FTO Regulated Intramuscular Fat by Targeting APMAP Gene via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent Manner in Rex Rabbits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Cell Experiment
2.4. Oil Red O Staining and Measurement of Triglyceride Content
2.5. RT-qPCR
2.6. Gene-specific m6A qPCR
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Measurement of IMF
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
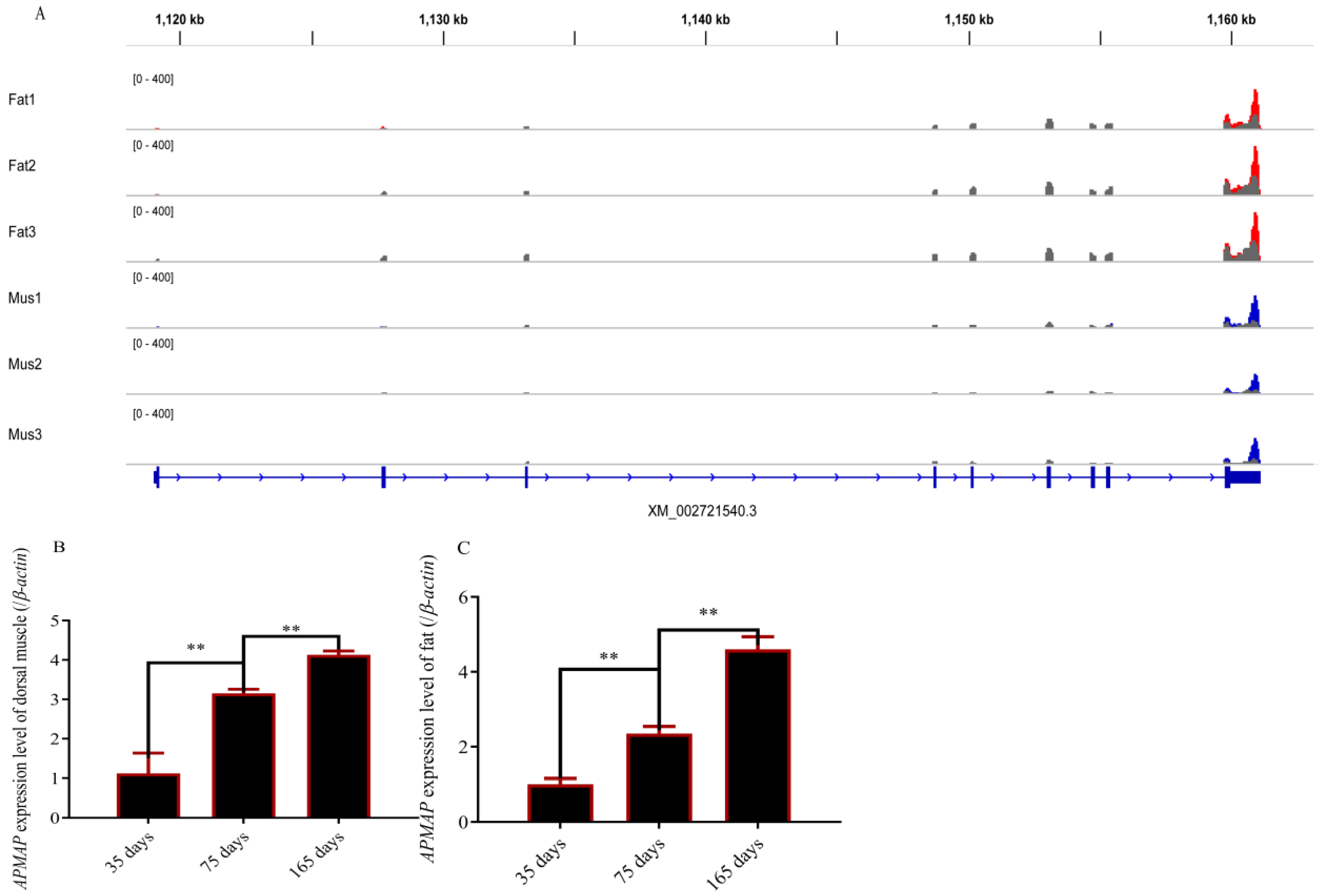
3.1. Methylation Modification of APMAP and APMAP Expression in Rabbits during Growth Periods
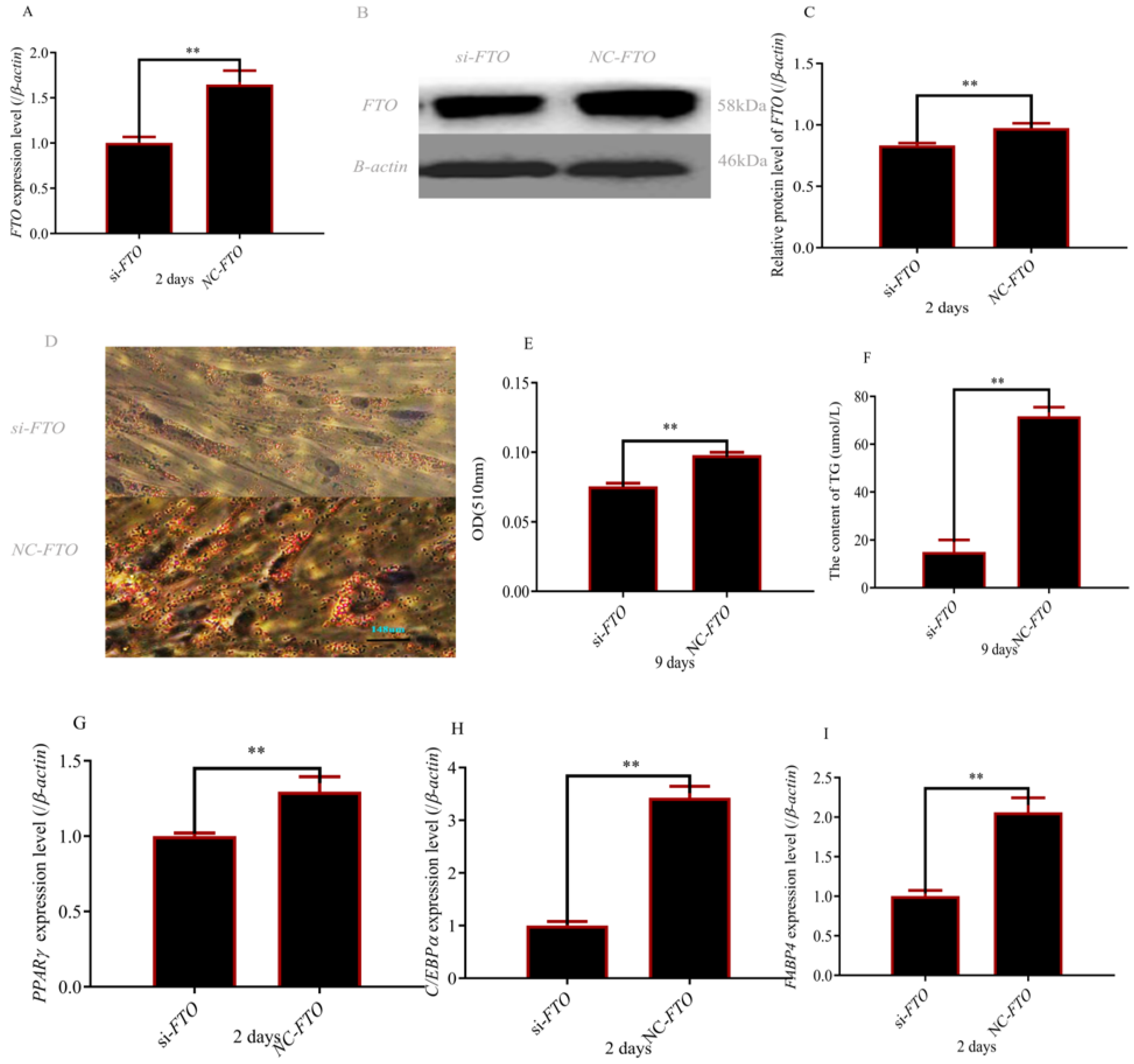
3.2. Preadipocytes Deletion of FTO Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation
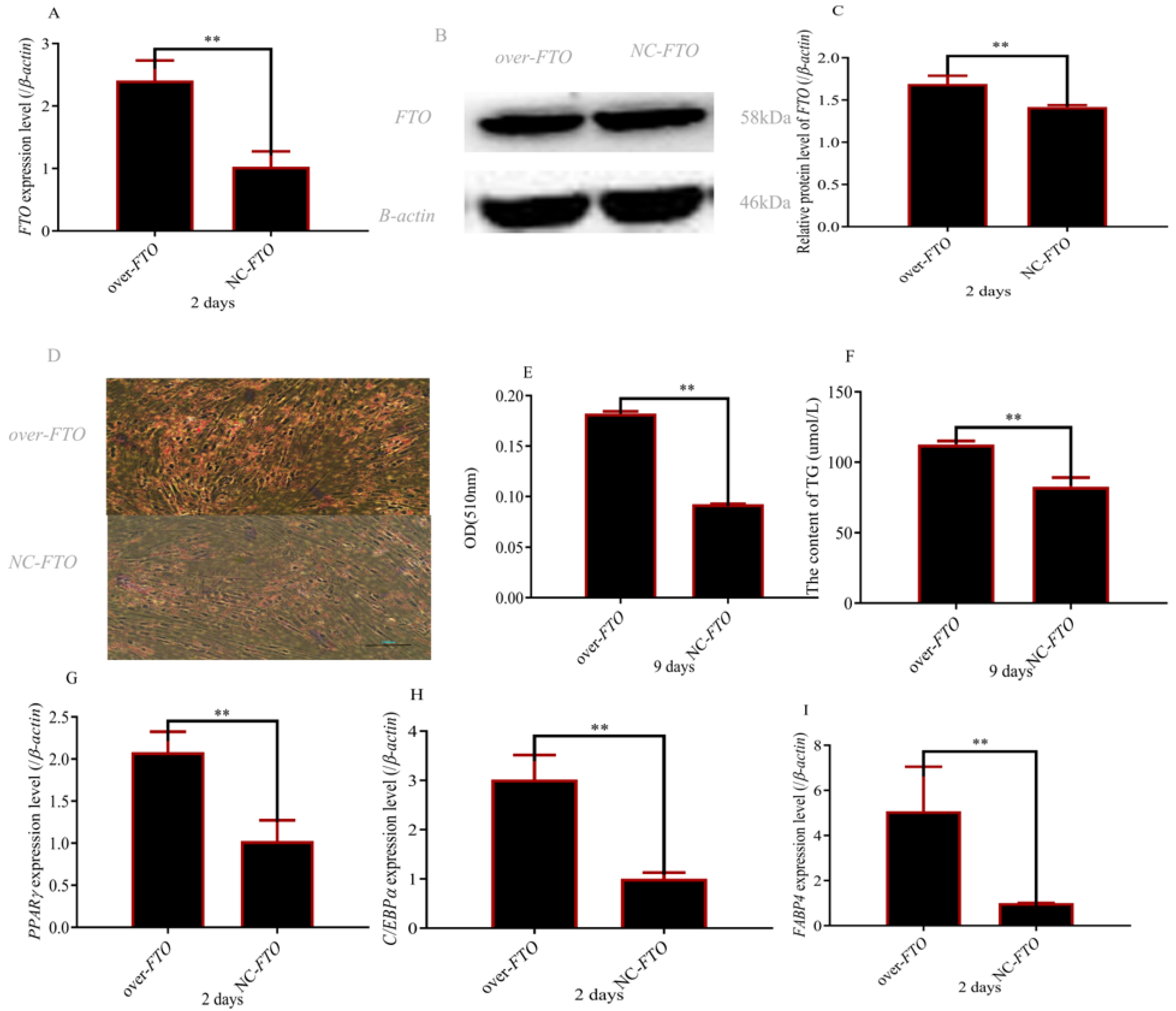
3.3. Upregulation of FTO Increased Preadipocyte Differentiation
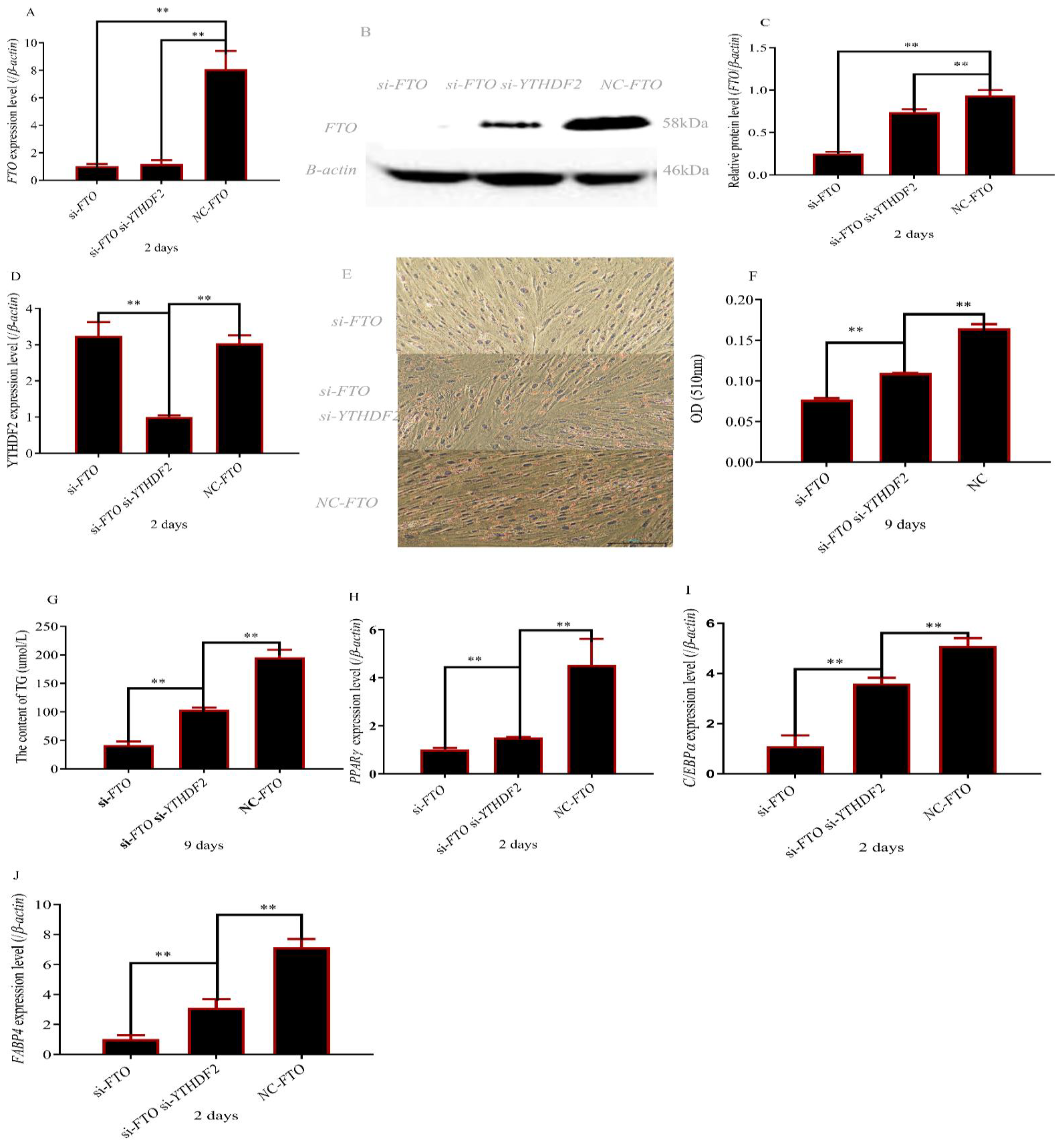
3.4. The Deletion of YTHDF2 Partially Restored Adipocyte Differentiation of FTO Depleted Cells
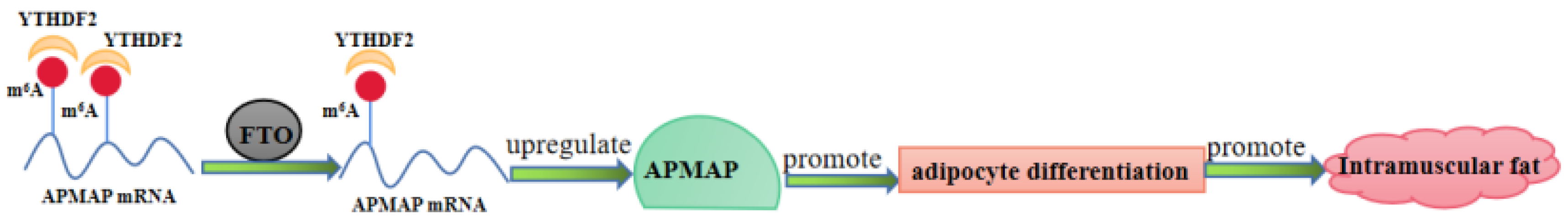
3.5. FTO and YTHDF2 Interact to Regulate APMAP Expression
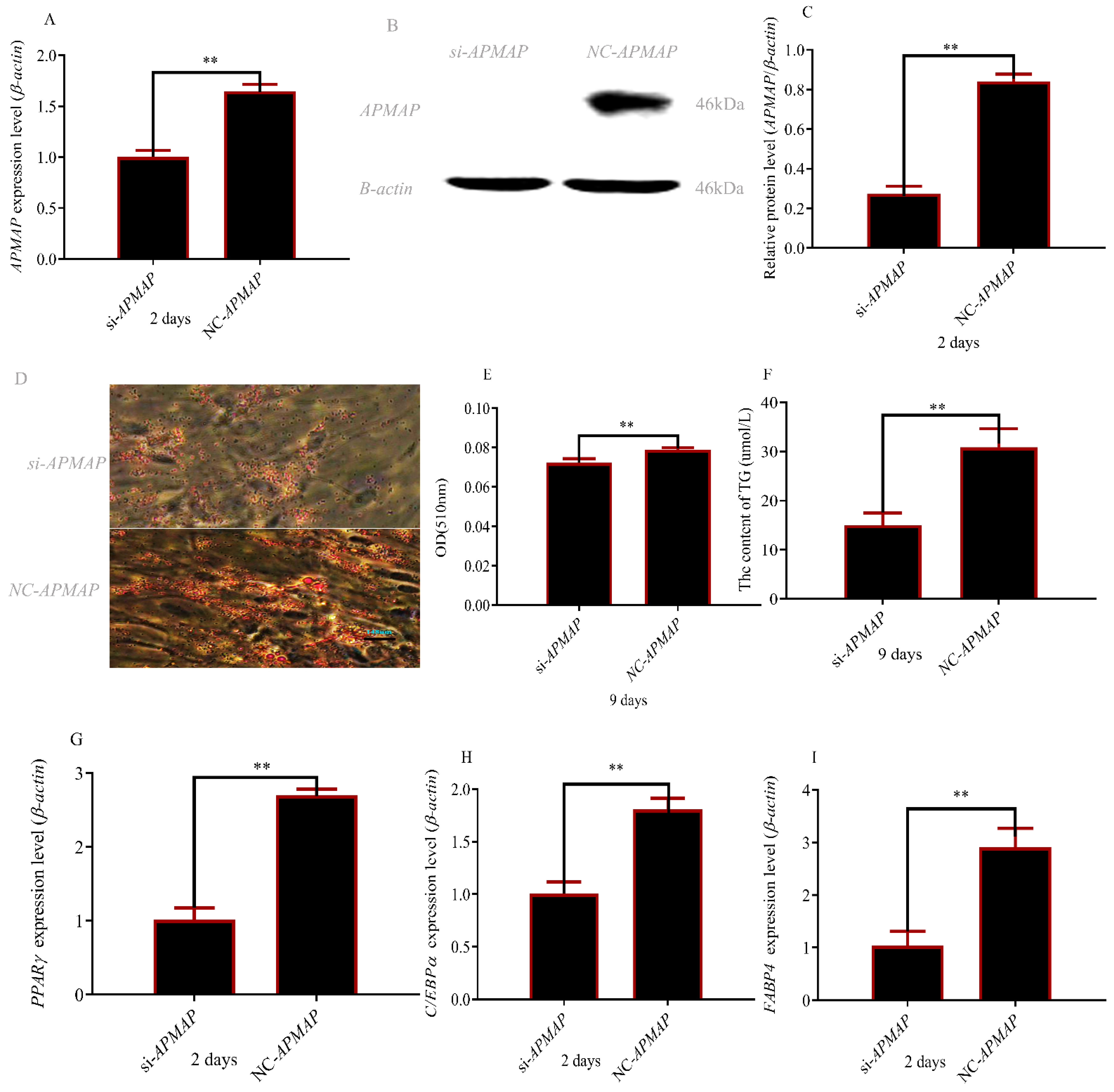
3.6. APMAP Is Essential for Adipogenesis In Vitro
3.7. Correlation Analysis between Intramuscular Fat Content and APMAP mRNA Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Castro Cardoso Pereira, P.M.; dos Reis Baltazar Vicente, A.F. B Meat nutritional composition and nutritive role in the human diet. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.; Eyres, G.T.; Piyasiri, U.; Cochet-Broch, M.; Delahunty, C.M.; Lundin, L.; Appelqvist, I.M. Effects of Agar Gel Strength and Fat on Oral Breakdown, Volatile Release, and Sensory Perception Using in Vivo and in Vitro Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9093–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezgebo, G.B.; Monahan, F.J.; McGee, M.; O’Riordan, E.G.; Richardson, I.R.; Brunton, N.P.; Moloney, A.P. Fatty acid, volatile and sensory characteristics of beef as affected by grass silage or pasture in the bovine diet. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, E.C. Manipulating beef quality through feeding. S. Afr. J. Anim. 2006, 7, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers, R.; Friderici, K.; Rottman, F. Identification of Methylated Nucleosides in Messenger RNA from Novikoff Hepatoma Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1974, 71, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.P.; Kelley, D.E. Existence of methylated messenger RNA in mouse L cells. Cell 1974, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear rna is a major substrate of the obesi-ty-associated fto. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 1, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.-M.; Li, C.J.; Vågbø, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Song, S.-H.; et al. ALKBH5 Is a Mammalian RNA Demethylase that Impacts RNA Metabolism and Mouse Fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2013, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Adhikari, S.; Dahal, U.; Chen, Y.-S.; Hao, Y.-J.; Sun, B.-F.; Sun, H.-Y.; Li, A.; Ping, X.-L.; Lai, W.-Y.; et al. Nuclear m 6 A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, H.; Guo, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, Y.; Qi, M.; Lu, Z.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Ythdc2 is an N6-methyladenosine binding protein that regulates mammalian spermatogenesis. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6a rna methylomes revealed by m6a-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayling, T.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Weedon, M.N.; Zeggini, E.; Freathy, R.M.; Lindgren, C.M.; Perry, J.R.B.; Elliott, K.S.; Lango, H.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. A Common Variant in the FTO Gene Is Associated with Body Mass Index and Predisposes to Childhood and Adult Obesity. Science 2007, 316, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelo, S.; Serena, S.; Chen, W.M.; Manuela, U.; Giuseppe, A.; James, S.; Samer, N.; Ramaiah, N.; Marco, O.; Gianluca, U. Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the fto gene are associated with obesity-related traits. PLoS Genetics 2007, 3, e115. [Google Scholar]
- Shuling, L.; Huiling, T.; He Qian, e.a. FTO is a transcriptional repressor to auto-regulate its own gene and potentially associated with homeostasis of body weight. J Mol Cell Biol 2019, 11, 118–132. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Bouchard, C. FTO: The first gene contributing to common forms of human obesity. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathrin, I.; Stefanie, K.; Julia, F.; Kaisers, W.; Eberhard, D.; Rüther, U. Fto is a relevant factor for the development of the metabolic syndrome in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105349. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Ren, W.; Li, A.; Ding, Y.; Guo, W.; Su, D.; Hu, C.; Xu, K.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.; et al. Fat Mass and Obesity-Associated Gene Enhances Oxidative Stress and Lipogenesis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 1004–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsen, T.; Richter, H.E.; Clausen, J.T.; Fleckner, J. Identification of a novel integral plasma membrane protein induced during adipocyte differentiation. Biochem. J. 2001, 359, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner-Strauss, J.G.; Prokesch, A.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Rieder, D.; Hackl, H.; Duszka, K.; Krogsdam, A.; Di Camillo, B.; Walenta, E.; Klatzer, A.; et al. Reconstruction of gene association network reveals a transmembrane protein required for adipogenesis and targeted by PPARγ. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 4049–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessentheiner, A.R.; Huber, K.; Pelzmann, H.J.; Prokesch, A.; Radner, F.P.W.; Wolinski, H.; Lindroos-Christensen, J.; Hoefler, G.; Rülicke, T.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; et al. APMAP interacts with lysyl oxidase–like proteins, and disruption of Apmap leads to beneficial visceral adipose tissue expansion. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 4088–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Hu, S.; Lai, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Lai, S. MiR-9-5p promotes rabbit preadipocyte differentiation by suppressing leptin gene expression. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2020, 19, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Cai, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. FTO regulates adipogenesis by controlling cell cycle progression via m6A-YTHDF2 dependent mechanism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Cai, M.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, W.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Liang, X.; Zheng, T.; Hu, S.; et al. miR-148a-3p promotes rabbit preadipocyte differentiation by targeting PTEN. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2018, 54, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uezumi, A.; Ito, T.; Morikawa, D.; Shimizu, N.; Yoneda, T.; Segawa, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ogawa, R.; Matev, M.M.; Miyagoe-Suzuki, Y.; et al. Fibrosis and adipogenesis originate from a common mesenchymal progenitor in skeletal muscle. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2015. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Luo, G.; Wang, S.; Ai, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, Z. N6-Methyladenosine Methylome Profiling of Muscle and Adipose Tissues Reveals Methylase–mRNA Metabolic Regulatory Networks in Fat Deposition of Rex Rabbits. Biology 2022, 11, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wåhlén, K.; Sjölin, E.; Hoffstedt, J. The common rs9939609 gene variant of the fat mass- and obesity-associated gene FTO is related to fat cell lipolysis. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, D.; Löffler, D.; Schönberg, M.; Bernhard, F.; Büttner, P.; Landgraf, K.; Kiess, W.; Körner, A. Impact of metabolic reg-ulators on the expression of the obesity associated genes fto and nampt in human preadipocytes and adipocytes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravard, A.; Lefai, E.; Meugnier, E.; Pesenti, S.; Disse, E.; Vouillarmet, J.; Peretti, N.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Laville, M.; Vidal, H.; et al. FTO Is Increased in Muscle During Type 2 Diabetes, and Its Overexpression in Myotubes Alters Insulin Signaling, Enhances Lipogenesis and ROS Production, and Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Diabetes 2010, 60, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerken, T.; Girard, C.A.; Loraine Tung, Y.-C.; Webby, C.J.; Saudek, V.; Hewitson, K.S.; Yeo, G.S.H.; McDonough, M.A.; Cunliffe, S.; McNeill, L.A.; et al. The obesity-associated fto gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science 2007, 318, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratigopoulos, G.; Padilla, S.L.; LeDuc, C.A.; Watson, E.; Hattersley, A.T.; McCarthy, M.I.; Zeltser, L.M.; Chung, W.K.; Leibel, R.L. Regulation of Fto/Ftm gene expression in mice and humans. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 294, R1185–R1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, G.; Yong-Hyun, S.; Min, L.; Fei, W.; Qiang, T.; Zhang, P.; Krisztian, S. The fat mass and obesity associated gene fto functions in the brain to regulate postnatal growth in mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14005. [Google Scholar]
- Cusi, K.; Maezono, K.; Osman, A.; Pendergrass, M.; Patti, M.E.; Pratipanawatr, T.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Kahn, C.R.; Mandarino, L.J. Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase– and MAP kinase–mediated signaling in human muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T. Insights into insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes from knockout mouse models. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, J.; Yin, J.; Gu, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Huang, Q.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Identification of a Novel Function of Adipocyte Plasma Membrane-Associated Protein (APMAP) in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Proteomic Analysis of Omental Adipose Tissue. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dominissini, D.; Rechavi, G.; He, C. Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Roundtree, I.A.; Tempel, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; He, C.; Min, J. Structural basis for selective binding of m6A RNA by the YTHDC1 YTH domain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P.J.; Liu, C.; He, C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; He, C. N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger rna translation efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Yao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Cai, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Epigallocatechin gallate targets FTO and inhibits adipogenesis in an mRNA m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, C. Activins in adipogenesis and obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 37, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.; Hacohen, N.; Golub, T.R.; Van Parijs, L.; Lodish, H.F. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Suppresses Adipocyte-Specific Genes and Activates Expression of Preadipocyte Genes in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1319–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Lodish, H.F. Insulin resistance in adipose tissue: Direct and indirect effects of tumor necrosis factor-α. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003, 14, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, K.; Usui, I.; Kanatani, Y.; Bukhari, A.; He, J.; Fujisaka, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Hiratani, K.; Ishiki, M.; et al. Chronic Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Treatment Causes Insulin Resistance via Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Serine Phosphorylation and Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling-3 Induction in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 2994–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrone, G.; Rosa, G.; Greco, A.; Manco, M.; Vega, N.; Nanni, G.; Castagneto, M.; Vidal, H. Intramyocitic lipid accumulation and SREBP-1c expression are related to insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk in morbid obesity. Atherosclerosis 2003, 170, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, A. Adipocyte insensitivity syndromes – novel approach to nutritional metabolic problems including obesity and obesity related disorders. Med Hypotheses 2005, 64, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Witkowski, A.; Joshi, A.K. Structural and functional organization of the animal fatty acid synthase. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenkovich, C.F. Regulation of fatty acid synthase (FAS). Prog. Lipid Res. 1997, 36, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Wang, L.; Hu, S.; Du, K.; Wang, J.; Lai, S. Association of leptin mRNA expression with meat quality trait in Tianfu black rabbits. Anim. Biotechnol. 2020, 33, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | (Tm/°C) | CG% | (Product Size/bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTO | ATCCCGATCTCTCACCACAC | 60 | 55 | 183 |
| ACATCTGCGGACCATACAAA | 45 | |||
| YTHDF2 | CAGACACAGCCATTGCCTCCAC | 60 | 59 | 122 |
| CCGTTATGACCGAACCCACTGC | 59 | |||
| APMAP | GCTGCTGGATTCTCCCATAG | 60 | 55 | 163 |
| AAACATCACGTCCCCGATAT | 45 | |||
| PPARγ | GAGGACATCCAGGACAACC | 61 | 58 | 168 |
| GTCCGTCTCCGTCTTCTTT | 53 | |||
| β-actin | GGAGATCGTGCGGGACAT | 61.4 | 61 | 318 |
| GTTGAAGGTGGTCTCGTGGAT | 52 | |||
| C/EBPα | GCGGGAACGAACAACAT | 64 | 53 | 172 |
| GGCGGTCATTGTCACTGGTC | 6 | |||
| FABP4 | GGCCAGGAATTTGATGAAGTC | 61.4 | 48 | 140 |
| AGTTTATCGCCCTCCCGTT | 53 | |||
| si-YTHDF2 | CAUGAAUACUAUAGACCAATT | 29 | ||
| UUGGUCUAUAGUAUUCAUGTT | 29 | |||
| si-FTO | GCAGCUGAAAUAUCCUAAATT | 33 | ||
| UUUAGGAUAUUUCAGCUGCTT | 33 | |||
| si-APMAP | GUGGAAAGGCUAUUUGAAATT | 33 | ||
| UUUCAAAUAGCCUUUCCACTT | 33 | |||
| over-FTO | GCTAGCGCCACCATGAAGC | 63 | ||
| CTCGAGCTAAGGCTTTGCTTCC | 55 | |||
| Negative Control | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT | 48 | ||
| ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT | 48 |
| Model | Coefficient | Std Error | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.0001347 | 0.0199996 | 0.99472 |
| APMAP Expression in longissimus lumborum | 0.0007015 | 0.0001804 | 0.00164 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, G.; Hong, T.; Yu, L.; Ren, Z. FTO Regulated Intramuscular Fat by Targeting APMAP Gene via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent Manner in Rex Rabbits. Cells 2023, 12, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030369
Luo G, Hong T, Yu L, Ren Z. FTO Regulated Intramuscular Fat by Targeting APMAP Gene via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent Manner in Rex Rabbits. Cells. 2023; 12(3):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030369
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Gang, Tingting Hong, Lin Yu, and Zhanjun Ren. 2023. "FTO Regulated Intramuscular Fat by Targeting APMAP Gene via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent Manner in Rex Rabbits" Cells 12, no. 3: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030369
APA StyleLuo, G., Hong, T., Yu, L., & Ren, Z. (2023). FTO Regulated Intramuscular Fat by Targeting APMAP Gene via an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent Manner in Rex Rabbits. Cells, 12(3), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030369






