Novel Optical Criteria and Mechanisms of Critical Decline in Liver Regenerative Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
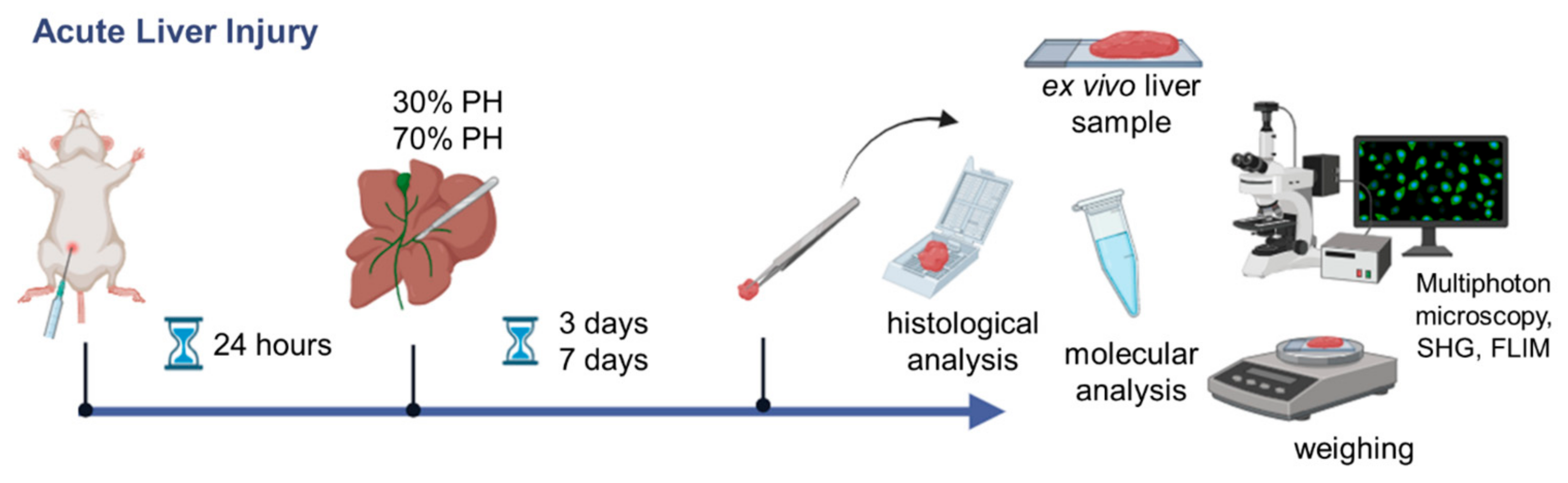
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Morphological Analysis
2.3. Biochemical Blood Tests
2.4. FLIM Analysis
2.5. Real-Time PCR
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
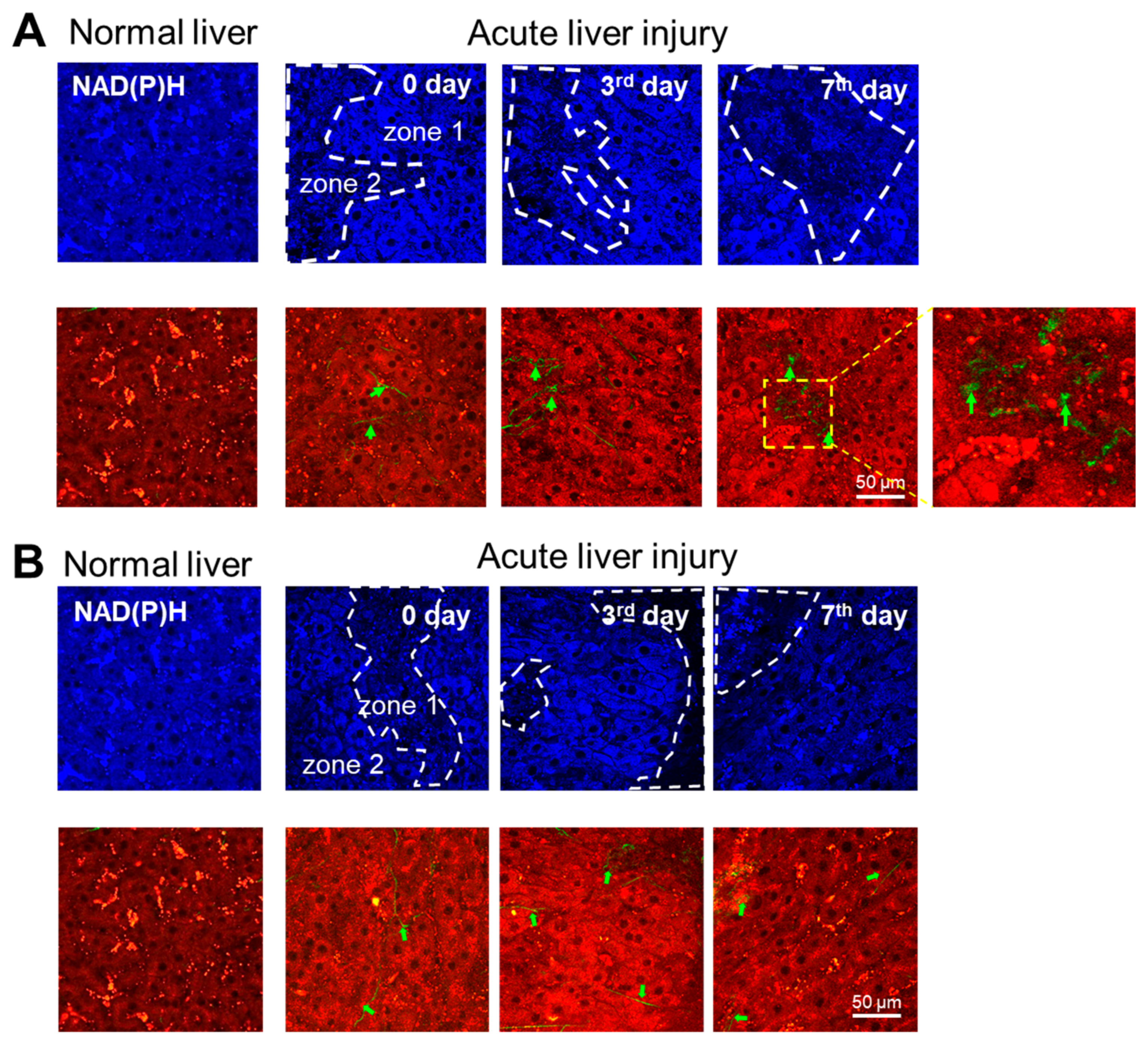
3.1. Multiphoton Microscopy
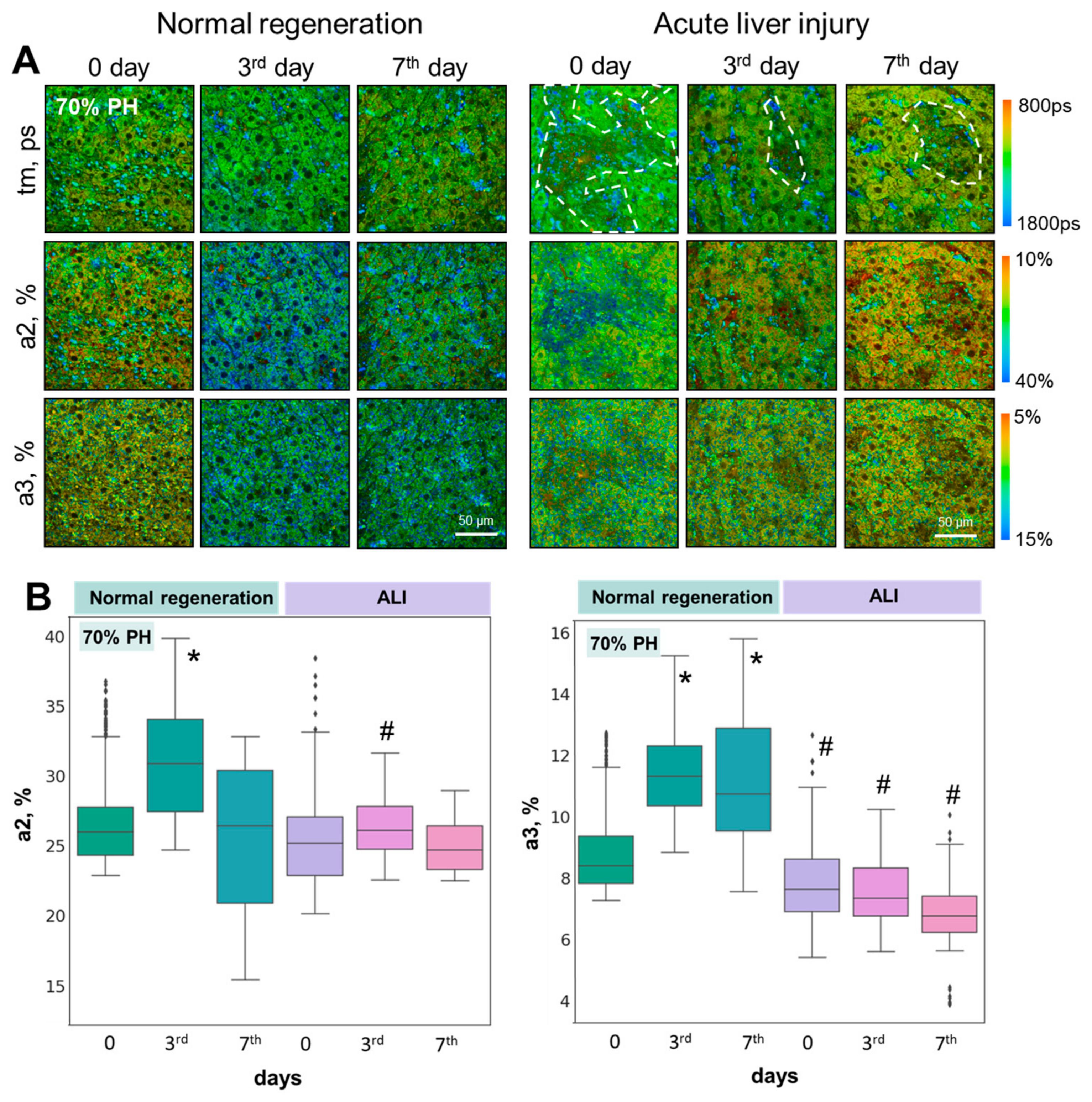
3.2. FLIM Microscopy
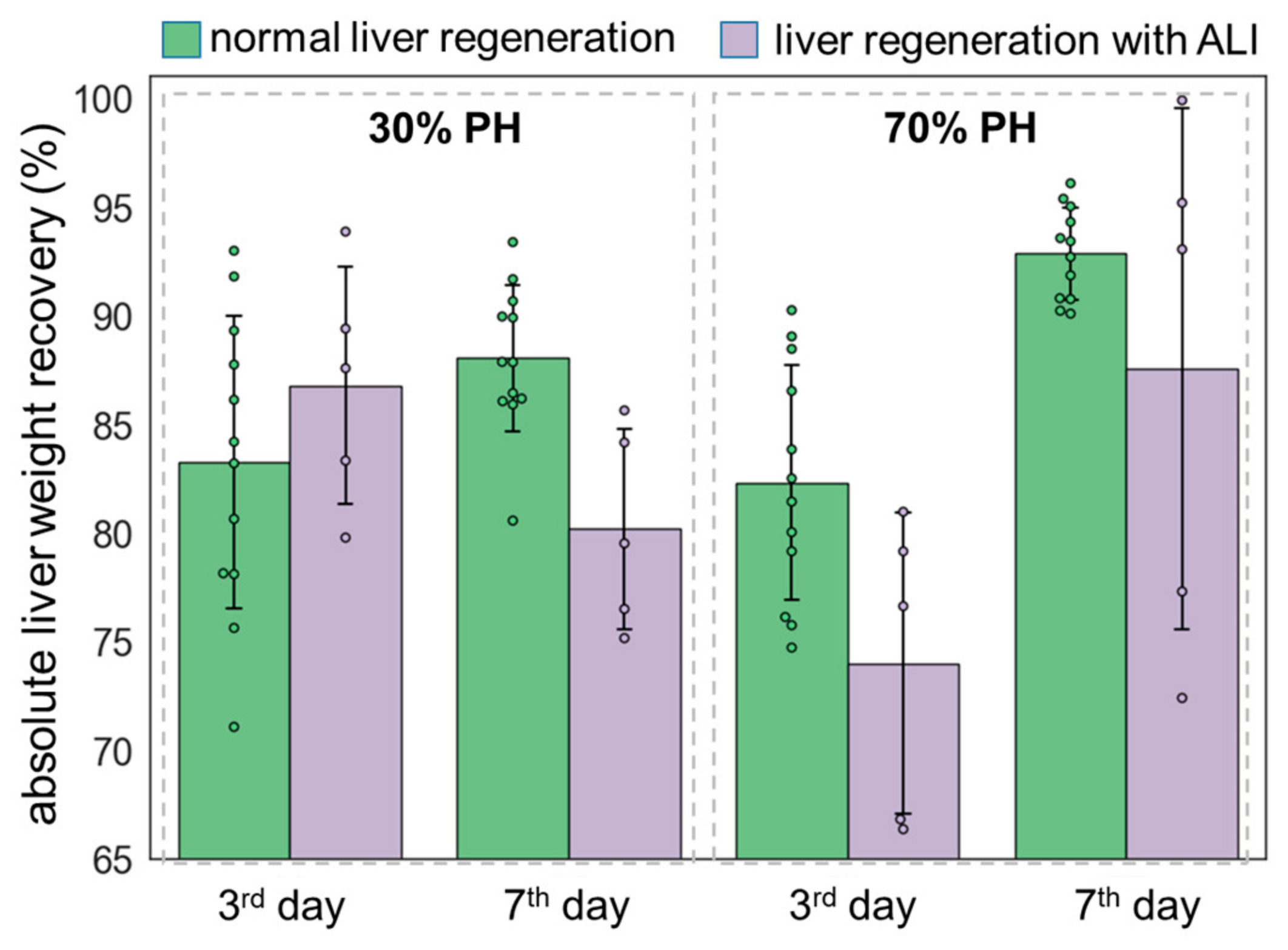
3.3. Liver Weight Restoration Assessment
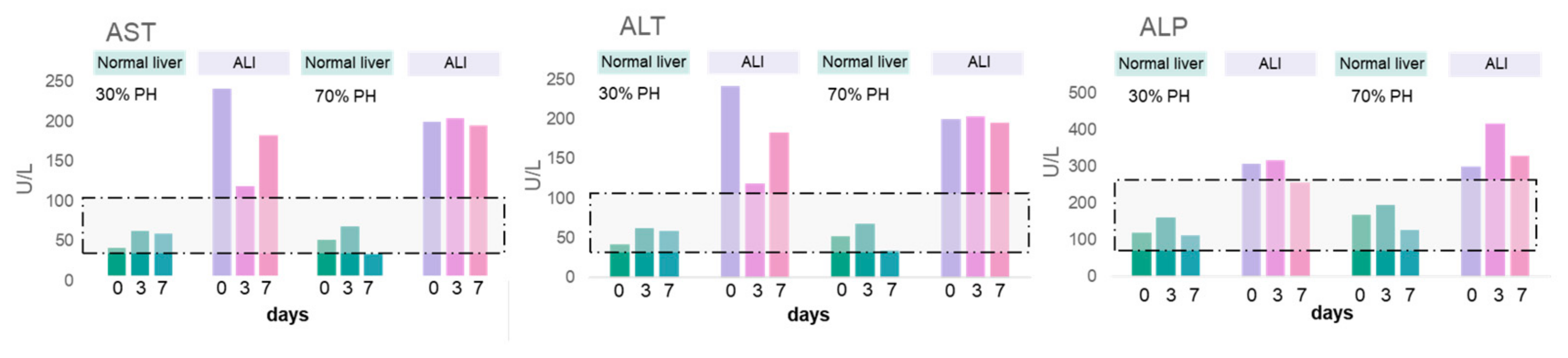
3.4. Morphological Analysis and Biochemical Blood Tests
3.5. Real-Time PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forbes, S.J.; Newsome, N. Liver Regeneration—Mechanisms and models to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.M. Recent developments in acute liver failure. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 26, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narzikulov, R.M. The Use of Excimer Laser in the Treatment of Vitiligo. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Res. Technol. 2021, 8, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Simonova, A.Y.; Ilyashenko, K.K.; Klychnikova, E.V.; Evseev, A.K.; Potskhveriya, M.M.; Belova, M.V.; Tazina, E.V.; Shabanov, A.S.; Kuzovlev, A.N. Parameters of the blood oxidant/antioxidant system in elderly patients with acute poisoning. Gen. Reanimatol. 2022, 18, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Graudins, A. Risk prediction of hepatotoxicity in paracetamol poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, M.E.; Yeager, L.H.; Freeman, W.E. Metabolic and mitochondrial treatments for severe paracetamol poisoning: A systematic review. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 1284–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.-C.; Mao, Y.-M.; Chen, C.-W.; Chen, J.-J.; Chen, J.; Cong, W.-M.; Ding, Y.; Duan, Z.-P.; Fu, Q.-C.; Guo, X.-Y.; et al. Chinese Medical Association (CMA). CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skala, M.C.; Riching, K.M.; Gendron-Fitzpatrick, A.; Eickhoff, J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; White, J.G.; Ramanujam, N. In vivo multiphoton microscopy of NADH and FAD redox states, fluorescence lifetimes, and cellular morphology in precancerous epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19494–19499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Thomas, J.A.; Bridle, K.R.; Thorling, C.A.; Grice, J.E.; Xu, Z.P.; Liu, X.; Crawford, D.H.; et al. Real-time histology in liver disease using multiphoton microscopy with fluorescence lifetime imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Bridle, K.R.; Jayachandran, A.; Thomas, J.A.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, J.; Xu, Z.P.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Liang, X.; et al. Two-photon dual imaging platform for in vivo monitoring cellular oxidative stress in liver injury. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Gravot, G.; Thorling, C.A.; Crawford, D.H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Roberts, M.S. Visualizing liver anatomy, physiology and pharmacology using multiphoton microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.C. Dysregulation of glutathione synthesis in liver disease. Liver Res. 2020, 4, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiff, R.D.; Miller, C.H.; Munn, R.J. Manual hematoxylin and eosin staining of mouse tissue sections. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2014, 2014, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, R.; Filimon, M.N.; Dumitrescu, G.; Ciochina, L.; Dumitrascu, V.; Vlad, D.; Verdes, D. Histological and morphometrical studies in liver regeneration in mice. Sci. Pap. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 45, 203–207. [Google Scholar]
- Rodimova, S.A.; Kuznetsova, D.S.; Bobrov, N.V.; Gulin, A.A.; Reunov, D.G.; Karabut, M.M.; Shcheslavskiy, V.I.; Vdovina, N.V.; Zagainov, V.E.; Zagaynova, E.V. Interrogation of the liver during regeneration by fluorescence lifetime imaging and mass spectrometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2021, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodimova, S.; Bobrov, N.; Mozherov, A.; Elagin, V.; Karabut, M.; Shchechkin, I.; Kozlov, D.; Krylov, D.; Gavrina, A.; Zagainov, V.; et al. Optical Biomedical Imaging Reveals Criteria for Violated Liver Regenerative Potential. Cells 2023, 12, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodimova, S.; Bobrov, N.; Mozherov, A.; Elagin, V.; Karabut, M.; Ermakova, P. The Effect of diabetes mellitus type 1 on the energy metabolism of hepatocytes: Multiphoton microscopy and fluorescence lifetime imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, M.; Gilgenkrantz, H. The impact of steatosis on liver regeneration. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2020, 41, 20180050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, R.D.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Yang, X.; Gill, S.; Schnackenberg, L.K.; Sun, J.; James, L. Translational biomarkers of acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1497–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitch, J.H. The pathology of acute liver failure. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2016, 23, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Song, X.; Xiang, P.; et al. ZHX2 emerges as a negative regulator of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation during acute liver injury. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; Ramachandran, A. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Paradigm for understanding mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2024, 19, 453–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, C.E.; Kitteringham, N.R.; Elsby, R.; Randle, L.E.; Clement, Y.N.; Williams, D.; McMahon, M.; Hayes, J.D.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; et al. Activation of hepatic Nrf2 in vivo by acetaminophen in CD-1 mice. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanim, B.Y.; Ahmad, M.I.; Abdallah, Q.M.; Qatouseh, L.A.; Qinna, N.A. Modulation of NRF2/ARE pathway-and cell death-related genes during drug-induced liver injury. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 2223–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, H.; Kwon, D.; Yun, J.; Jung, Y.S. Downregulation of glutathione-mediated detoxification capacity by binge drinking aggravates acetaminophen-induced liver injury through IRE1α ER stress signaling. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinin, E.; Ducheix, S.; Peres, C.; Arconzo, M.; Vegliante, M.C.; Ferretta, A.; Bellafante, E.; Villani, G.; Moschetta, A. PGC-1β Induces Susceptibility to Acetaminophen-Driven Acute Liver Failure. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, V.; Gheeraert, C.; Vankrunkelsven, W.; Dubois-Chevalier, J.; Dehondt, H.; Bobowski-Gerard, M.; Vinod, M.; Zummo, F.P.; Güiza, F.; Ploton, M.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress actively suppresses hepatic molecular identity in damaged liver. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campana, L.; Esser, H.; Huch, M.; Forbes, S. Liver regeneration and inflammation: From fundamental science to clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, S.Z.; Cai, Q.; Ma, D.; Jiang, L.; Yang, L.; Yu, Z.Y. Identifying the key genes in mouse liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy by bioinformatics analysis and in vitro/vivo experiments. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 670706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilgenkrantz, H.; de l’Hortet, A.C. Understanding liver regeneration: From mechanisms to regenerative medicine. Am. J. Pat. 2018, 188, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Gunewardena, S.; Edwards, G.; Apte, U. Comparison of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy and acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: A global picture based on transcriptome analysis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 139, 111186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, P.; Sharma, Y.; Gupta, P.; Gupta, S. Replicative stress and alterations in cell cycle checkpoint controls following acetaminophen hepatotoxicity restrict liver regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2018, 51, e12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, Q.; Zhao, J.; Song, M.; Yang, C.; Han, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. CMTM6 inhibits tumor growth and reverses chemoresistance by preventing ubiquitination of p21 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzalini, O.; Perucca, P.; Riva, F.; Stivala, L.A.; Bianchi, L.; Vannini, V.; Ducommun, B.; Prosperi, E. p21CDKN1A does not interfere with loading of PCNA at DNA replication sites, but inhibits subsequent binding of DNA polymerase d at the G1/S phase transition. Cell Cycle 2003, 2, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinsimon, S.; Longmuss, E.; Rolff, J.; Jäger, S.; Eggert, A.; Delebinski, C.; Seifert, G. GADD45A and CDKN1A are involved in apoptosis and cell cycle modulatory effects of viscumTT with further inactivation of the STAT3 pathway. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borude, P.; Bhushan, B.; Apte, U. DNA damage response regulates initiation of liver regeneration following acetaminophen overdose. Gene Expr. 2018, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress and acute hepatic injury. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhi, R.; Lotfinia, M.; Gramignoli, R.; Najimi, M.; Vosough, M. Metabolic hallmarks of liver regeneration. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldez, M.J.; Van Hul, N.; Koh, H.W.; Teo, X.Q.; Fan, J.J.; Tan, P.Y.; Dewhurst, M.R.; Too, P.G.; Talib, S.Z.A.; Chiang, B.E.; et al. Metabolic remodeling during liver regeneration. Dev. Cell 2018, 47, 425–438.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli Esposti, D.; Hamelin, J.; Bosselut, N.; Saffroy, R.; Sebagh, M.; Pommier, A.; Martel, C.; Lemoine, A. Mitochondrial roles and cytoprotection in chronic liver injury. Biochem. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 387626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihari, C.; Anand, L.; Rooge, S.; Kumar, D.; Saxena, P.; Shubham, S.; Sukriti; Trehanpati, N.; Kumar, G.; Pamecha, V.; et al. Bone marrow stem cells and their niche components are adversely affected in advanced cirrhosis of the liver. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodimova, S.; Kozlova, V.; Bobrov, N.; Kozlov, D.; Mozherov, A.; Elagin, V.; Shchechkin, I.; Kuzmin, D.; Gavrina, A.; Zagainov, V.; et al. Novel Optical Criteria and Mechanisms of Critical Decline in Liver Regenerative Potential. Cells 2024, 13, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232015
Rodimova S, Kozlova V, Bobrov N, Kozlov D, Mozherov A, Elagin V, Shchechkin I, Kuzmin D, Gavrina A, Zagainov V, et al. Novel Optical Criteria and Mechanisms of Critical Decline in Liver Regenerative Potential. Cells. 2024; 13(23):2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodimova, Svetlana, Vera Kozlova, Nikolai Bobrov, Dmitry Kozlov, Artem Mozherov, Vadim Elagin, Ilya Shchechkin, Dmitry Kuzmin, Alena Gavrina, Vladimir Zagainov, and et al. 2024. "Novel Optical Criteria and Mechanisms of Critical Decline in Liver Regenerative Potential" Cells 13, no. 23: 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232015
APA StyleRodimova, S., Kozlova, V., Bobrov, N., Kozlov, D., Mozherov, A., Elagin, V., Shchechkin, I., Kuzmin, D., Gavrina, A., Zagainov, V., Zagaynova, E., & Kuznetsova, D. (2024). Novel Optical Criteria and Mechanisms of Critical Decline in Liver Regenerative Potential. Cells, 13(23), 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13232015





