JAK/STAT Inhibition Normalizes Lipid Composition in 3D Human Epidermal Equivalents Challenged with Th2 Cytokines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Culture of 3D Epidermal Equivalents and Stimulation with Cytokines and a JAK1/3 Inhibitor
2.4. Isolation of RNA and Analysis of mRNA by Real-Time RT-PCR
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Histology, Morphometry, and Immunofluorescence Analysis of HEEs
2.7. Lipid Extraction
2.8. GCMS Analysis
2.9. LC Separations
2.10. HRMS
2.11. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
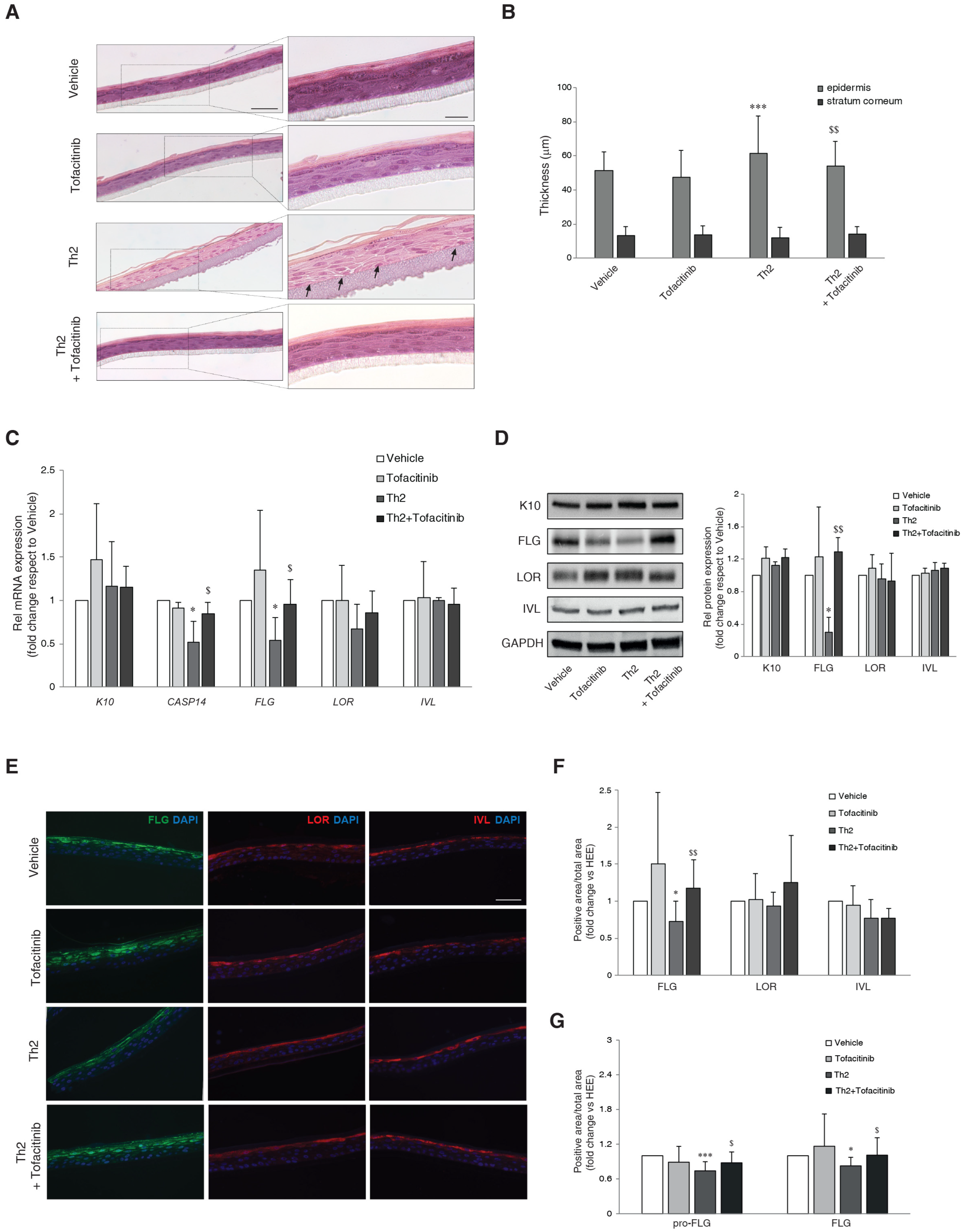
3.1. Effects of JAK/STAT Inhibition by Tofacitinib on Th2 Cytokine-Mediated Changes in Epidermal Morphology and Barrier Protein Expression
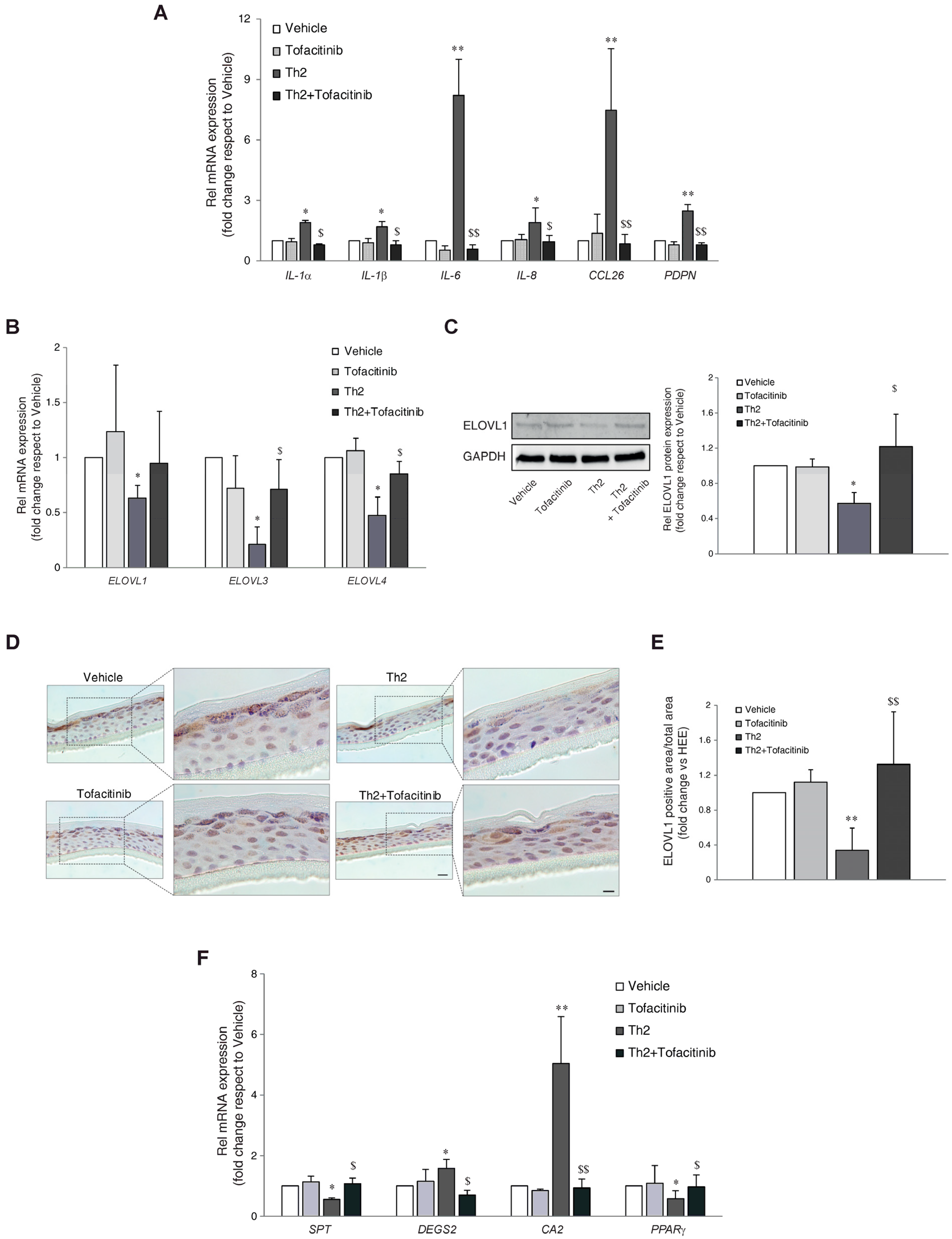
3.2. JAK/STAT Inhibition Counteracts the Induction of Inflammatory Genes in Th2-Treated Epidermal Equivalents
3.3. Modulation of Lipid Genes by Th2 Cytokines and Counteracting Effects of Tofacitinib
3.4. Alteration of Lipid Profiles Induced by Th2 Cytokines and Modulating Effects of Tofacitinib
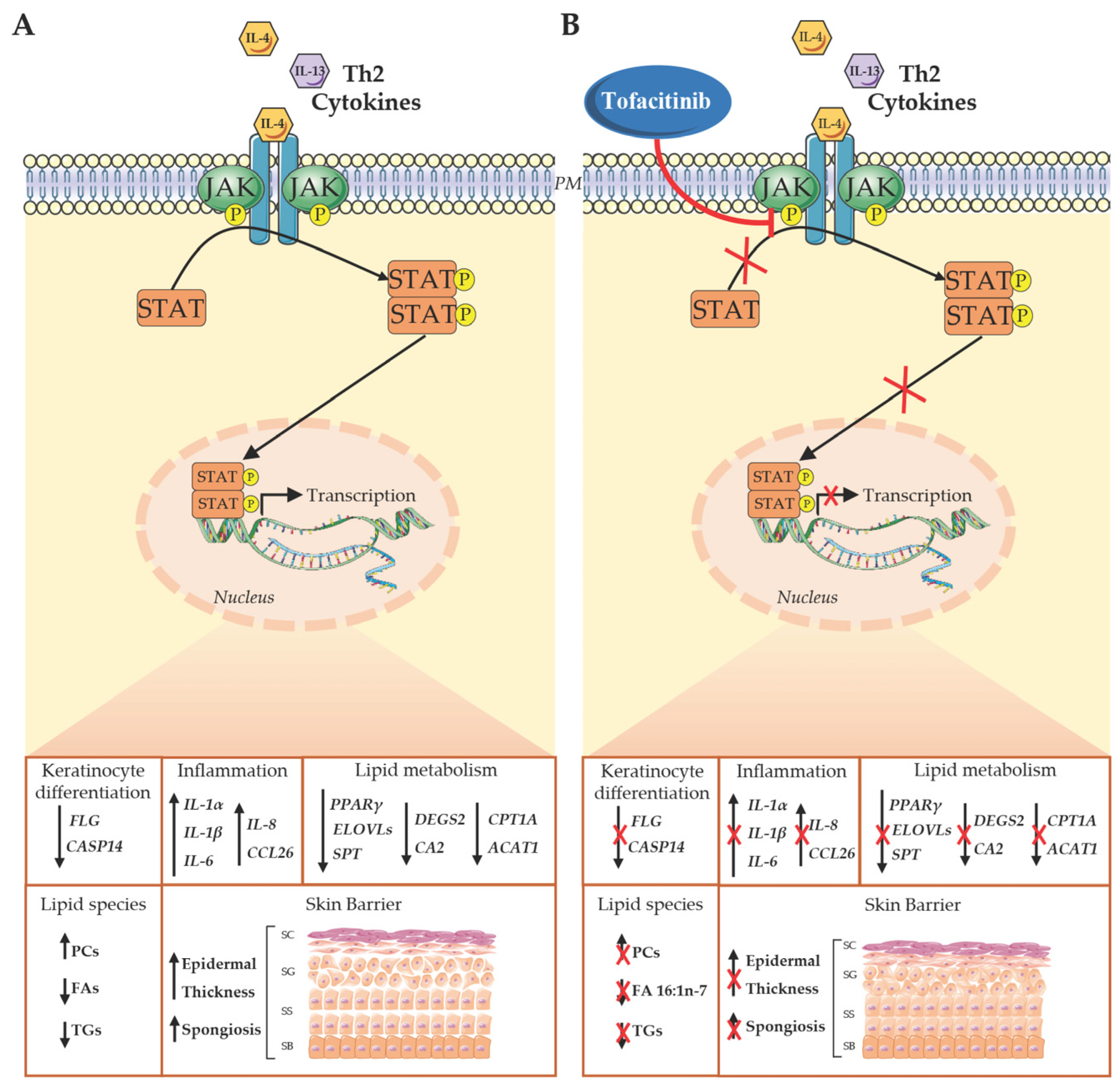
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wolf, R.; Wolf, D. Abnormal epidermal barrier in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, N.A.; Pirozzi, G.; Graham, N.M.H. Commonality of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in atopic diseases. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Seok, J.K.; Kang, H.C.; Cho, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.Y. Skin Barrier Abnormalities and Immune Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Phinney, B.S.; Salemi, M.; Wu, P.; Naeem, M.; Rice, R.H. Human stratum corneum proteomics reveals cross-linking of a broad spectrum of proteins in cornified envelopes. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishitsuka, Y.; Roop, D.R. Loricrin: Past, Present, and Future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Filaggrin, Loricrin, and Involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: Pathogenic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drislane, C.; Irvine, A.D. The role of filaggrin in atopic dermatitis and allergic disease. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 124, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.E.; Leung, D.Y.; Boguniewicz, M.; Howell, M.D. Loricrin and involucrin expression is down-regulated by Th2 cytokines through STAT-6. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 126, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, W.; Nakajima, S.; Kunugi, H.; Numata, Y.; Kitoh, A.; Egawa, G.; Dainichi, T.; Honda, T.; Otsuka, A.; Kimoto, Y.; et al. The Janus kinase inhibitor JTE-052 improves skin barrier function through suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 667–677.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Chen, X.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, X.; Dean, J.M.; Razani, B.; Lodhi, I.J. Acetyl-CoA Derived from Hepatic Peroxisomal β-Oxidation Inhibits Autophagy and Promotes Steatosis via mTORC1 Activation. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 30–42.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chan, L.S. The involvement of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway in chronic inflammatory skin disease atopic dermatitis. JAKSTAT 2013, 2, e24137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, C.; Yanagihara, S.; Otsuka, A. Innovation in the treatment of atopic dermatitis: Emerging topical and oral Janus kinase inhibitors. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, Y.; Adachi, Y.; Elias, P.M.; Crumrine, D.; Sakai, T.; Kurahashi, R.; Katagiri, K.; Fujiwara, S. The Th2 cytokine, interleukin-4, abrogates the cohesion of normal stratum corneum in mice: Implications for pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunduz, O. JAK/STAT pathway modulation: Does it work in dermatology? Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.A.; Torres, T. JAK/STAT inhibitors for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 31, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimani, F.; Meier, K.; Ghoreschi, K. Emerging Topical and Systemic JAK Inhibitors in Dermatology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.-H.; Chung, W.; Wu, P.; Chen, C. JAK-STAT signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis: An updated review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1068260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.J.; Plenge, R. JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity 2012, 36, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Papp, K.A.; Poulin, Y.; Gooderham, M.; Raman, M.; Mallbris, L.; Wang, C.; Purohit, V.; Mamolo, C.; Papacharalambous, J.; et al. Topical tofacitinib for atopic dermatitis: A phase IIa randomized trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 902–911. Available online: https://api.istex.fr/ark:/67375/WNG-2B42NBR1-3/fulltext.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Stahle, M.; Pivarcsi, A.; Sonkoly, E. Tofacitinib Represses the Janus Kinase-Signal Transducer and Activators of Transcription Signalling Pathway in Keratinocytes. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2018, 98, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeoghan, F.; Camera, E.; Maiellaro, M.; Menon, M.; Huang, M.; Dewan, P.; Ziaj, S.; Caley, M.P.; Donaldson, M.; Enright, A.J.; et al. RNA sequencing and lipidomics uncovers novel pathomechanisms in recessive X-linked ichthyosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1176802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovici, M.; Kozul, N.; Materazzi, S.; Risoluti, R.; Picardo, M.; Camera, E. Influence of the sebaceous gland density on the stratum corneum lipidome. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11500–11507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, E.; Ludovici, M.; Galante, M.; Sinagra, J.L.; Picardo, M. Comprehensive analysis of the major lipid classes in sebum by rapid resolution high-performance liquid chromatography and electrospray mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3377–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiellaro, M.; Bottillo, G.; Cavallo, A.; Camera, E. Comparison between ammonium formate and ammonium fluoride in the analysis of stratum corneum lipids by reversed phase chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Züllig, T.; Trötzmüller, M.; Köfeler, H.C. Lipidomics from sample preparation to data analysis: A primer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2191–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köfeler, H.C.; Ahrends, R.; Baker, E.S.; Ekroos, K.; Han, X.; Hoffmann, N.; Holčapek, M.; Wenk, M.R.; Liebisch, G. Recommendations for good practice in MS-based lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarysse, K.; Pfaff, C.M.; Marquardt, Y.; Huth, L.; Kortekaas Krohn, I.; Kluwig, D.; Lüscher, B.; Gutermuth, J.; Baron, J. JAK1/3 inhibition preserves epidermal morphology in full-thickness 3D skin models of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 33, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.; Kemperman, P.; Devos, M.; Denecker, G.; Kezic, S.; Yau, N.; Gilbert, B.; Lippens, S.; De Groote, P.; Roelandt, R.; et al. Caspase-14 Is Required for Filaggrin Degradation to Natural Moisturizing Factors in the Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, M.; Minami-Hori, M.; Takahashi, H.; Iizuka, H. Podoplanin expression in wound and hyperproliferative psoriatic epidermis: Regulation by TGF-beta and STAT-3 activating cytokines, IFN-gamma, IL-6, and IL-22. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 65, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Lu, B.; Kim, P.; Paragh, G.; Schmitz, G.; Elias, P.M.; Feingold, K.R. PPAR and LXR Activators Regulate ABCA12 Expression in Human Keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, K.; Nakayama, H.; Oizumi, A.; Suga, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Takamori, K. Role of Ceramide from Glycosphingolipids and Its Metabolites in Immunological and Inflammatory Responses in Humans. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 120748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Fahy, E.; Aoki, J.; Dennis, E.A.; Durand, T.; Ejsing, C.S.; Fedorova, M.; Feussner, I.; Griffiths, W.J.; Köfeler, H.; et al. Update on LIPID MAPS classification, nomenclature, and shorthand notation for MS-derived lipid structures. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlhoff, M.; Camera, E.; Picardo, M.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Chan, L.; Chang, B.H.; Schneider, M.R. PLIN2, the major perilipin regulated during sebocyte differentiation, controls sebaceous lipid accumulation in vitro and sebaceous gland size in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, P. The New Face of the Lipid Droplet: Lipid Droplet Proteins. Proteomics 2019, 19, e1700223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobs, B.S.; Wanders, R.J. Fatty acid beta-oxidation in peroxisomes and mitochondria: The first, unequivocal evidence for the involvement of carnitine in shuttling propionyl-CoA from peroxisomes to mitochondria. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 213, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, P.; Leman, G.; Hermann, M.; Ploner, C.; Eichmann, T.O.; Minzaghi, D.; Radner, F.P.W.; Del Frari, B.; Gruber, R.; Dubrac, S. Peroxisomal Fatty Acid Oxidation and Glycolysis Are Triggered in Mouse Models of Lesional Atopic Dermatitis. JID Innov. 2021, 1, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houten, S.M.; Violante, S.; Ventura, F.V.; Wanders, R.J.A. The Biochemistry and Physiology of Mitochondrial Fatty Acid β-Oxidation and Its Genetic Disorders. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Fernández, S.; Garcés-Rimón, M.; Vera, G.; Astier, J.; Landrier, J.F.; Miguel, M. High Fat/High Glucose Diet Induces Metabolic Syndrome in an Experimental Rat Model. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamecq, J.; Andreoletti, P.; El Kebbaj, R.; Saih, F.; Latruffe, N.; El Kebbaj, M.H.S.; Lizard, G.; Nasser, B.; Cherkaoui-Malki, M. Peroxisomal Acyl-CoA Oxidase Type 1: Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Aging Properties with a Special Emphasis on Studies with LPS and Argan Oil as a Model Transposable to Aging. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6986984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, G.; Pavel, P.; Hermann, M.; Crumrine, D.; Elias, P.M.; Minzaghi, D.; Goudounèche, D.; Roshardt Prieto, N.M.; Cavinato, M.; Wanner, A.; et al. Mitochondrial Activity Is Upregulated in Nonlesional Atopic Dermatitis and Amenable to Therapeutic Intervention. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 2623–2634.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.; Sun, K.; Hu, Z.; Dong, X. Role of Omega-Hydroxy Ceramides in Epidermis: Biosynthesis, Barrier Integrity and Analyzing Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehues, H.; Bouwstra, J.A.; El Ghalbzouri, A.; Brandner, J.M.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; van den Bogaard, E.H. 3D skin models for 3R research: The potential of 3D reconstructed skin models to study skin barrier function. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, J.P.H.; Niehues, H.; Rikken, G.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.M.J.J.; van de Zande, G.W.H.J.F.; Zeeuwen, P.L.J.M.; Schalkwijk, J.; van den Bogaard, E.H. Immortalized N/TERT keratinocytes as an alternative cell source in 3D human epidermal models. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikken, G.; Niehues, H.; van den Bogaard, E.H. Organotypic 3D Skin Models: Human Epidermal Equivalent Cultures from Primary Keratinocytes and Immortalized Keratinocyte Cell Lines. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2154, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabionet, M.; Gorgas, K.; Sandhoff, R. Ceramide synthesis in the epidermis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, M.; van Smeden, J.; Gooris, G.S.; Bras, W.; Portale, G.; Caspers, P.J.; Vreeken, R.J.; Hankemeier, T.; Kezic, S.; Wolterbeek, R.; et al. Increase in short-chain ceramides correlates with an altered lipid organization and decreased barrier function in atopic eczema patients. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goleva, E.; Berdyshev, E.; Leung, D.Y. Epithelial barrier repair and prevention of allergy. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Berdyshev, E.; Goleva, E. Cutaneous barrier dysfunction in allergic diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langan, S.M.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, D.E.C.; van Smeden, J.; Al-Khakany, H.; Melnik, E.; van Dijk, R.; Absalah, S.; Vreeken, R.J.; Haenen, C.C.P.; Lavrijsen, A.P.M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; et al. Skin of atopic dermatitis patients shows disturbed beta-glucocerebrosidase and acid sphingomyelinase activity that relates to changes in stratum corneum lipid composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158673. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, E.; Yoshida, N.; Sugiura, A.; Imokawa, G. Th1 cytokines accentuate but Th2 cytokines attenuate ceramide production in the stratum corneum of human epidermal equivalents: An implication for the disrupted barrier mechanism in atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2012, 68, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, H.J.; He, C.; Zhao, H.; Dong, Y.; An, I.; An, S. Intercellular and intracellular functions of ceramides and their metabolites in skin (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpin-Nolan, S.M.; Brüning, J.C. The role of ceramides in metabolic disorders: When size and localization matters. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaess, M.; Deigner, H. Derailed Ceramide Metabolism in Atopic Dermatitis (AD): A Causal Starting Point for a Personalized (Basic) Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsurumaki, H.; Katano, H.; Sato, K.; Imai, R.; Niino, S.; Hirabayashi, Y.; Ichikawa, S. WP1066, a small molecule inhibitor of the JAK/STAT3 pathway, inhibits ceramide glucosyltransferase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 491, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, C.; Sakane, F. Sphingomyelin synthase-related protein generates diacylglycerol via the hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids in the absence of ceramide. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günenc, A.N.; Graf, B.; Stark, H.; Chari, A. Fatty Acid Synthase: Structure, Function, and Regulation. In Macromolecular Protein Complexes IV; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 99, pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Smeden, J.; Janssens, M.; Gooris, G.S.; Bouwstra, J.A. The important role of stratum corneum lipids for the cutaneous barrier function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Villarreal, M.; Stewart, S.; Choi, J.; Ganguli-Indra, G.; Babineau, D.C.; Philpot, C.; David, G.; Yoshida, T.; Boguniewicz, M.; et al. Altered composition of epidermal lipids correlates with Staphylococcus aureus colonization status in atopic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, e125–e127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, A.; Camera, E.; Bottillo, G.; Maiellaro, M.; Truglio, M.; Marini, F.; Chavagnac-Bonneville, M.; Fauger, A.; Perrier, E.; Pigliacelli, F.; et al. Biosignatures of defective sebaceous gland activity in sebum-rich and sebum-poor skin areas in adult atopic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e15066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, K.; Karahashi, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Tsuji, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Okazaki, M.; Mitsumoto, A.; Kudo, N.; Kawashima, Y. Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Plays a Key Role in Regulating cis-Palmitoleic Acid Levels in the Liver. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, H.; Flowers, M.T.; Liu, X.; Paton, C.M.; Sullivan, R.; Chu, K.; Zhao, M.; Ntambi, J.M. Skin-specific deletion of stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 alters skin lipid composition and protects mice from high fat diet-induced obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19961–19973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwara, A.; Wertheim-Tysarowska, K.; Mika, A. Alterations of Ultra Long-Chain Fatty Acids in Hereditary Skin Diseases-Review Article. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 730855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdyshev, E.; Goleva, E.; Bronova, I.; Dyjack, N.; Rios, C.; Jung, J.; Taylor, P.; Jeong, M.; Hall, C.F.; Richers, B.N.; et al. Lipid abnormalities in atopic skin are driven by type 2 cytokines. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, P.; Blunder, S.; Moosbrugger-Martinz, V.; Elias, P.M.; Dubrac, S. Atopic Dermatitis: The Fate of the Fat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wen, X.; Hou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, W.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, J. Integrated metabolomics and lipidomics study of patients with atopic dermatitis in response to dupilumab. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1002536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berdyshev, E.; Goleva, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Bronova, I.; Bronoff, A.S.; Richers, B.N.; Garcia, S.; Ramirez-Gama, M.; Taylor, P.; Praestgaard, A.; et al. Dupilumab significantly improves skin barrier function in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Allergy 2022, 77, 3388–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Padilla, C.; Tsoi, L.C.; Nagaraja, V.; Khanna, P.P.; Tabib, T.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Young, A.; Huang, S.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; et al. Tofacitinib blocks IFN-regulated biomarker genes in skin fibroblasts and keratinocytes in a systemic sclerosis trial. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e159566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, N.; Sato, W.J.; Kelly, A.; Ganguli-Indra, G.; Indra, A.K. Epidermal Lipids: Key Mediators of Atopic Dermatitis Pathogenesis. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chinnappan, M.; Prestwood, C.A.; Edwards, M.; Artami, M.; Thompson, B.M.; Eckert, K.M.; Vale, G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; McDonald, J.G.; et al. Interleukins 4 and 13 drive lipid abnormalities in skin cells through regulation of sex steroid hormone synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100749118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodington, D.W.; Desai, H.R.; Woo, M. JAK/STAT—Emerging Players in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.L.; Rutherford, S.L.; Feingold, K.R. Effects of cholesterol sulfate on lipid metabolism in cultured human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. J. Lipid Res. 1987, 28, 955–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponec, M.; Kempenaar, J.; Weerheim, A.; de Lannoy, L.; Kalkman, I.; Jansen, H. Triglyceride metabolism in human keratinocytes cultured at the air-liquid interface. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1995, 287, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schneider, M.R.; Zhang, S.; Li, P. Lipid droplets and associated proteins in the skin: Basic research and clinical perspectives. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2016, 308, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurer, N.Y.; Monger, D.J.; Hincenbergs, M.; Williams, M.L. Fatty acid metabolism in human keratinocytes cultivated at an air-medium interface. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 92, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radner, F.P.W.; Fischer, J. The important role of epidermal triacylglycerol metabolism for maintenance of the skin permeability barrier function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1841, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moessinger, C.; Klizaite, K.; Steinhagen, A.; Philippou-Massier, J.; Shevchenko, A.; Hoch, M.; Ejsing, C.S.; Thiele, C. Two different pathways of phosphatidylcholine synthesis, the Kennedy Pathway and the Lands Cycle, differentially regulate cellular triacylglycerol storage. BMC Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, L.; Kragballe, K. Abnormalities in Epidermal Lipid Metabolism in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flori, E.; Cavallo, A.; Mosca, S.; Kovacs, D.; Cota, C.; Zaccarini, M.; Di Nardo, A.; Bottillo, G.; Maiellaro, M.; Camera, E.; et al. JAK/STAT Inhibition Normalizes Lipid Composition in 3D Human Epidermal Equivalents Challenged with Th2 Cytokines. Cells 2024, 13, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13090760
Flori E, Cavallo A, Mosca S, Kovacs D, Cota C, Zaccarini M, Di Nardo A, Bottillo G, Maiellaro M, Camera E, et al. JAK/STAT Inhibition Normalizes Lipid Composition in 3D Human Epidermal Equivalents Challenged with Th2 Cytokines. Cells. 2024; 13(9):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13090760
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlori, Enrica, Alessia Cavallo, Sarah Mosca, Daniela Kovacs, Carlo Cota, Marco Zaccarini, Anna Di Nardo, Grazia Bottillo, Miriam Maiellaro, Emanuela Camera, and et al. 2024. "JAK/STAT Inhibition Normalizes Lipid Composition in 3D Human Epidermal Equivalents Challenged with Th2 Cytokines" Cells 13, no. 9: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13090760
APA StyleFlori, E., Cavallo, A., Mosca, S., Kovacs, D., Cota, C., Zaccarini, M., Di Nardo, A., Bottillo, G., Maiellaro, M., Camera, E., & Cardinali, G. (2024). JAK/STAT Inhibition Normalizes Lipid Composition in 3D Human Epidermal Equivalents Challenged with Th2 Cytokines. Cells, 13(9), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13090760








