Pirfenidone Reverts Global DNA Hypomethylation, Promoting DNMT1/UHRF/PCNA Coupling Complex in Experimental Hepatocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3. Biochemical Determination of γ-GTP and ALT
2.4. Histologic Assessment of Liver Sections
2.5. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.6. Proteins Extraction and Western Blot Assay
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Global Methylation Assessment in Genomic DNA
2.9. Dot Blot of Global DNA Methylation
2.10. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis through the STRING Platform
2.11. Molecular Docking Protein–Protein
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Liver Damage Caused by Chemicals Is Prevented by Pirfenidone
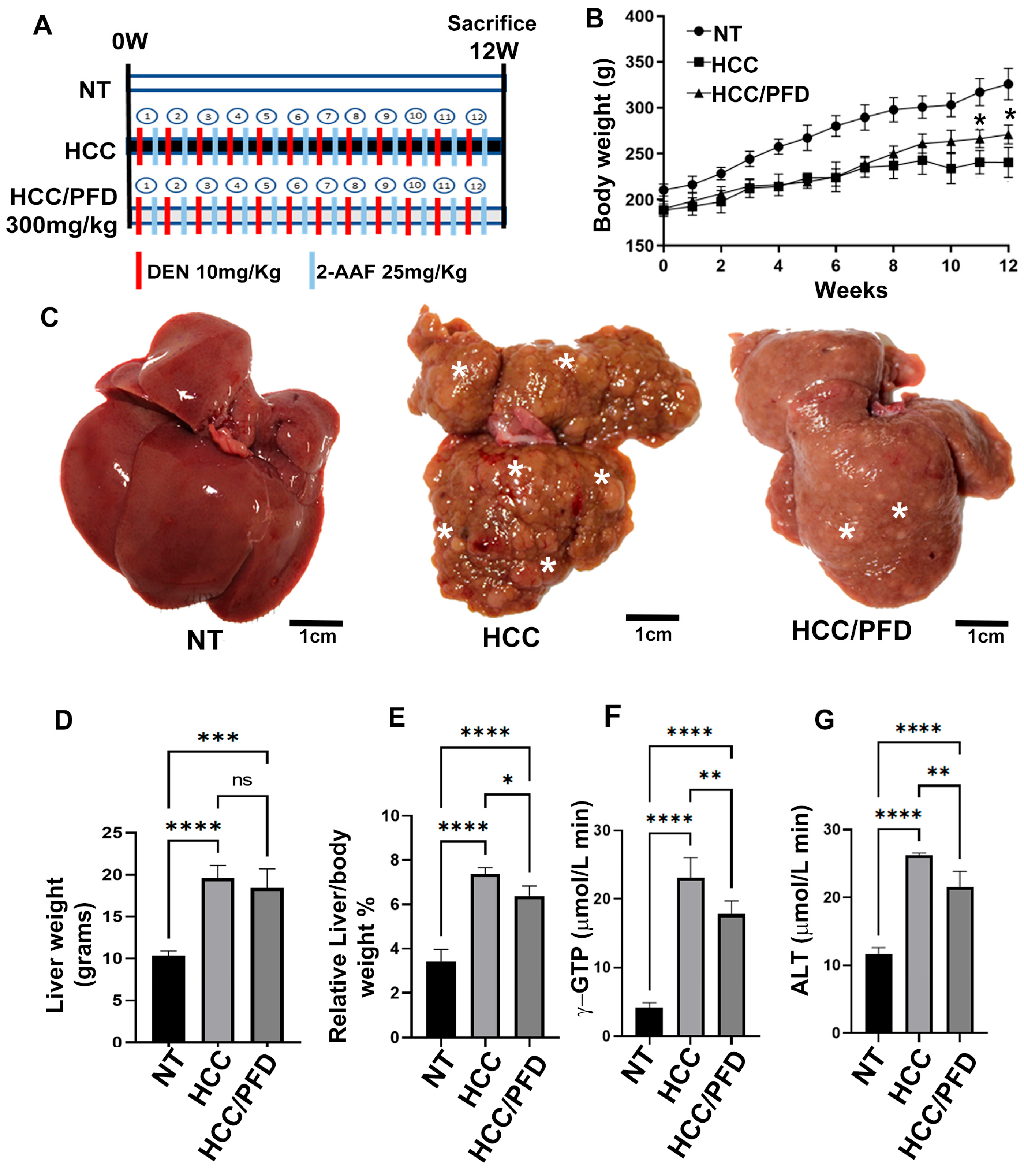
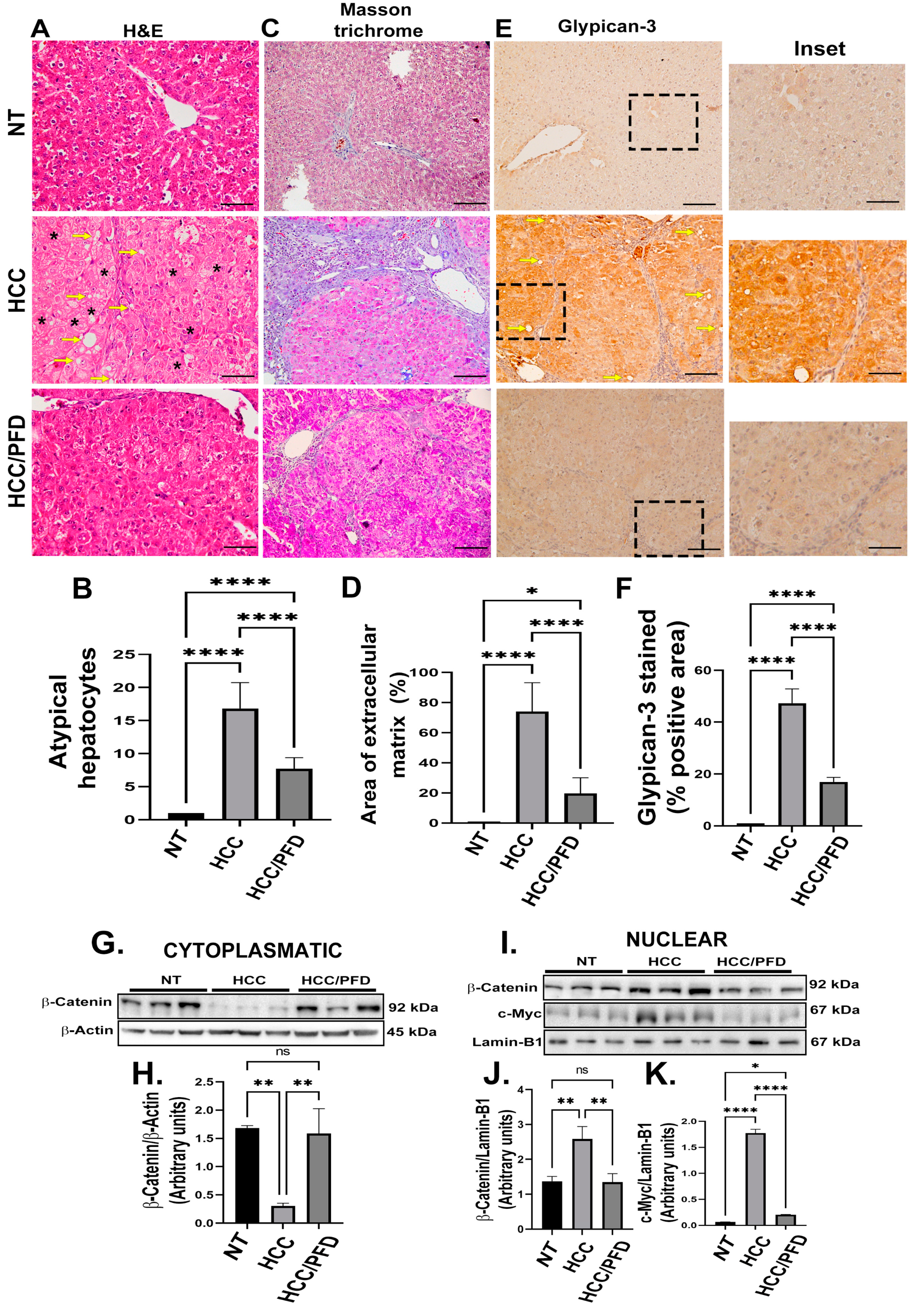
3.2. Pirfenidone Slows down the Expression of Carcinogenic Markers, Reduces Fibrosis, and Decreases Damage in Liver Architecture
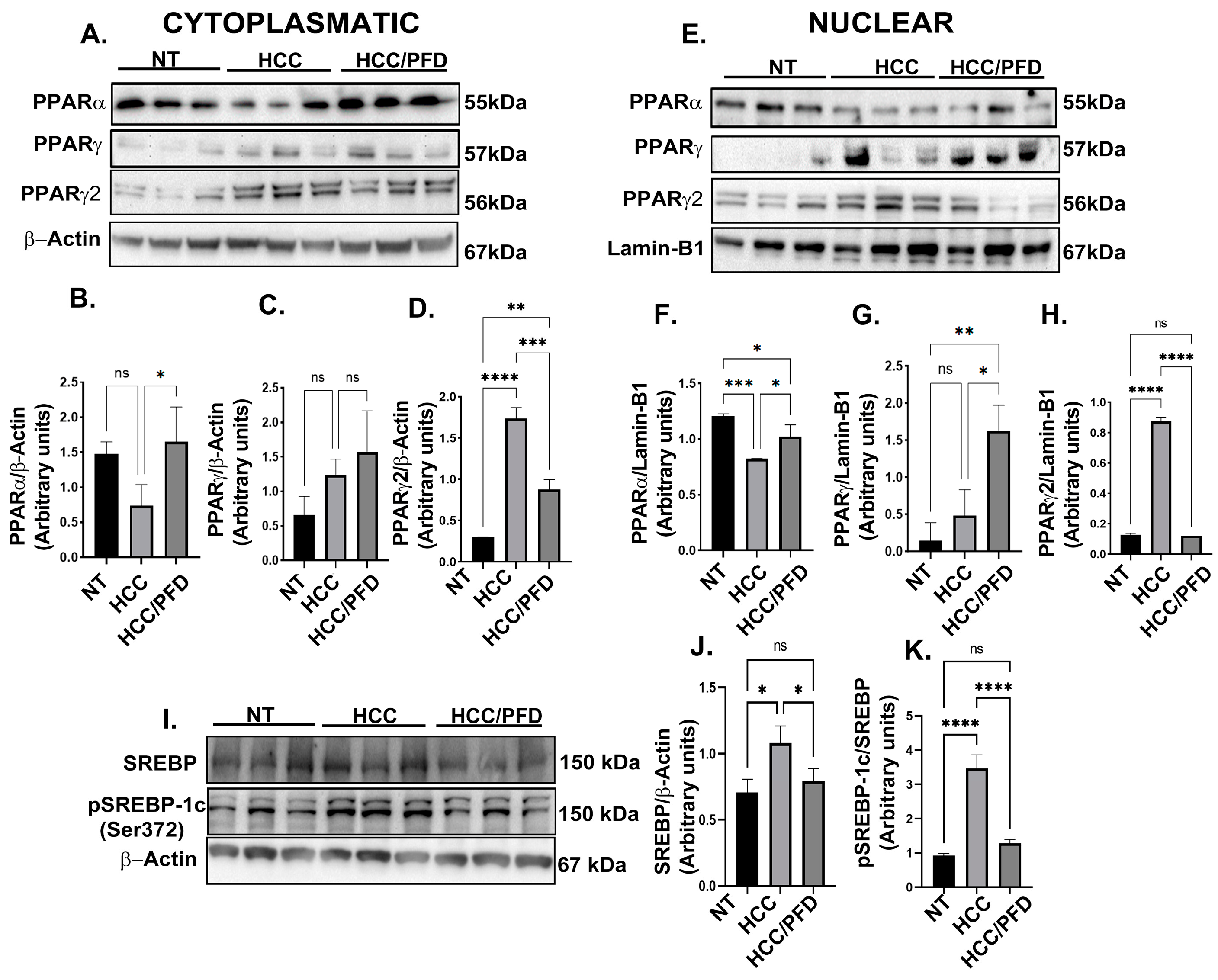
3.3. Pirfenidone Regulates Expression and Translocation of PPARγ and PPARγ2
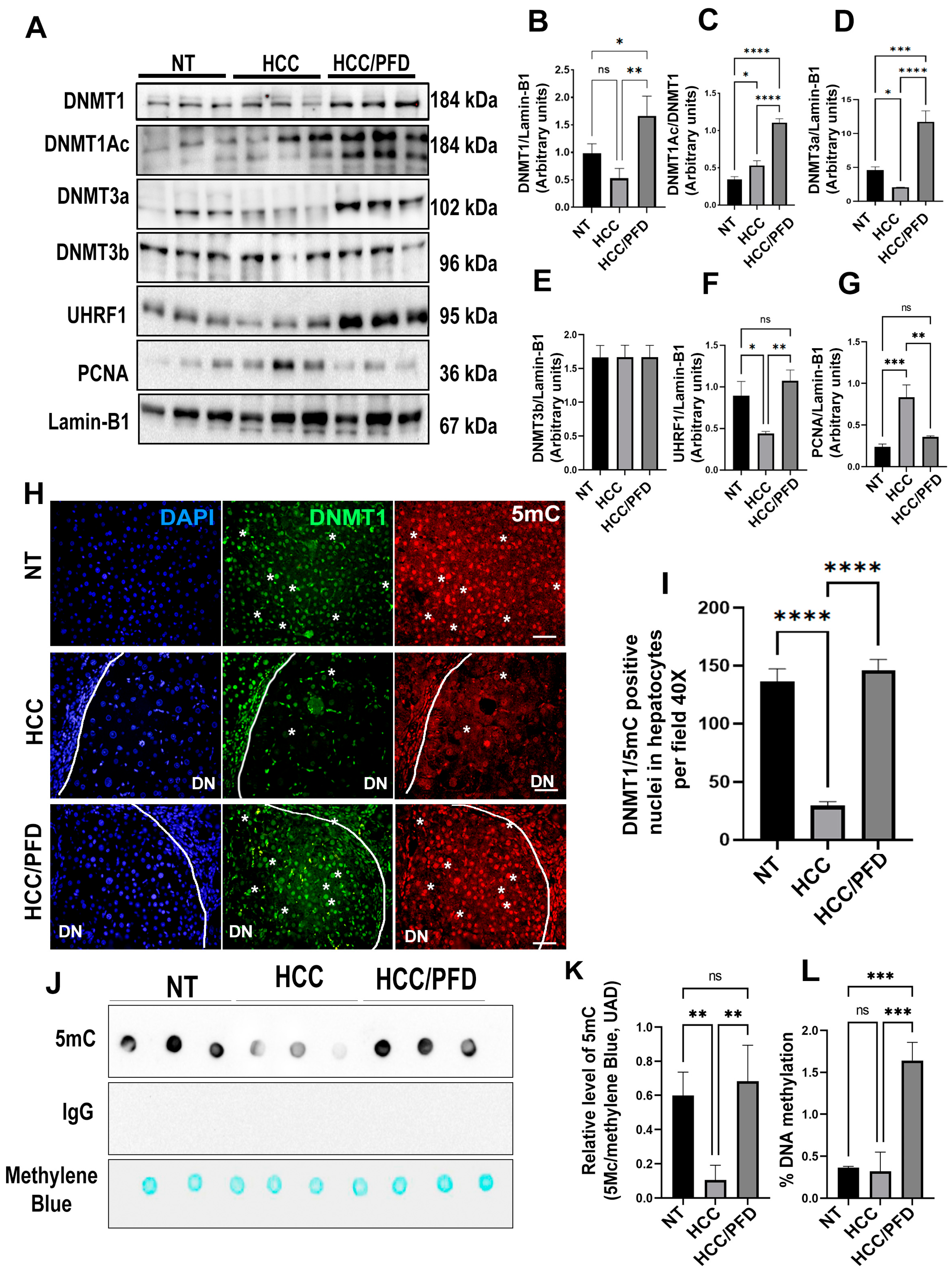
3.4. Pirfenidone Reverses Global DNA Hypomethylation through Regulation of DNMT1
3.5. Pirfenidone Regulates DNMT1 Expression and Prevents Global DNA Hypomethylation In Vitro
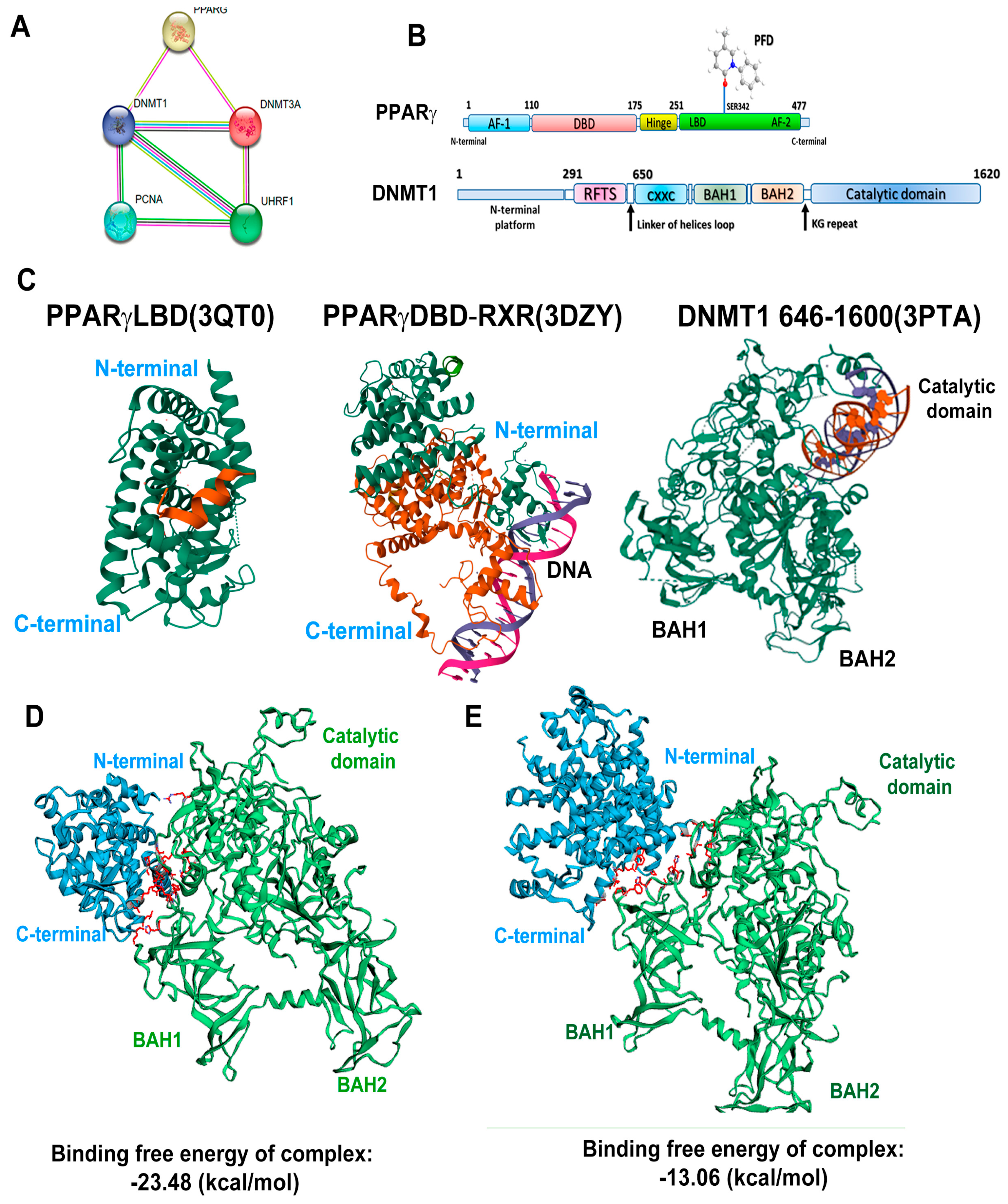
3.6. In Silico Analysis Reveals That PPARγ Complexes with DNMT1
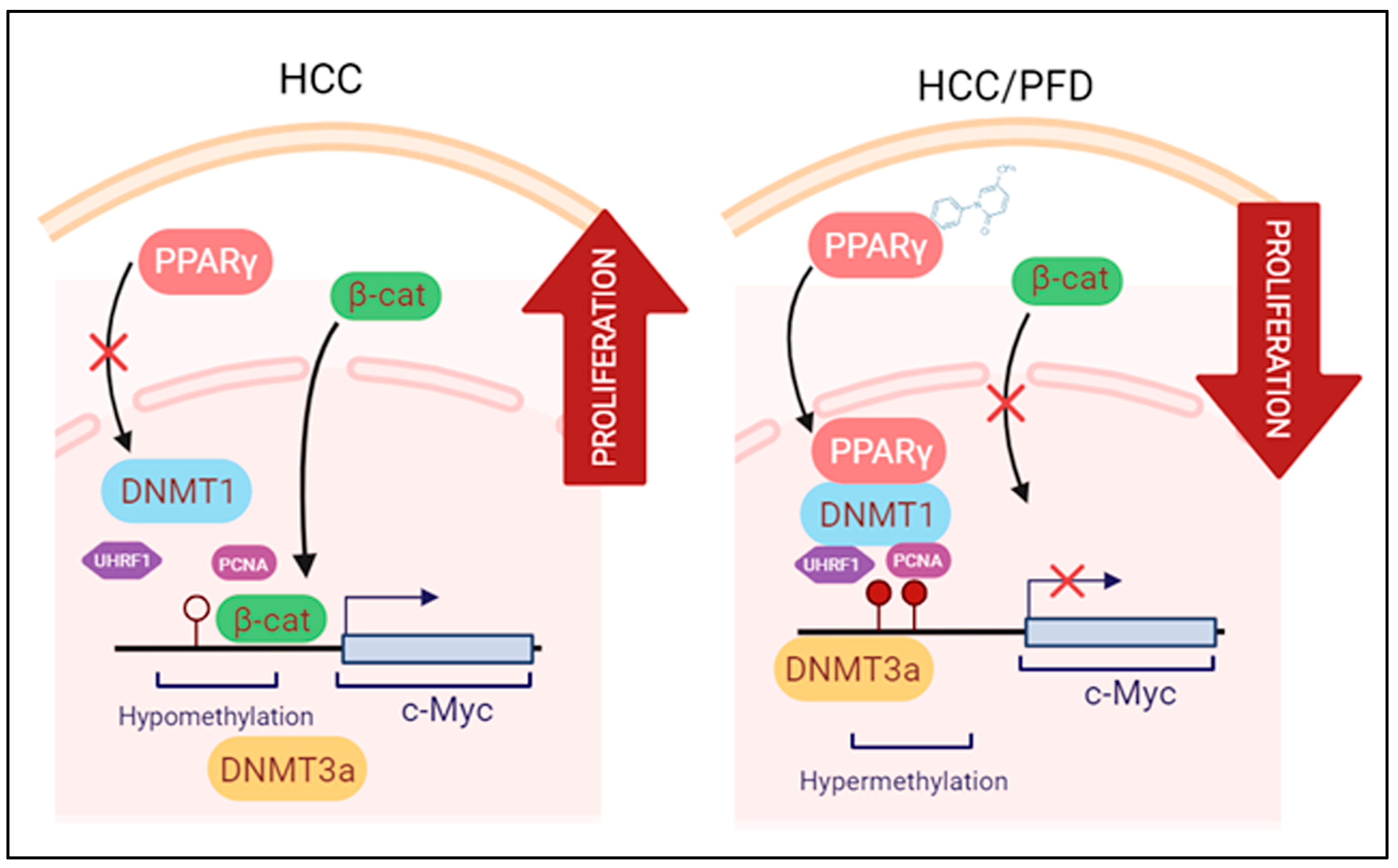
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, A.; Khan, Z.; Alloghbi, A.; Ahmed, T.S.S.; Ashraf, M.; Hammouda, D.M. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Molecular Mechanisms and Targeted Therapies. Medicina 2019, 55, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refolo, M.G.; Messa, C.; Guerra, V.; Carr, B.I.; D’alessandro, R. Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Barrena, M.G.; Arechederra, M.; Colyn, L.; Berasain, C.; Avila, M.A. Epigenetics in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Therapy: The Tip of the Iceberg. JHEP Rep. 2020, 2, 100167–100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braghini, M.R.; Lo Re, O.; Romito, I.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; Barbaro, B.; Pomella, S.; Rota, R.; Vinciguerra, M.; Avila, M.A.; Alisi, A. Epigenetic Remodelling in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galicia-Moreno, M.; Silva-Gomez, J.A.; Lucano-Landeros, S.; Santos, A.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Liver Cancer: Therapeutic Challenges and the Importance of Experimental Models. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 2021, 8837811–8837821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Gil, M.P.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, R.; Torres-Mena, J.E.; López-Torres, C.D.; Quintanar-Jurado, V.; Gabiño-López, N.B.; Villa-Treviño, S.; del-Pozo-Jauner, L.; Arellanes-Robledo, J.; Pérez-Carreón, J.I. Enrichment of Progenitor Cells by 2-Acetylaminofluorene Accelerates Liver Carcinogenesis Induced by Diethylnitrosamine in Vivo. Mol. Carcinog. 2021, 60, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-de la Mora, D.A.; Sanchez-Roque, C.; Montoya-Buelna, M.; Sanchez-Enriquez, S.; Lucano-Landeros, S.; Macias-Barragan, J.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Role and New Insights of Pirfenidone in Fibrotic Diseases. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 12, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poo, J.L.; Torre, A.; Aguilar-Ramírez, J.R.; Cruz, M.; Mejía-Cuán, L.; Cerda, E.; Velázquez, A.; Patiño, A.; Ramírez-Castillo, C.; Cisneros, L.; et al. Benefits of prolonged-release pirfenidone plus standard of care treatment in patients with advanced liver fibrosis: PROMETEO study. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.J.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, T.P.; Shen, Y.P.; Zhao, A.S.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, S. Pirfenidone Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 6107–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Meza-Rios, A.; Garcia-Bañuelos, J.; Vera-Cruz, J.; Gutiérrez-Cuevas, J.; Silva-Gomez, J.; Staels, B.; Dominguez-Rosales, J.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; et al. Pirfenidone Is an Agonistic Ligand for PPARα and Improves NASH by Activation of SIRT1/LKB1/PAMPK. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Gomez, J.A.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; Miranda-Roblero, H.O.; Lucano-Landeros, S.; Santos, A.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Hepatocarcinogenesis Prevention by Pirfenidone Is PPARγ Mediated and Involves Modification of Nuclear NF-κB p65/p50 Ratio. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgeirsson, S.S.; Grisham, J.W. Molecular Pathogenesis of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, G.; Wang, E.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Hou, T. HawkDock: A web server to predict and analyze the protein-protein complex based on computational docking and MM/GBSA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W322–W330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Nagasaka, T.; Nishimura, T.; Ikai, I.; Richard, C.; Goel, A. Aberrant methylation of multiple tumor suppressor genes in aging liver, chronic hepatitis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2008, 47, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Chu, E.S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liang, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Teoh, N.; Farrell, G.; Sung, J.J.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis through mediating NF-κB signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 30, 8330–8340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.B.; Cai, S.H.; Liu, L.L.; Yang, X.; Yun, J.P. Decreased expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha indicates unfavorable outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 26, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Urbani, S.; Jemelin, S.; Deffert, C.; Carnesecchi, S.; Basset, O.; Szyndralewiez, C.; Heitz, F.; Page, P.; Montet, X.; Michalik, L.; et al. Targeting vascular NADPH oxidase 1 blocks tumor angiogenesis through a PPARα mediated mechanism. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14665–e14678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Shen, B.; Chu, E.S.H.; Teoh, N.; Cheung, K.F.; Wu, C.W.; Wang, S.; Lam, C.N.Y.; Feng, H.; Zhao, J.; et al. Inhibitory Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma in Hepatocarcinogenesis in Mice and in Vitro. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, K.L.; Wada, K.; Takahashi, H.; Matsuhashi, N.; Ohnishi, S.; Wolfe, M.M.; Turner, J.R.; Nakajima, A.; Borkan, S.C.; Saubermann, L.J. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ Inhibition Prevents Adhesion to the Extracellular Matrix and Induces Anoikis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, H.; Sakisaka, S.; Harada, M.; Takagi, T.; Hanada, S.; Taniguchi, E.; Kawaguchi, T.; Sasatomi, K.; Kimura, R.; Hashimoto, O.; et al. Involvement of p21WAF1/Cip1, p27Kip1, and p18INK4c in Troglitazone-Induced Cell-Cycle Arrest in Human Hepatoma Cell Lines. Hepatology 2001, 33, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ghoshal, S.; Sojoodi, M.; Arora, G.; Masia, R.; Erstad, D.J.; Lanuti, M.; Hoshida, Y.; Baumert, T.F.; Tanabe, K.K.; et al. Pioglitazone Reduces Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Two Rodent Models of Cirrhosis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2019, 23, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Park, J.E.; Lee, M.; Hardwick, J.P. Hepatic Lipid Homeostasis by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma 2. Liver Res. 2018, 2, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurro, M.I.; Xiang, Y.Y.; Lobe, C.; Filmus, J. Glypican-3 Promotes the Growth of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Stimulating Canonical Wnt Signaling. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6245–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Ke, C.; Guo, X.; Ren, P.; Tong, Y.; Luo, S.; He, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cheng, B.; Li, R.; et al. Both Glypican-3/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Autophagy Contributed to the Inhibitory Effect of Curcumin on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroy-Ramírez, H.C.; Silva-Gómez, J.A.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; Santos-García, A.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J. Analysis of the Molecular Interaction of Pirfenidone with PPAR-Gamma and Effects on the Beta-Catenine Pathway in HEPG2 Line. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgia, S.; Kanji, M.; Bhushan, A. DNMT1 Represses P53 to Maintain Progenitor Cell Survival during Pancreatic Organogenesis. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, A.P. The Epigenetics of Cancer Etiology. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2004, 14, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, A.J.; Baylin, S.B. The Epigenomic of Cancer. Cell 2007, 128, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylin, S.B.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetic Determinants of Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a019505–a019540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, M. DNA Hypomethylation in Cancer Cells. Epigenomics 2009, 1, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Wu, H.C.; Yazici, H.; Yu, M.W.; Lee, P.H.; Santella, R.M. Global Hypomethylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Relationship to Aflatoxin B1 Exposure. World J. Hepatol. 2012, 4, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, B.; Kim, H.; Park, H.; Shim, Y.; Choi, J.; Park, C.; Park, Y.N. DNA methyltransferase expression and DNA methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinicopathological correlation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, E.; Kanai, Y. DNA Methylation Profiles in Precancerous Tissue and Cancers: Carcinogenetic Risk Estimation and Prognostication Based on DNA Methylation Status. Epigenomics 2010, 2, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascale, R.M.; Simile, M.M.; Satta, G.; Seddaiu, M.A.; Daino, L.; Pinna, G.; Vinci Gaspa, M.A.L.; Feo, F. Comparative Effects of L-Methionine, S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine and 5’-Methylthioadenosine on the Growth of Preneoplastic Lesions and DNA Methylation in Rat Liver during the Early Stages of Hepatocarcinogenesis. Anticancer. Res. 1991, 11, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Valencia Antúnez, C.A.; Chayeb, L.T.; Rodriguez-Segura, M.Á.; López Álvarez, G.S.; Garcia-Cuéllar, C.M.; Treviño, S.V. DNA Methyltransferases 3a and 3b Are Differentially Expressed in the Early Stages of a Rat Liver Carcinogenesis Model. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2093–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cheung, H.H.; Lee, T.L.; Rennert, O.M.; Chan, W.Y. DNA methylation of cancer genome. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo. Today. 2009, 87, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eden, A.; Gaudet, F.; Waghmare, A.; Jaenisch, R. Chromosomal Instability and Tumors Promoted by DNA Hypomethylation. Science 2003, 300, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Magaña, A.; Blanco, F.J. Human PCNA Structure, Function and Interactions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimori, H.; Tsukishiro, T.; Nambu, S.; Okada, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Miyabayashi, C.; Higuchi, K.; Watanabe, A. Analyses of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-positive cells in hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparisons with clinical findings. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1994, 9, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikoo, K.; Ali, I.Y.; Gupta, J.; Gupta, C. 5-Azacytidine prevents cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity and potentiates anticancer activity of cisplatin by involving inhibition of metallothionein, pAKT and DNMT1 expression in chemical induced cancer rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 19, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazienza, V.; Tavano, F.; Benegiamo, G.; Vinciguerra, M.; Burbaci, F.P.; Copetti, M.; Di Mola, F.F.; Andriulli, A.; Di Sebastiano, P. Correlations among PPARγ, DNMT1, and DNMT3B Expression Levels and Pancreatic Cancer. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 461784–461791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, V.; Ronchetti, S.; Marchetti, M.C.; Calvitti, M.; Riccardi, C.; Grignani, F.; Vecchini, A. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Eicosapentaenoic Acid Inhibition of HDAC1 and DNMT Expression and Activity in Carcinoma Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194481–194493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Tobar-Tosse, F.; Dakal, T.C.; Liu, H.; Biswas, A.; Menon, A.; Paruchuri, A.; Katsonis, P.; Lichtarge, O.; Gromiha, M.M.; et al. PPAR-Responsive Elements Enriched with Alu Repeats May Contribute to Distinctive PPARγ–DNMT1 Interactions in the Genome. Cancers 2021, 13, 3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Groups | No of Rats with Nodules/Total Rats | Nodule Incidence (%) | Total No. of Nodules | Average No. of Nodules/Nodule Bearing Liver (Nodule Multiplicity) | Nodules Relative to Size (% of Total No.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥3 mm | <3 to >1 mm | ≤1 mm | |||||
| NT | 0/0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| HCC | 6/6 | 100 | 424 | 106 ± 36.36 | 12 | 30 | 58 |
| HCC/PFD | 6/6 | 90 | 227 | 57 ± 12.66 | 8 | 15 | 76 |
| Histological Parameter | NT | HCC | HCC/PFD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperplasia | − | + | + |
| Dysplasia | − | + | − |
| Cancer cell | − | + (MD) | + (WD) |
| Cellular infiltration | − | 1 | 0 |
| Fibrosis | − | 3 | 2 |
| Oval cells | − | 3 | 1 |
| Ballooning degeneration | − | 3 | 1 |
| Steatosis | − | ++ | − |
| Cholestasis | − | 0 | 0 |
| Mallory bodies | − | + | − |
| Lobular inflammation | − | 1 | 0 |
| Periportal bile ducts proliferation | − | 1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miranda-Roblero, H.O.; Saavedra-Salazar, L.F.; Galicia-Moreno, M.; Arceo-Orozco, S.; Caloca-Camarena, F.; Sandoval-Rodriguez, A.; García-Bañuelos, J.; Frias-Gonzalez, C.; Almeida-López, M.; Martínez-López, E.; et al. Pirfenidone Reverts Global DNA Hypomethylation, Promoting DNMT1/UHRF/PCNA Coupling Complex in Experimental Hepatocarcinoma. Cells 2024, 13, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13121013
Miranda-Roblero HO, Saavedra-Salazar LF, Galicia-Moreno M, Arceo-Orozco S, Caloca-Camarena F, Sandoval-Rodriguez A, García-Bañuelos J, Frias-Gonzalez C, Almeida-López M, Martínez-López E, et al. Pirfenidone Reverts Global DNA Hypomethylation, Promoting DNMT1/UHRF/PCNA Coupling Complex in Experimental Hepatocarcinoma. Cells. 2024; 13(12):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13121013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiranda-Roblero, Hipolito Otoniel, Liliana Faridi Saavedra-Salazar, Marina Galicia-Moreno, Scarlet Arceo-Orozco, Fernando Caloca-Camarena, Ana Sandoval-Rodriguez, Jesús García-Bañuelos, Claudia Frias-Gonzalez, Mónica Almeida-López, Erika Martínez-López, and et al. 2024. "Pirfenidone Reverts Global DNA Hypomethylation, Promoting DNMT1/UHRF/PCNA Coupling Complex in Experimental Hepatocarcinoma" Cells 13, no. 12: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13121013
APA StyleMiranda-Roblero, H. O., Saavedra-Salazar, L. F., Galicia-Moreno, M., Arceo-Orozco, S., Caloca-Camarena, F., Sandoval-Rodriguez, A., García-Bañuelos, J., Frias-Gonzalez, C., Almeida-López, M., Martínez-López, E., Armendariz-Borunda, J., & Monroy-Ramirez, H. C. (2024). Pirfenidone Reverts Global DNA Hypomethylation, Promoting DNMT1/UHRF/PCNA Coupling Complex in Experimental Hepatocarcinoma. Cells, 13(12), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13121013






