Mitophagy Effects of Protodioscin on Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Inhibition of p38MAPK Targeting NIX/LC3 Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.4. Measurement of Apoptotic Profile and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
2.5. Measurement of Autophagy and Mitophagy
2.6. siRNA Transient Transfection
2.7. Immunoblotting
2.8. Molecular Docking
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
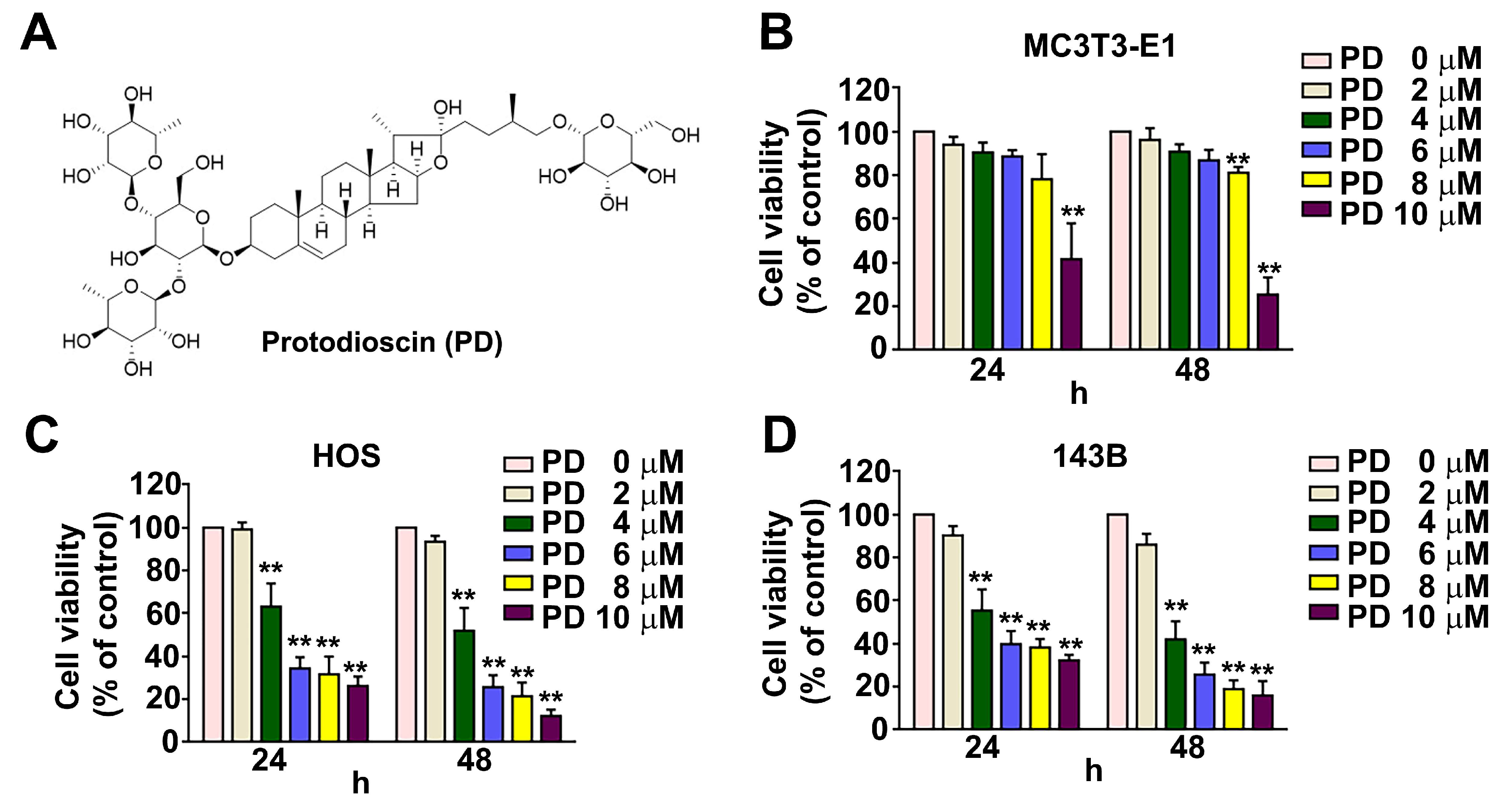
3.1. Effect of PD on Human OS Cell Viability
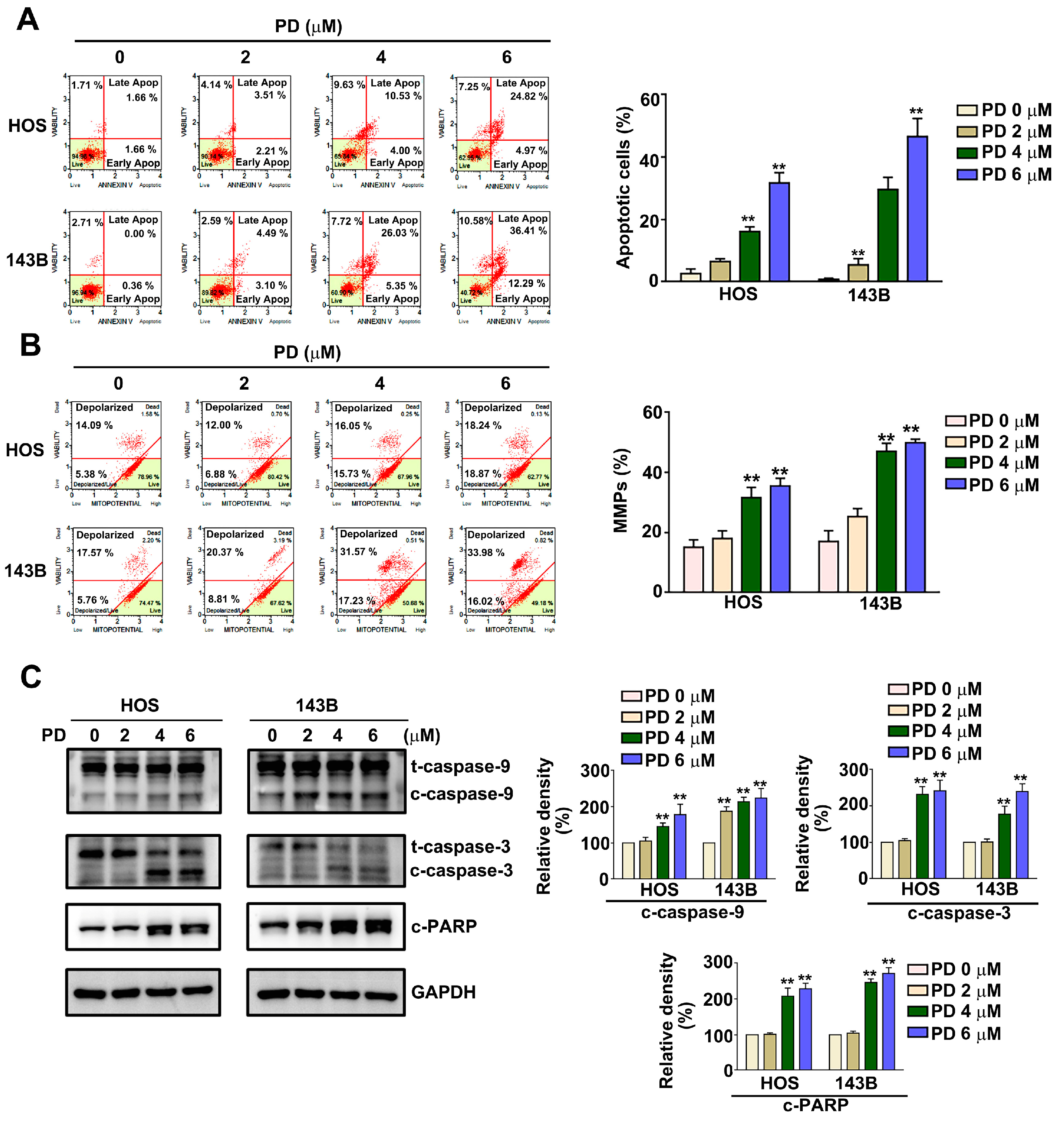
3.2. Effect of PD on Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Human OS Cells
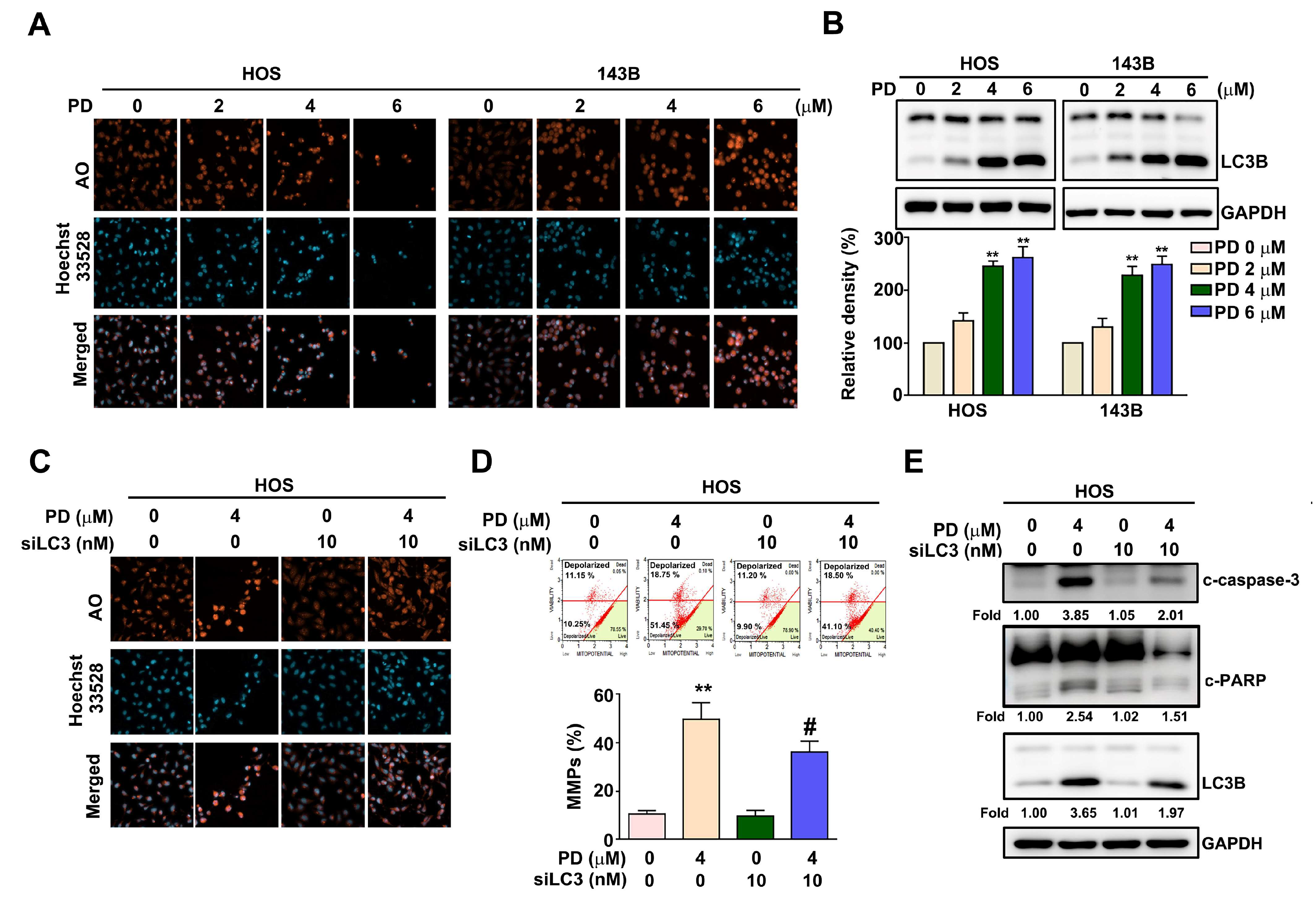
3.3. Effect of PD on the Autophagy in Human OS Cells
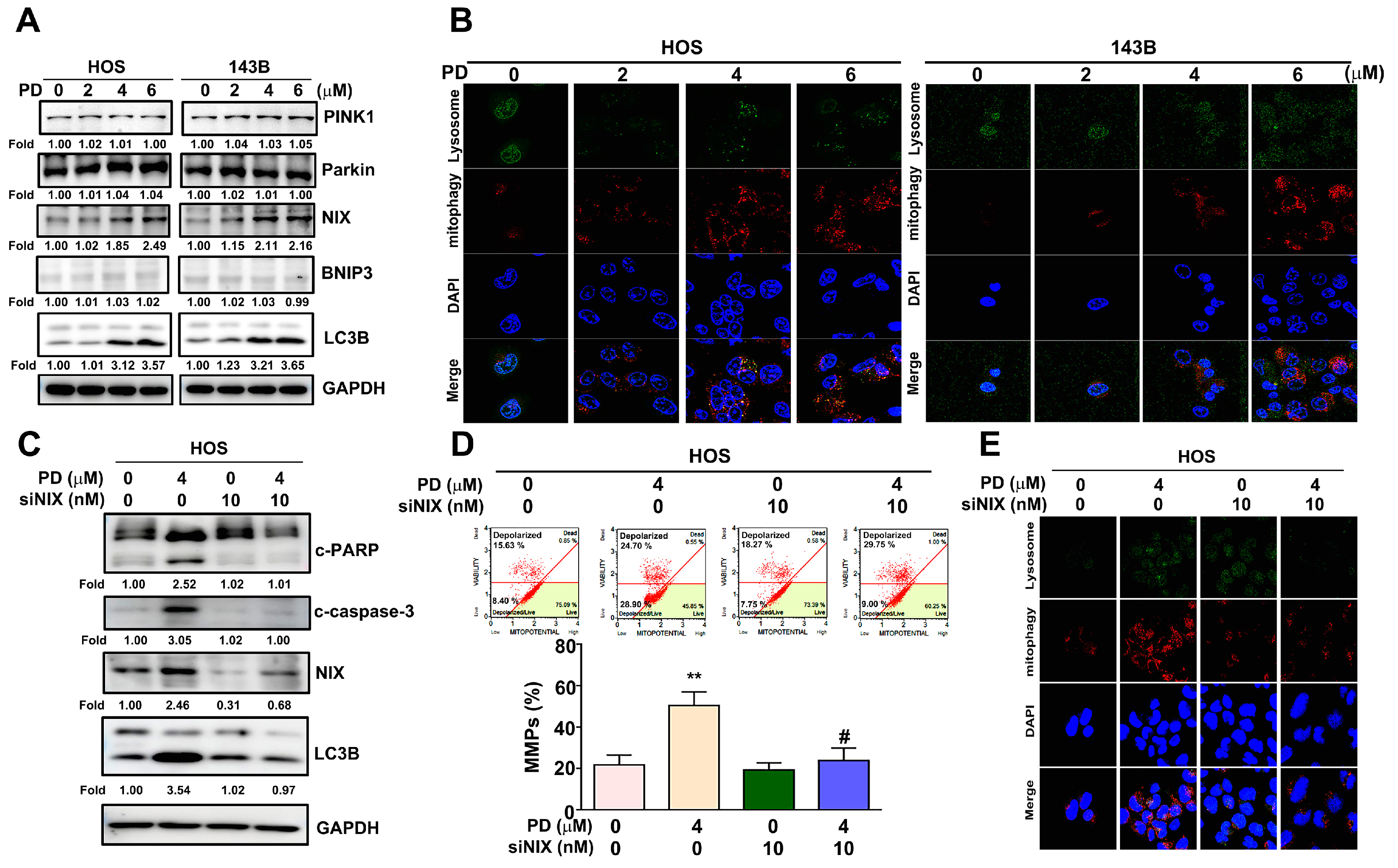
3.4. Effect of PD on the Mitophagy in Human OS Cells
3.5. p38 MAPK Mediates PD-Induced Mitophagy in Human OS Cells
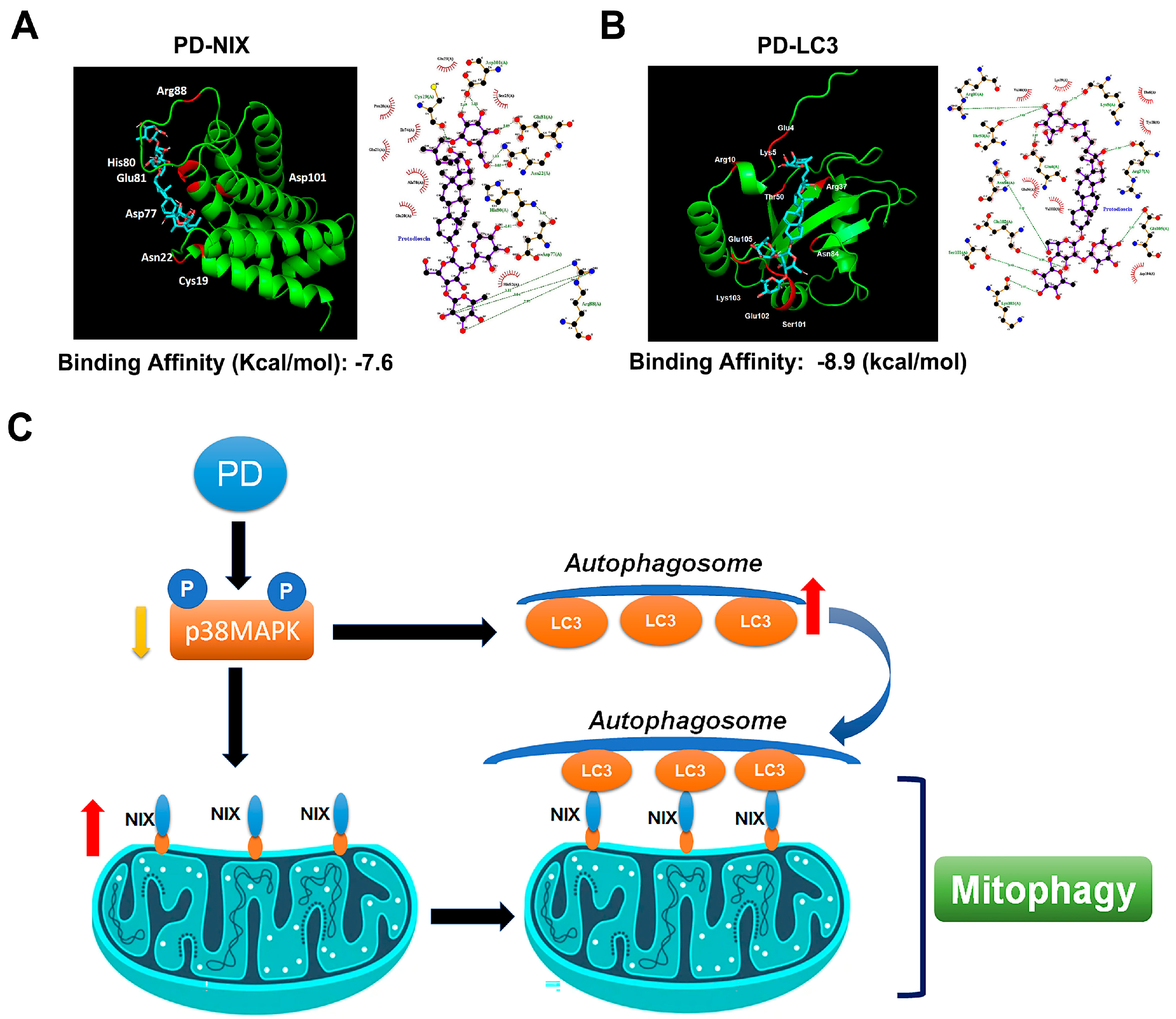
3.6. PD-NIX and PD-LC3 Complexes Provide the PD-Regulated Mitophagy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hameed, M.; Mandelker, D. Tumor Syndromes Predisposing to Osteosarcoma. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2018, 25, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampo, M.; Koivikko, M.; Taskinen, M.; Kallio, P.; Kivioja, A.; Tarkkanen, M.; Bohling, T. Incidence, epidemiology and treatment results of osteosarcoma in Finland—A nationwide population-based study. Acta Oncol. 2011, 50, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Dean, D.; Hornicek, F.J.; Chen, Z.; Duan, Z. The role of extracelluar matrix in osteosarcoma progression and metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Shen, K.; Li, Q.; Ni, Y.; Huang, L. Mitophagy in carcinogenesis, drug resistance and anticancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Lu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, L.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, Z.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; et al. BNIP3L/NIX-mediated mitophagy: Molecular mechanisms and implications for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.M.; Jung, Y.K. A Molecular Approach to Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Dynamics. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waris, G.; Ahsan, H. Reactive oxygen species: Role in the development of cancer and various chronic conditions. J. Carcinog. 2006, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Wei, L. Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce toxicity in CAL 27 oral cancer cell lines by activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3441–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Pan, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, N.; Geng, Q. Mitophagy: A novel perspective for insighting into cancer and cancer treatment. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.Z.; Xing, Y.Z.; Li, F.W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.K.; Zhang, J.; Bian, X.L.; et al. Orphan nuclear receptor TR3 acts in autophagic cell death via mitochondrial signaling pathway. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, X.; Meng, Z.; Guo, C. Protodioscin ameliorates fructose-induced renal injury via inhibition of the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2016, 23, 1504–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.L.; Lee, H.L.; Yang, S.F.; Wang, S.W.; Lin, C.P.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chiou, H.L. Protodioscin Induces Mitochondrial Apoptosis of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Through Eliciting ER Stress-Mediated IP3R Targeting Mfn1/Bak Expression. J. Hepatocell Carcinoma 2022, 9, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.L.; Lee, C.H.; Chen, C.M.; Cheng, C.W.; Chen, P.N.; Ying, T.H.; Hsieh, Y.H. Protodioscin Induces Apoptosis Through ROS-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress via the JNK/p38 Activation Pathways in Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 46, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xue, X.; Xian, L.; Guo, Z.; Ito, Y.; Sun, W. Potential neuroprotection of protodioscin against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats through intervening inflammation and apoptosis. Steroids 2016, 113, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibasami, H.; Moteki, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Katsuzaki, H.; Imai, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Ishii, Y.; Komiya, T. Protodioscin isolated from fenugreek (Trigonella foenumgraecum L.) induces cell death and morphological change indicative of apoptosis in leukemic cell line H-60, but not in gastric cancer cell line KATO III. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003, 11, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Yao, X. Protodioscin (NSC-698 796): Its spectrum of cytotoxicity against sixty human cancer cell lines in an anticancer drug screen panel. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ney, P.A. Role of BNIP3 and NIX in cell death, autophagy, and mitophagy. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Tian, J.; Han, H. Guangsangon E triggers mitochondria dysfunction and mitophagy in triple-negative breast cancer and leads to non-apoptotic cell death. Mol. Carcinog. 2022, 61, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Nie, S.; Xie, M. Aloe gel glucomannan induced colon cancer cell death via mitochondrial damage-driven PINK1/Parkin mitophagy pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 295, 119841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shang, C.; Liu, Z.; Han, J.; Li, W.; Xiao, P.; Li, N.; Li, S.; Xiu, Z.; Song, G.; et al. Apoptin mediates mitophagy and endogenous apoptosis by regulating the level of ROS in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.; Bian, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Puerarin alleviates cadmium-induced mitochondrial mass decrease by inhibiting PINK1-Parkin and Nix-mediated mitophagy in rat cortical neurons. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2021, 230, 113127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Cheng, C.S.; Gao, H.; Zhan, L.; Wang, F.; Qu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Meng, Z.; et al. Natural Compound Methyl Protodioscin Suppresses Proliferation and Inhibits Glycolysis in Pancreatic Cancer. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 7343090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.C.; Shen, T.S.; Wu, C.C.; Chang, I.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.P.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, C.L. Methyl Protodioscin Induces Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Caspase-Dependent and MAPK Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem 2017, 65, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.J.; Lin, C.W.; Chen, M.K.; Chien, S.Y.; Lo, Y.S.; Chuang, Y.C.; Hsi, Y.T.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, J.C.; Yang, S.F. Inhibition of cathepsin S confers sensitivity to methyl protodioscin in oral cancer cells via activation of p38 MAPK/JNK signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Qu, X.Y.; Yin, J.Q.; Wu, L.; Jiang, H.; Long, H.W.; Jia, Q. Methyl protodioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells. Pharm. Mag. 2014, 10, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.R.; Wang, S.C.; Huang, S.P.; Su, C.C.; Liu, P.L.; Cheng, W.C.; Chuu, C.P.; Chen, J.K.; Bao, B.Y.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Protodioscin inhibits bladder cancer cell migration and growth, and promotes apoptosis through activating JNK and p38 signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharm. 2022, 156, 113929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, S.; Ohta, T.; Shoyama, Y.; Uto, T. Steroidal Saponins Isolated from the Rhizome of Dioscorea tokoro Inhibit Cell Growth and Autophagy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Life 2021, 11, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, M.; Canals, D.; Adada, M.; Coant, N.; Salama, M.F.; Helke, K.L.; Arthur, J.S.; Shroyer, K.R.; Kitatani, K.; Obeid, L.M.; et al. P38 delta MAPK promotes breast cancer progression and lung metastasis by enhancing cell proliferation and cell detachment. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6649–6657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, J.; Das, M.; Howlader, M.S.I.; Prateeksha, P.; Barthels, D.; Das, H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits osteoclastic differentiation by modulating mitophagy and mitochondrial functions. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.C.; Yang, S.F.; Chiou, H.L.; Hsieh, S.C.; Wen, S.H.; Lu, K.H.; Hsieh, Y.H. Licochalcone A-Induced Apoptosis Through the Activation of p38MAPK Pathway Mediated Mitochondrial Pathways of Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells 2019, 8, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Rounds, S.; Lu, Q. Sustained adenosine exposure causes endothelial mitochondrial dysfunction via equilibrative nucleoside transporters. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894020924994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Yao, G.D.; Shang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Song, X.Y.; Hayashi, T.; Zhang, Y.; Song, S.J. Eclalbasaponin I causes mitophagy to repress oxidative stress-induced apoptosis via activation of p38 and ERK in SH-SY5Y cells. Free Radic. Res. 2019, 53, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potocnjak, I.; Simic, L.; Vukelic, I.; Baticic, L.; Domitrovic, R. Oleanolic acid induces HCT116 colon cancer cell death through the p38/FOXO3a/Sirt6 pathway. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 363, 110010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Manipulation of Mitophagy by “All-in-One” nanosensitizer augments sonodynamic glioma therapy. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1413–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, A.; Verma, N.; Swaroop, A.; Bagchi, M.; Preuss, H.G.; Tiwari, K.; Bagchi, D. Efficacy of Furosap(TM), a novel Trigonella foenum-graecum seed extract, in Enhancing Testosterone Level and Improving Sperm Profile in Male Volunteers. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-F.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-F.; Kuo, C.-H.; Wang, P.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Lin, R.-C. Mitophagy Effects of Protodioscin on Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Inhibition of p38MAPK Targeting NIX/LC3 Axis. Cells 2023, 12, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030395
Huang C-F, Hsieh Y-H, Yang S-F, Kuo C-H, Wang P-H, Liu C-J, Lin R-C. Mitophagy Effects of Protodioscin on Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Inhibition of p38MAPK Targeting NIX/LC3 Axis. Cells. 2023; 12(3):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030395
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chien-Feng, Yi-Hsien Hsieh, Shun-Fa Yang, Chao-Hung Kuo, Pei-Han Wang, Chung-Jung Liu, and Renn-Chia Lin. 2023. "Mitophagy Effects of Protodioscin on Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Inhibition of p38MAPK Targeting NIX/LC3 Axis" Cells 12, no. 3: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030395
APA StyleHuang, C.-F., Hsieh, Y.-H., Yang, S.-F., Kuo, C.-H., Wang, P.-H., Liu, C.-J., & Lin, R.-C. (2023). Mitophagy Effects of Protodioscin on Human Osteosarcoma Cells by Inhibition of p38MAPK Targeting NIX/LC3 Axis. Cells, 12(3), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030395







