Redox Biol. 2024, 69, 103031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Misra, V.; Thimmulappa, R.K.; Lee, H.; Ames, S.; O Hoque, M.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B.; Sidransky, D.; Gabrielson, E.; et al. Dysfunctional KEAP1-NRF2 interaction in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Venkannagari, S.; Oh, K.H.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Rohde, J.M.; Liu, L.; Nimmagadda, S.; Sudini, K.; Brimacombe, K.R.; Gajghate, S.; et al. Small Molecule Inhibitor of NRF2 Selectively Intervenes Therapeutic Resistance in KEAP1-Deficient NSCLC Tumors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 3214–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Vikash, V.; Ye, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W. ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4350965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pu, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, K.; Deng, L.; Chen, W. Antioxidative and antiapoptosis: Neuroprotective effects of dauricine in Alzheimer’s disease models. Life Sci. 2020, 243, 117237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Lei, P.; Su, X.; Gao, J.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Ma, W. Dauricine Inhibits Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Development by Regulating PTEN/AKT/mTOR and Ras/MEK1/2/ERK1/2 Pathways in a FLT4-dependent Manner. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2024, 24, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zu, X.B.; Chen, M.F.; Qi, L. Dauricine can inhibit the activity of proliferation of urinary tract tumor cells. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 5, 973–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fei, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Zhong, L. Dauricine suppresses the growth of pancreatic cancer in vivo by modulating the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 4403–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, Y.; Qiu, J. Dauricine inhibits viability and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7403–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhai, C.; Yi, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Du, B.; Wu, H.; Guo, X.; et al. Dauricine induces apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and invasion through inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway in colon cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 225, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Kong, Q.; et al. Dynasore-induced potent ubiquitylation of the exon 19 deletion mutant of epidermal growth factor receptor suppresses cell growth and migration in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 105, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, F.; et al. Cholesterol content in cell membrane maintains surface levels of ErbB2 and confers a therapeutic vulnerability in ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. USP39 phase separates into the nucleolus and drives lung adenocarcinoma progression by promoting GLI1 expression. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2025, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, M.Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Sun, Q.; et al. Dynasore potentiates c-Met inhibitors against hepatocellular carcinoma through destabilizing c-Met. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 680, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.Z.; Rehman, A.U.; Yousuf, W.; Khan, A.I.; Farooqui, N.A.; Zang, S.; Xin, Y.; Wang, L. Effect of crude polysaccharide from seaweed, Dictyopteris divaricata (CDDP) on gut microbiota restoration and anti-diabetic activity in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced T1DM mice. Gut Pathog. 2022, 14, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Zaky, M.Y.; Yousuf, W.; Sun, Q.; et al. The deubiquitylase USP2 maintains ErbB2 abundance via counteracting endocytic degradation and represents a therapeutic target in ErbB2-positive breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 2710–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Xiao, M.; Hu, S.; Wang, M. Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: A key mechanism in the occurrence and development of cancer. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1381467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Lin, B.; Jin, W.; Tang, L.; Hu, S.; Cai, R. NRF2, a Superstar of Ferroptosis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrik, I.N.; Golks, A.; Krammer, P.H. Caspases: Pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2665–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, J.K.; Letai, A. Control of mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloni, D.; Diepstraten, S.T.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. BCL-2 protein family: Attractive targets for cancer therapy. Apoptosis Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2023, 28, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamas-Din, A.; Kale, J.; Leber, B.; Andrews, D.W. Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czabotar, P.E.; Lessene, G.; Strasser, A.; Adams, J.M. Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family: Implications for physiology and therapy, Nature Reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.-L.; Zhou, Z.-G.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Fei, H.-X.; Bai, Y. Phenolic alkaloids from Menispermum dauricum inhibits BxPC-3 pancreatic cancer cells by blocking of Hedgehog signaling pathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-D.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, K.-Y. Dauricine inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I-induced hypoxia inducible factor 1α protein accumulation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.K.; Chan, G.; Awang, K.; Kadir, H.A. Deoxyelephantopin from Elephantopus scaber Inhibits HCT116 Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth through Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest. Molecules 2016, 21, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-H.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q.-H.; Hong, P.; Zhang, W.-X.; Liu, Y.-P.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B.; He, Q.-Y. Direct targeting of HSP90 with daurisoline destabilizes β-catenin to suppress lung cancer tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-Q.; Wang, S.-Z.; Lei, H.-B.; Liu, X. Dauricine: Review of Pharmacological Activity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2024, 18, 4371–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Li, X. New insights into crosstalk between Nrf2 pathway and ferroptosis in lung disease. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, P.F.; Fouladdel, S.; Cristofanon, S.; Ghaffari, S.M.; Amin, G.R.; Azizi, E. Comparative cellular and molecular analysis of cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction by doxorubicin and Baneh in human breast cancer T47D cells. Cytotechnology 2011, 63, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yousuf, W.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Ali, P.; Cheng, S.; Ansari, I.; Song, J.; Dai, M.; Qiu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Dauricine Impedes the Tumorigenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Nrf2 and Reactive Oxygen Species. Cells 2025, 14, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100698
Yousuf W, Siddiqui NZ, Ali P, Cheng S, Ansari I, Song J, Dai M, Qiu Z, Zhu Y, Zhang Y, et al. Dauricine Impedes the Tumorigenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Nrf2 and Reactive Oxygen Species. Cells. 2025; 14(10):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100698
Chicago/Turabian StyleYousuf, Waleed, Nimra Zafar Siddiqui, Perbhat Ali, Shaoxuan Cheng, Immad Ansari, Jialiang Song, Minghe Dai, Zhiyuan Qiu, Yue Zhu, Yaowen Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Dauricine Impedes the Tumorigenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Nrf2 and Reactive Oxygen Species" Cells 14, no. 10: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100698
APA StyleYousuf, W., Siddiqui, N. Z., Ali, P., Cheng, S., Ansari, I., Song, J., Dai, M., Qiu, Z., Zhu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, S., Zhang, Y., Liu, Z., & Liu, H. (2025). Dauricine Impedes the Tumorigenesis of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Regulating Nrf2 and Reactive Oxygen Species. Cells, 14(10), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14100698





