Fundamental Characterization of Antibody Fusion-Single-Chain TNF Recombinant Proteins Directed against Costimulatory TNF Receptors Expressed by T-Lymphocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid
2.2. Recombinant Protein
2.3. Flow Cytometry
2.4. ELISA
2.5. Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. CD4+ and CD8+ T Cell Stimulation Assay
2.7. Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Response
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
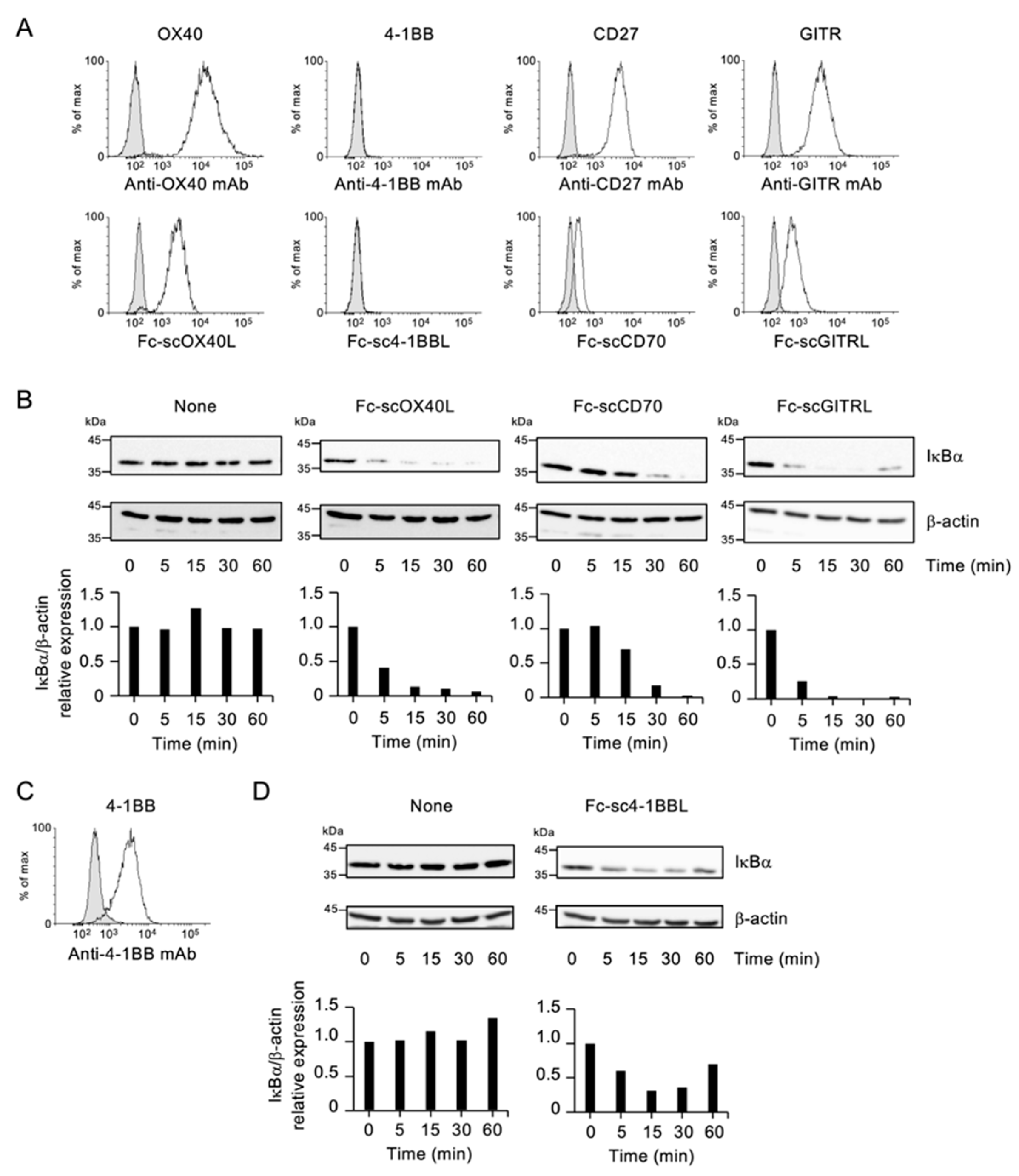
3.1. Specific Binding of Fc−scTNFL Fusion Protein to Corresponding TNFR on T Cells
3.2. NF-kB Activation by Fc−scTNFL
3.3. Activation of Costimulatory Signaling Pathway by Fc−scTNFL in CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells
3.4. DTH Response Mediated by Fc−scGITRL
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- So, T.; Ishii, N. The TNF-TNFR Family of Co-signal Molecules. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1189, 53–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- So, T.; Croft, M. Regulation of PI-3-Kinase and Akt Signaling in T Lymphocytes and Other Cells by TNFR Family Molecules. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M. The role of TNF superfamily members in T-cell function and diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, T.H. TNF/TNFR family members in costimulation of T cell responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 23–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Kavanagh, L.K.; Lin, W.W.; Sedy, J.R.; Ware, C.F. The TNF Receptor Superfamily in Co-stimulating and Co-inhibitory Responses. Immunity 2016, 44, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M.; So, T.; Duan, W.; Soroosh, P. The significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-cell biology and immune disease. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lin, G.H.; McPherson, A.J.; Watts, T.H. Immune regulation by 4-1BB and 4-1BBL: Complexities and challenges. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 192–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, M.A.; van Olffen, R.W.; van Gisbergen, K.P.; van Lier, R.A. Timing and tuning of CD27-CD70 interactions: The impact of signal strength in setting the balance between adaptive responses and immunopathology. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 229, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, S.L.; Rogel, A.; Al-Shamkhani, A. The immunobiology of CD27 and OX40 and their potential as targets for cancer immunotherapy. Blood 2018, 131, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snell, L.M.; Lin, G.H.; McPherson, A.J.; Moraes, T.J.; Watts, T.H. T-cell intrinsic effects of GITR and 4-1BB during viral infection and cancer immunotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 244, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clouthier, D.L.; Watts, T.H. Cell-specific and context-dependent effects of GITR in cancer, autoimmunity, and infection. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014, 25, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugamura, K.; Ishii, N.; Weinberg, A.D. Therapeutic targeting of the effector T-cell co-stimulatory molecule OX40. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, N.; Takahashi, T.; Soroosh, P.; Sugamura, K. OX40-OX40 ligand interaction in T-cell-mediated immunity and immunopathology. Adv. Immunol. 2010, 105, 63–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Paulete, A.R.; Labiano, S.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Azpilikueta, A.; Etxeberria, I.; Bolaños, E.; Lang, V.; Rodriguez, M.; Aznar, M.A.; Jure-Kunkel, M.; et al. Deciphering CD137 (4-1BB) signaling in T-cell costimulation for translation into successful cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Immunol. 2016, 46, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Redmond, W.L. Current Clinical Trial Landscape of OX40 Agonists. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, C.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Wang, J.; Melero, I. Immunotherapy targeting 4-1BB: Mechanistic rationale, clinical results, and future strategies. Blood 2018, 131, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Ven, K.; Borst, J. Targeting the T-cell co-stimulatory CD27/CD70 pathway in cancer immunotherapy: Rationale and potential. Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knee, D.A.; Hewes, B.; Brogdon, J.L. Rationale for anti-GITR cancer immunotherapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedan, S.; Posey, A.D.; Jr Shaw, C.; Wing, A.; Da, T.; Patel, P.R.; McGettigan, S.E.; Casado-Medrano, V.; Kawalekar, O.U.; Uribe-Herranz, M.; et al. Enhancing CAR T cell persistence through ICOS and 4-1BB costimulation. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e96976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinkove, R.; George, P.; Dasyam, N.; McLellan, A.D. Selecting costimulatory domains for chimeric antigen receptors: Functional and clinical considerations. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2019, 8, e1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Simpson, E.L.; Reich, K.; Kabashima, K.; Igawa, K.; Suzuki, T.; Mano, H.; Matsui, T.; Esfandiari, E.; Furue, M.; et al. An anti-OX40 antibody to treat moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2b study. Lancet 2023, 401, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.W.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Curti, B.; Pedersen, K.S.; Bauer, T.M.; Groenland, S.L.; Carvajal, R.D.; Chhaya, V.; Kirby, G.; McGlinchey, K.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of MEDI0562, an OX40 Agonist mAb, in Combination with Durvalumab or Tremelimumab in Adult Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3709–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, N.H.; Logan, T.F.; Hodi, F.S.; McDermott, D.; Melero, I.; Hamid, O.; Schmidt, H.; Robert, C.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Ascierto, P.A.; et al. Results from an Integrated Safety Analysis of Urelumab, an Agonist Anti-CD137 Monoclonal Antibody. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmanoukian, A.S.; Infante, J.R.; Aljumaily, R.; Naing, A.; Chintakuntlawar, A.V.; Rizvi, N.A.; Ross, H.J.; Gordon, M.; Mallinder, P.R.; Elgeioushi, N.; et al. Safety and Clinical Activity of MEDI1873, a Novel GITR Agonist, in Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 6196–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locksley, R.M.; Killeen, N.; Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001, 104, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, J.L.; Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, A.K.; Pettinello, R.; Bakke, F.K.; Dooley, H. Sharks Provide Evidence for a Highly Complex TNFSF Repertoire in the Jawed Vertebrate Ancestor. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucka, K.; Wajant, H. Receptor Oligomerization and Its Relevance for Signaling by Receptors of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 615141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippner-Heidenreich, A.; Grunwald, I.; Zimmermann, G.; Kühnle, M.; Gerspach, J.; Sterns, T.; Shnyder, S.D.; Gill, J.H.; Männel, D.N.; Pfizenmaier, K.; et al. Single-chain TNF, a TNF derivative with enhanced stability and antitumoral activity. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 8176–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellermeier, S.; Beha, N.; Meyer, J.E.; Ring, S.; Bader, S.; Kontermann, R.E.; Müller, D. Advancing targeted co-stimulation with antibody-fusion proteins by introducing TNF superfamily members in a single-chain format. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1238540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschmoneit, N.; Kocher, K.; Siegemund, M.; Lutz, M.S.; Kuhl, L.; Seifert, O.; Kontermann, R.E. Fc-based Duokines: Dual-acting costimulatory molecules comprising TNFSF ligands in the single-chain format fused to a heterodimerizing Fc (scDk-Fc). Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2028961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, J.; Stringhini, M.; Villa, A.; Weller, M.; Weiss, T.; Neri, D. An engineered 4-1BBL fusion protein with “activity on demand”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 31780–31788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.M.; Marschall, V.; Billian-Frey, K.; Heinonen, K.; Merz, C.; Redondo Muller, M.; Sefrin, J.P.; Schröder, M. HERA-GITRL activates T cells and promotes anti-tumor efficacy independent of FcgammaR-binding functionality. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiemann, M.; Richards, D.M.; Heinonen, K.; Kluge, M.; Marschall, V.; Merz, C.; Müller, R.M.; Schnyder, T. A Single-Chain-Based Hexavalent CD27 Agonist Enhances T Cell Activation and Induces Anti-Tumor Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Maben, Z.; Wang, C.; Lindquist, K.C.; Li, M.; Rayannavar, V.; Armenta, I.L.; Nager, A. Structural delineation and phase-dependent activation of the costimulatory CD27:CD70 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, Y.; Nagashima, H.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Croft, M.; Ishii, N.; So, T. IQGAP1 restrains T-cell cosignaling mediated by OX40. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Azuma, M.; Nagai, H.; Imai, W.; Kawaguchi, K.; Morita, M.; Okuyama, Y.; Ishii, N.; So, T. OX40 Ligand-Mannose-Binding Lectin Fusion Protein Induces Potent OX40 Cosignaling in CD4+ T Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2022, 45, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suda, T.; Nagata, S. Purification and characterization of the Fas-ligand that induces apoptosis. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, S.; Nagata, S. pEF-BOS, a powerful mammalian expression vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, H.; Yamamura, K.; Miyazaki, J. Efficient selection for high-expression transfectants with a novel eukaryotic vector. Gene 1991, 108, 193–199. [Google Scholar]
- Nagashima, H.; Okuyama, Y.; Fujita, T.; Takeda, T.; Motomura, Y.; Moro, K.; Hidaka, T.; Omori, K.; Sakurai, T.; Machiyama, T.; et al. GITR cosignal in ILC2s controls allergic lung inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1939–1943.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, E.; Azuma, M.; Nagashima, H.; Omori, K.; Akiyama, S.; Fujimori, Y.; Oishi, M.; Shibui, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Morita, M.; et al. TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 5 Limits IL-27 Receptor Signaling in CD4+ T Lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2022, 208, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, T.; Soroosh, P.; Eun, S.Y.; Altman, A.; Croft, M. Antigen-independent signalosome of CARMA1, PKCtheta, and TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) determines NF-kappaB signaling in T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2903–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, T.; Choi, H.; Croft, M. OX40 complexes with phosphoinositide 3-kinase and protein kinase B (PKB) to augment TCR-dependent PKB signaling. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kaneko, M.; Neyazaki, M.; Nogi, T.; Kato, Y.; Takagi, J. PA tag: A versatile protein tagging system using a super high affinity antibody against a dodecapeptide derived from human podoplanin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 95, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramaglia, I.; Weinberg, A.D.; Lemon, M.; Croft, M. Ox-40 ligand: A potent costimulatory molecule for sustaining primary CD4 T cell responses. J. Immunol. 1998, 161, 6510–6517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, A.D.; Vella, A.T.; Croft, M. OX-40: Life beyond the effector T cell stage. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinay, D.S.; Kwon, B.S. Role of 4-1BB in immune responses. Semin. Immunol. 1998, 10, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraban, V.Y.; Rowley, T.F.; O'Brien, L.; Chan, H.T.C.; Haswell, L.E.; Green, M.H.A.; Tutt, A.L.; Glennie, M.J.; Al-Shamkhani, A. Expression and costimulatory effects of the TNF receptor superfamily members CD134 (OX40) and CD137 (4-1BB), and their role in the generation of anti-tumor immune responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 3617–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannons, J.L.; Lau, P.; Ghumman, B.; DeBenedette, M.A.; Yagita, H.; Okumura, K.; Watts, T.H. 4-1BB ligand induces cell division, sustains survival, and enhances effector function of CD4 and CD8 T cells with similar efficacy. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravestein, L.A.; Blom, B.; Nolten, L.A.; de Vries, E.; Van Der Horst, G.; Ossendorp, F.; Borst, J.; Loenen, W.A.M. Cloning and expression of murine CD27: Comparison with 4-1BB, another lymphocyte-specific member of the nerve growth factor receptor family. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamaru, F.; Youngnak, P.; Hashiguchi, M.; Nishioka, T.; Takahashi, T.; Sakaguchi, S.; Ishikawa, I.; Azuma, M. Costimulation via Glucocorticoid-Induced TNF Receptor in Both Conventional and CD25+ Regulatory CD4+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7306–7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocentini, G.; Giunchi, L.; Ronchetti, S.; Krausz, L.T.; Bartoli, A.; Moraca, R.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. A new member of the tumor necrosis factor/nerve growth factor receptor family inhibits T cell receptor-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6216–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, G.L.; McHugh, R.S.; Whitters, M.J.; Young, D.A.; Luxenberg, D.; Carreno, B.M.; Collins, M.; Shevach, E.M. Engagement of glucocorticoid-induced TNFR family-related receptor on effector T cells by its ligand mediates resistance to suppression by CD4+CD25+ T cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5008–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Karin, M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 693–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Pettmann, J.; Kruger, P.; Dushek, O. Quantitative contributions of TNF receptor superfamily members to CD8+ T-cell responses. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2021, 17, e10560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loenen, W.A.; De Vries, E.; Gravestein, L.A.; Hintzen, R.Q.; Van Lier, R.A.; Borst, J. The CD27 membrane receptor, a lymphocyte-specific member of the nerve growth factor receptor family, gives rise to a soluble form by protein processing that does not involve receptor endocytosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kober, J.; Leitner, J.; Klauser, C.; Woitek, R.; Majdic, O.; Stöckl, J.; Herndler-Brandstetter, D.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B.; Reipert, B.M.; Pickl, W.F.; et al. The capacity of the TNF family members 4-1BBL, OX40L, CD70, GITRL, CD30L and LIGHT to costimulate human T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 2678–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwas, K.M.; Meyer, M.; Goncalves, M.; Moldenhauer, G.; Bulbuc, N.; Knabe, S.; Luckner-Minden, C. Co-Stimulatory Bispecific Antibodies Induce Enhanced T Cell Activation and Tumor Cell Killing in Breast Cancer Models. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 719116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Arias, R.S.; Sadun, R.E.; Nien, Y.C.; Zhang, N.; Sabzevari, H.; Christine Lutsiak, M.E. Construction and preclinical characterization of Fc-mGITRL for the immunotherapy of cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyland, R.; Watkins, A.; Mulgrew, K.; Holoweckyj, N.; Bamber, L.; Tigue, N.J.; Offer, E. A novel murine GITR ligand fusion protein induces antitumor activity as a monotherapy, which is further enhanced in combination with an OX40 agonist. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3416–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigue, N.J.; Bamber, L.; Andrews, J.; Ireland, S.; Hair, J.; Carter, E.; Sridharan, S.; Jovanović, J.; Rees, D.G.; Springall, J.S.; et al. MEDI1873, a potent, stabilized hexameric agonist of human GITR with regulatory T-cell targeting potential. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1280645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Belmar, N.; Ho, S.; Rogers, B.; Stickler, M.; Graham, M.; Lee, E.; Tran, N.; Zhang, D.; Gupta, P.; et al. An anti-PD-1-GITR-L bispecific agonist induces GITR clustering-mediated T cell activation for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Vlaming, M.; van Meerten, T.; Bremer, E. The Implementation of TNFRSF Co-Stimulatory Domains in CAR-T Cells for Optimal Functional Activity. Cancers 2022, 14, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalekar, O.U.; O’Connor, R.S.; Fraietta, J.A.; Guo, L.; McGettigan, S.E.; Posey, A.D., Jr.; Patel, P.R. Distinct Signaling of Coreceptors Regulates Specific Metabolism Pathways and Impacts Memory Development in CAR T Cells. Immunity 2016, 44, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, D.; Hu, P.; Alabanza, L.; Steimle, B.; Mahmud, H. Trispecific CD19-CD20-CD22-targeting duoCAR-T cells eliminate antigen-heterogeneous B cell tumors in preclinical models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabc6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Qi, K.; Wang, G.; Xu, K. A chimeric antigen receptor with antigen-independent OX40 signaling mediates potent antitumor activity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eaba7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.G.; Ye, Q.; Poussin, M.; Harms, G.M.; Figini, M.; Powell, D.J., Jr. CD27 costimulation augments the survival and antitumor activity of redirected human T cells in vivo. Blood 2012, 119, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xie, W.; Song, D.G.; Powell, D.J., Jr. Control of triple-negative breast cancer using ex vivo self-enriched, costimulated NKG2D CAR T cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Berahovich, R.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Xu, S.; Guan, J.; Harto, H.; Li, L.; Wu, L. GITR domain inside CAR co-stimulates activity of CAR-T cells against cancer. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 2245–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.K.; Wang, Z.; Ke, Q.; Hong, M.; Qian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Signaling by the Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 protein induces potent cytotoxic CD4+ and CD8+ T cell responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E686–E695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Kostel Bal, S.; Edwards, E.S.J.; Pillay, B.; Jimenez Heredia, R.; Erol Cipe, F.; Rao, G. Extended clinical and immunological phenotype and transplant outcome in CD27 and CD70 deficiency. Blood 2020, 136, 2638–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhassani, H.; Edwards, E.S.; Ikinciogullari, A.; Jing, H.; Borte, S.; Buggert, M.; Du, L. Combined immunodeficiency and Epstein-Barr virus-induced B cell malignancy in humans with inherited CD70 deficiency. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhairy, O.K.; Perez-Becker, R.; Driessen, G.J.; Abolhassani, H.; van Montfrans, J.; Borte, S.; Choo, S.; Wang, N.; Tesselaar, K.; Fang, M.; et al. Novel mutations in TNFRSF7/CD27: Clinical, immunologic, and genetic characterization of human CD27 deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 703–712.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosaimi, M.F.; Hoenig, M.; Jaber, F.; Platt, C.D.; Jones, J.; Wallace, J.; Debatin, K.M. Immunodeficiency and EBV-induced lymphoproliferation caused by 4-1BB deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 574–583.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somekh, I.; Thian, M.; Medgyesi, D.; Gulez, N.; Magg, T.; Gallon Duque, A.; Stauber, T. CD137 deficiency causes immune dysregulation with predisposition to lymphomagenesis. Blood 2019, 134, 1510–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, B.; Hoshino, A.; Bruneau, J.; Bachelet, C.; Fusaro, M.; Klifa, R.; Lévy, R. Inherited TNFSF9 deficiency causes broad Epstein-Barr virus infection with EBV+ smooth muscle tumors. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211682. [Google Scholar]
- Qui, H.Z.; Hagymasi, A.T.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Rose, M.-C.S.; Ramanarasimhaiah, R.; Ménoret, A.; Mittler, R.S.; Gordon, S.M.; Reiner, S.L.; Vella, A.T.; et al. CD134 plus CD137 dual costimulation induces Eomesodermin in CD4 T cells to program cytotoxic Th1 differentiation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3555–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidts, A.; Ormhøj, M.; Choi, B.D.; Taylor, A.O.; Bouffard, A.A.; Scarfò, I.; Larson, R.C.; Frigault, M.J.; Gallagher, K.; Castano, A.P.; et al. Rational design of a trimeric APRIL-based CAR-binding domain enables efficient targeting of multiple myeloma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3248–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagai, H.; Azuma, M.; Sato, A.; Shibui, N.; Ogawara, S.; Tsutsui, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Wakaizumi, T.; Ito, A.; Matsuyama, S.; et al. Fundamental Characterization of Antibody Fusion-Single-Chain TNF Recombinant Proteins Directed against Costimulatory TNF Receptors Expressed by T-Lymphocytes. Cells 2023, 12, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121596
Nagai H, Azuma M, Sato A, Shibui N, Ogawara S, Tsutsui Y, Suzuki A, Wakaizumi T, Ito A, Matsuyama S, et al. Fundamental Characterization of Antibody Fusion-Single-Chain TNF Recombinant Proteins Directed against Costimulatory TNF Receptors Expressed by T-Lymphocytes. Cells. 2023; 12(12):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121596
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagai, Hodaka, Mitsuki Azuma, Ayaka Sato, Nagito Shibui, Sayaka Ogawara, Yuta Tsutsui, Ayano Suzuki, Tomomi Wakaizumi, Aya Ito, Shimpei Matsuyama, and et al. 2023. "Fundamental Characterization of Antibody Fusion-Single-Chain TNF Recombinant Proteins Directed against Costimulatory TNF Receptors Expressed by T-Lymphocytes" Cells 12, no. 12: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121596
APA StyleNagai, H., Azuma, M., Sato, A., Shibui, N., Ogawara, S., Tsutsui, Y., Suzuki, A., Wakaizumi, T., Ito, A., Matsuyama, S., Morita, M., Hikosaka Kuniishi, M., Ishii, N., & So, T. (2023). Fundamental Characterization of Antibody Fusion-Single-Chain TNF Recombinant Proteins Directed against Costimulatory TNF Receptors Expressed by T-Lymphocytes. Cells, 12(12), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121596








