A Non-Canonical p75HER2 Signaling Pathway Underlying Trastuzumab Action and Resistance in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Chemicals and Antibodies
2.3. Plasmids
2.4. Plasmid Transfection
2.5. Cell Proliferation (Viability) Assay by MTT
2.6. Subcellular Fractionation
2.7. Cell Lysates and Immunoblotting
2.8. Immunofluorescence
3. Results
3.1. Trastuzumab Specifically Binds to HER2
3.2. Trastuzumab Inhibits Proliferation of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells
3.3. Proteolytic Cleavage of HER2 and Its Inhibition by Trastuzumab
3.4. p75HER2 Is Cytosolic and Translocated to Nucleus
3.5. Phosphorylation of p75HER2 and the Effects of Trastuzumab
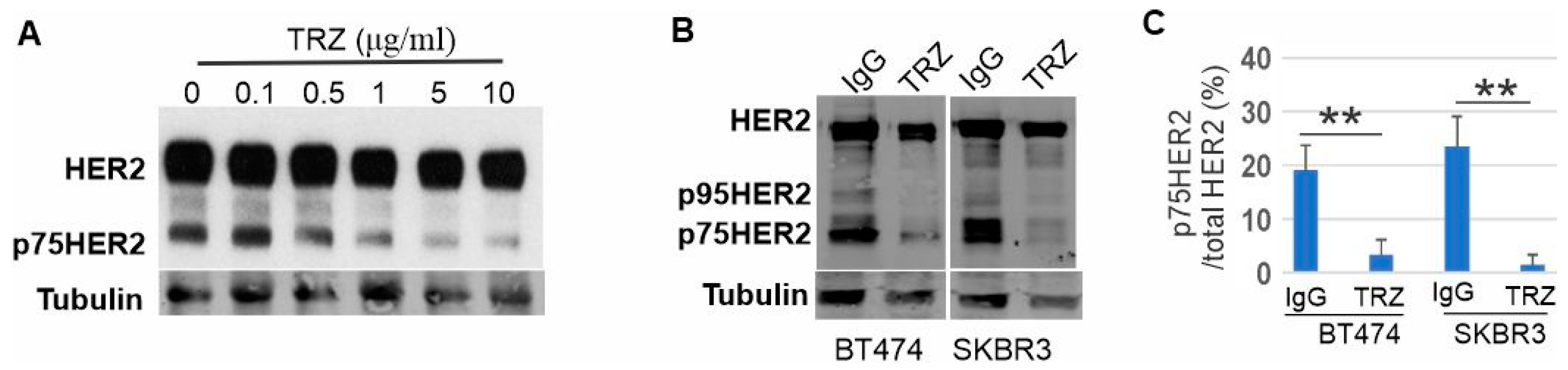
3.6. Generation of p75HER2 by Two Proteolytic Cleavages and Its Inhibition by Trastuzumab
3.7. The Role of p75HER2 in Cell Proliferation and in Trastuzumab Resistance
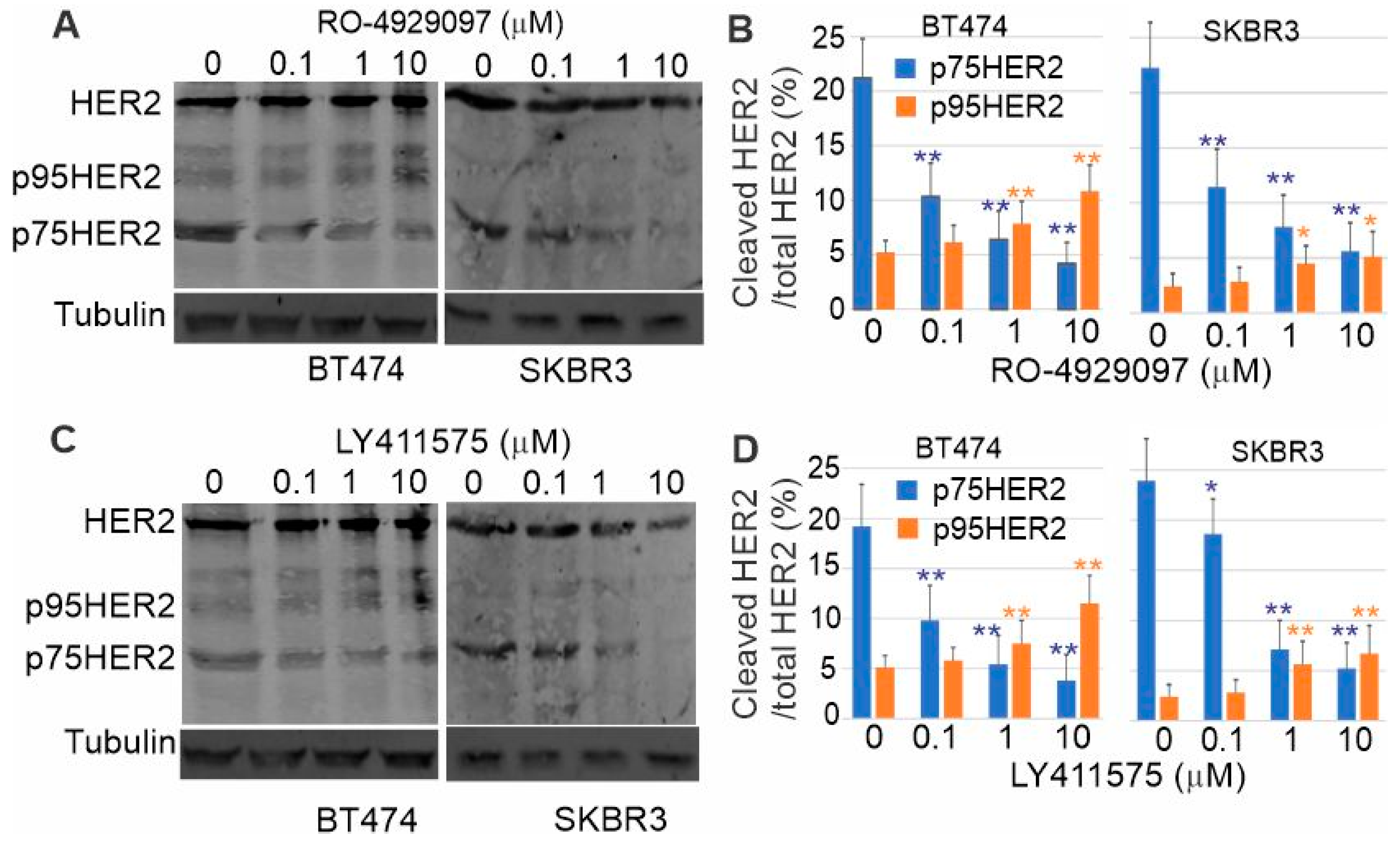
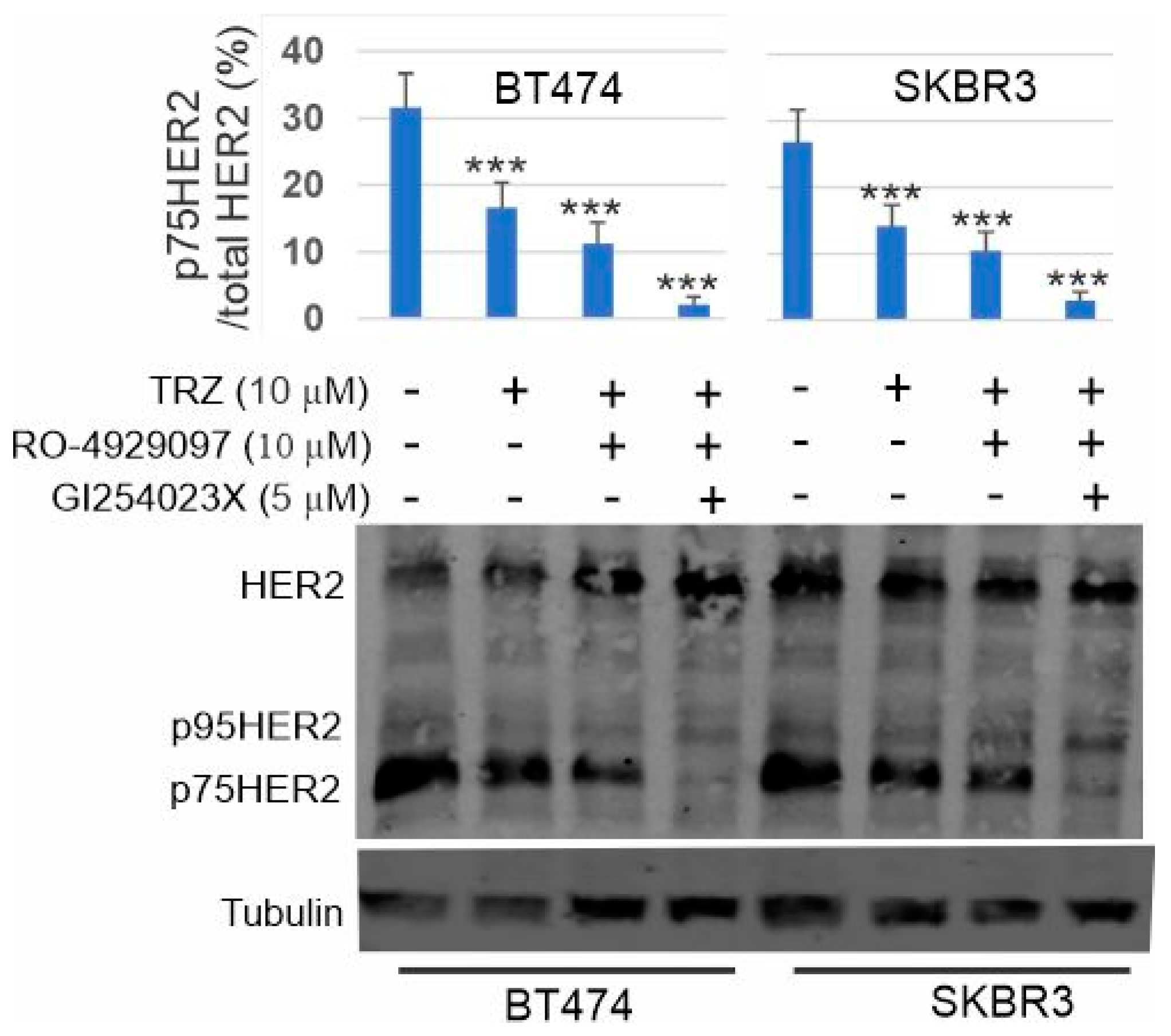
3.8. Inhibition of p75HER2 by the Combination of Trastuzumab and Inhibitors to ADAM10 and γ-Secretase
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yarden, Y.; Sliwkowski, M.X. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Yarden, Y. EGF-ERBB signalling: Towards the systems level. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, N.E.; Lane, H.A. ERBB receptors and cancer: The complexity of targeted inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z. ErbB Receptors and Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1652, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Godolphin, W.; Jones, L.A.; Holt, J.A.; Wong, S.G.; Keith, D.E.; Levin, W.J.; Stuart, S.G.; Udove, J.; Ullrich, A. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989, 244, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullick, W.J. The c-erbB3/HER3 receptor in human cancer. Cancer Surv. 1996, 27, 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Reese, D.M.; Slamon, D.J. HER-2/neu signal transduction in human breast and ovarian cancer. Stem. Cells 1997, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 34–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimawi, M.F.; Schiff, R.; Osborne, C.K. Targeting HER2 for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Annu. Rev. Med. 2015, 66, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.S.; Slodkowska, E.A.; Symmans, W.F.; Pusztai, L.; Ravdin, P.M.; Hortobagyi, G.N. The HER-2 receptor and breast cancer: Ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and personalized medicine. Oncologist 2009, 14, 320–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Cortes, J. Use of pertuzumab for the treatment of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Adv. Ther. 2013, 30, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, N.L.; Blackwell, K.L. Understanding the mechanisms behind trastuzumab therapy for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5838–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiszman, G.L.; Jasnis, M.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Trastuzumab Resistance in HER2 Overexpressing Breast Cancer. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2011, 2011, 352182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuti, M.; Bellati, F.; Visconti, V.; Napoletano, C.; Domenici, L.; Caccetta, J.; Zizzari, I.G.; Ruscito, I.; Rahimi, H.; Benedetti-Panici, P.; et al. Immune effects of trastuzumab. J. Cancer 2011, 2, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nami, B.; Maadi, H.; Wang, Z. Mechanisms Underlying the Action and Synergism of Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab in Targeting HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maadi, H.; Soheilifar, M.H.; Choi, W.S.; Moshtaghian, A.; Wang, Z. Trastuzumab Mechanism of Action; 20 Years of Research to Unravel a Dilemma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clynes, R.A.; Towers, T.L.; Presta, L.G.; Ravetch, J.V. Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytotoxicity against tumor targets. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnould, L.; Gelly, M.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Benoit, L.; Bonnetain, F.; Migeon, C.; Cabaret, V.; Fermeaux, V.; Bertheau, P.; Garnier, J.; et al. Trastuzumab-based treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer: An antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mechanism? Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchetta, S.; Gibelli, N.; Oliviero, B.; Nardini, E.; Gennari, R.; Gatti, G.; Silva, L.S.; Villani, L.; Tagliabue, E.; Menard, S.; et al. Elements related to heterogeneity of antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in patients under trastuzumab therapy for primary operable breast cancer overexpressing Her2. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11991–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kute, T.; Stehle, J.R., Jr.; Ornelles, D.; Walker, N.; Delbono, O.; Vaughn, J.P. Understanding key assay parameters that affect measurements of trastuzumab-mediated ADCC against Her2 positive breast cancer cells. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petricevic, B.; Laengle, J.; Singer, J.; Sachet, M.; Fazekas, J.; Steger, G.; Bartsch, R.; Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Bergmann, M. Trastuzumab mediates antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and phagocytosis to the same extent in both adjuvant and metastatic HER2/neu breast cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, M.N.; Cleret, A.; Matera, E.L.; Chettab, K.; Mathe, D.; Valsesia-Wittmann, S.; Clemenceau, B.; Dumontet, C. Adipose cells promote resistance of breast cancer cells to trastuzumab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Fan, X.; Deng, H.; Brezski, R.J.; Rycyzyn, M.; Jordan, R.E.; Strohl, W.R.; Zou, Q.; Zhang, N.; An, Z. Trastuzumab triggers phagocytic killing of high HER2 cancer cells in vitro and in vivo by interaction with Fcgamma receptors on macrophages. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4379–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaltriti, M.; Verma, C.; Guzman, M.; Jimenez, J.; Parra, J.L.; Pedersen, K.; Smith, D.J.; Landolfi, S.; Ramon y Cajal, S.; Arribas, J.; et al. Lapatinib, a HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces stabilization and accumulation of HER2 and potentiates trastuzumab-dependent cell cytotoxicity. Oncogene 2009, 28, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadi, H.; Nami, B.; Tong, J.; Li, G.; Wang, Z. The effects of trastuzumab on HER2-mediated cell signaling in CHO cells expressing human HER2. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, T.A.; Doherty, J.K.; Lin, Y.J.; Ramsey, E.E.; Holmes, R.; Keenan, E.J.; Clinton, G.M. NH2-terminally truncated HER-2/neu protein: Relationship with shedding of the extracellular domain and with prognostic factors in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5123–5129. [Google Scholar]
- Molina, M.A.; Codony-Servat, J.; Albanell, J.; Rojo, F.; Arribas, J.; Baselga, J. Trastuzumab (herceptin), a humanized anti-Her2 receptor monoclonal antibody, inhibits basal and activated Her2 ectodomain cleavage in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4744–4749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scaltriti, M.; Rojo, F.; Ocana, A.; Anido, J.; Guzman, M.; Cortes, J.; Di Cosimo, S.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Ramon y Cajal, S.; Arribas, J.; et al. Expression of p95HER2, a truncated form of the HER2 receptor, and response to anti-HER2 therapies in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperinde, J.; Jin, X.; Banerjee, J.; Penuel, E.; Saha, A.; Diedrich, G.; Huang, W.; Leitzel, K.; Weidler, J.; Ali, S.M.; et al. Quantitation of p95HER2 in paraffin sections by using a p95-specific antibody and correlation with outcome in a cohort of trastuzumab-treated breast cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4226–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, J.; Esselens, C. ADAM17 as a therapeutic target in multiple diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2319–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijsen, M.; King, P.; Perera, T.; Parker, P.J.; Harris, A.L.; Larijani, B.; Kong, A. HER2 phosphorylation is maintained by a PKB negative feedback loop in response to anti-HER2 herceptin in breast cancer. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, J.; Hirsch, D.S.; Wu, W.J. Trastuzumab-induced recruitment of Csk-homologous kinase (CHK) to ErbB2 receptor is associated with ErbB2-Y1248 phosphorylation and ErbB2 degradation to mediate cell growth inhibition. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuello, M.; Ettenberg, S.A.; Clark, A.S.; Keane, M.M.; Posner, R.H.; Nau, M.M.; Dennis, P.A.; Lipkowitz, S. Down-regulation of the erbB-2 receptor by trastuzumab (herceptin) enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast and ovarian cancer cell lines that overexpress erbB-2. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4892–4900. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yakes, F.M.; Chinratanalab, W.; Ritter, C.A.; King, W.; Seelig, S.; Arteaga, C.L. Herceptin-induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Akt Is required for antibody-mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor action. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4132–4141. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, C.D.; De Maziere, A.M.; Pisacane, P.I.; van Dijk, S.M.; Eigenbrot, C.; Sliwkowski, M.X.; Klumperman, J.; Scheller, R.H. Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 5268–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valabrega, G.; Montemurro, F.; Sarotto, I.; Petrelli, A.; Rubini, P.; Tacchetti, C.; Aglietta, M.; Comoglio, P.M.; Giordano, S. TGFalpha expression impairs Trastuzumab-induced HER2 downregulation. Oncogene 2005, 24, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longva, K.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; Haslekas, C.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. Herceptin-induced inhibition of ErbB2 signaling involves reduced phosphorylation of Akt but not endocytic down-regulation of ErbB2. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Bisi, J.; Strum, J.; Liu, L.; Carrick, K.; Graham, K.M.; Treece, A.L.; Hardwicke, M.A.; Dush, M.; Liao, Q.; et al. Regulation of survivin by ErbB2 signaling: Therapeutic implications for ErbB2-overexpressing breast cancers. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraway, K.L., 3rd; Cantley, L.C. A neu acquaintance for erbB3 and erbB4: A role for receptor heterodimerization in growth signaling. Cell 1994, 78, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas-Kramarski, R.; Soussan, L.; Waterman, H.; Levkowitz, G.; Alroy, I.; Klapper, L.; Lavi, S.; Seger, R.; Ratzkin, B.J.; Sela, M.; et al. Diversification of Neu differentiation factor and epidermal growth factor signaling by combinatorial receptor interactions. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2452–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Yatabe, Y. Epidermal growth factor receptor in relation to tumor development: EGFR gene and cancer. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rio, C.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Peschon, J.J.; Corfas, G. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme is required for cleavage of erbB4/HER4. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 10379–10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jung, K.M.; Huang, Y.Z.; Bennett, L.B.; Lee, J.S.; Mei, L.; Kim, T.W. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6318–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.Y.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Carpenter, G. γ-Secretase cleavage and nuclear localization of ErbB-4 receptor tyrosine kinase. Science 2001, 294, 2179–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhibber-Goel, J.; Coleman-Vaughan, C.; Agrawal, V.; Sawhney, N.; Hickey, E.; Powell, J.C.; McCarthy, J.V. γ-Secretase Activity Is Required for Regulated Intramembrane Proteolysis of Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Receptor 1 and TNF-mediated Pro-apoptotic Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 5971–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urra, S.; Escudero, C.A.; Ramos, P.; Lisbona, F.; Allende, E.; Covarrubias, P.; Parraguez, J.I.; Zampieri, N.; Chao, M.V.; Annaert, W.; et al. TrkA receptor activation by nerve growth factor induces shedding of the p75 neurotrophin receptor followed by endosomal gamma-secretase-mediated release of the p75 intracellular domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7606–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omerovic, J.; Santangelo, L.; Puggioni, E.M.; Marrocco, J.; Dall’Armi, C.; Palumbo, C.; Belleudi, F.; Di Marcotullio, L.; Frati, L.; Torrisi, M.R.; et al. The E3 ligase Aip4/Itch ubiquitinates and targets ErbB-4 for degradation. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2849–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, G.A.; Naresh, A.; Marrero, L.; Jones, F.E. Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase processing regulates multiple ERBB4/HER4 activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 19777–19783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Makino, K.; Xia, W.; Matin, A.; Wen, Y.; Kwong, K.Y.; Bourguignon, L.; Hung, M.C. Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Lien, H.C.; Xia, W.; Chen, I.F.; Lo, H.W.; Wang, Z.; Ali-Seyed, M.; Lee, D.F.; Bartholomeusz, G.; Ou-Yang, F.; et al. Binding at and transactivation of the COX-2 promoter by nuclear tyrosine kinase receptor ErbB-2. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Y.; Chen, H.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Wang, Y.N.; Chu, H.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Chien, P.J.; Ma, H.T.; Tsai, H.C.; et al. Nuclear ErbB2 enhances translation and cell growth by activating transcription of ribosomal RNA genes. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4269–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, L.Y.; Wei, Y.L.; Hsu, S.C.; Tsai, S.L.; Chiu, P.C.; Huang, W.P.; Wang, Y.N.; Chen, C.H.; et al. Nuclear translocation of epidermal growth factor receptor by Akt-dependent phosphorylation enhances breast cancer-resistant protein expression in gefitinib-resistant cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20558–20568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Carpenter, R.L.; Cao, X.; Lo, H.W. STAT1 gene expression is enhanced by nuclear EGFR and HER2 via cooperation with STAT3. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Liu, J. Identification of novel nuclear localization signal within the ErbB-2 protein. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocco, E.; Lopez, S.; Santin, A.D.; Scaltriti, M. Prevalence and role of HER2 mutations in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 199, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anido, J.; Scaltriti, M.; Bech Serra, J.J.; Santiago Josefat, B.; Todo, F.R.; Baselga, J.; Arribas, J. Biosynthesis of tumorigenic HER2 C-terminal fragments by alternative initiation of translation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 3234–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas, J.; Baselga, J.; Pedersen, K.; Parra-Palau, J.L. p95HER2 and breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.X.; Lasut, A.L.; Wynn, R.; Neff, N.T.; Hollis, G.F.; Ramaker, M.L.; Rupar, M.J.; Liu, P.; Meade, R. Purification of Her-2 extracellular domain and identification of its cleavage site. Protein Expr. Purif. 2003, 29, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.C.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Covington, M.; Wynn, R.; Huber, R.; Hillman, M.; Yang, G.; Ellis, D.; Marando, C.; et al. Identification of ADAM10 as a major source of HER2 ectodomain sheddase activity in HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J. The EGFR as a target for anticancer therapy—Focus on cetuximab. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, S16–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.; Angelini, P.D.; Laos, S.; Bach-Faig, A.; Cunningham, M.P.; Ferrer-Ramon, C.; Luque-Garcia, A.; Garcia-Castillo, J.; Parra-Palau, J.L.; Scaltriti, M.; et al. A naturally occurring HER2 carboxy-terminal fragment promotes mammary tumor growth and metastasis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3319–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, M.A.; Saez, R.; Ramsey, E.E.; Garcia-Barchino, M.J.; Rojo, F.; Evans, A.J.; Albanell, J.; Keenan, E.J.; Lluch, A.; Garcia-Conde, J.; et al. NH(2)-terminal truncated HER-2 protein but not full-length receptor is associated with nodal metastasis in human breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Saez, A.; Andreu, F.J.; Segui, M.A.; Bare, M.L.; Fernandez, S.; Dinares, C.; Rey, M. HER-2 gene amplification by chromogenic in situ hybridisation (CISH) compared with fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) in breast cancer—A study of two hundred cases. Breast 2006, 15, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipton, A.; Goodman, L.; Leitzel, K.; Cook, J.; Sperinde, J.; Haddad, M.; Kostler, W.J.; Huang, W.; Weidler, J.M.; Ali, S.; et al. HER3, p95HER2, and HER2 protein expression levels define multiple subtypes of HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 141, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.; Reddy, K.B.; Esteva, F.J.; Moore, H.C.; Budd, G.T.; Tubbs, R.R. Calpain regulates sensitivity to trastuzumab and survival in HER2-positive breast cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Merilahti, J.A.M.; Ojala, V.K.; Knittle, A.M.; Pulliainen, A.T.; Elenius, K. Genome-wide screen of gamma-secretase-mediated intramembrane cleavage of receptor tyrosine kinases. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zha, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, S.; Ma, W.; Zheng, J.; Shi, M. β2-AR activation promotes cleavage and nuclear translocation of Her2 and metastatic potential of cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4417–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.L.; Cobleigh, M.A.; Tripathy, D.; Gutheil, J.C.; Harris, L.N.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Slamon, D.J.; Murphy, M.; Novotny, W.F.; Burchmore, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of trastuzumab as a single agent in first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.; Leung, R.; Kwong, A.; Chiu, J.; Liang, R.; Swanton, C.; Yau, T. Integrating molecular mechanisms and clinical evidence in the management of trastuzumab resistant or refractory HER-2+ metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist 2011, 16, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, B.; Maadi, H.; Wang, Z. The Effects of Pertuzumab and Its Combination with Trastuzumab on HER2 Homodimerization and Phosphorylation. Cancers 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadi, H.; Soheilifar, M.H.; Wang, Z. Analysis of Cell Cycle by Flow Cytometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2579, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasbach, A.; Abel, T.; Münch, R.C.; Boller, K.; Schneider-Schaulies, J.; Buchholz, C.J. The receptor attachment function of measles virus hemagglutinin can be replaced with an autonomous protein that binds Her2/neu while maintaining its fusion-helper function. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6246–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Z. Identification of EGF Receptor C-terminal Sequences 1005-1017 and Di-leucine Motif 1010LL1011 as Essential in EGF Receptor Endocytosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3349–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdrabou, A.; Wang, Z. Regulation of the nuclear speckle localization and function of Rac1. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, B.; Wang, Z. Application of Immunofluorescence Staining to Study ErbB Family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1652, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.C.; Hung, M.C. Characterization of a novel tripartite nuclear localization sequence in the EGFR family. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10432–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordo Russo, R.I.; Beguelin, W.; Diaz Flaque, M.C.; Proietti, C.J.; Venturutti, L.; Galigniana, N.; Tkach, M.; Guzman, P.; Roa, J.C.; O’Brien, N.A.; et al. Targeting ErbB-2 nuclear localization and function inhibits breast cancer growth and overcomes trastuzumab resistance. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3413–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguelin, W.; Diaz Flaque, M.C.; Proietti, C.J.; Cayrol, F.; Rivas, M.A.; Tkach, M.; Rosemblit, C.; Tocci, J.M.; Charreau, E.H.; Schillaci, R.; et al. Progesterone receptor induces ErbB-2 nuclear translocation to promote breast cancer growth via a novel transcriptional effect: ErbB-2 function as a coactivator of Stat3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 5456–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturutti, L.; Romero, L.V.; Urtreger, A.J.; Chervo, M.F.; Cordo Russo, R.I.; Mercogliano, M.F.; Inurrigarro, G.; Pereyra, M.G.; Proietti, C.J.; Izzo, F.; et al. Stat3 regulates ErbB-2 expression and co-opts ErbB-2 nuclear function to induce miR-21 expression, PDCD4 downregulation and breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2208–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, D.M.; Montagna, D.R.; Gu, Y.; Selkoe, D.J.; Wolfe, M.S. Nicastrin functions to sterically hinder gamma-secretase-substrate interactions driven by substrate transmembrane domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E509–E518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nami, B.; Wang, Z. A Non-Canonical p75HER2 Signaling Pathway Underlying Trastuzumab Action and Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171452
Nami B, Wang Z. A Non-Canonical p75HER2 Signaling Pathway Underlying Trastuzumab Action and Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cells. 2024; 13(17):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171452
Chicago/Turabian StyleNami, Babak, and Zhixiang Wang. 2024. "A Non-Canonical p75HER2 Signaling Pathway Underlying Trastuzumab Action and Resistance in Breast Cancer" Cells 13, no. 17: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171452
APA StyleNami, B., & Wang, Z. (2024). A Non-Canonical p75HER2 Signaling Pathway Underlying Trastuzumab Action and Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cells, 13(17), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13171452





