Mechanisms of Action in FLASH Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical and Biological Processes on Cancerous and Normal Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of the FLASH Effect in RT
2.1. Physicochemical Process on Cell Killing
2.1.1. Oxygen Depletion Effect
2.1.2. ROS and Free Radical Effect
2.1.3. Other Physicochemical Processes
2.2. Biological Process on Cell Killing
2.2.1. Cell and Preclinical Models in Brain and Lung
2.2.2. Cell and Preclinical Models in Gastrointestinal Tract, Skin, and Subcutaneous Tissue
2.2.3. Biological Models in Big Animal and Human
3. Future Prospective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, R.-X.; Zhou, P.-K. DNA damage response signaling pathways and targets for radiotherapy sensitization in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabbrizi, M.R.; Parsons, J.L. Radiotherapy and the cellular DNA damage response: Current and future perspectives on head and neck cancer treatment. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020, 3, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chow, J.C. Gold nanoparticle DNA damage in radiotherapy: A Monte Carlo study. AIMS Bioeng. 2016, 3, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Niedermann, G.; Burnet, N.G.; Siva, S.; Lee, A.W.; Hegi-Johnson, F. Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzuol, L.; Coppes, R.P.; van Luijk, P. Prevention and treatment of radiotherapy-induced side effects. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1538–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhide, S.; Nutting, C. Recent advances in radiotherapy. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.; Gaya, A. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: A Review. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 22, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staffurth, J. A Review of the Clinical Evidence for Intensity-modulated Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 22, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacas, B.; Bourhis, J.; Overgaard, J.; Zhang, Q.; Nankivell, M.; Zackrisson, B.; Szutkowski, Z.; O’Sullivan, B.; Corvò, R.; Laskar, S.G.; et al. Role of radiotherapy fractionation in head and neck cancers (MARCH): An updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.L.; Ruda, H.E. Flash radiotherapy: Innovative cancer treatment. Encyclopedia 2023, 3, 808–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popanda, O.; Marquardt, J.U.; Chang-Claude, J.; Schmezer, P. Genetic variation in normal tissue toxicity induced by ionizing radiation. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2009, 667, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, A.A.; Prise, K.M.; Butterworth, K.T.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Favaudon, V. Radiobiology of the FLASH effect. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 1993–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Huang, D.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, G.; Dai, T.; Du, X. Mechanisms of FLASH effect. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 995612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kacem, H.; Almeida, A.; Cherbuin, N.; Vozenin, M.-C. Understanding the FLASH effect to unravel the potential of ultra-high dose rate irradiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, D.L.; Boag, J.W. Modification of the oxygen effect when bacteria are given large pulses of radiation. Nature 1959, 183, 1450–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaudon, V.; Caplier, L.; Monceau, V.; Pouzoulet, F.; Sayarath, M.; Fouillade, C.; Poupon, M.-F.; Brito, I.; Hupé, P.; Bourhis, J.; et al. Ultrahigh dose-rate FLASH irradiation increases the differential response between normal and tumor tissue in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 245ra93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, B.S.; Sitarz, M.K.; Ankjærgaard, C.; Johansen, J.; Andersen, C.E.; Kanouta, E.; Overgaard, C.; Grau, C.; Poulsen, P. In Vivo validation and tissue sparing factor for acute damage of pencil beam scanning proton FLASH. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 167, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diffenderfer, E.S.; Verginadis, I.I.; Kim, M.M.; Shoniyozov, K.; Velalopoulou, A.; Goia, D.; Putt, M.; Hagan, S.; Avery, S.; Teo, K.; et al. Design, implementation, and in vivo validation of a novel proton FLASH radiation therapy system. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Ruda, H.E.; Chow, J.C.L. FLASH Radiotherapy and the Use of Radiation Dosimeters. Cancers 2023, 15, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.; Kang, M.; Wei, S.; Choi, J.; Press, R.H.; Hasan, S.; Chhabra, A.M.; Cengel, K.A.; Lin, H.; Simone, C.B. FLASH radiation therapy: Review of the literature and considerations for future research and proton therapy FLASH trials. Appl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 10, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenderfer, E.S.; Sørensen, B.S.; Mazal, A.; Carlson, D.J. The current status of preclinical proton FLASH radiation and future directions. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, G.; Pei, H. The clinical prospect of FLASH radiotherapy. Radiat. Med. Prot. 2023, 4, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.R.; Parsons, J.L. FLASH radiotherapy: Current knowledge and future insights using proton-beam therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, F.; Bailat, C.; Jorge, P.G.; Lerch, M.L.F.; Darafsheh, A. Ultra-high dose rate dosimetry: Challenges and opportunities for FLASH radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4912–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceberg, S.; Mannerberg, A.; Konradsson, E.; Blomstedt, M.; Kügele, M.; Kadhim, M.; Edvardsson, A.; Bäck, S.J.; Petersson, K.; Gustafsson, C.J.; et al. FLASH radiotherapy and the associated dosimetric challenges. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2630, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, F.; Barca, P.; Barone, S.; Bortoli, E.; Borgheresi, R.; De Stefano, S.; Di Francesco, M.; Grasso, L.; Linsalata, S.; Marfisi, D.; et al. FLASH radiotherapy with electrons: Issues related to the production, monitoring, and dosimetric characterization of the beam. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 570697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Xie, D.; Wang, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, D.; et al. Comparison of intratumor and local immune response between MV X-ray FLASH and conventional radiotherapies. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 38, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polevoy, G.G.; Kumar, D.S.; Daripelli, S.; Prasanna, M., Sr.; Kumar, D.; Prasanna, M. Flash therapy for cancer: A potentially new radiotherapy methodology. Cureus 2023, 15, e46928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.M.; Zou, W. Ultra-high dose rate FLASH radiation therapy for cancer. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 58–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarts, S.G.; Flood, A.B.; Swartz, H.M. Implications of “FLASH” radiotherapy for biodosimetry. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2023, 199, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Yin, J.; Liu, Y.; Xue, J. FLASH radiotherapy: A new milestone in the field of cancer radiotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2024, 587, 216651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarbe, R.; Hotoiu, L.; Barbier, J.; Favaudon, V. A physicochemical model of reaction kinetics supports peroxyl radical recombination as the main determinant of the FLASH effect. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 153, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.S.; Teo, B.K.; Dong, L.; Friberg, A.; Koumenis, C.; Diffenderfer, E.; Zou, J.W. Modeling ultra-high dose rate electron and proton FLASH effect with the physicochemical approach. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 145013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.-C.; Hendry, J.; Limoli, C. Biological benefits of ultra-high dose rate FLASH radiotherapy: Sleeping beauty awoken. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 31, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujitsuka, M.; Majima, T. Reaction dynamics of excited radical ions revealed by femtosecond laser flash photolysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2018, 35, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunbul, N.H.B.; Zhang, W.; Oraiqat, I.; Litzenberg, D.W.; Lam, K.L.; Cuneo, K.; Moran, J.M.; Carson, P.L.; Wang, X.; Clarke, S.D.; et al. A simulation study of ionizing radiation acoustic imaging (iRAI) as a real-time dosimetric technique for ultra-high dose rate radiotherapy (UHDR-RT). Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 6137–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khatib, M.; Van Slyke, A.L.; Velalopoulou, A.; Kim, M.M.; Shoniyozov, K.; Allu, S.R.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Busch, T.M.; Wiersma, R.D.; Koch, C.J.; et al. Ultrafast tracking of oxygen dynamics during proton FLASH. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Rodriguez, A.; Sanchez-Parcerisa, D.; Ibáñez, P.; Vera-Sánchez, J.A.; Mazal, A.; Fraile, L.M.; Manuel Udías, J. Radical production with pulsed beams: Understanding the transition to FLASH. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Méndez, J.; Domínguez-Kondo, N.; Schuemann, J.; McNamara, A.; Moreno-Barbosa, E.; Faddegon, B. LET-dependent intertrack yields in proton irradiation at ultra-high dose rates relevant for FLASH therapy. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Pratx, G. 3D computational model of oxygen depletion kinetics in brain vasculature during FLASH RT and its implications for in vivo oximetry experiments. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 3914–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, R.J.; Almeida, A.; Grilj, V.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Godfroid, C.; Petit, B.; Bailat, C.; Limoli, C.L.; Vozenin, M.C. Hypoxic tumors are sensitive to FLASH radiotherapy. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Lázaro, M. Dual role of hydrogen peroxide in cancer: Possible relevance to cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Cancer Lett. 2007, 252, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lan, T.; Feng, X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Ma, X.; Du, J.; Hou, G.; et al. FLASH radiotherapy: A promising new method for radiotherapy. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolfath, R.; Grosshans, D.; Mohan, R. Oxygen depletion in FLASH ultra-high-dose-rate radiotherapy: A molecular dynamics simulation. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 6551–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.; Knoll, J.; Beyreuther, E.; Pawelke, J.; Skuza, R.; Hanley, R.; Brons, S.; Pagliari, F.; Seco, J. Does FLASH deplete oxygen? Experimental evaluation for photons, protons, and carbon ions. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 3982–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epp, E.R.; Weiss, H.; Djordjevic, B.; Santomasso, A. The radiosensitivity of cultured mammalian cells exposed to single high intensity pulses of electrons in various concentrations of oxygen. Radiat. Res. 1972, 52, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, G.; Konradsson, E.; Lempart, M.; Bäck, S.; Ceberg, C.; Petersson, K. The FLASH effect depends on oxygen concentration. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 92, 20190702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, G.; Konradsson, E.; Beyer, S.; Wittrup, A.; Butterworth, K.T.; McMahon, S.J.; Ghita, M.; Petersson, K.; Ceberg, C. Cancer cells can exhibit a sparing FLASH effect at low doses under normoxic in vitro-conditions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 686142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limoli, C.L.; Vozenin, M.-C. Reinventing Radiobiology in the Light of FLASH Radiotherapy. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2023, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Gao, H.; Shen, X.; Bai, X.; Tang, M. A FLASH model of radiolytic oxygen depletion and reactive oxygen species for differential tumor and normal-tissue response. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.R.; Jones, D.; Jones, G.D.; Petersson, K. FLASH irradiation induces lower levels of DNA damage ex vivo, an effect modulated by oxygen tension, dose, and dose rate. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, G.; Vandenborre, J.; Villoing, D.; Fiegel, V.; Fois, G.R.; Haddad, F.; Koumeir, C.; Maigne, L.; Métivier, V.; Poirier, F.; et al. Proton irradiations at ultra-high dose rate vs. conventional dose rate: Strong impact on hydrogen peroxide yield. Radiat. Res. 2022, 198, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Qiu, R.; Li, W.B.; Zhou, W.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. Radical recombination and antioxidants: A hypothesis on the FLASH effect mechanism. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2023, 99, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsch, L.; Pawelke, J.; Brand, M.; Hans, S.; Hideghéty, K.; Jansen, J.; Lessmann, E.; Löck, S.; Schürer, M.; Schurig, R.; et al. Beam pulse structure and dose rate as determinants for the flash effect observed in zebrafish embryo. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 173, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Acharya, M.M.; Petersson, K.; Alikhani, L.; Yakkala, C.; Allen, B.D.; Ollivier, J.; Petit, B.; Jorge, P.G.; Syage, A.R.; et al. Long-term neurocognitive benefits of FLASH radiotherapy driven by reduced reactive oxygen species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10943–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, D.R.; Buettner, G.R.; Petronek, M.S.; St-Aubin, J.J.; Flynn, R.T.; Waldron, T.J.; Limoli, C.L. An integrated physico-chemical approach for explaining the differential impact of FLASH versus conventional dose rate irradiation on cancer and normal tissue responses. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Jia, X.; Chi, Y. Modeling the effect of oxygen on the chemical stage of water radiolysis using GPU-based microscopic Monte Carlo simulations, with an application in FLASH radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 025004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitz, D.R.; Buettner, G.R.; Limoli, C.L. Response to letter regarding “An integrated physico-chemical approach for explaining the differential impact of FLASH versus conventional dose rate irradiation on cancer and normal tissue responses”. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronek, M.S.; Spitz, D.R.; Buettner, G.R.; Allen, B.G. Linking cancer metabolic dysfunction and genetic instability through the lens of iron metabolism. Cancers 2019, 11, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panieri, E.; Santoro, M.M. ROS homeostasis and metabolism: A dangerous liason in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaerts, E.; Macaeva, E.; Isebaert, S.; Haustermans, K. Potential Molecular Mechanisms behind the Ultra-High Dose Rate “FLASH” Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturri, L.; Bertho, A.; Lamirault, C.; Brisebard, E.; Juchaux, M.; Gilbert, C.; Espenon, J.; Sébrié, C.; Jourdain, L.; de Marzi, L.; et al. Oxygen supplementation in anesthesia can block FLASH effect and anti-tumor immunity in conventional proton therapy. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturri, L.; Bertho, A.; Lamirault, C.; Juchaux, M.; Gilbert, C.; Espenon, J.; Sebrie, C.; Jourdain, L.; Pouzoulet, F.; Verrelle, P.; et al. Proton FLASH radiation therapy and immune infiltration: Evaluation in an orthotopic glioma rat model. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 116, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.J.; Petersson, K.; Olcina, M.M. The importance of hypoxia in radiotherapy for the immune response, metastatic potential and FLASH-RT. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 98, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertho, A.; Iturri, L.; Prezado, Y. Radiation-induced immune response in novel radiotherapy approaches FLASH and spatially fractionated radiotherapies. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 376, 37–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Pei, P.; Shen, W.; Hu, L.; Yang, K. Radiation-Induced Immunogenic Cell Death for Cancer Radioimmunotherapy. Small Methods 2023, 7, e2201401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatson, R.E.; Parente-Pereira, A.C.; Halim, L.; Cozzetto, D.; Hull, C.; Whilding, L.M.; Martinez, O.; Taylor, C.A.; Obajdin, J.; Hoang, K.N.; et al. TGF-β1 potentiates Vγ9Vδ2 T cell adoptive immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, R.J.; Ahmed, M.M.; Amendola, B.; Belyakov, O.; Bentzen, S.M.; Butterworth, K.T.; Chang, S.; Coleman, C.N.; Djonov, V.; Formenti, S.C.; et al. Understanding high-dose, ultra-high dose rate, and spatially fractionated radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 766–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Perentesis, J.; Khuntia, D.; Pfister, S.; Sharma, R. Can rational combination of ultra-high dose rate FLASH radiotherapy with immunotherapy provide a novel approach to cancer treatment? Clin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.D.; Hammond, E.M.; Higgins, G.S.; Petersson, K. Ultra-high dose rate (FLASH) radiotherapy: Silver bullet or fool’s gold? Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouillade, C.; Curras-Alonso, S.; Giuranno, L.; Quelennec, E.; Heinrich, S.; Bonnet-Boissinot, S.; Beddok, A.; Leboucher, S.; Karakurt, H.U.; Bohec, M.; et al. FLASH irradiation spares lung progenitor cells and limits the incidence of radio-induced senescence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lu, C.; Mei, Z.; Sun, X.; Han, J.; Qian, J.; Liang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Kong, D.; Xu, S.; et al. Association of cancer stem cell radio-resistance under ultra-high dose rate FLASH irradiation with lysosome-mediated autophagy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 672693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Debbio, F.; Bertilacchi, M.S.; Gonnelli, A.; Da Pozzo, E.; Tozzini, V.; Martini, C.; Capaccioli, S.; Costa, B. An insight into hypothesized biological processs contributing to the Flash effect. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Petersson, K.; Jaccard, M.; Boivin, G.; Germond, J.-F.; Petit, B.; Doenlen, R.; Favaudon, V.; Bochud, F.; Bailat, C.; et al. Irradiation in a flash: Unique sparing of memory in mice after whole brain irradiation with dose rates above 100 Gy/s. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, J.; Li, H.; Gong, Z.; Wang, B.; Du, K.; Zhang, C.; Bi, H.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; et al. Circular RNA HIPK2 Promotes A1 Astrocyte Activation after Spinal Cord Injury through Autophagy and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Modulating miR-124-3p-Mediated Smad2 Repression. ACS Omega 2023, 9, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montay-Gruel, P.; Acharya, M.M.; Gonçalves Jorge, P.; Petit, B.; Petridis, I.G.; Fuchs, P.; Leavitt, R.; Petersson, K.; Gondré, M.; Ollivier, J.; et al. Hypofractionated FLASH-RT as an effective treatment against glioblastoma that reduces neurocognitive side effects in mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Togno, M.; Ballesteros-Zebadua, P.; Franco-Perez, J.; Geyer, R.; Schaefer, R.; Petit, B.; Grilj, V.; Meer, D.; Safai, S.; et al. Dosimetric and biologic intercomparison between electron and proton FLASH beams. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 190, 109953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, R.; Chang, C.-W.; Charyyev, S.; Zhou, J.; Bradley, J.D.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. A potential revolution in cancer treatment: A topical review of FLASH radiotherapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.C.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Limoli, C.; Germond, J.F. All irradiations that are ultra-high dose rate may not be FLASH: The critical importance of beam parameter characterization and in vivo validation of the FLASH effect. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, J.; Bezak, E.; Le, H.; Kempson, I. The current status of FLASH particle therapy: A systematic review. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2023, 46, 529–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, K.; Natarajan, S.; Wang, J.; Chow, S.; Eggold, J.T.; Loo, P.E.; Manjappa, R.; Melemenidis, S.; Lartey, F.M.; Schüler, E.; et al. Abdominal FLASH irradiation reduces radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity for the treatment of ovarian cancer in mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggold, J.T.; Chow, S.; Melemenidis, S.; Wang, J.; Natarajan, S.; Loo, P.E.; Manjappa, R.; Viswanathan, V.; Kidd, E.A.; Engleman, E.; et al. Abdominopelvic FLASH irradiation improves PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibition in preclinical models of ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.M.; Verginadis, I.I.; Goia, D.; Haertter, A.; Shoniyozov, K.; Zou, W.; Maity, A.; Busch, T.M.; Metz, J.M.; Cengel, K.A.; et al. Comparison of FLASH proton entrance and the spread-out Bragg peak dose regions in the sparing of mouse intestinal crypts and in a pancreatic tumor model. Cancers 2021, 13, 4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.; Cooley, J.; Wagner, M.M.; Yu, T.; Zwart, T. Demonstration of the FLASH effect within the spread-out bragg peak after abdominal irradiation of mice. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2022, 8, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gerweck, L.E.; Cascio, E.; Gu, L.; Yang, Q.; Dong, X.; Huang, P.; Bertolet, A.; Nesteruk, K.P.; Sung, W.; et al. Absence of Tissue-Sparing Effects in Partial Proton FLASH Irradiation in Murine Intestine. Cancers 2023, 15, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, C.M.; Schüler, E.; Taniguchi, C.M. The Therapeutic Potential of FLASH-RT for Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-E.; Gwak, S.-H.; Hong, B.-J.; Oh, J.-M.; Choi, H.-S.; Kim, M.S.; Oh, D.; Lartey, F.M.; Rafat, M.; Schüler, E.; et al. Effects of ultra-high doserate FLASH irradiation on the tumor microenvironment in lewis lung carcinoma: Role of myosin light chain. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 109, 1440–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Rigor, R.R.; Pivetti, C.D.; Wu, M.H.; Yuan, S.Y. Myosin light chain kinase in microvascular endothelial barrier function. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, L.A.; Casey, K.M.; Wang, J.; Blaney, A.; Manjappa, R.; Breitkreutz, D.; Skinner, L.; Dutt, S.; Ko, R.B.; Bush, K.; et al. FLASH irradiation results in reduced severe skin toxicity compared to conventional-dose-rate irradiation. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesulu, B.P.; Sharma, A.; Pollard-Larkin, J.M.; Sadagopan, R.; Symons, J.; Neri, S.; Singh, P.K.; Tailor, R.; Lin, S.H.; Krishnan, S. Ultra high dose rate (35 Gy/sec) radiation does not spare the normal tissue in cardiac and splenic models of lymphopenia and gastrointestinal syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudigkeit, S.; Schmid, T.E.; Dombrowsky, A.C.; Stolz, J.; Bartzsch, S.; Chen, C.-B.; Matejka, N.; Sammer, M.; Bergmaier, A.; Dollinger, G.; et al. Proton-FLASH: Effects of ultra-high dose rate irradiation on an in-vivo mouse ear model. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozenin, M.C.; De Fornel, P.; Petersson, K.; Favaudon, V.; Jaccard, M.; Germond, J.F.; Petit, B.; Burki, M.; Ferrand, G.; Patin, D.; et al. The advantage of FLASH radiotherapy confirmed in mini-pig and cat-cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konradsson, E.; Arendt, M.L.; Jensen, K.B.; Børresen, B.; Hansen, A.E.; Bäck, S.; Kristensen, A.T.; Rosenschöld, P.M.A.; Ceberg, C.; Petersson, K. Establishment and initial experience of clinical FLASH radiotherapy in canine cancer patients. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 658004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velalopoulou, A.; Karagounis, I.V.; Cramer, G.M.; Kim, M.M.; Skoufos, G.; Goia, D.; Hagan, S.; Verginadis, I.I.; Shoniyozov, K.; Chiango, J.; et al. FLASH proton radiotherapy spares normal epithelial and mesenchymal tissues while preserving sarcoma response. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 4808–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, J.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Jorge, P.G.; Bailat, C.; Petit, B.; Ollivier, J.; Jeanneret-Sozzi, W.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Moeckli, R.; et al. Clinical translation of FLASH radiotherapy: Why and how? Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, J.; Sozzi, W.J.; Jorge, P.G.; Gaide, O.; Bailat, C.; Duclos, F.; Patin, D.; Ozsahin, M.; Bochud, F.; Germond, J.-F.; et al. Treatment of a first patient with FLASH-radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 139, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabi, S.; Van To, T.H.; Leavitt, R.; Poglio, S.; Jorge, P.G.; Jaccard, M.; Petersson, K.; Petit, B.; Roméo, P.H.; Pflumio, F.; et al. Ultra-high-dose-rate FLASH and conventional-dose-rate irradiation differentially affect human acute lymphoblastic leukemia and normal hematopoiesis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 109, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, A.; McCauley, S.; Speth, J.; Nunez, S.A.; Boivin, G.; Vilalta, M.; Sharma, R.A.; Perentesis, J.P.; Sertorio, M. Impact of multiple beams on the FLASH effect in soft tissue and skin in mice. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 118, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüler, E.; Acharya, M.; Montay-Gruel, P.; Loo, B.W., Jr.; Vozenin, M.C.; Maxim, P.G. Ultra-high dose rate electron beams and the FLASH effect: From preclinical evidence to a new radiotherapy paradigm. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2082–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, H.; Brüningk, S.C.; Box, C.; Oelfke, U.; Bartzsch, S.H. Quantification of differential response of tumour and normal cells to microbeam radiation in the absence of FLASH effects. Cancers 2021, 13, 3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Buonanno, M.; Harken, A.; Zhou, G.; Hei, T.K. Mitochondrial damage response and fate of normal cells exposed to FLASH irradiation with protons. Radiat. Res. 2022, 197, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhlen, T.T.; Germond, J.; Bourhis, J.; Bailat, C.; Bochud, F.; Moeckli, R. The minimal FLASH sparing effect needed to compensate the increase of radiobiological damage due to hypofractionation for late-reacting tissues. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 7672–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Matsuya, Y.; Fukunaga, H. Possible mechanisms and simulation modeling of FLASH radiotherapy. Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2024, 17, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Cascio, E.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Gerweck, L.; Huang, P.; Gottschalk, B.; Flanz, J.; Schuemann, J. FLASH investigations using protons: Design of delivery system, preclinical setup and confirmation of FLASH effect with protons in animal systems. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Naqa, I.; Pogue, B.W.; Zhang, R.; Oraiqat, I.; Parodi, K. Image guidance for FLASH radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 4109–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; No, H.J.; Breitkreutz, D.Y.; Mascia, A.E.; Moeckli, R.; Bourhis, J.; Schüler, E.; Maxim, P.G.; Loo, B.W. Technological basis for clinical trials in FLASH radiation therapy: A review. Appl. Rad. Oncol. 2021, 10, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, A.; Labate, L.; Piccinini, S.; Panaino, C.M.; Andreassi, M.G.; Gizzi, L.A. FLASH Radiotherapy: Expectations, Challenges, and Current Knowledge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
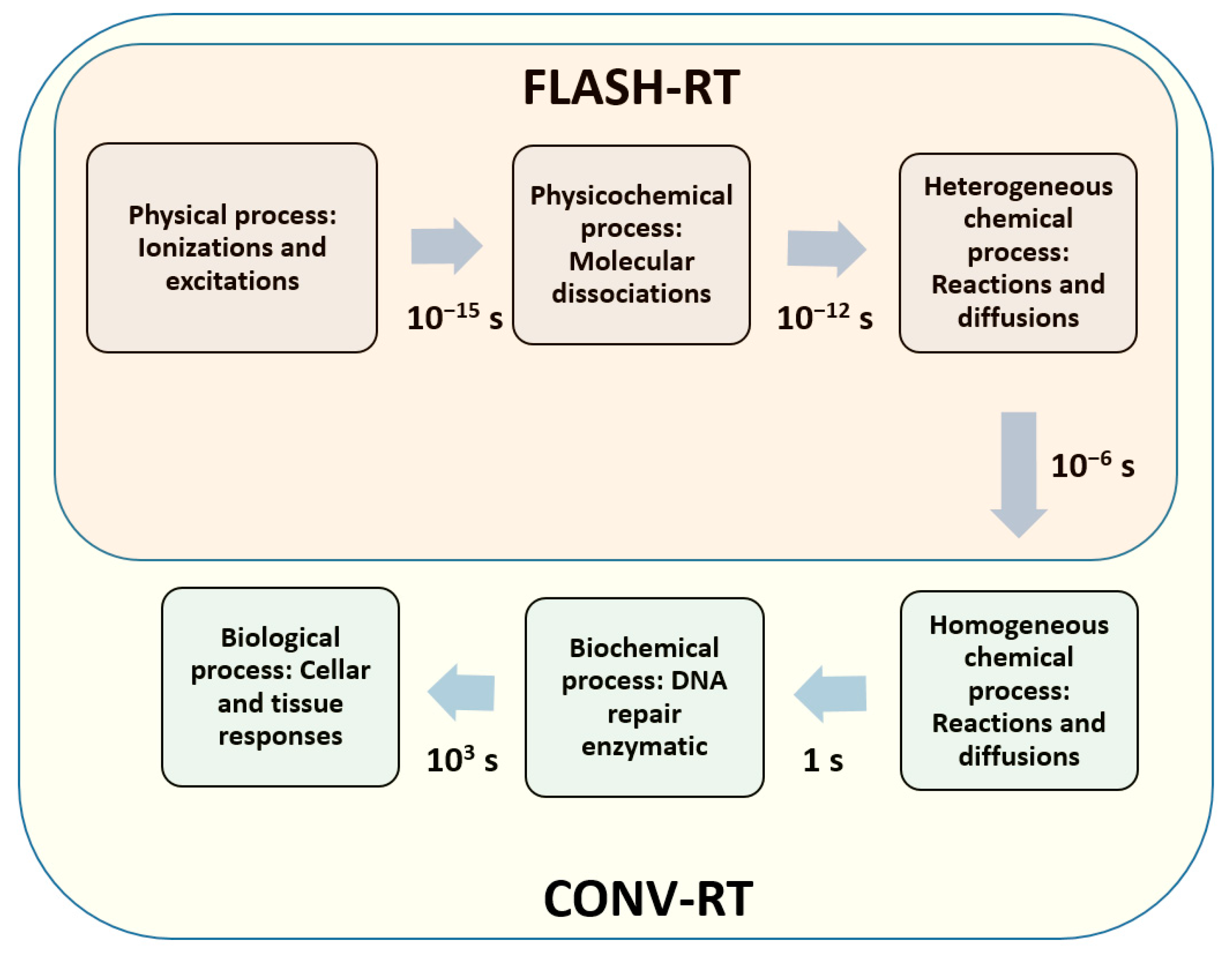
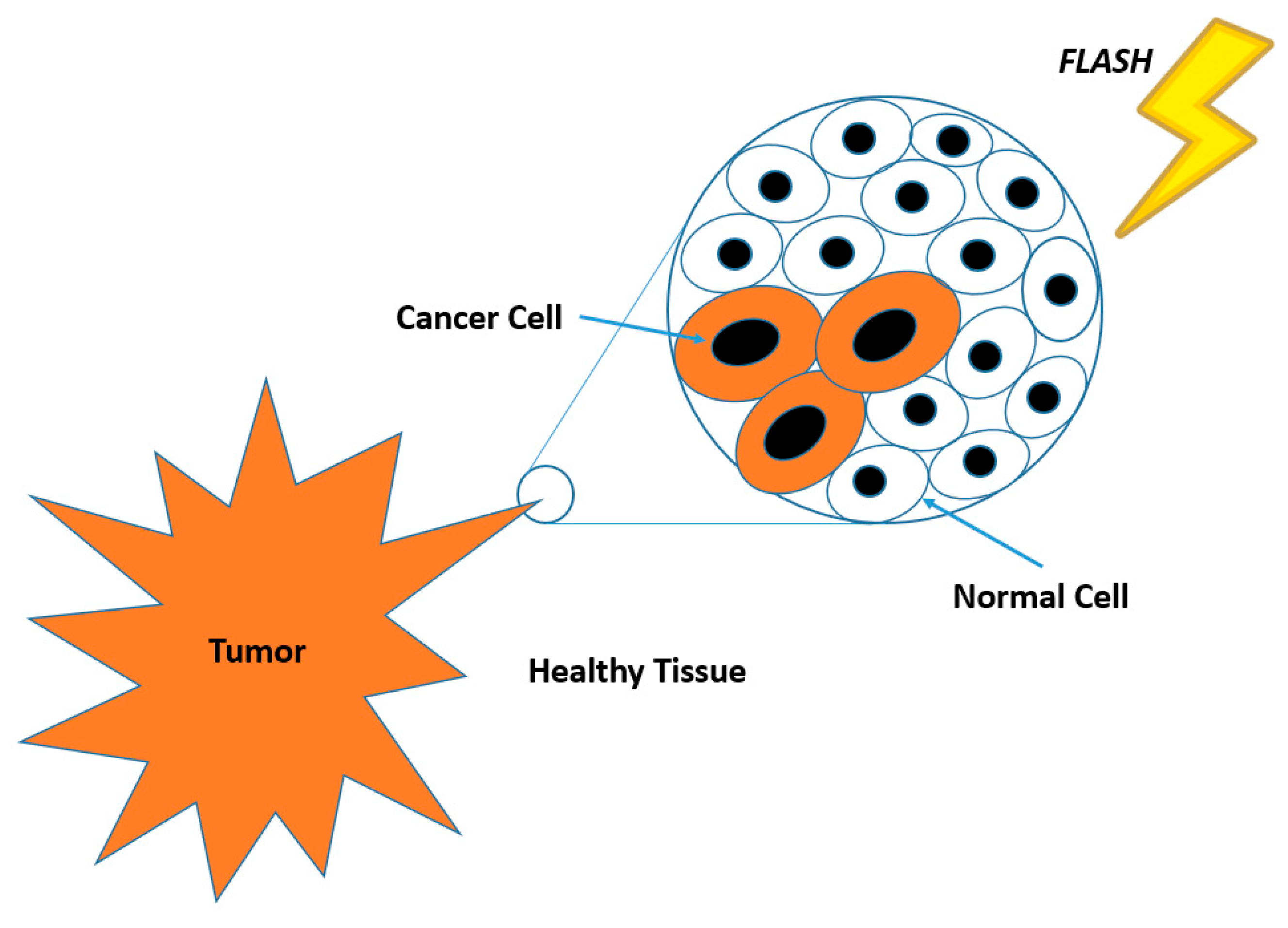

| Aspect | FLASH-RT | CONV-RT |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment Time | Ultra-fast (milliseconds) | Typically seconds to minutes |
| Dose Rate | Extremely high (>40 Gy/s) | Moderate to high (0.001–0.4 Gy/s) |
| Normal Cell Sparing | Enhanced due to UHDR | Limited, increased risk to normal cells |
| Oxygen Effect | Reduced due to ultra-short exposure | Present, potential impact on tumor response |
| Radiobiological Effect | Increased therapeutic index | Standard radiobiological principles |
| Fractionation | Single or few fractions possible | Multiple fractions common |
| Patient Comfort | Reduced overall treatment time | Longer treatment sessions |
| Machine Wear and Tear | Potentially reduced | Standard wear and tear |
| Integration with Imaging | Compatibility with advanced imaging | Standard imaging requirements |
| Organ Motion during Treatment | Reduced impact due to faster delivery if the tumor position is known immediately prior to treatment | Continuous monitoring and adaptation |
| Patient Throughput | Potentially increased | Treatment duration may impact throughput |
| Clinical Trial Status | Investigational, ongoing research | Established, widely practiced |
| Cost and Accessibility | Potential for higher costs | Generally more accessible |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chow, J.C.L.; Ruda, H.E. Mechanisms of Action in FLASH Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical and Biological Processes on Cancerous and Normal Cells. Cells 2024, 13, 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100835
Chow JCL, Ruda HE. Mechanisms of Action in FLASH Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical and Biological Processes on Cancerous and Normal Cells. Cells. 2024; 13(10):835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100835
Chicago/Turabian StyleChow, James C. L., and Harry E. Ruda. 2024. "Mechanisms of Action in FLASH Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical and Biological Processes on Cancerous and Normal Cells" Cells 13, no. 10: 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100835
APA StyleChow, J. C. L., & Ruda, H. E. (2024). Mechanisms of Action in FLASH Radiotherapy: A Comprehensive Review of Physicochemical and Biological Processes on Cancerous and Normal Cells. Cells, 13(10), 835. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13100835






