Dual Effects of miR-181b-2-3p/SOX21 Interaction on Microglia and Neural Stem Cells after Gamma Irradiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Models
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining
2.3. Mouse Brain RNA Extraction
2.4. Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis for miR-181b-2-3p
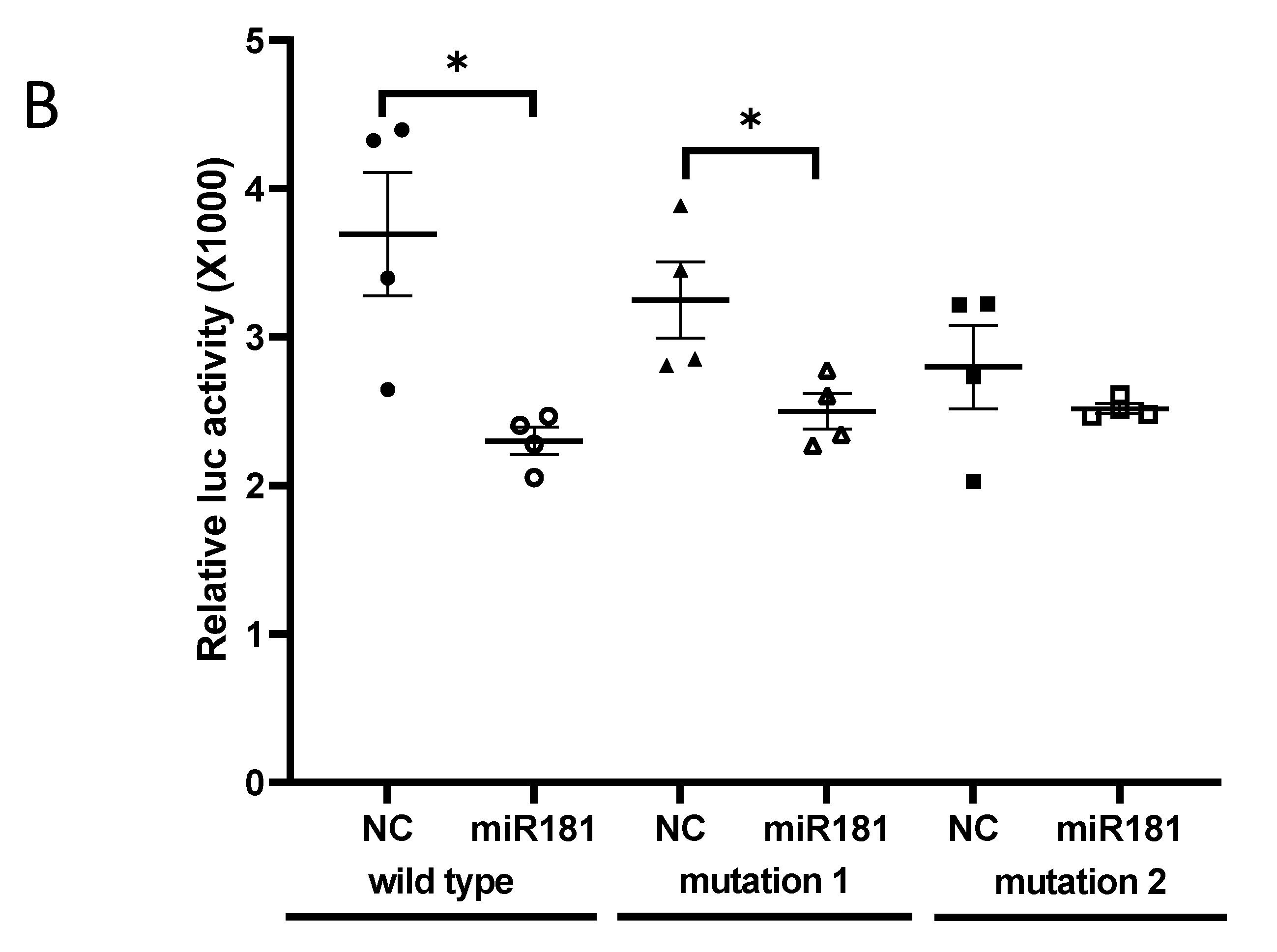
2.5. Predication of miR-181b-2-3p Targets and Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.6. Culture of BV2 and Neural Stem Cells (NSCs)
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. RNA Extraction from Cells and Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis for miRNA and mRNA
2.9. Knock-Down Gene Expression of SOX21 by SOX21 siRNA in BV2
2.10. TNF-a in BV2 by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.11. Cell Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assay in NSCs
2.12. Overexpression of SOX21 in NSCs
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
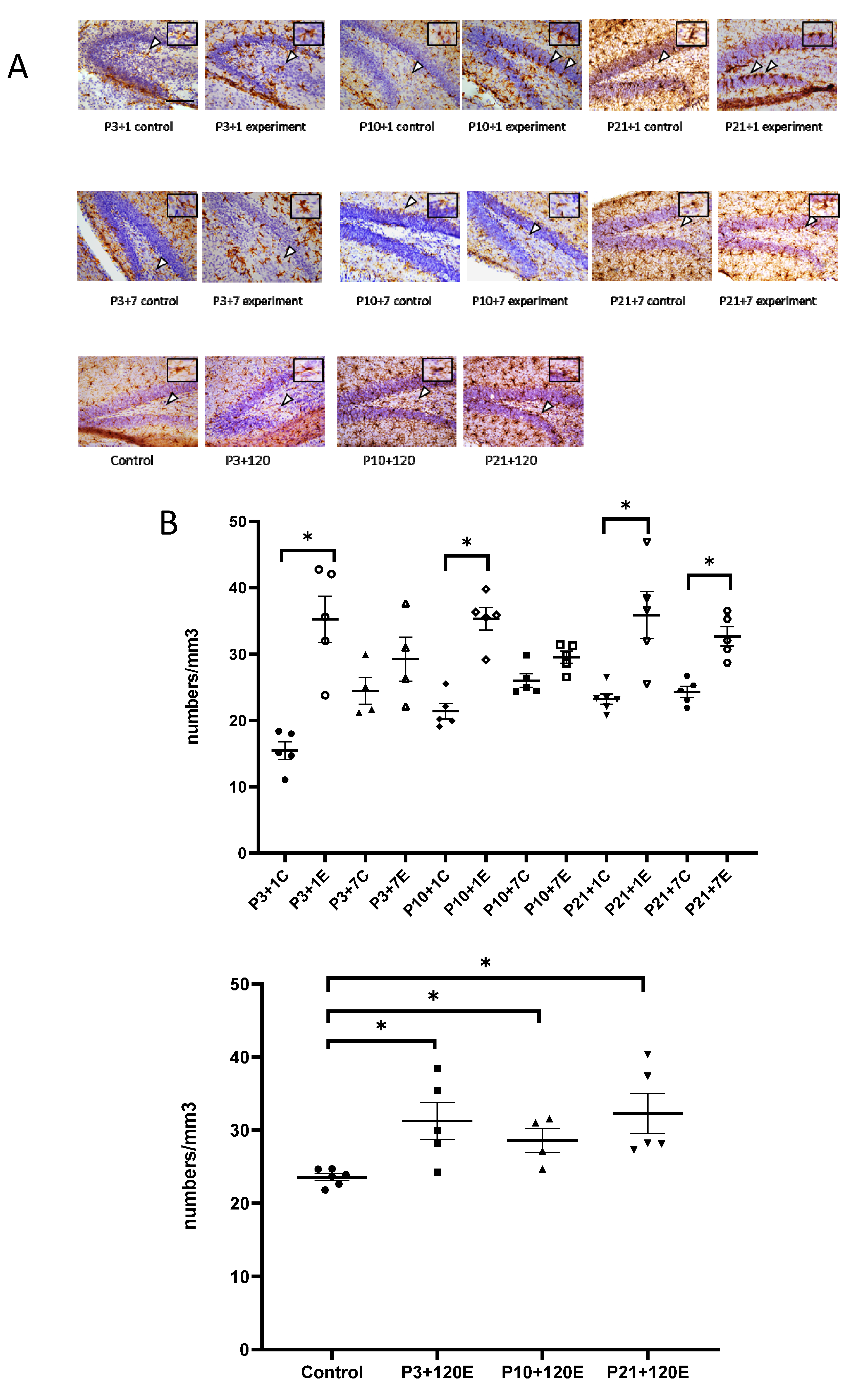
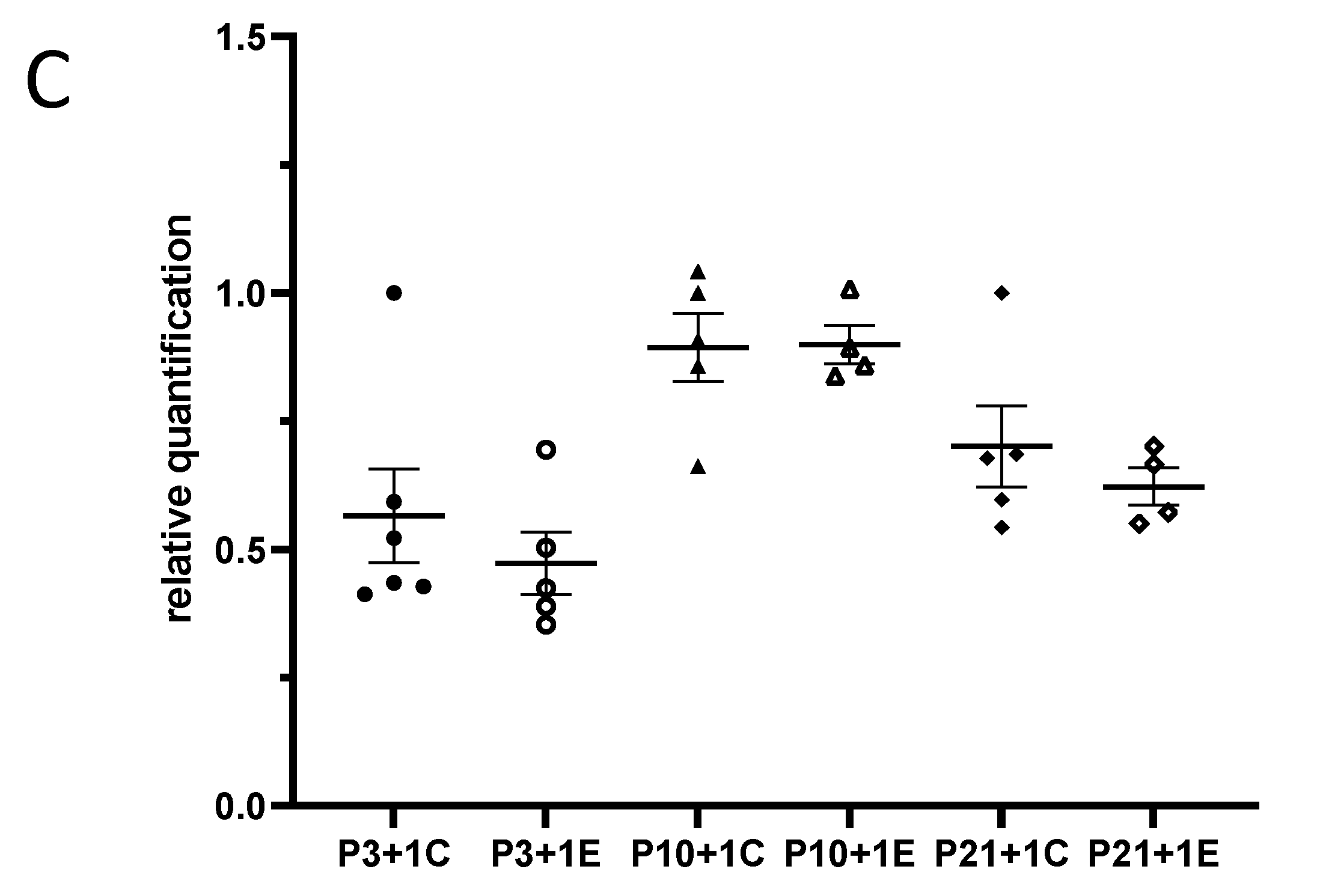
3.1. Exposure to γ-Radiation Induced Microglial Activation and Proliferation in the Mouse Dentate Gyrus
3.2. SOX21 Was Highly Expressed in Microglia as the Target of miR-181b-2-3p
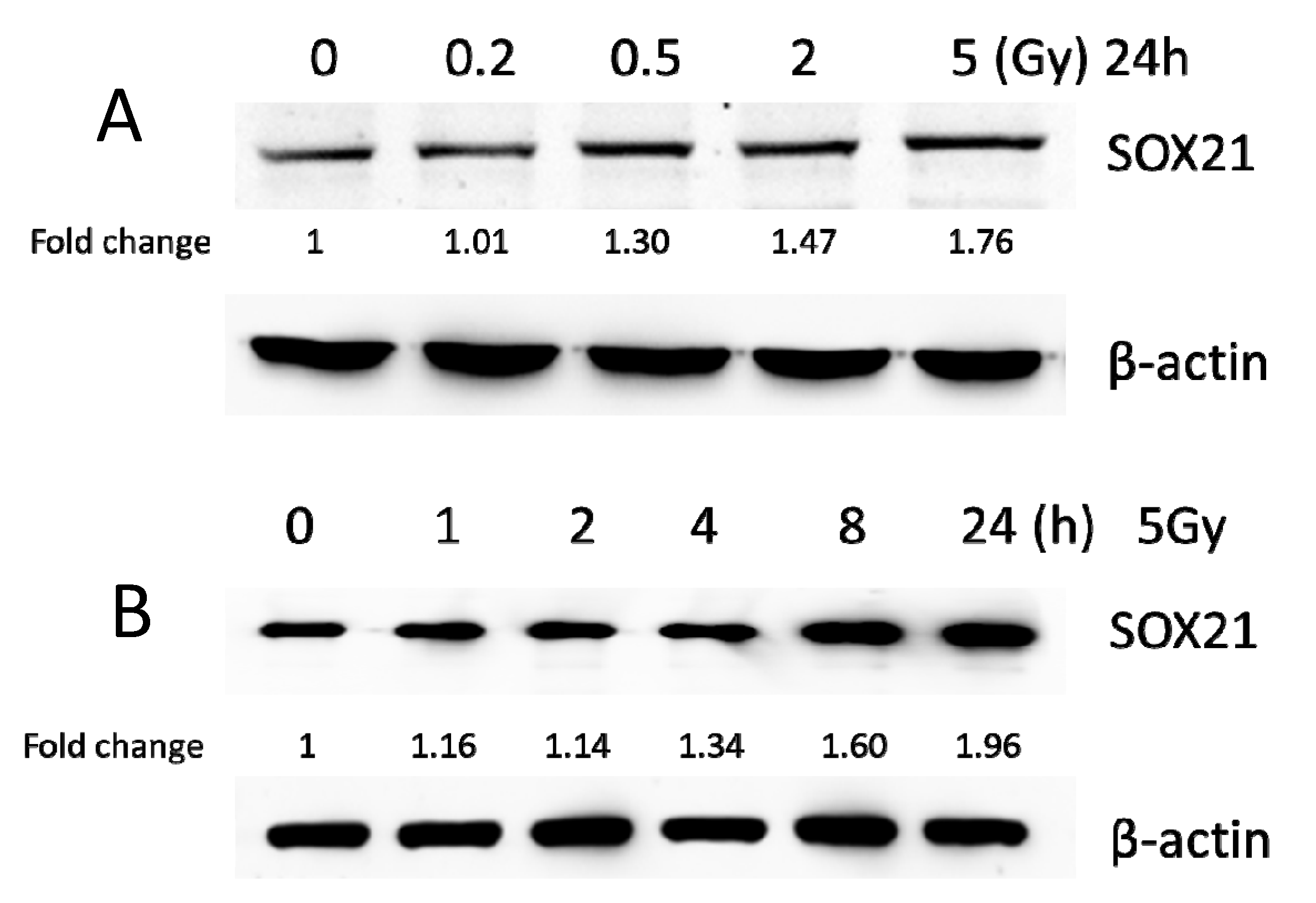
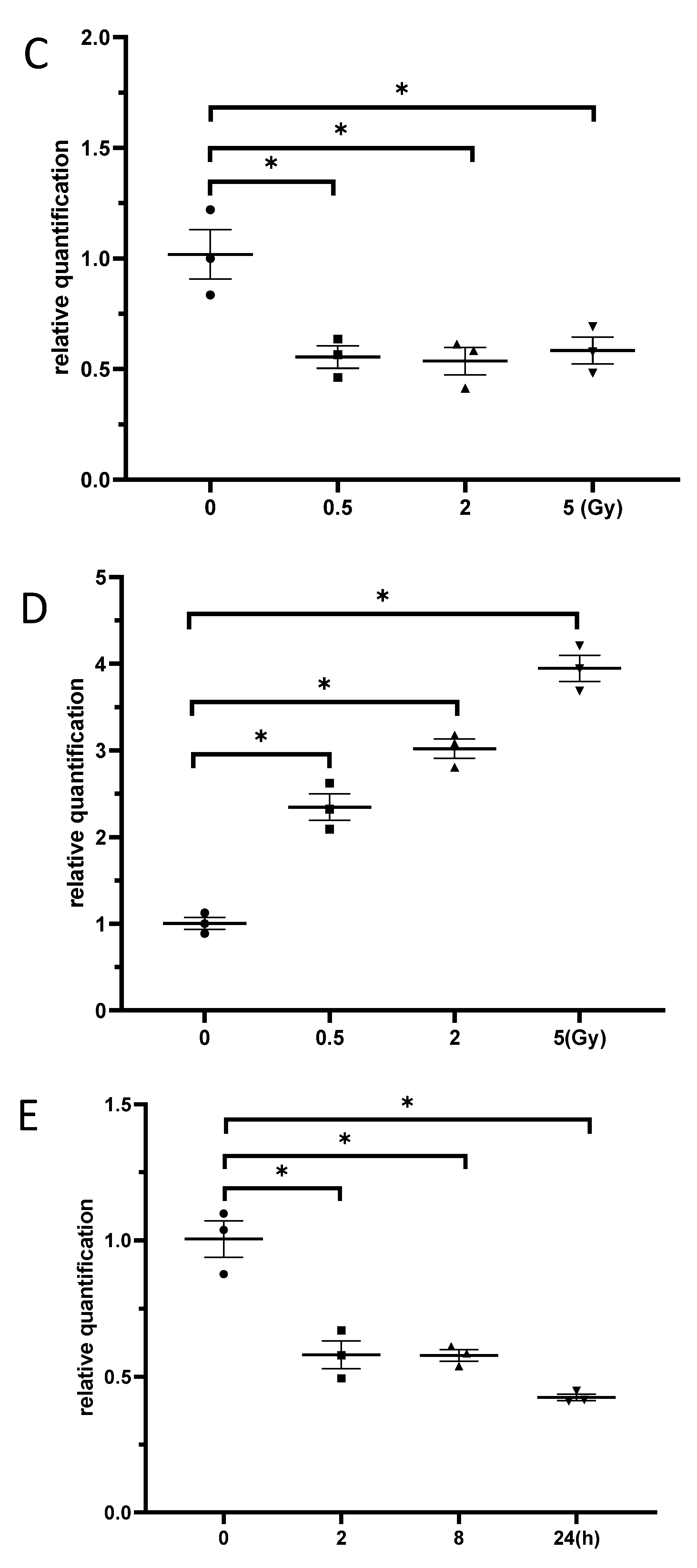
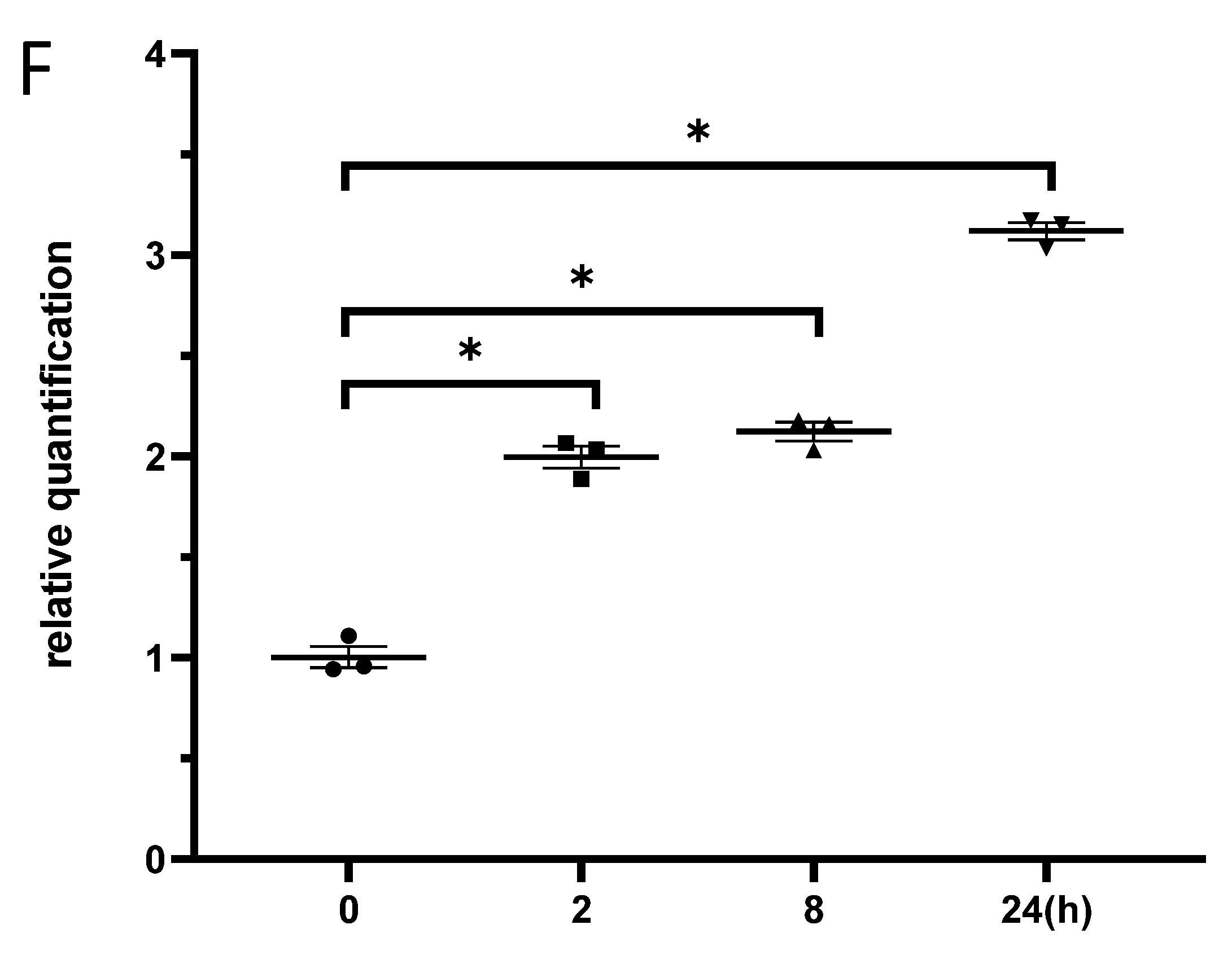
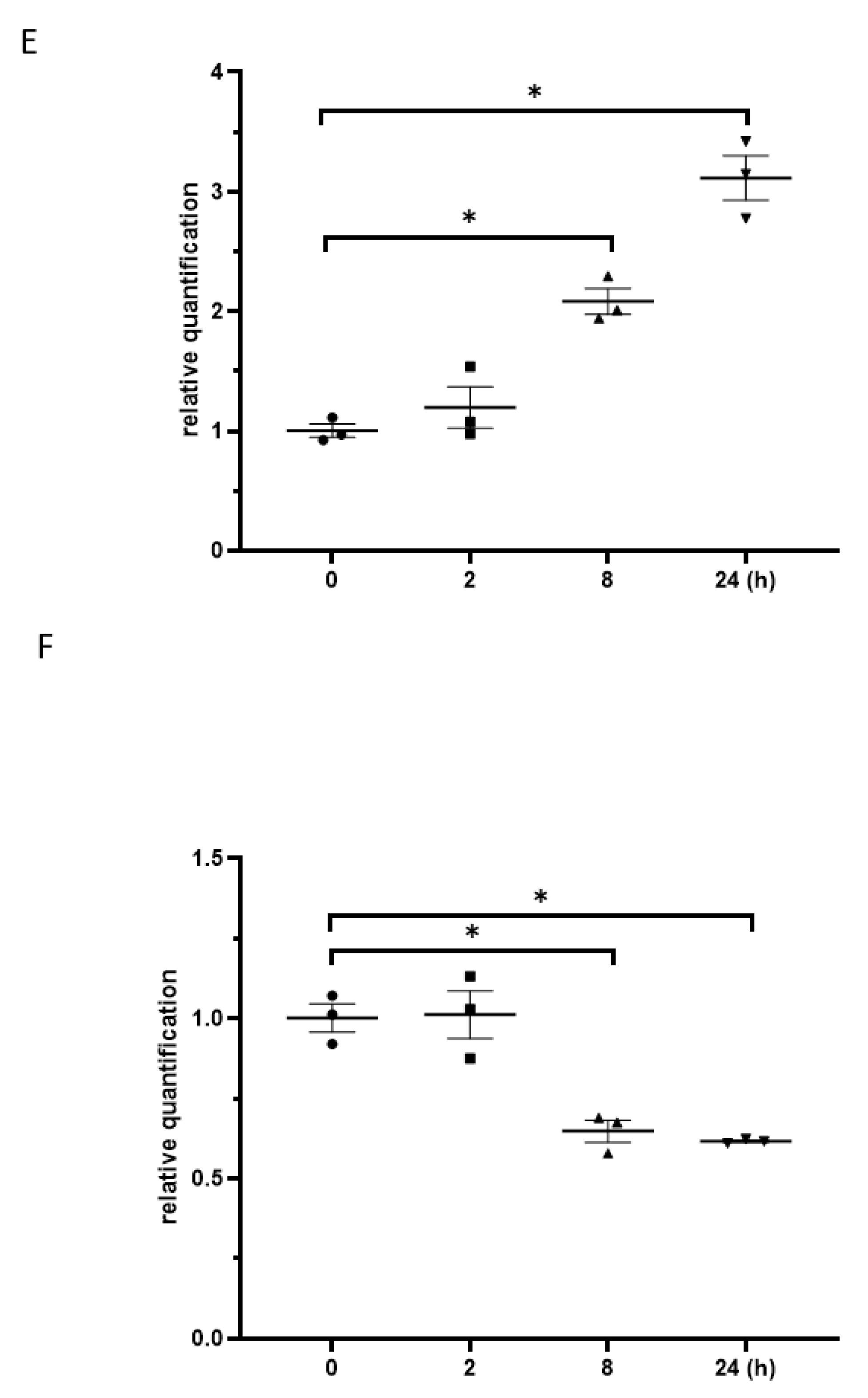
3.3. Exposure to γ-Irradiation Significantly Decreased miR-181b-2-3p Expression and Increased the mRNA and Protein Levels of SOX21 in BV2
3.4. The Knockdown of SOX21 by SOX21 siRNA Blocked the Activation of Microglia Induced by γ-Irradiation
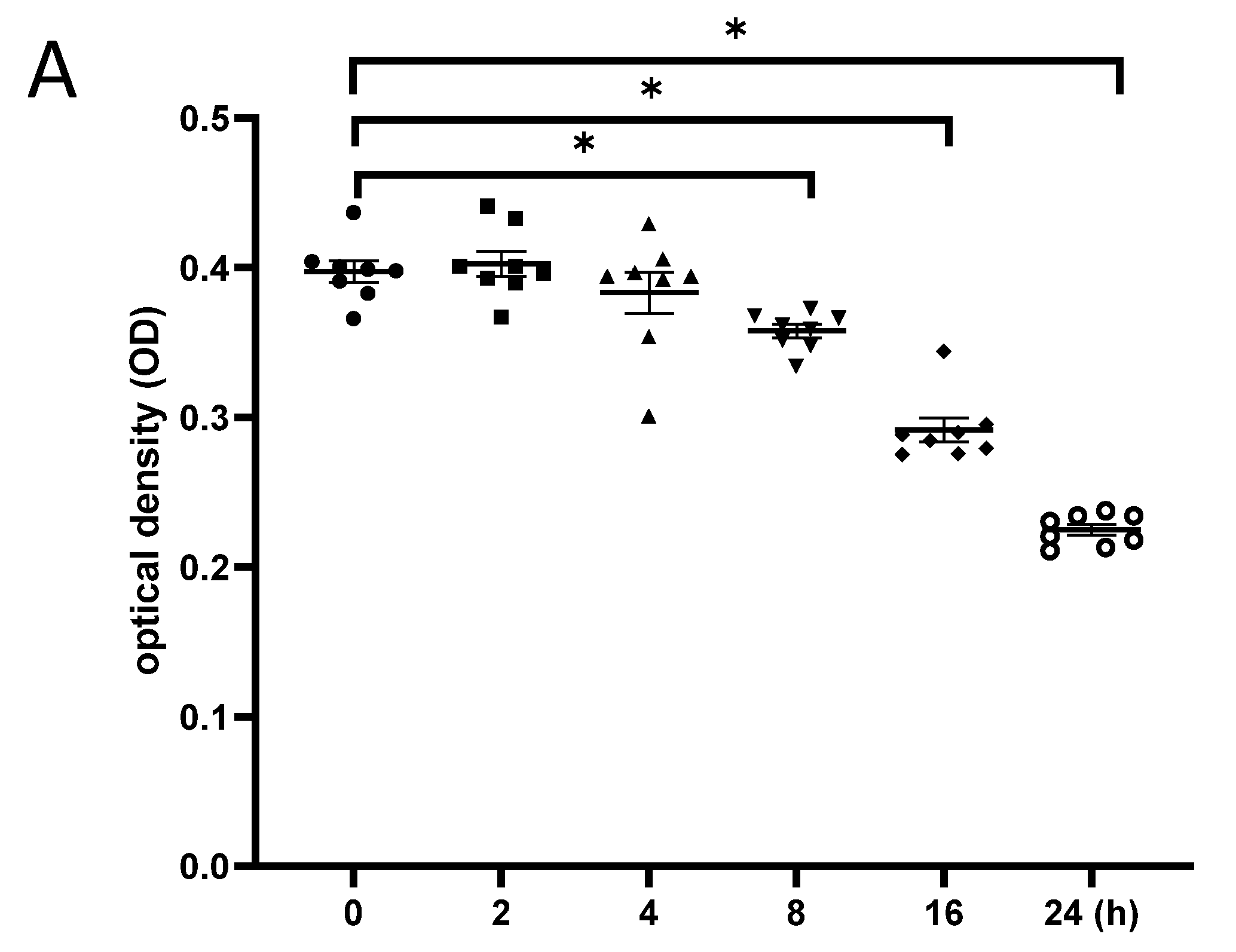
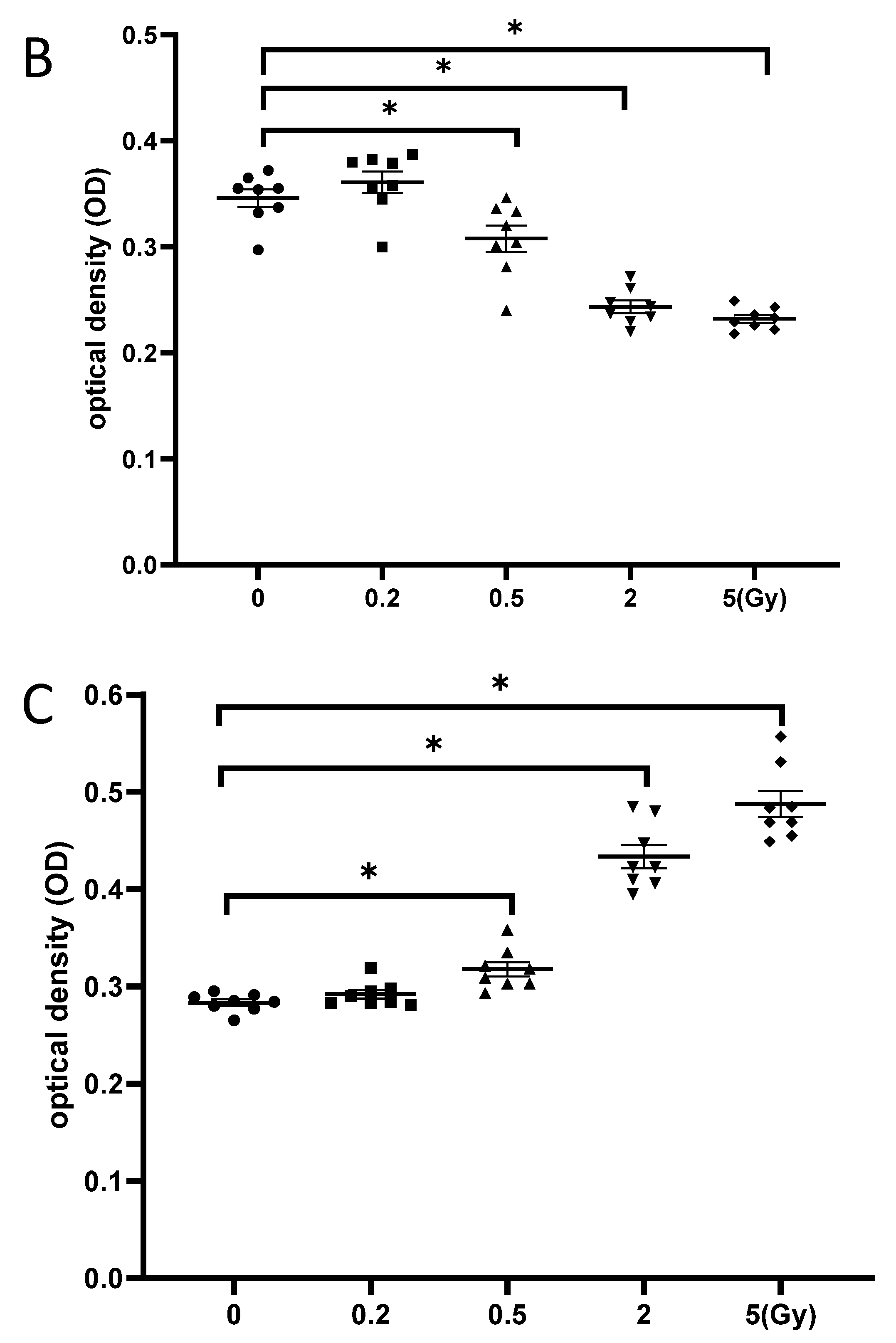
3.5. Exposure to γ-Irradiation Caused Cytotoxicity in NSCs and Induced the Impairment of Cell Proliferation
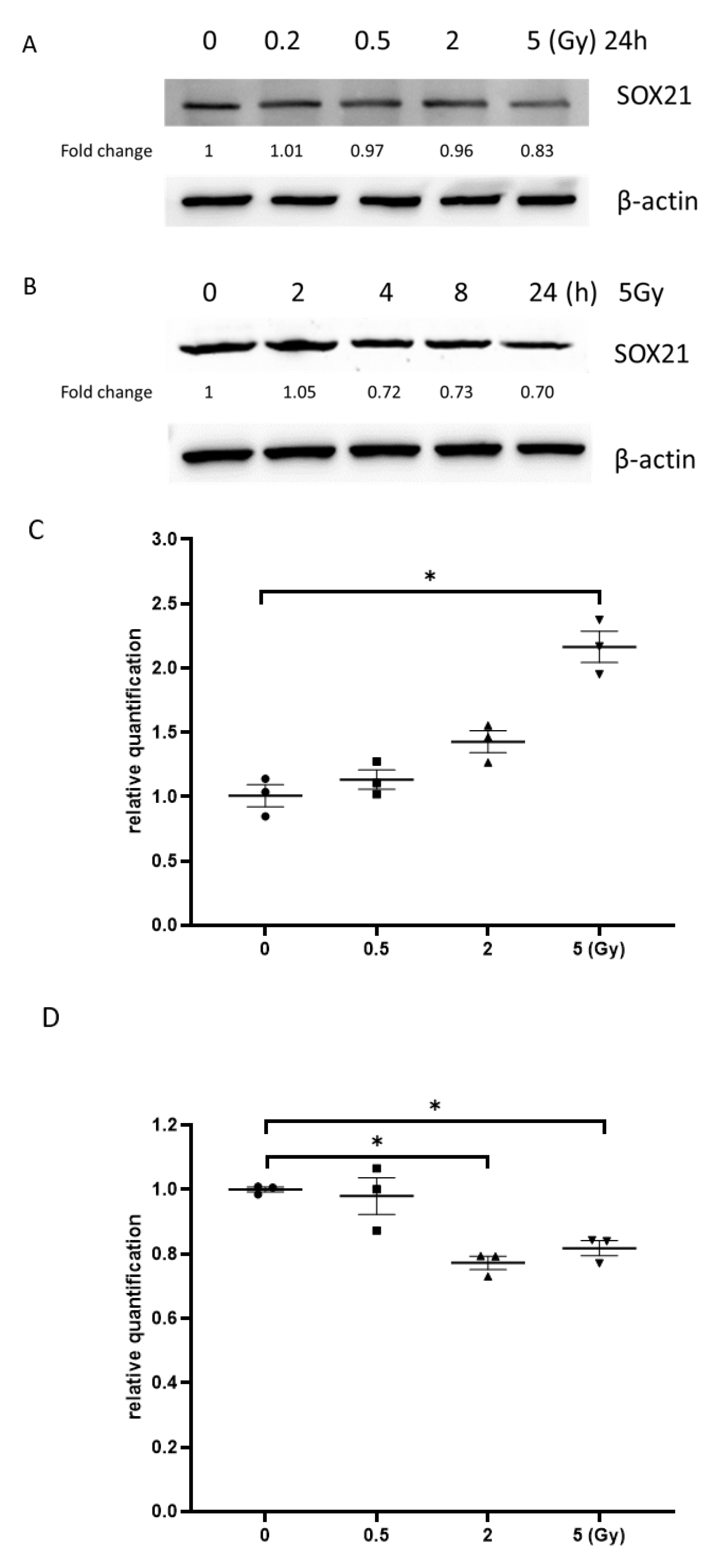
3.6. Exposure to γ-Irradiation Increased the Expression of miR-181b-2-3p and Decreased the mRNA and Protein Expression of SOX21 in NSC
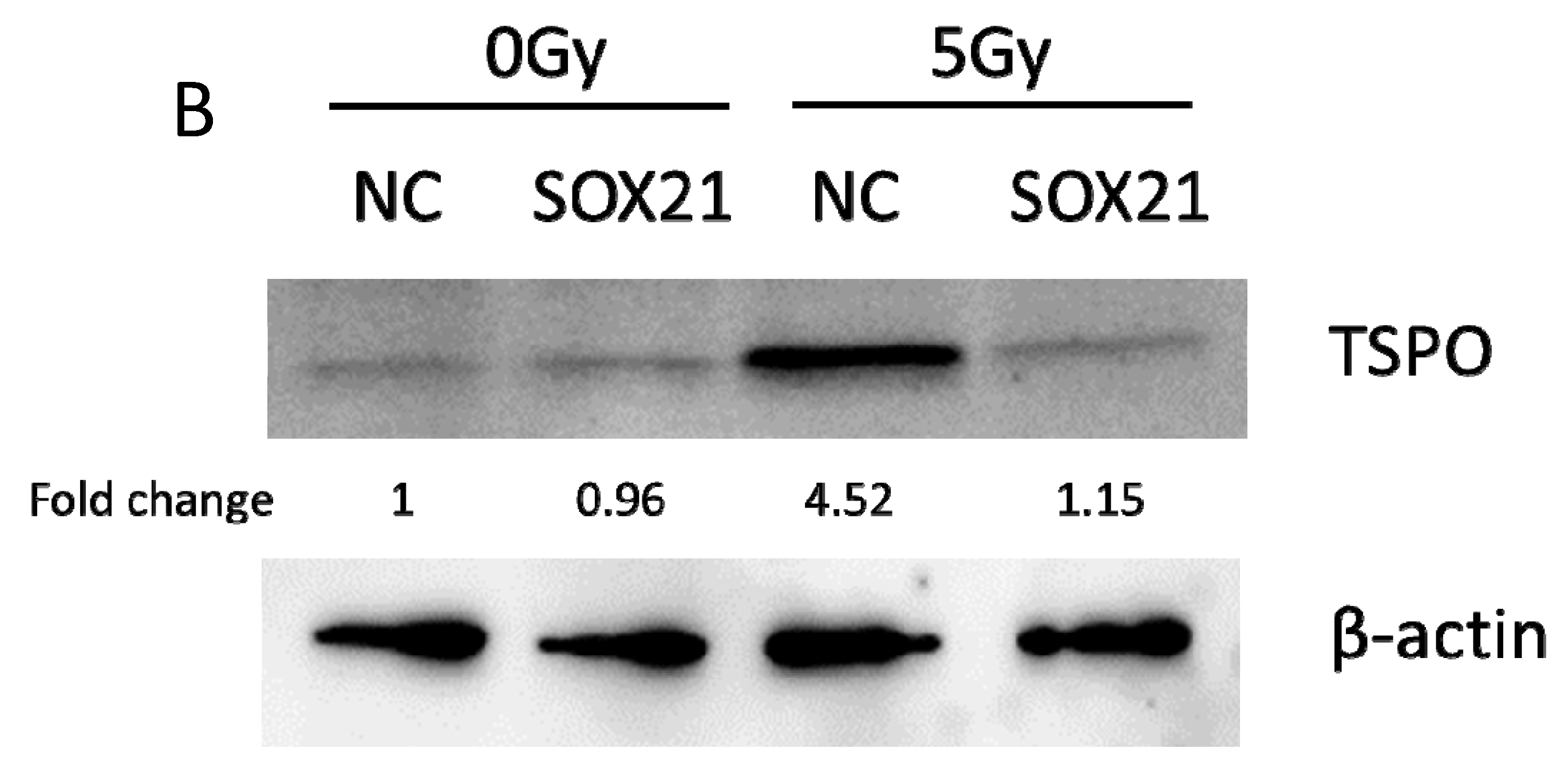
3.7. The Overexpression of SOX21 Blocked the Decreased Cell Viability Induced by γ-Irradiation in NSCs
4. Discussion
4.1. Irradiation-Induced Microglial Reaction Was Primarily Regulated by the Downregulation of miR-181b-2-3p with Upregulated SOX21
4.2. The Irradiation-Induced Impairment of Neurogenesis Was Regulated by the Upregulated miR-181b-2-3p with Downregulated SOX21
4.3. Study Limitations and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minnier, J.; Emmett, M.R.; Perez, R.; Ding, L.H.; Barnette, B.L.; Larios, R.E.; Hong, C.; Hwang, T.H.; Yu, Y.; Fallgren, C.M.; et al. Associations between lipids in selected brain regions, plasma miRNA, and behavioral and cognitive measures following (28)Si ion irradiation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segaran, R.C.; Chan, L.Y.; Wang, H.; Sethi, G.; Tang, F.R. Neuronal Development-Related miRNAs as Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease, Depression, Schizophrenia and Ionizing Radiation Exposure. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 19–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, Z.; Shen, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Ren, B.; Wong, P.; Sethi, G.; Tang, F. Early Life Irradiation-Induced Hypoplasia and Impairment of Neurogenesis in the Dentate Gyrus and Adult Depression Are Mediated by MicroRNA- 34a-5p/T-Cell Intracytoplasmic Antigen-1 Pathway. Cells 2021, 10, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, E.R.; Kawamoto, E.M.; Taub, D.D.; Lal, A.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wood, W.H., 3rd; Lehrmann, E.; Camandola, S.; Becker, K.G.; et al. Evidence for miR-181 involvement in neuroinflammatory responses of astrocytes. Glia 2013, 61, 1018–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Guo, X.; Liu, H. MicroRNA-181 regulates CARM1 and histone arginine methylation to promote differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e53146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhao, H.; Tao, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, P.; Han, Z.; Ma, S.; Luo, Y.; Jia, J. MicroRNA-181c Exacerbates Brain Injury in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2016, 7, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaseelan, K.; Lim, K.Y.; Armugam, A. MicroRNA expression in the blood and brain of rats subjected to transient focal ischemia by middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 2008, 39, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.B.; Lu, Y.; Yue, S.; Xu, L.J.; Xiong, X.X.; White, R.E.; Sun, X.; Giffard, R.G. miR-181 regulates GRP78 and influences outcome from cerebral ischemia in vitro and in vivo. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.M.; Xu, L.; Giffard, R.G. Inhibition of microRNA-181 reduces forebrain ischemia-induced neuronal loss. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, L.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Hong, Z.; Wei, W.S. The microRNA miR-181c controls microglia-mediated neuronal apoptosis by suppressing tumor necrosis factor. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.J.; Wu, X.Y.; Hong, Z.; Wei, W.S. MicroRNA-181c negatively regulates the inflammatory response in oxygen-glucose-deprived microglia by targeting Toll-like receptor 4. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; He, X.; Lu, F.; Mao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Yao, L.; Luo, W.; Sun, X.; Wang, B.; Qian, C.; et al. A lincRNA-p21/miR-181 family feedback loop regulates microglial activation during systemic LPS- and MPTP- induced neuroinflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, M.A.; Omaruddin, R.A.; Brumbaugh, C.D.; Tariq, M.A.; Pourmand, N. Identification of radiation-induced microRNA transcriptome by next-generation massively parallel sequencing. J. Radiat. Res. 2013, 54, 808–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Icli, B.; Wara, A.K.; Belkin, N.; He, S.; Kobzik, L.; Hunninghake, G.M.; Vera, M.P.; Blackwell, T.S.; Baron, R.M.; et al. MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-κB-mediated vascular inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1973–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tektemur, A.; Tektemur, N.K.; Güzel, E.E. The therapeutic effect of hesperetin on doxorubicin-induced testicular toxicity: Potential roles of the mechanistic target of rapamycin kinase (mTOR) and dynamin-related protein 1 (DRP1). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2022, 435, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Fan, D.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yuan, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C.; Han, J.; et al. Curcumol enhances the sensitivity of doxorubicin in triple-negative breast cancer via regulating the miR-181b-2-3p-ABCC3 axis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 174, 113795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylund, M.; Andersson, E.; Novitch, B.G.; Muhr, J. Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1-3 activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, V.; Khudyakov, J.; Ellis, P.; Pevny, L. SOX2 functions to maintain neural progenitor identity. Neuron 2003, 39, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, M.; Kallstrom, M.; Muhr, J. Sox21 promotes the progression of vertebrate neurogenesis. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Kuwako, K.; Okano, H.J.; Tsutsumi, S.; Aburatani, H.; Saga, Y.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Akaike, A.; Sugimoto, H.; Okano, H. Sox21 promotes hippocampal adult neurogenesis via the transcriptional repression of the Hes5 gene. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 12543–12557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozareva, D.A.; Moloney, G.M.; Hoban, A.E.; Rossini, V.; Nally, K.; Cryan, J.F.; Nolan, Y.M. A role for the orphan nuclear receptor TLX in the interaction between neural precursor cells and microglia. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2019, 3, Ns20180177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, M.; Prabhakar, A.; Ray, K.; Roy, K.; Kumari, P.; Jha, P.K.; Kishore, K.; Kumar, S.; Panjwani, U. Inhibiting the microglia activation improves the spatial memory and adult neurogenesis in rat hippocampus during 48 h of sleep deprivation. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, T.; Huang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, Q.; Chen, Z.; Guo, A.Y. MicroRNA regulatory pathway analysis identifies miR-142-5p as a negative regulator of TGF-beta pathway via targeting SMAD3. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71504–71513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Dong, J.H.; Huang, G.D.; Qu, X.F.; Wu, G.; Dong, X.R. NF-kappaB signaling modulates radiationinduced microglial activation. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 2555–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, M.L.; Mizumatsu, S.; Fike, J.R.; Palmer, T.D. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betlazar, C.; Middleton, R.J.; Howell, N.; Storer, B.; Davis, E.; Davies, J.; Banati, R.; Liu, G.J. Mitochondrial Translocator Protein (TSPO) Expression in the Brain after Whole Body Gamma Irradiation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 715444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Sonntag, W.E.; Mitschelen, M.; Yan, H.; Lee, Y.W. Irradiation induces regionally specific alterations in pro-inflammatory environments in rat brain. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.L.; Toda, H.; Palmer, T.D. Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 2003, 302, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chong, Z.Z.; De Toledo, S.M.; Azzam, E.I.; Elkabes, S.; Souayah, N. Delayed activation of human microglial cells by high dose ionizing radiation. Brain Res. 2016, 1646, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.X.; Huen, I.; Wu, Z.J.; Wang, H.; Duan, M.Y.; Guenther, I.; Bhanu Prakash, K.N.; Tang, F.R. Early postnatal irradiation-induced age-dependent changes in adult mouse brain: MRI based characterization. BMC Neurosci. 2021, 22, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, R.J.; Acharya, M.M.; Baulch, J.E.; Limoli, C.L. Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miR-124 Resolves Radiation-Induced Brain Injury. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, M.; Fan, W.; Sun, F.; Li, M.; Lin, M.; Yu, Y.; Liang, S.; Liao, H.; Jie, W.; Cai, Y.; et al. Nasal Delivery of AntagomiR-741 Protects Against the Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in Mice. Radiat. Res. 2021, 195, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collignon, J.; Sockanathan, S.; Hacker, A.; Cohen-Tannoudji, M.; Norris, D.; Rastan, S.; Stevanovic, M.; Goodfellow, P.N.; Lovell-Badge, R. A comparison of the properties of Sox-3 with Sry and two related genes, Sox-1 and Sox-2. Development 1996, 122, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, N.; Cheah, P.S.; Szarek, E.; Banerjee, K.; Schwartz, J.; Thomas, P. Expression of the murine transcription factor SOX3 during embryonic and adult neurogenesis. Gene Expr. Patterns GEP 2013, 13, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, L.; Israsena, N.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhao, L.R.; Jalali, A.; Sahni, V.; Kessler, J.A. Sox1 acts through multiple independent pathways to promote neurogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2004, 269, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimadamore, F.; Amador-Arjona, A.; Chen, C.; Huang, C.T.; Terskikh, A.V. SOX2-LIN28/let-7 pathway regulates proliferation and neurogenesis in neural precursors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3017–E3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaletel, I.; Schwirtlich, M.; Perović, M.; Jovanović, M.; Stevanović, M.; Kanazir, S.; Puškaš, N. Early Impairments of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in 5xFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease are Associated with Altered Expression of SOXB Transcription Factors. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2018, 65, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, S.; Javanmehr, N.; Ghasemi-Kasman, M.; Bali, H.Y.; Pirzadeh, M. Stem Cell-based Therapeutic and Diagnostic Approaches in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2021, 20, 1093–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, Y.; Abolhassani, N.; Mazzei, G.; Sakumi, K.; Saito, T.; Saido, T.C.; Ninomiya, T.; Iwaki, T.; Yamasaki, R.; Kira, J.I.; et al. Mutyh Actively Contributes to Microglial Activation and Impaired Neurogenesis in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8635088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittington, N.; Cunningham, D.; Le, T.K.; De Maria, D.; Silva, E.M. Sox21 regulates the progression of neuronal differentiation in a dose-dependent manner. Dev. Biol. 2015, 397, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capilla-Gonzalez, V.; Guerrero-Cazares, H.; Bonsu, J.M.; Gonzalez-Perez, O.; Achanta, P.; Wong, J.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A. The subventricular zone is able to respond to a demyelinating lesion after localized radiation. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arango-Gonzalez, B.; Schatz, A.; Bolz, S.; Eslava-Schmalbach, J.; Willmann, G.; Zhour, A.; Zrenner, E.; Fischer, M.D.; Gekeler, F. Effects of combined ketamine/xylazine anesthesia on light induced retinal degeneration in rats. PloS ONE 2012, 7, e35687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, M.M.; Angelucci, M.E.; Anselmo-Franci, J.A.; Canteras, N.S.; Da Cunha, C. Neuroprotective effect of ketamine/xylazine on two rat models of Parkinson’s disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2007, 40, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balentova, S.; Adamkov, M. Molecular, Cellular and Functional Effects of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27796–27815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balentova, S.; Hajtmanova, E.; Adamkov, M.; Lehotsky, J. Differential expression of doublecortin and microglial markers in the rat brain following fractionated irradiation. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroehl, M.E.; Lutz, S.; Wagner, B.D. Permutation-based methods for mediation analysis in studies with small sample sizes. Peer J. 2020, 8, e8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
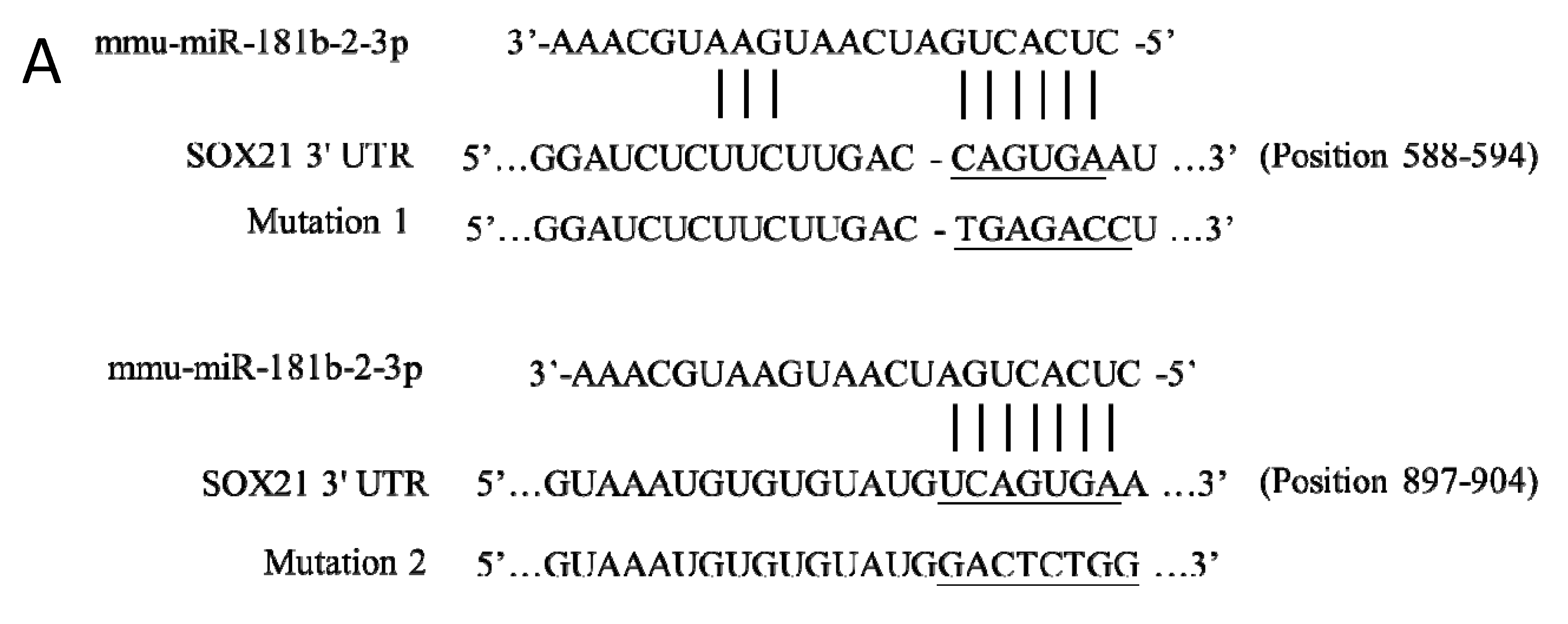


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Ma, Z.-W.; Ho, F.-M.; Sethi, G.; Tang, F.R. Dual Effects of miR-181b-2-3p/SOX21 Interaction on Microglia and Neural Stem Cells after Gamma Irradiation. Cells 2023, 12, 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040649
Wang H, Ma Z-W, Ho F-M, Sethi G, Tang FR. Dual Effects of miR-181b-2-3p/SOX21 Interaction on Microglia and Neural Stem Cells after Gamma Irradiation. Cells. 2023; 12(4):649. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040649
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hong, Zhao-Wu Ma, Feng-Ming Ho, Gautam Sethi, and Feng Ru Tang. 2023. "Dual Effects of miR-181b-2-3p/SOX21 Interaction on Microglia and Neural Stem Cells after Gamma Irradiation" Cells 12, no. 4: 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040649
APA StyleWang, H., Ma, Z.-W., Ho, F.-M., Sethi, G., & Tang, F. R. (2023). Dual Effects of miR-181b-2-3p/SOX21 Interaction on Microglia and Neural Stem Cells after Gamma Irradiation. Cells, 12(4), 649. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12040649