Novel Drug Delivery Particles Can Provide Dual Effects on Cancer “Theranostics” in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
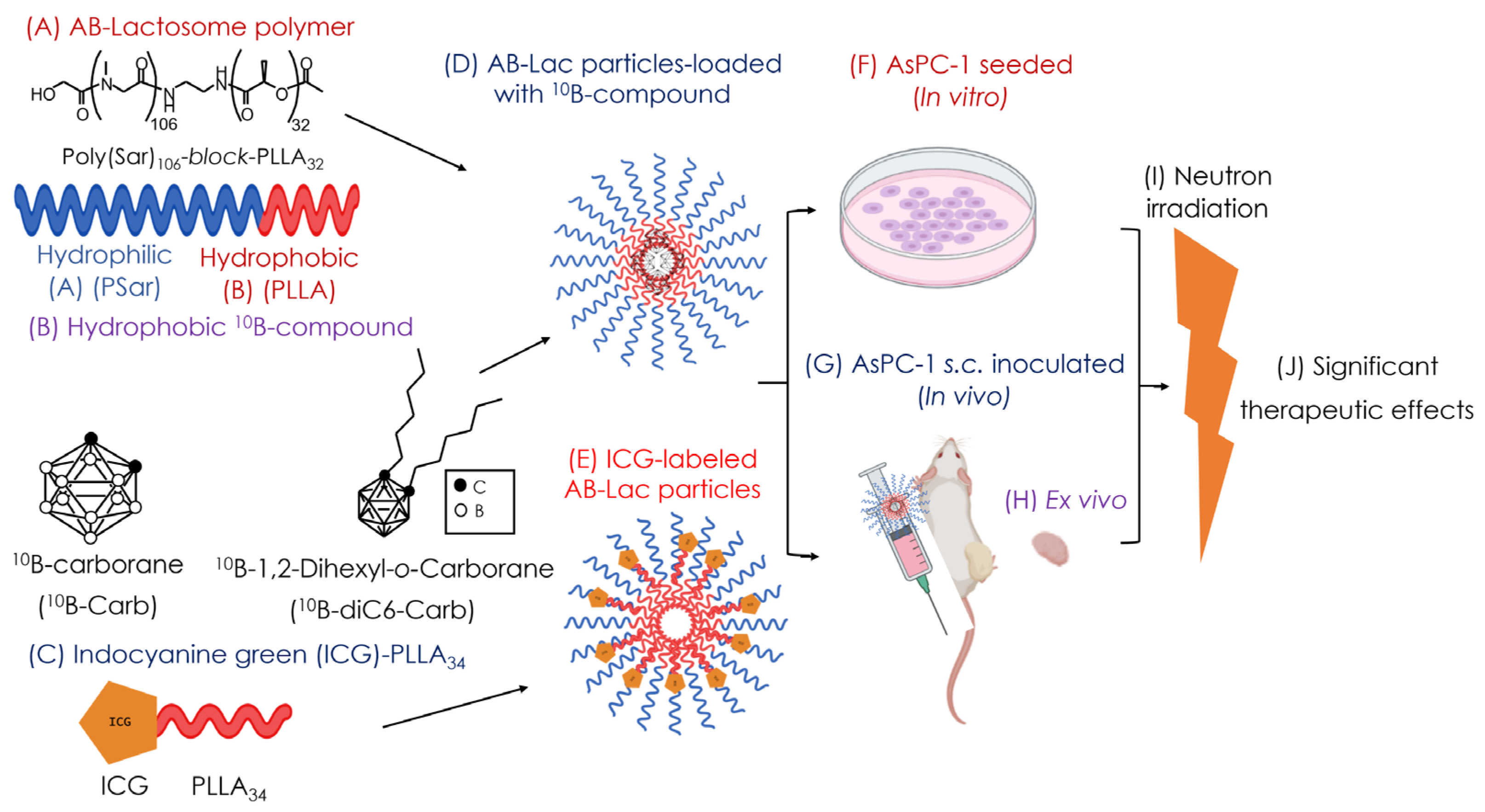
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Preparation of the B (10B)-Compound-Loaded AB-Lac Particles
2.4. Preparation of the ICG-Labeled AB-Lac Particles
2.5. Xenograft
2.6. Ex Vivo Biodistribution of 10B Compound-Loaded AB-Lac Particles
2.7. In Vivo and Ex Vivo NIRF Imaging
2.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
2.9. In Vitro Irradiation (For BNCT)
2.10. In Vivo Irradiation (For BNCT)
2.11. In Vitro Irradiation for Inducing Cell Death (Via ICG)
2.12. In Vivo Irradiation for Inducing Cell Death (Via ICG)
3. Results
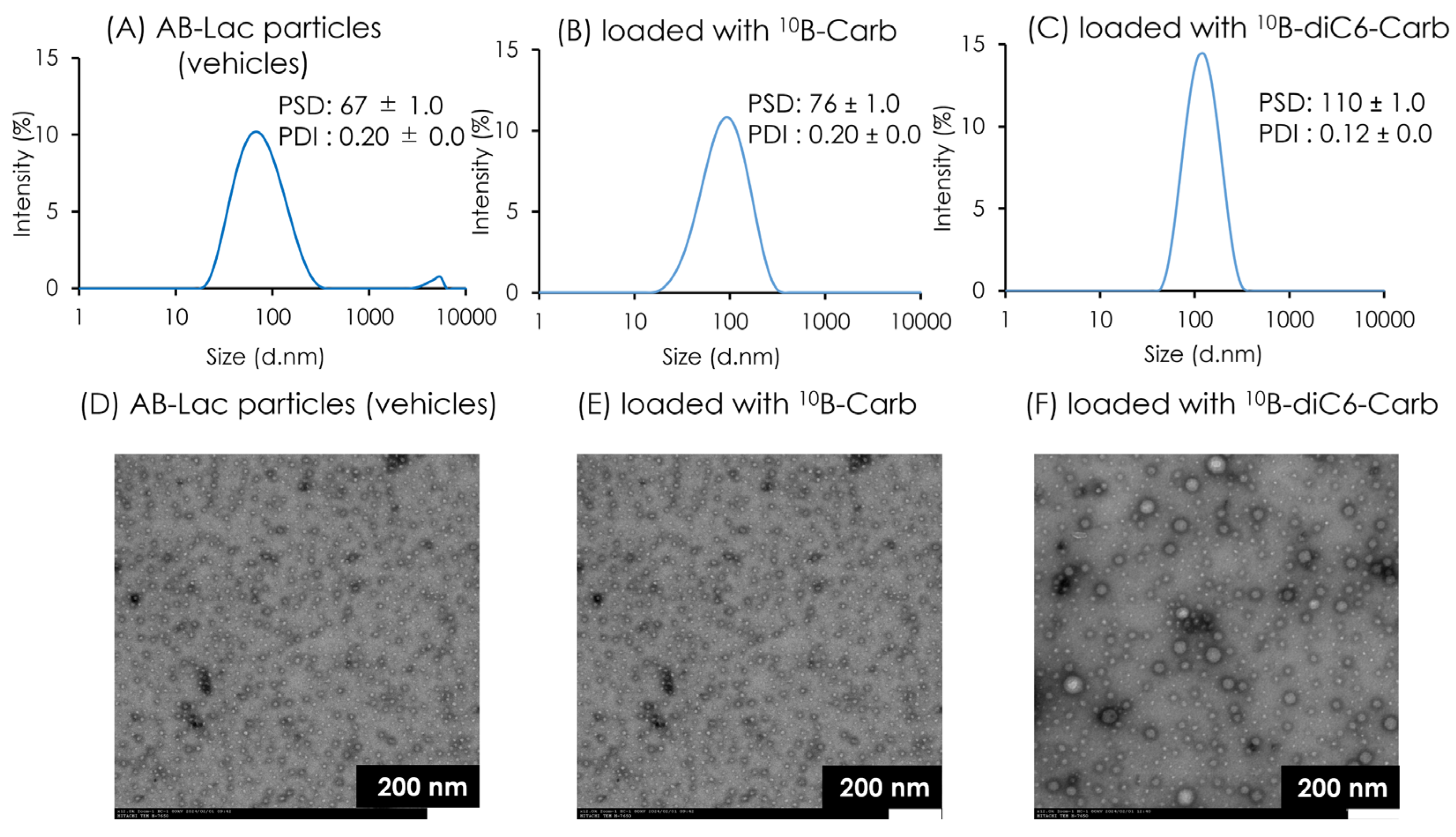
3.1. Characterization of AB-Lac Particles-Loaded with 10B Compounds
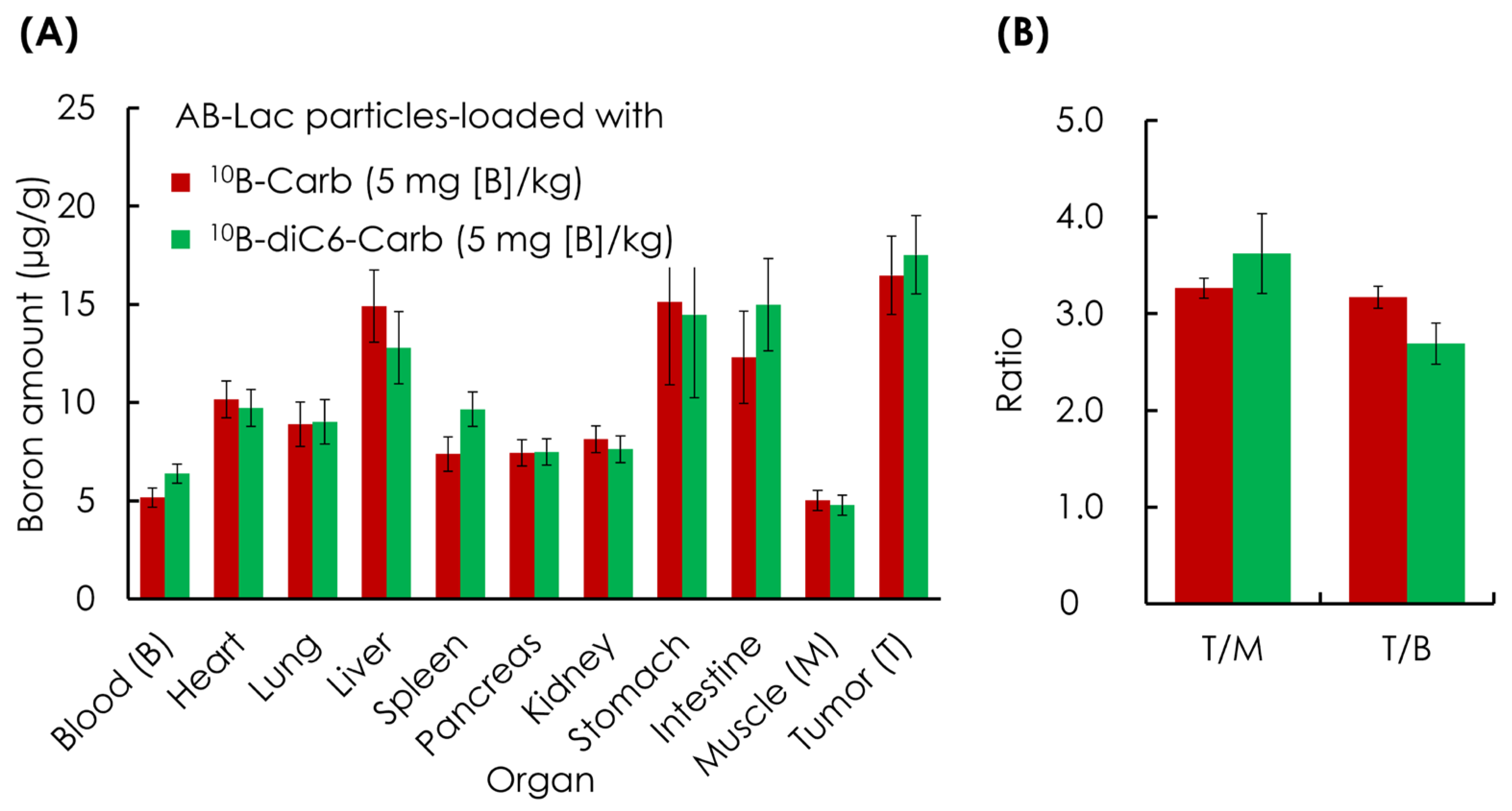
3.2. Ex Vivo B Biodistribution of 10B Compound-Loaded AB-Lac Particles in AsPC-1 Tumor-Bearing Mice for 24 h Post-Injection
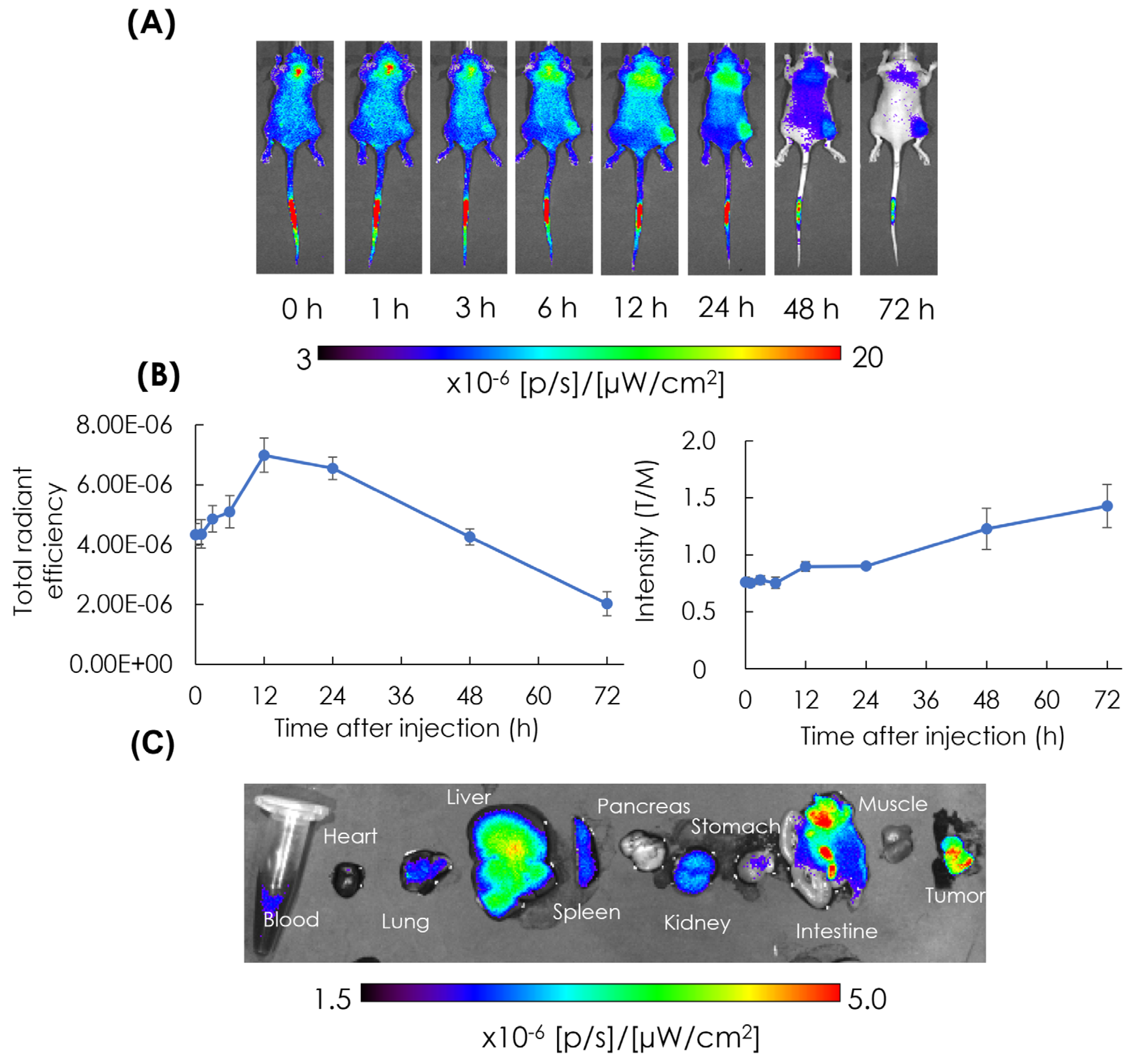
3.3. In Vivo and Ex Vivo NIRF Imaging: Biodistribution of AB-Lac Particles in AsPC-1 Cells-Xenografts
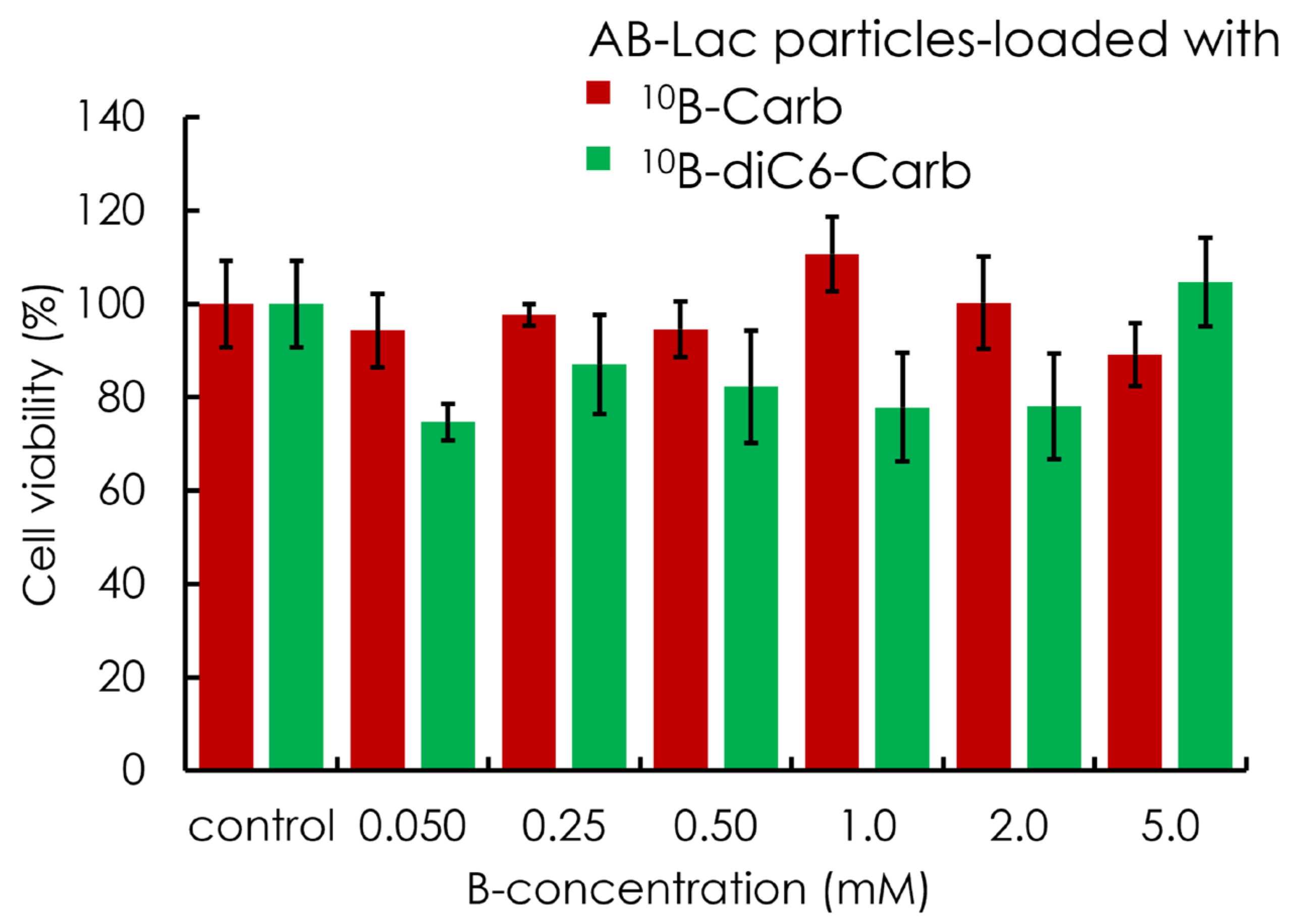
3.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity (Without Neutron Irradiation)
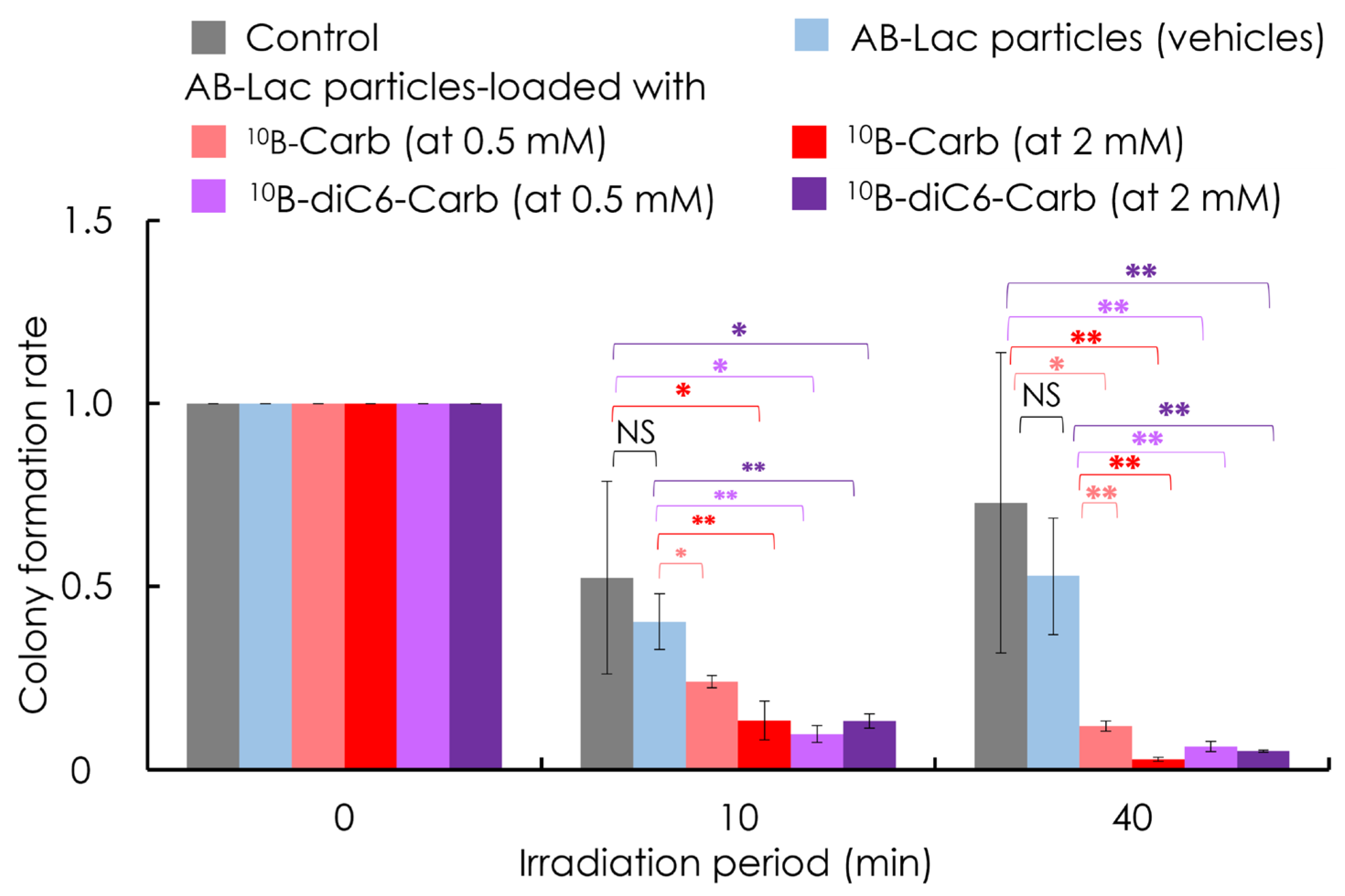
3.5. In Vitro Irradiation for BNCT
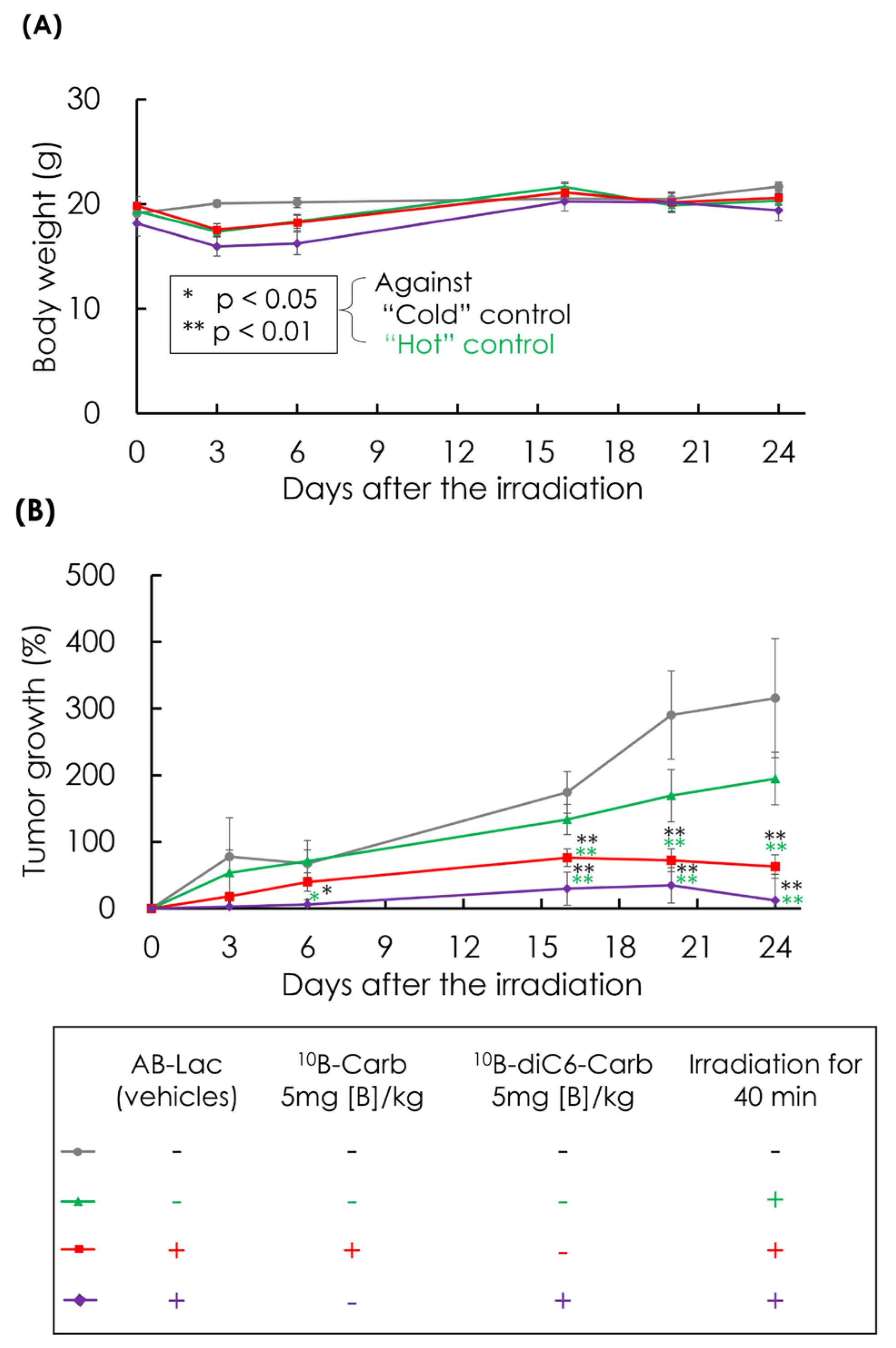
3.6. In Vivo Irradiation for BNCT
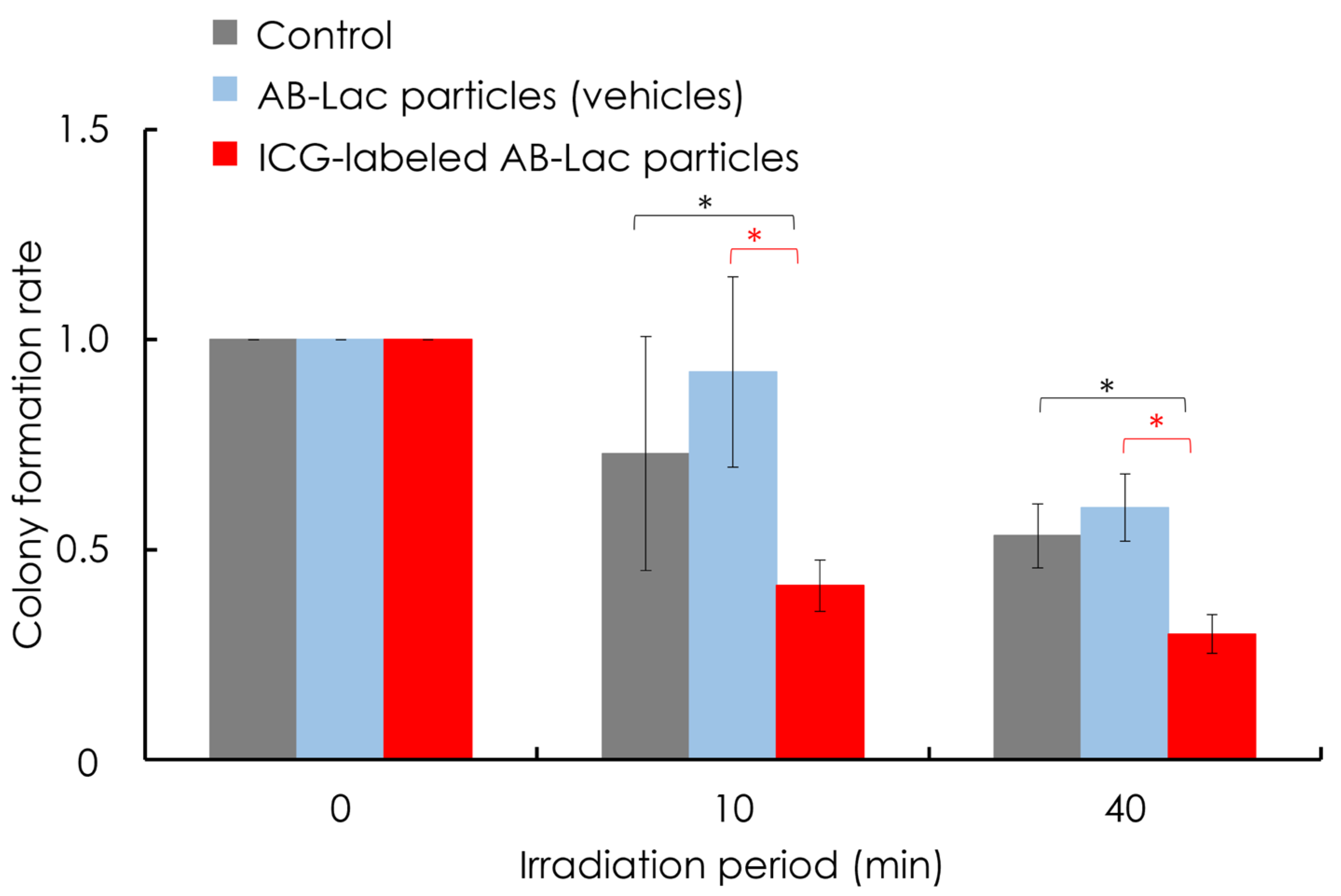
3.7. In Vitro ICG-Dependent Inhibition of Cancer Growth
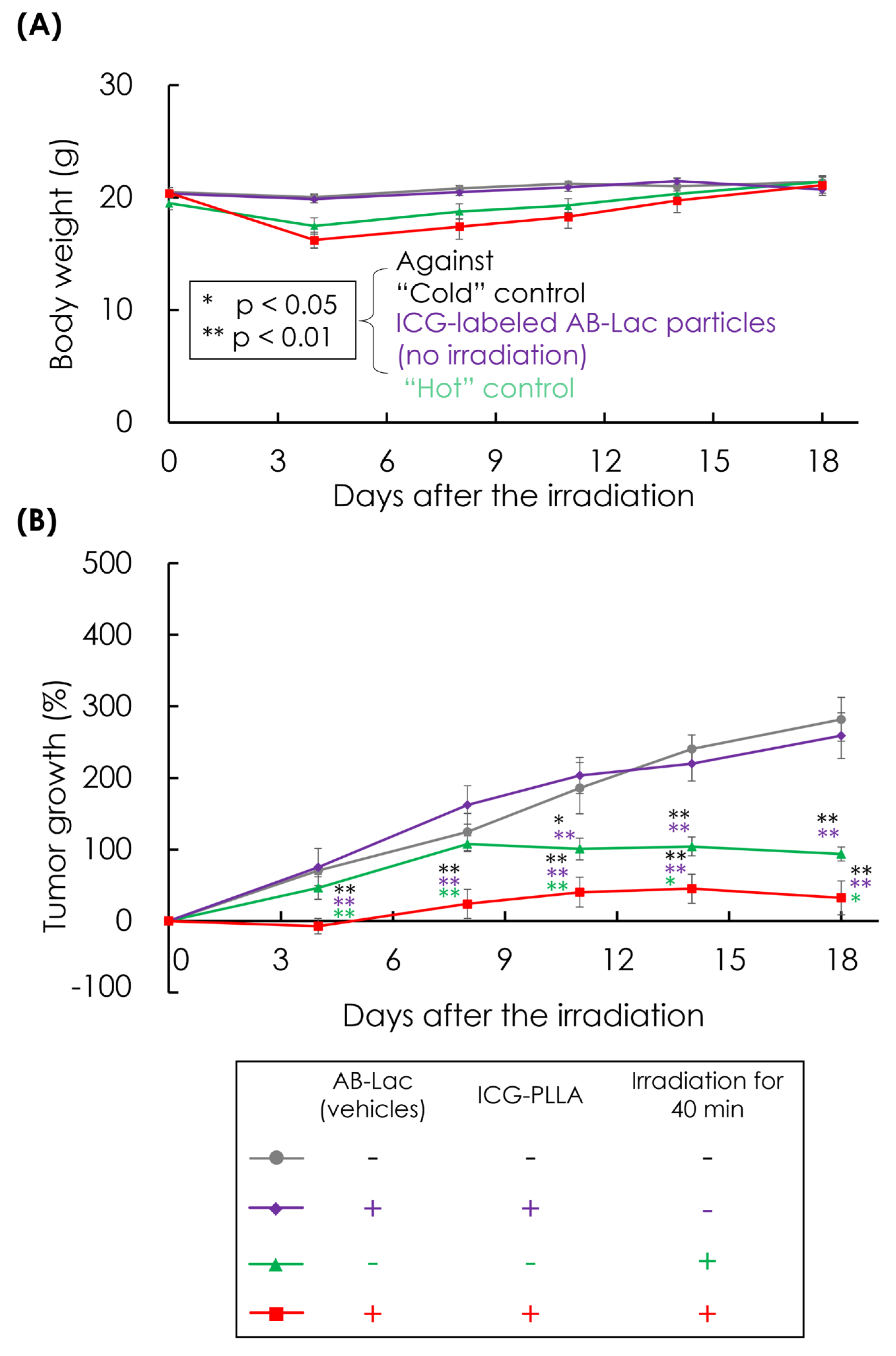
3.8. In Vivo ICG-Dependent Inhibition of Cancer Growth
4. Discussion
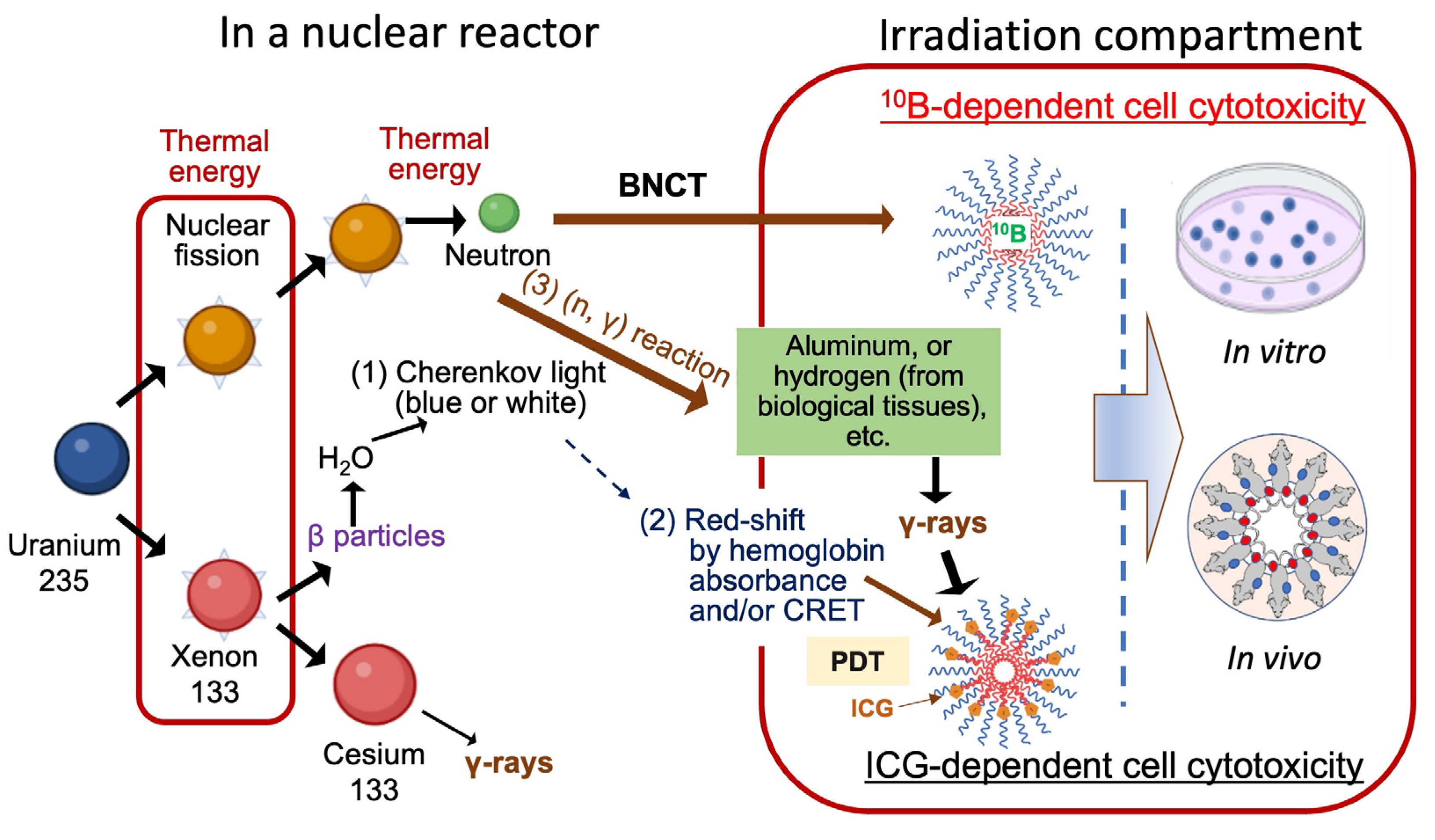
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.X.; Lin, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.F.; Chen, W.B.; Liu, Q.C.; Li, Q.W.; Gao, F. Pancreatic cancer: A review of epidemiology, trend, and risk factors. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4298–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society Key Statistics for Pancreatic Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/pancreatic-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 2 May 2023).
- Suzuki, M. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): A unique role in radiotherapy with a view to entering the accelerator-based BNCT era. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.S.; Hosmane, N.; Zhu, Y. Boron chemistry for medical applications. Molecules 2020, 25, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauerwein, W.A.G. Principles and Roots of Neutron Capture Therapy. In Neutron Capture Therapy; Sauerwein, W., Wittig, A., Moss, R., Nakagawa, Y., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kueffer, P.J.; Maitz, C.A.; Khan, A.A.; Schuster, S.A.; Shlyakhtina, N.I.; Jalisatgi, S.S.; Brockman, J.D.; Nigg, D.W.; Hawthorne, M.F. Boron neutron capture therapy demonstrated in mice bearing EMT6 tumors following selective delivery of boron by rationally designed liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6512–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitto-Barry, A. Polymers and boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): A potent combination. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 2035–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, R.F.; Mi, P.; Yang, W. Boron delivery agents for neutron capture therapy of cancer. Cancer. Commun. 2018, 38, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockmann, P.; Gozzi, M.; Kuhnert, R.; Sárosi, M.B.; Hey-Hawkins, E. New keys for old locks: Carborane-containing drugs as platforms for mechanism-based therapies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3497–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahoshi, A.; Matsuura, E.; Ozeki, E.; Matsui, H.; Watanabe, K.; Ohtsuki, T. Enhanced cellular uptake of lactosomes using cell-penetrating peptides. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 17, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, E.; Ueda, M.; Makino, A.; Hara, I.; Ozeki, E.; Kimura, S. Factors Influencing In Vivo Disposition of Polymeric Micelles on Multiple Administrations. ACS. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Kizaka-Kondoh, S.; Yamahara, R.; Hara, I.; Kanzaki, T.; Ozeki, E.; Hiraoka, M.; Kimura, S. Near-infrared fluorescence tumor imaging using nanocarrier composed of poly (l-lactic acid)-block-poly (sarcosine) amphiphilic polydepsipeptide. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5156–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauerwein, W.A.G.; Sancey, L.; Hey-Hawkins, E.; Kellert, M.; Panza, L.; Imperio, D.; Balcerzyk, M.; Rizzo, G.; Scalco, E.; Herrmann, K.; et al. Theranostics in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Life 2021, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforzi, J.; Lanfranco, A.; Stefania, R.; Alberti, D.; Bitonto, V.; Parisotto, S.; Renzi, P.; Protti, N.; Altieri, S.; Deagostino, A.; et al. A novel pH sensitive theranostic PLGA nanoparticle for boron neutron capture therapy in mesothelioma treatment. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meher, N.; Seo, K.; Wang, S.; Bidkar, A.P.; Fogarty, M.; Dhrona, S.; Huang, X.; Tang, R.; Blaha, C.; Evans, M.J.; et al. Synthesis and Preliminary Biological Assessment of Carborane-Loaded Theranostic Nanoparticles to Target Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54739–54752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalot, G.; Godard, A.; Busser, B.; Pliquett, J.; Broekgaarden, M.; Motto-Ros, V.; Wegner, K.D.; Resch-Genger, U.; Köster, U.; Denat, F.; et al. Aza-BODIPY: A New Vector for Enhanced Theranostic Boron Neutron Capture Therapy Applications. Cells 2020, 9, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fithroni, A.B.; Kobayashi, K.; Uji, H.; Ishimoto, M.; Akehi, M.; Ohtsuki, T.; Matsuura, E. Novel Self-Forming Nanosized DDS Particles for BNCT: Utilizing A Hydrophobic Boron Cluster and Its Molecular Glue Effect. Cells 2022, 11, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Yamahara, R.; Ozeki, E.; Kimura, S. Preparation of novel polymer assemblies, “lactosome”, composed of poly (L-lactic acid) and poly (sarcosine). Chem. Lett. 2007, 36, 1220–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Suzuki, M.; Kuroda, R.; Tanaka, T.; Aoki, S. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Boron-Containing Macrocyclic Polyamines and Their Zinc (II) Complexes for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8523–8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, C.; Bagga, M.; Kaur, A.; Westermarck, J.; Abankwa, D. ColonyArea: An ImageJ plugin to automatically quantify colony formation in clonogenic assays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, A.; Kimura, S. Solid tumor-targeting theranostic polymer nanoparticle in nuclear medicinal Fields. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 424513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barth, R.F.; Coderre, J.A.; Vicente, M.G.H.; Blue, T.E. Boron neutron capture therapy of cancer: Current status and future prospects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3987–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soloway, A.H.; Tjarks, W.; Barnum, B.A.; Rong, F.-G.; Barth, R.F.; Codogni, I.M.; Wilson, J.G. The Chemistry of Neutron Capture Therapy. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1515–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, E.; Makino, A.; Kurihara, K.; Yamamoto, F.; Ozeki, E.; Kimura, S. Pharmacokinetic change of nanoparticulate formulation Lactosome on multiple administrations. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 14, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurihara, K.; Ueda, M.; Hara, I.; Hara, E.; Sano, K.; Makino, A.; Ozeki, E.; Yamamoto, F.; Saji, H.; Togashi, K.; et al. Inflammation-induced synergetic enhancement of nanoparticle treatments with DOXIL® and 90Y-Lactosome for orthotopic mammary tumor. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifschneider, O.; Schütz, C.L.; Brochhausen, C.; Hampel, G.; Ross, T.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U. Quantitative bioimaging of p-boronophenylalanine in thin liver tissue sections as a tool for treatment planning in boron neutron capture therapy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2365–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurubuchi, T.; Shirakawa, M.; Kurosawa, W.; Matsumoto, K.; Ubagai, R.; Umishio, H.; Suga, Y.; Yamazaki, J.; Arakawa, A.; Maruyama, Y.; et al. Evaluation of a novel boron-containing α-D-mannopyranoside for BNCT. Cells 2020, 9, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirata, C.; Kaneko, J.; Inagaki, Y.; Kokudo, T.; Sato, M.; Kiritani, S.; Akamatsu, N.; Arita, J.; Sakamoto, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; et al. Near-infrared photothermal/photodynamic therapy with indocyanine green induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T.; Kaibori, M.; Hishikawa, H.; Nakatake, R.; Okumura, T.; Ozeki, E.; Hara, I.; Morimoto, Y.; Yoshii, K.; Kon, M. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging and photodynamic therapy with indocyanine green lactosome has antineoplastic effects for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Takahata, R.; Nomura, S.; Yoshida, K.; Horiguchi, H.; Hiraki, S.; Ono, S.; Miyazaki, H.; Saito, D.; et al. Photodynamic therapy using nanoparticle loaded with indocyanine green for experimental peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 1626–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yang, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, T.; Xing, D. In vivo photoacoustic therapy with cancer-targeted indocyanine green-containing nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luksiene, Z.; Kalvelyte, A.; Supino, R. On the combination of photodynamic therapy with ionizing radiation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 1999, 52, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hishikawa, H.; Kaibori, M.; Tsuda, T.; Matsui, K.; Okumura, T.; Ozeki, E.; Yoshii, K. Near-infrared fluorescence imaging and photodynamic therapy with indocyanine green lactosomes has antineoplastic effects for gallbladder cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 5622–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.; Lee, S.; Amatya, R.; Cheong, H.; Moon, C.; Kwak, H.D.; Min, K.A.; Shin, M.C. ICG-loaded pegylated BSA-silver nanoparticles for effective photothermal cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5459–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, G.; Lee, B.Y.; Kim, E.J.; Park, M.H.; Hyun, H. Indocyanine green and methyl-β-cyclodextrin complex for enhanced photothermal cancer therapy. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.; Shim, G.; Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, Y.B.; Byun, Y.; Oh, Y.-K. Image-guided synergistic photothermal therapy using photoresponsive imaging agent-loaded graphene-based nanosheets. J. Control. Release 2015, 211, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaibori, M.; Matsui, K.; Hayashi, M. Theranostics Using Indocyanine Green Lactosomes. Cancers 2022, 14, 3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-H.; Kankala, R.; Wang, S.-B.; Chen, A.-Z. Leveraging Engineering of Indocyanine Green-Encapsulated Polymeric Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of the Environment. 2.2 Nuclear Disaster. In BOOKLET to Provide Basic Information Regarding Health Effects of Radiation; Ministry of the Environment, Ed.; Radiation Health Management Division, Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan & National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology: Tokyo, Japan, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of the Environment. Chapter 1 Basic Knowledge on Radiation. In BOOKLET to Provide Basic Information Regarding Health Effects of Radiation; Ministry of the Environment, Ed.; Ministry of the Environment, Government of Japan & National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology: Tokyo, Japan, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mauerhofer, E.; Ilic, Z.; Stieghorst, C.; Révay, Z.; Vezhlev, E.; Ophoven, N.; Randriamalala, T.H.; Brückel, T. Prompt gamma rays from fast neutron inelastic scattering on aluminum, titanium and copper. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2022, 331, 3987–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavadiya, S.; Biswas, P. Design of Cerenkov Radiation–Assisted Photoactivation of TiO2 Nanoparticles and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation for Cancer Treatment. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daouk, J.; Dhaini, B.; Petit, J.; Frochot, C.; Barberi-Heyob, M.; Schohn, H. Can Cerenkov Light Really Induce an Effective Photodynamic Therapy? Radiation 2020, 1, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.; Döbber, A.; Rodat, T.; Lützen, U.; Zhao, Y.; Zuhayra, M.; Peifer, C. Photopharmacological Applications for Cherenkov Radiation Generated by Clinically Used Radionuclides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratx, G.; Kapp, D.S. Is Cherenkov luminescence bright enough for photodynamic therapy? Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhard, Y.; Collin, B.; Decreaú, R.A. Redshifted Cherenkov Radiation for in vivo Imaging: Coupling Cherenkov Radiation Energy Transfer to multiple Förster Resonance Energy Transfers. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lioret, V.; Bellaye, P.-S.; Arnould, C.; Collin, B.; Decréau, R.A. Dual Cherenkov Radiation-Induced Near-Infrared Luminescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy toward Tumor Resection. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 9446–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneller, P.; Collet, C.; Been, Q.; Rocchi, P.; Lux, F.; Tillement, O.; Barberi-Heyob, M.; Schohn, H.; Daouk, J. Added Value of Scintillating Element in Cerenkov-Induced Photodynamic Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsouza, A.; Lin, H.; Gunn, J.R.; Gladstone, D.J.; Jarvis, L.A.; Pogue, B.W. Cherenkov-excited Multi-Fluorophore Sensing in Tissue-Simulating Phantoms and In Vivo from External Beam Radiotherapy. Radiat. Res. 2018, 189, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Su, X.; Sun, X. Cerenkov radiation-activated probes for deep cancer theranostics: A review. Theranostics 2022, 12, 7404–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, A.; Manchanda, R.; Lei, T.; Carvajal, D.A.; Tang, Y.; Kazmi, S.Z.R.; McGoron, A.J. Comparative study of the optical and heat generation properties of IR820 and indocyanine green. Mol. Imaging 2012, 11, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazerabadi, A.R.; Sazgarnia, A.; Bahreyni-Toosi, M.H.; Ahmadi, A.; Aledavood, A. The effects of combined treatment with ionizing radiation and indocyanine green-mediated photodynamic therapy on breast cancer cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2012, 109, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yang, P.; Li, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Dong, C.; Meng, W.; Zhou, H. Ionizing radiation triggers mitophagy to enhance DNA damage in cancer cells. Cell. Death Discov. 2023, 9, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Hur, E.; Kol, R.; Marko, R.; Riklis, E.; Rosenthal, I. Combined Action of Phthalocyanine Photosensitization and Gamma-radiation on Mammalian Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1988, 54, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukanishi, T.; Funayama, T.; Ozeki, E.; Hara, I.; Abe, T.; Onishi, S.; Yamazaki, M.; Sakane, M. Indocyanine Green-lactosome and Near-infrared Light-based Intraoperative Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy for Metastatic Bone Tumors. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2014, 27, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, S.; Deng, W.; Camilleri, E.; Wilson, B.C.; Goldys, E.M. X-ray induced singlet oxygen generation by nanoparticle-photosensitizer conjugates for photodynamic therapy: Determination of singlet oxygen quantum yield. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Laan, A.C.; Plomp, J.; Parnell, S.R.; Men, Y.; Dalgliesh, R.M.; Eelkema, R.; Denkova, A.G. Ionizing Radiation-Induced Release from Poly (ϵ-caprolactone-b-ethylene glycol) Micelles. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friso, E.; Roncucci, G.; Dei, D.; Soncin, M.; Fabris, C.; Chiti, G.; Colautti, P.; Esposito, J.; De Nardo, L.; Riccardo Rossi, C.; et al. A novel 10B-enriched carboranyl-containing phthalocyanine as a radio- and photo-sensitising agent for boron neutron capture therapy and photodynamic therapy of tumours: In vitro and in vivo studies. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2006, 5, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, R.; Kawabata, S.; Tanaka, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Ono, K.; Miyatake, S.I.; Kuroiwa, T.; Hao, E.; Vicente, M.G.H. Tetrakis(p-carboranylthio-tetrafluorophenyl) chlorin (TPFC): Application for photodynamic therapy and boron neutron capture therapy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.S.H.; Ohtsuki, T.; Takenaka, F.; Kobayashi, K.; Akehi, M.; Uji, H.; Kobuchi, H.; Sasaki, T.; Ozeki, E.; Matsuura, E. A Novel 89Zr-labeled DDS device utilizing human IgG variant (scFv): “Lactosome” nanoparticle-based theranostics for PET imaging and targeted therapy. Life 2021, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.S.H.; Nishiyama, Y.; Ohtsuki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Kobuchi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuura, E. Lactosome-Conjugated siRNA Nanoparticles for Photo-Enhanced Gene Silencing in Cancer Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakushiji, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Takenaka, F.; Kishi, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Akehi, M.; Sasaki, T.; Ohno, E.; Matsuura, E. Novel single-chain variant of antibody against mesothelin established by phage library. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 2722–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, J.A.; Button, T.M.; Micca, P.L.; Fisher, C.D.; Nawrocky, M.M.; Liu, H.B. Neutron capture therapy of the 9l rat gliosarcoma using the p-boronophenylalanine-fructose complex. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 30, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fithroni, A.B.; Inoue, H.; Zhou, S.; Hakim, T.F.N.; Tada, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sakurai, Y.; Ishimoto, M.; Yamada, N.; Sauriasari, R.; et al. Novel Drug Delivery Particles Can Provide Dual Effects on Cancer “Theranostics” in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells 2025, 14, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14010060
Fithroni AB, Inoue H, Zhou S, Hakim TFN, Tada T, Suzuki M, Sakurai Y, Ishimoto M, Yamada N, Sauriasari R, et al. Novel Drug Delivery Particles Can Provide Dual Effects on Cancer “Theranostics” in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells. 2025; 14(1):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14010060
Chicago/Turabian StyleFithroni, Abdul Basith, Haruki Inoue, Shengli Zhou, Taufik Fatwa Nur Hakim, Takashi Tada, Minoru Suzuki, Yoshinori Sakurai, Manabu Ishimoto, Naoyuki Yamada, Rani Sauriasari, and et al. 2025. "Novel Drug Delivery Particles Can Provide Dual Effects on Cancer “Theranostics” in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy" Cells 14, no. 1: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14010060
APA StyleFithroni, A. B., Inoue, H., Zhou, S., Hakim, T. F. N., Tada, T., Suzuki, M., Sakurai, Y., Ishimoto, M., Yamada, N., Sauriasari, R., Sauerwein, W. A. G., Watanabe, K., Ohtsuki, T., & Matsuura, E. (2025). Novel Drug Delivery Particles Can Provide Dual Effects on Cancer “Theranostics” in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Cells, 14(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14010060









