Modulation of Kinase Activities In Vitro by Hepatitis C Virus Protease NS3/NS4A Mediated-Cleavage of Key Immune Modulator Kinases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Peptide Synthesis
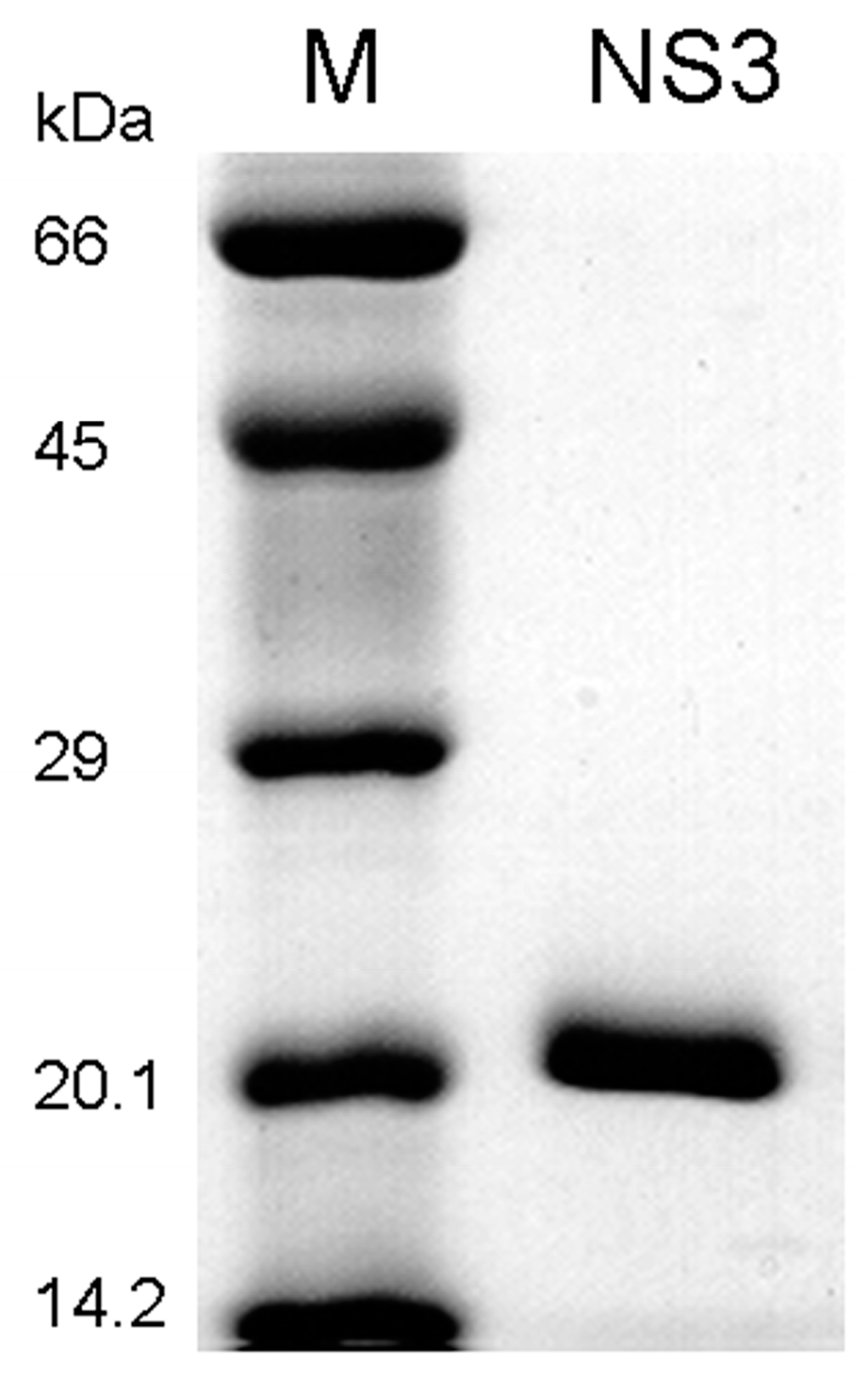
2.2. Protein Expression and Purification of HCV NS3
2.3. Purification of Recombinant Human IKKα, IKKβ, IKKε, and TBK 1
2.4. Kinase Digestion Condition for Western Blot Analysis
2.5. MALDI-TOF and Nano-LC MS/MS Analysis
2.6. Kinase Digestion Conditions for Pre-Steady-State Kinetic Assays
2.7. Kinase Digestion Condition for Kinase Activity Assay
2.8. Protease Inhibition Assay
2.9. Kinase Activity Assay
3. Results
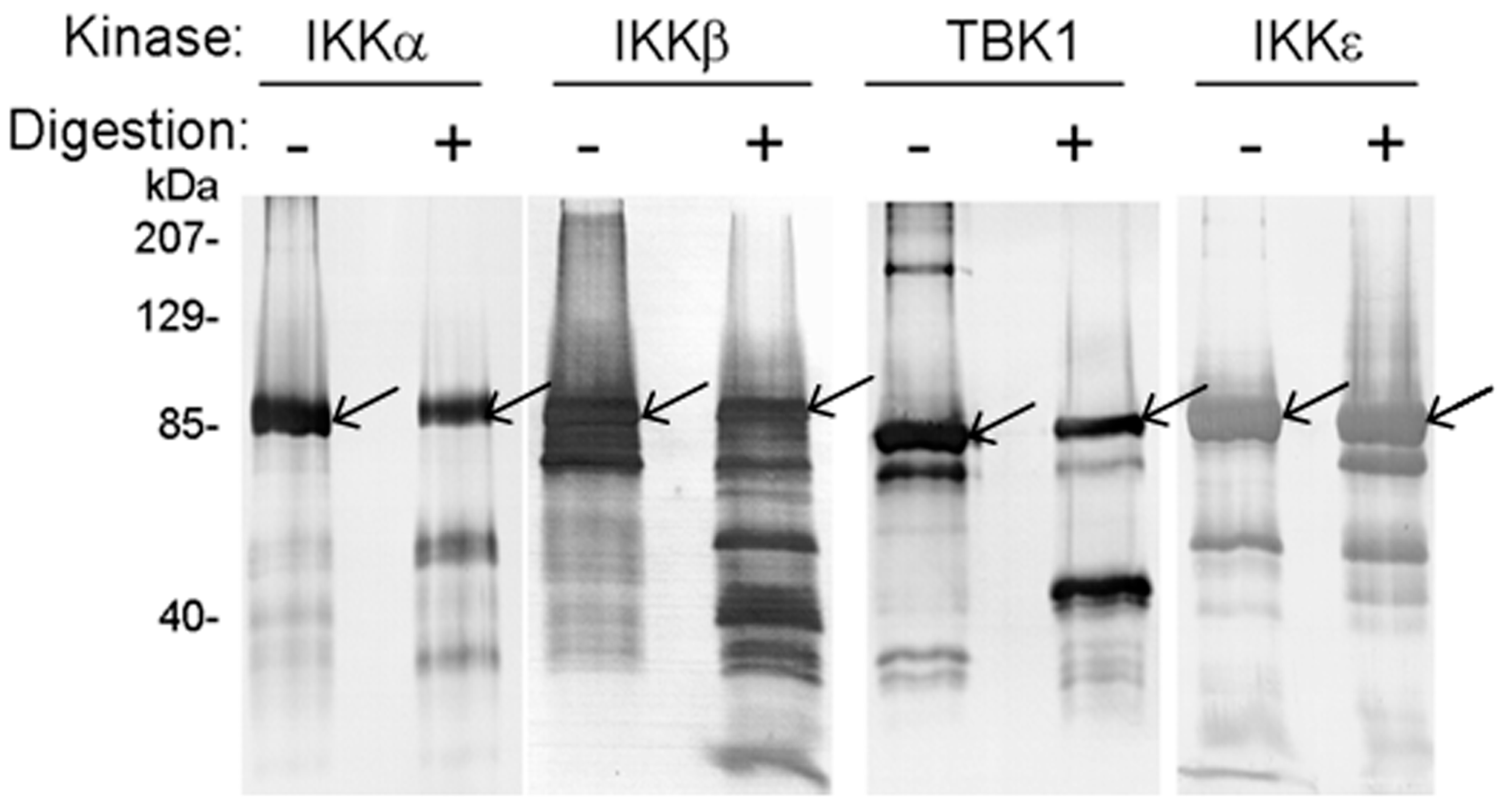
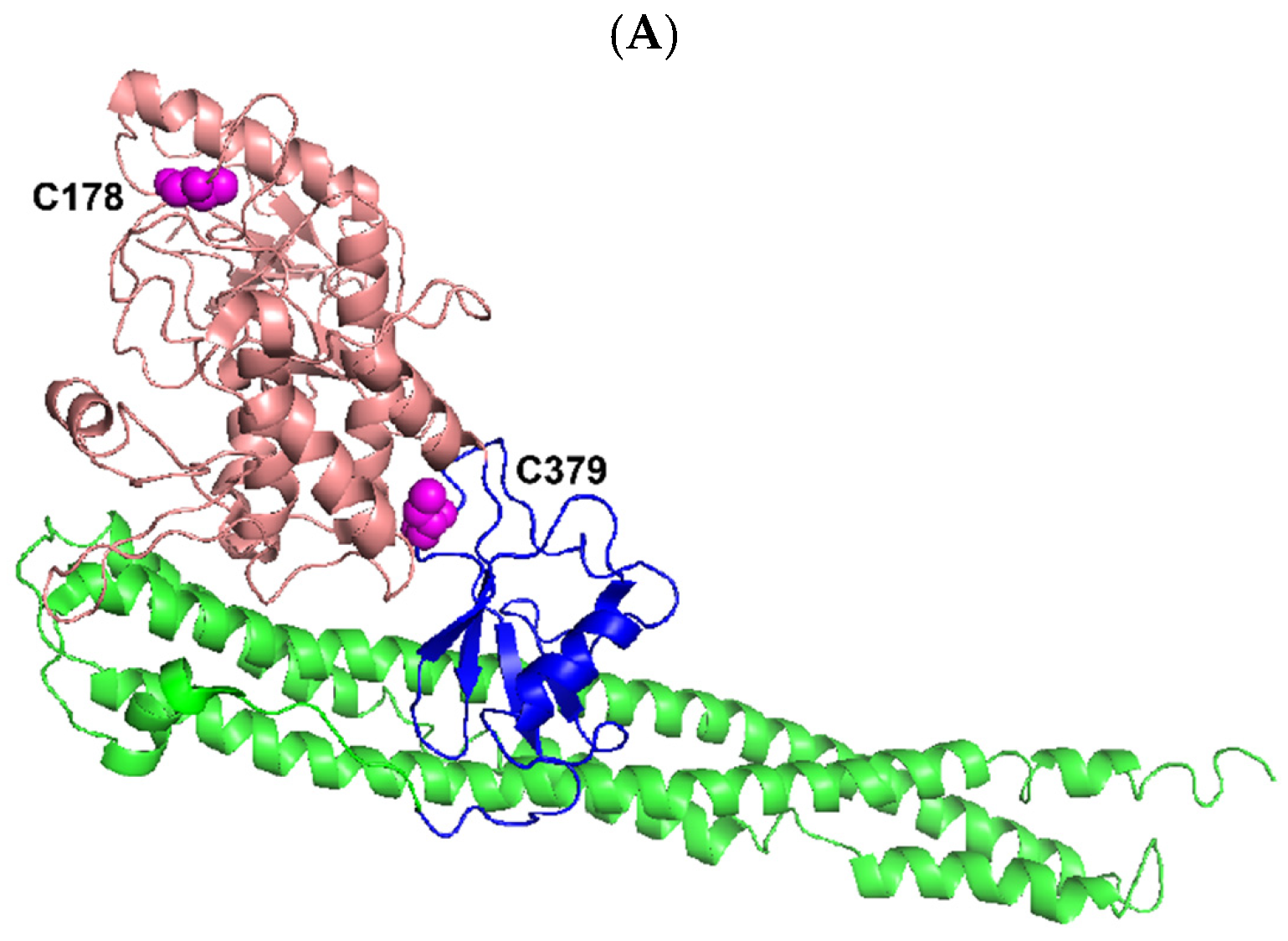
3.1. IKKα, IKKβ, IKKε, and TBK1 Are Substrates for NS3/NS4A Protease In Vitro
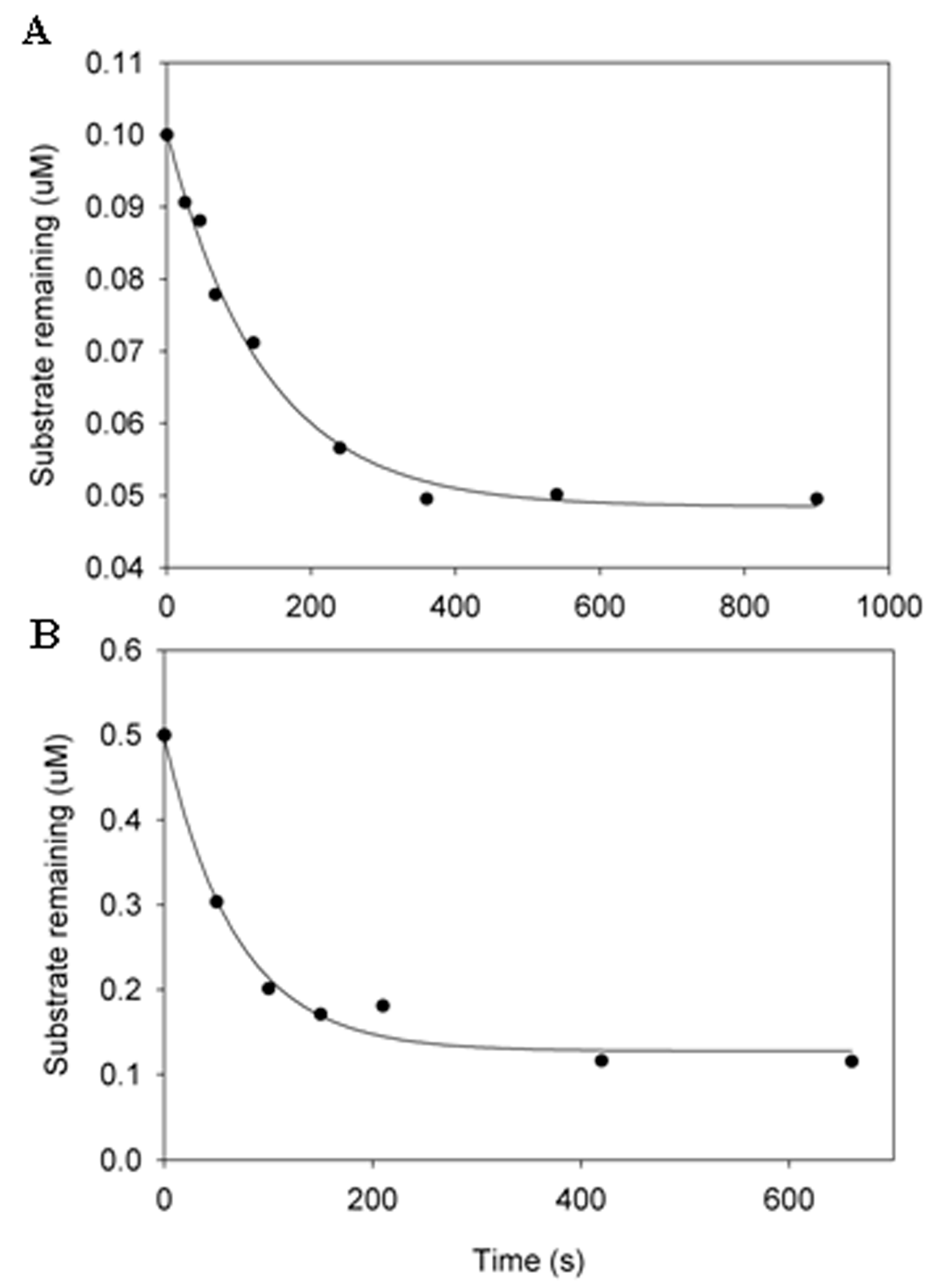
3.2. Estimation of the Substrate Specificity of IKKε by Pre-Steady-State Kinetic Methods
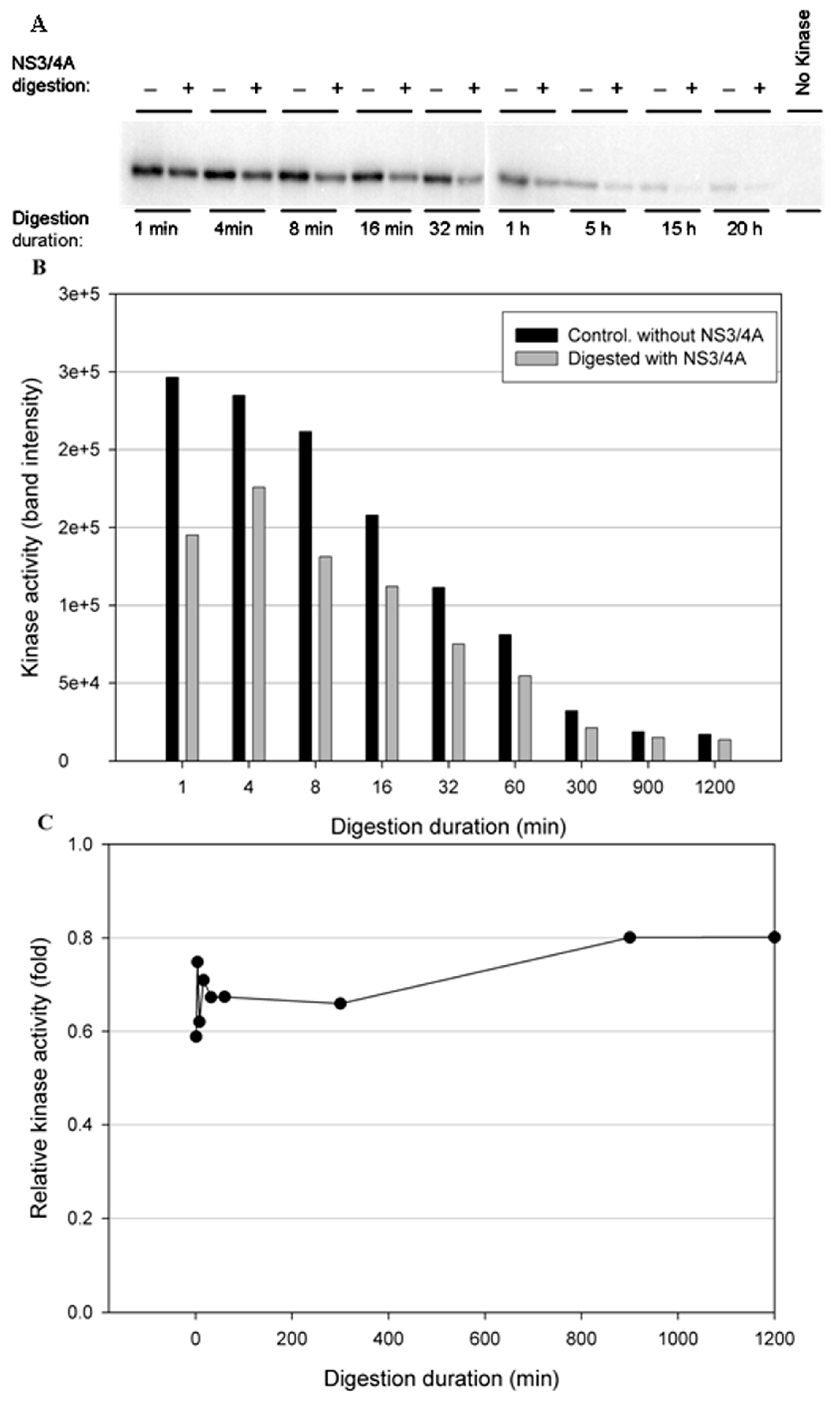
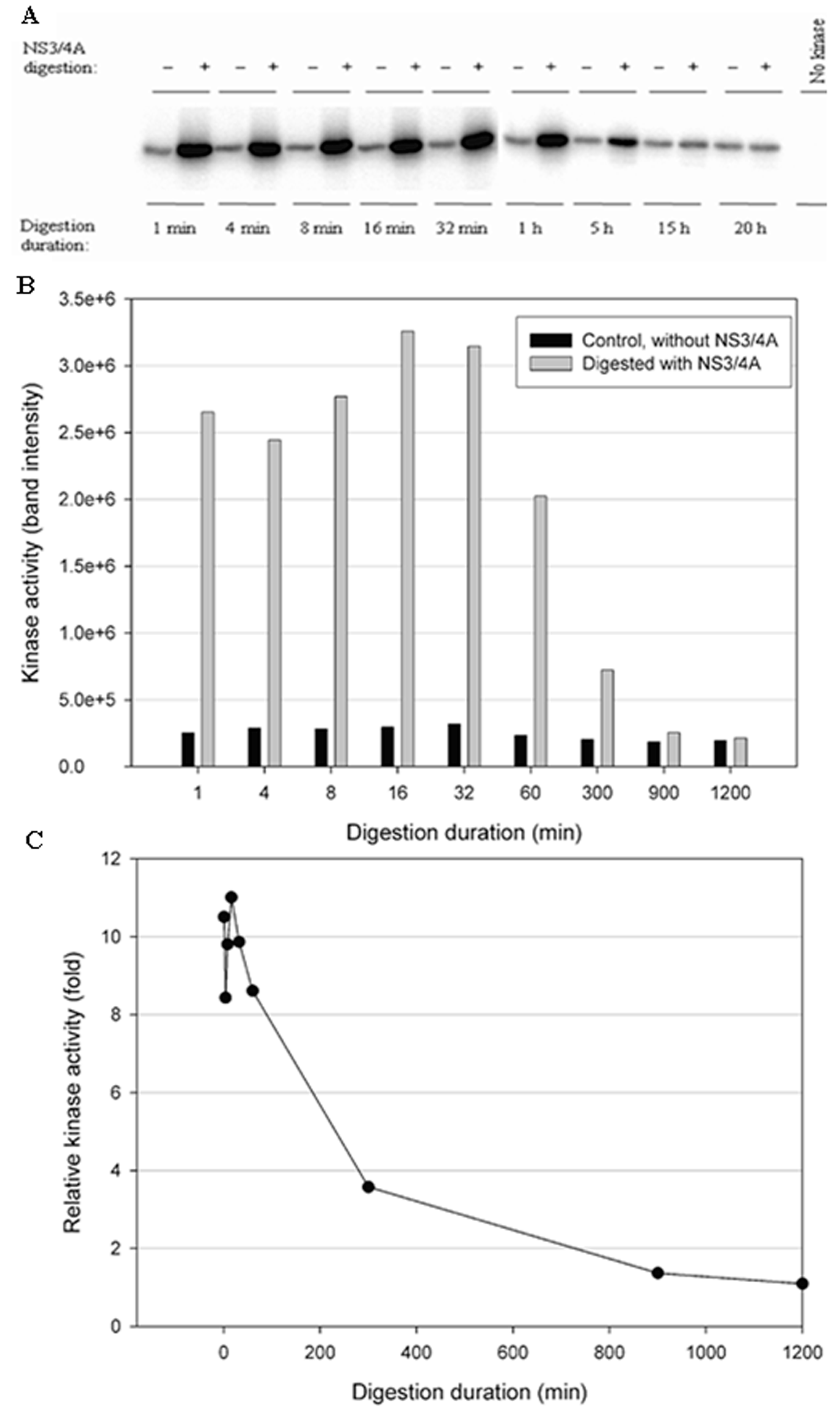
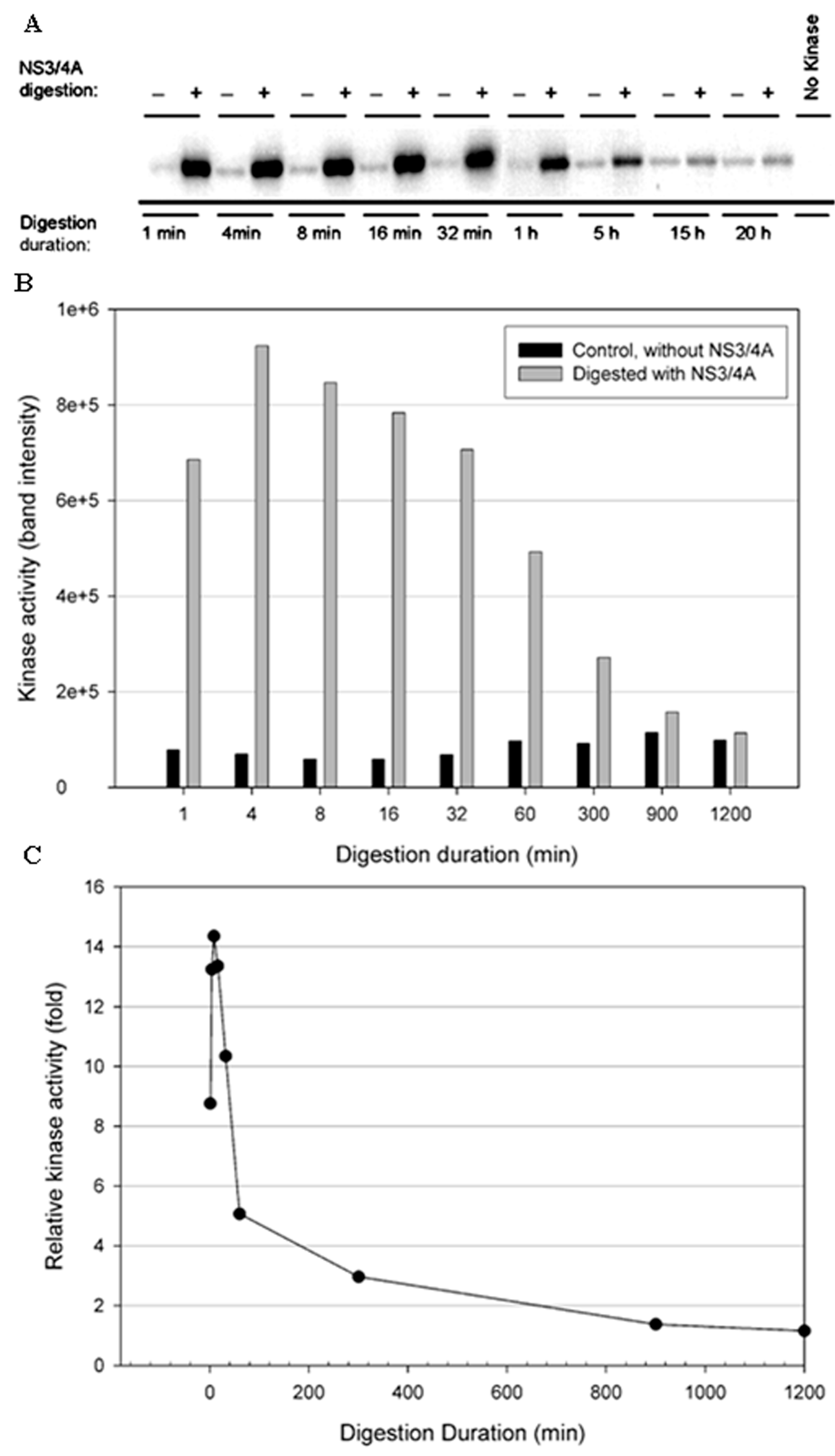
3.3. NS3/NS4A Modulates Kinase Activity
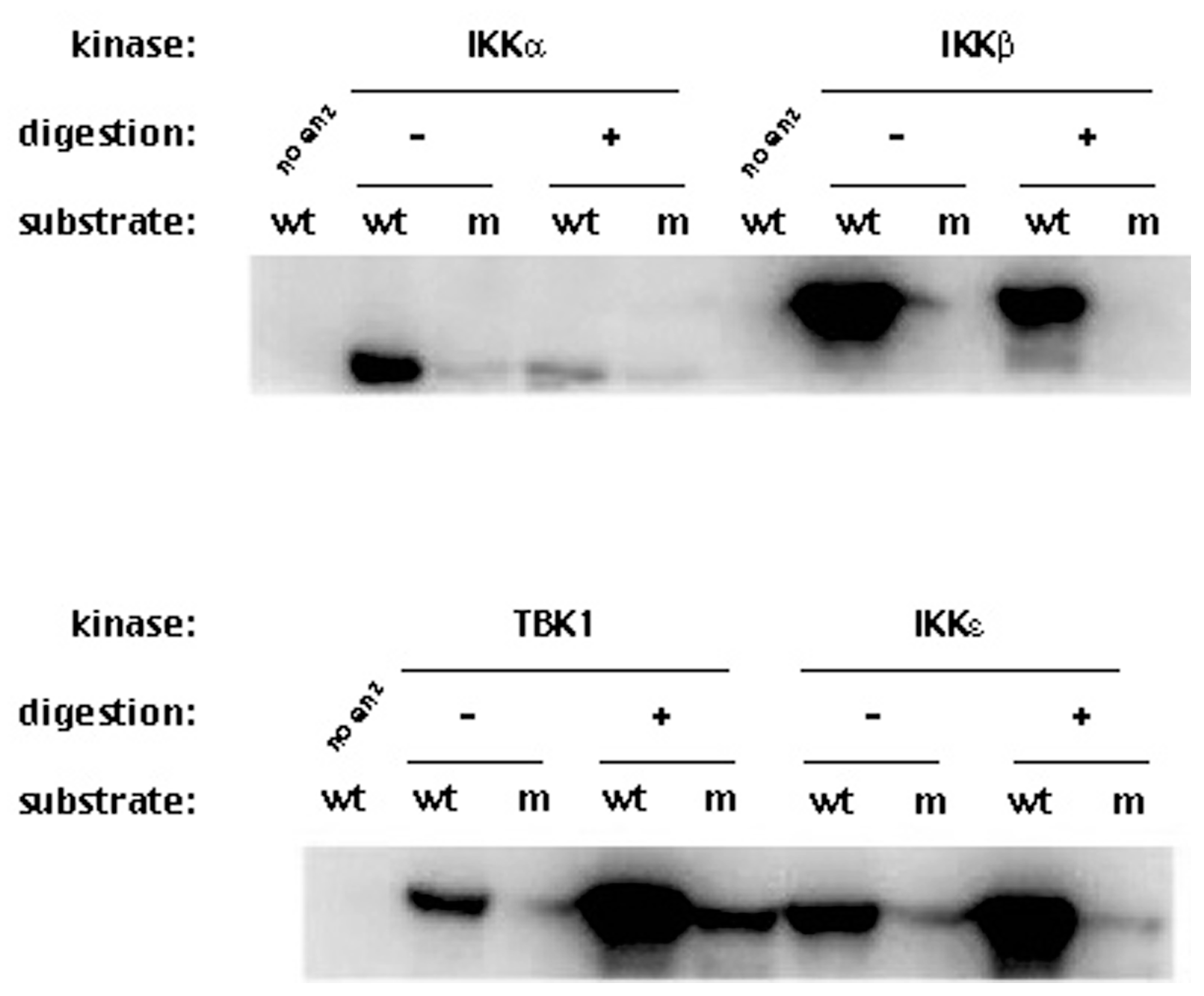
3.4. The NS3/NS4A Proteolytic Activity Is Essential for Modulation of the Kinase Activities of Both IKKε and TBK1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cohen, J. The Scientific Challenge of Hepatitis C. Science 1999, 285, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaris Observatory, H.C.V.C. Global change in hepatitis C virus prevalence and cascade of care between 2015 and 2020: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 396–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, Y. Progress on global hepatitis elimination targets. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 8199–8200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, R.K.; Premkumar, M. Hepatitis C Virus Elimination by 2030: Conquering Mount Improbable. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 16, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihama, A.; Nagata, K. Viral RNA polymerase. Crit. Rev. Biochem. 1988, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, C.M.; Lenches, E.M.; Eddy, S.R.; Shin, S.J.; Sheets, R.L.; Strauss, J.H. Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: Implication for flavivirus gene expression and evolution. Science 1985, 229, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamizawa, A.; Mori, C.; Fuke, L.; Manabe, S.; Murakami, S.; Fujita, J.; Onishi, E.; Andoh, T.; Yoshida, I.; Okayama, H. Structure and organization of the hepatitis C virus genome isolated from human carriers. J. Virol. 1991, 65, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, T.; Lau, G.M.; Lau, G.M.; Sugiyama, M.; Mizokami, M. An updated analysis of hepatitis C virus genotypes and subtypes based on the complete coding region. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grakoui, A.; McCourt, D.W.; Wychowski, C.; Feinstone, S.M.; Rice, C.M. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus-encoded serine proteinase: Determination of proteinase-dependent polyprotein cleavage sites. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 2832–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Lindenbach, B.D.; Prágai, B.M.; McCourt, D.W.; Rice, C.M. Processing in the hepatitis C virus E2-NS2 region: Identification of p7 and two distinct E2-specific products with different termini. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, H.; Hijikata, M.; Asabe, S.; Hirota, M.; Kimura, K.; Shimotohno, K. Two hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E2 products with different C termini. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 6215–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Failla, C.; Tomei, L.; De Francesco, R. Both NS3 and NS4A are required for proteolytic processing of hepatitis C virus nonstructural proteins. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3753–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomei, L.; Failla, C.; Santolini, E.; Francesco, R.D.; Monica, N.L. NS3 is a serine protease required for processing of hepatitis C virus polyprotein. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4017–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartenschlager, R.; Lohmann, V.; Wilkinson, T.; Koch, J.O. Complex formation between the NS3 serine-type proteinase of the hepatitis C virus and NS4A and its importance for polyprotein maturation. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 7519–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, B.; Han, D.S.; Back, S.H.; Song, O.-K.; Cho, M.-J.; Kim, C.-J.; Shimotohno, K.; Jang, S.K. NS3-4A of hepatitis C virus is a chymotrypsin-like protease. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2534–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Peterson, D.L. Expression, isolation and characterization of the hepatitis C virus ATPase/RNA helicase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995, 323, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Gwack, Y.; Han, J.H.; Choe, J. C-terminal domain of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protein contains an RNA helicase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cento, V.; Mirabelli, C.; Salpini, R.; Dimonte, S.; Artese, A.; Costa, G.; Mercurio, F.; Svicher, V.; Parrotta, L.; Bertoli, A.; et al. HCV genotypes are differently prone to the development of resistance to linear and macrocyclic protease inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, N.; Reichert, P.; Taremi, S.S.; Prosise, W.W.; Weber, P.C. Molecular views of viral polyprotein processing revealed by the crystal structure of the hepatitis C virus bifunctional protease-helicase. Structure 1999, 7, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganta, N.M.; Gedda, G.; Rathnakar, B.; Satyanarayana, M.; Yamajala, B.; Ahsan, M.J.; Jadav, S.S.; Balaraju, T. A review on HCV inhibitors: Significance of non-structural polyproteins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 576–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kish, T.; Aziz, A.; Sorio, M. Hepatitis C in a New Era: A Review of Current Therapies. P T. 2017, 42, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borowski, P.; Oehlmann, K.; Heiland, M.; Laufs, R. Nonstructural Protein 3 of hepatitis C virus blocks the distribution of the free catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 2838–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamuro, D.; Furukawa, T.; Takegami, T. Hepatitis C Virus Nonstructural Protein NS3 Transforms NIH 3T3 Cells. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3893–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemel, R.; Gerechet, S.; Greif, H.; Bachmatove, L.; Birk, Y.; Golan-Goldhirsh, A.; Kunin, M.; Berdichevsky, Y.; Benhar, I.; Tur-Kaspa, R. Cell transformation induced by hepatitis C virus NS3 serine protease. J. Viral Hepat. 2001, 8, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, R.-X.; Ouyang, X.-M.; Zheng, H. Effect of hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein NS3 on proliferation and MAPK phosphorylation of normal hepatocyte line. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2157–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolganiuc, A.; Oak, S.; Kodys, K.; Golenbock, D.T.; Finberg, R.W.; Kurt-Jones, E.; Szabo, G. Hepatitis C core and nonstructural 3 proteins trigger toll-like receptor 2-mediated pathways and inflammation activation. Gastroenterobiology 2004, 127, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, E.; Li, K.; Wang, C.; Sumpter, R.J.; Ikeda, M.; Lemon, S.M.; Gale, M.J. Regulation of interferon regulatory factor-3 by the hepatitis C virus serine protease. Science 2003, 300, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, E.; Li, K.; Sumpter, R., Jr.; Loo, Y.M.; Johnson, C.L.; Wang, C.; Fish, P.M.; Yoneyama, M.; Fujita, T.; Lemon, S.M.; et al. Control of antiviral defenses through hepatitis C virus disruption of retinoic acid-inducible gene-I signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2986–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Foy, E.; Ferreon, J.C.; Nakamura, M.; Ferreon, A.C.M.; Ikeda, M.; Ray, S.C.; Gale, M.J.; Lemon, S.M. Immune evasion by hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease-mediated cleavage of the Toll-like receptor 3 adaptor protein TRIF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2992–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-D.; Sun, L.; Seth, R.B.; Pineda, G.; Chen, Z.J. Hepatitis C virus protease NS3/4A cleaves mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein off the mitochondria to evade innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17717–17722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meylan, E.; Curran, J.; Hofmann, K.; Moradpur, D.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Tschopp, J. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005, 437, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, A.A.; Taggart, D.J.; Xu, G.; Fowler, J.D.; Wu, H.; Suo, Z. The inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta) phosphorylates IkappaBalpha twice in a single binding event through a sequential mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 299, 102796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Lo, Y.C.; Li, Q.; Napolitano, G.; Wu, X.; Jiang, X.; Dreano, M.; Karin, M.; Wu, H. Crystal structure of inhibitor of kappaB kinase beta. Nature 2011, 472, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappaB, an evolutionarily conserved mediator of immune and inflammatory responses. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2005, 560, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, S.; Passos, D.O.; Huang, D.B.; Mulero, M.C.; Mazumder, A.; Biswas, T.; Verma, I.M.; Lyumkis, D.; Ghosh, G. Structural Basis for the Activation of IKK1/alpha. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Ben-Neriah, Y. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: The control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 621–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Helgason, E.; Phung, Q.T.; Quan, C.L.; Iyer, R.S.; Lee, M.W.; Bowman, K.K.; Starovasnik, M.A.; Dueber, E.C. Molecular basis of Tank-binding kinase 1 activation by transautophosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9378–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi, A.; Devos, J.M.; Ng, S.L.; Nanao, M.H.; Round, A.; Maniatis, T.; Panne, D. Crystal structure and mechanism of activation of TANK-binding kinase 1. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, C.; Tomei, L.; De Francesco, R. An amino-terminal domain of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protease is essential for interaction with NS4A. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Brown, J.A.; Newmister, S.A.; Suo, Z. Polymerization fidelity of a replicative DNA polymerase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus P2. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7492–7501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkuhler, C.; Urbani, A.; Tomei, L.; Biasiol, G.; Sardana, M.; Bianchi, E.; Pessi, A.; De Francesco, R. Activity of purified hepatitis C virus protease NS3 on peptide substrates. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 6694–6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.H.; Brown, J.A.; Suo, Z.; Blum, P.; Nohmi, T.; Ling, H. Structural insight into dynamic bypass of the major cisplatin-DNA adduct by Y-family polymerase Dpo4. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.A.; Newmister, S.A.; Fiala, K.A.; Suo, Z. Mechanism of double-base lesion bypass catalyzed by a Y-family DNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3867–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.S.; Peters, R.T.; Dang, L.C.; Maniatis, T. MEKK1 activates both IkB kinase a, IkB kinase b. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9319–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.T.; Liao, S.-M.; Maniatis, T. IKKe is part of a novel PMA-inducible IkB kinase complex. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, E.; Urbani, A.; Biasiol, G.; Brunetti, M.; Pessi, A.; Defrancesco, R.; Steinkuhler, C. Complex formation between the hepatitis C virus serine protease and a synthetic NS4A cofactor peptide. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 7890–7897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardana, V.V.; Blue, J.T.; Zugay-Murphy, J.; Sardana, M.K.; Kuo, L.C. An uniquely purified HCV NS3 protease and NS4A(21-34) peptide form a highly active serine protease complex in peptide hydrolysis. Protein Expr. Purif. 1999, 16, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, E.; Tramontano, A.; Tomei, L.; La Monica, N.; Failla, C.; Sardana, M.; Wood, T.; De Francesco, R. Molecular model of the specificity pocket of the hepatitis C virus protease: Implications for substrate recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliani, M.; Bianchi, E.; Narjes, F.; Fossatelli, M.; Urbani, A.; Steinkuhler, C.; De Francesco, R.; Pessi, A. A continuous assay of hepatitis C virus protease based on resonance energy transfer depsipeptide substrates. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 240, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, K.A.; Suo, Z. Pre-Steady-State Kinetic Studies of the Fidelity of Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 DNA Polymerase IV. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrer, S.M.; Beyer, D.C.; Xia, C.X.; Fowler, J.D.; Suo, Z. Kinetic Basis of Sugar Selection by a Y-Family DNA Polymerase from Sulfolobus solfataricus P2. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 10179–10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, B.A.; Suo, Z. Kinetic Basis for the Differing Response to an Oxidative Lesion by a Replicative and a Lesion Bypass DNA Polymerase from Solfolobus solfataricus. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 3485–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landro, J.A.; Raybuck, S.A.; Luong, Y.P.; O’Malley, E.T.; Harbeson, S.L.; Morgenstern, K.A.; Rao, G.; Livingston, D.J. Mechanistic role of an NS4A peptide cofactor with the truncated NS3 protease of hepatitis C virus: Elucidation of the NS4A stimulatory effect via kinetic analysis and inhibitor mapping. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 9340–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellinghuisen, T.L.; Rice, C.M. Interaction between hepatitis C virus proteins and host cell factors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, M.; Kato, N.; Moriyama, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Wang, Y.; Dharel, N.; Kawabe, T.; Omata, M. Interaction Between the HCV NS3 Protein and the Host TBK1 Protein Leads to Inhibition of Cellular Antiviral Responses. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbani, A.; Bianchi, E.; Narjes, F.; Tramontano, A.; De Francesco, R.; Steinkuhler, C.; Pessi, A. Substrate specificity of the hepatitis C virus serine protease NS3. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 9204–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.A. Transient-state kinetic analysis of enzyme reaction pathways. In The Enzymes, 3rd ed.; Sigman, D.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 20, pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zahurancik, W.J.; Klein, S.J.; Suo, Z. Kinetic Mechanism of DNA Polymerization Catalyzed by Human DNA Polymerase epsilon. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 7041–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, K.A.; Suo, Z. Mechanism of DNA Polymerization Catalyzed by Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 DNA Polymerase IV. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 2116–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; Suo, Z. Elucidating the kinetic mechanism of DNA polymerization catalyzed by Sulfolobus solfataricus P2 DNA polymerase B1. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 7502–7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Reed, A.J.; Zahurancik, W.J.; Daskalova, S.M.; Hecht, S.M.; Suo, Z. Interlocking activities of DNA polymerase beta in the base excision repair pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2118940119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinkuhler, C.; Biasiol, G.; Brunetti, M.; Urbani, A.; Koch, U.; Cortese, R.; Pessi, A.; De Francesco, R. Product inhibition of the hepatitis C virus NS3 protease. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 8899–8905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, A.; Grandvaux, N.; Lin, R.; Ottone, C.; Akira, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Fujita, T.; Hiscott, J.; Meurs, E.F. Inhibition of RIG-I-dependent signaling to the interferon pathway during hepatitis C virus expression and restoration of signaling by IKKepsilon. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 3969–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, J.H. Management of hepatitis C: Current and future perspective. J. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, T.; Kawai, T.; Takeda, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Inoue, J.; Tatsumi, Y.; Kanamaru, A.; Akira, S. IKK-i, a novel lipopolysaccharide-inducible kinase that is related to IkappaB kinases. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.A.; Guan, J.-L. Residues within the first subdomain of the FERM-like domain in Focal Adhesion Kinase are important in its regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 8197–8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zu, Y.L.; Ai, Y.; Huang, C.K. Characterization of an autoinhibitory domain in human mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; DeLano Scientific: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Misquitta, Y.R.; Olland, A.; Johnson, M.A.; Kelleher, K.S.; Kriz, R.; Lin, L.L.; Stahl, M.; Mosyak, L. Crystal structure of a human IkappaB kinase beta asymmetric dimer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 22758–22767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woronicz, J.D.; Gao, X.; Cao, Z.; Rothe, M.; Goeddel, D.V. IkappaB kinase-beta: NF-kappaB activation and complex formation with IkappaB kinase-alpha and NIK. Science 1997, 278, 866–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandi, E.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Delhase, M.; Hayakawa, M.; Karin, M. The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for IkappaB phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. Cell 1997, 91, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, F.; Zhu, H.; Murray, B.W.; Shevchenko, A.; Bennett, B.L.; Li, J.; Young, D.B.; Barbosa, M.; Mann, M.; Manning, A.; et al. IKK-1 and IKK-2: Cytokine-activated IkappaB kinases essential for NF-kappaB activation. Science 1997, 278, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Hayakawa, M.; Rothwarf, D.M.; Zandi, E.; Karin, M. A cytokine-responsive IkappaB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Nature 1997, 388, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, S.; Huang, D.B.; Hauenstein, A.V.; Fusco, A.J.; Zhong, X.; Vu, D.; Schrofelbauer, B.; Kim, Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Verma, I.M.; et al. A structural basis for IkappaB kinase 2 activation via oligomerization-dependent trans auto-phosphorylation. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

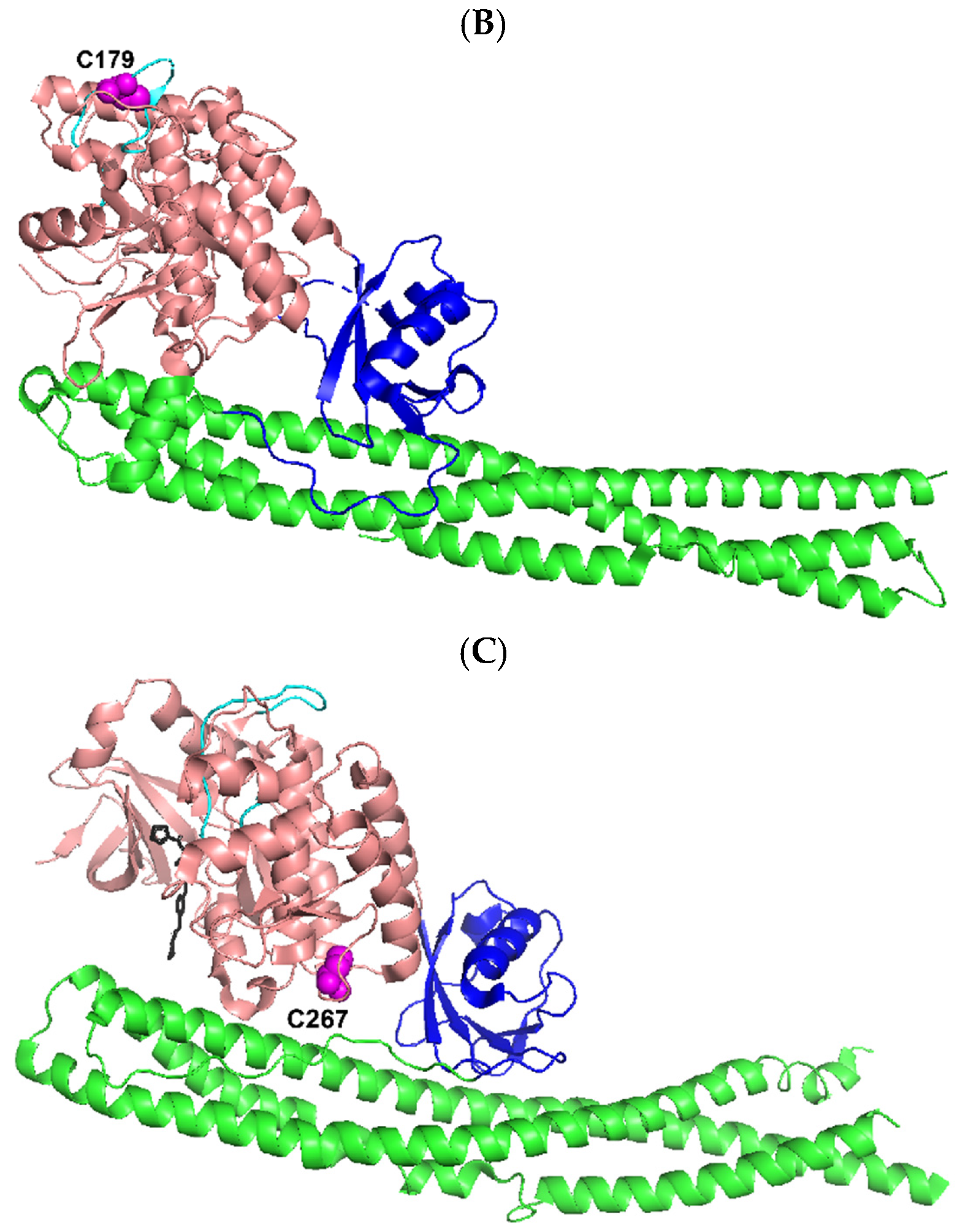
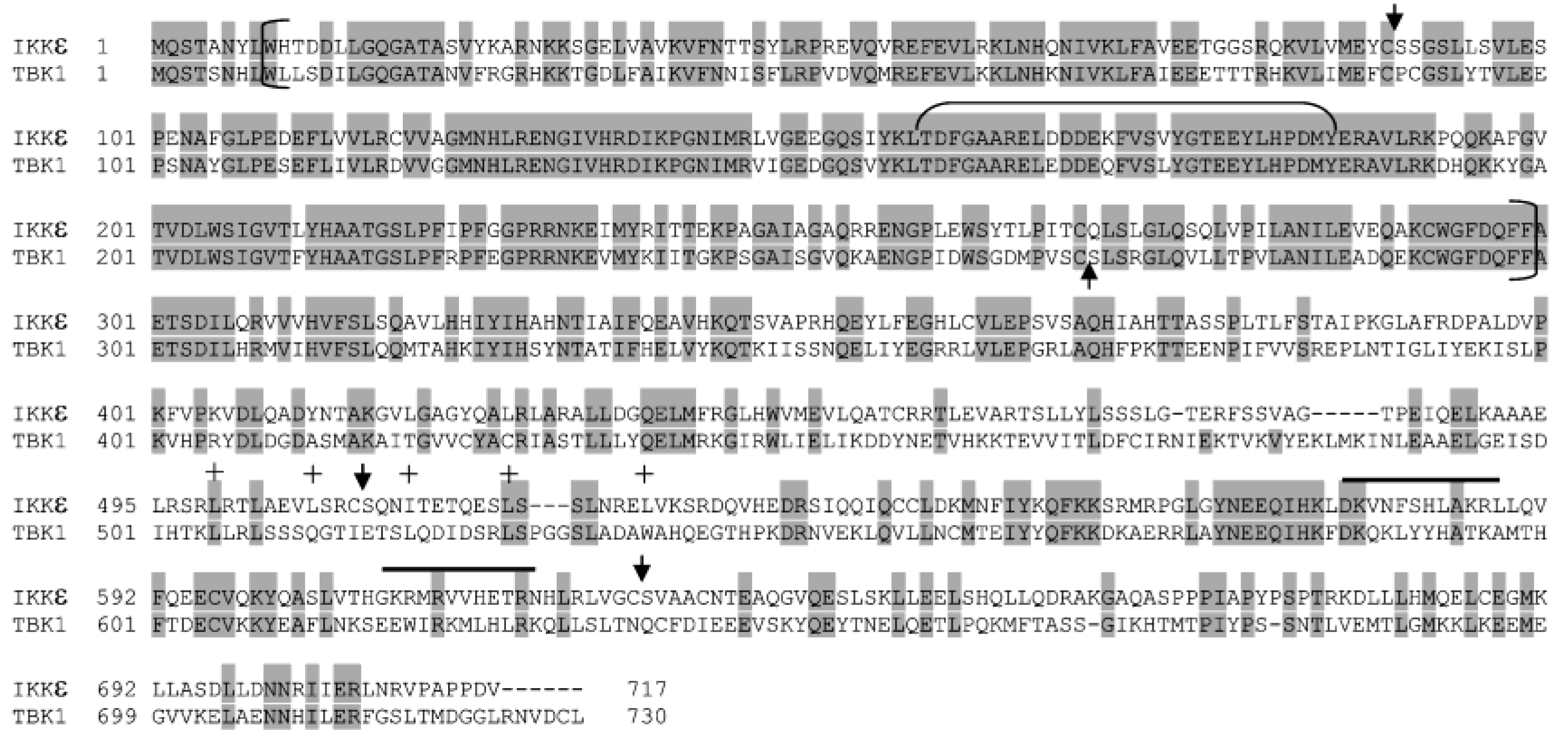
| Proteins | Residue Number of P6 | P6 P5 P4 P3 P2 P1 ↓ P1′ P2′ P3′ P4′ |
|---|---|---|
| NS4A/NS4B | D E M E E C ↓ A S H L | |
| NS4B/NS5A | D C S T P C ↓ S G S W | |
| NS5A/NS5B | E D V V C C ↓ S M S Y | |
| IKKα | 173 | D Q G S L C ↓ T S F V |
| 374 | D G V R G C ↓ D S Y M | |
| 691 | D H S L S C ↓ V V T P | |
| 711 | E E N L N C ↓ L G H L | |
| IKKβ | 174 | D Q G S L C ↓ T S F V |
| 711 | E A H N L C ↓ T L L E | |
| IKKε | 84 | L V M E Y C ↓ S S G S |
| 504 | E V L S R C ↓ S Q N I | |
| 621 | L R L V G C ↓ S V A A | |
| TBK1 | 262 | D M P V S C ↓ S L S R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, M.A.F.; McWhirter, S.M.; Suo, Z. Modulation of Kinase Activities In Vitro by Hepatitis C Virus Protease NS3/NS4A Mediated-Cleavage of Key Immune Modulator Kinases. Cells 2023, 12, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030406
Abdullah MAF, McWhirter SM, Suo Z. Modulation of Kinase Activities In Vitro by Hepatitis C Virus Protease NS3/NS4A Mediated-Cleavage of Key Immune Modulator Kinases. Cells. 2023; 12(3):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030406
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Mohd Amir F., Sarah M. McWhirter, and Zucai Suo. 2023. "Modulation of Kinase Activities In Vitro by Hepatitis C Virus Protease NS3/NS4A Mediated-Cleavage of Key Immune Modulator Kinases" Cells 12, no. 3: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030406
APA StyleAbdullah, M. A. F., McWhirter, S. M., & Suo, Z. (2023). Modulation of Kinase Activities In Vitro by Hepatitis C Virus Protease NS3/NS4A Mediated-Cleavage of Key Immune Modulator Kinases. Cells, 12(3), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030406






