The Role of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
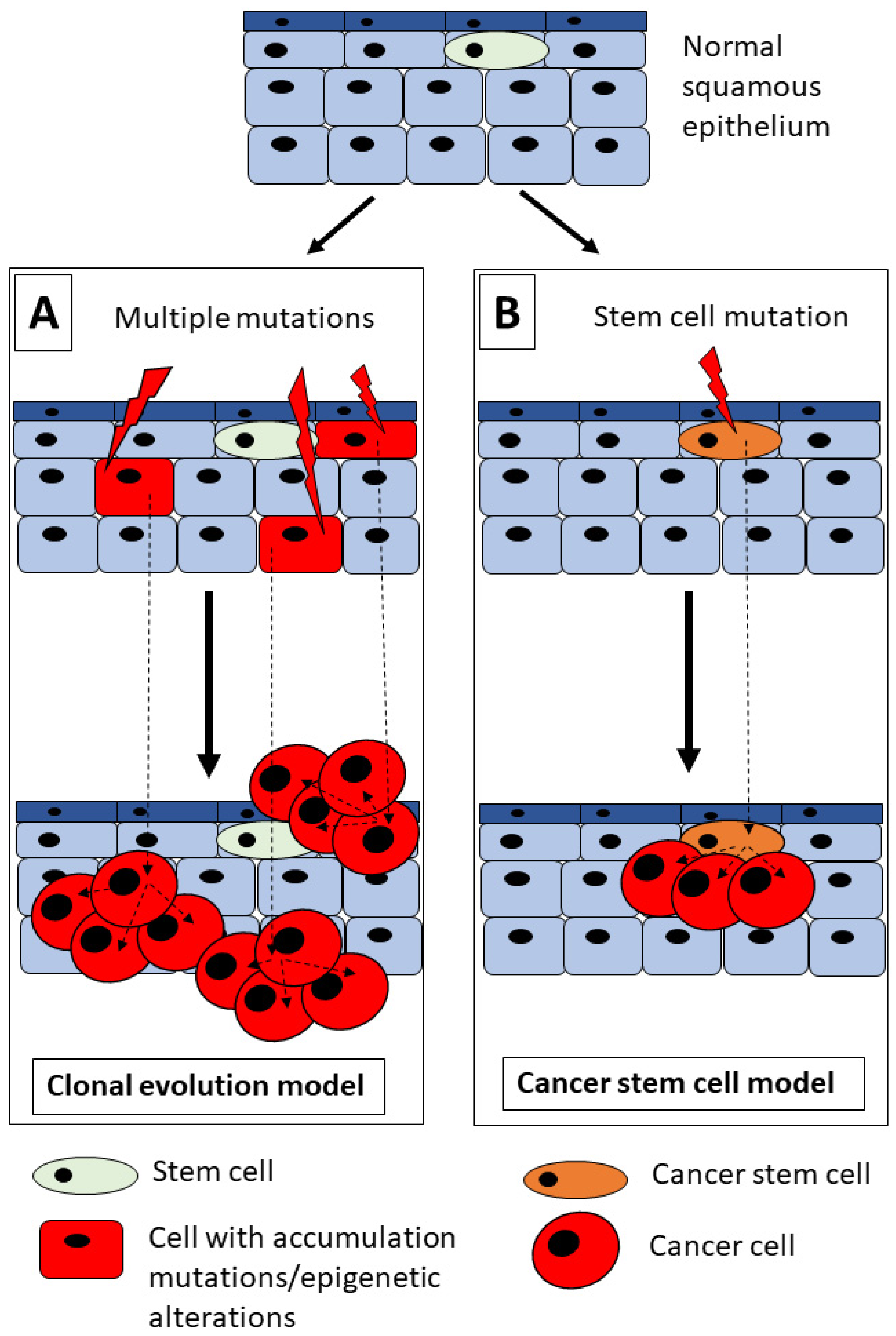
2. HNSCC and Tumorigenesis Model
3. The HH Signaling Pathway
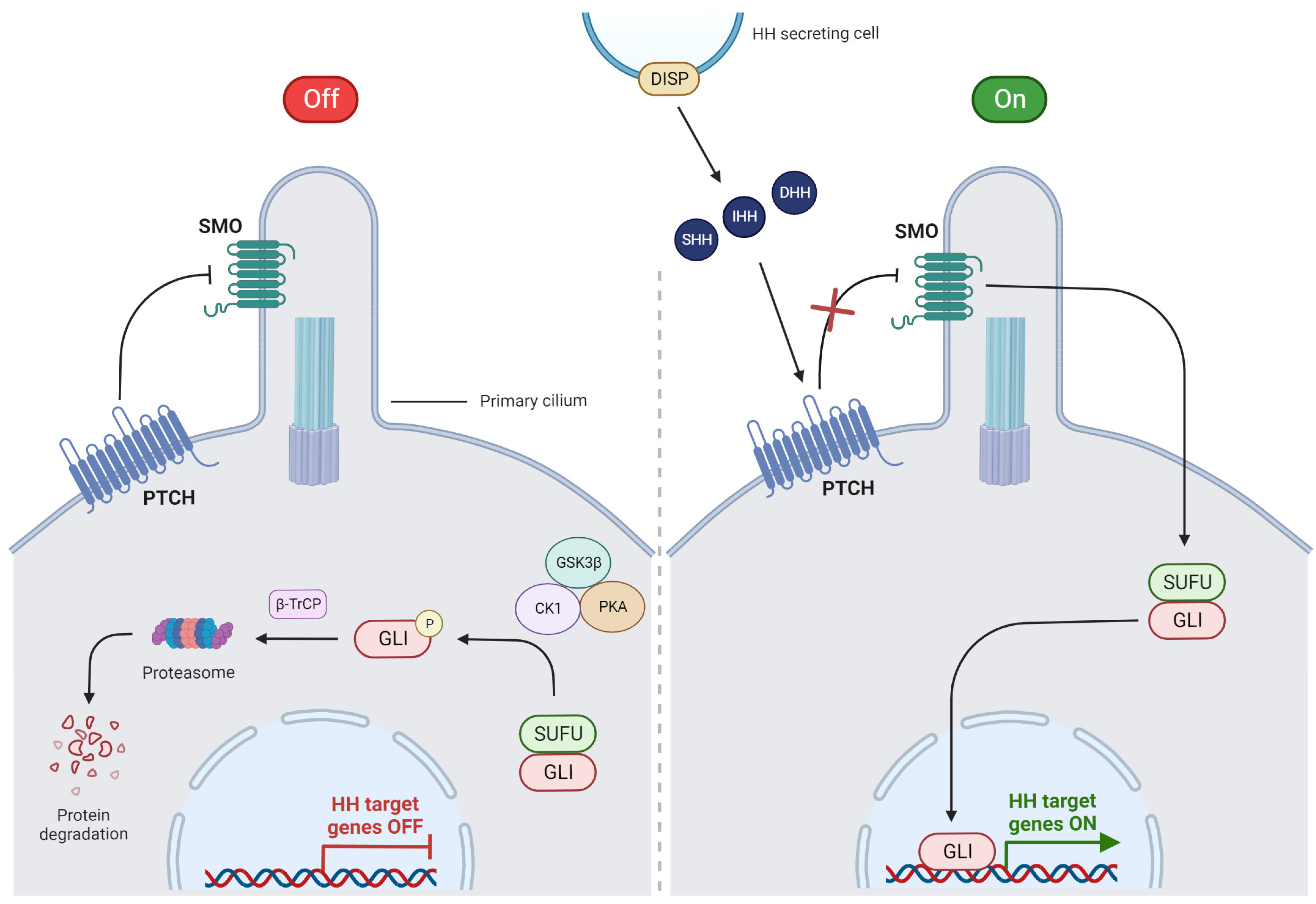
3.1. Overview of HH Signaling
3.2. Canonical Pathway
3.3. Non-Canonical Pathway
4. HH Pathway in Head and Neck Tissue Formation
5. Aberration of HH Signaling Pathway in HNSCC
| HH Protein Overexpression | Clinical Findings | Author, Year, Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SHH | Worse OS | Schneider et al., 2011 [50] |
| Lymph node metastasis | Fan et al., 2014 [60] | |
| Advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, tumor recurrence | Huaitong et al., 2017 [54] | |
| Worse OS, shorter DFS | Noman et al., 2020 [67] | |
| Lower pT stage | Lu et al., 2020 [58] | |
| Poor prognosis, worse OS, advanced pT stage | Cierpikowski et al., 2021 [57] | |
| PTCH1 | Lymph node metastasis, worse OS | Wang et al., 2012 [59] |
| Higher tumor grade | Leovic et al., 2012 [66] | |
| Advanced pT stage, tumor grade | Lu et al., 2020 [58] | |
| SMO | Lower clinical stage | Cavicchioli Buim et al., 2011 [70] |
| Worse OS, shorter DFS | Richtig et al., 2019 [68] | |
| Advanced pT stage, higher tumor grade | Lu et al., 2020 [58] | |
| Lymph node metastasis | Schlaepfer Sales et al., 2021 [64] | |
| GLI1 | Poor prognosis, regional–distant metastasis | Chung et al., 2011 [71] |
| Larger tumor size, tumor recurrence, lymph node metastasis, worse OS | Wang et al., 2012 [59] | |
| Lower tumor grade | Leovic et al., 2012 [66] | |
| Advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, worse OS | Fan et al., 2014 [60] | |
| Better OS | Enzenhofer et al., 2016 [69] | |
| Advanced clinical stage, lymph node metastasis, tumor recurrence | Huaitong et al., 2017 [54] | |
| Lymph node metastasis, higher tumor grade | Chen et al., 2018 [55] | |
| Advanced clinical stage | Dantas et al., 2021 [61] | |
| GLI2 | Better OS, longer DFS | Enzenhofer et al., 2016 [69] |
| Advanced clinical stage, higher tumor grade | Chen et al., 2018 [55] | |
| GLI3 | Advanced pT stage | Rodrigues et al., 2018 [56] |
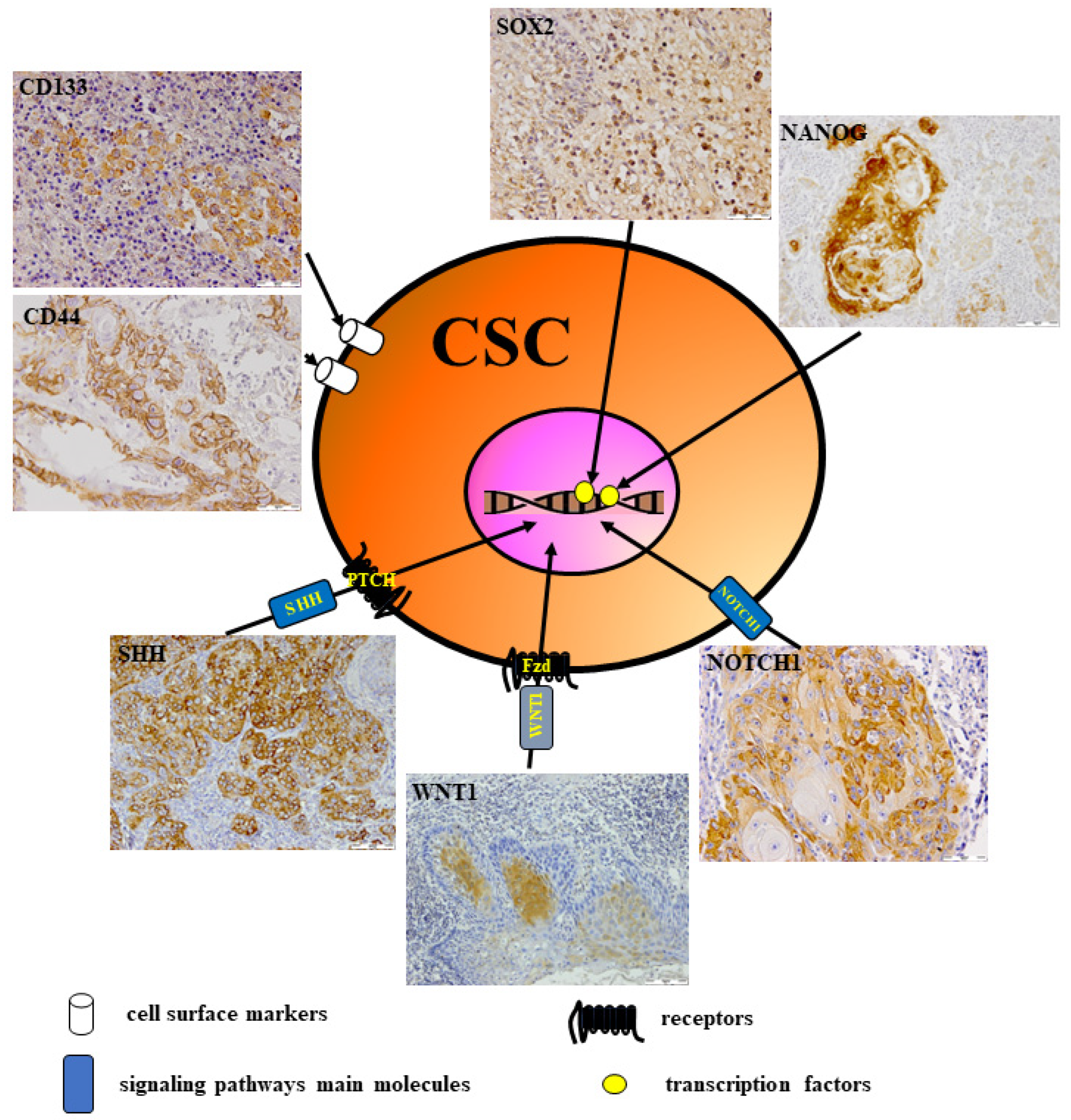
6. CSCs in Head and Neck Cancer
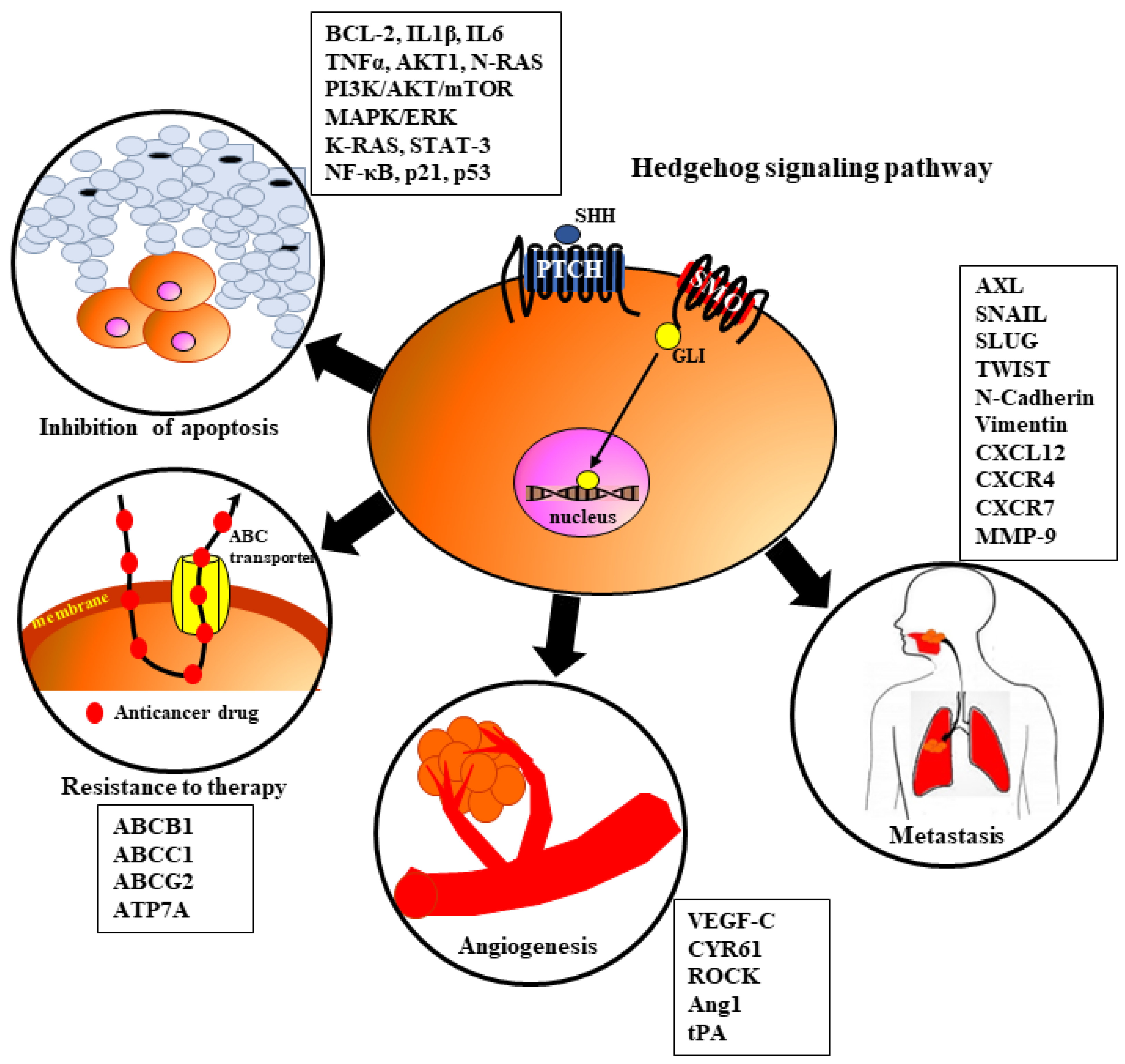
7. The Role of HH Signaling in HNSCC Tumorigenesis
7.1. Angiogenesis
7.2. Metastasis
7.3. Resistance to Therapy
7.4. Inhibition of Apoptosis
8. The HH Signaling and Viral Infections
9. Crosstalk between HH Signaling and Other Pathways
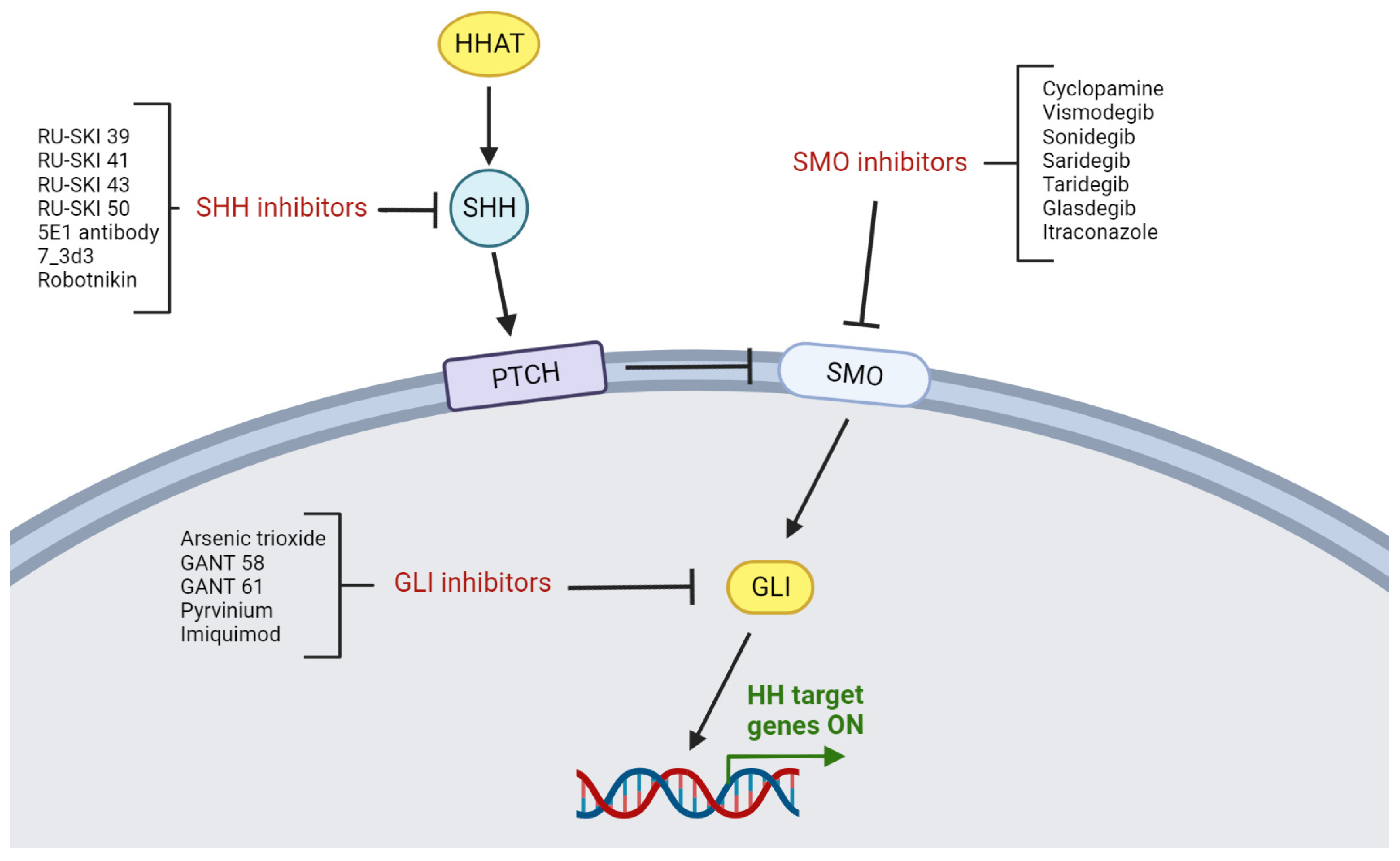
10. Targeting the HH Pathway in HNSCC
10.1. Characterization of HH Inhibition
10.2. SHH Inhibitors
10.3. SMO Inhibitors
10.4. GLI Inhibitors
11. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.E.; Burtness, B.; Leemans, C.R.; Lui, V.W.Y.; Bauman, J.E.; Grandis, J.R. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, M.N.; Faísca, P.; Ferreira, H.A.; Gaspar, M.M.; Reis, C.P. Current Insights and Progress in the Clinical Management of Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 6079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; Mazul, A.L.; Farquhar, D.; Brennan, P.; Anantharaman, D.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Weissler, M.C.; Hayes, D.N.; Olshan, A.F.; Zevallos, J.P. Long-Term Survival in Head and Neck Cancer: Impact of Site, Stage, Smoking, and Human Papillomavirus Status. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, B.; Tiwari, A.K.; Pandey, R.K.; Singh, A.P.; Kumar, S.; Sinha, A.; Jain, S.K.; Khattri, A. Therapeutic Approaches for the Treatment of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma–An Update on Clinical Trials. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 21, 101426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y. Molecular Targeted Therapy for Anticancer Treatment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1670–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baniebrahimi, G.; Mir, F.; Khanmohammadi, R. Cancer Stem Cells and Oral Cancer: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Approaches. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Alikhani, M.; Yazdanian, A.; Yazdanian, M.; Tebyanian, H.; Seifalian, A. The Current Markers of Cancer Stem Cell in Oral Cancers. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nüsslein-Volhard, C.; Wieschaus, E. Mutations Affecting Segment Number and Polarity in Drosophila. Nature 1980, 287, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J. Hedgehog Signaling Mechanism and Role in Cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.; Cho, J. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors as Targeted Cancer Therapy and Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouban, A. SALL4 Stemness Agent Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Cancer and Its Clinical Significance. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Clevers, H. Cancer Stem Cells Revisited. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, C.-Y. Targeting Cancer Stem Cells in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Precis. Clin. Med. 2019, 2, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.Y.; Seo, D. Cancer Stem Cells: Biological Features and Targeted Therapeutics. Hanyang Med. Rev. 2015, 35, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, P.C. The Clonal Evolution of Tumor Cell Populations. Science 1976, 194, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, S.R.; Dahler, A.L.; Endo-Munoz, L.B.; Jabbar, I.; Thomas, G.P.; Leo, P.J.; Poth, K.; Rickwood, D.; Guminski, A.; Saunders, N.A. Tumor-Initiating Activity and Tumor Morphology of HNSCC Is Modulated by Interactions between Clonal Variants within the Tumor. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchardt, T.; Magnes, T.; Hufnagl, C.; Thorner, A.R.; Ducar, M.; Neureiter, D.; Tränkenschuh, W.; Klieser, E.; Gaggl, A.; Rösch, S.; et al. Clonal Evolution and Heterogeneity in Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer-An Analysis of the Austrian Study Group of Medical Tumour Therapy Study Group. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 93, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Sánchez, A.; Suárez-Martínez, E.; Sánchez-Díaz, L.; Carnero, A. Therapeutic Targeting of Signaling Pathways Related to Cancer Stemness. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreso, A.; Dick, J.E. Evolution of the Cancer Stem Cell Model. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarstefano, V.; Belloni, A.; Sabbatini, S.; Pro, C.; Orilisi, G.; Monterubbianesi, R.; Tosco, V.; Byrne, H.J.; Vaccari, L.; Giorgini, E. Cytotoxic Effects of 5-Azacytidine on Primary Tumour Cells and Cancer Stem Cells from Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An In Vitro FTIRM Analysis. Cells 2021, 10, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doheny, D.; Manore, S.G.; Wong, G.L.; Lo, H.-W. Hedgehog Signaling and Truncated GLI1 in Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoda, A.M.; Simovic, D.; Karin, V.; Kardum, V.; Vranic, S.; Serman, L. The Role of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, R.; Joyner, A.L. Roles for Hedgehog Signaling in Adult Organ Homeostasis and Repair. Development 2014, 141, 3445–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Pathways for Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patni, A.P.; Harishankar, M.K.; Joseph, J.P.; Sreeshma, B.; Jayaraj, R.; Devi, A. Comprehending the Crosstalk between Notch, Wnt and Hedgehog Signaling Pathways in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma—Clinical Implications. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, A.; Silvano, M.; Miele, E.; Capalbo, C.; Eramo, A.; Salvati, V.; Todaro, M.; Besharat, Z.M.; Catanzaro, G.; Cucchi, D.; et al. Noncanonical GLI1 Signaling Promotes Stemness Features and in Vivo Growth in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4641–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niyaz, M.; Khan, M.S.; Mudassar, S. Hedgehog Signaling: An Achilles’ Heel in Cancer. Transl. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, D.; Barrichello, A.; Fernandes, G.; Pereira, A. Targeting the Hedgehog Pathway in Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Cells 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, I.; Roa, J.C. Activated Status of Hedgehog Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): The Door Is Still Open. Transl. Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, W.H. Cancer Stem Cell Signaling Pathways. Medicine 2016, 95, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, A.; Shalehin, N.; Takebe, H.; Shimo, T.; Irie, K. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling and Tooth Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramyan, J. Hedgehog Signaling and Embryonic Craniofacial Disorders. J. Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Hao, X.; Bao, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Y.; Peng, L.; Huang, H.; Ding, Y.; et al. A392V and R945X Mutations Cause Orofacial Clefts via Impairing PTCH1 Function. Genomics 2022, 114, 110507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaka, H. The Roles of Hedgehog Signaling in Upper Lip Formation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 901041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyne, G.W.; Melberg, C.G.; Doroodchi, P.; Parins, K.F.; Kietzman, H.W.; Everson, J.L.; Ansen-Wilson, L.J.; Lipinski, R.J. Definition of Critical Periods for Hedgehog Pathway Antagonist-Induced Holoprosencephaly, Cleft Lip, and Cleft Palate. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppala, M.; Fraser, G.J.; Birjandi, A.A.; Xavier, G.M.; Cobourne, M.T. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling and Development of the Dentition. J. Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Panda, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Kumar, H.; Mohiddin, G. Sonic Hedgehog Signalling Pathway and Ameloblastoma—A Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, ZE10–ZE13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, C.A.S.; Buim, M.E.C.; Carvalho, K.C.; Sales, C.B.S.; Reis, M.G.; de Souza, R.O.; de Faro Valverde, L.; de Azevedo, R.A.; Dos Santos, J.N.; Soares, F.A.; et al. Transcriptional Profiles of SHH Pathway Genes in Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor and Ameloblastoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2014, 43, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, K.S.; Santos, H.B.d.P.; de Morais, E.F.; Freitas, R.d.A. Immunohistochemical Analysis of SHH, SMO and GLI-1 Proteins in Epithelial Odontogenic Lesions. Braz. Dent. J. 2022, 33, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Hong, Y.; Qu, J.; Chen, F.; Li, T. Effect of the Sonic Hedgehog Inhibitor GDC-0449 on an in Vitro Isogenic Cellular Model Simulating Odontogenic Keratocysts. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, N.; Naruto, T.; Kohmoto, T.; Komori, T.; Imoto, I. A Novel PTCH1 Mutation in a Patient with Gorlin Syndrome. Hum. Genome Var. 2014, 1, 14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, H.; Wicking, C.; Zaphiropoulous, P.G.; Gailani, M.R.; Shanley, S.; Chidambaram, A.; Vorechovsky, I.; Holmberg, E.; Unden, A.B.; Gillies, S.; et al. Mutations of the Human Homolog of Drosophila Patched in the Nevoid Basal Cell Carcinoma Syndrome. Cell 1996, 85, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.L.; Rothman, A.L.; Xie, J.; Goodrich, L.V.; Bare, J.W.; Bonifas, J.M.; Quinn, A.G.; Myers, R.M.; Cox, D.R.; Epstein, E.H.; et al. Human Homolog of Patched, a Candidate Gene for the Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome. Science 1996, 272, 1668–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampala, S.; Yang, J.-Y. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors against Tumor Microenvironment. Cells 2021, 10, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Tang, H.; Xiao, Q.; He, M.; Zhao, L.; Fu, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Yan, Y.; et al. The Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Breast Cancer Patients with the CD44+/CD24− Phenotype. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 5261–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.-H. Sonic Hedgehog Pathway as the Prognostic Marker in Patients with Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian-Hui, C.; Er-Tao, Z.; Si-Le, C.; Hui, W.; Kai-Ming, W.; Xin-Hua, Z.; Chuang-Qi, C.; Shi-Rong, C.; Yu-Long, H. CD44, Sonic Hedgehog, and Gli1 Expression Are Prognostic Biomarkers in Gastric Cancer Patients after Radical Resection. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 1013045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Xuan, Y. Gli1, a Potential Cancer Stem Cell Marker, Is Strongly Associated with Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4957–4966. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.; Niu, M.; Xie, P.; Yue, C.; Liu, N.; Qi, Z.; Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Shi, Q.; Yu, R.; et al. Smoothened Is a Poor Prognosis Factor and a Potential Therapeutic Target in Glioma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Thurnher, D.; Kloimstein, P.; Leitner, V.; Petzelbauer, P.; Pammer, J.; Brunner, M.; Erovic, B.M. Expression of the Sonic Hedgehog Pathway in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin and the Mucosa of the Head and Neck. Head Neck 2011, 33, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinath, S.; Iyengar, A.R.; Mysorekar, V. Sonic Hedgehog in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Immunohistochemical Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2016, 20, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrova, K.; Stoehr, M.; Dehghani, F.; Dietz, A.; Wichmann, G.; Bertolini, J.; Mozet, C. Overexpression of the Hedgehog Signalling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Onkologie 2013, 36, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, A.C.; Ferreira, M.; Ariel, T.; Reis, S.R.; Andrade, Z.; Peixoto Medrado, A. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Hedgehog Signalling in Epithelial/Mesenchymal Interactions in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Transformation: A Pilot Study. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huaitong, X.; Yuanyong, F.; Yueqin, T.; Peng, Z.; Wei, S.; Kai, S. Microvesicles Releasing by Oral Cancer Cells Enhance Endothelial Cell Angiogenesis via Shh/RhoA Signaling Pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yan, M.; Li, R.R.; Chen, W.T. Sonic Hedgehog Signalling Activation Contributes to ALCAM Over-Expression and Poor Clinical Outcome in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.F.S.D.; Miguita, L.; De Andrade, N.P.; Heguedusch, D.; Rodini, C.O.; Moyses, R.A.; Toporcov, T.N.; Gama, R.R.; Tajara, E.E.; Nunes, F.D. GLI3 Knockdown Decreases Stemness, Cell Proliferation and Invasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 2458–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cierpikowski, P.; Lis-Nawara, A.; Bar, J. Sonic Hedgehog Is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Neoplasma 2021, 68, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, H. Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Multidrug Resistance by Regulation of ABC Transporters in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-P.; Chang, S.-Y.; Chu, P.-Y.; Tai, S.-K.; Li, W.-Y.; Chao, K.S.C.; Chen, Y.-J. Expression of Hedgehog Signaling Molecules as a Prognostic Indicator of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Liu, N.; Chen, D.; Sun, M.; Zheng, J.-H. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling May Promote Invasion and Metastasis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Activating MMP-9 and E-Cadherin Expression. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, R.C.M.; Guimarães, V.S.N.; de Souza, R.O.; Valverde, L.F.; Vidal, M.T.A.; Nogueira, R.L.R.; da Rocha, L.O.S.; Araújo, G.T.; Dos Santos, J.N.; Rocha, C.A.G. Immunodetection of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Tumor Proliferation Markers in GLi-1-Positive Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honami, T.; Shimo, T.; Okui, T.; Kurio, N.; Hassan, N.M.M.; Iwamoto, M.; Sasaki, A. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Growth of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Associated with Bone Destruction. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhao, N.; Pu, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Guo, C. Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor 1α Promotes Osteolytic Lesion of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by SHH-Dependent Osteoclastogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 1639–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, C.B.S.; Guimarães, V.S.; Valverde, L.F.; Dias, R.B.; Freitas, R.D.; Rocha, L.d.O.S.d.; de Miranda, M.C.; Bôas, D.S.V.; Agra, I.M.G.; dos Santos, J.N.; et al. Glypican-1, -3, -5 (GPC1, GPC3, GPC5) and Hedgehog Pathway Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2021, 29, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluszczak, J.; Wiśniewska, D.; Kostrzewska-Poczekaj, M.; Kiwerska, K.; Grénman, R.; Mielcarek-Kuchta, D.; Jarmuż-Szymczak, M. Prognostic Significance of the Methylation of Wnt Pathway Antagonists-CXXC4, DACT2, and the Inhibitors of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling-ZIC1, ZIC4, and HHIP in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leovic, D.; Sabol, M.; Ozretic, P.; Musani, V.; Car, D.; Marjanovic, K.; Zubcic, V.; Sabol, I.; Sikora, M.; Grce, M.; et al. Hh-Gli Signaling Pathway Activity in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.S.M.; Parag, R.R.; Rashid, M.I.; Rahman, M.Z.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Sultana, A.; Jerin, C.; Siddiqua, A.; Rahman, L.; Shirin, A.; et al. Widespread Expression of Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) and Nrf2 in Patients Treated with Cisplatin Predicts Outcome in Resected Tumors and Are Potential Therapeutic Targets for HPV-Negative Head and Neck Cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920911229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richtig, G.; Aigelsreiter, A.M.; Asslaber, M.; Weiland, T.; Pichler, M.; Eberhard, K.; Sygulla, S.; Schauer, S.; Hoefler, G.; Aigelsreiter, A. Hedgehog Pathway Proteins SMO and GLI Expression as Prognostic Markers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Histopathology 2019, 75, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzenhofer, E.; Parzefall, T.; Haymerle, G.; Schneider, S.; Kadletz, L.; Heiduschka, G.; Pammer, J.; Oberndorfer, F.; Wrba, F.; Loader, B.; et al. Impact of Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Expression on Outcome in HPV Negative Head and Neck Carcinoma Patients after Surgery and Adjuvant Radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli Buim, M.E.; Gurgel, C.A.S.; Gonçalves Ramos, E.A.; Lourenço, S.V.; Soares, F.A. Activation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas: A Preliminary Study. Hum. Pathol. 2011, 42, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.H.; Dignam, J.J.; Hammond, M.E.; Klimowicz, A.C.; Petrillo, S.K.; Magliocco, A.; Jordan, R.; Trotti, A.; Spencer, S.; Cooper, J.S.; et al. Glioma-Associated Oncogene Family Zinc Finger 1 Expression and Metastasis in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Radiation Therapy (RTOG 9003). J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peitzsch, C.; Nathansen, J.; Schniewind, S.I.; Schwarz, F.; Dubrovska, A. Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Identification, Characterization and Clinical Implications. Cancers 2019, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, C.; Uchida, D.; Kawamata, H. Diversity of the Origin of Cancer Stem Cells in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Its Clinical Implications. Cancers 2022, 14, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peitzsch, C.; Kurth, I.; Ebert, N.; Dubrovska, A.; Baumann, M. Cancer Stem Cells in Radiation Response: Current Views and Future Perspectives in Radiation Oncology. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Is Organized as a Hierarchy That Originates from a Primitive Hematopoietic Cell. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, M.E.; Sivanandan, R.; Kaczorowski, A.; Wolf, G.T.; Kaplan, M.J.; Dalerba, P.; Weissman, I.L.; Clarke, M.F.; Ailles, L.E. Identification of a Subpopulation of Cells with Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvader, J.E.; Lindeman, G.J. Cancer Stem Cells: Current Status and Evolving Complexities. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisis, V.; Venou, M.; Poulopoulos, A.; Andreadis, D. Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Treatment Modalities. Balk. J. Dent. Med. 2021, 25, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heft Neal, M.E.; Brenner, J.C.; Prince, M.E.P.; Chinn, S.B. Advancement in Cancer Stem Cell Biology and Precision Medicine-Review Article Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cell Plasticity and the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 660210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltenyi, S.; Müller, W.; Weichel, W.; Radbruch, A. High Gradient Magnetic Cell Separation with MACS. Cytometry 1990, 11, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseb, H.O.; Fohrer-Ting, H.; Lewis, D.W.; Lagasse, E.; Gollin, S.M. Identification, Expansion and Characterization of Cancer Cells with Stem Cell Properties from Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 348, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Fang, F.; Liu, S.; Liao, X.; Tao, S.; Mai, H. Characterisation of a Subpopulation of CD133 + Cancer Stem Cells from Chinese Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picon, H.; Guddati, A.K. Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Cancer. Am. J. Stem Cells 2021, 10, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Wynter, E.A.; Coutinho, L.H.; Pei, X.; Marsh, J.C.; Hows, J.; Luft, T.; Testa, N.G. Comparison of Purity and Enrichment of CD34+ Cells from Bone Marrow, Umbilical Cord and Peripheral Blood (Primed for Apheresis) Using Five Separation Systems. Stem Cells 1995, 13, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, A.; Yan, Y.; Gerson, S.L. Concise Reviews: Cancer Stem Cell Targeted Therapies: Toward Clinical Success. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.W.; Earle, C.; Shiina, M. Activation of Matrix Hyaluronan-Mediated CD44 Signaling, Epigenetic Regulation and Chemoresistance in Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.S.; Cirillo, N. The Molecular Markers of Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Tumors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierpikowski, P.; Lis-Nawara, A.; Bar, J. SHH Expression Is Significantly Associated With Cancer Stem Cell Markers in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 5405–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierpikowski, P.; Lis-Nawara, A.; Bar, J. Prognostic Value of WNT1, NOTCH1, PDGFRβ, and CXCR4 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2023, 43, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcher, L.; Kistenmacher, A.-K.; Suo, H.; Kitte, R.; Dluczek, S.; Strauß, A.; Blaudszun, A.-R.; Yevsa, T.; Fricke, S.; Kossatz-Boehlert, U. Cancer Stem Cells-Origins and Biomarkers: Perspectives for Targeted Personalized Therapies. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberg, M.; Götz, C.; Haidari, S.; Dorfner, C.; Jesinghaus, M.; Drecoll, E.; Boskov, M.; Wolff, K.D.; Weichert, W.; Haller, B.; et al. Immunohistochemical Expression of CD44 in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Relation to Histomorphological Parameters and Clinicopathological Factors. Histopathology 2018, 73, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, P.; Gupta, R.; Mishra, A.; Kumar, V.; Bhadauria, S.; Bhatt, M.L.B. Evaluation of Correlation between CD44, Radiotherapy Response, and Survival Rate in Patients with Advanced Stage of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakob, M.; Sharaf, K.; Schirmer, M.; Leu, M.; Küffer, S.; Bertlich, M.; Ihler, F.; Haubner, F.; Canis, M.; Kitz, J. Role of Cancer Stem Cell Markers ALDH1, BCL11B, BMI-1, and CD44 in the Prognosis of Advanced HNSCC. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2021, 197, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerer, R.M.; Ludwig, N.; Kampmann, A.; Bittermann, G.; Spalthoff, S.; Jungheim, M.; Gellrich, N.-C.; Tavassol, F. CD24+ Tumor-Initiating Cells from Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Induce Initial Angiogenesis in Vivo. Microvasc. Res. 2017, 112, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, L.-L.; Hu, F.-W.; Lee, S.-S.; Yu, C.-H.; Yu, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-C. Oct4 Mediates Tumor Initiating Properties in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas through the Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modur, V.; Joshi, P.; Nie, D.; Robbins, K.T.; Khan, A.U.; Rao, K. CD24 Expression May Play a Role as a Predictive Indicator and a Modulator of Cisplatin Treatment Response in Head and Neck Squamous Cellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Gao, W.; Li, F.; Bo, Y.; Zhu, M.; Fu, R.; Liu, Q.; Wen, S.; Wang, B. Identification and Characterization of CD133+CD44+ Cancer Stem Cells from Human Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahoumi, L.A. Oral Cancer Stem Cells: Therapeutic Implications and Challenges. Front. Oral Health 2021, 2, 685236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Hoque, M.O. Targeting Cancer Stem Cells: A Strategy for Effective Eradication of Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiani, M.; Schöler, H.R. Regulatory Networks in Embryo-Derived Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.H.; Jung, H.R.; Jung, A.R.; Lee, Y.C.; Kong, M.; Lee, J.-S.; Eun, Y.-G. SOX2 Activation Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.-Y.; Hsieh, I.-C.; Cheng, J.-T.; Tsai, M.-H.; Hou, Y.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Liou, H.-H.; Huang, S.-F.; Chen, H.-C.; Yen, L.-M.; et al. Association of OCT4, SOX2, and NANOG Expression with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Xia, J. Prognostic Value of Cancer Stem Cell Markers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.-H.; Kim, R.H. An Updated Review of Oral Cancer Stem Cells and Their Stemness Regulation. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2018, 23, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmeera, D.; Ajumeera, R. Drug Repurposing: A Novel Strategy to Target Cancer Stem Cells and Therapeutic Resistance. Genes Dis. 2023, 11, 148–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tang, T.; Eastham-Anderson, J.; Dunlap, D.; Alicke, B.; Nannini, M.; Gould, S.; Yauch, R.; Modrusan, Z.; DuPree, K.J.; et al. Canonical Hedgehog Signaling Augments Tumor Angiogenesis by Induction of VEGF-A in Stromal Perivascular Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, K.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Davidson, C.J.; Gopinathan, A.; McIntyre, D.; Honess, D.; Madhu, B.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Caldwell, M.E.; Allard, D.; et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog Signaling Enhances Delivery of Chemotherapy in a Mouse Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Science 2009, 324, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Tao, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, D. Role of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in the Chemoresistance Modulation of Colorectal Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9390878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.Y.; Sugumar, V.; Alshanon, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Fung, S.Y.; Looi, C.Y. Defining the Role of GLI/Hedgehog Signaling in Chemoresistance: Implications in Therapeutic Approaches. Cancers 2021, 13, 4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.; Fritz, S.; Bolm, L.; Wellner, U.F.; Fernandez-Del-Castillo, C.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P.; Liss, A.S. Hedgehog Signaling Promotes Angiogenesis Directly and Indirectly in Pancreatic Cancer. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makena, M.R.; Ranjan, A.; Thirumala, V.; Reddy, A.P. Cancer Stem Cells: Road to Therapeutic Resistance and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, D.M.; Karhadkar, S.S.; Maitra, A.; Montes De Oca, R.; Gerstenblith, M.R.; Briggs, K.; Parker, A.R.; Shimada, Y.; Eshleman, J.R.; Watkins, D.N.; et al. Widespread Requirement for Hedgehog Ligand Stimulation in Growth of Digestive Tract Tumours. Nature 2003, 425, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzobo, K.; Senthebane, D.A.; Ganz, C.; Thomford, N.E.; Wonkam, A.; Dandara, C. Advances in Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells within the Tumor Microenvironment: An Updated Review. Cells 2020, 9, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor Angiogenesis: Causes, Consequences, Challenges and Opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciuti, B.; Foglietta, J.; Bianconi, V.; Sahebkar, A.; Pirro, M. Enzymes Involved in Tumor-Driven Angiogenesis: A Valuable Target for Anticancer Therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 56, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, K.-S.; Chang, C.-F.; Lin, S.-S. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Organogenesis, Tumors, and Tumor Microenvironments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabatake, K.; Shimo, T.; Murakami, J.; Anqi, C.; Kawai, H.; Yoshida, S.; Wathone Oo, M.; Haruka, O.; Sukegawa, S.; Tsujigiwa, H.; et al. The Role of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapouly, C.; Guimbal, S.; Hollier, P.-L.; Renault, M.-A. Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Vasculature Development, Differentiation, and Maintenance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepicelli, C.V.; Lewis, P.M.; McMahon, A.P. Sonic Hedgehog Regulates Branching Morphogenesis in the Mammalian Lung. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Cuneo, K.C.; Cooper, M.K.; Wang, H.; Sekhar, K.; Fu, A.; Hallahan, D.E. Hedgehog Signaling in the Murine Melanoma Microenvironment. Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Renault, M.-A.; Chapouly, C.; Vandierdonck, S.; Belloc, I.; Jaspard-Vinassa, B.; Daniel-Lamazière, J.-M.; Laffargue, M.; Merched, A.; Desgranges, C.; et al. Sonic Hedgehog Mediates a Novel Pathway of PDGF-BB-Dependent Vessel Maturation. Blood 2014, 123, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, R.; Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Ma, X. The Role of Hedgehog and Notch Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iriana, S.; Asha, K.; Repak, M.; Sharma-Walia, N. Hedgehog Signaling: Implications in Cancers and Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, H.; Kurio, N.; Shimo, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Masui, M.; Takabatake, K.; Okui, T.; Ibaragi, S.; Kunisada, Y.; Obata, K.; et al. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma-Derived Sonic Hedgehog Promotes Angiogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6731–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, V.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, Y.-G. Hhip Regulates Tumor-Stroma-Mediated Upregulation of Tumor Angiogenesis. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Carpenter, R.L.; Han, W.; Lo, H.-W. The GLI1 Splice Variant TGLI1 Promotes Glioblastoma Angiogenesis and Growth. Cancer Lett. 2014, 343, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, L.d.F.; Pereira, T.d.A.; Dias, R.B.; Guimarães, V.S.N.; Ramos, E.A.G.; Santos, J.N.; Gurgel Rocha, C.A. Macrophages and Endothelial Cells Orchestrate Tumor-Associated Angiogenesis in Oral Cancer via Hedgehog Pathway Activation. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 9233–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Kannagi, R.; Yang, R.-B. Inhibition of Endothelial SCUBE2 (Signal Peptide-CUB-EGF Domain-Containing Protein 2), a Novel VEGFR2 (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2) Coreceptor, Suppresses Tumor Angiogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1202–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy Chaudhuri, T.; Straubinger, N.L.; Pitoniak, R.F.; Hylander, B.L.; Repasky, E.A.; Ma, W.W.; Straubinger, R.M. Tumor-Priming Smoothened Inhibitor Enhances Deposition and Efficacy of Cytotoxic Nanoparticles in a Pancreatic Cancer Model. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qi, M.; Li, L.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X.; Fu, J. Natural Cordycepin Induces Apoptosis and Suppresses Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Hedgehog Pathway. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Yang, Q. Hedgehog Pathway Is Involved in Nitidine Chloride Induced Inhibition of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem Cells-like Properties in Breast Cancer Cells. Cell Biosci. 2016, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Cuaran, S.; Bouaoud, J.; Karabajakian, A.; Fayette, J.; Saintigny, P. Precision Medicine Approaches to Overcome Resistance to Therapy in Head and Neck Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 614332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, H.-L.; Chiou, J.-F.; Chen, Y.-J. Molecular Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Head and Neck Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Yan, L.; Lu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, F.; Yang, J.; Jing, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, J.; Guo, H. Activation of Hedgehog Signaling and Its Association with Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian Epithelial Tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5569–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sari, I.N.; Phi, L.T.H.; Jun, N.; Wijaya, Y.T.; Lee, S.; Kwon, H.Y. Hedgehog Signaling in Cancer: A Prospective Therapeutic Target for Eradicating Cancer Stem Cells. Cells 2018, 7, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, E.; Hanna, A.; Samant, R.S.; Shevde, L.A. The Impact of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway on DNA Repair Mechanisms in Human Cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 1333–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramini, B.; Masciale, V.; Grisendi, G.; Bertolini, F.; Maur, M.; Guaitoli, G.; Chrystel, I.; Morandi, U.; Stella, F.; Dominici, M.; et al. Dissecting Tumor Growth: The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in Drug Resistance and Recurrence. Cancers 2022, 14, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuelei, M.; Jingwen, H.; Wei, D.; Hongyu, Z.; Jing, Z.; Changle, S.; Lei, L. ERCC1 Plays an Important Role in Predicting Survival Outcomes and Treatment Response for Patients with HNSCC: A Meta-Analysis. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Ma, R.; Huang, S.; Liao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Q.; Tan, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L. Oroxylin A Increases the Sensitivity of Temozolomide on Glioma Cells by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α/Hedgehog Pathway under Hypoxia. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17392–17404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Nagle, P.W.; Wang, H.H.; Smit, J.K.; Faber, H.; Baanstra, M.; Karrenbeld, A.; Chiu, R.K.; Plukker, J.T.M.; Coppes, R.P. Hedgehog Pathway as a Potential Intervention Target in Esophageal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.-T.; Ding, J.; Li, H.-Y.; Zuo, J.-L.; Ge, S.-Y.; Jia, H.-L.; Wu, J. Hedgehog Signalling Mediates Drug Resistance through Targeting TAP1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 4298–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keysar, S.B.; Le, P.N.; Anderson, R.T.; Morton, J.J.; Bowles, D.W.; Paylor, J.J.; Vogler, B.W.; Thorburn, J.; Fernandez, P.; Glogowska, M.J.; et al. Hedgehog Signaling Alters Reliance on EGF Receptor Signaling and Mediates Anti-EGFR Therapeutic Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3381–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Po, A.; Citarella, A.; Catanzaro, G.; Besharat, Z.M.; Trocchianesi, S.; Gianno, F.; Sabato, C.; Moretti, M.; De Smaele, E.; Vacca, A.; et al. Hedgehog-GLI Signalling Promotes Chemoresistance through the Regulation of ABC Transporters in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyuga, T.; Alcantara, M.; Kajioka, D.; Haraguchi, R.; Suzuki, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Kojima, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamada, G. Hedgehog Signaling for Urogenital Organogenesis and Prostate Cancer: An Implication for the Epithelial-Mesenchyme Interaction (EMI). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.M.; Heguedusch, D.; Rodini, C.O.; Nunes, F.D.; Rodrigues, M.F.S.D. Mechanisms Involved in Cancer Stem Cell Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudás, J.; Skvortsov, S.; Ganswindt, U.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.-I. Therapy Resistance Mediated by Cancer Stem Cells. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 53, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Zhou, L.; Lim, L.Y.; Fu, H.; Yuan, Z.-X.; Lin, J. Targeting Strategies for Renal Cancer Stem Cell Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 1964–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wicha, M.S. Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Redox Metabolism to Enhance Therapy Responses. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.R. Drug and Apoptosis Resistance in Cancer Stem Cells: A Puzzle with Many Pieces. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 850–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pádua, D.; Barros, R.; Amaral, A.L.; Mesquita, P.; Freire, A.F.; Sousa, M.; Maia, A.F.; Caiado, I.; Fernandes, H.; Pombinho, A.; et al. A SOX2 Reporter System Identifies Gastric Cancer Stem-Like Cells Sensitive to Monensin. Cancers 2020, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Gu, D.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Xie, J. GLI1-Mediated Regulation of Side Population Is Responsible for Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27412–27427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, L.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Q.; Hu, X.; Chen, Q. The Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Promotes Chemotherapy Resistance via Multidrug Resistance Protein 1 in Ovarian Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Fang, T.; Duan, Z.; Xiang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhai, F.; Cui, X.; Yang, L. Dihydroartemisinin Sensitizes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma to Cisplatin by Inhibiting Sonic Hedgehog Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 596788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, H.-D. Bcl-2 Family Proteins as Regulators of Cancer Cell Invasion and Metastasis: A Review Focusing on Mitochondrial Respiration and Reactive Oxygen Species. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5193–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, J.-B.; Espenel, S.; Louati, S.; Gauthier, A.; Garcia, M.-A.; Vial, N.; Malésys, C.; Ardail, D.; Alphonse, G.; Wozny, A.-S.; et al. Combining Radiation to EGFR and Bcl-2 Blockade: A New Approach to Target Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 147, 1905–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, L.; Dou, T.; Wan, G.; Tang, H.; Tian, J. BMI1’S Maintenance of the Proliferative Capacity of Laryngeal Cancer Stem Cells. Head Neck 2011, 33, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallin, L.E.; Ma, Q.; Naipauer, J.; Gupta, S.; Kurian, M.; Locatelli, P.; Romanelli, P.; Nadji, M.; Goldschmidt-Clermont, P.J.; Mesri, E.A. KSHV-Induced Ligand Mediated Activation of PDGF Receptor-Alpha Drives Kaposi’s Sarcomagenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, J.; Jin, B.; He, S.; Dang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Jin, Z. The Emerging Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Viral Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 870316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, T.d.A.; Witek, R.P.; Syn, W.-K.; Choi, S.S.; Bradrick, S.; Karaca, G.F.; Agboola, K.M.; Jung, Y.; Omenetti, A.; Moylan, C.A.; et al. Viral Factors Induce Hedgehog Pathway Activation in Humans with Viral Hepatitis, Cirrhosis, and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2010, 90, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, M.; Zompetta, C.; Vescarelli, E.; Rizzello, C.; Cardi, A.; Valia, S.; Antonelli, G.; Marchese, C.; Torrisi, M.R.; Faggioni, A.; et al. HCV Derived from Sera of HCV-Infected Patients Induces pro-Fibrotic Effects in Human Primary Fibroblasts by Activating GLI2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-León, V.; García, C.; Valencia, C.; Méndez, M.-A.; Wood, C.; Covarrubias, L. The E6/E7 Oncogenes of Human Papilloma Virus and Estradiol Regulate Hedgehog Signaling Activity in a Murine Model of Cervical Cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 381, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkiewicz, M.; Dorobisz, K.; Zatoński, T. Human Papillomavirus-Associated Head and Neck Cancers. Where Are We Now? A Systematic Review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fertig, E.J.; Markovic, A.; Danilova, L.V.; Gaykalova, D.A.; Cope, L.; Chung, C.H.; Ochs, M.F.; Califano, J.A. Preferential Activation of the Hedgehog Pathway by Epigenetic Modulations in HPV Negative HNSCC Identified with Meta-Pathway Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Vashishta, M.; Kong, L.; Wu, X.; Lu, J.J.; Guha, C.; Dwarakanath, B.S. The Role of Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt Signaling Pathways in the Resistance of Tumors to Anticancer Therapies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 650772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballo, G.B.; Honorato, J.R.; de Lopes, G.P.F.; Spohr, T.C.L. de S.E. A Highlight on Sonic Hedgehog Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y.-G.; Zheng, D.-L. Roles of the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 7, 590912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcheri, C.; Meisel, C.T.; Mitsiadis, T. Multifactorial Contribution of Notch Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Sheng, T.; Stelter, A.A.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Sinha, M.; Luxon, B.A.; Xie, J. Suppressing Wnt Signaling by the Hedgehog Pathway through SFRP-1*. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35598–35602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, F.; Itasaki, N.; Briscoe, J. Inhibitory Gli3 Activity Negatively Regulates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Hui, C.-C.; Mainprize, T.G.; Scherer, S.W.; Wainwright, B.; Hogg, D.; Rutka, J.T. Failure of a Medulloblastoma-Derived Mutant of SUFU to Suppress WNT Signaling. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4577–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Kou, Y.; Feng, Q.; Wang, H.; Su, R.; Hasegawa, T.; Liu, H.; et al. Notum Leads to Potential Pro-Survival of OSCC through Crosstalk between Shh and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling via p-GSK3β. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 153, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noubissi, F.K.; Goswami, S.; Sanek, N.A.; Kawakami, K.; Minamoto, T.; Moser, A.; Grinblat, Y.; Spiegelman, V.S. Wnt Signaling Stimulates Transcriptional Outcome of the Hedgehog Pathway by Stabilizing GLI1 MRNA. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8572–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinke, J.; Schneider, F.T.; Harter, P.N.; Thom, S.; Ziegler, N.; Toftgård, R.; Plate, K.H.; Liebner, S. β-Catenin-Gli1 Interaction Regulates Proliferation and Tumor Growth in Medulloblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hibbs, M.A.; Gard, A.L.; Shylo, N.A.; Yun, K. Genome-Wide Analysis of N1ICD/RBPJ Targets In Vivo Reveals Direct Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt, SHH, and Hippo Pathway Effectors by Notch1. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreck, K.C.; Taylor, P.; Marchionni, L.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Bar, E.E.; Gaiano, N.; Eberhart, C.G. The Notch Target Hes1 Directly Modulates Gli1 Expression and Hedgehog Signaling: A Potential Mechanism of Therapeutic Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6060–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steg, A.D.; Katre, A.A.; Goodman, B.; Han, H.-D.; Nick, A.M.; Stone, R.L.; Coleman, R.L.; Alvarez, R.D.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K.; et al. Targeting the Notch Ligand Jagged1 in Both Tumor Cells and Stroma in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, R.; Pelullo, M.; Zema, S.; Nardozza, F.; Checquolo, S.; Lauer, D.M.; Bufalieri, F.; Palermo, R.; Felli, M.P.; Vacca, A.; et al. Maml1 Acts Cooperatively with Gli Proteins to Regulate Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiulewicz, M.; Gray, S.D.; Mastromina, I.; Silva, J.C.; Björklund, M.; Seymour, P.A.; Booth, D.; Thompson, C.; Green, R.J.; Hall, E.A.; et al. A Conserved Role for Notch Signaling in Priming the Cellular Response to Shh through Ciliary Localisation of the Key Shh Transducer Smo. Development 2015, 142, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.A.; Liao, Z.W.; Yamagata, N.; Pouliot, G.P.; Stevenson, K.E.; Neuberg, D.S.; Thorner, A.R.; Ducar, M.; Silverman, E.A.; Hunger, S.P.; et al. Hedgehog Pathway Mutations Drive Oncogenic Transformation in High-Risk T-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Joshi, J.; Raval, A.; Shah, F. Identification of Natural Compounds to Inhibit Sonic Hedgehog Pathway in Oral Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Peng, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Li, M. Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis, Suppresses Migration, and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8453011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozet, C.; Stoehr, M.; Dimitrova, K.; Dietz, A.; Wichmann, G. Hedgehog Targeting by Cyclopamine Suppresses Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Enhances Chemotherapeutic Effects. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 2415–2424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gan, G.N.; Eagles, J.; Keysar, S.B.; Wang, G.; Glogowska, M.J.; Altunbas, C.; Anderson, R.T.; Le, P.N.; Morton, J.J.; Frederick, B.; et al. Hedgehog Signaling Drives Radioresistance and Stroma-Driven Tumor Repopulation in Head and Neck Squamous Cancers. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7024–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlgans, S.; Booms, P.; Güllülü, Ö.; Sader, R.; Rödel, C.; Balermpas, P.; Rödel, F.; Ghanaati, S. Radiation Sensitization of Basal Cell and Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma by the Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor Vismodegib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, R.D.; Dias, R.B.; Vidal, M.T.A.; Valverde, L.d.F.; Costa, R.G.A.; Damasceno, A.K.A.; Sales, C.B.S.; Rocha, L.d.O.S.d.; dos Reis, M.G.; Soares, M.B.P.; et al. Inhibition of CAL27 Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cell by Targeting Hedgehog Pathway With Vismodegib or Itraconazole. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 563838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Paradise, B.D.; Ma, W.W.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Recent Advances in the Clinical Targeting of Hedgehog/GLI Signaling in Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebig, H.; Günther, G.; Kolb, M.; Mozet, C.; Boehm, A.; Dietz, A.; Wichmann, G. Reduced Proliferation and Colony Formation of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) after Dual Targeting of EGFR and Hedgehog Pathways. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, S.; Lv, D.; Wei, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, Z. Combined Effects of EGFR and Hedgehog Signaling Blockade on Inhibition of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 9816–9828. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Yen, C.-J.; Xia, W.; Izzo, J.G.; Lang, J.-Y.; Li, C.-W.; Hsu, J.L.; Miller, S.A.; Wang, X.; et al. The Crosstalk of MTOR/S6K1 and Hedgehog Pathways. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleszcz, R.; Frąckowiak, M.; Dorna, D.; Paluszczak, J. Combinations of PRI-724 Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Inhibitor with Vismodegib, Erlotinib, or HS-173 Synergistically Inhibit Head and Neck Squamous Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, B.E.; Steg, A.D.; Kovac, S.; Landen, C.N.; Amm, H.M. The Use of Hedgehog Antagonists in Cancer Therapy: A Comparison of Clinical Outcomes and Gene Expression Analyses. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2020, 21, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, D.W.; Keysar, S.B.; Eagles, J.R.; Wang, G.; Glogowska, M.J.; McDermott, J.D.; Le, P.N.; Gao, D.; Ray, C.E.; Rochon, P.J.; et al. A Pilot Study of Cetuximab and the Hedgehog Inhibitor IPI-926 in Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2016, 53, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.D.; Haensel, D.; Gaddam, S.; Patel, T.; Atwood, S.X.; Sarin, K.Y.; Whitson, R.J.; McKellar, S.; Shankar, G.; Aasi, S.; et al. AP-1 and TGFß Cooperativity Drives Non-Canonical Hedgehog Signaling in Resistant Basal Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.-C.; Teo, W.-H.; Huang, T.-F.; Lee, T.-C.; Lo, J.-F. Combinatorial Low Dose Arsenic Trioxide and Cisplatin Exacerbates Autophagy via AMPK/STAT3 Signaling on Targeting Head and Neck Cancer Initiating Cells. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko-Fabian, M.; Niehr, F.; Distel, L.; Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. Increased Growth-Inhibitory and Cytotoxic Activity of Arsenic Trioxide in Head and Neck Carcinoma Cells with Functional P53 Deficiency and Resistance to EGFR Blockade. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, R.L.R.; de Araújo, T.B.S.; Valverde, L.F.; Silva, V.A.O.; Cavalcante, B.R.R.; Rossi, E.A.; Allahdadi, K.J.; dos Reis, M.G.; Pereira, T.A.; Coletta, R.D.; et al. Arsenic Trioxide Triggers Apoptosis of Metastatic Oral Squamous Cells Carcinoma with Concomitant Downregulation of GLI1 in Hedgehog Signaling. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaoka, T.; Ota, A.; Ono, T.; Karnan, S.; Konishi, H.; Furuhashi, A.; Ohmura, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Hosokawa, Y.; Kazaoka, Y. Combined Arsenic Trioxide-Cisplatin Treatment Enhances Apoptosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 37, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KOTOWSKI, U.; HEIDUSCHKA, G.; BRUNNER, M.; EROVIC, B.M.; MARTINEK, H.; THURNHER, D. Arsenic Trioxide Enhances the Cytotoxic Effect of Cisplatin in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 3, 1326–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Gao, Q.; Ning, Y.; Wang, Z.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Polverini, P.J. Arsenic Trioxide Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Radiation Treatment of Oral Squamous Carcinoma While Protecting Bone. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Wang, L.; Zuo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Mao, L.; Zhang, P. HH/GLI Signalling as a New Therapeutic Target for Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2011, 47, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, T.B.S.; Rocha, L.d.O.S.d.; Vidal, M.T.A.; Coelho, P.L.C.; dos Reis, M.G.; Souza, B.S.d.F.; Soares, M.B.P.; Pereira, T.A.; Della Coletta, R.; Bezerra, D.P.; et al. GANT61 Reduces Hedgehog Molecule (GLI1) Expression and Promotes Apoptosis in Metastatic Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubčić, V.; Rinčić, N.; Kurtović, M.; Trnski, D.; Musani, V.; Ozretić, P.; Levanat, S.; Leović, D.; Sabol, M. GANT61 and Lithium Chloride Inhibit the Growth of Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines Through the Regulation of GLI3 Processing by GSK3β. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cierpikowski, P.; Leszczyszyn, A.; Bar, J. The Role of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells 2023, 12, 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162083
Cierpikowski P, Leszczyszyn A, Bar J. The Role of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells. 2023; 12(16):2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162083
Chicago/Turabian StyleCierpikowski, Piotr, Anna Leszczyszyn, and Julia Bar. 2023. "The Role of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma" Cells 12, no. 16: 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162083
APA StyleCierpikowski, P., Leszczyszyn, A., & Bar, J. (2023). The Role of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cells, 12(16), 2083. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12162083








