A Review of the Biosynthesis and Structural Implications of Insulin Gene Mutations Linked to Human Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
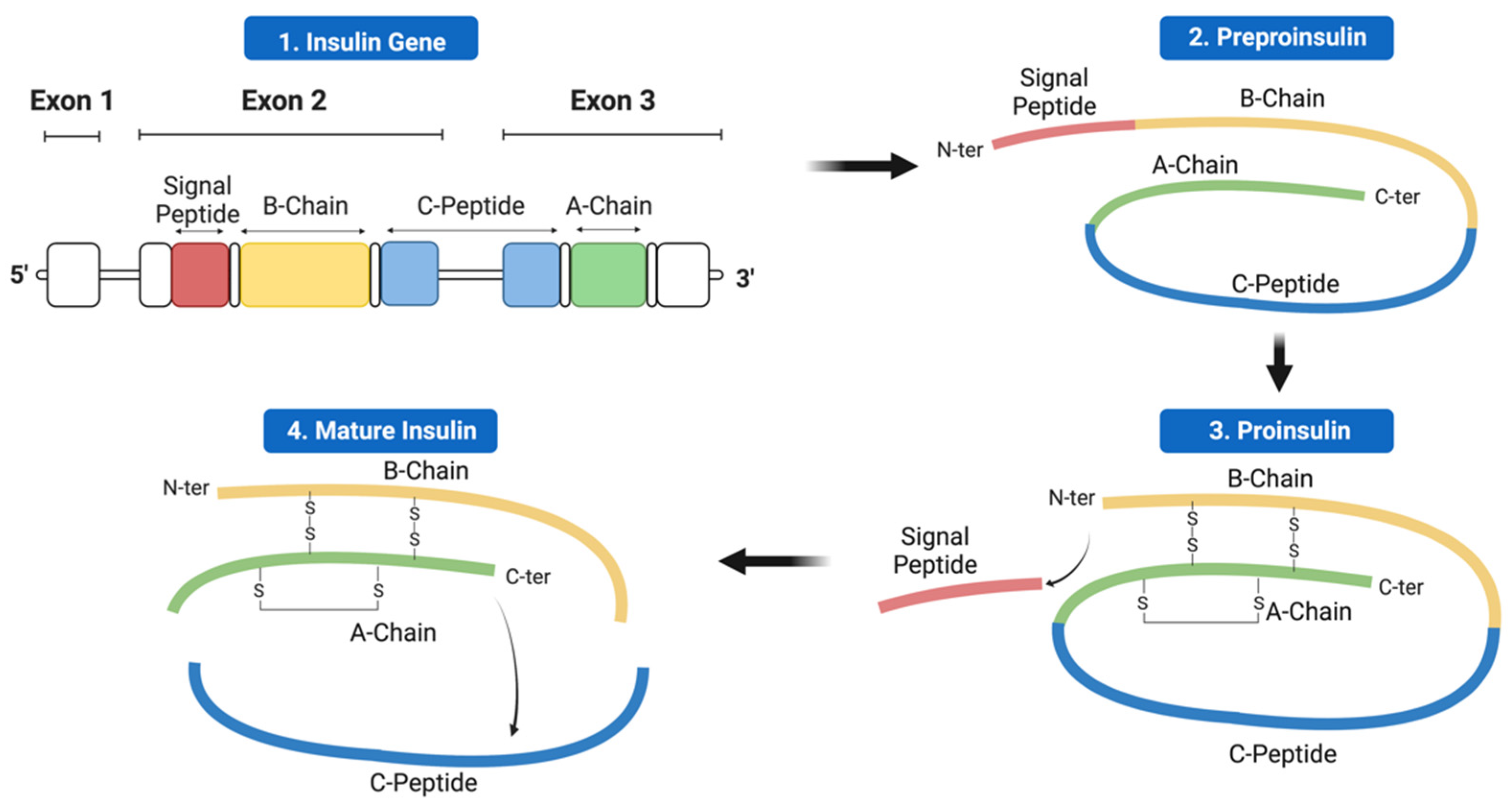
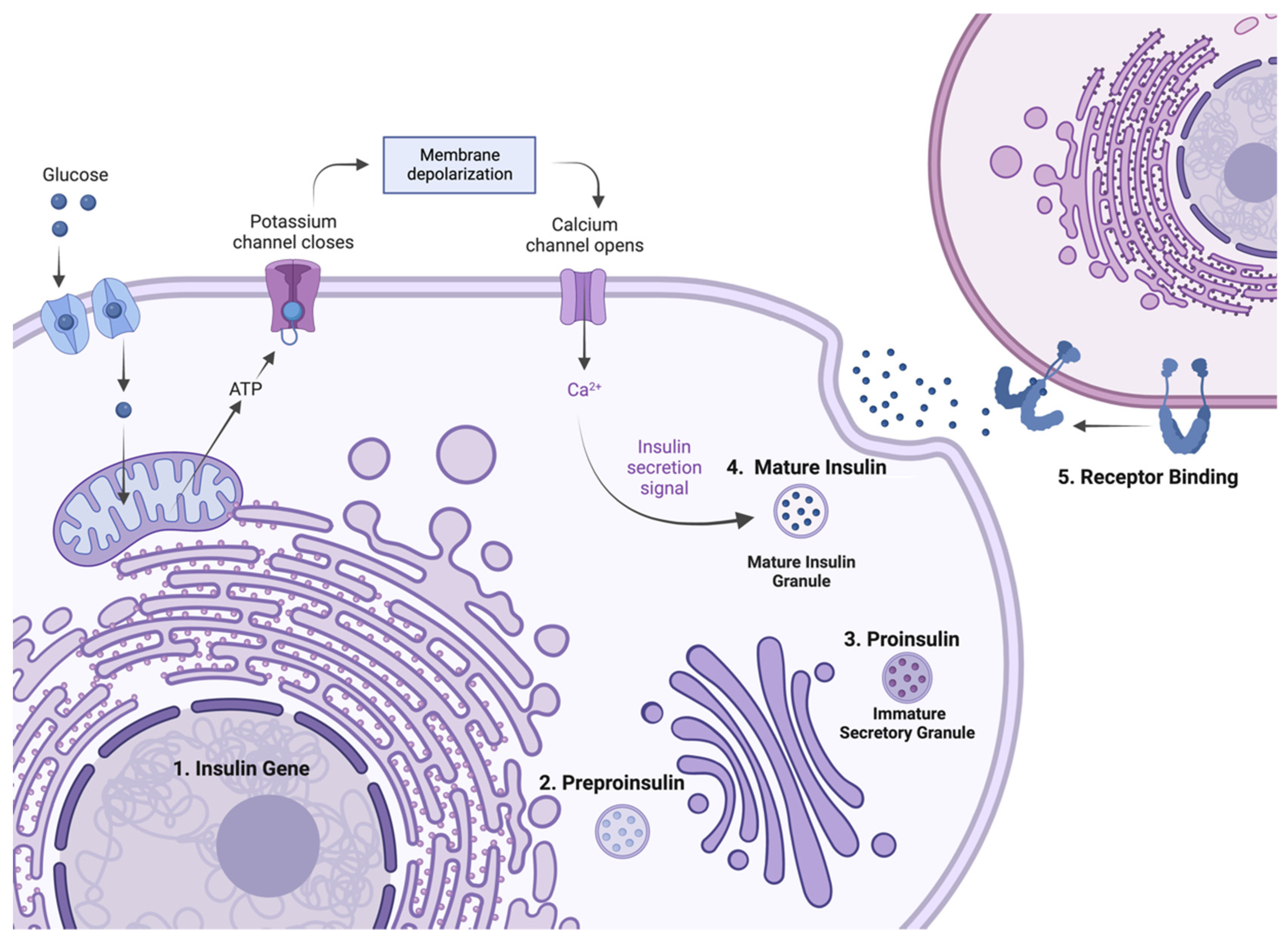
2. Insulin Expression—From Genome to Protein
3. Methods and Search Criteria
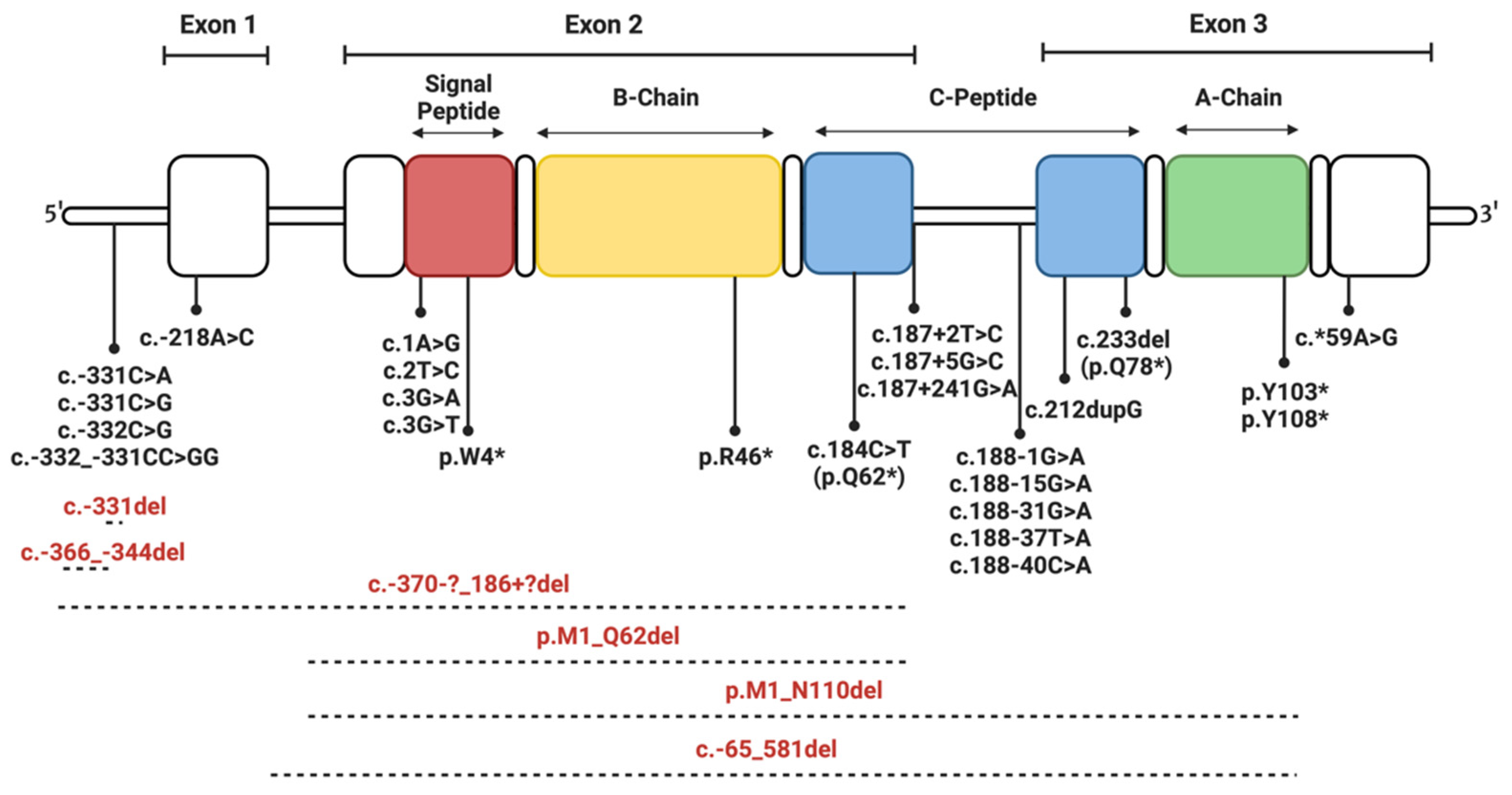
4. Insulin Gene Mutations
- Transcription and translation.
- Preproinsulin trafficking and proinsulin sorting.
- Insulin-IR interaction.
4.1. Mutations Affecting Transcription and Translation
4.2. Mutations Affecting Preproinsulin Trafficking and Proinsulin Processing
4.2.1. Signal Peptide Mutations
4.2.2. C-Peptide Mutations
4.2.3. Mutations of Cysteine Residues
4.2.4. Mutations Introducing Cysteine Residues
4.2.5. Non-Cysteine Mutations Impacting Disulfide Bonding and Structural Integrity
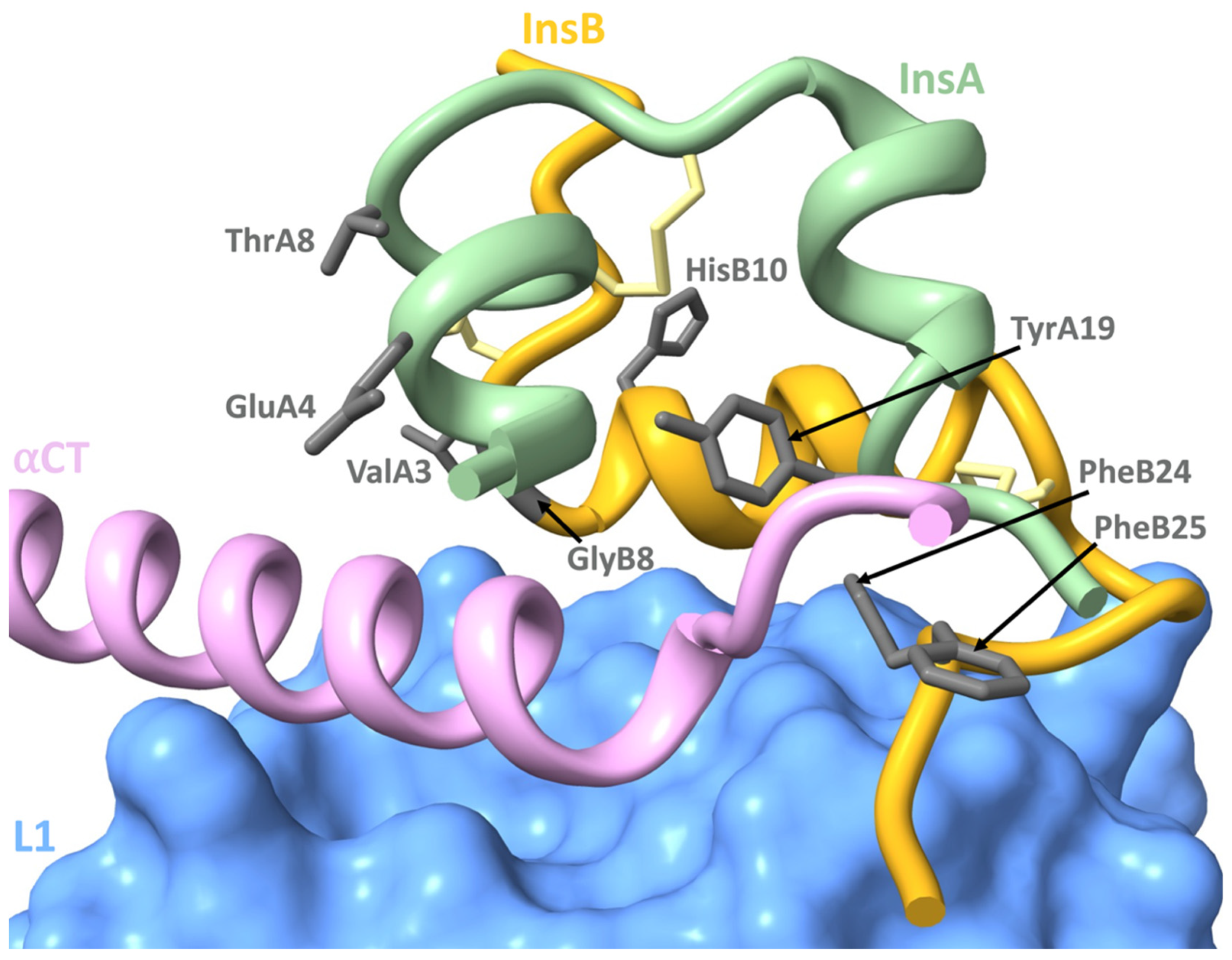
4.3. Mutations Affecting Insulin-IR Binding
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- White, M.F.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin action at a molecular level—100 years of progress. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Kleinridders, A.; Kahn, C.R. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatting, M.; Tavares, C.D.J.; Sharabi, K.; Rines, A.K.; Puigserver, P. Insulin regulation of gluconeogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1411, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Støy, J.; De Franco, E.; Ye, H.; Park, S.-Y.; Bell, G.I.; Hattersley, A.T. In celebration of a century with insulin—Update of insulin gene mutations in diabetes. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Owen, K.R. Genetics of Monogenic Diabetes: Present Clinical Challenges. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.C. Understanding insulin and its receptor from their three-dimensional structures. Mol. Metab. 2021, 52, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikkalinou, A.; Papazafiropoulou, A.K.; Melidonis, A. Type 2 diabetes and quality of life. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, M.; Nanjo, K. Insulin gene mutations and diabetes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2011, 2, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chan, L. Monogenic Diabetes: What It Teaches Us on the Common Forms of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2016, 37, 190–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, B. Insulin gene mutations and posttranslational and translocation defects: Associations with diabetes. Endocrine 2020, 70, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, J.; Cui, J.; Chen, W.; Guo, H.; Barbetti, F.; Arvan, P. INS-gene mutations: From genetics and beta cell biology to clinical disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 42, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbetti, F.; D’Annunzio, G. Genetic causes and treatment of neonatal diabetes and early childhood diabetes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Kastner, K.; Abdul-Wahid, B.; Izaguirre, J.A. Evaluation of conformational changes in diabetes-associated mutation in insulin a chain: A molecular dynamics study. Proteins 2015, 83, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iafusco, D.; Zanfardino, A.; Bonfanti, R.; Rabbone, I.; Tinto, N.; Iafusco, F.; Meola, S.; Gicchino, M.F.; Ozen, G.; Casaburo, F.; et al. Congenital diabetes mellitus. Minerva Pediatr. 2020, 72, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Hodish, I.; Haataja, L.; Lara-Lemus, R.; Rajpal, G.; Wright, J.; Arvan, P. Proinsulin misfolding and diabetes: Mutant INS gene-induced diabetes of youth. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R. Economics of Genetic Testing for Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, F.; Menting, J.G.; Margetts, M.B.; Chan, S.J.; Xu, Y.; Tennagels, N.; Wohlfart, P.; Langer, T.; Müller, C.W.; Dreyer, M.K.; et al. The signalling conformation of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Gilbert, E.R.; Liu, D. Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.-x.; Chu, Y.-C.; Jia, W.; Phillips, N.F.B.; Wang, R.-y.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Mechanism of Insulin Chain Combination: ASYMMETRIC ROLES OF A-CHAIN α-HELICES IN DISULFIDE PAIRING*. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43443–43453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.G.; Choi, K.D.; Jang, S.H.; Shin, H.C. Role of disulfide bonds in the structure and activity of human insulin. Mol. Cells 2003, 16, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Oslowski, C.M.; Urano, F. A switch from life to death in endoplasmic reticulum stressed β-cells. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2010, 12 Suppl 2, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Weiss, M.A.; Arunagiri, A.; Yong, J.; Rege, N.; Sun, J.; Haataja, L.; Kaufman, R.J.; Arvan, P. Biosynthesis, structure, and folding of the insulin precursor protein. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20 (Suppl. 2), 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J. Molecular mechanisms and regulation of insulin exocytosis as a paradigm of endocrine secretion. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 259, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, C.; Yu, H.; Choi, E. Insulin receptor endocytosis in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Camillo, B.; Carlon, A.; Eduati, F.; Toffolo, G.M. A rule-based model of insulin signalling pathway. BMC Syst. Biol. 2016, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tager, H.; Given, B.; Baldwin, D.; Mako, M.; Markese, J.; Rubenstein, A.; Olefsky, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Kolterman, O.; Poucher, R. A structurally abnormal insulin causing human diabetes. Nature 1979, 281, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garin, I.; Edghill, E.L.; Akerman, I.; Rubio-Cabezas, O.; Rica, I.; Locke, J.M.; Maestro, M.A.; Alshaikh, A.; Bundak, R.; del Castillo, G.; et al. Recessive mutations in the INS gene result in neonatal diabetes through reduced insulin biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3105–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, M.; Demirbilek, H.; Çelik, K.; Okur, N.; Hussain, K.; Ozbek, M.N. Neonatal diabetes due to homozygous INS gene promoter mutations: Highly variable phenotype, remission and early relapse during the first 3 years of life. Pediatr. Diabetes 2020, 21, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, M.; Akcay, T.; Aydin, B.; Akgun, A.; Dogan, B.B.; De Franco, E.; Ellard, S.; Onal, H. Emergence of insulin resistance following empirical glibenclamide therapy: A case report of neonatal diabetes with a recessive INS gene mutation. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 31, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, C.W.; Docherty, K. Comparative analysis of insulin gene promoters: Implications for diabetes research. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3201–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Miyagi-Shiohira, C.; Nakashima, Y.; Kinjo, T.; Saitoh, I.; Watanabe, M. Mutations in the C1 element of the insulin promoter lead to diabetic phenotypes in homozygous mice. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De León, D.D.; Stanley, C.A. Permanent Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus. In GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Everman, D.B., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Carmody, D.; Park, S.Y.; Ye, H.; Perrone, M.E.; Alkorta-Aranburu, G.; Highland, H.M.; Hanis, C.L.; Philipson, L.H.; Bell, G.I.; Greeley, S.A. Continued lessons from the INS gene: An intronic mutation causing diabetes through a novel mechanism. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 52, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusatkova, L.; Dusatkova, P.; Vosahlo, J.; Vesela, K.; Cinek, O.; Lebl, J.; Pruhova, S. Frameshift mutations in the insulin gene leading to prolonged molecule of insulin in two families with Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 58, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, S.; Furuta, H.; Kosaka, K.; Doi, A.; Yorifuji, T.; Fukuda, T.; Senmaru, T.; Uraki, S.; Matsutani, N.; Furuta, M.; et al. Identification of a variant associated with early-onset diabetes in the intron of the insulin gene with exome sequencing. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Tang, W.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z. Novel frameshift mutation in the insulin (INS) gene in a family with maturity onset diabetes of the young (MODY). J. Diabetes 2019, 11, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Støy, J.; Steiner, D.F.; Park, S.-Y.; Ye, H.; Philipson, L.H.; Bell, G.I. Clinical and molecular genetics of neonatal diabetes due to mutations in the insulin gene. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2010, 11, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raile, K.; O’Connell, M.; Galler, A.; Werther, G.; Kühnen, P.; Krude, H.; Blankenstein, O. Diabetes caused by insulin gene (INS) deletion: Clinical characteristics of homozygous and heterozygous individuals. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 165, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, K.M.; Bedwell, D.M. Suppression of nonsense mutations as a therapeutic approach to treat genetic diseases. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 2, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shu, H.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, T.; Zhen, J.; Sun, J.; Feng, W.; Xiong, Y.; et al. A Novel Nonsense INS Mutation Causes Inefficient Preproinsulin Translocation Into the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Eames, S.C.; Park, S.Y.; Labno, C.; Bell, G.I.; Prince, V.E.; Philipson, L.H. In vitro processing and secretion of mutant insulin proteins that cause permanent neonatal diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E403–E410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Mohd Ali, J.; Jalaludin, M.Y.; Harun, F. Permanent neonatal diabetes due to a novel insulin signal peptide mutation. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesgaard, T.W.; Pruhova, S.; Andersson, E.A.; Cinek, O.; Obermannova, B.; Lauenborg, J.; Damm, P.; Bergholdt, R.; Pociot, F.; Pisinger, C.; et al. Further evidence that mutations in INS can be a rare cause of Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY). BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edghill, E.L.; Flanagan, S.E.; Patch, A.M.; Boustred, C.; Parrish, A.; Shields, B.; Shepherd, M.H.; Hussain, K.; Kapoor, R.R.; Malecki, M.; et al. Insulin mutation screening in 1,044 patients with diabetes: Mutations in the INS gene are a common cause of neonatal diabetes but a rare cause of diabetes diagnosed in childhood or adulthood. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meur, G.; Simon, A.; Harun, N.; Virally, M.; Dechaume, A.; Bonnefond, A.; Fetita, S.; Tarasov, A.I.; Guillausseau, P.-J.; Boesgaard, T.W.; et al. Insulin gene mutations resulting in early-onset diabetes: Marked differences in clinical presentation, metabolic status, and pathogenic effect through endoplasmic reticulum retention. Diabetes 2010, 59, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenzano, S.E.; McFall, C.; Nguyen, L.; Savla, D.; Coufal, N.G.; Wright, M.S.; Tokita, M.; Dimmock, D.; Kingsmore, S.F.; Newfield, R.S. Neonatal diabetes mellitus due to a novel variant in the INS gene. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2019, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Ge, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Y.; Lu, M.; et al. Identification of Ala2Thr mutation in insulin gene from a Chinese MODY10 family. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2020, 470, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfanti, R.; Colombo, C.; Nocerino, V.; Massa, O.; Lampasona, V.; Iafusco, D.; Viscardi, M.; Chiumello, G.; Meschi, F.; Barbetti, F. Insulin gene mutations as cause of diabetes in children negative for five type 1 diabetes autoantibodies. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimova, R.; Tankova, T.; Gergelcheva, I.; Tournev, I.; Konstantinova, M. A family with permanent neonatal diabetes due to a novel mutation in INS gene. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 108, e28–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Lara-Lemus, R.; Shan, S.-o.; Wright, J.; Haataja, L.; Barbetti, F.; Guo, H.; Larkin, D.; Arvan, P. Impaired cleavage of preproinsulin signal peptide linked to autosomal-dominant diabetes. Diabetes 2012, 61, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahren, J.; Ekberg, K.; Johansson, J.; Henriksson, M.; Pramanik, A.; Johansson, B.-L.; Rigler, R.; Jörnvall, H. Role of C-peptide in human physiology. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 278, E759–E768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritani, M.; Yokota, I.; Tsubouchi, K.; Takaya, R.; Takemoto, K.; Minamitani, K.; Urakami, T.; Kawamura, T.; Kikuchi, N.; Itakura, M.; et al. Identification of INS and KCNJ11 gene mutations in type 1B diabetes in Japanese children with onset of diabetes before 5 years of age. Pediatr. Diabetes 2013, 14, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, M.; Dechaume, A.; Cavé, H.; Nimri, R.; Crosnier, H.; Sulmont, V.; de Kerdanet, M.; Scharfmann, R.; Lebenthal, Y.; Froguel, P.; et al. Heterozygous missense mutations in the insulin gene are linked to permanent diabetes appearing in the neonatal period or in early infancy: A report from the French ND (Neonatal Diabetes) Study Group. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1115–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Xiao, X. Identification of insulin gene variants in patients with neonatal diabetes in the Chinese population. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhayalan, B.; Chatterjee, D.; Chen, Y.-S.; Weiss, M.A. Structural Lessons From the Mutant Proinsulin Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 754693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, P.; Eisler, K.; Kamber, B.; Riniker, B.; Rittel, W.; Märki, F.; de Gasparo, M. Synthesis and biological activity of two disulphide bond isomers of human insulin: [A7-A11,A6-B7-cystine]- and [A6-A7,A11-B7-cystine]insulin (human). Biol. Chem. 1978, 359, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.X.; Jia, W.; Frank, B.H.; Phillips, N.F.; Weiss, M.A. A protein caught in a kinetic trap: Structures and stabilities of insulin disulfide isomers. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 14700–14715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.X.; Mayer, J.P.; Jia, W.; Zhang, J.; Weiss, M.A. The folding nucleus of the insulin superfamily: A flexible peptide model foreshadows the native state. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28131–28142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Tang, J.G. Characteristic, activity and conformational studies of [A6-Ser, A11-Ser]-insulin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1296, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.A.; Hua, Q.X.; Jia, W.; Chu, Y.C.; Wang, R.Y.; Katsoyannis, P.G. Hierarchical protein “un-design”: Insulin’s intrachain disulfide bridge tethers a recognition alpha-helix. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 15429–15440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Feng, Y.M. Effects of cysteine to serine substitutions in the two inter-chain disulfide bonds of insulin. Biol. Chem. 2001, 382, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Cavener, D.; Arvan, P. Proinsulin disulfide maturation and misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13209–13212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, N.T.B.; Vu, D.C.; Bui, T.P.; Nguyen, K.N.; Nguyen, D.P.; Craig, M.; Ellard, S.; Nguyen, H.T. AB125. Neonatal diabetes mellitus due to insulin gene mutation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3 (Suppl. 2), AB125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, P.; Day, J.; Torrens, L.; Shepherd, M.H.; Knight, B.A.; Ford, T.J.; Flanagan, S.E.; Chakera, A.; Hattersley, A.T.; Zeman, A. Cognitive, Neurological, and Behavioral Features in Adults With KCNJ11 Neonatal Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, M.A.; Kurtoglu, S.; Bastug, O.; Korkmaz, L.; Daar, G.; Memur, S.; Halis, H.; Günes, T.; Hussain, K.; Ellard, S. Neonatal diabetes in an infant of diabetic mother: Same novel INS missense mutation in the mother and her offspring. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 27, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirruddin, N.S.; Tan, Y.S.; Verma, C.S.; Gardner, D.; Bee, Y.M.; Hoon, S.; Teo, A. 1784-P: Studying the Impact of Heterozygous Human INS Gene Mutation on Pancreatic ß Cell. Diabetes 2019, 68 (Suppl. 1), 1784-P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, S.; Gowri, P.; Panda, J.K.; Sathyanarayana, S.O.; Gupta, S.; Chandru, S.; Chandni, R.; Raghupathy, P.; Dayal, D.; Mohan, V.; et al. Insulin gene mutations linked to permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus in Indian population. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2021, 35, 108022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredheim, S.; Svensson, J.; Pørksen, S.; Hansen, L.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.B.; Mortensen, H.B.; Barbetti, F.; Nielsen, L.B. Intrafamilial Variability of Early-Onset Diabetes due to an INS Mutation. Case Rep. Genet. 2011, 2011, 258978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendler, W.; Borowiec, M.; Antosik, K.; Jaroszewska-Swiatek, B.; Szwalkiewicz-Warowicka, E.; Malecki, M.; Mysliwiec, M.; Mlynarski, W. Paternally Inherited Proinsulin Mutations May Result in Earlier Onset of Monogenic Diabetes Mutation Identity Effect in Monogenic Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Ye, H.; Steiner, D.F.; Bell, G.I. Mutant proinsulin proteins associated with neonatal diabetes are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum and not efficiently secreted. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molven, A.; Ringdal, M.; Nordbø, A.M.; Raeder, H.; Støy, J.; Lipkind, G.M.; Steiner, D.F.; Philipson, L.H.; Bergmann, I.; Aarskog, D.; et al. Mutations in the insulin gene can cause MODY and autoantibody-negative type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, N.K.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Dhayalan, B.; Wickramasinghe, N.P.; Chen, Y.-S.; Rahimi, L.; Guo, H.; Haataja, L.; Sun, J.; et al. Evolution of insulin at the edge of foldability and its medical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29618–29628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohma, Y.; Hua, Q.X.; Liu, M.; Phillips, N.B.; Hu, S.Q.; Whittaker, J.; Whittaker, L.J.; Ng, A.; Roberts, C.T., Jr.; Arvan, P.; et al. Contribution of residue B5 to the folding and function of insulin and IGF-I: Constraints and fine-tuning in the evolution of a protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5040–5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, C.; Porzio, O.; Liu, M.; Massa, O.; Vasta, M.; Salardi, S.; Beccaria, L.; Monciotti, C.; Toni, S.; Pedersen, O.; et al. Seven mutations in the human insulin gene linked to permanent neonatal/infancy-onset diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Cabezas, O.; Edghill, E.L.; Argente, J.; Hattersley, A.T. Testing for monogenic diabetes among children and adolescents with antibody-negative clinically defined Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2009, 26, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moritani, M.; Yokota, I.; Horikawa, R.; Urakami, T.; Nishii, A.; Kawamura, T.; Kikuchi, N.; Kikuchi, T.; Ogata, T.; Sugihara, S.; et al. Identification of monogenic gene mutations in Japanese subjects diagnosed with type 1B diabetes between >5 and 15.1 years of age. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 2016, 29, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, H.; Hufnagel, R.B.; Miraldi Utz, V.; Zhang, K.; Valencia, C.A.; Leslie, N.D.; Crimmins, N.A. Bilateral cataracts in a 6-yr-old with new onset diabetes: A novel presentation of a known INS gene mutation. Pediatr. Diabetes 2016, 17, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.H.; Zhao, M.; Hua, Q.X.; Hu, S.Q.; Wan, Z.L.; Jia, W.; Weiss, M.A. Chiral mutagenesis of insulin. Foldability and function are inversely regulated by a stereospecific switch in the B chain. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 4984–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D.J.; Halban, P.A.; Kahn, C.R.; Weir, G.C.; Villa-Komaroff, L. Partial diversion of a mutant proinsulin (B10 aspartic acid) from the regulated to the constitutive secretory pathway in transfected AtT-20 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4107–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.P.; Burke, G.T.; Katsoyannis, P.G. A superactive insulin: [B10-aspartic acid]insulin(human). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6408–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ding, S.; Li, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, C.; Fang, C.; et al. A novel mutation in INS gene linked to permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2019, 64, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Globa, E.; Zelinska, N.; Mackay, D.J.G.; Temple, K.I.; Houghton, J.A.L.; Hattersley, A.T.; Flanagan, S.E.; Ellard, S. Neonatal diabetes in Ukraine: Incidence, genetics, clinical phenotype and treatment. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 2015, 28, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccini, B.; Artuso, R.; Lenzi, L.; Guasti, M.; Braccesi, G.; Barni, F.; Casalini, E.; Giglio, S.; Toni, S. Clinical and molecular characterization of a novel INS mutation identified in patients with MODY phenotype. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 59, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Du, W.; Ma, J.; Gu, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Song, H.; Gao, G. A Novel c.125 T>G (p.Val42Gly) Mutation in The Human INS Gene Leads to Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus via a Decrease in Insulin Synthesis. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 128, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.H.; Hua, Q.X.; Hu, S.Q.; Jia, W.; Wang, S.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Chiral mutagenesis of insulin. Contribution of the B20-B23 beta-turn to activity and stability. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22386–22396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Saint-Martin, C.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Wang, R.; Feng, W.; Liu, M.; Shu, H.; Fan, Z.; Haataja, L.; et al. Biological behaviors of mutant proinsulin contribute to the phenotypic spectrum of diabetes associated with insulin gene mutations. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2020, 518, 111025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Støy, J.; Olsen, J.; Park, S.Y.; Gregersen, S.; Hjørringgaard, C.U.; Bell, G.I. In vivo measurement and biological characterisation of the diabetes-associated mutant insulin p.R46Q (GlnB22-insulin). Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Xu, B.; Huang, K.; Chu, Y.-C.; Li, B.; Nakagawa, S.H.; Qu, Y.; Hu, S.-Q.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Enhancing the Activity of Insulin at the Receptor Interface: Crystal Structure and Photo-Cross-Linking of A8 Analogues. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 16119–16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R.A.; Moeller, H.P.; Thomson, E.A.; Horton, T.M.; Lee, S.; Freeman, R.; Prahalad, P.; Poon, A.S.Y.; Annes, J.P. Novel Pathogenic De Novo INS p.T97P Variant Presenting With Severe Neonatal DKA. Endocrinology 2022, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Gong, C.; Wu, D.; Lu, C.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Genetic Analysis and Follow-Up of 25 Neonatal Diabetes Mellitus Patients in China. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 6314368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshirsagar, V.Y.; Ahmed, M.; Colaco, S.M.; Houghton, J.A.; Ellard, S. Permanent neonatal diabetes due to a novel L105P (c.314T>C; p.Leu105Pro) heterozygous mutation in insulin gene. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2013, 33, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wan, Z.L.; Chu, Y.C.; Aladdin, H.; Klaproth, B.; Choquette, M.; Hua, Q.X.; Mackin, R.B.; Rao, J.S.; De Meyts, P.; et al. Crystal structure of a “nonfoldable” insulin: Impaired folding efficiency despite native activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35259–35272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyts, P. Insulin/receptor binding: The last piece of the puzzle? What recent progress on the structure of the insulin/receptor complex tells us (or not) about negative cooperativity and activation. Bioessays 2015, 37, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menting, J.G.; Whittaker, J.; Margetts, M.B.; Whittaker, L.J.; Kong, G.K.W.; Smith, B.J.; Watson, C.J.; Záková, L.; Kletvíková, E.; Jiráček, J.; et al. How insulin engages its primary binding site on the insulin receptor. Nature 2013, 493, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glendorf, T.; Sørensen, A.R.; Nishimura, E.; Pettersson, I.; Kjeldsen, T. Importance of the solvent-exposed residues of the insulin B chain alpha-helix for receptor binding. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 4743–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Polonsky, K.S.; Zeidler, A.; Rubenstein, A.H.; Tager, H.S. Human insulin B24 (Phe----Ser). Secretion and metabolic clearance of the abnormal insulin in man and in a dog model. J. Clin. Investig. 1984, 73, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckworth, W.C.; Bennett, R.G.; Hamel, F.G. Insulin Degradation: Progress and Potential*. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.L.; Huang, K.; Xu, B.; Hu, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Chu, Y.C.; Katsoyannis, P.G.; Weiss, M.A. Diabetes-associated mutations in human insulin: Crystal structure and photo-cross-linking studies of a-chain variant insulin Wakayama. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 5000–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Haataja, L.; Wright, J.; Wickramasinghe, N.P.; Hua, Q.X.; Phillips, N.F.; Barbetti, F.; Weiss, M.A.; Arvan, P. Mutant INS-gene induced diabetes of youth: Proinsulin cysteine residues impose dominant-negative inhibition on wild-type proinsulin transport. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; McGown, I.; Oppermann, U.; Conwell, L.S.; Harris, M.; Duncan, E.L. A novel INS mutation in a family with maturity-onset diabetes of the young: Variable insulin secretion and putative mechanisms. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 19, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoelson, S.; Fickova, M.; Haneda, M.; Nahum, A.; Musso, G.; Kaiser, E.T.; Rubenstein, A.H.; Tager, H. Identification of a mutant human insulin predicted to contain a serine-for-phenylalanine substitution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 7390–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.C.; Steiner, D.F.; Rubenstein, A.H.; Tager, H.S. Identification of a point mutation in the human insulin gene giving rise to a structurally abnormal insulin (insulin Chicago). Diabetes 1983, 32, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Bhayye, S.; Adeniyi, A.A.; Soliman, M.E.; Pillay, T.S. Diabetes mellitus caused by mutations in human insulin: Analysis of impaired receptor binding of insulins Wakayama, Los Angeles and Chicago using pharmacoinformatics. J. Biomol. Struct Dyn 2017, 35, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haneda, M.; Chan, S.J.; Kwok, S.C.; Rubenstein, A.H.; Steiner, D.F. Studies on mutant human insulin genes: Identification and sequence analysis of a gene encoding [SerB24]insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 6366–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.; Haneda, M.; Blix, P.; Nanjo, A.; Sanke, T.; Inouye, K.; Steiner, D.; Rubenstein, A.; Tager, H. Three mutant insulins in man. Nature 1983, 302, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avital-Shmilovici, M.; Whittaker, J.; Weiss, M.A.; Kent, S.B. Deciphering a molecular mechanism of neonatal diabetes mellitus by the chemical synthesis of a protein diastereomer, [D-AlaB8]human proinsulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 23683–23692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, T.; Schäfer, I.B.; Poojari, C.; Brankatschk, B.; Vattulainen, I.; Strauss, M.; Coskun, Ü. Cryo-EM structure of the complete and ligand-saturated insulin receptor ectodomain. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.A.; Wan, Z.; Zhao, M.; Chu, Y.C.; Nakagawa, S.H.; Burke, G.T.; Jia, W.; Hellmich, R.; Katsoyannis, P.G. Non-standard insulin design: Structure-activity relationships at the periphery of the insulin receptor. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 315, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauguin, L.; Klaproth, B.; Sajid, W.; Andersen, A.S.; McNeil, K.A.; Forbes, B.E.; De Meyts, P. Structural basis for the lower affinity of the insulin-like growth factors for the insulin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarsholm, N.C.; Norris, K.; Jørgensen, R.J.; Mikkelsen, J.; Ludvigsen, S.; Olsen, O.H.; Sørensen, A.R.; Havelund, S. Engineering stability of the insulin monomer fold with application to structure-activity relationships. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10773–10778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Freychet, P.; Rosselin, G.; DeMeyts, P. Enhanced binding affinity of chicken insulin in rat liver membranes and human lymphocytes: Relationship tothe kinetic properties of the hormone- receptor interaction. Endocrinology 1977, 100, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendorf, T.; Knudsen, L.; Stidsen, C.E.; Hansen, B.F.; Hegelund, A.C.; Sørensen, A.R.; Nishimura, E.; Kjeldsen, T. Systematic evaluation of the metabolic to mitogenic potency ratio for B10-substituted insulin analogues. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ataie-Ashtiani, S.; Forbes, B. A Review of the Biosynthesis and Structural Implications of Insulin Gene Mutations Linked to Human Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071008
Ataie-Ashtiani S, Forbes B. A Review of the Biosynthesis and Structural Implications of Insulin Gene Mutations Linked to Human Disease. Cells. 2023; 12(7):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071008
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtaie-Ashtiani, Sara, and Briony Forbes. 2023. "A Review of the Biosynthesis and Structural Implications of Insulin Gene Mutations Linked to Human Disease" Cells 12, no. 7: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071008
APA StyleAtaie-Ashtiani, S., & Forbes, B. (2023). A Review of the Biosynthesis and Structural Implications of Insulin Gene Mutations Linked to Human Disease. Cells, 12(7), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12071008




