Genomic Redistribution of Metal-Response Transcription Factor-1 (MTF-1) in Cadmium Resistant Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Total RNA Extraction
2.3. CUT&RUN
2.4. CUT&RUN Library Preparation, Sequencing and Data Processing
2.5. Peak Calling
2.6. Analysis of Motif Enrichment
2.7. ATAC-Seq Library Preparation, Sequencing and Data Processing
2.8. RNA-Seq Library Preparation, Sequencing and Data Processing
2.9. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.10. Gene Ontology
2.11. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
3. Results
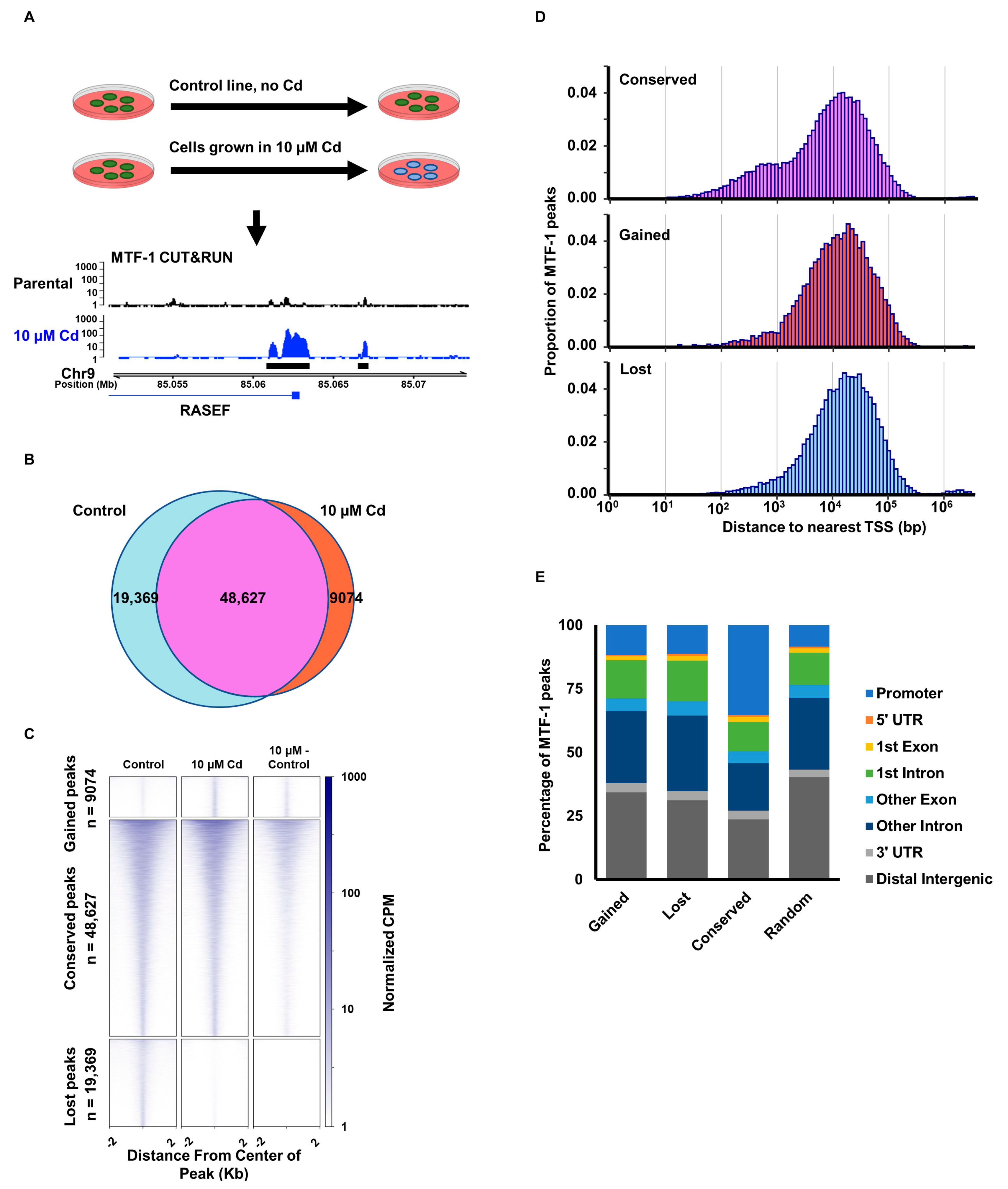
3.1. Cadmium Promotes Relocalization of MTF-1
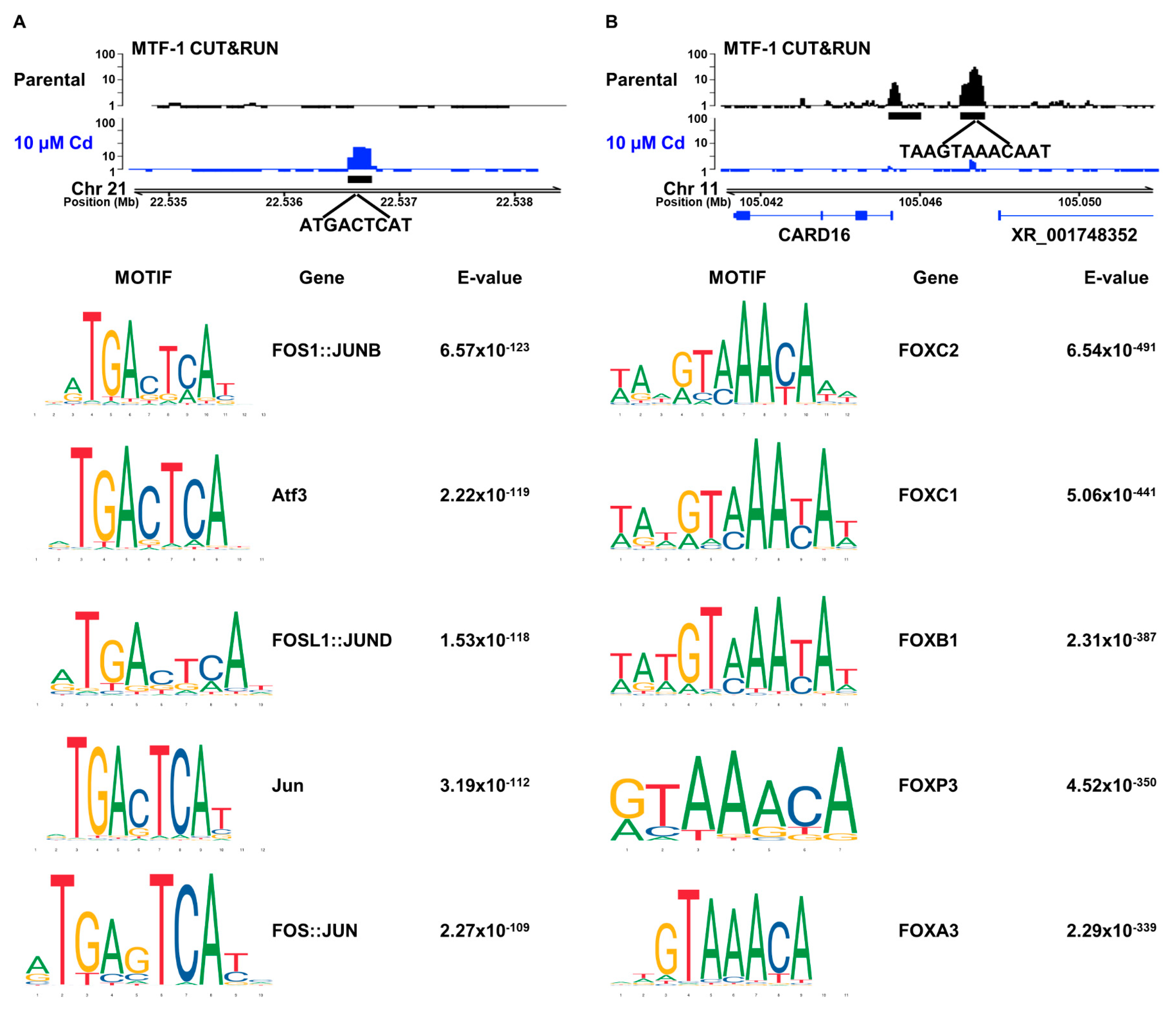
3.2. Cadmium Relocalizes MTF-1 to FOS/JUN Motifs
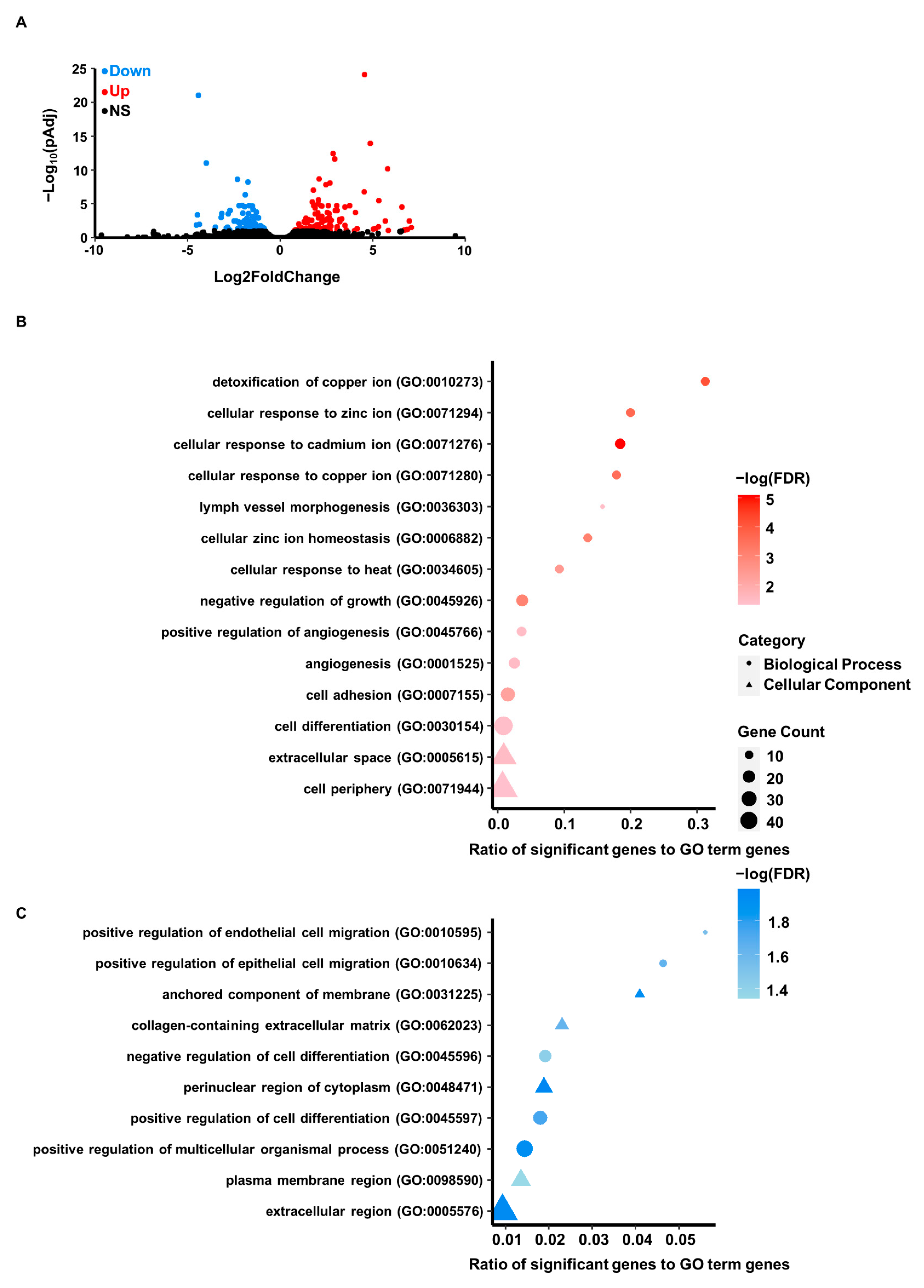
3.3. Differential Gene Expression Resulting from Cadmium Exposure
3.4. Cadmium-Induced MTF-1 Binding Does Not Alter Chromatin Accessibility
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paithankar, J.G.; Saini, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Sharma, A.; Chowdhuri, D.K. Heavy Metal Associated Health Hazards: An Interplay of Oxidative Stress and Signal Transduction. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, G.W.; Searle, P.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Brinster, R.L.; Palmiter, R.D. A 12-Base-Pair DNA Motif That Is Repeated Several Times in Metallothionein Gene Promoters Confers Metal Regulation to a Heterologous Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 7318–7322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Searle, P.F.; Stuart, G.W.; Palmiter, R.D. Building a Metal-Responsive Promoter with Synthetic Regulatory Elements. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westin, G.; Schaffner, W. A Zinc-Responsive Factor Interacts with a Metal-Regulated Enhancer Element (MRE) of the Mouse Metallothionein-I Gene. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 3763–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnera, E.; Georgiev, O.; Radtke, F.; Heuchel, R.; Baker, E.; Sutherland, G.R.; Schaffner, W. Cloning, Chromosomal Mapping and Characterization of the Human Metal-Regulatory Transcription Factor MTF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Séguin, C.; Prévost, J. Detection of a Nuclear Protein That Interacts with a Metal Regulatory Element of the Mouse Metallothionein 1 Gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10547–10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, F.; Heuchel, R.; Georgiev, O.; Hergersberg, M.; Gariglio, M.; Dembic, Z.; Schaffner, W. Cloned Transcription Factor MTF-1 Activates the Mouse Metallothionein I Promoter. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hua, H.; Balamurugan, K.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L.; George, G.N.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W.; Giedroc, D.P. Copper Sensing Function of Drosophila Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor-1 Is Mediated by a Tetranuclear Cu(I) Cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3128–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Steiner, K.; Petrov, B.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. Short-Lived Mammals (Shrew, Mouse) Have a Less Robust Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor than Humans and Bats. BioMetals 2016, 29, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, D.; Selvaraj, A.; Yepiskoposyan, H.; Zhang, B.; Hafen, E.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. Knockout of “metal-Responsive Transcription Factor” MTF-1 in Drosophila by Homologous Recombination Reveals Its Central Role in Heavy Metal Homeostasis. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, T.P.; Li, Q.; Bittel, D.; Liang, L.; Andrews, G.K. Oxidative Stress Activates Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor-1 Binding Activity. Occupancy in Vivo of Metal Response Elements in the Metallothionein-I Gene Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26233–26241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stitt, M.S.; Wasserloos, K.J.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Pitt, B.R.; St Croix, C.M. Nitric Oxide-Induced Nuclear Translocation of the Metal Responsive Transcription Factor, MTF-1 Is Mediated by Zinc Release from Metallothionein. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2006, 44, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydam, N.; Georgiev, O.; Nakano, M.Y.; Greber, U.F.; Schaffner, W. Nucleo-Cytoplasmic Trafficking of Metal-Regulatory Transcription Factor 1 Is Regulated by Diverse Stress Signals. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25487–25495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lorenzi, I.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor-1 (MTF-1) Selects Different Types of Metal Response Elements at Low vs. High Zinc Concentration. Biol. Chem. 2004, 385, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chu, M.; Giedroc, D.P. MRE-Binding Transcription Factor-1: Weak Zinc-Binding Finger Domains 5 and 6 Modulate the Structure, Affinity, and Specificity of the Metal-Response Element Complex. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 12915–12925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselman, J.; Shaw, J.R.; Glaholt, S.P.; Colbourne, J.K.; De Schamphelaere, K.A.C. Transcription Patterns of Genes Encoding Four Metallothionein Homologs in Daphnia Pulex Exposed to Copper and Cadmium Are Time- and Homolog-Dependent. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 142–143, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Amin, K.; Sato, B.G.; Samuelsson, S.J.; Sambucetti, L.; Haroon, Z.A.; Laderoute, K.; Murphy, B.J. The Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor-1 Protein Is Elevated in Human Tumors. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, J.A.; Shafer, M.M.; Trentham-Dietz, A.; Hampton, J.M.; Newcomb, P.A. Cadmium Exposure and Breast Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouybari, L.; Saei Ghare Naz, M.; Sanagoo, A.; Kiani, F.; Sayehmiri, F.; Sayehmiri, K.; Hasanpour Dehkordi, A. Toxic Elements as Biomarkers for Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Tokar, E.J.; Diwan, B.A.; Dill, A.L.; Coppin, J.-F.; Waalkes, M.P. Cadmium Malignantly Transforms Normal Human Breast Epithelial Cells into a Basal-like Phenotype. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, V.; del Carmen Escobar, M.; Gómez-Quiroz, L.; Bucio, L.; Hernández, E.; Cossio, E.C.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.C. Acute Cadmium Exposure Enhances AP-1 DNA Binding and Induces Cytokines Expression and Heat Shock Protein 70 in HepG2 Cells. Toxicology 2004, 197, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tvermoes, B.E.; Bird, G.S.; Freedman, J.H. Cadmium Induces Transcription Independently of Intracellular Calcium Mobilization. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewit, C.L.; Gengler, B.; Vegas, E.; Puckett, R.; Louie, M.C. Cadmium Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation by Potentiating the Interaction between ERα and C-Jun. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimmer, U.; Wang, Y.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. Two Major Branches of Anti-Cadmium Defense in the Mouse: MTF-1/Metallothioneins and Glutathione. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 5715–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnam, D.M.; Palmiter, R.D. Induction of Metallothionein-I MRNA in Cultured Cells by Heavy Metals and Iodoacetate: Evidence for Gratuitous Inducers. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1984, 4, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, H.; Koizumi, S. DNA Microarray Analysis of Human Gene Expression Induced by a Non-Lethal Dose of Cadmium. Ind. Health 2002, 40, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASPAR CORE Database. Available online: https://jaspar.genereg.net/ (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Khojastehfar, A.; Aghaei, M.; Gharagozloo, M.; Panjehpour, M. Cadmium Induces Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Apoptosis in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cell Line. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, W.S.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Identification of Cadmium-Produced Lipid Hydroperoxides, Transcriptomic Changes in Antioxidant Enzymes, Xenobiotic Transporters, and pro-Inflammatory Markers in Human Breast Cancer Cells (MCF7) and Protection with Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 1978–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannino, G.; Ferruggia, E.; Luparello, C.; Rinaldi, A.M. Effects of Cadmium Chloride on Some Mitochondria-Related Activity and Gene Expression of Human MDA-MB231 Breast Tumor Cells. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skene, P.J.; Henikoff, S. An Efficient Targeted Nuclease Strategy for High-Resolution Mapping of DNA Binding Sites. eLife 2017, 6, e21856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Reddy, R.C.; Chadchan, K.S.; Patil, A.J.; Biradar, M.S.; Das, K.K. Nickel and Oxidative Stress: Cell Signaling Mechanisms and Protective Role of Vitamin C. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 20, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolma, A.; Yan, J.; Whitington, T.; Toivonen, J.; Nitta, K.R.; Rastas, P.; Morgunova, E.; Enge, M.; Taipale, M.; Wei, G.; et al. DNA-Binding Specificities of Human Transcription Factors. Cell 2013, 152, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolma, A.; Kivioja, T.; Toivonen, J.; Cheng, L.; Wei, G.; Enge, M.; Taipale, M.; Vaquerizas, J.M.; Yan, J.; Sillanpää, M.J.; et al. Multiplexed Massively Parallel SELEX for Characterization of Human Transcription Factor Binding Specificities. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindert, U.; Cramer, M.; Meuli, M.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor 1 (MTF-1) Activity Is Regulated by a Nonconventional Nuclear Localization Signal and a Metal-Responsive Transactivation Domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 6283–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Signatures Database. Available online: https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/msigdb/index.jsp (accessed on 5 January 2022).
- Seo, J.; Koçak, D.D.; Bartelt, L.C.; Williams, C.A.; Barrera, A.; Gersbach, C.A.; Reddy, T.E. AP-1 Subunits Converge Promiscuously at Enhancers to Potentiate Transcription. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavera-Montañez, C.; Hainer, S.J.; Cangussu, D.; Gordon, S.J.V.; Xiao, Y.; Reyes-Gutierrez, P.; Imbalzano, A.N.; Navea, J.G.; Fazzio, T.G.; Padilla-Benavides, T. The Classic Metal-Sensing Transcription Factor MTF1 Promotes Myogenesis in Response to Copper. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 14556–14574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Jin, X.; Snow, E.T. Effect of Arsenic on Transcription Factor AP-1 and NF-KappaB DNA Binding Activity and Related Gene Expression. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 133, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtlen, P.; Wang, Y.; Belser, T.; Georgiev, O.; Certa, U.; Sack, R.; Schaffner, W. Target Gene Search for the Metal-Responsive Transcription Factor MTF-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.J.; Stapleton, S.R. Characterization of Cd-Induced Molecular Events Prior to Cellular Damage in Primary Rat Hepatocytes in Culture: Activation of the Stress Activated Signal Protein JNK and Transcription Factor AP-1. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2004, 18, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, S.; Qian, S.Y.; Hong, J.-S.; Kadiiska, M.B.; Tennant, R.W.; Waalkes, M.P.; Liu, J. Cadmium-Induced Toxicity in Rat Primary Mid-Brain Neuroglia Cultures: Role of Oxidative Stress from Microglia. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 98, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lim, K.-T. Preventive Effect of Phytoglycoprotein (27 KDa) on Inflammatory Factors at Liver Injury in Cadmium Chloride-Exposed ICR Mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandravanshi, L.; Shiv, K.; Kumar, S. Developmental Toxicity of Cadmium in Infants and Children: A Review. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2021, 36, e2021003-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, P.K. Fortuitous Convergences: The Beginnings of JUN. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Grigoriadis, A.E.; Möhle-Steinlein, U.; Wagner, E.F. A Novel Target Cell for C-Fos-Induced Oncogenesis: Development of Chondrogenic Tumours in Embryonic Stem Cell Chimeras. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 2437–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoriadis, A.E.; Schellander, K.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wagner, E.F. Osteoblasts Are Target Cells for Transformation in C-Fos Transgenic Mice. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Karin, M. JunB Differs from C-Jun in Its DNA-Binding and Dimerization Domains, and Represses c-Jun by Formation of Inactive Heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1993, 7, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakiri, L.; Matsuo, K.; Wisniewska, M.; Wagner, E.F.; Yaniv, M. Promoter Specificity and Biological Activity of Tethered AP-1 Dimers. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 4952–4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, G.L.; Nakamura, K. The C-Jun Kinase/Stress-Activated Pathway: Regulation, Function and Role in Human Disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noonan, C.W.; Sarasua, S.M.; Campagna, D.; Kathman, S.J.; Lybarger, J.A.; Mueller, P.W. Effects of Exposure to Low Levels of Environmental Cadmium on Renal Biomarkers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyno, E.; Klose, C.; Krieger-Liszkay, A. Origin of Cadmium-Induced Reactive Oxygen Species Production: Mitochondrial Electron Transfer versus Plasma Membrane NADPH Oxidase. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.K.; Aggarwal, B.B. Reactive Oxygen Intermediates in TNF Signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 39, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piette, J.; Piret, B.; Bonizzi, G.; Schoonbroodt, S.; Merville, M.P.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Bours, V. Multiple Redox Regulation in NF-KappaB Transcription Factor Activation. Biol. Chem. 1997, 378, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wright, G.M.; Black, J.C. Genomic Redistribution of Metal-Response Transcription Factor-1 (MTF-1) in Cadmium Resistant Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060953
Wright GM, Black JC. Genomic Redistribution of Metal-Response Transcription Factor-1 (MTF-1) in Cadmium Resistant Cells. Cells. 2023; 12(6):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060953
Chicago/Turabian StyleWright, Gregory M., and Joshua C. Black. 2023. "Genomic Redistribution of Metal-Response Transcription Factor-1 (MTF-1) in Cadmium Resistant Cells" Cells 12, no. 6: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060953
APA StyleWright, G. M., & Black, J. C. (2023). Genomic Redistribution of Metal-Response Transcription Factor-1 (MTF-1) in Cadmium Resistant Cells. Cells, 12(6), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12060953





