HC-HA/PTX3 from Human Amniotic Membrane Induced Differential Gene Expressions in DRG Neurons: Insights into the Modulation of Pain
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Animals
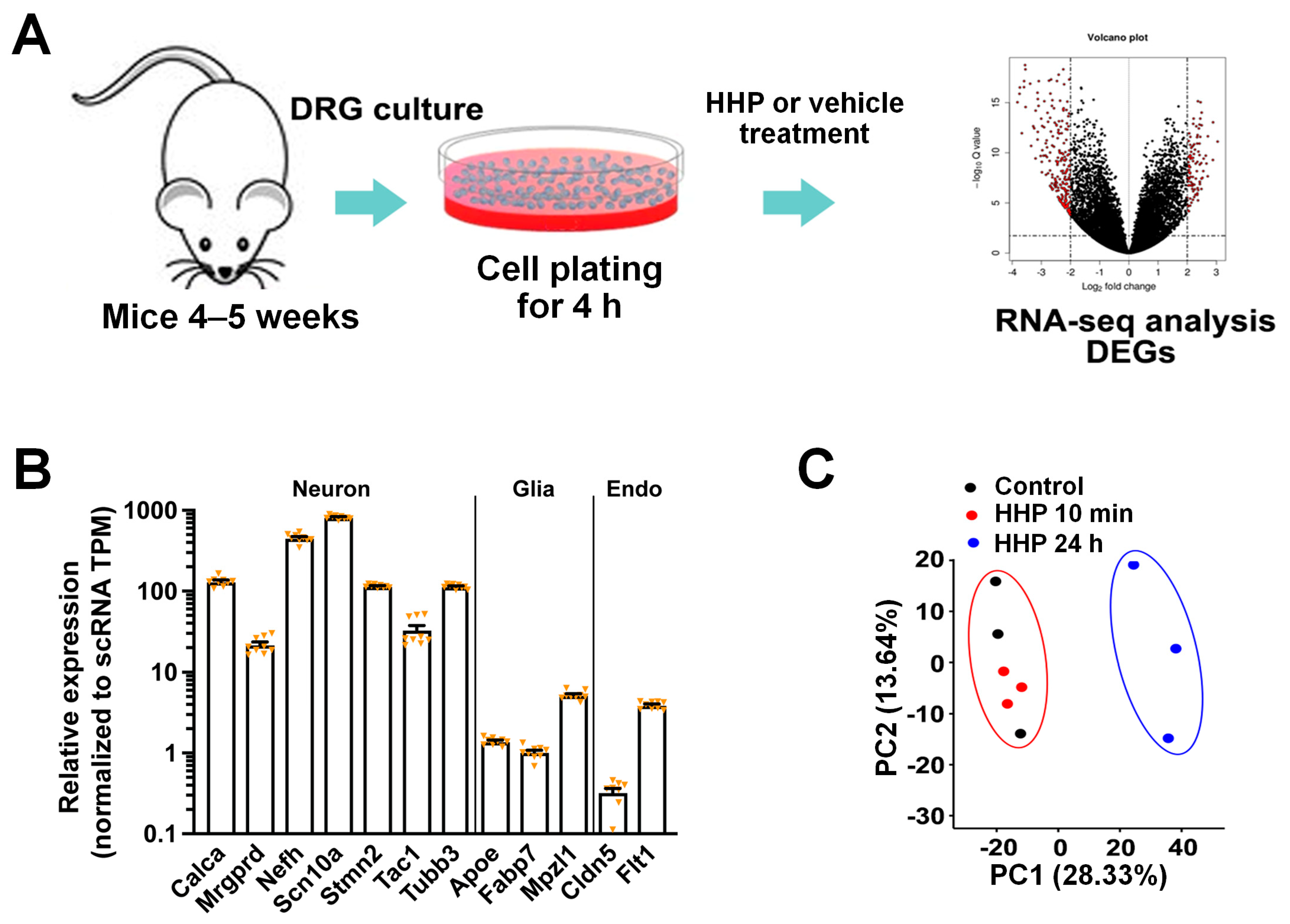
2.2. Culturing DRG Neurons for RNA-Seq
2.3. RNA Isolation, Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.4. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
2.5. Enrichment and Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
2.6. Preparation of HC-HA/PTX3
2.7. Immunoblotting
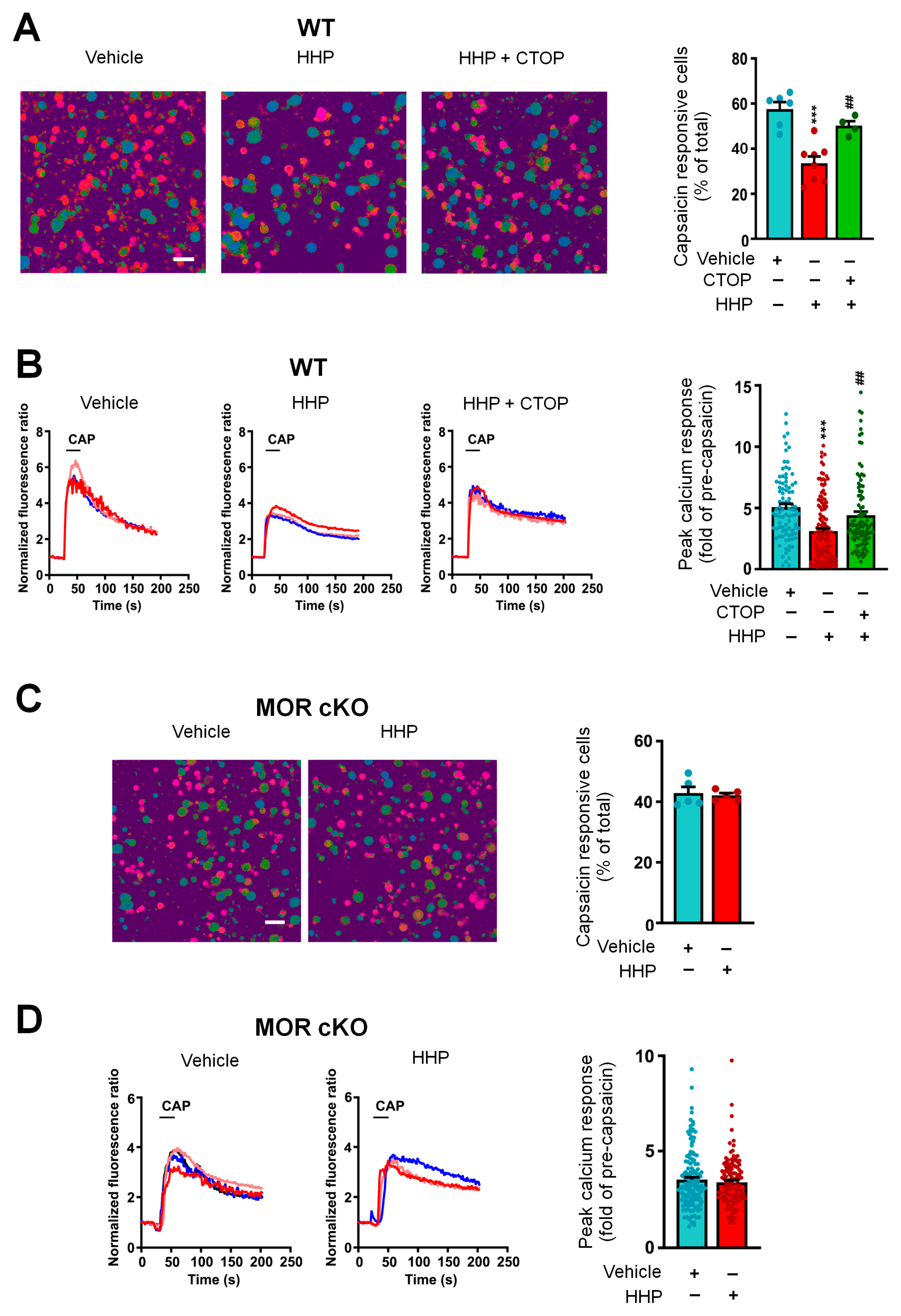
2.8. In Vitro Calcium Imaging
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HC-HA/PTX3 Treatment of Cultured DRG Neurons for RNA-Sequencing
3.2. HC-HA/PTX3 Treatment (24 h) Broadly Changed the Gene Expressions in DRG Neurons
3.3. HC-HA/PTX3 Treatment Altered the Expression of Pain-Related Genes
3.4. The Functional Upregulation of POMC May Contribute to Neuronal Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AM | amniotic membrane |
| AME | amniotic membrane extract |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| DRG | dorsal root ganglia |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| FLO | Clarix Flo |
| GLPs | good laboratory practices |
| GO | gene ontology |
| HA | hyaluronic acid |
| HC-HA/PTX3 | Heavy-chain hyaluronic acid/pentraxin 3 |
| LEPCs | limbal basal epithelial progenitor cells |
| LNCs | limbal niche cells |
| LTMRs | low-threshold mechanoreceptors |
| MORs | mu-opioid receptors |
| POMC | pro-opiomelanocortin |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
References
- Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.T.; Chen, S.Y.; He, H.; Tseng, S.C. Constitutive expression of pentraxin 3 (PTX3) protein by human amniotic membrane cells leads to formation of the heavy chain (HC)-hyaluronan (HA)-PTX3 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13531–13542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tighe, S.; Mead, O.G.; Lee, A.; Tseng, S.C.G. Basic science review of birth tissue uses in ophthalmology. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 10, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Tighe, S.; Lin, S.Y.; Tseng, S.C.G. HC-HA/PTX3 Purified From Human Amniotic Membrane Reverts Human Corneal Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts to Keratocytes by Activating BMP Signaling. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.M.; Zhao, D.; Chen, R.; Yin, H.Y.; Tighe, S.; Sheha, H.; Casas, V.; Tseng, S.C. Accelerated Restoration of Ocular Surface Health in Dry Eye Disease by Self-Retained Cryopreserved Amniotic Membrane. Ocul. Surf. 2016, 14, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheha, H.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Tseng, S.C. Sutureless amniotic membrane transplantation for severe bacterial keratitis. Cornea 2009, 28, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, R.; Tighe, S. Injectable Amniotic Membrane/Umbilical Cord Particulate for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective, Single-Center Pilot Study. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 2283–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, O.G.; Mead, L.P. Intra-Articular Injection of Amniotic Membrane and Umbilical Cord Particulate for the Management of Moderate to Severe Knee Osteoarthritis. Orthop. Res. Rev. 2020, 12, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buksh, A.B. Ultrasound-guided injections of amniotic membrane/umbilical cord particulate for painful neuropathy of the lower extremity. Cogent Med. 2020, 7, 1724067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Flaherty, K.; Lezgiyeva, K.; Wagner, D.E.; Klein, A.M.; Ginty, D.D. The emergence of transcriptional identity in somatosensory neurons. Nature 2020, 577, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, D.; Furlan, A.; Islam, S.; Abdo, H.; Lonnerberg, P.; Lou, D.; Hjerling-Leffler, J.; Haeggstrom, J.; Kharchenko, O.; Kharchenko, P.V.; et al. Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, Q.; Ford, N.C.; Limjunyawong, N.; Lin, Q.; Yang, F.; Cui, X.; Uniyal, A.; Liu, J.; Mahabole, M.; et al. Human Birth Tissue Products as a Non-Opioid Medicine to Inhibit Post-Surgical Pain; eLife Sciences Publications, Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhilko, A.; Nash, A.; Cader, M.Z. Common transcriptional signatures of neuropathic pain. Pain 2020, 161, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Zafra, T.; Gao, T.; Jurczak, A.; Sandor, K.; Hore, Z.; Agalave, N.M.; Su, J.; Estelius, J.; Lampa, J.; Hokfelt, T.; et al. Exploring the transcriptome of resident spinal microglia after collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Pain 2019, 160, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, D.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Bao, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of somatosensory neurons uncovers temporal development of neuropathic pain. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 904–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockley, J.R.F.; Taylor, T.S.; Callejo, G.; Wilbrey, A.L.; Gutteridge, A.; Bach, K.; Winchester, W.J.; Bulmer, D.C.; McMurray, G.; Smith, E.S.J. Single-cell RNAseq reveals seven classes of colonic sensory neuron. Gut 2019, 68, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renthal, W.; Tochitsky, I.; Yang, L.; Cheng, Y.C.; Li, E.; Kawaguchi, R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Woolf, C.J. Transcriptional Reprogramming of Distinct Peripheral Sensory Neuron Subtypes after Axonal Injury. Neuron 2020, 108, 128–144.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Hu, M.W.; Wang, X.W.; Cui, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Cao, X.; Zhou, F.Q.; Qian, J.; He, S.Q.; et al. scRNA-sequencing reveals subtype-specific transcriptomic perturbations in DRG neurons of Pirt(EGFPf) mice in neuropathic pain condition. elife 2022, 11, e76063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, D.G.; Moss, A.; Kennedy, M.; Jones, S.; Nenadic, G.; Robertson, D.L.; Sidders, B. The pain interactome: Connecting pain-specific protein interactions. Pain 2014, 155, 2243–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barpujari, A.; Ford, N.; He, S.Q.; Huang, Q.; Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Dong, X.; Guan, Y.; Raja, S. Role of peripheral sensory neuron mu-opioid receptors in nociceptive, inflammatory, and neuropathic pain. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2020, 45, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.J.; Patel, K.N.; Jeske, N.A.; Bierbower, S.M.; Zou, W.; Tiwari, V.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, Z.; Mo, G.C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Tmem100 Is a Regulator of TRPA1-TRPV1 Complex and Contributes to Persistent Pain. Neuron 2015, 85, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, R.; Wang, F.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y. Three Differential Expression Analysis Methods for RNA Sequencing: Limma, EdgeR, DESeq2. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 175, e62528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.W.; Alhamdoosh, M.; Su, S.; Dong, X.; Tian, L.; Smyth, G.K.; Ritchie, M.E. RNA-seq analysis is easy as 1-2-3 with limma, Glimma and edgeR. F1000Res 2016, 5, ISCB Comm J-1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Parmigiani, G.; Johnson, W.E. ComBat-seq: Batch effect adjustment for RNA-seq count data. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2020, 2, lqaa078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenfuhrer, J.; Lengauer, T. Improved scoring of functional groups from gene expression data by decorrelating GO graph structure. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, W.; Tseng, D.Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.Y.; Day, A.J.; Tseng, S.C. Biochemical characterization and function of complexes formed by hyaluronan and the heavy chains of inter-alpha-inhibitor (HC*HA) purified from extracts of human amniotic membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20136–20146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tang, Z.; Surdenikova, L.; Kim, S.; Patel, K.N.; Kim, A.; Ru, F.; Guan, Y.; Weng, H.J.; Geng, Y.; et al. Sensory neuron-specific GPCR Mrgprs are itch receptors mediating chloroquine-induced pruritus. Cell 2009, 139, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lun, A.T.; Smyth, G.K. From reads to genes to pathways: Differential expression analysis of RNA-Seq experiments using Rsubread and the edgeR quasi-likelihood pipeline. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Huang, K.; Hu, Y.; Du, G.; Xue, Z.; Zhu, X.; Fan, G. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals distinct injury responses in different types of DRG sensory neurons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Han, B.; Zhu, Y.T.; Mahabole, M.; Huang, J.; Beebe, D.C.; Tseng, S.C. HC-HA/PTX3 Purified From Amniotic Membrane Promotes BMP Signaling in Limbal Niche Cells to Maintain Quiescence of Limbal Epithelial Progenitor/Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harno, E.; Gali Ramamoorthy, T.; Coll, A.P.; White, A. POMC: The Physiological Power of Hormone Processing. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 2381–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology, C. The Gene Ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D325–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.X.; Liu, X.J.; Gong, L.Q.; Yao, J.R.; Li, K.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Lin, L.B.; Lu, Y.J.; Xiao, H.S.; Bao, L.; et al. Inhibition of inflammatory pain by activating B-type natriuretic peptide signal pathway in nociceptive sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 10927–10938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Polgar, E.; Solinski, H.J.; Mishra, S.K.; Tseng, P.Y.; Iwagaki, N.; Boyle, K.A.; Dickie, A.C.; Kriegbaum, M.C.; Wildner, H.; et al. Circuit dissection of the role of somatostatin in itch and pain. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, W.W.; Lyu, N.; Cao, H.; Xu, W.D.; Zhang, Y.Q. Growth Differentiation Factor-15 Produces Analgesia by Inhibiting Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Nav1.8 Sodium Channel Activity in Rat Primary Sensory Neurons. Neurosci. Bull. 2021, 37, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, E.; Sandner-Kiesling, A.; Schippinger, W.; Stohscheer, I.; Osprian, I.; Bitsche, S.; Eisner, F.; Verebes, J.; Hofmann, G.; Samonigg, H. IL-7, IL-18, MCP-1, MIP1-beta, and OPG as biomarkers for pain treatment response in patients with cancer. Pain Physician 2012, 15, 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Antin, J.H.; Lee, S.J.; Neuberg, D.; Alyea, E.; Soiffer, R.J.; Sonis, S.; Ferrara, J.L. A phase I/II double-blind, placebo-controlled study of recombinant human interleukin-11 for mucositis and acute GVHD prevention in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2002, 29, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wu, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, B.; Xia, S.; Liang, L.; Zhang, L.; Govindarajalu, G.; Bunk, A.; Kadakia, F.; et al. A nerve injury-specific long noncoding RNA promotes neuropathic pain by increasing Ccl2 expression. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e153563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, K.; Pawlik, K.; Ciapala, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Makuch, W.; Mika, J. Bidirectional Action of Cenicriviroc, a CCR2/CCR5 Antagonist, Results in Alleviation of Pain-Related Behaviors and Potentiation of Opioid Analgesia in Rats with Peripheral Neuropathy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 615327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, H.; Ji, Z. Downregulating lncRNA PVT1 Relieves Astrocyte Overactivation Induced Neuropathic Pain Through Targeting miR-186-5p/CXCL13/CXCR5 Axis. Neurochem Res. 2021, 46, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Xu, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Lo, E.H. Matrix metalloprotease regulation of neuropathic pain. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Li, W.; Liao, Z.; Yan, M.; Chen, X.; Tang, Z. Selective MMP-13 Inhibitors: Promising Agents for the Therapy of Osteoarthritis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 3753–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Wang, P.; Nguyen, N.U.N.; Nakada, Y.; Menendez-Montes, I.; Ismail, M.; Bachoo, R.; Henkemeyer, M.; Sadek, H.A.; Kandil, E.S. Identification of tetracycline combinations as EphB1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors for treatment of neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2016265118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, S.; Alvarado-Vazquez, P.A.; Eisenach, J.C.; Romero-Sandoval, E.A.; Boada, M.D. Tachykinins modulate nociceptive responsiveness and sensitization: In vivo electrical characterization of primary sensory neurons in tachykinin knockout (Tac1 KO) mice. Mol. Pain 2019, 15, 1744806919845750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, A.; Sathyamurthy, A.; Thompson, J.; Seltzer, M.; Levine, A.; Chesler, A. A spinoparabrachial circuit defined by Tacr1 expression drives pain. elife 2021, 10, e61135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhan, S.E.; Avramut, M. Matrix metalloproteinases in neuropathic pain and migraine: Friends, enemies, and therapeutic targets. Pain Res. Treat. 2012, 2012, 952906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, T.M.; Talbot, J.; Pinto, L.G.; Vieira, S.M.; Souza, G.R.; Guerrero, A.T.; Sonego, F.; Verri, W.A., Jr.; Zamboni, D.S.; Ferreira, S.H.; et al. Caspase-1 is involved in the genesis of inflammatory hypernociception by contributing to peripheral IL-1beta maturation. Mol. Pain 2010, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhof, A.K.; Gluck, L.; Gajda, M.; Lupp, A.; Brauer, R.; Schaible, H.G.; Schulz, S. Differential antiinflammatory and antinociceptive effects of the somatostatin analogs octreotide and pasireotide in a mouse model of immune-mediated arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2352–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, D.; Agarwal, N.; Fleming, T.; Gaveriaux-Ruff, C.; Klose, C.S.N.; Tappe-Theodor, A.; Kuner, R.; Nawroth, P. Loss of POMC-mediated antinociception contributes to painful diabetic neuropathy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.M.S.; Tighe, S.; Sheha, H.; Tseng, S.C.G. Adjunctive role of self-retained cryopreserved amniotic membrane in treating immune-related dry eye disease. Int. Ophthalmol. 2018, 38, 2219–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, A.; Hochgerner, H.; Lonnerberg, P.; Johnsson, A.; Memic, F.; van der Zwan, J.; Haring, M.; Braun, E.; Borm, L.E.; La Manno, G.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the Mouse Nervous System. Cell 2018, 174, 999–1014.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Iskols, M.; Shi, D.; Reddy, P.; Walker, C.; Lezgiyeva, K.; Voisin, T.; Pawlak, M.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Chiu, I.; et al. A DRG genetic toolkit reveals molecular, morphological, and functional diversity of somatosensory neuron subtypes. bioRxiv 2023. [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, S.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.-W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Lin, Q.; He, H.; Yang, D.-Z.; Tseng, S.C.; Guan, Y. HC-HA/PTX3 from Human Amniotic Membrane Induced Differential Gene Expressions in DRG Neurons: Insights into the Modulation of Pain. Cells 2024, 13, 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13221887
He S-Q, Zhang C, Wang X-W, Huang Q, Liu J, Lin Q, He H, Yang D-Z, Tseng SC, Guan Y. HC-HA/PTX3 from Human Amniotic Membrane Induced Differential Gene Expressions in DRG Neurons: Insights into the Modulation of Pain. Cells. 2024; 13(22):1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13221887
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Shao-Qiu, Chi Zhang, Xue-Wei Wang, Qian Huang, Jing Liu, Qing Lin, Hua He, Da-Zhi Yang, Scheffer C. Tseng, and Yun Guan. 2024. "HC-HA/PTX3 from Human Amniotic Membrane Induced Differential Gene Expressions in DRG Neurons: Insights into the Modulation of Pain" Cells 13, no. 22: 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13221887
APA StyleHe, S.-Q., Zhang, C., Wang, X.-W., Huang, Q., Liu, J., Lin, Q., He, H., Yang, D.-Z., Tseng, S. C., & Guan, Y. (2024). HC-HA/PTX3 from Human Amniotic Membrane Induced Differential Gene Expressions in DRG Neurons: Insights into the Modulation of Pain. Cells, 13(22), 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13221887





