GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Constructs
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. In-Cell Arrestin-GPCR Interaction Assay
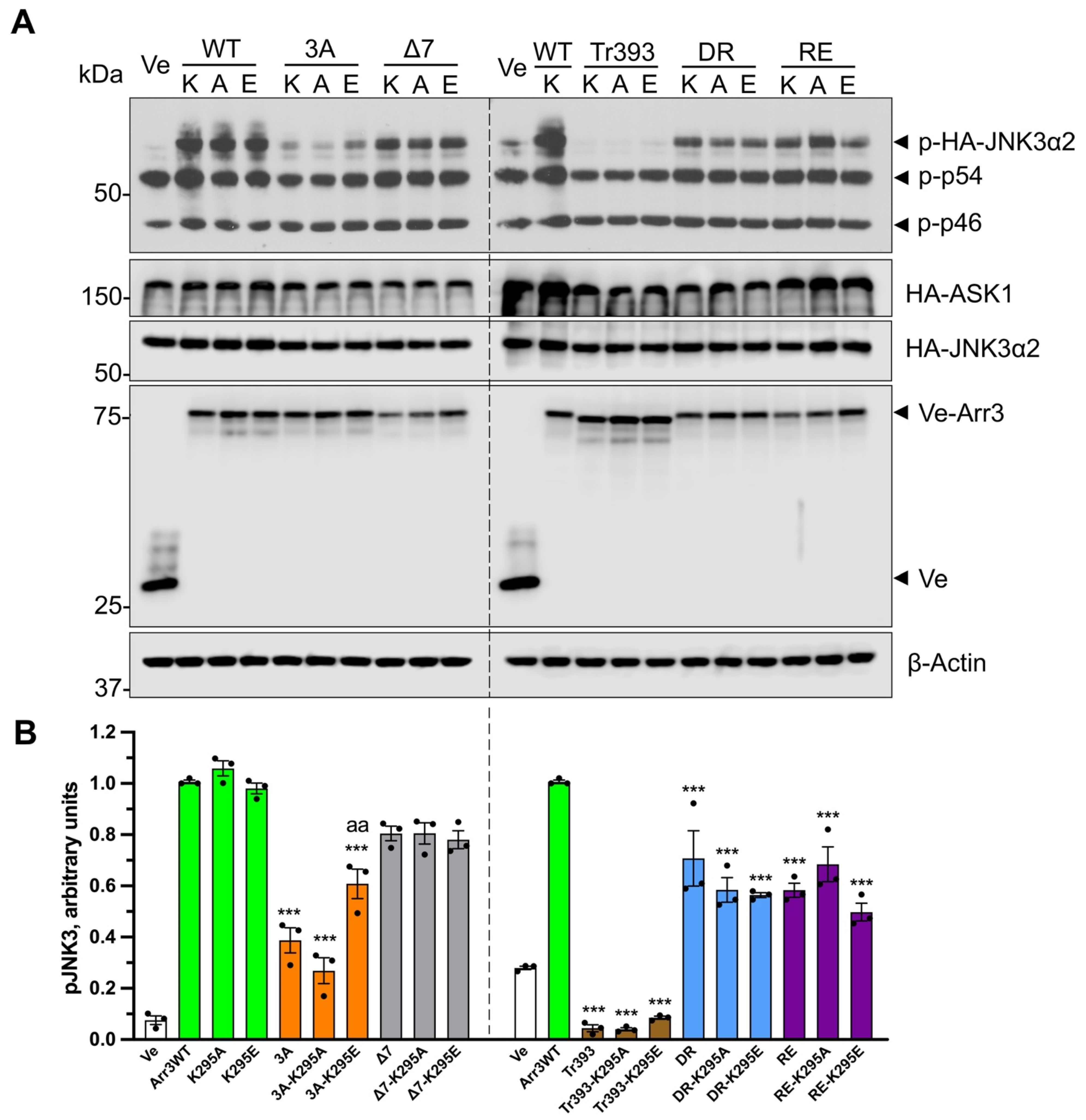
2.4. JNK3 Activation Assay
2.5. Subcellular Localization of Arrestin-3
2.6. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Functional Role of Arrestin-3 Conformational Equilibrium
3.2. Functional Role of Lariat Loop Lysine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carman, C.V.; Benovic, J.L. G-protein-coupled receptors: Turn-ons and turn-offs. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1998, 8, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrischek, H.; Prohaska, S.J.; Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V.; Stadler, P.F. Uncovering missing pieces: Duplication and deletion history of arrestins in deuterostomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, X.; Gimenez, L.E.; Gurevich, V.V.; Spiller, B.W. Crystal structure of arrestin-3 reveals the basis of the difference in receptor binding between two non-visual arrestins. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barak, L.S.; Ferguson, S.S.; Zhang, J.; Caron, M.G. A beta-arrestin/green fluorescent protein biosensor for detecting G protein-coupled receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27497–27500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, Y.K.; Luttrell, L.M. The Diverse Roles of Arrestin Scaffolds in G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2017, 69, 256–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. Plethora of functions packed into 45 kDa arrestins: Biological implications and possible therapeutic strategies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 4413–4421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.H.; Chow, C.W.; Miller, W.E.; Laporte, S.A.; Field, M.E.; Lin, F.T.; Davis, R.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Beta-arrestin 2: A receptor-regulated MAPK scaffold for the activation of JNK3. Science 2000, 290, 1574–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrell, L.M.; Roudabush, F.L.; Choy, E.W.; Miller, W.E.; Field, M.E.; Pierce, K.L.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Activation and targeting of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by beta-arrestin scaffolds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2449–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Coffa, S.; Fu, H.; Gurevich, V.V. How does arrestin assemble MAPKs into a signaling complex? J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 685–695. [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Whalen, E.J. β-arrestins: Traffic cops of cell signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffa, S.; Breitman, M.; Spiller, B.W.; Gurevich, V.V. A single mutation in arrestin-2 prevents ERK1/2 activation by reducing c-Raf1 binding. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6951–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breitman, M.; Kook, S.; Gimenez, L.E.; Lizama, B.N.; Palazzo, M.C.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. Silent scaffolds: Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 3 activity in the cell by a dominant-negative arrestin-3 mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 19653–19664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luttrell, L.M.; Ferguson, S.S.; Daaka, Y.; Miller, W.E.; Maudsley, S.; Della Rocca, G.J.; Lin, F.; Kawakatsu, H.; Owada, K.; Luttrell, D.K.; et al. Beta-arrestin-dependent formation of beta2 adrenergic receptor-Src protein kinase complexes. Science 1999, 283, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, A.I.; Perry, N.A.; Gurevich, V.V.; Iverson, T.M. Phosphorylation barcode-dependent signal bias of the dopamine D1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14139–14149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Gurevich, V.V.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Klug, C.S.; Marchese, A. A non-GPCR-binding partner interacts with a novel surface on β-arrestin1 to mediate GPCR signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14111–14124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Perez, A.; Gimenez, L.E.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Gurevich, V.V. Arrestin-3 binds the MAP kinase JNK3α2 via multiple sites on both domains. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 766–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, N.A.; Kaoud, T.S.; Ortega, O.O.; Kaya, A.I.; Marcus, D.J.; Pleinis, J.M.; Berndt, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhan, X.; Dalby, K.N.; et al. Arrestin-3 scaffolding of the JNK3 cascade suggests a mechanism for signal amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, X.; Stoy, H.; Kaoud, T.S.; Perry, N.A.; Chen, Q.; Perez, A.; Els-Heindl, S.; Slagis, J.V.; Iverson, T.M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; et al. Peptide mini-scaffold facilitates JNK3 activation in cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry-Hauser, N.A.; Kaoud, T.S.; Stoy, H.; Zhan, X.; Chen, Q.; Dalby, K.N.; Iverson, T.M.; Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. Short Arrestin-3-Derived Peptides Activate JNK3 in Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Zhan, X.; Song, X.; Kook, S.; Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. Ubiquitin ligase parkin promotes Mdm2-arrestin interaction but inhibits arrestin ubiquitination. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 3749–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cleghorn, W.M.; Branch, K.M.; Kook, S.; Arnette, C.; Bulus, N.; Zent, R.; Kaverina, I.; Gurevich, E.V.; Weaver, A.M.; Gurevich, V.V. Arrestins regulate cell spreading and motility via focal adhesion dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanson, S.M.; Cleghorn, W.M.; Francis, D.J.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Raman, D.; Song, S.; Nair, K.S.; Slepak, V.Z.; Klug, C.S.; Gurevich, V.V. Arrestin mobilizes signaling proteins to the cytoskeleton and redirects their activity. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.; Raman, D.; Gurevich, E.V.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Gurevich, V.V. Visual and both non-visual arrestins in their “inactive” conformation bind JNK3 and Mdm2 and relocalize them from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21491–21499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perry, S.J.; Baillie, G.S.; Kohout, T.A.; McPhee, I.; Magiera, M.M.; Ang, K.L.; Miller, W.E.; McLean, A.J.; Conti, M.; Houslay, M.D.; et al. Targeting of cyclic AMP degradation to beta 2-adrenergic receptors by beta-arrestins. Science 2002, 298, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Rajagopal, S. Biased signalling: From simple switches to allosteric microprocessors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. Biased GPCR signaling: Possible mechanisms and inherent limitations. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 211, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wingler, L.M.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Conformational Basis of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Signaling Versatility. Trends Cell. Biol. 2020, 30, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celver, J.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Chavkin, C.; Gurevich, V.V. Conservation of the phosphate-sensitive elements in the arrestin family of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9043–9048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gimenez, L.E.; Babilon, S.; Wanka, L.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Gurevich, V.V. Mutations in arrestin-3 differentially affect binding to neuropeptide Y receptor subtypes. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1523–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Curto, E.; Inoue, A.; Jenkins, L.; Raihan, S.Z.; Prihandoko, R.; Tobin, A.B.; Milligan, G. Targeted Elimination of G Proteins and Arrestins Defines Their Specific Contributions to Both Intensity and Duration of G Protein-coupled Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 27147–27159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundmann, M.; Merten, N.; Malfacini, D.; Inoue, A.; Preis, P.; Simon, K.; Rüttiger, N.; Ziegler, N.; Benkel, T.; Schmitt, N.K.; et al. Lack of beta-arrestin signaling in the absence of active G proteins. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Zhan, X.; Chen, Q.; Iverson, T.M.; Gurevich, V.V. Arrestin expression in E. coli and purification. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2014, 67, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dijon, N.C.; Nesheva, D.N.; Holliday, N.D. Luciferase Complementation Approaches to Measure GPCR Signaling Kinetics and Bias. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2268, 249–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.E.; He, Y.; de Waal, P.W.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Van Eps, N.; Yin, Y.; Pal, K.; Goswami, D.; White, T.A.; et al. Identification of Phosphorylation Codes for Arrestin Recruitment by G protein-Coupled Receptors. Cell 2017, 170, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V. The selectivity of visual arrestin for light-activated phosphorhodopsin is controlled by multiple nonredundant mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15501–15506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Benovic, J.L. Visual arrestin binding to rhodopsin: Diverse functional roles of positively charged residues within the phosphorylation-recignition region of arrestin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6010–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovoor, A.; Celver, J.; Abdryashitov, R.I.; Chavkin, C.; Gurevich, V.V. Targeted construction of phosphorylation-independent b-arrestin mutants with constitutive activity in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6831–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M.; Onorato, J.J. Agonist-receptor-arrestin, an alternative ternary complex with high agonist affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28849–28852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Hofmann, K.P.; Ernst, O.P.; Scheerer, P.; Choe, H.W.; Sommer, M.E. Crystal structure of pre-activated arrestin p44. Nature 2013, 497, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Pulvermuller, A.; Hofmann, K.P. Arrestin and its splice variant Arr1-370A (p44). Mechanism and biological role of their interaction with rhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43987–43996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granzin, J.; Stadler, A.; Cousin, A.; Schlesinger, R.; Batra-Safferling, R. Structural evidence for the role of polar core residue Arg175 in arrestin activation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, A.K.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Xiao, K.; Reis, R.I.; Tseng, W.C.; Staus, D.P.; Hilger, D.; Uysal, S.; Huang, L.Y.; et al. Structure of active beta-arrestin-1 bound to a G-protein-coupled receptor phosphopeptide. Nature 2013, 497, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakata, H.; Kameyama, K.; Haga, K.; Haga, T. Location of agonist-dependent-phosphorylation sites in the third intracellular loop of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (m2 subtype). Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 220, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Gurevich, V.V.; Lee, K.B.; Ptasienski, J.; Benovic, J.L.; Hosey, M.M. Internalization of the m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: Arrestin-independent and -dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23682–23689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.B.; Ptasienski, J.A.; Pals-Rylaarsdam, R.; Gurevich, V.V.; Hosey, M.M. Arrestin binding to the M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor is precluded by an inhibitory element in the third intracellular loop of the receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9284–9289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouvier, M.; Hausdorff, W.P.; De Blasi, A.; O’Dowd, B.F.; Kobilka, B.K.; Caron, M.G.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Removal of phosphorylation sites from the beta 2-adrenergic receptor delays onset of agonist-promoted desensitization. Nature 1988, 333, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.E.; McDonald, P.H.; Cai, S.F.; Field, M.E.; Davis, R.J.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Identification of a motif in the carboxyl terminus of beta -arrestin2 responsible for activation of JNK3. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27770–27777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, M.G.; Le Rouzic, E.; Périanin, A.; Pierotti, V.; Enslen, H.; Benichou, S.; Marullo, S.; Benmerah, A. Differential nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of beta-arrestins. Characterization of a leucine-rich nuclear export signal in beta-arrestin2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37693–37701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granzin, J.; Wilden, U.; Choe, H.W.; Labahn, J.; Krafft, B.; Buldt, G. X-ray crystal structure of arrestin from bovine rod outer segments. Nature 1998, 391, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Gurevich, V.V.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Sigler, P.B.; Schubert, C. Crystal structure of beta-arrestin at 1.9 A: Possible mechanism of receptor binding and membrane translocation. Structure 2001, 9, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, J.A.; Schubert, C.; Gurevich, V.V.; Sigler, P.B. The 2.8 A crystal structure of visual arrestin: A model for arrestin’s regulation. Cell 1999, 97, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sander, C.L.; Luu, J.; Kim, K.; Furkert, D.; Jang, K.; Reichenwallner, J.; Kang, M.; Lee, H.J.; Eger, B.T.; Choe, H.W.; et al. Structural evidence for visual arrestin priming via complexation of phosphoinositols. Structure 2022, 30, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.B.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Robert, J.; Hanson, S.M.; Raman, D.; Knox, B.E.; Kono, M.; Navarro, J.; Gurevich, V.V. Crystal Structure of Cone Arrestin at 2.3Å: Evolution of Receptor Specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 354, 1069–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, S.K.; Pace, H.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Brenner, C.; Benovic, J.L. Scaffolding functions of arrestin-2 revealed by crystal structure and mutagenesis. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 3321–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilden, U. Duration and amplitude of the light-induced cGMP hydrolysis in vertebrate photoreceptors are regulated by multiple phosphorylation of rhodopsin and by arrestin binding. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilden, U.; Hall, S.W.; Kühn, H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Benovic, J.L. Visual arrestin interaction with rhodopsin: Sequential multisite binding ensures strict selectivity towards light-activated phosphorylated rhodopsin. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 11628–11638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sente, A.; Peer, R.; Srivastava, A.; Baidya, M.; Lesk, A.M.; Balaji, S.; Shukla, A.K.; Babu, M.M.; Flock, T. Molecular mechanism of modulating arrestin conformation by GPCR phosphorylation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2018, 25, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Li, Z.; Jin, M.; Yin, Y.L.; de Waal, P.W.; Pal, K.; Yin, Y.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. A complex structure of arrestin-2 bound to a G protein-coupled receptor. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staus, D.P.; Hu, H.; Robertson, M.J.; Kleinhenz, A.L.W.; Wingler, L.M.; Capel, W.D.; Latorraca, N.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J.; Skiniotis, G. Structure of the M2 muscarinic receptor-β-arrestin complex in a lipid nanodisc. Nature 2020, 579, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Warne, T.; Nehmé, R.; Pandey, S.; Dwivedi-Agnihotri, H.; Chaturvedi, M.; Edwards, P.C.; García-Nafría, J.; Leslie, A.G.W.; Shukla, A.K.; et al. Molecular basis of β-arrestin coupling to formoterol-bound β(1)-adrenoceptor. Nature 2020, 583, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Masureel, M.; Qianhui, Q.; Janetzko, J.; Inoue, A.; Kato, H.E.; Robertson, M.J.; Nguyen, K.C.; Glenn, J.S.; Skiniotis, G.; et al. Structure of the neurotensin receptor 1 in complex with β-arrestin 1. Nature 2020, 579, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Perry, N.A.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Berndt, S.; Gilbert, N.C.; Zhuo, Y.; Singh, P.K.; Tholen, J.; Ohi, M.D.; Gurevich, E.V.; et al. Structural basis of arrestin-3 activation and signaling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schleicher, A.; Kuhn, H.; Hofmann, K.P. Kinetics, binding constant, and activation energy of the 48-kDa protein-rhodopsin complex by extra-metarhodopsin II. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 1770–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Hanson, S.M.; Song, X.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Gurevich, E.V. The functional cycle of visual arrestins in photoreceptor cells. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2011, 30, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Huh, E.K.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. The finger loop as an activation sensor in arrestin. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, Y.; Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Zhan, X.; Gurevich, V.V.; Klug, C.S. Identification of receptor binding-induced conformational changes in non-visual arrestins. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 20991–21002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Zheng, C.; May, M.B.; Karnam, P.C.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. Lysine in the lariat loop of arrestins does not serve as phosphate sensor. J. Neurochem. 2021, 156, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Gao, X.; He, Y.; Ke, J.; Tan, M.H.E.; Zhang, C.; Moeller, A.; Yang, H.; Suino-Powell, K.M.; et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin bound to arrestin determined by femtosecond X-ray laser. Nature 2015, 523, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bous, J.; Fouillen, A.; Orcel, H.; Trapani, S.; Cong, X.; Fontanel, S.; Saint-Paul, J.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Urbach, S.; Sibille, N.; et al. Structure of the vasopressin hormone-V2 receptor-β-arrestin1 ternary complex. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Barros-Álvarez, X.; Zhang, S.; Kim, K.; Dämgen, M.A.; Panova, O.; Suomivuori, C.M.; Fay, J.F.; Zhong, X.; Krumm, B.E.; et al. Signaling snapshots of a serotonin receptor activated by the prototypical psychedelic LSD. Neuron 2022, 110, 3154–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oakley, R.H.; Laporte, S.A.; Holt, J.A.; Caron, M.G.; Barak, L.S. Differential affinities of visual arrestin, beta arrestin1, and beta arrestin2 for G protein-coupled receptors delineate two major classes of receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17201–17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, K.; McClatchy, D.B.; Shukla, A.K.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Shenoy, S.K.; Yates, J.R.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Functional specialization of beta-arrestin interactions revealed by proteomic analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12011–12016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. The structural basis of arrestin-mediated regulation of G protein-coupled receptors. Pharm. Ther. 2006, 110, 465–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vishnivetskiy, S.A.; Hirsch, J.A.; Velez, M.-G.; Gurevich, Y.V.; Gurevich, V.V. Transition of arrestin in the active receptor-binding state requires an extended interdomain hinge. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43961–43968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. The nature of the arrestin x receptor complex determines the ultimate fate of the internalized receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11623–11632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seyedabadi, M.; Gharghabi, M.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. Receptor-Arrestin Interactions: The GPCR Perspective. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffa, S.; Breitman, M.; Hanson, S.M.; Callaway, K.; Kook, S.; Dalby, K.N.; Gurevich, V.V. The Effect of Arrestin Conformation on the Recruitment of c-Raf1, MEK1, and ERK1/2 Activation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodman, O.B., Jr.; Krupnick, J.G.; Santini, F.; Gurevich, V.V.; Penn, R.B.; Gagnon, A.W.; Keen, J.H.; Benovic, J.L. Beta-arrestin acts as a clathrin adaptor in endocytosis of the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Nature 1996, 383, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Benovic, J.L. Differential roles of arrestin-2 interaction with clathrin and adaptor protein 2 in G protein-coupled receptor trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30760–30768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laporte, S.A.; Oakley, R.H.; Zhang, J.; Holt, J.A.; Ferguson, S.S.G.; Caron, M.G.; Barak, L.S. The 2-adrenergic receptor/arrestin complex recruits the clathrin adaptor AP-2 during endocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3712–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. The new face of active receptor bound arrestin attracts new partners. Structure 2003, 11, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, C.; Weinstein, L.D.; Nguyen, K.K.; Grewal, A.; Gurevich, E.V.; Gurevich, V.V. GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements. Cells 2023, 12, 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121563
Zheng C, Weinstein LD, Nguyen KK, Grewal A, Gurevich EV, Gurevich VV. GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements. Cells. 2023; 12(12):1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121563
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Chen, Liana D. Weinstein, Kevin K. Nguyen, Abhijeet Grewal, Eugenia V. Gurevich, and Vsevolod V. Gurevich. 2023. "GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements" Cells 12, no. 12: 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121563
APA StyleZheng, C., Weinstein, L. D., Nguyen, K. K., Grewal, A., Gurevich, E. V., & Gurevich, V. V. (2023). GPCR Binding and JNK3 Activation by Arrestin-3 Have Different Structural Requirements. Cells, 12(12), 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12121563






